- IP Multicast Routing Technology Overview
- Configuring Basic IP Multicast Routing
- Configuring Multicast Routing over GRE Tunnel
- Configuring VRF-lite
- Configuring IGMP
- Configuring IGMP Proxy
- IGMP Explicit Tracking
- Constraining IP Multicast in Switched Ethernet
- Configuring Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM)
- Configuring PIM MIB Extension for IP Multicast
- Configuring MSDP
- Configuring SSM
- Configuring the Service Discovery Gateway
- IP Multicast Optimization: PIM Dense Mode State Refresh
- IP Multicast Optimization: Optimizing PIM Sparse Mode in a Large IP Multicast Deployment
- IP Multicast Optimization: Multicast Subsecond Convergence
- IP Multicast Optimization: IP Multicast Load Splitting across Equal-Cost Paths
- IP Multicast Optimization: SSM Channel Based Filtering for Multicast
- IP Multicast Optimization: IGMP State Limit
- Restrictions for Configuring the Service Discovery Gateway
- Information about the Service Discovery Gateway and mDNS
- Example: Specify Alternative Source Interface for Outgoing mDNS Packets
- Example: Redistribute Service Announcements
- Example: Creating a Service-List, Applying a Filter and Configuring Parameters
- Example: Enabling mDNS Gateway and Redistributing Services
- Example: Global mDNS Configuration
- Example: Interface mDNS Configuration
Configuring the Service Discovery Gateway
- Restrictions for Configuring the Service Discovery Gateway
- Information about the Service Discovery Gateway and mDNS
- How to Configure the Service Discovery Gateway
- Monitoring Service Discovery Gateway
- Configuration Examples
- Where to Go Next for Configuring Services Discovery Gateway
- Additional References
- Feature History and Information for Services Discovery Gateway
Restrictions for Configuring the Service Discovery Gateway
The following are restrictions for configuring the Service Discovery Gateway:
-
The Service Discovery Gateway does not support topologies with multiple hops. All network segments must be connected directly to it. The Service Discovery Gateway can learn services from all connected segments to build its cache and respond to requests acting as a proxy.
-
The use of third-party mDNS servers or applications are not supported with this feature.
Information about the Service Discovery Gateway and mDNS
mDNS
mDNS was defined to achieve zero configuration, with zero configuration being defined as providing the following features:
-
Addressing—Allocating IP addresses to hosts
-
Naming—Using names to refer to hosts instead of IP addresses
-
Service discovery—Finding services automatically on the network
With mDNS, network users no longer have to assign IP addresses, assign host names, or type in names to access services on the network. Users only need to ask to see what network services are available, and choose from a list.
With mDNS, addressing is accomplished through the use of DHCP/DHCPv6 or IPv4 and IPv6 Link Local scoped addresses. The benefit of zero-configuration occurs when no infrastructure services such as DHCP or DNS are present and self-assigned link-local addressing can be used. The client can then select a random IPv4 address in the link-local range (169.254.0.0/24) or use its IPv6 link-local address (FE80::/10) for communication.
With mDNS, naming (name-to-address translation on a local network using mDNS) queries are sent over the local network using link-local scoped IP multicast. Because these DNS queries are sent to a multicast address (IPv4 address 224.0.0.251 or IPv6 address FF02::FB), no single DNS server with global knowledge is required to answer the queries. When a service or device sees a query for any service it is aware of, it provides a DNS response with the information from its cache.
With mDNS, service discovery is accomplished by browsing. An mDNS query is sent out for a given service type and domain, and any device that is aware of matching services replies with service information. The result is a list of available services for the user to choose from.
The mDNS protocol (mDNS-RFC), together with DNS Service Discovery (DNS-SD-RFC) achieves the zero-configuration addressing, naming, and service discovery.
mDNS-SD
Multicast DNS Service Discovery (mDNS-SD) uses DNS protocol semantics and multicast over well-known multicast addresses to achieve zero configuration service discovery. DNS packets are sent to and received on port 5353 using a multicast address of 224.0.0.251 and its IPv6 equivalent FF02::FB.
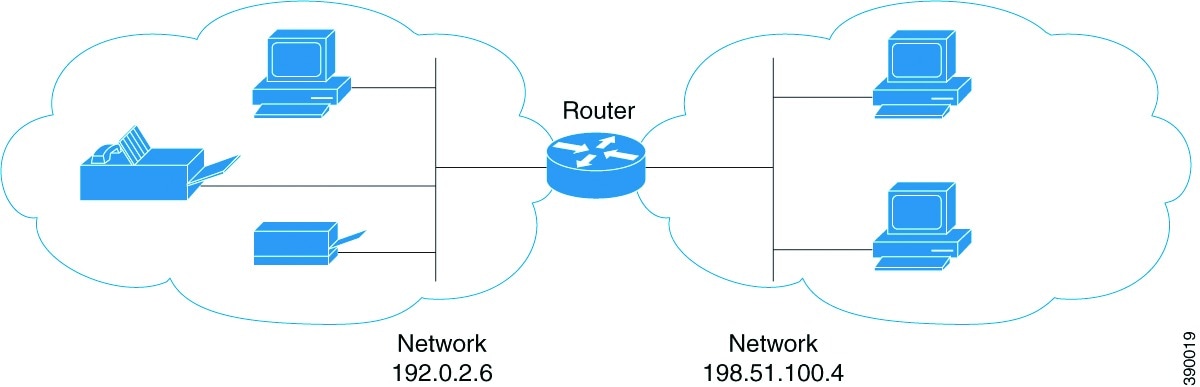
Because mDNS uses a link-local multicast address, its scope is limited to a single physical or logical LAN. If the networking reach needs to be extended to a distributed campus or to a wide-area environment consisting of many different networking technologies, mDNS gateway is implemented. An mDNS gateway provides a transport for mDNS packets across Layer 3 boundaries by filtering, caching, and redistributing services from one Layer 3 domain to another.
Service Discovery Gateway
The Service Discovery Gateway feature enables multicast Domain Name System (mDNS) to operate across Layer 3 boundaries (different subnets). An mDNS gateway provides transport for service discovery across Layer 3 boundaries by filtering, caching, and redistributing services from one Layer 3 domain (subnet) to another. Prior to implementation of this feature, mDNS was limited in scope to within a subnet because of the use of link-local scoped multicast addresses. This feature enhances Bring Your Own Device (BYOD).
mDNS Gateway and Subnets
You need to enable an mDNS gateway for service discovery to operate across subnets. You can enable mDNS gateway for a device or for an interface.
 Note | You need to configure service routing globally before configuring at the interface level. |
After the device or interface is enabled, you can redistribute service discovery information across subnets. You can create service policies and apply filters on either incoming service discovery information (called IN-bound filtering) or outgoing service discovery information (called OUT-bound filtering).
 Note | If redistribution is enabled globally, global configuration is given higher priority than interface configuration. |
Filtering
After configuring the mDNS gateway and subnets, you can filter services that you want to redistribute. While creating a service list, the permit or deny command options are used:
The permit command option allows you to permit or transport specific service list information.
The deny option allows you to deny service list information that is available to be transported to other subnets.
You need to include a sequence number when using the permit or deny command option. The same service list name can be associated with multiple sequence numbers and each sequence number will be mapped to a rule.
 Note | If no filters are configured, then the default action is to deny service list information to be transported through the device or interface. |
Query is another option provided when creating service lists. You can create queries using a service list. If you want to browse for a service, then active queries can be used. This function is helpful to keep the records refreshed in the cache.
 Note | Active queries can only be used globally and cannot be used at the interface level. |
A service end-point (such as a printer or fax) sends unsolicited announcements when a service starts up. After that, it sends unsolicited announcements whenever a network change event occurs (such as an interface coming up or going down). The device always respond to queries.
After creating a service list and using the permit or deny command options, you can filter using match statements (commands) based on service-instance, service-type, or message-type (announcement or query).
How to Configure the Service Discovery Gateway
Configuring the Service List
This procedure describes how to create a service list, apply a filter for the service list, and configure parameters for the service list name.
Proceed to enable the mDNS gateway and redistribution of services.
Enabling mDNS Gateway and Redistributing Services
After enabling mDNS gateway for a device, you can apply filters (apply IN-bound filtering or OUT-bound filtering) and active queries by using service-policy and service-policy-query commands, respectively. You can redistribute services and service announcements using the redistribute mdns-sd command, and set some part of the system memory for cache using the cache-memory-max command.
 Note | By default, mDNS gateway is disabled on all interfaces. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example:
Device> enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||||
| Step 2 | configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal | |||||
| Step 3 |
service-routing mdns-sd
Example:
Device (config)# service-routing mdns-sd
|
Enables mDNS gateway functionality for a device and enters multicast DNS configuration (config-mdns) mode.
| ||||
| Step 4 |
service-policy
service-policy-name {IN |
OUT}
Example:
Device (config-mdns)# service-policy serv-pol1 IN
|
(Optional) For a service list, applies a filter on incoming service discovery information (IN-bound filtering) or outgoing service discovery information (OUT-bound filtering). | ||||
| Step 5 | redistribute mdns-sd
Example:
Device (config-mdns)# redistribute mdns-sd
|
(Optional) Redistributes services or service announcements across subnets.
| ||||
| Step 6 | cache-memory-max
cache-config-percentage
Example:
Device (config-mdns)# cache-memory-max 20
|
(Optional) Sets some part of the system memory (in percentage) for cache.
| ||||
| Step 7 |
service-policy-query
service-list-query-name
service-list-query-periodicity
Example:
Device (config-mdns)# service-policy-query sl-query1 100
|
(Optional) Configures service list-query periodicity. | ||||
| Step 8 | exit
Example:
Device (config-mdns)#exit
|
(Optional) Returns to global configuration mode. | ||||
| Step 9 | end
Example: Device(config)# end |
Monitoring Service Discovery Gateway
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
show mdns requests [detail | name record-name| type record-type [ name record-name]] |
This command displays information for outstanding mDNS requests, including record name and record type information. |
show mdns cache [interface type number | name record-name [type record-type]| type record-type] |
This command displays mDNS cache information. |
show mdns statistics {all | service-list list-name | service-policy {all | interface type number }} |
This command displays mDNS statistics. |
Configuration Examples
Example: Specify Alternative Source Interface for Outgoing mDNS Packets
The following example displays how to specify an alternate source interface for outgoing mDNS packets, so its IP address can be used when there is none configured on the outgoing interface.
Device(config)# service-routing mdns-sd Device(config-mdns)# source-interface if-name
Example: Redistribute Service Announcements
The following example displays how to redistribute service announcements received on one interface over all the interfaces or over a specific interface.
Device(config)# service-routing mdns-sd Device(config-mdns)# Redistribute mdns-sd if-name
Example: Creating a Service-List, Applying a Filter and Configuring Parameters
The following example shows the creation of a service-list sl1. The permit command option is being applied on sequence number 3 and all services with message-type announcement are filtered and available for transport across various subnets associated with the device.
Device# configure terminal Device(config)# service-list mdns-sd sl1 permit 3 Device(config-mdns-sd-sl)#match message-type announcement Device(config-mdns)# exit
Example: Enabling mDNS Gateway and Redistributing Services
The following example shows how to enable an mDNS gateway for a device and enable redistribution of services across subnets. IN-bound filtering is applied on the service-list serv-pol1. Twenty percent of system memory is made available for cache and service-list-query periodicity is configured at 100 seconds.
Device# configure terminal Device# service-routing mdns-sd Device(config-mdns)# service-policy serv-pol1 IN Device(config-mdns)# redistribute mdns-sd Device(config-mdns)# cache-memory-max 20 Device(config-mdns)# service-policy-query sl-query1 100 Device(config-mdns)# exit
Example: Global mDNS Configuration
The following example displays how to globally configure mDNS.
Device# configure terminal Device(config)# service-list mdns-sd mypermit-all permit 10 Device(config-mdns-sd-s1)# exit Device(config)# service-list mdns-sd querier query Device(config-mdns-sd-s1)# service-type _dns._udp Device(config-mdns-sd-s1)# end Device# configure terminal Device(config)# service-routing mdns-sd Device(config-mdns)# service-policy mypermit-all IN Device(config-mdns)# service-policy mypermit-all OUT
Example: Interface mDNS Configuration
The following example displays how to configure mDNS for an interface.
Device(config)#interface Vlan136 Device(config-if)# description *** Mgmt VLAN *** Device(config-if)# ip address 9.7.136.10 255.255.255.0 Device(config-if)# ip helper-address 9.1.0.100 Device(config-if)# service-routing mdns-sd Device(config-if-mdns-sd)# service-policy mypermit-all IN Device(config-if-mdns-sd)# service-policy mypermit-all OUT Device(config-if-mdns-sd)# service-policy-query querier 60
Where to Go Next for Configuring Services Discovery Gateway
You can configure the following:
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic | Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Configuring DNS |
IP Addressing: DNS Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE |
|
DNS conceptual information |
'Information About DNS' section in IP Addressing: DNS Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE |
|
Platform-independent configuration information |
IP Addressing: DNS Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE |
Error Message Decoder
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
To help you research and resolve system error messages in this release, use the Error Message Decoder tool. |
https://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/index.cgi |
Standards and RFCs
| Standard/RFC | Title |
|---|---|
|
RFC 6763 |
DNS-Based Service Discovery |
|
Multicast DNS Internet-Draft |
MIBs
| MIB | MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
All supported MIBs for this release. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature History and Information for Services Discovery Gateway
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1a |
This feature was introduced. |
 Feedback
Feedback