Cisco Cloud Services Platform 2100 Quick Start Guide, Release 2.2.0
Available Languages
Contents
- Setting Up Your Cisco CSP 2100 and Configuring Services
- Summary Steps
- Upgrading the Cisco CSP 2100 Software
- Performing the Initial Setup
- Logging In to the Cisco CSP 2100
- Generating and Installing an SSL Certificate
- Accessing the Cisco CSP 2100 Web Interface
- Overview of the Cisco CSP 2100 Web Interface
- Uploading Service Images Using the Cisco CSP 2100 Web Interface
- Creating a Service Instance
- Verifying Your Service Instance
First Published: March 15, 2017
Last Updated: August 03, 2017
Setting Up Your Cisco CSP 2100 and Configuring Services
Summary Steps
ProcedureSetting up your Cisco Cloud Services Platform 2100 (Cisco CSP 2100) and creating services consists of the following high-level steps:
Upgrading the Cisco CSP 2100 Software
You can upgrade the Cisco CSP 2100 software from Cisco CSP 2100 Release 2.1.x to Release 2.2.0 by using the Cisco Integrated Management Controller (CIMC) KVM console. Map the ISO image to the Virtual CD/DVD by using the CIMC KVM console and then install the image.
Performing the Initial Setup
Before You BeginProcedure
Make sure that the Cisco CSP 2100 is set up correctly and is cabled for network access. For information about setting up the Cisco CSP 2100, see the Cisco Cloud Services Platform 2100 Hardware Installation Guide.
Choose a hostname for your Cisco CSP 2100.
Obtain the following information about the Cisco CSP 2100 from your network administrator:
Port channel or physical network interface card (pNIC) to be used as the management interface
VLAN values for the management port channel, the management interface, and the dedicated service management interface (optional)
Two pNIC members for the port channel to be used as the management interface (optional)
Password for the admin user
Management IP address
Netmask for the management interface
Default gateway IP address
Domain name server (DNS) (optional)
Domain name
Port channel or pNIC to be used as the dedicated service management interface (optional)
Two pNIC members for the port channel to be used as the dedicated service management interface (optional)
The following example shows the prompts described in this procedure.
localhost login: admin Password: ********************************************** ********************************************** ********************************************** **** **** **** Cisco Cloud Services Platform 2100 **** **** Version 2.2.0 **** **** Built on 2017-02-19 **** **** Cisco Systems Inc, copyright 2017 **** **** **** ********************************************** ********************************************** ********************************************** Verifying server information ... System Information Manufacturer: Cisco Systems Inc Product Name: CSP-2100 Version: 2.2.0 PNIC Remote Connectivity Information from LLDP ================================================== PNIC enp1s0f0 : system = No lldp detectd intf = No lldp detected state = down PNIC enp1s0f1 : system = sw-lab-n5k-3 intf = Ethernet100/1/46 state = up PNIC enp7s0f0 : system = sw-lab-n5k-3 intf = Ethernet100/1/48 state = up PNIC enp7s0f1 : system = No lldp detectd intf = No lldp detected state = down PNIC enp4s0f0 : system = sw-lab-n5k-3 intf = Ethernet100/1/45 state = up PNIC enp4s0f1 : system = sw-lab-n5k-3 intf = Ethernet100/1/47 state = up PNIC enp4s0f2 : system = No lldp detectd intf = No lldp detected state = down PNIC enp4s0f3 : system = No lldp detectd intf = No lldp detected state = down Enable port channel for mgmt pnic (yes or no): no Choose a PNIC for the management interface: enp1s0f0, enp1s0f1, enp7s0f0, enp7s0f1, enp4s0f0, enp4s0f1, enp4s0f2, enp4s0f3: enp4s0f0 Allow management interface to be shared with service VMs (yes or no)?: yes Shared Management Interface Physical NIC : enp4s0f0 Define a vlan for the mgmt interface(yes or no)?: yes Choose a vlan for the management interface, valid values are between 1 and 4094: 180 Management vlan set to : 180 Do you want to save these settings (yes or no)?: yes Please enter a password for the CSP-2100 admin user The password must: have at least 8 characters and at most 64 characters have at least 1 digits have at least 1 special character[allowed _-~#@=+^] have at least 1 upper case character have at least 1 lower case character not have two or more same characters consecutively not be an exact dictionary word match Password: Enter it again for verification: Password: Enter your hostname: csp1 Enter your management IP address: 1.2.3.4 Enter your netmask: 255.255.255.0 Enter your default gateway: 1.2.3.1 Do you want to configure a Domain Name Server (DNS) (yes or no)?: yes Enter your Domain Name Server (DNS): 5.6.7.8 Enter your domain name: cisco.com System Hostname : csp1 Management IP Address : 1.2.3.4 Management Netmask : 255.255.255.0 Management Gateway : 1.2.3.1 Domain Name Server (DNS) : 5.6.7.8 Domain Name : cisco.com Do you want to save these settings (yes or no)?: yes Saving configuration............ Do you wish to configure s Dedicated Service Management Port (yes or no)?: yes Do you want to set the service mgmt port up as port channel (yes or no)?: yes Port channel name: SRV-MGMT Choose the first PNIC for the service mgmt port channel: enp1s0f0, enp1s0f1, enp7s0f0, enp7s0f1, enp4s0f0, enp4s0f1, enp4s0f2, enp4s0f3: enp1s0f0 Service Mgmt Pnic member 1 set to : enp1s0f0 Choose the second PNIC for the service mgmt port channel: enp1s0f0, enp1s0f1, enp7s0f0, enp7s0f1, enp4s0f0, enp4s0f1, enp4s0f2, enp4s0f3: enp1s0f1 Service Mgmt Pnic member 2 set to : enp1s0f1 Choose bond-mode for service mgmt port-channel(balance-slb or active-backup or balance-tcp)?: balance-slb Choose lacp-type for service mgmt port-channel (active or passive or off)?: active Choose vlan trunk for service mgmt port-channel: 72 Service Mgmt Port Channel: SRV-MGMT Service Mgmt Member 1 : enp1s0f0 Service Mgmt Member 2 : enp1s0f1 Service Mgmt Bond Mode : balance-slb Service Mgmt LACP type : active Service Mgmt VLAN Trunk : 72 Do you want to save these settings (yes or no)?: yes CSP-2100 expects HyperThreading to be disabled in BIOS No Cavium card in the system No Cavium card in the system Welcome to the Cisco Cloud Services Platform CLI TAC support: http://www.cisco.com/tac Copyright (c) 2015-2016, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. The copyrights to certain works contained in this software are owned by other third parties and used and distributed under license. Certain components of this software are licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2.0 or the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) Version 2.1. A copy of each such license is available at http://www.opensource.org/licenses/gpl-2.0.php and http://www.opensource.org/licenses/lgpl-2.1.php admin connected from 127.0.0.1 using console on csp1 csp1#Logging In to the Cisco CSP 2100
You can log in to the Cisco CSP 2100 by using one of the following modes: web interface (accessible through a web browser), CLI, or REST APIs (accessible through cURL tool or Windows PowerShell). However, before logging in to the web interface or using the REST APIs, you must install an SSL certificate using the CLI. For detailed information about the CLI and available commands, see the Cisco Cloud Services Platform 2100 Command Reference Guide.
Generating and Installing an SSL Certificate
Procedure
Note
For proof-of-concept (POC) or lab deployments, an SSL certificate is not required. You can skip this section and go to Accessing the Cisco CSP 2100 Web Interface.
You must generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) to send to a Certification Authority (CA) to obtain an SSL certificate and use the CLI to install the SSL certificate on Cisco CSP 2100. The default self-signed certificate installed on the Cisco CSP 2100 is only for temporary use.
Step 1 Log in to the Cisco CSP 2100 CLI in EXEC mode. Step 2 On the command prompt, use the following command to create a CSR: csp# certificate request sha sha256 keysize 2048After you enter the command, you are prompted for some information such as country name, state, city, email, common name, and so on. For detailed information about this command, see the Cisco Cloud Services Platform 2100 Command Reference Guide.
Note The common name is the DNS name of the host, including the domain name; for example, myserver.mycompany.com.
Step 3 Provide the required information in the prompt. After you provide the required information, the following two files are generated in the /osp/certificates directory:
myhost.csr—The server certificate request file
myPrivate.key—The server key file
Note To enable the Cisco CSP 2100 to start without entering a password, the myPrivate.key file is not protected with a passphrase. However, you can use a passphrase to protect it. When the myPrivate.key file is protected with a passphrase, the administrator must enter the password every time the Cisco CSP 2100 starts.
Step 4 Send the myhost.csr file to a CA to obtain an SSL certificate. After you submit the CSR to a CA, the CA generates an SSL certificate and sends a certificate file to you. The CA may also send a certificate chain file.
Step 5 Copy the SSL certificate files that you received from the CA to the /osp/certificates directory using the scp command from an external server. Step 6 On the Cisco CSP 2100 command prompt, enter the following command to install the certificate: csp# certificate install-certificateAfter you enter the command, you are prompted for some information such as localhost (hostname including the domain name), key filename, certificate filename, and chain filename. For detailed information about this command, see the Cisco Cloud Services Platform 2100 Command Reference Guide.
Step 7 Provide the required information in the prompt. After you provide the required information, the SSL certificate is installed.
To verify that the certificate is installed, follow the instructions in the next section to log in to the Cisco CSP 2100 web interface using a web browser. After logging in, click the lock icon in the address bar to see information about the installed certificate.
Accessing the Cisco CSP 2100 Web Interface
Procedure
Step 1 Enter https://hostname or https://ip-address in a web browser.
Note The hostname should resolve to the IP address that you entered as the management IP address in Performing the Initial Setup. The hostname should also match the hostname specified in Generating and Installing an SSL Certificate.
Step 2 Enter the username admin and the password. The Cisco CSP 2100 web interface is displayed.
Overview of the Cisco CSP 2100 Web Interface
The Cisco CSP 2100 web interface consists of the following tabs and pages:
Dashboard: The Dashboard tab consists of the following pages:
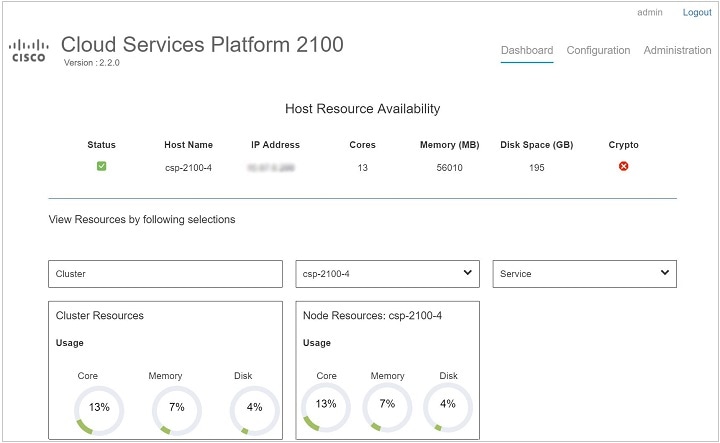
Overview: Use the Overview page to view information about the host resources. You can filter resources by clusters, nodes, and services.
Services View: Use the Services View page to view information about the services traffic rate.
Network View: Use the Network View page to view information about statistics for a pNIC.
Configuration: The Configuration page consists of the following pages:
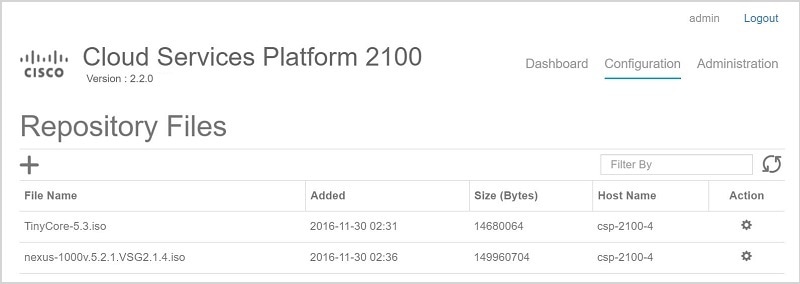
Repository: Use the Repository page to upload or remove an image and to view all available images.
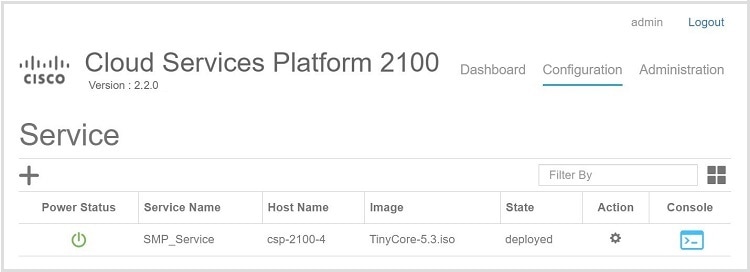
Services: Use the Services page to create a new service or configure existing services, change the power mode of a service, and export a service. You can create a new service using a template or save a service as a template.
Service Templates: Use the Services Templates page to view all available service templates and delete a service template.
pNICs: Use the pNICs page to view information about pNICs and port channels and to configure or unconfigure a pNIC as the management interface.
Port Channel: Use the Port Channel page to create a port channel, delete or edit a port channel, and to configure or unconfigure a port channel as the management interface.
SRIOV: Use the SRIOV page to enable, disable, configure, or unconfigure an SR-IOV interface.
Administration: The Administration page consists of the following pages:
Password: Use the Password page to change the password for the admin user.
Host: Use the Host page to configure the host. You can configure the hostname, host domain name, DNS server, host IP, gateway IP, management MTU, management pNIC mode, and session idle timeout.
NTP Server: Use the NTP Server page to configure an NTP server.
- User: Use the User page to create, modify, or delete a local user.
Cluster: Use the Cluster page to create, configure, and delete clusters.
NFS: Use the NFS page to create and configure NFS storage.
SNMP: Use the SNMP page to create and configure SNMP agent, communities, users, groups, and traps.
- AAA: Use the AAA page to specify the AAA authentication mode and to create, modify, or delete a TACACS+ or RADIUS server.
- IP Receive ACL: Use the IP Receive ACL page to configure the Access Control List (ACL) access for the management interface. You can specify the source network IP address, service type, priority, and action for the packets received from the specified source network.
Uploading Service Images Using the Cisco CSP 2100 Web Interface
Before You BeginProcedureBe sure to download the service image to your local machine or a location on your local network that is accessible to your Cisco CSP 2100.
Step 1 Click the Configuration tab and then choose Repository. Step 2 On the Repository Files page, click the add button (+). Step 3 Click Browse. Step 4 Navigate to the service image, select a service image, and click Open. Step 5 Click Upload. After the service image is uploaded, the image name and other relevant information are displayed in the Repository Files table.
Tip You can also use this procedure to upload the banner files and the configuration files to the repository.
Creating a Service Instance
Procedure
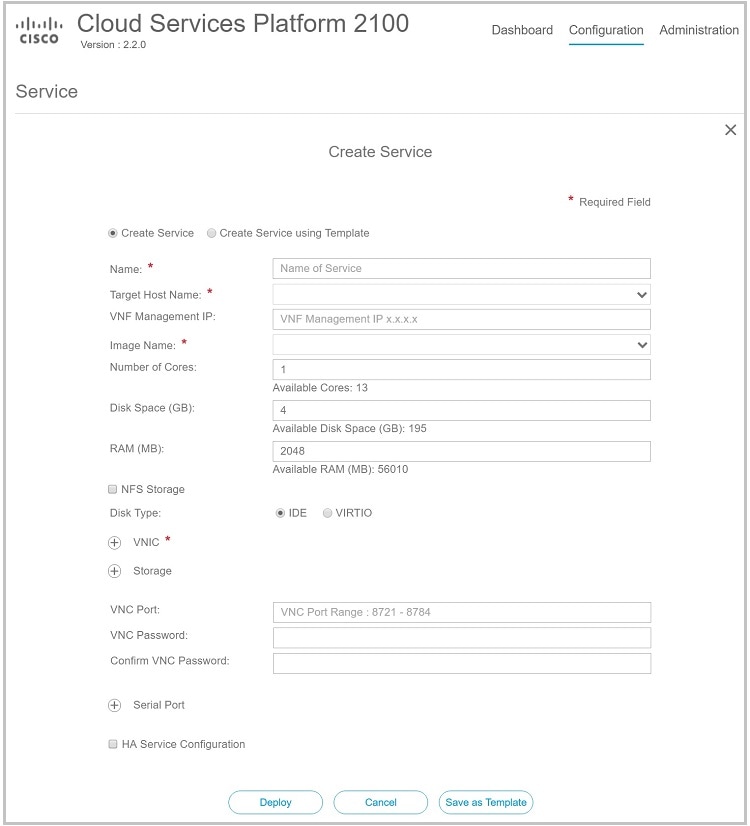
Step 1 Click the Configuration tab and then choose Services. Step 2 On the Service page, click the add (+) button. The Create Service page is displayed.
Step 3 In the Name field, enter a name for the service. Step 4 From the Target Host Name drop-down list, choose the target host. Step 5 (Optional)In the VNF Management IP field, enter the VNF management IP address to be used in the service.
Note The VNF Management IP value entered in this field does not get configured in the service. This field serves only as a reference to the VNF management IP address mapped to a service.
Step 6 From the Image Name drop-down list, choose an image file for the service. You can use an ISO or OVA, or a QCOW software image file to create the service.
Note With Cisco VSM and Cisco VSG services, only ISO image files are supported.
Depending on the type of image selected, additional fields are displayed. If your service requires additional information, as is the case with Cisco VSM and Cisco VSG services, you must enter this information in the Additional Image Questionnaires section. For details about the additional information that your service requires, see the documentation for that service.
Step 7 (Optional)In the Number of Cores field, specify the number of cores. Make sure that the new value does not exceed the available resources. Step 8 (Optional)In the Disk Space (GB) field, specify the hard disk space. Make sure that the new value does not exceed the available resources. Step 9 (Optional)In the RAM (MB) field, specify the RAM. Make sure that the new value does not exceed the available resources. Step 10 (Optional)If you want to deploy the service on an NFS storage, select the NFS Storage check box and then select an NFS storage from the NFS drop-down list. Step 11 (Optional)In the Disk Type field, specify the disk type. Valid choices are IDE or VIRTIO. Step 12 Click VNIC and in the VNIC Configuration dialog box, do the following:
To add more vNICs, click VNIC and repeat all tasks described in this step.
Step 13 (Optional)Click Storage and in the Storage Configuration dialog box, do the following:
To add more storage, click Storage and repeat all tasks described this step.
Step 14 (Optional)In the VNC Port field, enter a VNC port for the service. Valid range is from 8721 to 8784. Step 15 (Optional)In the VNC Password field, enter a password and then enter the same password in the Confirm VNC Password field.
Caution We strongly advise that you secure your remote access with a complex alphanumeric password for VNC.
Note The VNC console password is in clear text which might be indicated as a security issue. To ensure that the VNC console access is secure in Cisco CSP 2100, the VNC console is accessible only through the web interface which is protected by a user name and a password.
Step 16 Click Serial Port and in the Serial Port dialog box, do the following:
- In the Type field, specify the port type. Valid choices are Telnet and Console.
- If you have selected Telnet type in Step a, then in the Service Port Number field, enter a value. Valid range is from 7000 to 8700.
- When you are satisfied with the serial port configuration, click Submit.
To add more serial ports, click Serial Port and repeat all tasks described in this step.
Step 17 (Optional)If you are configuring the services in redundancy, select the HA Service Configuration check box. The Cisco CSP 2100s must be in the cluster mode. Do the following:
Step 18 Click Deploy. The Service Test Creation dialog box is displayed indicating that the service is available.
Copyright © 2017, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)

 Feedback
Feedback