|
election specifically
determined by existing
|
Connect two powered-on switch stacks through the StackWise
Plus ports.
|
Only one of the two
becomes the new
.
None of the other stack members become the
.
|
|
election specifically
determined by the stack member priority value
|
-
Connect two switches through their StackWise Plus ports.
-
Use the
switch
stack-member-number priority
new-priority-number
global configuration command to set one
stack member with a higher member priority value.
-
Restart both stack members at the same time.
|
The stack member with the higher priority value is elected
.
|
|
election specifically
determined by the configuration file
|
Assuming that both stack members have the same priority value:
-
Make sure that one stack member has a default
configuration and that the other stack member has a saved (nondefault)
configuration file.
-
Restart both stack members at the same time.
|
The stack member with the saved configuration file is elected
.
|
|
election specifically determined by the cryptographic software image and the IP
services feature set and the IP services feature set.
|
Assuming that all stack members have the same priority value:
-
Make sure that one stack member has the cryptographic
image installed and the IP services feature set enabled and that the other
stack member has the noncryptographic image installed and the IP services
feature set enabled.
-
Restart both stack members at the same time.
|
The stack member with the cryptographic image and the IP
services feature set is elected
.
| Note
|
Only Catalyst 3650-E or 3750 switches running Cisco IOS
Release 12.2(53)SE or earlier could be running the noncyrptographic image.
|
|
|
election specifically determined by the cryptographic software image and the IP
base feature.
|
Assuming that all stack members have the same priority value:
-
Make sure that one stack member has the cryptographic
image installed and the IP base feature set enabled and that the other stack
member has the noncryptographic image installed and the IP base feature set
enabled.
-
Restart both stack members at the same time.
|
The stack member with the cryptographic image and the IP base
feature set is elected
.
| Note
|
Only Catalyst 3650-E or 3750 switches running Cisco IOS
Release 12.2(53)SE or earlier could be running the noncyrptographic image.
|
|
|
election specifically determined by the MAC address.
|
Assuming that both stack members have the same priority value,
configuration file, and feature set, restart both stack members at the same
time.
|
The stack member with the lower MAC address is elected
.
|
|
Stack member number conflict
|
Assuming that one stack member has a higher priority value
than the other stack member:
-
Ensure that both stack members have the same stack member
number. If necessary, use the
switch
current-stack-member-number
renumber
new-stack-member-number global
configuration command.
-
Restart both stack members at the same time.
|
The stack member with the higher priority value retains its
stack member number. The other stack member has a new stack member number.
|
|
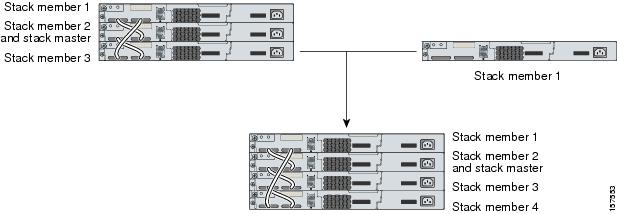
Add a stack member
|
-
Power off the new switch.
-
Through their StackWise Plus ports, connect the new switch
to a powered-on switch stack.
-
Power on the new switch.
|
The
is retained. The new switch is added to the switch stack.
|
|
failure
|
Remove (or power off) the
.
|
Based on the factors described in the
Stack Master Election and Re-Election section, one
of the remaining stack members becomes the new stack master. All other stack
members in the stack remain as stack members and do not reboot.
|
|
Add more than nine stack members
|
-
Through their StackWise Plus ports, connect ten switches.
-
Power on all switches.
|
Two switches become
.
One
has nine stack members. The other
remains as a standalone switch.
Use the Mode button and port LEDs on the switches to identify
which switches are
and which switches belong to each
.
For information about using the Mode button and the LEDs, see the hardware
installation guide.
|


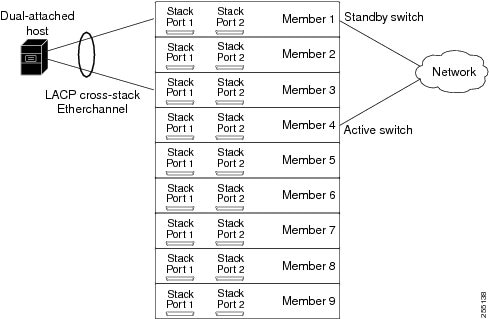
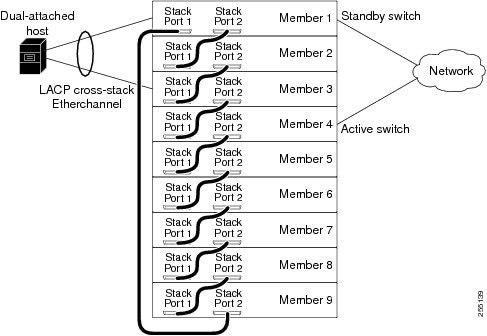
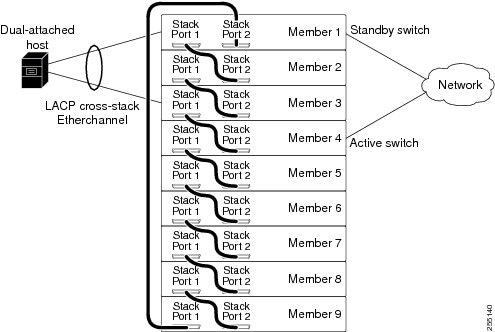
 Feedback
Feedback