Administration FAQs
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the role of a Cisco Secure Email Encryption Service (Encryption Service) corporate account administrator.
Q. What is a Cisco Secure Email Encryption Service Corporate Account?
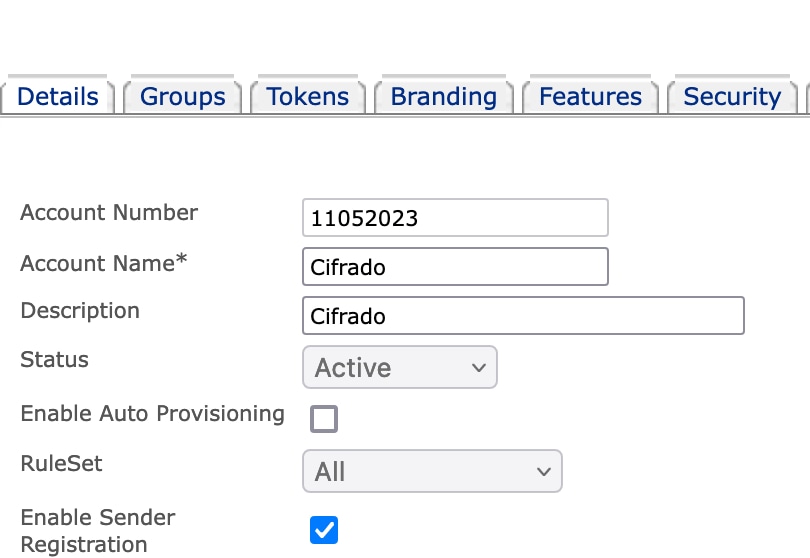
A. Each organization that uses encryption technology and Encryption Service has a corporate account with the service. This account can be used in conjunction with one or more Cisco Secure Email Gateways that send encrypted messages.
Typically, an organization has a single corporate account, and the account administrator(s) manages only that account.
Q. What are the typical tasks of an account administrator?
A. Typical administrative tasks include:
-
Configuring the corporate account (for example, uploading an organization’s logo to display it on Secure Messages sent using the account)
. -
Monitoring account usage (for example, viewing statistics about user registration and user account activation).
-
Managing messages sent using the account (for example, disabling access to a particular message).
 Note |
Account administrators cannot access the content of user messages that they manage in the Administration Console. |
For more information about administrative tasks, see the Common Tasks.
Q. Which email administration topics are covered in this guide?
A. Administration of a Cisco Secure Email solution involves two distinct areas of responsibility:
-
Managing Cisco Secure Email Gateways and Cisco Encryption appliances
-
Managing a Encryption Service corporate account
This guide contains information about managing a Encryption Service corporate account. For information about managing Cisco Secure Email Gateways, see the product documentation available on the Cisco Customer Support Portal.
Q. What is recipient enrollment?
A. Recipient enrollment, also called user registration, is the process of creating a Encryption Service user account for a first-time recipient of a Registered Secure Message. Most message recipients must complete the enrollment process by providing user profile information and choosing a password before opening the encrypted messages that they receive. However, if the message uses low security, the user can open the message without registering.
Cisco Secure Email Encryption Service Accounts
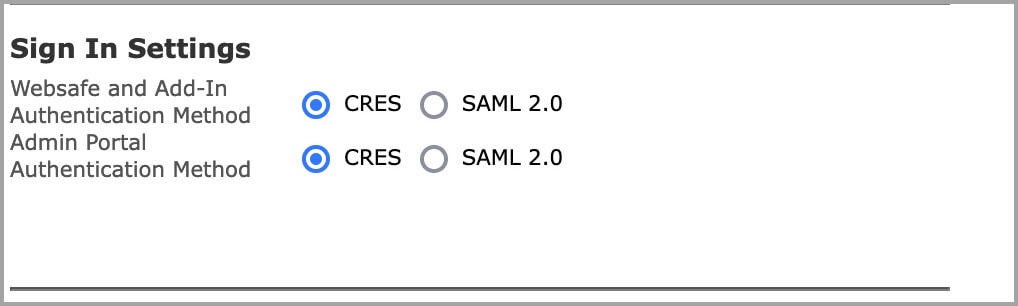
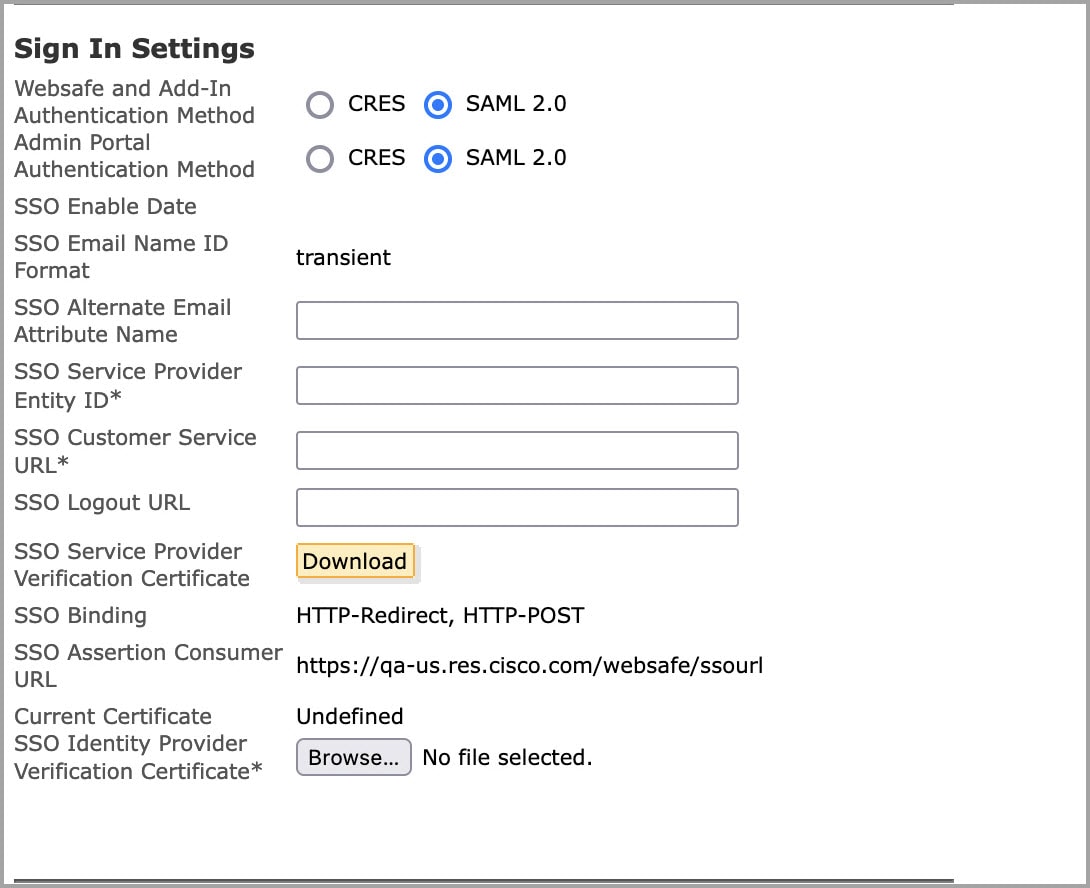
Q. When a user enrolls with Encryption Service, why is the user not associated with a particular sender’s corporate account.
A. Senders and recipients have Encryption Service accounts. The sender Encryption Service account allows the sender of an encrypted message to manage their secure messages either by expiring or recalling them.
Users
User account administration is handled by system administrators at Encryption Service. Typically, corporate account administrators do not manage individual user accounts.
Corporate administrator manages internal Encryption Service users for the purpose of resetting passwords or locking existing accounts. If a Encryption Service administrator wishes to manage their user accounts, a customer support ticket must be filed to add the managed domains to the account.
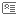
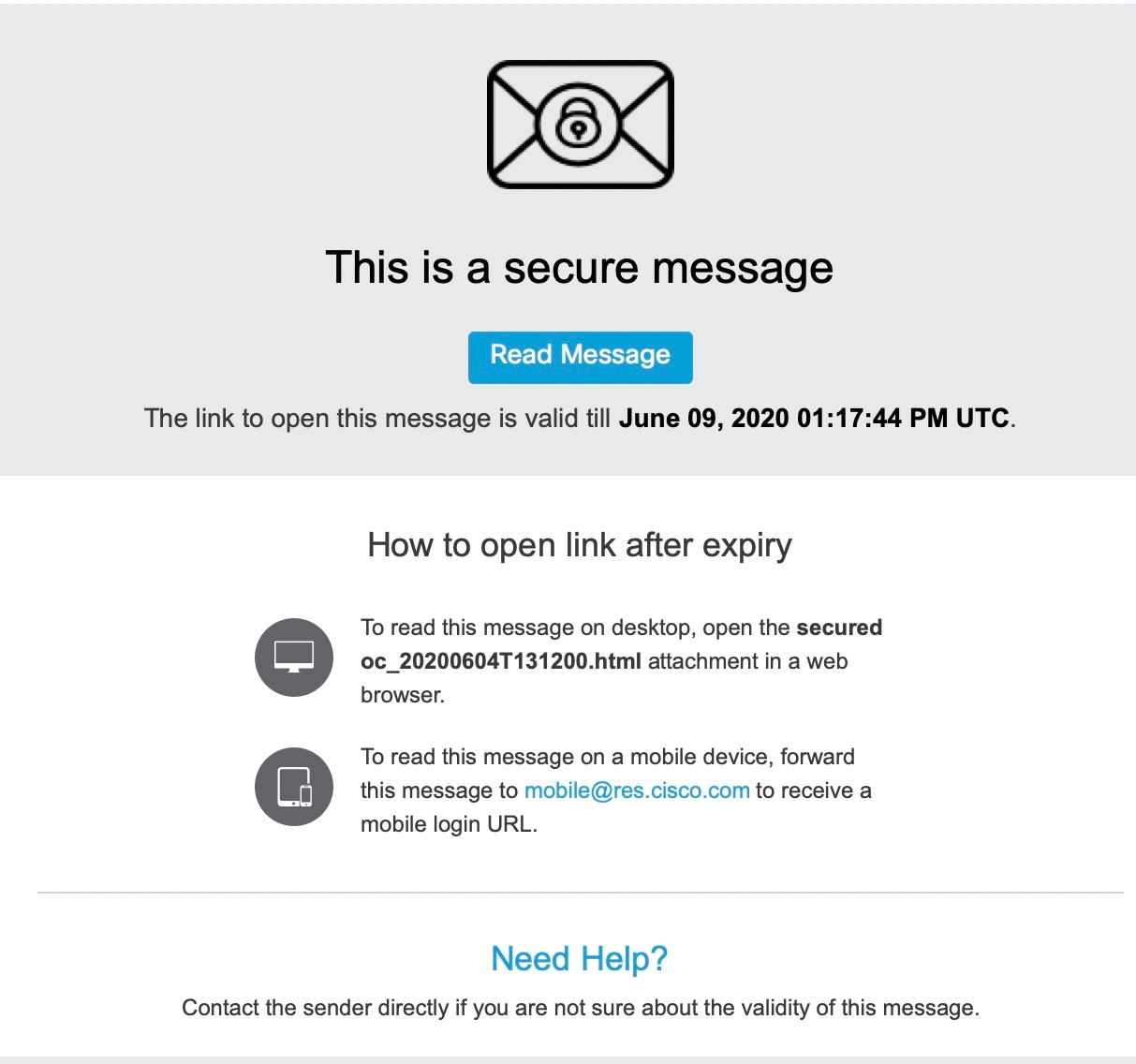
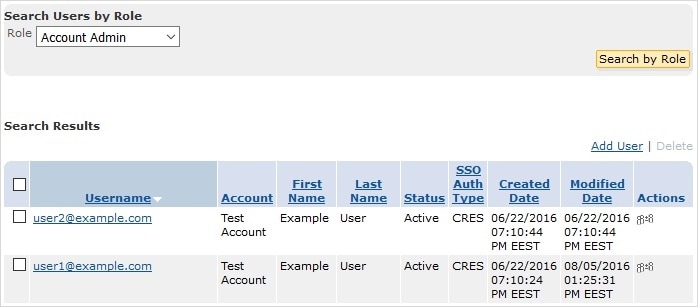
Q. What are user groups and roles?
A. Groups are lists of enrolled users. Roles are sets of privileges that you can associate with groups. For example, to create an account administrator, someone with administrative privileges for the account must add the user to the account administrator group. Roles are not associated with individuals.
 Note |
Every user in a particular account administrator group can administer that account. |


 Feedback
Feedback