The interconnections between users and applications are evolving to complex digital business architectures due to emergence
of multi-cloud IaaS and SaaS vendors. This requires the network to be both fast and flexible to meet the expanding changes
and demand.
Current Landscape
Distribution of Applications from Data Centers to IaaS and SaaS
Applications reside in multiple locations, including the private data center; in the cloud in the form of infrastructure as
a service (IaaS) with providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform; or as software as a service (SaaS) with providers
such as ServiceNow and Salesforce, Box, Office 365, to name a few. Regardless of an organization’s cloud strategy, most will
have applications across all locations.
Digitization is placing unprecedented demands on IT to increase the speed of services and products delivered to customers,
partners, and employees, all while maintaining a high level of security. With the adoption of multi-cloud infrastructure,
the need to connect multiple user groups in an agile and secure manner places additional demands on the IT teams.
Challenges
-
It is becoming increasingly difficult to apply security policies uniformly across multi-cloud applications.
-
Some IaaS and SaaS vendors may not provide the required security options.
-
The IaaS and SaaS providers that do the security options you need may not necessarily do so in a way that is consistent with
your enterprise policy.
-
There is inconsistency in application of policies across products and applications.
Business Impact
The business impact of the rising complexity resulting from multi-cloud adoption and the increasing demand for flexibility
and security can be categorized as follows.
-
Latency and Increased Costs: As enterprises embrace cloud, they are required to backhaul traffic to their data centers to apply security policies and
to gain visibility in the incoming and outgoing IaaS and SaaS traffic. This hairpinning of traffic causes latency and increases
costs.
-
Inefficiency: A majority of changes that are being implemented in response to the changing IT landscape are still being implemented manually.
This lack of network agility and automation has led to inefficiency in service enablement.
-
Under-utilization The existing infrastructure is designed for maximum capacity, but has low utilization.
-
Security: The attack surfaces are expanding due to increasing numbers of security vendors and connectivity to cloud-hosted services.
This has led to an increased time in detecting and remediating network attacks.
How SAE can Help Overcome the Challenges
As enterprises adopt a multi-cloud strategy, they must look at optimizing traffic patterns for experience, securing interactions,
reducing circuit costs, and providing flexibility.
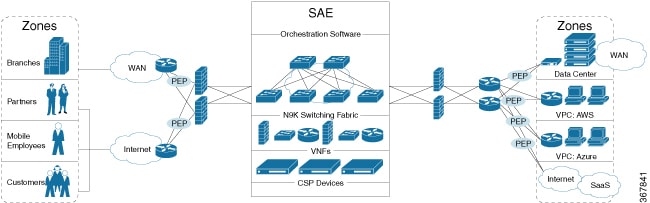
The success of multi-cloud solutions depends on a new cloud-edge capability, where all consumer networks terminate in a carrier-neutral
facility and security policies can be enforced centrally.
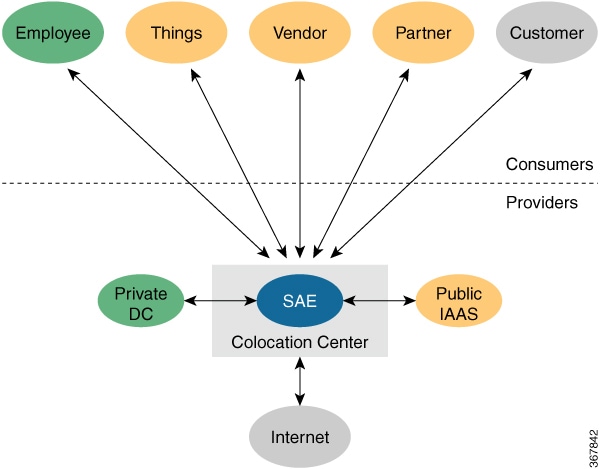
This is where SAE comes in. SAE offers the capability of virtualizing your network edge and extending it to colocation centers.
SAE provides segmentation, virtualization, automation, and orchestration for your enterprise within a carrier-neutral facility.
Virtualization, automation, and orchestration are foundational to SAE. Virtualization negates the need to design infrastructure
for future requirements of scale by providing an agile way of scaling up and down as required.

Note |
It is possible to place SAE in your private data center; however, we recommend deploying SAE in a carrier-neutral facility
to truly benefit from the agility it offers. Deploying SAE in a carrier-neutral or colocation facility offers the following
benefits.
-
Proximity to clouds, which helps maintain app SLAs
-
Security and telemetry across multiple clouds
-
Single location to view and audit traffic and user-app relationships
|


 Feedback
Feedback