Contents
- Overview of DiffServ for Quality of Service
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About Differentiated Services
- Differentiated Services Definition
- DS Field Definition
- Per-Hop Behaviors
- Default PHB
- Class-Selector PHB
- Assured Forwarding PHB
- Expedited Forwarding PHB
- Benefits of Implementing Differentiated Services
- Differentiated Services Components
- Differentiated Services Feature Sets
- Sample DiffServ Implementation
- Sample DiffServ Configurations
- DiffServ Implementation Troubleshooting Logs
- Accounting Functionality and DiffServ
- Where to Go Next
- Additional References
Overview of DiffServ for Quality of Service
This module contains an overview of implementing Differentiated Services (DiffServ) on your network. DiffServ is a set of end-to-end quality of service (QoS) capabilities. End-to-end QoS is the ability of the network to deliver service required by specific network traffic from one end of the network to another. Cisco IOS QoS software supports three types of service models: best-effort services, Integrated Services (IntServ), and Differentiated Services.
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About Differentiated Services
- Where to Go Next
- Additional References
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About Differentiated Services
- Differentiated Services Definition
- DS Field Definition
- Per-Hop Behaviors
- Benefits of Implementing Differentiated Services
- Differentiated Services Components
- Differentiated Services Feature Sets
- Sample DiffServ Implementation
- Accounting Functionality and DiffServ
Differentiated Services Definition
Differentiated Services is a multiple service model that can satisfy differing QoS requirements. With Differentiated Services, the network tries to deliver a particular kind of service based on the QoS specified by each packet. This specification can occur in different ways, for example, using the 6-bit differentiated services code point (DSCP) setting in IP packets or source and destination addresses. The network uses the QoS specification to classify, mark, shape, and police traffic and to perform intelligent queueing.
Differentiated Services is used for several mission-critical applications and for providing end-to-end QoS. Typically, Differentiated Services is appropriate for aggregate flows because it performs a relatively coarse level of traffic classification.
DS Field Definition
A replacement header field, called the DS field, is defined by Differentiated Services. The DS field supersedes the existing definitions of the IP version 4 (IPv4) type of service (ToS) octet (RFC 791) and the IPv6 traffic class octet. Six bits of the DS field are used as the DSCP to select the Per-Hop Behavior (PHB) at each interface. A currently unused 2-bit (CU) field is reserved for explicit congestion notification (ECN). The value of the CU bits is ignored by DS-compliant interfaces when determining the PHB to apply to a received packet.
Per-Hop Behaviors
RFC 2475 defines PHB as the externally observable forwarding behavior applied at a DiffServ-compliant node to a DiffServ Behavior Aggregate (BA).
With the ability of the system to mark packets according to DSCP setting, collections of packets with the same DSCP setting that are sent in a particular direction can be grouped into a BA. Packets from multiple sources or applications can belong to the same BA.
In other words, a PHB refers to the packet scheduling, queueing, policing, or shaping behavior of a node on any given packet belonging to a BA, as configured by a service level agreement (SLA) or a policy map.
Default PHB
The default PHB essentially specifies that a packet marked with a DSCP value of 000000 (recommended) receives the traditional best-effort service from a DS-compliant node (that is, a network node that complies with all of the core DiffServ requirements). Also, if a packet arrives at a DS-compliant node, and the DSCP value is not mapped to any other PHB, the packet will get mapped to the default PHB.
Class-Selector PHB
To preserve backward-compatibility with any IP precedence scheme currently in use on the network, DiffServ has defined a DSCP value in the form xxx000, where x is either 0 or 1. These DSCP values are called Class-Selector Code Points. (The DSCP value for a packet with default PHB 000000 is also called the Class-Selector Code Point.)
The PHB associated with a Class-Selector Code Point is a Class-Selector PHB. These Class-Selector PHBs retain most of the forwarding behavior as nodes that implement IP Precedence-based classification and forwarding.
For example, packets with a DSCP value of 11000 (the equivalent of the IP Precedence-based value of 110) have preferential forwarding treatment (for scheduling, queueing, and so on), as compared to packets with a DSCP value of 100000 (the equivalent of the IP Precedence-based value of 100). These Class-Selector PHBs ensure that DS-compliant nodes can coexist with IP Precedence-based nodes.
Assured Forwarding PHB
Assured Forwarding (AF) PHB is nearly equivalent to Controlled Load Service available in the integrated services model. An AF PHB defines a method by which BAs can be given different forwarding assurances.
For example, network traffic can be divided into the following classes:
- Gold: Traffic in this category is allocated 50 percent of the available bandwidth.
- Silver: Traffic in this category is allocated 30 percent of the available bandwidth.
- Bronze: Traffic in this category is allocated 20 percent of the available bandwidth.
Further, the AF PHB defines four AF classes: AF1, AF2, AF3, and AF4. Each class is assigned a specific amount of buffer space and interface bandwidth, according to the SLA with the service provider or policy map.
Within each AF class, you can specify three drop precedence (dP) values: 1, 2, and 3.
Assured Forwarding PHB can be expressed as follows:
AFny
In this example, n represents the AF class number (1, 2, 3, or 4) and y represents the dP value (1, 2, or 3) within the AFn class.
In instances of network traffic congestion, if packets in a particular AF class (for example, AF1) need to be dropped, packets in the AF1 class will be dropped according to the following guideline:
dP(AFny) >= dP(AFnz) >= dP(AFnx)
where dP (AFny) is the probability that packets of the AFny class will be dropped. In other words, y denotes the dP within an AFn class.
In the following example, packets in the AF13 class will be dropped before packets in the AF12 class, which in turn will be dropped before packets in the AF11 class:
dP(AF13) >= dP (AF12) >= dP(AF11)
The dP method penalizes traffic flows within a particular BA that exceed the assigned bandwidth. Packets on these offending flows could be re-marked by a policer to a higher drop precedence.
An AFx class can be denoted by the DSCP value, xyzab0, where xyz can be 001, 010, 011, or 100, and ab represents the dP value.
The table below lists the DSCP value and corresponding dP value for each AF PHB class.
|
Drop Precedence |
Class 1 |
Class 2 |
Class 3 |
Class 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Low Drop Precedence |
001010 |
010010 |
011010 |
100010 |
|
Medium Drop Precedence |
001100 |
010100 |
011100 |
100100 |
|
High Drop Precedence |
001110 |
010110 |
011110 |
100110 |
Expedited Forwarding PHB
Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP), a component of the integrated services model, provides a guaranteed bandwidth service. Applications such as Voice over IP (VoIP), video, and online trading programs require this kind of robust service. The EF PHB, a key ingredient of DiffServ, supplies this kind of robust service by providing low loss, low latency, low jitter, and assured bandwidth service.
EF can be implemented using PQ, along with rate-limiting on the class (or BA). When implemented in a DiffServ network, EF PHB provides a virtual leased line, or premium service. For optimal efficiency, however, EF PHB should be reserved for only the most critical applications because, in instances of traffic congestion, it is not feasible to treat all or most traffic as high priority.
EF PHB is ideally suited for applications that require low bandwidth, guaranteed bandwidth, low delay, and low jitter.
The recommended DSCP value for EF PHB is 101110.
Benefits of Implementing Differentiated Services
Use the Implementing DiffServ for End-to-End Quality of Service feature set to implement the Differentiated Services architecture. The benefits of implementing Differentiated Services include the following:
- Reduces the burden on network devices and easily scales as the network grows.
- Allows customers to keep any existing Layer 3 ToS prioritization scheme that may be in use.
- Allows customers to mix DiffServ-compliant devices with any existing ToS-enabled equipment in use.
- Alleviates bottlenecks through efficient management of current corporate network resources.
Differentiated Services Components
The following components make up the foundation of a Cisco Differentiated Services implementation:
- Traffic conditioning (traffic policing and traffic shaping)--Traffic conditioning is performed at the edges of a DiffServ domain. Traffic conditioners perform traffic shaping and policing functions to ensure that traffic entering the DiffServ domain conforms to the rules specified by the Traffic Conditioning Agreement (TCA) and complies with the service provisioning policy of the domain. Traffic conditioning may range from simple code point re-marking to complex policing and shaping operations.
- Packet classification--Packet classification uses a traffic descriptor (for example, the DSCP) to categorize a packet within a specific group in order to define that packet. After the packet has been defined (that is, classified), the packet is accessible for QoS handling on the network.
Using packet classification, you can partition network traffic into multiple priority levels or classes of service. When traffic descriptors are used to classify traffic, the source agrees to adhere to the contracted terms and the network promises a QoS. Traffic policers and traffic shapers use the traffic descriptor of the packet (that is, the classification of the packet) to ensure adherence to that agreement.
- Packet marking--Packet marking is related to packet classification. Packet marking allows you to classify a packet based on a specific traffic descriptor (such as the DSCP value). This classification can then be used to apply user-defined differentiated services to the packet and to associate a packet with a local QoS group.
Associating a packet with a local QoS group allows users to associate a group ID with a packet. The group ID can be used to classify packets into QoS groups based on prefix, autonomous system, and community string. A user can set up to 64 DSCP values and 100 QoS group markings.
- Congestion management--Congestion management (or scheduling) is achieved through traffic scheduling and traffic queueing. When there is network congestion, a scheduling mechanism such as CBWFQ is used to provide guaranteed bandwidth to the different classes of traffic.
- Congestion avoidance--Congestion avoidance techniques monitor network traffic loads in an effort to anticipate and avoid congestion at common network bottlenecks. Congestion avoidance is achieved through packet dropping. Among the more commonly used congestion avoidance mechanisms is WRED.
With WRED and Differentiated Services, you have the option of allowing WRED to use the DSCP value when WRED calculates the drop probability of a packet.
Differentiated Services Feature Sets
This section lists many of the feature sets that correspond to the DiffServ components listed earlier. The feature sets listed below provide the necessary functionality that allows you to implement DiffServ:
- Modular QoS Command-Line Interface (CLI) (MQC)--The MQC provides a CLI structure that allows you to apply QoS features on your network.
- Packet Marking (Marking Network Traffic)--Packet marking allows you to differentiate packets by designating them different identifying values. For example, you can mark packets by setting the IP Precedence bits or the IP differentiated services code point (DSCP) in the type of service (ToS) byte.
- Committed Access Rate (CAR)--CAR performs packet classification through IP Precedence and QoS group settings. CAR can also perform metering and class-based policing of traffic, providing bandwidth management.
- Traffic Policing--This feature allows you to limit the input or output transmission rate of a class of traffic based on user-defined criteria. It also enables the system to mark packets according to a user-defined criterion, such as the IP Precedence value, the QoS group, or the DSCP value, among others. Such traffic can then be dropped or transmitted, as desired.
- Traffic Shaping (Regulating Packet Flow)--Traffic shaping "shapes" the flow of traffic by reducing outbound flow traffic to avoid congestion. Traffic shaping constrains traffic to a particular bit rate using a token bucket mechanism.
- Class-Based Weighted Fair Queueing (CBWFQ)--CBWFQ is a scheduling mechanism used to provide a minimum bandwidth guarantee to traffic classes during times of network congestion at an interface.
- Low Latency Queueing (LLQ)--LLQ is a scheduling mechanism that brings strict priority queueing (PQ) to CBWFQ. Strict PQ allows delay-sensitive data such as voice to be dequeued and sent before packets in other queues are dequeued.
- Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) and Weighted Fair Queueing (WFQ)--WRED and WFQ are intelligent queueing schemes that can be used with CAR for implementing Differentiated Services.
- DiffServ Compliant WRED--This feature provides support for the DiffServ standard. It enables WRED to use either the DSCP value or the IP Precedence value when calculating the drop probability for a packet. This feature should be used in conjunction with CBWFQ.
- Enhanced show policy-map interface Command--The show policy-map interface command displays information such as the incoming traffic rate, the dropped packet rate, the number of matched packets, and the number of matched bytes for traffic classes that are attached to the specified interface. This feature collects and displays common statistics that are used for billing and accounting purposes.
- Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Class of Service (CoS) Enhancements--This feature allows the service provider to set the MPLS experimental (EXP) field instead of overwriting the value in the customer IP Precedence field (the first three bits of the DSCP field in the header of an IP packet).
Sample DiffServ Implementation
The following section provides a sample DiffServ implementation. It includes sample configurations and troubleshooting logs, which can be used for monitoring system performance.
The figure below shows a sample DiffServ implementation with three routers: remote router 1, central router, and remote router 2.
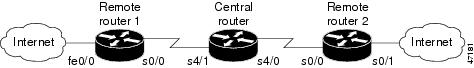
In this example, we want to give end-to-end QoS to several different types of traffic classes using the Cisco IOS Differentiated Services feature set.
Traffic classes along with the SLAs for each traffic class in use on the sample DiffServ implementation are described as follows:
- Voice is considered premium class. The gold class of traffic consists of TACACS sessions, along with traffic marked with DSCP values 12 and 14. The silver traffic class consists of Telnet, Simple Main Transfer Protocol (SMTP), and FTP sessions. The bronze traffic class consists of web traffic and traffic marked with DSCP values 28 and 30. Anything else is considered as belonging to the "best-effort" traffic class.
- The premium class should be forwarded with the lowest delay possible up to a maximum of 500 kBps during periods of congestion. The gold class should be treated preferentially over the silver class, which in turn should be treated preferentially over the bronze class. The gold, silver, and bronze classes should have 35 percent, 25 percent, and 15 percent, respectively, of the interface bandwidth as the minimum bandwidth guarantees. The bronze class should be shaped to 320 kBps, and the best-effort class should be policed to 56 kBps.
- To provision for the various traffic classes, the traffic needs to be classified based on DSCP values in a DiffServ domain. So that traffic can be classified based on DSCP values, the traffic should be premarked with the appropriate DSCP values at the time of entering the network.
In the figure above, the correct place to do this kind of traffic marking is in the incoming direction of Fast Ethernet interface 0/0 of remote router 1 and in the incoming direction of serial interface 0/1 of remote router 2. This marking can be achieved through an input service policy.
The table below lists the DSCP values used to mark different classes of traffic entering into the sample network.
|
Traffic Class |
Traffic Type |
DSCP Value |
|---|---|---|
|
Premium |
Voice |
46 |
|
Gold |
TACACS |
10 |
|
Silver |
Telnet |
18 |
|
SMTP |
20 |
|
|
FTP |
22 |
|
|
Bronze |
HTTP |
26 |
To achieve the marking scheme noted in the table above, use the following configuration for the policy map called SETDSCP in the input direction of Fast Ethernet interface 0/0 of remote router 1:
class-map match-all EF match access-group 101 class-map match-all AF1 match access-group 102 class-map match-all AF21 match access-group 108 class-map match-all AF22 match access-group 109 class-map match-all AF23 match access-group 110 class-map match-all AF3 match access-group 104 policy-map SETDSCP class EF set ip dscp 46 class AF1 set ip dscp 10 class AF21 set ip dscp 18 class AF22 set ip dscp 20 class AF23 set ip dscp 22 class AF3 set ip dscp 26
Once the traffic classes are marked with the appropriate DSCP values using the SETDSCP policy map, the different behavior aggregate requirements for each of the traffic classes can be met by using the configuration for the following policy map called VOIP in the output direction:
class-map match-all premium match ip dscp 46 class-map match-all gold match ip dscp 10 12 14 class-map match-all silver match ip dscp 18 20 22 class-map match-all bronze match ip dscp 26 28 30 class-map best-effort match access-group 105 policy-map VOIP class premium priority 500 class gold bandwidth percent 35 class silver shape average 320000 bandwidth percent 25 class bronze bandwidth percent 15 class best-effort police 56000 1750 1750 conform-action set-dscp-transmit 0
Sample DiffServ Configurations
This section contains the configurations for each of the routers shown in the figure above.
The examples demonstrate how marking, shaping, policing, and monitoring are done through the Modular QoS CLI.
Remote Router 1 Configuration
Current configuration:
Remote1#
show running-config
Building configuration...
!
version 12.1
no service single-slot-reload-enable
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Remote1
!
logging rate-limit console 10 except errors
no logging console
!
ip subnet-zero
!
ip dhcp smart-relay
!
ip cef
!
class-map match-all gold
match ip dscp 10 12 14
class-map match-all EF
match access-group 101
class-map match-all AF21
match access-group 108
class-map match-all AF23
match access-group 110
class-map match-all AF22
match access-group 109
class-map match-all bronze
match ip dscp 26 28 30
class-map match-all platinum
match ip dscp 46
class-map match-all silver
match ip dscp 18 20 22
class-map match-all best-effort
match access-group 105
class-map match-all AF3
match access-group 104
class-map match-all AF1
match access-group 102
!
policy-map VOIP
class platinum
priority 500
class gold
bandwidth percent 50
class bronze
shape average 320000
bandwidth percent 15
class silver
bandwidth percent 35
class best-effort
police 56000 1750 1750 conform-action set-dscp-transmit 0 exceed-action drop violate-action drop
policy-map SETDSCP
class EF
set ip dscp 46
class AF1
set ip dscp 10
class AF3
set ip dscp 26
class AF21
set ip dscp 18
class AF22
set ip dscp 20
class AF23
set ip dscp 22
!
call rsvp-sync
cns event-service server
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 4.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
load-interval 60
speed auto
half-duplex
service-policy input SETDSCP
!
interface Serial0/0
bandwidth 2000
ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
load-interval 60
service-policy output VOIP
!
interface Serial0/1
no ip address
shutdown
!
ip classless
ip route 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 2.1.1.2
ip route 3.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 2.1.1.2
!
access-list 101 permit udp any any range 16384 32768
access-list 102 permit tcp any any eq tacacs
access-list 104 permit tcp any any eq www
access-list 105 permit ip any any
access-list 108 permit tcp any any eq telnet
access-list 109 permit tcp any any eq smtp
access-list 110 permit tcp any any eq ftp
!
voice-port 1/0/0
!
voice-port 1/0/1
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
dial-peer voice 11 pots
destination-pattern 2220
port 1/0/0
!
dial-peer voice 1 voip
destination-pattern 1110
session target ipv4:1.1.1.2
ip precedence 5
!
line con 0
transport input none
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
no scheduler allocate
end
Central Router Configuration
Current configuration:
Central# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
version 12.1
no service single-slot-reload-enable
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Central
!
logging rate-limit console 10 except errors
no logging console
ip dhcp smart-relay
!
ip cef
!
class-map match-all gold
match ip dscp 10 12 14
class-map match-all bronze
match ip dscp 26 28 30
class-map match-all platinum
match ip dscp 46
class-map match-all silver
match ip dscp 18 20 22
class-map match-all best-effort
match ip dscp 0
!
policy-map AVVID
class silver
bandwidth percent 35
random-detect dscp-based
random-detect dscp 18 20 40 10
random-detect dscp 20 20 40 30
random-detect dscp 22 2 3 3
class gold
bandwidth percent 50
random-detect dscp-based
random-detect dscp 10 20 40 10
random-detect dscp 12 20 40 15
random-detect dscp 14 20 40 20
class bronze
bandwidth percent 15
random-detect dscp-based
random-detect dscp 26 20 40 10
random-detect dscp 28 20 40 20
random-detect dscp 30 20 40 30
class platinum
priority 500
!
cns event-service server
!
interface Serial4/0
bandwidth 2000
ip address 3.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
no ip mroute-cache
load-interval 60
service-policy output AVVID
!
interface Serial4/1
ip address 2.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
no ip mroute-cache
service-policy output AVVID
clockrate 2015232
!
interface Serial4/2
no ip address
no ip mroute-cache
shutdown
!
interface Serial4/3
no ip address
no ip mroute-cache
shutdown
!
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.153.1
ip route 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 3.1.1.2
ip route 4.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 2.1.1.1
ip http server
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
transport input none
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
line vty 5 15
end
Remote Router 2 Configuration
Remote2# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
version 12.1
no service single-slot-reload-enable
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Remote2
!
logging rate-limit console 10 except errors
no logging console
!
ip dhcp smart-relay
!
ip cef
!
class-map match-all gold
match ip dscp 10 12 14
class-map match-all EF
match access-group 101
class-map match-all AF21
match access-group 108
class-map match-all AF23
match access-group 110
class-map match-all AF22
match access-group 109
class-map match-all bronze
match ip dscp 26 28 30
class-map match-all platinum
match ip dscp 46
class-map match-all silver
match ip dscp 18 20 22
class-map match-all best-effort
match access-group 105
class-map match-all AF3
match access-group 104
class-map match-all AF1
match access-group 102
!
!
policy-map VOIP
class platinum
priority 500
class gold
bandwidth percent 50
class bronze
shape average 320000
bandwidth percent 15
class silver
bandwidth percent 35
class best-effort
police 56000 1750 1750 conform-action set-dscp-transmit 0 exceed-action drop
violate-action drop
policy-map SETDSCP
class EF
set ip dscp 46
class AF1
set ip dscp 10
class AF3
set ip dscp 26
class AF21
set ip dscp 18
class AF22
set ip dscp 20
class AF23
set ip dscp 22
!
interface Serial0/0
bandwidth 2000
ip address 3.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
load-interval 60
service-policy output VOIP
clockrate 2000000
!
interface Serial0/1
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
load-interval 60
no keepalive
service-policy input SETDSCP
clockrate 2000000
!
ip kerberos source-interface any
ip classless
ip route 2.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 3.1.1.1
ip route 4.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 3.1.1.1
no ip http server
!
access-list 101 permit udp any any range 16384 32768
access-list 102 permit tcp any any eq tacacs
access-list 104 permit tcp any any eq www
access-list 105 permit ip any any
access-list 108 permit tcp any any eq telnet
access-list 109 permit tcp any any eq smtp
access-list 110 permit tcp any any eq ftp
!
voice-port 1/0/0
!
voice-port 1/0/1
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
dial-peer voice 1 voip
destination-pattern 2220
session target ipv4:2.1.1.1
ip precedence 5
!
dial-peer voice 11 pots
destination-pattern 1110
port 1/0/0
!
!
line con 0
transport input none
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
no scheduler allocate
end
DiffServ Implementation Troubleshooting Logs
This section contains sample troubleshooting logs for remote router 1 and the central router. These logs can be used for monitoring and maintaining the DiffServ implementation.
Remote Router 1
Remote1#
show policy-map SETDSCP
Policy Map SETDSCP
Class EF
set ip dscp 46
Class AF1
set ip dscp 10
Class AF3
set ip dscp 26
Class AF21
set ip dscp 18
Class AF22
set ip dscp 20
Class AF23
set ip dscp 22
Remote1# show policy-map VOIP
Policy Map VOIP
Class platinum
Weighted Fair Queueing
Strict Priority
Bandwidth 500 (kbps) Burst 12500 (Bytes)
Class gold
Weighted Fair Queueing
Bandwidth 50 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
Class bronze
Traffic Shaping
Average Rate Traffic Shaping
CIR 320000 (bps) Max. Buffers Limit 1000 (Packets)
Weighted Fair Queueing
Bandwidth 15 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
Class silver
Weighted Fair Queueing
Bandwidth 35 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
Class best-effort
police 56000 1750 1750 conform-action set-dscp-transmit 0 exceed-action drop violate-action drop
Remote1# show policy-map interface f0/0
FastEthernet0/0
Service-policy input: SETDSCP (1611)
Class-map: EF (match-all) (1612/3)
2154221 packets, 176646532 bytes
1 minute offered rate 642000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 101 (1614)
QoS Set
ip dscp 46
Packets marked 2154256
Class-map: AF1 (match-all) (1616/12)
46351 packets, 69711904 bytes
1 minute offered rate 254000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 102 (1618)
QoS Set
ip dscp 10
Packets marked 46352
Class-map: AF3 (match-all) (1620/11)
81757 packets, 122962528 bytes
1 minute offered rate 483000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 104 (1622)
QoS Set
ip dscp 26
Packets marked 81951
Class-map: AF21 (match-all) (1624/4)
84585 packets, 127215840 bytes
1 minute offered rate 484000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 108 (1626)
QoS Set
ip dscp 18
Packets marked 84780
Class-map: AF22 (match-all) (1628/6)
75440 packets, 113461760 bytes
1 minute offered rate 423000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 109 (1630)
QoS Set
ip dscp 20
Packets marked 75612
Class-map: AF23 (match-all) (1632/5)
66212 packets, 99582848 bytes
1 minute offered rate 362000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 110 (1634)
QoS Set
ip dscp 22
Packets marked 66428
Class-map: class-default (match-any) (1636/0)
2555349 packets, 778812687 bytes
1 minute offered rate 2896000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: any (1638)
2555358 packets, 778810855 bytes
1 minute rate 2896000 bps
Remote1# show policy-map interface s0/0
Serial0/0
Service-policy output: VOIP (1558)
Class-map: platinum (match-all) (1559/8)
2988402 packets, 215165016 bytes
1 minute offered rate 564000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: ip dscp 46 (1561)
Weighted Fair Queueing
Strict Priority
Output Queue: Conversation 264
Bandwidth 500 (kbps)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 2988422/215166384
(total drops/bytes drops) 330478/23794416
Class-map: gold (match-all) (1563/2)
64300 packets, 96064200 bytes
1 minute offered rate 252000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: ip dscp 10 12 14 (1565)
Weighted Fair Queueing
Output Queue: Conversation 265
Bandwidth 50 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 64300/96064200
(depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
Class-map: bronze (match-all) (1567/7)
115945 packets, 173221830 bytes
1 minute offered rate 479000 bps, drop rate 56000 bps
Match: ip dscp 26 28 30 (1569)
Traffic Shaping
Target Byte Sustain Excess Interval Increment Adapt
Rate Limit bits/int bits/int (ms) (bytes) Active
320000 2000 8000 8000 25 1000 -
Queue Packets Bytes Packets Bytes
Depth Delayed Delayed Active
64 80006 119528964 72784 108739296 yes
Weighted Fair Queueing
Output Queue: Conversation 266
Bandwidth 15 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 80006/119528964
(depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/12749/0
Class-map: silver (match-all) (1572/9)
315979 packets, 472072626 bytes
1 minute offered rate 1258000 bps, drop rate 646000 bps
Match: ip dscp 18 20 22 (1574)
Weighted Fair Queueing
Output Queue: Conversation 267
Bandwidth 35 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 316253/472481982
(depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/158914/0
Class-map: best-effort (match-all) (1576/10)
3548921 packets, 1051813080 bytes
1 minute offered rate 2801000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 105 (1578)
police:
56000 bps, 1750 limit, 1750 extended limit
conformed 0 packets, 0 bytes; action: set-dscp-transmit 0
exceeded 0 packets, 0 bytes; action: drop
violated 0 packets, 0 bytes; action: drop
Class-map: class-default (match-any) (1580/0)
3549281 packets, 1051837716 bytes
1 minute offered rate 2801000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: any (1582)
3549281 packets, 1051837644 bytes
1 minute rate 2801000 bps
Remote1# show queue serial 0/0
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 631823
Queueing strategy: weighted fair
Output queue: 101/1000/64/593935 (size/max total/threshold/drops)
Conversations 4/7/256 (active/max active/max total)
Reserved Conversations 3/3 (allocated/max allocated)
Available Bandwidth 1000 kilobits/sec
(depth/weight/total drops/no-buffer drops/interleaves) 5/0/346494/0/0
Conversation 264, linktype: ip, length: 72
source: 0.0.0.0, destination: 1.1.1.2, id: 0x0000, ttl: 59,
TOS: 184 prot: 17, source port 0, destination port 16384
(depth/weight/total drops/no-buffer drops/interleaves) 63/45/166791/0/0
Conversation 267, linktype: ip, length: 1494
source: 0.0.0.0, destination: 1.1.1.2, id: 0x0000, ttl: 59,
TOS: 72 prot: 6, source port 0, destination port 23
(depth/weight/total drops/no-buffer drops/interleaves) 35/104/13461/0/0
Conversation 266, linktype: ip, length: 1494
source: 0.0.0.0, destination: 1.1.1.2, id: 0x0000, ttl: 59,
TOS: 104 prot: 6, source port 0, destination port 80
(depth/weight/total drops/no-buffer drops/interleaves) 1/32384/67216/0/0
Conversation 89, linktype: ip, length: 1482
source: 0.0.0.0, destination: 1.1.1.2, id: 0x0000, ttl: 59,
TOS: 0 prot: 17, source port 0, destination port 67
Remote1# show interface serial 0/0
Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is PowerQUICC Serial
Internet address is 2.1.1.1/24
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 2000 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 207/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Last input 00:00:03, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 00:50:30
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 595699
Queueing strategy: weighted fair
Output queue: 114/1000/64/560199 (size/max total/threshold/drops)
Conversations 4/7/256 (active/max active/max total)
Reserved Conversations 3/3 (allocated/max allocated)
Available Bandwidth 1000 kilobits/sec
1 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
1 minute output rate 1624000 bits/sec, 962 packets/sec
354 packets input, 22827 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 354 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
2918044 packets output, 616834104 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
0 carrier transitions
DCD=up DSR=up DTR=up RTS=up CTS=up
Central Router
Central# show policy-map interface serial 4/0
Serial4/0
Service-policy output: AVVID (2022)
Class-map: silver (match-all) (2023/2)
251162 packets, 375236028 bytes
1 minute offered rate 612000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: ip dscp 18 20 22 (2025)
Weighted Fair Queueing
Output Queue: Conversation 265
Bandwidth 25 (%)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 3/4482
(depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
mean queue depth: 0
Dscp Random drop Tail drop Minimum Maximum Mark
(Prec) pkts/bytes pkts/bytes threshold threshold probability
0(0) 0/0 0/0 20 40 1/10
1 0/0 0/0 22 40 1/10
2 0/0 0/0 24 40 1/10
3 0/0 0/0 26 40 1/10
4 0/0 0/0 28 40 1/10
(...up to DSCP 63......)
61 0/0 0/0 30 40 1/10
62 0/0 0/0 32 40 1/10
63 0/0 0/0 34 40 1/10
rsvp 0/0 0/0 36 40 1/10
Class-map: gold (match-all) (2027/3)
102479 packets, 153103626 bytes
1 minute offered rate 250000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: ip dscp 10 12 14 (2029)
Weighted Fair Queueing
Output Queue: Conversation 266
Bandwidth 35 (%)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 0/0
(depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
mean queue depth: 0
Dscp Random drop Tail drop Minimum Maximum Mark
(Prec) pkts/bytes pkts/bytes threshold threshold probability
0(0) 0/0 0/0 20 40 1/10
1 0/0 0/0 22 40 1/10
2 0/0 0/0 24 40 1/10
3 0/0 0/0 26 40 1/10
...up to DSCP 63......)
61 0/0 0/0 30 40 1/10
62 0/0 0/0 32 40 1/10
63 0/0 0/0 34 40 1/10
rsvp 0/0 0/0 36 40 1/10
Class-map: bronze (match-all) (2031/4)
106605 packets, 159267870 bytes
1 minute offered rate 262000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: ip dscp 26 28 30 (2033)
Weighted Fair Queueing
Output Queue: Conversation 267
Bandwidth 15 (%)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 0/0
(depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 0/0/0
mean queue depth: 0
Dscp Random drop Tail drop Minimum Maximum Mark
(Prec) pkts/bytes pkts/bytes threshold threshold probability
0(0) 0/0 0/0 20 40 1/10
1 0/0 0/0 22 40 1/10
2 0/0 0/0 24 40 1/10
3 0/0 0/0 26 40 1/10
4 0/0 0/0 28 40 1/10
5 0/0 0/0 30 40 1/10
6 0/0 0/0 32 40 1/10
(...up to DSCP 63......)
61 0/0 0/0 30 40 1/10
62 0/0 0/0 32 40 1/10
63 0/0 0/0 34 40 1/10
rsvp 0/0 0/0 36 40 1/10
Class-map: platinum (match-all) (2035/5)
4253851 packets, 306277272 bytes
1 minute offered rate 499000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: ip dscp 46 (2037)
Weighted Fair Queueing
Strict Priority
Output Queue: Conversation 264
Bandwidth 500 (kbps)
(pkts matched/bytes matched) 4248148/305866656
(total drops/bytes drops) 5/360
Class-map: class-default (match-any) (2039/0)
4719109 packets, 1000522466 bytes
1 minute offered rate 1625000 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: any (2041)
4719109 packets, 1000522466 bytes
1 minute rate 1625000 bps
Central# show queue serial 4/0
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 5
Queueing strategy: weighted fair
Output queue: 0/1000/64/5 (size/max total/threshold/drops)
Conversations 0/2/256 (active/max active/max total)
Reserved Conversations 3/3 (allocated/max allocated)
Available Bandwidth 1000 kilobits/sec
Central# show queue serial 4/1
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: weighted fair
Output queue: 0/1000/64/0 (size/max total/threshold/drops)
Conversations 0/1/256 (active/max active/max total)
Reserved Conversations 3/3 (allocated/max allocated)
Available Bandwidth 1011 kilobits/sec
Accounting Functionality and DiffServ
The accounting functionality of DiffServ allows you to collect and display service policy statistics on a per-class basis. The show policy-map interface command has been enhanced to include additional information related to traffic classes on a particular interface. The show policy-map interface command displays information including the incoming traffic rate, the dropped packet rate, the number of matched packets, and the number of matched bytes, for traffic classes that are attached to the specified interface. These details can be used for billing and accounting purposes, and for managing projects, as appropriate.
Where to Go Next
Decide which of the QoS feature sets you want to use in your DiffServ implementation and see the corresponding section of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide. For more information about the specific section to use, see Where to Go Next below.
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to implementing DiffServ for end-to-end QoS.
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
QoS commands (including the show policy-map interface command) |
Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Command Reference, Release 12.4T. |
|
MQC configuration tasks |
"Applying QoS Features Using the MQC" module of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide |
|
Packet marking |
"Marking Network Traffic" module in the "Classification" part of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide. |
|
CAR |
"Classification" part of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide. |
|
Traffic policing |
"Policing and Shaping" part of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide. |
|
Traffic shaping (regulating packet flow) |
"Regulating Packet Flow" module of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide. |
|
LLQ and CBWFQ |
"Congestion Management" part of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide. |
|
WRED, DiffServ-compliant WRED |
"Congestion Avoidance" part of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide. |
|
MPLS CoS enhancements |
Cisco IOS IP Switching Configuration Guide |
|
Two additional types of service models: best-effort services and Integrated Services (IntServ) |
"Quality of Service Overview" module of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide. |
|
Additional QoS features not listed in the module |
"Quality of Service Overview" module of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide. |
RFCs
|
RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
|
RFC 2474 |
Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers |
|
RFC 2475 |
An Architecture for Differentiated Services Framework |
|
RFC 2597 |
Assured Forwarding PHB |
|
RFC 2598 |
An Expedited Forwarding PHB |
|
RFC 2697 |
A Single Rate Three Color Marker |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |