- Device Manager Help
- Configuring Cisco DCNM-SAN Server
- Configuring Authentication in Cisco DCNM-SAN
- Configuring Cisco DCNM-SAN Client
- Device Manager
- Configuring Performance Manager
- Configuring High Availability
- Configuring Trunking
- Configuring PortChannels
- Configuring N Port Virtualization
- Configuring Interfaces
- Configuration of Fibre Channel Interfaces
- Using the CFS Infrastructure
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring Domain Parameters
- Configuring and Managing Zones
- Configuring FCoE
- Configuring Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
- Configuring and Managing VSANs
- Discovering SCSI Targets
- Configuring SAN Device Virtualization
- Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
- Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
- Configuring FICON
- Creating Dynamic VSANs
- Distributing Device Alias Services
- Configuring Advanced Fabric Features
- Configuring Users and Common Role
- Configuring Security Features on an External AAA Server
- Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
- Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
- Configuring Cisco TrustSec Fibre Channel Link Encryption
- Configuring FIPS
- Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 Access Control Lists
- Configuring IPsec Network Security
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Fabric Binding
- Configuring FCIP
- Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
- Configuring iSCSI
- Configuring IP Services
- Configuring IP Storage
- Configuring IPv4 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring IPv6 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring SCSI Flow Services
- Configuring SCSI Flow Statistics
- Configuring Fibre Channel Write Acceleration
- Monitoring the Network
- Monitoring Performance
- Configuring Call Home
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Scheduling Maintenance Jobs
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring Fabric Configuration Server
- Monitoring Network Traffic Using SPAN
- Monitoring System Processes and Logs
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring Port Tracking
- Configuring FlexAttach Virtual pWWN
- Configuring Interface Buffers
- Verifying Ethernet Interfaces
Cisco DCNM SAN Client Online Help
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- May 11, 2016
Chapter: Configuring SCSI Flow Services
Configuring SCSI Flow Services
This chapter describes SCSI flow services which is supported on the Storage Services Module (SSM).
Information About SCSI Flow Services
This section includes the following topics:
- SCSI Flow Services Overview
- SCSI Flow Specification Attributes
- SCSI Flow Manager
- SCSI Flow Configuration Client
- SCSI Flow Data Path Support
SCSI Flow Services Overview
An SCSI initiator and target combination is an SCSI flow. SCSI flow services provide enhanced features for SCSI flows, such as Write Acceleration and flow monitoring for statistics obtained on an SSM.
The SCSI flow services functional architecture consists of the following components:
- SCSI flow manager (SFM) on the supervisor—The SFM resides on a supervisor module and handles the configuration of SCSI flows, validating them and relaying configuration information to the appropriate SSM. It also handles any dynamic changes to the status of the SCSI flow due to external events and registers changes that occur due to various operations.
- SCSI flow configuration CLI on the supervisor—The SFCC resides on the CPP of the SSM. It receives flow configuration requests from the SFM, programs the DPP corresponding to the initiator and target port interfaces, and responds to the SFM with the status of the configuration request.
- SCSI flow configuration client on the Control Path Processor (CPP) of an SSM.
- SCSI flow feature set support on the Data Path Processor (DPP) of an SSM—The DPP on the SSM examines all the messages between the initiator and target and provides SCSI flow features, such as Fibre Channel Write Acceleration and statistics monitoring.
Figure 45-1 shows an example of the SCSI flow services functional architecture.
Figure 45-1 SCSI Flow Services Functional Architecture
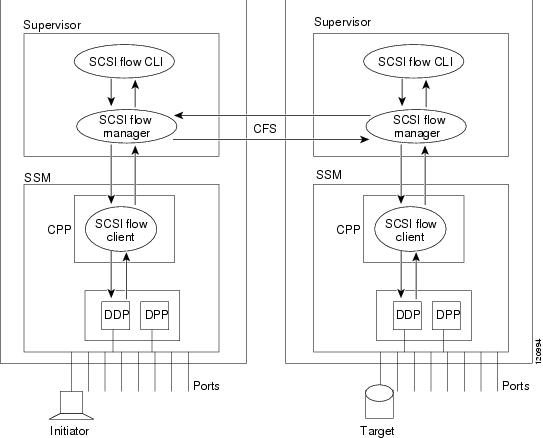

Note The SCSI target and initiator must be connected to different SSMs on different switches.

Note For statistics monitoring, the target device is not required to be connected to an SSM.
SCSI Flow Manager
The SCSI flow manager (SFM) resides on a supervisor module and handles the configuration of SCSI flows, validating them and relaying configuration information to the appropriate SSM. It also handles any dynamic changes to the status of the SCSI flow due to external events. The SFM registers events resulting from operations, such as port up or down, VSAN suspension, and zoning that affects the SCSI flow status, and updates the flow status and configuration accordingly.
The SFM on the initiator communicates to its peer on the target side using Cisco Fabric Services (CFS). Peer communication allows the initiator SFM to validate target parameters and program information on the target side.
SCSI Flow Configuration Client
A SCSI flow configuration client (SFCC) resides on the CPP of the SSM. It receives flow configuration requests from the SFM, programs the DPP corresponding to the initiator and target port interfaces, and responds to the SFM with the status of the configuration request.
Licensing Requirements for SCSI Flow Services
The following table shows the licensing requirements for SCSI Flow Services:
Guidelines and Limitations
The SCSI flow specification is a distributed configuration because the SCSI initiator and the target might be physically connected to SSMs on two different switches located across the fabric. The configuration does not require information to identify either the switch name or the SSM slot location for either the initiator or the target. The manual SCSI flow configuration is performed only at the initiator side. This simplifies the configuration process. The initiator switch sends the configuration to the SFM on the target switch using CFS. No SCSI flow configuration is necessary on the target switch.
Default Settings
Table 45-1 lists the default settings for SCSI flow services parameters.
Configuring SCSI Flow Services
This section includes the following topics:
- Enabling SCSI Flow Services
- Enabling Intelligent Storage Services
- Configuring Fibre Channel Using DCNM-SAN
- Disabling Intelligent Storage Services
Restrictions <Optional>
Enabling SCSI flow services on interfaces has the following restrictions:
- The fewest number of interfaces that you can enable is four. You can specify fc1 through fc4, but not fc1 through fc2.
- The first interface in the group must be 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 25, or 29. You can specify fc5 through fc8, but not fc7 through fc10.
- The groups of four interfaces do not need to be consecutive. You can specify fc1 through fc8 and fc17 through fc20.
A SCSI flow identifier is unique on a switch such as VSAN identifiers and is chosen by the user. To configure a SCSI flow identifier, follow these steps:
Restrictions <Optional>
The port range must be a multiple of four (for example fc4/1 through fc4-12).
To configure the values to associate with the fast, medium, and slow migration rates, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand End Devices and then select SSM Features in the Physical Attributes pane.
You see the Intelligent Storage Services configuration in the Information pane.
You see the set of configured services in the Information pane.
Step 3 Click Create Row to enable a new service on an SSM.
You see the Create SSM dialog box.
Step 4 Select the switch and SSM card you want to configure.
Step 5 (Optional) Uncheck the Use All Ports on Module check box if you want to provision a subset of the ports on the card to use this service.
Step 6 Select the port range you want to provision for using this service (starting port and ending port).
Step 7 Select the feature you want to enable on these ports from the drop-down list of services.
Step 8 Set the PartnerImageURI field if you are enabling a third-party application that requires an image loaded onto the SSM.
Step 9 Click Create to create this row and enable this service.
Configuring Fibre Channel Using DCNM-SAN
To configure a Fibre Channel using DCNM-SAN, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand End Devices and then select SSM Features in the Physical Attributes pane.
You see the Intelligent Storage Services configuration, showing the FCWA tab in the Information pane.
Step 2 Click Create Row in the Information pane to create a SCSI flow or click a row in the FCWA table to modify an existing SCSI flow.
You see the FC Write Acceleration dialog box.
Step 3 Select the initiator and target WWNs and VSAN IDs and check the WriteAcc check box to enable Fibre Channel Write Acceleration on this SCSI flow.
Step 4 (Optional) Enable SCSI flow statistics on this SCSI flow by checking the Enable Statistics check box.
Step 5 (Optional) Change the BufCount value to set the number of 2K buffers used by the SCSI target.
Disabling Intelligent Storage Services
To disable Intelligent Storage Services in DCNM-SAN for an SSM and free up a group of ports that use these services, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand End Devices and then select SSM Features in the Physical Attributes pane.
You see the Intelligent Storage Services configuration in the Information pane.
You see the set of configured services in the Information pane.
Step 3 Select the row in the table that you want to disable.
Step 4 (Optional) Check the Reboot Module on Delete check box if you want to force the card to reboot after disabling the service. This is equivalent to the CLI force option.
Step 5 Click Delete Row. The ports that were provisioned for this service become available for provisioning in another service.

Note If Reboot Module on Delete was checked, then the SSM module reboots.
Verifying SCSI Flow Services
To display SCSI Flow Services configuration information, perform one of the following tasks:
Displays the SCSI flow services configuration for all specific SCSI flow identifiers. |
|
Displays the SCSI flow services configuration for a specific SCSI flow identifiers. |
For detailed information about the fields in the output from these commands, refer to the Cisco DC-OS Command Reference .
Displaying SCSI Flow Services Information
Use the show scsi-flow command to display information about SCSI flow services (see Example 45-1 to Example 45-3).
Example 45-1 Displays Applications Provisioned on an SSM
Example 45-2 Displays SCSI Flow Services Configuration for All SCSI Flow Identifiers
Example 45-3 Displays SCSI Flow Services Configuration for a Specific SCSI Flow Identifier
 Feedback
Feedback