Static MAC Address Support for Service Instances and Pseudowires
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Prerequisites for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Restrictions for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Information About Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Benefits of Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
How to Configure a Static MAC Address on Service Instances or Pseudowires
Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Service Instance
Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Pseudowire
Displaying Configured Static MAC Addresses
Configuration Examples for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Example: Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Service Instance
Example: Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Pseudowire
Feature Information for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
First Published: November 20, 2009Last Updated: February 5, 2011The Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires feature supports configuration of a static MAC address on a pseudoport. Use of a static MAC address for broadband network gateway (BNG) upstream traffic enables traffic forwarding while conserving MAC table resources and limiting the traffic flood by creating multicast groups.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the "Feature Information for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires" section.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
•
Restrictions for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
•
Information About Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
•
How to Configure a Static MAC Address on Service Instances or Pseudowires
•
Feature Information for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Prerequisites for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
•
Knowledge of both port and bridge domain limitations.
•
Knowledge of service instances.
•
Layer 2 virtual forwarding instance (L2VFI) must be integrated with the bridge domain.
Restrictions for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
•
Multicast static MAC addresses are not allowed in MAC address security configurations.
•
Static MAC addresses are programmed only on switch processors (both active and standby).
Information About Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
•
Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
•
Benefits of Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Static MAC address configuration on service instances and pseudowires eliminates the need for MAC address learning, which is required for traffic forwarding. In the upstream direction, without MAC address learning, MAC address table resources can be conserved and network resources optimized.
Static MAC address configuration requires L2VFI integration with a bridge domain, which allows a pseudoport to be created on the bridge domain for a pseudowire. After the pseudoport is created, the static MAC configuration can be associated to the bridge domain pseudoport.
Multicast static MAC addresses are allowed on multiple pseudoports in the same bridge domain.
Figure 1 shows static MAC addresses in a network configured with broadband remote access server (BRAS) redundancy.
Figure 1
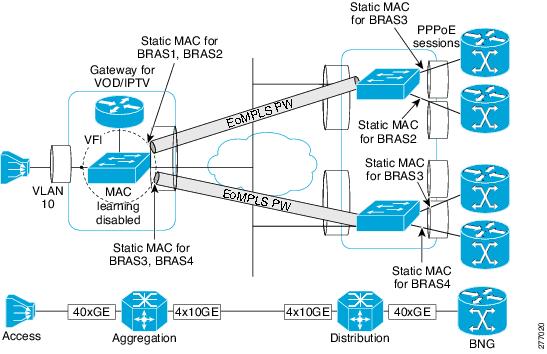
Active/Active Aggregation Node and BRAS Redundancy
When a bridge domain ID is either changed or deleted for a service instance or for an L2VFI, all static MAC addresses are removed.
When a service instance or a pseudowire is deleted, all static MAC addresses on that pseudoport are removed.
Benefits of Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
•
Facilitates optimization of network resources
•
Conserves MAC table resources when used for upstream traffic
How to Configure a Static MAC Address on Service Instances or Pseudowires
•
Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Service Instance
•
Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Pseudowire
•
Displaying Configured Static MAC Addresses
Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Service Instance
Perform this task to manually configure a static MAC address on a service instance.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface type number
4.
service instance id ethernet [evc-id]
5.
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id [,vlan-id [-vlan-id]] [native]
6.
bridge-domain bridge-id [split-horizon [group group-id]]
7.
mac static address mac-addr [auto-learn] [disable-snooping]
8.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Pseudowire
Perform this task to manually configure a static MAC address on a Pseudowires.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
l2 vfi name manual
4.
vpn {vrf vrf-name | id vpn-id}
5.
bridge-domain bridge-id vlan vlan-name
6.
neighbor remote-router-id vc-id {encapsulation encapsulation-type | pw-class pw-name} [no-split-horizon]
7.
mac static address mac-addr [auto-learn] [disable-snooping]
8.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Displaying Configured Static MAC Addresses
Perform this task to display the static MAC addresses that are configured. Output of these commands may be useful for troubleshooting. The show commands can be issued in any order.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
show bridge-domain [[bridge-id] [c-mac] [mac {security [address | last violation | statistics] | static address | table [mac-address | aging-time | count]}] | split-horizon [group {group-number | all | none}] | stats]
3.
show ethernet service instance [detail | id id interface type number [detail | mac {security [address | last violation | statistics] | static address}] | platform | stats] | interface type number [detail | platform | stats | summary] | mac security [address | last violation | statistics] | platform | policy-map | stats | summary]
4.
show vfi [checkpoint [summary] | mac static address | memory [detail] | name vfi-name [checkpoint | mac static address] | neighbor ip-addr vcid vcid mac static address]
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
•
Example: Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Service Instance
•
Example: Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Pseudowire
Example: Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Service Instance
Router> enableRouter# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface ethernet 1/0Router(config-if)# service instance 1 ethernetRouter(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 100Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 100Router(config-if-srv)# mac static address 0000.bbbb.ccccRouter(config-if-srv)# exitExample: Configuring a Static MAC Address on a Pseudowire
Router> enableRouter# configure terminalRouter(config)# l2 vfi test-core manualRouter(config-vfi)# vpn id 100Router(config-vfi)# bridge-domain 100 vlan vlan10Router(config-vfi)# neighbor 209.165.202.129 5 pw-class TestClassRouter(config-vfi-neighbor)# mac static address 0000.aaaa.bbbbRouter(config-vfi-neighbor)# exitAdditional References
Related Documents
Standards
MIBs
None
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL:
RFCs
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for Static MAC Address Support on Service Instances and Pseudowires
Table 1 lists the release history for this feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.

Note
Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2009-2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback