Clock Recovery System for SAToP
The Clock Recovery System recovers the service clock using Adaptive Clock Recovery (ACR) and Differential Clock Recovery (DCR).
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About Clock Recovery
- Prerequisites for Clock Recovery
- Restrictions for Clock Recovery
- How to Configure ACR and DCR
- Associated Commands
- Additional References for Clock Recovery
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About Clock Recovery
Adaptive Clock Recovery (ACR)
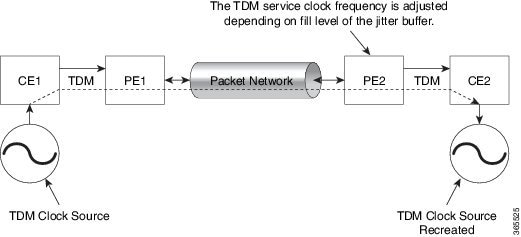
Adaptive Clock Recovery (ACR) is an averaging process that negates the effect of random packet delay variation and captures the average rate of transmission of the original bit stream. ACR recovers the original clock for a synchronous data stream from the actual payload of the data stream. In other words, a synchronous clock is derived from an asynchronous packet stream. ACR is a technique where the clock from the TDM domain is mapped through the packet domain, but is most commonly used for Circuit Emulation (CEM).
Effective Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1, ACR is supported on the 8-port T1/E1 interface module.
Differential Clock Recovery (DCR)
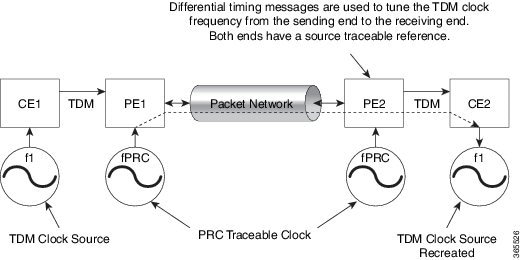
Differential Clock Recovery (DCR) is another technique used for Circuit Emulation (CEM) to recover clocks based on the difference between PE clocks. TDM clock frequency are tuned to receive differential timing messages from the sending end to the receiving end. A traceable clock is used at each end, which ensures the recovered clock is not affected by packet transfer.
Benefits of Clock Recovery
Scaling Information
|
IM Card |
Pseudowires Supported (Number of Clocks Derived) |
|---|---|
|
48-Port T1/E1 CEM Interface Module |
48 |
Prerequisites for Clock Recovery
Restrictions for Clock Recovery
How to Configure ACR and DCR
Configuring ACR for T1/E1
Configuring Adaptive Clock Recovery of T1/E1 Interfaces for SAToP
Before You Begin
Before configuring Adaptive Clock Recovery, CEM must be configured. Below are the guidelines to configure clock recovery:
-
The node (chassis) on which the DS1 is configured for ACR, must have its own clock derived from BITS/GPS/Stratum clock.
-
The minimum packet size of CEM pseudowires on the network that delivers robust clock recovery is 64 bytes.
enable configure terminal controller t1/e1 0/0/1 cem-group 0 unframed clock source recovered 1 exit
recovered-clock 0 0 clock recovered 1 adaptive cem 1 0 exit
 Note | The clock configuration on controller must be done before configuring the clock recovery on global configuration mode. |
To remove the clock configuration in ACR and DCR, you must remove the recovery clock configuration in global configuration mode and then remove the controller configuration.
Verifying the Adaptive Clock Recovery Configuration of T1/E1 Interfaces for SAToP
Router# show recovered-clock Recovered clock status for subslot 0/4 -------------------------------------- Clock Type Mode CEM Status Frequency Offset(ppb) Circuit-No 0 DS1 ADAPTIVE 0 ACQUIRED n/a 0 (Port)
Router# show running-config | section 0/0/1 controller T1/E1 0/0/1 framing unframed clock source recovered 1 linecode b8zs cablelength long 0db cem-group 0 unframed interface CEM0/0/1 no ip address cem 0
Router# show running-config | section recovered-clock recovered-clock 0 0 clock recovered 1 adaptive cem 1 0
Configuring DCR for T1/E1
Configuring Differential Clock Recovery of T1/E1 Interfaces for SAToP
Before You Begin
Before configuring Differential Clock Recovery, CEM must be configured. Below are the guidelines to configure Differential clock recovery:
-
Before you start configuring DCR, RTP must be enabled on the CEM interface. The RTP is used to carry the differential time.
-
The minimum packet size of CEM pseudowires on the network that delivers robust clock recovery is 64 bytes.
enable configure terminal controller t1/e1 0/0/1 cem-group 0 unframed clock source recovered 1 exit
interface cem 0/0/1 cem 0 rtp-present
recovered-clock 0 0 clock recovered 1 differential cem 1 0 exit
 Note | The clock configuration on controller must be done before configuring the clock recovery on global configuration mode. |
Verifying the Differential Clock Recovery Configuration of T1/E1 Interfaces for SAToP
Router# show recovered-clock Recovered clock status for subslot 0/4 --------------------------------------- Clock Type Mode CEM Status Frequency Offset(ppb) Circuit-No 0 DS1 DIFFERENTIAL 0 ACQUIRED n/a 0 (Port)
Router# show running-config | section 0/0/1 controller T1/E1 0/0/1 framing unframed clock source recovered 1 linecode b8zs cablelength long 0db cem-group 0 unframed interface CEM 0/0/1 no ip address cem 0 rtp-present
Router# show running-config | section recovered-clock recovered-clock 0 0 clock recovered 1 differential cem 1 0
Configuring Network Clock
To configure a network clock, use the following commands:
enable configure terminal controller E1/T1 0/5/0 clock source line cem-group 0 unframed exit enable configure terminal network-clock input-source 1 controller E1/T1 0/5/0 exit
Verifying Network Clocking Configuration
Use show run | sec network-cl command to verify the network clocking configuration.
network-clock synchronization automatic
network-clock synchronization mode QL-enabled
network-clock input-source 1 controller E1 0/1/0
network-clock wait-to-restore 10 global
rtr1#sh netw synchronization
Symbols: En - Enable, Dis - Disable, Adis - Admin Disable
NA - Not Applicable
* - Synchronization source selected
# - Synchronization source force selected
& - Synchronization source manually switched
Automatic selection process : Enable
Equipment Clock : 2048 (EEC-Option1)
Clock Mode : QL-Enable
ESMC : Enabled
SSM Option : 1
T0 : E1 0/1/0
Hold-off (global) : 300 ms
Wait-to-restore (global) : 10 sec
Tsm Delay : 180 ms
Revertive : No
Nominated Interfaces
Interface SigType Mode/QL Prio QL_IN ESMC Tx ESMC Rx
Internal NA NA/Dis 251 QL-SEC NA NA
*E1 0/1/0 NA NA/Dis 1 QL-SEC NA NA
rtr1#
Associated Commands
The commands used to configure adaptive clock recovery and differential clock recovery are:
|
Commands |
URL |
|---|---|
|
clock recovered adaptive cem |
|
|
clock recovered differential cem |
|
|
cem-group |
|
|
recovered-clock |
|
|
controller t1/e1 |
|
|
clock-source |
|
|
network-clock input-source |
Additional References for Clock Recovery
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
Standards and RFCs
|
Standard/RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
|
ITU -T G.8261 |
Timing and synchronization aspects in packet networks |
MIBs
|
MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
— |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
 Feedback
Feedback