- Application Firewall-Instant Message Traffic Enforcement
- E-mail Inspection Engine
- ESMTP Support for Cisco IOS Firewall
- Firewall N2H2 Support
- Firewall Support for SIP
- Firewall Support of Skinny Client Control Protocol
- Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP
- Granular Protocol Inspection
- TCP Out-of-Order Packet Support for Cisco IOS Firewall and Cisco IOS IPS
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Granular Inspection Protocol
- Restrictions for Granular Inspection Protocol
- Information About Granular Protocol Inspection
- How to Configure Granular Protocol Inspection
- Configuration Examples for Granular Protocol Inspection
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Granular Protocol Inspection
- Glossary
Granular Protocol Inspection
The Granular Protocol Inspection feature adds flexibility to the Cisco IOS Firewall by allowing it to perform a higher degree of inspection of TCP and User Data Protocol (UDP) traffic for most RFC 1700 application types.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Granular Inspection Protocol
- Restrictions for Granular Inspection Protocol
- Information About Granular Protocol Inspection
- How to Configure Granular Protocol Inspection
- Configuration Examples for Granular Protocol Inspection
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Granular Protocol Inspection
- Glossary
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for Granular Inspection Protocol
- Cisco IOS Firewall software must be installed in your network.
- Access control lists (ACLs) must be applied to specified interfaces to enable the existing firewall software to function properly.
Restrictions for Granular Inspection Protocol
Port ranges cannot be specified directly in the ip inspect name command; use the port-to-application mapping (PAM) table.
Information About Granular Protocol Inspection
Cisco IOS Firewall
The Cisco IOS Firewall is a security-specific option that provides inspection firewall functionality and intrusion detection for every network perimeter. By delivering state-of-the-art security features such as stateful, application-based filtering; dynamic per-user authentication and authorization; and URL filtering, the Cisco IOS Firewall adds greater depth and flexibility to existing Cisco IOS security solutions including authentication, encryption, and failover.
A firewall is a physical software or hardware barrier between one part of an internal network used to control access to and from external networks. This barrier is unique because it allows predefined traffic to pass through the firewall while being monitored for protocol anomalies. The difficult part is determining the criteria by which the packets are granted or denied access through the device.
As mentioned, a firewall blocks traffic and permits other types of traffic to traverse. Firewalls are not just access control lists (ACLs); rather, they are a stateful inspection application.
Granular Protocol Inspection
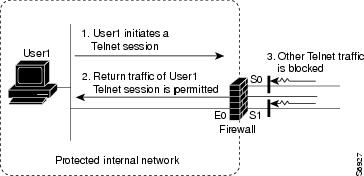
The Cisco IOS Firewall performs inspections for TCP and UDP traffic. For example, TCP inspections include Telnet traffic (port 23, by default) as well as all other applications on TCP such as Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), e-mail, instant message (IM) chatter, and so on. Therefore, there is no easy way to inspect Telnet traffic alone and deny all other TCP traffic.
The Granular Protocol Inspection feature allows you to specify TCP or UDP ports using the PAM table. As a result, the Cisco IOS Firewall can restrict traffic inspections to specific applications, thereby permitting a higher degree of granularity in selecting which protocols are to be permitted and denied as shown in the figure below.
Benefits
- Greater flexibility by allowing more granularity in the selection of protocols to be inspected
- Ease of use by providing for group inspection of multiple ports into a single, user-defined application keyword
- Enhanced functionality with the addition of more well-known ports, user-defined applications, and user-defined port ranges
- Improved performance and reduced CPU load resulting from focused inspection selections
How to Configure Granular Protocol Inspection
Defining Applications
Perform the following task to define your applications in the PAM table by using the ip port-map command.
DETAILED STEPS
Setting Up Inspection Rules
Perform the following task to set up your inspection rules by using the ip inspect name command.
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# ip inspect name abc user-10 |
Defines inspection rules.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# exit |
Exits global configuration mode. |
Verifying the Configuration
Perform the following task to verify your applications and inspection rules.
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
|
|
Example: Router# show ip port-map port 70 detail |
Establishes PAM entries. |
|
|
Example: Router# exit |
(Optional) Exits privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuration Examples for Granular Protocol Inspection
- Example Defining an Application for the PAM Table
- Example Setting Up an Inspection Rule
- Example Verifying the Configuration
Example Defining an Application for the PAM Table
In the following example from the ip port-map command, a user-defined application named user-10 is defined in the PAM table for five ports using the TCP protocol. Standard access list 77 is applied to define host-specific port mapping and "TEST STRING" is the description.
Router# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# ip port-map user-10 port tcp 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 list 77 description "TEST STRING" Router(config)# end
Example Setting Up an Inspection Rule
The following example from the ip inspect name command, lists user-10 as an application with the description "TEST STRING."
Router# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# ip inspect name abc ? bootpc Bootstrap Protocol Client bootps Bootstrap Protocol Server cisco-fna Cisco FNATIVE cisco-sys Cisco SYSMAINT cisco-tna Cisco TNATIVE cuseeme CUSeeMe Protocol echo Echo port esmtp Extended SMTP finger Finger fragment IP fragment inspection ftp File Transfer Protocol gopher Gopher gtpv0 GPRS Tunneling Protocol Version 0 gtpv1 GPRS Tunneling Protocol Version 1 h323 H.323 Protocol (e.g, MS NetMeeting, Intel Video Phone) http HTTP Protocol icmp ICMP Protocol imap IMAP Protocol imap3 Interactive Mail Access Protocol 3 kerberos Kerberos ldap Lightweight Directory Access Protocol netbios-dgm NETBIOS Datagram Service netshow Microsoft NetShow Protocol nntp Network News Transport Protocol parameter Specify inspection parameters pop3 POP3 Protocol pwdgen Password Generator Protocol rcmd R commands (r-exec, r-login, r-sh) realaudio Real Audio Protocol rpc Remote Prodedure Call Protocol rtsp Real Time Streaming Protocol secure-http Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol sip SIP Protocol skinny Skinny Client Control Protocol smtp Simple Mail Transfer Protocol snmp Simple Network Management Protocol snmptrap SNMP Trap sqlnet SQL Net Protocol sqlsrv SQL Service streamworks StreamWorks Protocol tacacs Login Host Protocol (TACACS) tacacs-ds TACACS-Database Service tcp Transmission Control Protocol telnet Telnet tftp TFTP Protocol udp User Datagram Protocol vdolive VDOLive Protocol user-10 TEST STRING <----- !user-defined application!
In the following example from the ip inspect name command, an inspection rule is established for user-10:
Router# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# ip inspect name abc user-10 Router(config)# end
Example Verifying the Configuration
The following example verifies your port-map configuration:
Router# show running-config | include port-map ip port-map user-10 port tcp 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 list 77 description "TEST STRING"
The following example verifies your inspection rule configuration:
Router# show running-config | include inspect ip inspect name abc user-10
The following example displays information about the user-defined application called user-10.
Router# show ip port-map user-10
Host specific: user-10 tcp port 4000...8000 in list 77 user defined
The following example displays detailed information about the user-defined application called user-10.
Router# show ip port-map user-10 detail
IP port-map entry for application 'user-10':
tcp 4000...8000 list 77 "TEST STRING" user defined
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| Cisco IOS commands |
|
| Security commands: complete command syntax, command mode, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples |
Cisco IOS Security Command Reference |
Standards
| Standards |
Title |
|---|---|
| None |
-- |
MIBs
| MIBs |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| None |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
| RFCs |
Title |
|---|---|
| None |
-- |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Granular Protocol Inspection
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for Granular Protocol Inspection |
| Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| Granular Protocol Inspection |
12.3(14)T |
The Granular Protocol Inspection feature adds flexibility to the Cisco IOS Firewall by allowing it to perform a higher degree of inspection of TCP and User Data Protocol (UDP) traffic for most RFC 1700 application types. The following commands were introduced or modified: ip inspect name, ip port-map, show ip port-map. |
Glossary
firewall --A router or access server, or several routers or access servers, designated as a buffer between any connected public networks and a private network. A firewall router uses access lists and other methods to ensure the security of the private network.
granular--Degree of componentization. Small, fine-grained components provide greater flexibility in assembling the right combination of functionality, but can be difficult to manage.
inspection rule --A rule that specifies what IP traffic (which application-layer protocols) will be inspected by CBAC at an interface.
PAM --port-to-application mapping. A flexible, per-application port mapping capability that allows the Cisco IOS Firewall to support applications running on nonstandard ports. This feature allows network administrators to customize access control for specific applications and services, in order to meet their distinct network needs.
traffic inspection --A way that CBAC inspects traffic that travels through the firewall to discover and manage state information for TCP and UDP sessions. This state information is used to create temporary openings in the firewall's access lists to allow return traffic and additional data connections for permissible sessions (sessions that originated from within the protected internal network).
UDP --User Data Protocol. A connectionless service--there are no actual sessions, so the software approximates sessions by examining the information in the packet and determining if the packet is similar to other UDP packets (for example, similar source/destination addresses and port numbers) and if the packet was detected soon after another similar UDP packet. "Soon" means within the configurable UDP idle timeout period.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback