IGMP Proxy
This module describes how to configure IGMP proxy to enable a device to send an IGMP report to a specified destination IP address.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for IGMP Proxy
- Information About IGMP Proxy
- How to Configure IGMP Proxy
- Configuration Examples for IGMP Proxy
- Additional References
- Feature Information for IGMP Proxy
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for IGMP Proxy
- All devices on the IGMP UDL have the same subnet address. If all devices on the UDL cannot have the same subnet address, the upstream device must be configured with secondary addresses to match all of the subnets to which the downstream devices are attached.
-
IP multicast is enabled and the PIM interfaces are configured.
Information About IGMP Proxy
IGMP Proxy
An IGMP proxy enables hosts in a unidirectional link routing (UDLR) environment that are not directly connected to a downstream router to join a multicast group sourced from an upstream network.
The figure below illustrates a sample topology that shows two UDLR scenarios:
- Traditional UDL routing scenario--A UDL device with directly connected receivers.
- IGMP proxy scenario--UDL device without directly connected receivers.
 Note |
IGMP UDLs are needed on the upstream and downstream devices. |
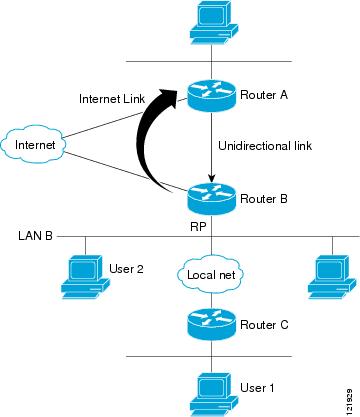
Scenario 1--Traditional UDLR Scenario (UDL Device with Directly Connected Receivers)
For scenario 1, no IGMP proxy mechanism is needed. In this scenario, the following sequence of events occurs:
- User 2 sends an IGMP membership report requesting interest in group G.
- Router B receives the IGMP membership report, adds a forwarding entry for group G on LAN B, and proxies the IGMP report to Router A, which is the UDLR upstream device.
- The IGMP report is then proxied across the Internet link.
- Router A receives the IGMP proxy and maintains a forwarding entry on the unidirectional link.
Scenario 2--IGMP Proxy Scenario (UDL Device without Directly Connected Receivers)
For scenario 2, the IGMP proxy mechanism is needed to enable hosts that are not directly connected to a downstream device to join a multicast group sourced from an upstream network. In this scenario, the following sequence of events occurs:
- User 1 sends an IGMP membership report requesting interest in group G.
- Router C sends a PIM Join message hop-by-hop to the RP (Router B).
- Router B receives the PIM Join message and adds a forwarding entry for group G on LAN B.
- Router B periodically checks its mroute table and proxies the IGMP membership report to its upstream UDL device across the Internet link.
- Router A creates and maintains a forwarding entry on the unidirectional link (UDL).
In an enterprise network, it is desirable to be able to receive IP multicast traffic via satellite and forward the traffic throughout the network. With unidirectional link routing (UDLR) alone, scenario 2 would not be possible because receiving hosts must be directly connected to the downstream device, Router B. The IGMP proxy mechanism overcomes this limitation by creating an IGMP report for (*, G) entries in the multicast forwarding table. To make this scenario functional, therefore, you must enable IGMP report forwarding of proxied (*, G) multicast static route (mroute) entries (using the ip igmp mroute-proxy command) and enable the mroute proxy service (using the ip igmp proxy-service command) on interfaces leading to PIM-enabled networks with potential members.
 Note |
Because PIM messages are not forwarded upstream, each downstream network and the upstream network have a separate domain. |
How to Configure IGMP Proxy
Configuring the Upstream UDL Device for IGMP UDLR
Perform this task to configure the upstream UDL device for IGMP UDLR.
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. interface type number
4. ip igmp unidirectional-link
5. end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the Downstream UDL Device for IGMP UDLR with IGMP Proxy Support
Perform this task to configure the downstream UDL device for IGMP UDLR with IGMP proxy support.
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. interface type number
4. ip igmp unidirectional-link
5. exit
6. interface type number
7. ip igmp mroute-proxy type number
8. exit
9. interface type number
10. ip igmp helper-address udl interface-type interface-number
11. ip igmp proxy-service
12. end
13. show ip igmp interface
14. show ip igmp udlr
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for IGMP Proxy
Example: IGMP Proxy Configuration
The following example shows how to configure the upstream UDL device for IGMP UDLR and the downstream UDL device for IGMP UDLR with IGMP proxy support.
Upstream Device Configuration
interface gigabitethernet 0/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip pim dense-mode ! interface gigabitethernet 1/0/0 ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip pim dense-mode ip igmp unidirectional-link ! interface gigabitethernet 2/0/0 ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0
Downstream Device Configuration
ip pim rp-address 10.5.1.1 5 access-list 5 permit 239.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 ! interface loopback 0 ip address 10.7.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip pim dense-mode ip igmp helper-address udl ethernet 0 ip igmp proxy-service ! interface gigabitethernet 0/0/0 ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 ip pim dense-mode ip igmp unidirectional-link ! interface gigabitethernet 1/0/0 ip address 10.5.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip pim sparse-mode ip igmp mroute-proxy loopback 0 ! interface gigabitethernet 2/0/0 ip address 10.6.1.1 255.255.255.0
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| Cisco IOS commands |
|
| Cisco IOS IP Multicast commands |
MIBs
| MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS XE releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for IGMP Proxy
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| IGMP Proxy |
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2SE |
IGMP proxy enables hosts in a unidirectional link routing (UDLR) environment that are not directly connected to a downstream router to join a multicast group sourced from an upstream network. The following commands were introduced or modified: ip igmp helper-address, ip igmp mroute-proxy, ip igmp proxy-service, ip igmp unidirectional-link. |
 Feedback
Feedback