- Preface
- New and Changed Security Features
- Configuring AAA Services
- Implementing Certification Authority Interoperability
- Implementing Keychain Management
- Implementing Lawful Intercept
- Implementing Management Plane Protection
- Configuring Software Authentication Manager
- Implementing Secure Shell
- Implementing Secure Socket Layer
- Configuring FIPS Mode
- Index
- Prerequisites for Implementing Lawful Intercept
- Restrictions for Implementing Lawful Intercept
- Information About Lawful Intercept Implementation
- Intercepting IPv4 and IPv6 Packets
- High Availability for Lawful Intercept
- Installing Lawful Intercept (LI) Package
- How to Configure SNMPv3 Access for Lawful Intercept on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
- Configuration Example for Inband Management Plane Feature Enablement
- Additional References
Implementing Lawful
Intercept
Lawful intercept is the process by which law enforcement agencies conduct electronic surveillance of circuit and packet-mode communications, authorized by judicial or administrative order. Service providers worldwide are legally required to assist law enforcement agencies in conducting electronic surveillance in both circuit-switched and packet-mode networks.
Only authorized service provider personnel are permitted to process and configure lawfully authorized intercept orders. Network administrators and technicians are prohibited from obtaining knowledge of lawfully authorized intercept orders, or intercepts in progress. Error messages or program messages for intercepts installed in the router are not displayed on the console.
Lawful Intercept is not a part of the Cisco IOS XR software by default. You have to install it separately by installing and activating c12k-li.pie .
Feature History for Implementing Lawful Intercept
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
Release 3.7.0 |
This feature was introduced. |
|
Release 3.8.0 |
Information erroneously stating that data interception was supported on the AAA RADIUS server was corrected. |
|
Release 4.0.0 |
Feature information to intercept IPV6 packets was added. Support for intercepting IPV6 packets based on Flow ID mapping, VRF aware matching including 6VPE, mapping packets in 6PE disposition and replicating tag2ip and ip2tag packets was added. |
|
Release 4.2.0 |
High Availability support for Lawful Intercept was added. |
|
Release 4.3.2 |
Lawful Intercept is available as a separate package. It is no longer a part of the Cisco IOS XR software. |
- Prerequisites for Implementing Lawful Intercept
- Restrictions for Implementing Lawful Intercept
- Information About Lawful Intercept Implementation
- Intercepting IPv4 and IPv6 Packets
- High Availability for Lawful Intercept
- Installing Lawful Intercept (LI) Package
- How to Configure SNMPv3 Access for Lawful Intercept on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
- Configuration Example for Inband Management Plane Feature Enablement
- Additional References
Prerequisites for Implementing Lawful Intercept
You must be in a user group associated with a task group that includes the proper task IDs. The command reference guides include the task IDs required for each command. If you suspect user group assignment is preventing you from using a command, contact your AAA administrator for assistance.
Lawful intercept implementation also requires that these prerequisites are met:
-
Provisioned router—The router must be already provisioned. For more information, see Cisco IOS XR Getting Started Guide for the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router.

TipFor the purpose of lawful intercept taps, provisioning a loopback interface has advantages over other interface types.
-
Understanding of SNMP Server commands in Cisco IOS XR software—Simple Network Management Protocol, version 3 (SNMP v3), which is the basis for lawful intercept enablement, is configured using commands described in the module SNMP Server Commands in Cisco IOS XR System Management Command Reference for the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router. To implement lawful intercept, you must understand how the SNMP server functions. For this reason, carefully review the information described in the module Implementing SNMP in Cisco IOS XR System Management Configuration Guide for the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router.
-
Lawful intercept must be explicitly disabled—It is automatically enabled on a provisioned router. However, you should not disable LI if there is an active tap in progress, because this deletes the tap.
-
Management plane configured to enable SNMPv3—Allows the management plane to accept SNMP commands, so that the commands go to the interface (preferably, a loopback) on the router. This allows the mediation device (MD) to communicate with a physical interface.
-
VACM views enabled for SNMP server—View-based access control model (VACM) views must be enabled on the router.
-
Provisioned MD—For detailed information, see the vendor documentation associated with your MD. For a list of MD equipment suppliers preferred by Cisco, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk583/tk799/tsd_technology_support_protocol_home.html.
- VoIP surveillance-specific requirements
-
Lawful-intercept-enabled call agent—A lawful-intercept-enabled call agent must support interfaces for communications with the MD, for the target of interest to provide signaling information to the MD. The MD extracts source and destination IP addresses and Real-Time Protocol (RTP) port numbers from the Session Description Protocol (SDP) signaling information for the target of interest. It uses these to form an SNMPv3 SET, which is sent to the router acting as the content IAP to provision the intercept for the target of interest.
The MD uses the CISCO-TAP2-MIB to set up communications between the router acting as the content IAP, and the MD.
The MD uses the CISCO-IP-TAP-MIB to set up the filter for the IP addresses and port numbers to be intercepted and derived from the SDP.
-
Routers to be used for calls by the target number must be provisioned for this purpose through the MD.
-
The MD that has been provisioned with the target number to be intercepted.
-
- Data session surveillance-specific requirements
-
Routers to be used by the data target that have been provisioned for this purpose through the MD.
-
The MD that has been provisioned with the user login ID, mac address of the user CPE device, or the DSLAM physical location ID—The IP address is the binding that is most frequently used to identify the target in the network. However, alternative forms of information that uniquely identify the target in the network might be used in some network architectures. Such alternatives include the MAC address and the acct-session-id.
-
The MD can be located anywhere in the network but must be reachable from the content IAP router, which is being used to intercept the target. MD should be reachable ONLY from global routing table and NOT from VRF routing table.
Restrictions for Implementing Lawful Intercept
-
Lawful intercept does not provide support for these features on Cisco XR 12000 Series Router:
-
Lawful intercept is applied only on IP traffic. If IP traffic is configured to leave an egress port as MPLS-encapsulated frames, then lawful intercept will not apply to the egress port, even if overlapping taps are configured.
Information About Lawful Intercept Implementation
Cisco lawful intercept is based on service-independent intercept (SII) architecture and SNMPv3 provisioning architecture. SNMPv3 addresses the requirements to authenticate data origin and ensure that the connection from the router to the MD is secure. This ensures that unauthorized parties cannot forge an intercept target.
Lawful intercept offers these capabilities:
-
Voice-over IP (VoIP) and data session intercept provisioning from the MD using SNMPv3
-
Delivery of intercepted VoIP and data session data to the MD
-
SNMPv3 lawful intercept provisioning interface
-
Lawful intercept MIB: CISCO-TAP2-MIB, version 2
-
CISCO-IP-TAP-MIB manages the Cisco intercept feature for IP and is used along with CISCO-TAP2-MIB to intercept IP traffic.
-
User datagram protocol (UDP) encapsulation to the MD
Replication and forwarding of intercepted packets to the MD
-
Voice-over IP (VoIP) call intercept, based on any rules configured for received packets.
-
Voice-over IP (VoIP) intercept with LI-enabled call agent
-
Data session call intercept based on IP address
- Provisioning for VoIP Calls
- Call Interception
- Provisioning for Data Sessions
- Data Interception
- Lawful Intercept Topology
- Scale or Performance Improvement
Provisioning for VoIP Calls
Lawful Intercept provisioning for VoIP occurs in these ways:
Call Interception
VoIP calls are intercepted in this manner:
-
The MD uses configuration commands to configure the intercept on the call control entity.
-
The call control entity sends intercept-related information about the target to the MD.
-
The MD initiates call content intercept requests to the content IAP router or trunk gateway through SNMPv3.
-
The content IAP router or trunk gateway intercepts the call content, replicates it, and sends it to the MD in Packet Cable Electronic Surveillance UDP format. Specifically, the original packet starting at the first byte of the IP header is prefixed with a four-byte CCCID supplied by the MD in TAP2-MIB. It is then put into a UDP frame with the destination address and port of the MD.
-
After replicated VoIP packets are sent to the MD, the MD then forwards a copy to a law-enforcement-agency-owned collection function, using a recognized standard.
Provisioning for Data Sessions
Provisioning for data sessions occurs in a similar way to the way it does for lawful intercept for VoIP calls. (See Provisioning for VoIP Calls.)
Data Interception
Data are intercepted in this manner:
- If a lawful intercept-enabled authentication or accounting server is not available, a sniffer device can be used to detect the presence of the target in the network.
-
The MD initiates communication content intercept requests to the content IAP router using SNMPv3.
-
The content IAP router intercepts the communication content, replicates it, and sends it to the MD in UDP format.
-
Intercepted data sessions are sent from the MD to the collection function of the law enforcement agency, using a supported delivery standard for lawful intercept.
Information About the MD
The MD performs these tasks:
Lawful Intercept Topology
This figure shows intercept access points and interfaces in a lawful intercept topology for both voice and data interception.
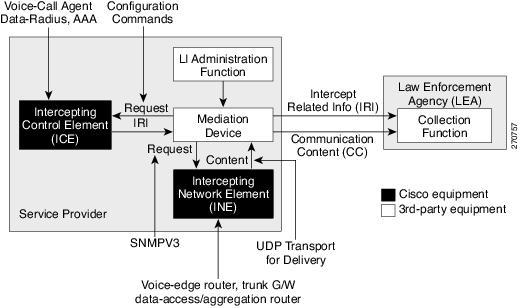
Scale or Performance Improvement
New enhancements introduced on the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router in terms of scalability and performance for lawful intercept are:
Intercepting IPv4 and IPv6 Packets
This section provides details for intercepting IPv4 and IPv6 packets supported on the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router.
- Lawful Intercept Filters
- Intercepting Packets Based on Flow ID (Applies to IPv6 only)
- Intercepting VRF (6VPE) and 6PE Packets
- Encapsulation Type Supported for Intercepted Packets
- Per Tap Drop Counter Support
Lawful Intercept Filters
The filters used for classifying a tap are:
Intercepting Packets Based on Flow ID (Applies to IPv6 only)
To further extend filteration criteria for IPv6 packets, an additional support to intercept IPv6 packets based on flow ID has been introduced on the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router. All IPv6 packets are intercepted based on the fields in the IPv6 header which comprises numerous fields defined in IPv6 Header Field Details table:
 Note | The field length or payload length is not used for intercepting packets. |
| IPv6 Field Name | Field Description | Field Length |
|---|---|---|
|
Version |
IPv6 version number. |
4 bits |
|
Traffic Class |
Internet traffic priority delivery value. |
8 bits |
|
Flow ID (Flow Label) |
Used for specifying special router handling from source to destination(s) for a sequence of packets. |
20 bits |
|
Payload Length |
Specifies the length of the data in the packet. When cleared to zero, the option is a hop-by-hop Jumbo payload. |
16 bits unassigned |
|
Next Header |
Specifies the next encapsulated protocol. The values are compatible with those specified for the IPv4 protocol field. |
8 bits |
|
Hop Limit |
For each router that forwards the packet, the hop limit is decremented by 1. When the hop limit field reaches zero, the packet is discarded. This replaces the TTL field in the IPv4 header that was originally intended to be used as a time based hop limit. |
8 bits unsigned |
|
Source Address |
The IPv6 address of the sending node. |
16 bytes |
|
Destination Address |
The IPv6 address of the destination node. |
16 bytes |
The flow ID or flow label is a 20 bit field in the IPv6 packet header that is used to discriminate traffic flows. Each flow has a unique flow ID. The filteration criteria to intercept packets matching a particular flow ID is defined in the tap configuration file. From the line card, the intercepted mapped flow IDs are sent to the next hop, specified in the MD configuration file. The intercepted packets are replicated and sent to the MD fom the line card.
Intercepting VRF (6VPE) and 6PE Packets
This section provides information about intercepting VRF aware packets and 6PE packets. Before describing how it works, a basic understanding of 6VPE networks is discussed.
The MPLS VPN model is a true peer VPN model. It enforces traffic separations by assigning unique VPN route forwarding (VRF) tables to each customer's VPN at the provider content IAP router. Thus, users in a specific VPN cannot view traffic outside their VPN.
Cisco XR 12000 Series Router supports intercepting IPv6 packets of the specified VRF ID for 6VPE. To distiguish traffic on VPN, VRFs are defined containing a specific VRF ID. The filter criteria to tap a particular VRF ID is specified in the tap. IPv6 packets are intercepted with the VRF context on both scenarios: imposition (ip2mpls) and disposition (mpls2ip).
The 6PE packets carry IPv6 packets over VPN. The packets do not have a VRF ID. Only IP traffic is intercepted; no MPLS based intercepts are supported. The IPv6 traffic is intercepted at the content IAP of the MPLS cloud at imposition (ip2mpls) and at disposition (mpls2ip).
Intercepting IPv6 packets is also performed for ip2tag and tag2ip packets. Ip2tag packets are those which are converted from IPv6 to Tagging (IPv6 to MPLS), and tag2ip packects are those which are converted from Tagging to IPv6 (MPLS to IPv6) at the provider content IAP router.
Encapsulation Type Supported for Intercepted Packets
Intercepted packets mapping the tap are replicated, encapsulated, and then sent to the MD. IPv4 and IPv6 packets are encapsulated using UDP (User Datagram Protocol) encapsulation. The replicated packets are forwarded to MD using UDP as the content delivery protocol. Both IPv4 and IPv6 MD encapsulations are supported. The encapsulation type (IPv4 or IPv6) depends on the address of MD.
The intercepted packet gets a new UDP header and IPv4 header. Information for IPv4 header is derived from MD configuration. Apart from the IP and UDP headers, a 4 byte channel identifier (CCCID) is also inserted after the UDP header in the packet. After adding the MD encapsulation, if the packet size is above the MTU, the egress LC CPU fragments the packet. Moreover, there is a possibility that the packet tapped is already a fragment. Each tap is associated with only one MD. Cisco XR 12000 Series Router does not support forwarding replicated packets to multiple MDs.
 Note | Encapsulation types, such as RTP and RTP-NOR, are not supported. |
Per Tap Drop Counter Support
Cisco XR 12000 Series Router line cards provide SNMP server as an interface to export each tap forwarded to MD packet and drop counts. Any intercepted packets that are dropped prior to getting forwarded to the MD due to policer action are counted and reported. The drops due to policer action are the only drops that are counted under per tap drop counters. If a lawful intercept filter is modified, the packet counts are reset to 0.
High Availability for Lawful Intercept
High availability for lawful intercept provides operational continuity of the TAP flows and provisioned MD tables to reduce loss of information due to route processor fail over (RPFO).
To achieve continuous interception of a stream, when RP fail over is detected; MDs are required to re-provision all the rows relating to CISCO-TAP2-MIB, CISCO-IP-TAP-MIB, and CISCO-USER-CONNECTION-TAP-MIB to synchronize database view across RP and MD.
 Note | The high availability for lawful intercept is enabled by default from Release 4.2.0 onwards. |
Preserving TAP and MD Tables during RP Fail Over
At any point in time, MD has the responsibility to detect the loss of the taps via SNMP configuration process.
After RPFO is completed, MD should re-provision all the entries in the stream tables, MD tables, and IP taps with the same values they had before fail over. As long as an entry is re-provisioned in time, existing taps will continue to flow without any loss.
The following restrictions are listed for re-provisioning MD and tap tables with respect to behavior of SNMP operation on citapStreamEntry, cTap2StreamEntry, cTap2MediationEntry MIB objects:
After RPFO, table rows that are not re-provisioned, shall return NO_SUCH_INSTANCE value as result of SNMP Get operation.
Entire row in the table must be created in a single configuration step, with exactly same values as before RPFO, and with the rowStatus as CreateAndGo. Only exception is the cTap2MediationTimeout object, that should reflect valid future time.
Replay Timer
The replay timer is an internal timeout that provides enough time for MD to re-provision tap entries while maintaining existing tap flows. It resets and starts on the active RP when RPFO takes place. The replay timer is a factor of number of LI entries in router with a minimum value of 10 minutes.
After replay timeout, interception stops on taps that are not re-provisioned.
 Note | In case high availability is not required, MD waits for entries to age out after fail over. MD cannot change an entry before replay timer expiry. It can either reinstall taps as is, and then modify; or wait for it to age out. |
Installing Lawful Intercept (LI) Package
As LI is not a part of the Cisco IOS XR image by default, you need to install it separately.
- Installing and Activating the LI Package
- Deactivating the LI PIE
- Upgrade and Downgrade Scenarios for the Lawful Intercept package
Installing and Activating the LI Package
The Package Installation Envelope (PIE) files, are installable software files with the .pie extension. PIE files are used to copy one or more software components onto the router. A PIE may contain a single component, a group of components (called a package), or a set of packages (called a composite package).
Use the show install committed command in EXEC mode to verify the committed software packages.
To install the Lawful Intercept (LI) package, you must install and activate the c12k-li.pie
For more information about installing PIEs, refer to Upgrading and Managing Cisco IOS XR Software section of the Cisco IOS XR System Management Configuration Guide for the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router.
1.
admin
2.
install add tftp://<IP address of tftp server>/<location of pie on server>
3.
install activate device:package
4.
install commit
5.
exit
6.
show install committed
DETAILED STEPS
Deactivating the LI PIE
To uninstall the Lawful Intercept package, deactivate c12k-li.pie as shown in the following steps:
1.
admin
2.
install deactivate device:package
3.
install commit
4.
install remove device:package
5.
exit
6.
show install committed
DETAILED STEPS
Upgrade and Downgrade Scenarios for the Lawful Intercept package
This section describes the possible upgrade and downgrade scenarios with respect to the Lawful Intercept (LI) package.
This example configuration demonstrates how to upgrade or downgrade the Cisco IOS XR software with or without the LI package. Suppose you have two versions of software images, V1 and V2. If you want to upgrade or downgrade from V1 to V2 without the LI package, you need to perform the following steps for the upgrade or the downgrade procedure:
 Note | Ensure that you use Turbo Boot to load the image for the downgrade process. |
Ensure that the device has booted with the V1 image. Check the Package Installation Envelope (PIE) files that have been installed in V1.
Save all the PIE files that exist in V2 in the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server. Copy the contents of the PIE files from the TFTP server by using the install add command in the admin mode.
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(admin)# install add tar tftp://223.255.254.254/install/files/pies.tar
To activate all the PIE files in V2 at once, run the following commands based on the type of upgrade:
At any point during the upgrade or the downgrade process, you can check the progress by using the show install request or the show issu command.
Release 4.3.1 base image: It is the Cisco IOS XR software for Release 4.3.1 that contains Cisco LI by default.
Release 4.3.2 base image: It is the Cisco IOS XR software for Release 4.3.2 that does not contain Cisco LI by default.
Separate LI package: It is the LI package that needs to be installed separately for Release 4.3.2 and higher versions.
| Upgrade From | Upgrade To | Result | Supported |
|---|---|---|---|
| Release 4.3.1 base image | Release 4.3.2 base image | Before the upgrade, the LI has to be configured and provisioned completely. After the upgrade to Release 4.3.2 version without the LI package, you cannot configure or provision LI. | Yes |
| Release 4.3.1 base image | Release 4.3.2 base image with the separate LI package | The Upgrade will reload the router. After the upgrade process completes, you need to reconfigure LI MDs/TAPs from the SNMP server. Also, all the LI configurations made in the earlier version is accepted. | Yes |
| Release 4.3.2 base image with the separate LI package | Release 4.3.3 base image with the separate LI package | After the upgrade, the LI configuration is not retained. | Yes |
| Release 4.3.2 base image with the separate LI package | Release 4.3.3 base image without the separate LI package | This upgrade is not possible as the installation process will not proceed without the LI PIE. | No |
| Release 4.3.2 base image without the separate LI package | Release 4.3.3 base image with the separate LI package | This upgrade is possible. | Yes |
| ISSU for Release 4.3.1 base image | Release 4.3.2 with the separate LI package | After this upgrade, to retain the LI configuration, you have to replay the configuration before the replay timeout occurs. | Yes |
| ISSU for Release 4.3.2 base image with the separate LI package | Release 4.3.3 with the separate LI package | After this upgrade, to retain the LI configuration, you have to replay the configuration before the replay timeout occurs. | Yes |
| Downgrade From | Downgrade To | Result | Supported |
|---|---|---|---|
| Release 4.3.2 base image without the separate LI package | Release 4.3.1 base image | After the downgrade, begin the provisioning process of LI. | Yes |
| Release 4.3.2 base image with the separate LI package | Release 4.3.1 base image | This scenario is not supported. | No |
| Release 4.3.3 base image with the separate LI package | Release 4.3.2 base image with the separate LI package | After the downgrade, the LI configuration is not retained. You have to provision the LI once again. | Yes |
| Release 4.3.3 base image with the separate LI package | Release 4.3.2 base image without the LI package | After the downgrade, the LI configuration is lost. You will not be able to provision it after downgrade. | Yes |
| Release 4.3.3 base image | Release 4.3.2 base image with the separate LI package | The LI configuration is accepted and can be provisioned only after the downgrade. | Yes |
| ISSU | No |
How to Configure SNMPv3 Access for Lawful Intercept on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
Perform these procedures in the order presented to configure SNMPv3 for the purpose of Lawful Intercept enablement:
- Disabling SNMP-based Lawful Intercept
- Configuring the Inband Management Plane Protection Feature
- Enabling the Mediation Device to Intercept VoIP and Data Sessions
Disabling SNMP-based Lawful Intercept
Lawful Intercept is enabled by default on the after installing and activating the .
-
To disable Lawful Intercept, enter the lawful-intercept disable command in global configuration mode.
-
To re-enable it, use the no form of this command.
Disabling SNMP-based Lawful Intercept: Example
RP/0/0/CPU0:router# configure RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config)# lawful-intercept disable
 Note | The lawful-intercept disable command is available on the router, only after installing and activating the . All SNMP-based taps are dropped when lawful intercept is disabled. |
Configuring the Inband Management Plane Protection Feature
If MPP was not earlier configured to work with another protocol, then ensure that the MPP feature is also not configured to enable the SNMP server to communicate with the mediation device for lawful interception. In such cases, MPP must be configured specifically as an inband interface to allow SNMP commands to be accepted by the router, using a specified interface or all interfaces.
 Note | Ensure this task is performed, even if you have recently migrated to Cisco IOS XR Software from Cisco IOS, and you had MPP configured for a given protocol. |
For lawful intercept, a loopback interface is often the choice for SNMP messages. If you choose this interface type, you must include it in your inband management configuration.
For a more detailed discussion of the inband management interface, see the Inband Management Interface.
Related Tasks
Related Examples
Enabling the Mediation Device to Intercept VoIP and Data Sessions
The following SNMP server configuration tasks enable the Cisco SII feature on a router running Cisco IOS XR Software by allowing the MD to intercept VoIP or data sessions.
1.
configure
2.
snmp-server view
view-name
ciscoTap2MIB
included
3.
snmp-server view
view-name
ciscoUserConnectionTapMIB
included
4.
snmp-server group
group-name
v3auth read
view-name
write
view-name
notify
view-name
5.
snmp-server host
ip-address
traps version 3 auth
username
udp-port
port-number
6. snmp-server user mduser-id groupname v3 auth md5 md-password
7.
commit
8.
show snmp users
9.
show snmp group
10.
show snmp view
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Example for Inband Management Plane Feature Enablement
This example illustrates how to enable the MPP feature, which is disabled by default, for the purpose of lawful intercept.
Configuring the Inband Management Plane Protection Feature: Example
You must specifically enable management activities, either globally or on a per-inband-port basis, using this procedure. To globally enable inbound MPP, use the keyword all with the interface command, rather than use a particular interface type and instance ID with it.
RP/0/0/CPU0:router# configure RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config)# control-plane RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-ctrl)# management-plane RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-mpp)# inband RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-mpp-inband)# interface loopback0 RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-mpp-inband-Loopback0)# allow snmp RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-mpp-inband-Loopback0)# commit RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-mpp-inband-Loopback0)# exit RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-mpp-inband)# exit RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-mpp)# exit RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-ctr)# exit RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config)# exit RP/0/0/CPU0:router# show mgmt-plane inband interface loopback0 Management Plane Protection - inband interface interface - Loopback0 snmp configured - All peers allowed RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config)# commit
Additional References
These sections provide references related to implementing lawful intercept.
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Lawful Intercept commands |
Cisco IOS XR System Security Command Reference for the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router |
|
Implementing SNMP |
Cisco IOS XR System Management Configuration Guide for the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router |
|
SNMP Server commands |
Cisco IOS XR System Management Command Reference for the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router |
Standards
|
Standards |
Title |
|---|---|
|
A modular, open architecture designed for simple implementation that easily interacts with third-party equipment to meet service provider lawful intercept requirements. |
See RFC-3924 under RFCs. |
|
An application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. Part of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol suite. |
Simple Network Management Protocol Version 3 (SNMPv3) |
MIBs
|
MIBs |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
To locate and download MIBs using Cisco IOS XR software, use the Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL and choose a platform under the Cisco Access Products menu: http://cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml |
RFCs
|
RFCs |
Title |
|---|---|
|
RFC-3924 |
Cisco Architecture for Lawful Intercept in IP Networks |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Technical Support website contains thousands of pages of searchable technical content, including links to products, technologies, solutions, technical tips, and tools. Registered Cisco.com users can log in from this page to access more content. |
 Feedback
Feedback