Built-in Device Types
Prime Cable Provisioning has built-in (out of the box) support for detecting and managing the following device types:
-
DOCSISModem
-
PacketCableMTA
-
STB
-
eRouter
-
RPD
-
CableHomeWanData
-
CableHomeWanMan
-
Computer
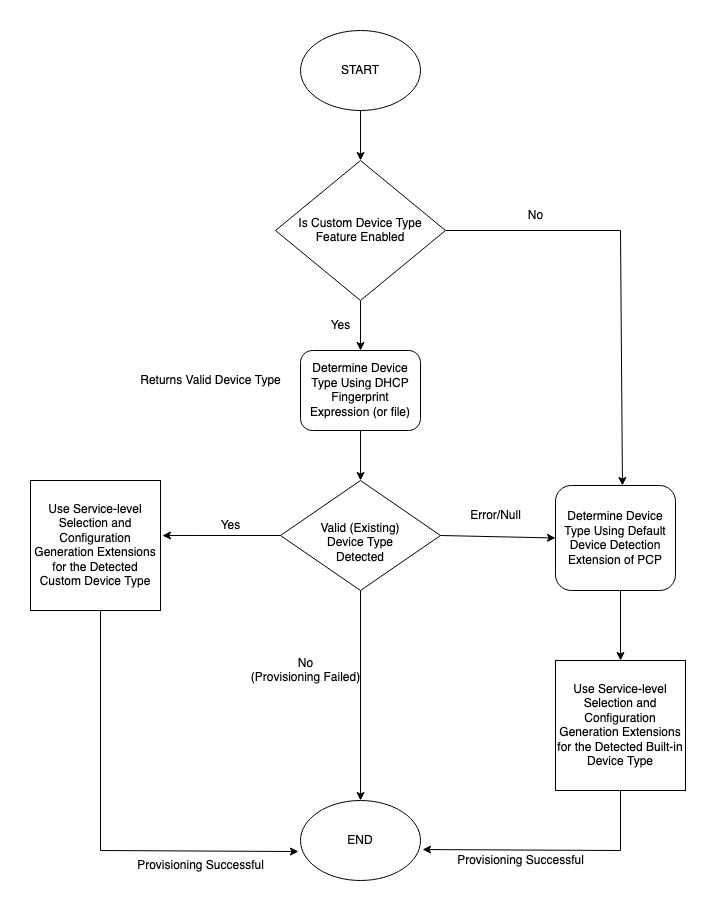
Device type detection process in RDU uses information extracted from DHCP configuration sent by CNR Extension Points. For built-in device types, DHCPv4 information such as class identifier, vendor specific information, relay agent circuit-id and remote-id and DHCPv6 information such as vendor-class, vendor-opts are used for detection.
Following sections describe in detail how DHCP configuration is used for the detection process for built-in device types and Custom Device Types.

 Feedback
Feedback