- IP Multicast Technology Overview
- Configuring Basic IP Multicast
- Configuring Basic IP Multicast in IPv6 Networks
- Using MSDP to Interconnect Multiple PIM-SM Domains
- PIM Allow RP
- Configuring Source Specific Multicast
- Implementing Multicast Stub Routing
- Tunneling to Connect Non-IP Multicast Areas
- BFD Support for Multicast (PIM)
- HSRP Aware PIM
- VRRP Aware PIM
- Verifying IP Multicast Operation
- SNMP Traps for IP Multicast
- Monitoring and Maintaining IP Multicast
- IPv6 Multicast: PIM Sparse Mode
- IPv6 Multicast: Static Multicast Routing for IPv6
- IPv6 Multicast: PIM Source-Specific Multicast
- IPv6 Source Specific Multicast Mapping
- IPv6 Multicast: Explicit Tracking of Receivers
- IPv6 Bidirectional PIM
- IPv6 Multicast: Routable Address Hello Option
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Multicast Stub Routing
- Restrictions for Multicast Stub Routing
- Information About Multicast Stub Routing
- How to Implement Multicast Stub Routing
- Configuration Examples for Implementing Multicast Stub Routing
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Implementing Multicast Stub Routing
Implementing Multicast Stub Routing
This module describes the concepts and configuration tasks used to implement multicast stub routing. Multicast stub routing can be used for the following purposes:
- To prevent multicast transit when it is enforced by unicast stub routing.
- To eliminate periodic flooding and pruning of dense mode traffic on low bandwidth links.
- To reduce overall processing of Protocol Indendent Multicast (PIM) control traffic; and protect against multicast spoofing of PIM Designated Router (DR) messages and PIM assert messages.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Multicast Stub Routing
- Restrictions for Multicast Stub Routing
- Information About Multicast Stub Routing
- How to Implement Multicast Stub Routing
- Configuration Examples for Implementing Multicast Stub Routing
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Implementing Multicast Stub Routing
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for Multicast Stub Routing
IP multicast is enabled and the Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) interfaces are configured using the tasks described in the "Configuring Basic IP Multicast" module of the IP Multicast: PIM Configuration Guide.
Restrictions for Multicast Stub Routing
-
Multicast stub routing does not prevent the configuration of other Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) that do not support stub routing, such as Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), and Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) to bypass this restriction. Multicast stub routing also does not prevent the configuration of static routing to bypass this restriction. Multicast stub routing is enforced by unicast stub routing. The proper unicast Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) stub routing configuration will assist in multicast stub routing. 
Note
For more information about unicast EIGRP stub routing, see the “Configuring EIGRP” module of the IP Routing: EIGRP Configuration Guide.
- Multicast stub routing can only be implemented in nonredundant stub network topologies.
Information About Multicast Stub Routing
- Multicast Stub Networks
- Multicast Stub Routing Between Stub and Distribution Devices
- Multicast Stub Routing Between the Stub Device and Interested Receivers
- Benefits of Multicast Stub Routing
Multicast Stub Networks
Multicast stub networks are those segments that receivers are directly connected to for any multicast group, even though there are receivers interested in multicast traffic beyond those segments. Multicast stub routing can only be implemented in nonredundant stub network topologies.
Multicast Stub Routing Between Stub and Distribution Devices
Implementing multicast stub routing between the stub and distribution device is useful in PIM dense mode (PIM-DM) where periodic flooding and subsequent pruning of multicast traffic occurs for unwanted multicast groups. Multicast stub routing in this scenario prevents periodic flooding and pruning and also allows multicast traffic to be forwarded for groups in which receivers are available on the stub network.
Implementing multicast stub routing between the stub and distribution device in PIM sparse mode (PIM-SM) and bidirectional PIM (bidir-PIM) environments eliminates the need to maintain the group-to-Rendezvous Point (RP) mapping cache on the stub device, and saves periodic update bandwidth--if Auto-RP or PIM bootstrap router (BSR) is used for distributing the RP information.
Multicast stub routing is intended to forward multicast traffic from the distribution to the stub device. Although it is possible to have sources directly connected to the stub network, it would only work in a PIM-DM environment. It is not possible in PIM-SM, Source Specific Multicast (SSM), and bidirectional PIM (bidir-PIM) environments because the first hop device will be filtered by the PIM neighbor filter applied on the distribution device, resulting in reverse path forwarding (RPF) failures. Furthermore, receivers must be directly connected to the stub device and cannot be further downstream.
Multicast Stub Routing Between the Stub Device and Interested Receivers
Implementing multicast stub routing between the stub device and interested receivers is used to reduce the overall processing of PIM control traffic, especially as the number of stub links increases on the stub device, and to protect against DoS attacks targeted at the PIM DR.
Benefits of Multicast Stub Routing
Multicast stub routing allows such stub networks to be configured easily for multicast connectivity and provides the following benefits:
- Prevents stub networks from being used for multicast transit when they are enforced by unicast stub routing (EIGRP).
- Eliminates periodic flooding and pruning of dense mode traffic on low bandwidth links.
- Reduces overall processing of PIM control traffic.
- Protects against multicast spoofing of PIM DR messages and PIM assert messages.
 Note |
Multicast stub routing can only be implemented in nonredundant stub network topologies. |
How to Implement Multicast Stub Routing
- Configuring the Stub Device for Multicast Stub Routing
- Configuring the Distribution Device for Multicast Stub Routing
Configuring the Stub Device for Multicast Stub Routing
Perform this task to configure a stub device for multicast stub routing.
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. interface type number
5. ip igmp helper-address ip-address
6. end
7. show ip pim interface [type number]
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the Distribution Device for Multicast Stub Routing
Perform the following task to configure the distribution device for multicast stub routing.
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. interface type number
5. end
6. show ip pim interface [type number]
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
||||||
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||||||
| Step 3 | interface type number Example: Device(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0 |
Enters interface configuration mode. |
||||||
| Step 4 | Do one of the following:
Example: Device(config-if)# ip pim passive Example: Device(config-if)# ip pim neighbor-filter 1 |
|
||||||
| Step 5 | end Example: Device(config-if)# end |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
||||||
| Step 6 | show ip pim interface [type number] Example: Device# show ip pim interface |
Displays information about interfaces configured for PIM. |
Configuration Examples for Implementing Multicast Stub Routing
- Example: Implementing Multicast Stub Routing - PIM-DM
- Example: Implementing Multicast Stub Routing - PIM-SM Static RP
- Example: Implementing Multicast Stub Routing - PIM-SSM
- Example Implementing Multicast Stub Routing - Bidir-PIM
Example: Implementing Multicast Stub Routing - PIM-DM
The following example shows the configuration of multicast stub routing in a PIM-DM environment. The example is based on the topology shown in the figure.
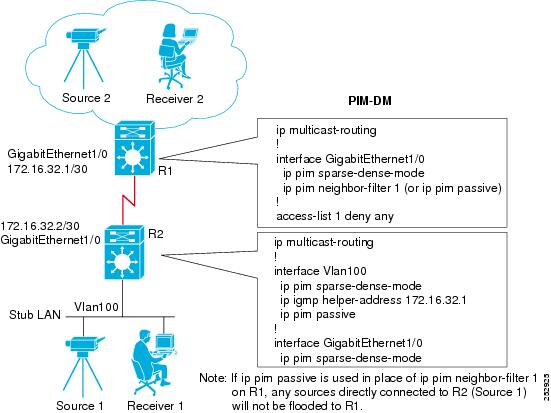
Distribution Device Configuration
ip multicast-routing ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0 ip pim sparse-dense-mode ip pim neighbor-filter 1 (or ip pim passive) ! access-list 1 deny any
Stub Device Configuration
ip multicast-routing ! interface Vlan100 ip pim sparse-dense-mode ip igmp helper-address 172.16.32.1 ip pim passive ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0 ip pim sparse-dense-mode
Example: Implementing Multicast Stub Routing - PIM-SM Static RP
The following example shows the configuration of multicast stub routing in a PIM-SM environment using static RP. The example is based on the topology shown in the figure.
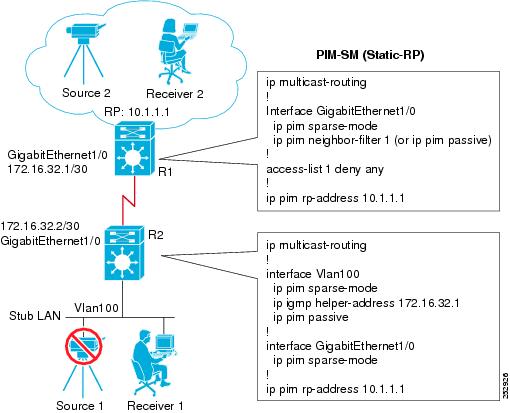
Distribution Device Configuration
ip multicast-routing ! Interface GigabitEthernet1/0 ip pim sparse-mode ip pim neighbor-filter 1 (or ip pim passive) ! access-list 1 deny any ! ip pim rp-address 10.1.1.1
Stub Device Configuration
ip multicast-routing ! interface Vlan100 ip pim sparse-mode ip igmp helper-address 172.16.32.1 ip pim passive ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0 ip pim sparse-mode ! ip pim rp-address 10.1.1.1
Example: Implementing Multicast Stub Routing - PIM-SSM
The following example shows the configuration of multicast stub routing in a PIM-SSM environment. The example is based on the topology shown in the figure.
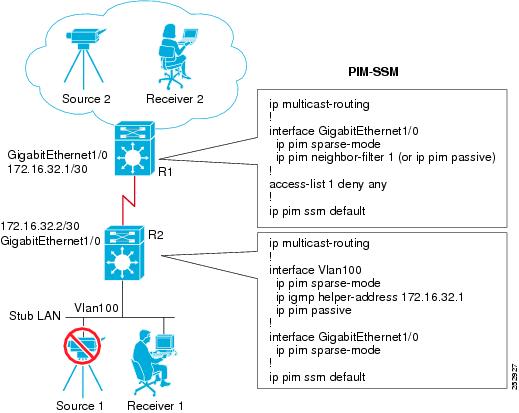
Distribution Device Configuration
ip multicast-routing ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0 ip pim sparse-mode ip pim neighbor-filter 1 (or ip pim passive) ! access-list 1 deny any ! ip pim ssm default
Stub Device Configuration
ip multicast-routing ! interface Vlan100 ip pim sparse-mode ip igmp helper-address 172.16.32.1 ip pim passive ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0 ip pim sparse-mode ! ip pim ssm default
Example Implementing Multicast Stub Routing - Bidir-PIM
The following example shows the configuration of multicast stub routing in a bidir-PIM environment using static RP. The example is based on the topology shown in the figure.
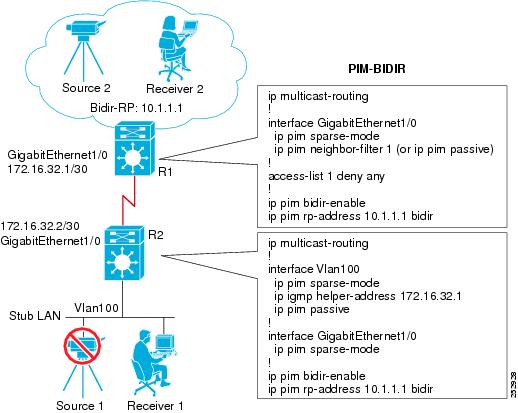
Distribution Device Configuration
ip multicast-routing ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0 ip pim sparse-mode ip pim neighbor-filter 1 (or ip pim passive) ! access-list 1 deny any ! ip pim bidir-enable ip pim rp-address 10.1.1.1 bidir
Stub Device Configuration
ip multicast-routing ! interface Vlan100 ip pim sparse-mode ip igmp helper-address 172.16.32.1 ip pim passive ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0 ip pim sparse-mode ! ip pim bidir-enable ip pim rp-address 10.1.1.1 bidir
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| Cisco IOS commands |
|
| Cisco IOS IP SLAs commands |
|
| Overview of the IP multicast technology area |
“ IP Multicast Technology Overview ” module |
| Concepts, tasks, and examples for configuring an IP multicast network using PIM |
“ Configuring a Basic IP Multicast Network ” module |
Standards and RFCs
| Standard/RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
| No new or modified standards or RFCs are supported by this feature. |
-- |
MIBs
| MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Implementing Multicast Stub Routing
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| PIM Stub |
12.2(37)SE 15.0(1)M 12.2(33)SRE Cisco IOS XE 3.1.0SG |
The PIM Stub feature introduces the capability to configure an interface to operate in PIM passive mode, which means that the router will not send PIM messages on the interface nor will it accept PIM messages from other routers across this interface. The router will instead consider that is is the only PIM router on the network and thus act as the DR and also as the DF (for all bidir-PIM group ranges). This mode is used primarily in multicast stub routing scenarios. The following commands were introduced or modified: ip pim passive. |
 Feedback
Feedback