PA-4R-FDX Full-Duplex Token Ring Port Adapter Installation and Configuration
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
PA-4R-FDX Full-Duplex Token Ring Port Adapter Installation and Configuration
Port Adapter Installation Prerequisites
Software and Hardware Requirements
Checking Hardware and Software Compatibility
Verifying Full-Duplex Token Ring Port Adapter Capability in Your Router
Electrical Equipment Guidelines
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Token Ring Connection Equipment
Token Ring Distance Limitations
Token Ring Speed Considerations
What Is the 4R-FDX Port Adapter?
Port Adapter Locations on the VIP2 and the Cisco 7200 Series Router
4R-FDX Port Adapter Receptacles, Cables, and Pinouts
4R-FDX Port Adapter Receptacle Pinout
VIP2 and the 4R-FDX Port Adapter
Installing or Replacing a Port Adapter on a VIP2
Attaching 4R-FDX Port Adapter Interface Cables
Determining Chassis Slot, Port Adapter, and Token Ring Interface Port Numbers
Configuring Full-Duplex Operation
Cisco 7200 Series and the 4R-FDX Port Adapter
Installing or Replacing a Port Adapter in Cisco 7200 Series Routers
Attaching 4R-FDX Port Adapter Interface Cables
Selecting Port Adapter Slot and Token Ring Interface Port Numbers
Configuring Full-Duplex Operation
Obtaining Technical Assistance
PA-4R-FDX Full-Duplex Token Ring Port Adapter Installation and Configuration
Product Number: PA-4R-FDX(=)
This configuration note describes how to install and configure the full-duplex Token Ring port adapter (PA-4R-FDX), which can be used in the following supported platforms:
•
Cisco 7200 series routers, which consists of the 2-slot Cisco 7202, 4-slot Cisco 7204, and the 6-slot Cisco 7206
•
Second-generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2) in all Cisco 7500 series and Cisco 7000 series routers. (Refer to the section "Software and Hardware Requirements" section.)

Note
For VIP2 users, use this configuration note in conjunction with the configuration note Second-Generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2) Installation and Configuration (Document Number 78-2658-xx), which shipped with your VIP2.
For Cisco 7200 series router users, use this configuration note in conjunction with the Cisco 72xx Installation and Configuration Guide that shipped with your Cisco 7200 series system.
Contents
This configuration note is organized into the following sections:
•
Port Adapter Installation Prerequisites
•
What Is the 4R-FDX Port Adapter?
•
VIP2 and the 4R-FDX Port Adapter
•
Cisco 7200 Series and the 4R-FDX Port Adapter
•
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Port Adapter Installation Prerequisites
This section provides software requirements, a list of parts and tools you will need to perform the port adapter installation, and safety and ESD-prevention guidelines to help you avoid injury and damage to the equipment during installation. Also included is information on the systems in which port adapters can be installed and overview information on interface specifications.
The following sections discuss general information and information about port adapter installation requirements:
•
Software and Hardware Requirements
•
Checking Hardware and Software Compatibility
•
Verifying Full-Duplex Token Ring Port Adapter Capability in Your Router
Software and Hardware Requirements
Following are specific hardware and software prerequisites to ensure proper operation of the 4R-FDX port adapter:
•
For 4R-FDX port adapters installed in a Cisco 7204 or a Cisco 7206, Cisco IOS Release 11.1(8)CA, or later, is required.
•
For 4R-FDX port adapters installed in a Cisco 7202, Cisco IOS Release 11.1(19)CC1 or later, or Cisco IOS Release 11.3(4)AA or later is required.
•
For 4R-FDX port adapters installed on the VIP2-15 or VIP2-40 in Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series routers, Cisco IOS Release 11.1(8)CA, or later, is required.
•
The 4R-FDX port adapter can be used in the VIP2 in all Cisco 7500 series routers and Cisco 7000 series routers that use the RSP7000 and RSP7000CI, and in Cisco 7200 series routers.

Note
The 4R-FDX port adapter can be installed in port adapter slot 0 or slot 1 on the VIP2 motherboard and in any available port adapter slot in Cisco 7200 series chassis.
In the Cisco 7000 series or Cisco 7500 series routers, the 4R port adapter requires the following VIP2 models:
•
VIP2-15(=) (1 MB of SRAM, 8 MB of DRAM)
•
VIP2-20= (1 MB of DRAM, 16 MB of SRAM)
•
VIP2-40(=) (2 MB of SRAM, 32 MB of DRAM)

CautionTo prevent system problems, the VIP2 requires that the Cisco 7000 series router has the 7000 Series Route Switch Processor (RSP7000) and 7000 Series Chassis Interface (RSP7000CI) installed. The VIP2 will not operate properly with the Route Processor (RP), Switch Processor (SP), or Silicon Switch Processor (SSP) installed in the Cisco 7000 series router.

Note
The minimum recommended VIP2 model is a VIP2-15.
Checking Hardware and Software Compatibility
To check the minimum software requirements of Cisco IOS software with the hardware installed on your router, Cisco maintains the Software Advisor tool on Cisco.com. This tool does not verify whether modules within a system are compatible, but it does provide the minimum IOS requirements for individual hardware modules or components.

Note
Access to this tool is limited to users with Cisco.com login accounts.
To access Software Advisor, click Login at Cisco.com and go to Technical Support Help—Cisco TAC: Tool Index: Software Advisor. You can also access the tool by pointing your browser directly to http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/support/CompNav/Index.pl.
Choose a product family or enter a specific product number to search for the minimum supported software release needed for your hardware.
Verifying Full-Duplex Token Ring Port Adapter Capability in Your Router
The PA-4R-FDX port adapter supports full-duplex operation. (The PA-4R port adapter does not support full-duplex operation.) For a Token Ring interface to support full-duplex operation, it must be a PA-4R-FDX interface installed in a host router that is running the appropriate Cisco IOS software.
To determine if a Token Ring interface installed in your system supports full-duplex operation, use the show interfaces tokenring command. If the interface does not support full-duplex, the following message is displayed, and no changes are made to the interface:
%TokenRing5/0 interface does not support full-duplex.If you do not have the appropriate Cisco IOS software release and 4R-FDX port adapter installed in your system, you cannot configure full-duplex operation. For specific full-duplex configuration requirements, refer to the sections "Configuring Full-Duplex Operation," on page 24 (for operation with VIP2), and to "Configuring Full-Duplex Operation," on page 38 (for operation with Cisco 7200 series routers).
List of Parts and Tools
You need the following parts and tools to install a port adapter. If you need additional equipment, contact a service representative for ordering information.
•
PA-4R-FDX(=) port adapter and one of the following:
–
VIP2-15(=), VIP2-20=, VIP2-40(=)
–
Cisco 7200 series router with at least one available port adapter slot
•
Cables appropriate for the port adapter's interfaces (Token Ring cables are not available from Cisco Systems; they are available from outside commercial cable vendors.)
•
Number 1 Phillips and a 3/16-inch, flat-blade screwdriver (for VIP2 installation only).
•
Your own ESD-prevention equipment or the disposable grounding wrist strap included with all upgrade kits, FRUs, and spares.
Safety Guidelines
Following are safety guidelines that you should observe when working with any equipment that connects to electrical power or telephone wiring.
Safety Warnings
Electrical Equipment Guidelines
Follow these basic guidelines when working with any electrical equipment:
•
Before beginning any procedures requiring access to the chassis interior, locate the emergency power-off switch for the room in which you are working.
•
Disconnect all power and external cables before moving a chassis.
•
Do not work alone when potentially hazardous conditions exist and never assume that power has been disconnected from a circuit; always check.
•
Do not perform any action that creates a potential hazard to people or makes the equipment unsafe. Carefully examine your work area for possible hazards such as moist floors, ungrounded power extension cables, and missing safety grounds.
Telephone Wiring Guidelines
Use the following guidelines when working with any equipment that is connected to telephone wiring or to other network cabling:
•
Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
•
Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed for wet locations.
•
Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been disconnected at the network interface.
•
Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, which can occur when electronic cards or components are improperly handled, results in complete or intermittent failures. Port adapters and processor modules comprise printed circuit boards that are fixed in metal carriers. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and connectors are integral components of the carrier. Although the metal carrier helps to protect the board from ESD, use a preventive antistatic strap during handling.
Following are guidelines for preventing ESD damage:
•
Always use an ESD wrist or ankle strap and ensure that it makes good skin contact.
•
Connect the equipment end of the strap to an unfinished chassis surface.
•
When installing a component, use any available ejector levers or captive installation screws to properly seat the bus connectors in the backplane or midplane. These devices prevent accidental removal, provide proper grounding for the system, and help to ensure that bus connectors are properly seated.
•
When removing a component, use any available ejector levers or captive installation screws to release the bus connectors from the backplane or midplane.
•
Handle carriers by available handles or edges only; avoid touching the printed circuit boards or connectors.
•
Place a removed component board-side-up on an antistatic surface or in a static shielding container. If you plan to return the component to the factory, immediately place it in a static shielding container.
•
Avoid contact between the printed circuit boards and clothing. The wrist strap only protects components from ESD voltages on the body; ESD voltages on clothing can still cause damage.
•
Never attempt to remove the printed circuit board from the metal carrier.

CautionFor safety, periodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap. The measurement should be between 1 and 10 megohms.
Token Ring Overview
The following sections describe Token Ring specifications, physical connections, connection equipment, and cables and connectors.
Token Ring Specifications
The term Token Ring refers to both IBM's Token Ring Network, which IBM developed in the 1970s, and to IEEE 802.5 networks. The IEEE 802.5 specification was modeled after, and still closely shadows, IBM's network. The two types are compatible, although the specifications differ slightly.
Token Ring and IEEE 802.5 are token passing networks, which move a small frame, called a token, around the network. Possession of the token grants the right to transmit; a station with information to transmit must wait until it detects a free token passing by.
The IBM Token Ring specifies a star topology, with all end stations connected through a device called a multistation access unit (MSAU) for half-duplex functionality or a Token Ring switch for full-duplex functionality. IEEE 802.5 does not specify any topology, although most implementations are based on a star configuration with end stations attached to a device called a media access unit (MAU) for half-duplex functionality or a Token Ring switch for full-duplex functionality. Also, IBM Token Ring specifies twisted-pair cabling, whereas IEEE 802.5 does not specify media type. Most Token Ring networks use shielded twisted-pair cabling; however, some networks that operate at 4 Mbps use unshielded twisted-pair cable. shows a comparison of the two types.
Figure 1 IBM Token Ring and IEEE 802.5 Comparison
All 4R-FDX port adapter interfaces support both 4- and 16-Mbps, half-duplex and full-duplex, operation and early token release. The default for all ports is for half-duplex 4-Mbps operation with early token release disabled. Both states are enabled with configuration commands in configuration mode.
To enable 16 Mbps, specify the slot/port address and use the configuration command ring-speed 16; to return to 4 Mbps operation, use the command ring-speed 4. To enable and disable early token release, specify the slot/port address and use the configuration command [no] early token release. To enable full-duplex operation, specify the slot/port address and use configuration command full-duplex. To return to half-duplex operation, use the no full-duplex or half-duplex command. For complete descriptions and examples of software commands, refer to the related software configuration documentation.
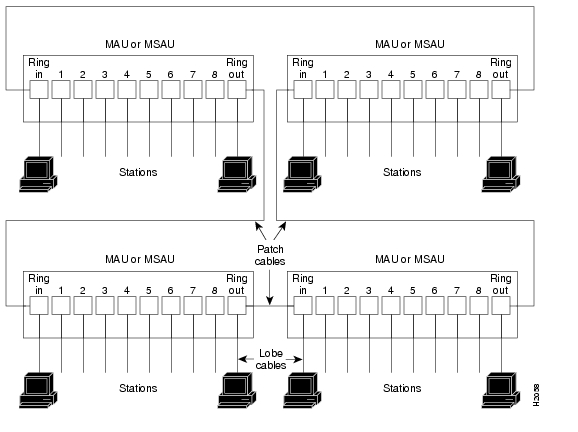
In the typical half-duplex Token Ring network, lobe cables connect each Token Ring station (4R-FDX port adapter interface) to the MSAU (or MAU), and patch cables connect adjacent MSAUs (or MAUs) to form one large ring. (See Figure 2.)
Figure 2 Half-Duplex Token Ring Network Physical Connections
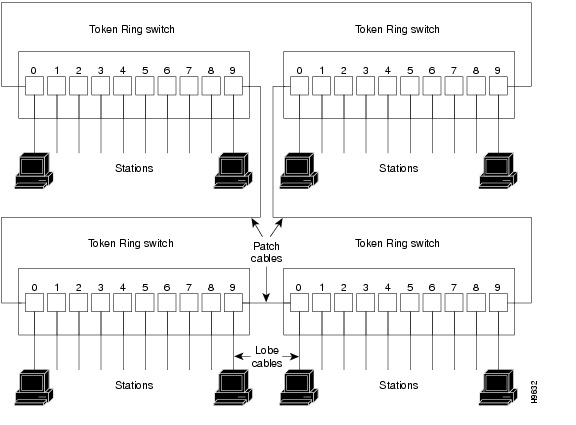
In the typical full-duplex Token Ring network, lobe cables connect each Token Ring station (4R-FDX port adapter interface) to the Token Ring switch, and patch cables connect adjacent Token Ring switches to form one large ring.Figure 3
Figure 3 Full-Duplex Token Ring Network Physical Connections
Token Ring Connection Equipment
You will need an 802.5 MAU, MSAU, or a Token Ring switch to provide the interface between the 4R-FDX port adapter Token Ring interfaces and the external ring, and a Token Ring lobe cable between each 4R-FDX port adapter interface and the MAU, MSAU, or the Token Ring switch. Lobe cables connect each Token Ring station (4R-FDX port adapter interface) to the MAU, MSAU, or Token Ring switch. Patch cables can connect adjacent MSAUs or Token Ring switches to form one large ring.
4R-FDX port adapter interfaces operate at either 4 or 16 Mbps. The default speed for all 4R-FDX port adapter interfaces is 4 Mbps, which you can change to 16 Mbps on any port by using the ring-speed n configuration command, where n is the speed (4 or 16) in Mbps. The speed of each Token Ring port must match the speed of the ring to which it is connected. Before you enable the Token Ring interfaces, ensure that each is set for the correct speed, or you risk bringing down the ring.

CautionEach 4R-FDX port adapter interface must be configured for the same ring speed as the ring to which it is connected, either 4 or 16 Mbps. If the port is set for a different speed, it will cause the ring to beacon, which effectively brings the ring down and makes it inoperable.
Token Ring Distance Limitations
The maximum transmission distance is not defined for IEEE 802.5 (Token Ring) networks. Shielded twisted-pair (STP) cabling is most commonly used for rates of 4 and 16 Mbps. Twisted-pair cabling is more susceptible to interference than other types of cabling; therefore, the network length and repeater spacing should be planned accordingly.
Token Ring Speed Considerations
Before you install the 4R-FDX port adapter, determine the ring speed (4 or 16 Mbps) of each ring to be connected to the server. There is no factory default for the interface speed; you must set the speed of each interface (within the setup command facility or with the ring-speed command) before you bring the interface up and insert it into the ring with the no shutdown command.

CautionEach Token Ring port must be configured for the same ring speed as the ring to which it is connected; either 4 or 16 Mbps. If the port is set for a different speed, it will cause the ring to beacon, which effectively brings the ring down and makes it inoperable.
What Is the 4R-FDX Port Adapter?
The following sections provide additional information specific to the 4R-FDX port adapter.
•
Port Adapter Locations on the VIP2 and the Cisco 7200 Series Router
•
4R-FDX Port Adapter Receptacles, Cables, and Pinouts
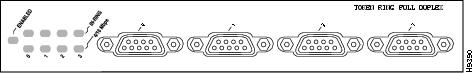
The 4R-FDX port adapter (see ) provides up to four IBM Token Ring or IEEE 802.5 Token Ring interfaces. Each Token Ring interface can be set for 4 Mbps or 16 Mbps, half-duplex or full-duplex operation. All Token Ring ports run at wire speed.
Figure 4 4R-FDX Port Adapter, Faceplate View
The 4R-FDX port adapter can be installed on the VIP2 in port adapter slot 0 and port adapter slot 1, or in the Cisco 7200 series routers in any of the chassis' port adapter slots: slot 1 and slot 2 of the Cisco 7202, slots 1 through 4 of the Cisco 7204,and slots 1 through 6 of the Cisco 7206.
Port Adapter Locations on the VIP2 and the Cisco 7200 Series Router
This section provides information about where you can install the 4R-FDX port adapter on the VIP2 and in the Cisco 7200 series routers.

Note
Port adapters have handles that allow for easy installation and removal; however, they are occasionally not shown in this publication to highlight port adapter faceplate detail.
shows a VIP2-15 or VIP2-40 with two installed port adapters. With the VIP2 oriented as shown, the left port adapter is in port adapter slot 0, and the right port adapter is in port adapter slot 1.
Figure 5 Two Port Adapters on a VIP2-15 or VIP2-40 (Horizontal Orientation Shown)

Note
In the Cisco 7000, Cisco 7507, and Cisco 7513 chassis, the VIP2 is installed vertically. In the Cisco 7010 and Cisco 7505 chassis, the VIP2 is installed horizontally.
In the Cisco 7200 series routers, port adapter slots are numbered from the lower left to the upper right, beginning with port adapter slot 1 and continuing through port adapter slot 2 for the Cisco 7202, slot 4 for the Cisco 7204, and slot 6 for the Cisco 7206. Port adapter slot 0 is reserved for the optional Fast Ethernet port on the I/O controller.

Note
The I/O controller is available with or without a Fast Ethernet port. You can install both I/O controller types in all Cisco 7200 series routers; however, when you install an I/O controller with a Fast Ethernet port in a Cisco 7202, the system software automatically disables the port.
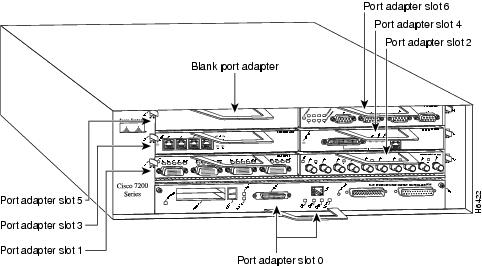
Figure 6Figure 6 shows a Cisco 7206 with installed port adapters and an I/O controller with a Fast Ethernet port. Not shown is the Cisco 7202, which has two port adapter slots, and the Cisco 7204, which has four port adapter slots. The 4R-FDX port adapter can be installed in any available port adapter slot in the Cisco 7200 series routers.
Figure 6 Port Adapters in the Cisco 7206
4R-FDX Port Adapter LEDs
The 4R-FDX port adapter has several LEDs that indicate status of the port adapter and its interfaces. The 4R-FDX port adapter's enabled LED (shown in ) goes on to indicate the following status of the 4R-FDX port adapter:
•
The port adapter is correctly connected to the backplane or midplane and receiving power.
•
A valid system software image for the port adapter has been downloaded successfully.
•
The system recognizes the port adapter or 4R-FDX-equipped VIP2.
If any of these conditions is not met, or if the initialization fails for other reasons, the port adapter's enabled LED does not go on.
Figure 7 4R-FDX Port Adapter LEDs
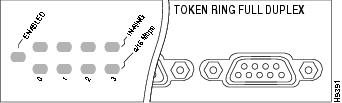
When a Token Ring interface is configured by using software commands, the In Ring and 4/16 Mbps LEDs (shown in ) indicate the following for each port:
•
In ring—Goes on when the interface is currently active and inserted into the ring; is off when the interface is not active and is not inserted into a ring.
•
4/16 Mbps—Goes on if the interface is operating at 16 Mbps; is off when the interface is operation at 4 Mbps (default).
4R-FDX Port Adapter Receptacles, Cables, and Pinouts
A network interface cable provides the connection between the 9-pin Token Ring receptacles on the 4R-FDX port adapter and a media access unit (MAU) or Token Ring switch. The 9-pin connector at the 4R-FDX port adapter end and the MAU or Token Ring switch connector at the network end are described in the section "Token Ring Connection Equipment" on page 9.
4R-FDX Port Adapter Cables
The Token Ring ports on the 4R-FDX port adapter are DB-9 (PC type) receptacles that require Type 1 or Type 3 lobe cables. Token Ring interface cables are not available from Cisco Systems, but are commercially available through outside cable vendors.
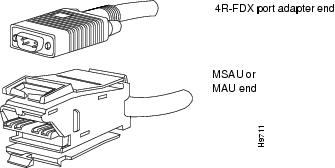
Type 1 lobe cables use shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable and terminate at the network end with a large MAU plug. (See Figure 8Figure 8.) The 4R-FDX port adapter end of the cable is a DB-9 plug.
Figure 8 Token Ring Type 1 Lobe Cable Connectors, DB-9 and MAU Types
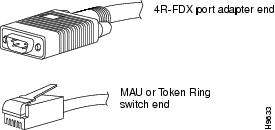
Type 3 lobe cables use either shielded or unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable and terminate at the network end with an RJ-11 plug. (See Figure 9.) The 4R-FDX port adapter end of the cable is a DB-9 plug.
Figure 9 Token Ring Type 3 Lobe Cable Connectors, DB-9 and RJ-11 Types
4R-FDX Port Adapter Receptacle Pinout
Table 1 lists the pinouts for the DB-9 receptacle used on the 4R-FDX port adapter.
Table 1 Token Ring Signals
VIP2 and the 4R-FDX Port Adapter
The following sections provide additional information specific to the 4R-FDX port adapter and its use on the VIP2 in Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series routers:
•
Installing or Replacing a Port Adapter on a VIP2
•
Attaching 4R-FDX Port Adapter Interface Cables
•
Configuring 4R-FDX Interfaces
The 4R-FDX port adapter can be installed in port adapter slot 0 or port adapter slot 1 on the VIP2. Figure 10 shows a 4R-FDX port adapter installed on a VIP2 in port adapter slot 0.
Figure 10 VIP2 with a 4R-FDX Port Adapter in Port Adapter Slot 0
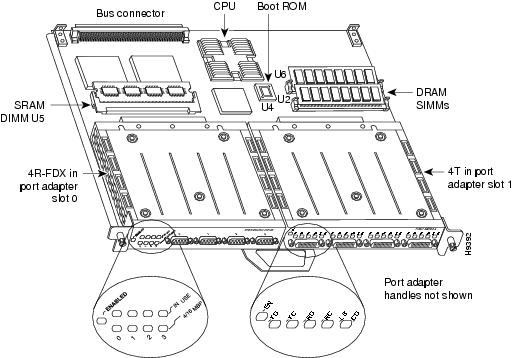

Note
Port adapters have a handle attached, but this handle is not shown to allow a full view of detail on each port adapter's faceplate.
Installing or Replacing a Port Adapter on a VIP2
Depending on the circumstances, you might need to install a new port adapter on a VIP2 motherboard or replace a failed port adapter in the field. In either case, you need a number 1 Phillips screwdriver, an antistatic mat onto which you can place the removed interface processor, and an antistatic container into which you can place a failed port adapter for shipment back to the factory.

Note
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) sizes available for the 4R-FDX port adapter might require additional VIP2 SRAM to ensure adequate buffers when two 4R-FDX port adapters, one 4R-FDX and one 4T, or one 4R-FDX and one FDDI port adapter are installed on a VIP2. We recommend the VIP2-20 for use with any combination of two of these port adapters on a VIP2.

CautionTo prevent system problems, do not remove port adapters from the VIP2 motherboard, or attempt to install other port adapters on the VIP2 motherboard while the system is operating. To install or replace port adapters, first remove the VIP2 from its interface processor slot.

Note
Each port adapter circuit board is mounted to a metal carrier and is sensitive to ESD damage. We strongly recommend that the following procedures be performed by a Cisco-certified service provider; however, this is not a requirement.
While the VIP2 supports online insertion and removal, individual port adapters do not. To replace port adapters, you must first remove the VIP2 from the chassis, then install or replace port adapters as required. If a blank port adapter is installed on the VIP2 in which you want to install a new port adapter, you must first remove the VIP2 from the chassis, then remove the blank port adapter.
When only one port adapter is installed on a VIP2, a blank port adapter must fill the empty slot to allow the VIP2 and router chassis to conform to electromagnetic interference (EMI) emissions requirements, and to permit proper airflow through the chassis. If you plan to install a new port adapter, you must first remove the blank port adapter.
Following is the standard procedure for removing and replacing any type of port adapter on the VIP2:
Step 1
Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap between you and an unfinished chassis surface.
Step 2
For a new port adapter installation or a port adapter replacement, disconnect all interface cables from the ports on the front of the port adapter. You can remove VIP2s with cables attached; however, we do not recommend it.
Step 3
To remove the VIP2 from the chassis, follow the steps in the section "Removing a VIP2" in the configuration note Second-Generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2) Installation and Configuration (Document Number 78-2658-xx), which shipped with your VIP2. Place the removed VIP2 on an antistatic mat.
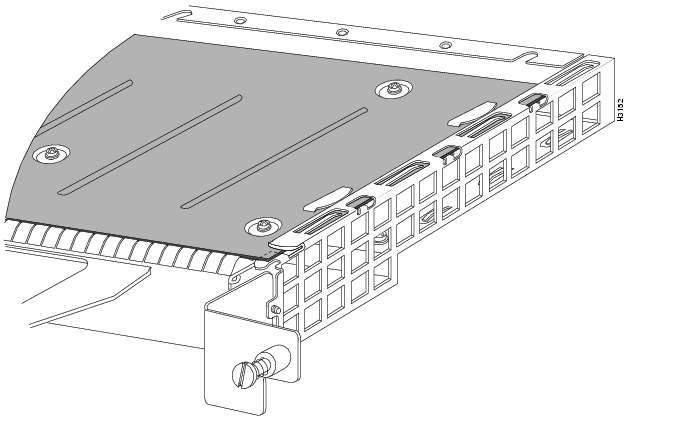
Step 4
Locate the screw at the rear of the port adapter (or blank port adapter) to be replaced. (See Figure 11.) This screw secures the port adapter (or blank port adapter) to its slot.
Figure 11 Location of Port Adapter Screw (Partial Port Adapter View)
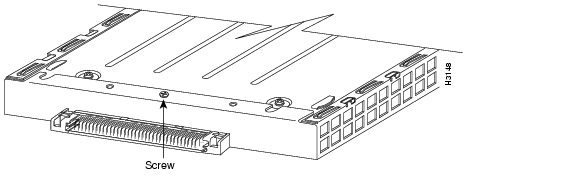
Step 5
Remove the screw that secures the port adapter (or blank port adapter).
Step 6
With the screw removed, grasp the handle on the front of the port adapter (or blank port adapter) and carefully pull it out of its slot, away from the edge connector at the rear of the slot. (See Figure 12.)
Figure 12 Pulling a Port Adapter Out of a Slot (Partial Port Adapter View)
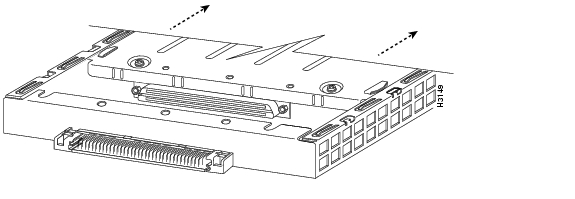
Step 7
If you removed a port adapter, place it in an antistatic container for safe storage or shipment back to the factory. If you removed a blank port adapter, no special handling is required; store the blank port adapter for potential future use.
Step 8
Remove the new port adapter from its antistatic container and position it at the opening of the slot. (See Figure 13Figure 13.)
Step 9
Carefully align the port adapter carrier between the upper and lower edges of the port adapter slot, as shown in Figure 13.
Figure 13 Aligning a Port Adapter in a Port Adapter Slot
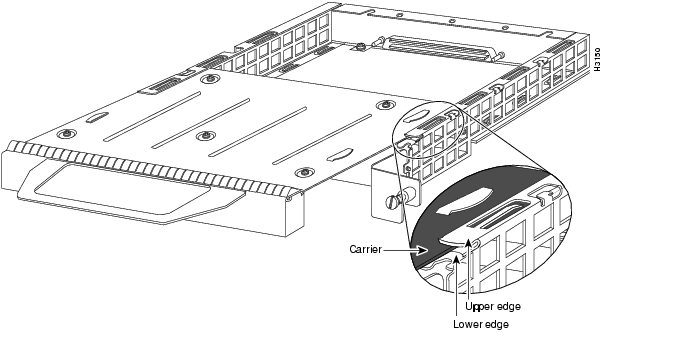

CautionTo prevent jamming the carrier between the upper and lower edges of the port adapter slot and to ensure that the edge connector at the rear of the port adapter seats in the connector at the rear of the port adapter slot, make certain that the leading edges of the carrier are between the upper and lower slot edges, as shown in the cutaway in Figure 13.

CautionTo ensure a positive ground attachment between the port adapter carrier and the VIP2 motherboard and port adapter slot, and to ensure that the connectors at the rear of the port adapter and slot seat properly, position the carrier between the upper and lower slot edges, as shown in Figure 14.
Step 10
Carefully slide the new port adapter into the port adapter slot until the connector on the port adapter is completely seated in the connector on the motherboard. (See Figure 14Figure 14.)
Figure 14 Port Adapter Installed in a Port Adapter Slot (Partial Port Adapter View)
Step 11
Replace the screw in the rear of the port adapter slot. (See Figure 11 for its location.) Do not overtighten this screw.
Step 12
Replace the VIP2 in the system. Follow the steps in the section "Installing a VIP2" in the configuration note Second-Generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2) Installation and Configuration.
Step 13
If disconnected, reconnect the interface cables to the interface processor.
This completes the procedure for installing a new port adapter or replacing a port adapter on a VIP2.
Attaching 4R-FDX Port Adapter Interface Cables
You need one Token Ring interface cable for each 4R-FDX port adapter interface you want to use. Token Ring interface cables are not available from Cisco Systems but are commercially available through outside cable vendors.
Use the following procedure to attach Token Ring cables to the 4R-FDX port adapter:
Step 1
Determine which 4R-FDX port adapter ports you want to use.

Note
The IBM Token Ring specifies a star topology, with all end stations connected through a device called an MSAU or token ring switch. IEEE 802.5 does not specify any topology, although most implementations are based on a star configuration with end stations attached to a device called an MAU or token ring switch. Also, IBM Token Ring specifies twisted-pair cabling, whereas IEEE 802.5 does not specify media type. Most Token Ring networks use shielded twisted-pair (STP) cabling; however, some networks that operate at 4 Mbps use UTP cable.
Step 2
Attach the port adapter end of a Token Ring interface cable, or other connection equipment, to the interface port.Figure 15

Note
Port adapters have a handle attached (see ), but this handle is not shown in Figure 15 to allow a full view of detail on the 4R-FDX port adapter's faceplate.
Figure 15 Token Ring Interface Cable Connections
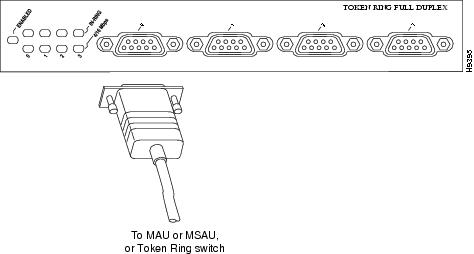

CautionEach 4R-FDX port adapter interface must be configured for the same ring speed as the ring to which it is connected; either 4 or 16 Mbps. If the 4R-FDX port adapter interface is set for a different speed, it will cause the ring to beacon, which effectively brings the ring down and makes it inoperable.
Step 3
Attach the network end of the Token Ring interface cable to the appropriate Token Ring equipment at your site: a MAU, MSAU, or token ring switch.
This completes the procedure for attaching a 4R-FDX interface cable.
Configuring 4R-FDX Interfaces
If you installed a new 4R-FDX-equipped VIP2 or if you want to change the configuration of an existing interface, you must use the privileged-level configure command. If you replaced a 4R-FDX port adapter that was previously configured, the system will recognize the new 4R-FDX port adapter interfaces and bring each of them up in their existing configuration.

Note
Configuration commands are executed from the privileged level of the EXEC command interpreter, which usually requires password access. Contact your system administrator, if necessary, to obtain access.
After you verify that the new 4R-FDX port adapter is installed correctly (the enabled LED goes on), use the configure command to configure the new interfaces. Be prepared with the information you will need, such as the following:
•
Protocols you plan to route on each new interface
•
Internet protocol (IP) addresses if you plan to configure the interfaces for IP routing
•
Whether the new interfaces will use bridging or source route bridging (SRB)

Note
The 4R-FDX interfaces on a VIP2 can be configured for 16-Mbps full-duplex operation but are configured for 4-Mbps half-duplex operation as a default.
For complete descriptions of interface subcommands and the configuration options available for Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7500 series-related interfaces, refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section.
Determining Chassis Slot, Port Adapter, and Token Ring Interface Port Numbers
This section describes how to identify chassis slot, port adapter, and Token Ring interface port numbers.

Note
Although the processor slots in the seven-slot Cisco 7507 and 13-slot Cisco 7513 are vertically oriented and those in the five-slot Cisco 7505 are horizontally oriented, all models use the same method for slot and port numbering.
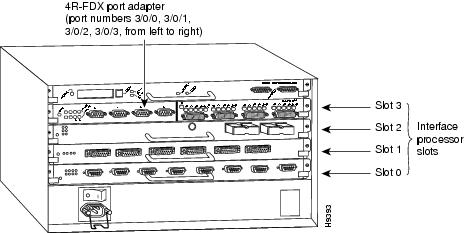
In the router, physical port addresses specify the actual physical location of each interface port on the router interface processor end. (See Figure 16.) This address is composed of a three-part number in the format chassis slot number/port adapter number/interface port number:
•
The first number identifies the chassis slot in which the VIP2 is installed (as shown in the sample system in Figure 16).
•
The second number identifies the physical port adapter number on the VIP2, and is either 0 or 1.
•
The third number identifies interface ports on each 4R-FDX port adapter, which are always numbered in sequence as interfaces 0 through 3.
Interface ports on the 4R-FDX port adapter maintain the same address regardless of whether other interface processors are installed or removed. However, when you move a VIP2 to a different slot, the first number in the address changes to reflect the new slot number.
Figure 16 shows some of the port adapter slots and interface ports of a sample Cisco 7505 system. The first port adapter slot number is always 0. The second port adapter slot number is always 1. The individual interface port numbers always begin with 0. The number of additional ports depends on the number of ports on a port adapter.
For example, the addresses for the 4R-FDX interface ports on the first port adapter on a VIP2 (see Figure 16) are 3/0/0 through 3/0/3 (chassis slot 3, port adapter slot 0, and interface ports 0 through 3). If the 4R-FDX port adapter were installed in port adapter slot 1, the interface addresses would be 3/1/0 through 3/1/3.

Note
If you remove the 4R-FDX-equipped VIP2 (shown in Figure 16) from chassis slot 3 and install it in slot 2, the addresses of those same ports become 2/0/0 through 2/0/3.
Figure 16 4R-FDX Token Ring Interface Port Number Example (Cisco 7505 Shown)
You can identify interface ports by physically checking the slot/port adapter/interface port location on the back of the router or by using software commands to display information about a specific interface or all interfaces in the router.
Shutting Down an Interface
Before you replace an interface cable, replace port adapters, or remove an interface that you will not replace, use the shutdown command to shut down (disable) the interfaces. Doing so prevents anomalies from occurring when you reinstall the new or reconfigured VIP2. You can shut down individual interfaces by specifying the chassis slot number, port adapter number, and interface port number. When you shut down an interface, it is designated administratively down in the show command displays.
Follow these steps to shut down an interface:
Step 1
Enter the privileged level of the EXEC command interpreter.
Router> enableThe EXEC prompts you for a privileged level password:
Password:Step 2
Enter the password.
For security purposes, the password is not displayed. (Also note that the password is case sensitive). When you enter the correct password, the system displays the privileged mode system prompt:
Router#Step 3
At the privileged-level prompt, enter configuration mode and specify that the console terminal will be the source of the configuration subcommands as follows:
Router# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.Router(config)#Step 4
Specify the slot/port address of the controller that you want shut down by entering the subcommand controller, followed by the type (tokenring) and chassis slot number/port adapter number/interface port number The example that follows is for a 4R-FDX port adapter in chassis slot 3:
Router(config)# controller tokenring 3/1/0Step 5
Enter the shutdown command as follows:
Router(config-cont)# shutdownStep 6
Write the new configuration to memory as follows:
Router# copy running-config startup-config[OK]Router#The system displays an OK message when the configuration has been stored.
Step 7
To verify that new interfaces are now in the correct state (shutdown), use the show interface tokenring chassis slot number/port adapter number/interface port number command to display the specific interface.
Router# show int tokenring 3/1/0TokenRing3/1/0 is down, line protocol is downHardware is cxBus Token Ring, address is 0000.0000.0000 (bia 0000.0000.0000)[display text omitted]Step 8
To reenable the interfaces, repeat the previous steps, but use the no shutdown command in Step 5; then write the new configuration to memory as follows:
Router(config)# int tokenring 3/1/0Router(config-int)# no shutdownCtrl-ZRouter#Router# copy running-config startup-config[OK]Router# show int tokenring 3/1/0TokenRing3/1/0 is up, line protocol is upHardware is cxBus Token Ring, address is 0000.0000.0000 (bia 0000.0000.0000)[display text omitted]
For complete descriptions of software configuration commands, refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section.
Configuring Interfaces
Following are instructions for a basic configuration using the configure command: enabling an interface setting interface ring speed, and specifying IP routing. You might also need to enter other configuration subcommands depending upon the requirements for your system configuration and the protocols you plan to route on the interface. For complete descriptions of configuration subcommands and the configuration options available, refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section.
Press the Return key after each step unless otherwise noted. At any time you can exit the privileged level and return to the user level by entering disable at the prompt as follows:
Router# disableRouter>Following is an example of a basic configuration procedure:
Step 1
At the privileged-mode prompt, enter configuration mode and specify that the console terminal will be the source of the configuration subcommands as follows:
Router# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#Step 2
At the prompt, specify the first Token Ring interface to configure by entering the subcommand interface followed by tokenring, and chassis slot number/port adapter number/interface port number. The following example is for the 4R-FDX in chassis slot 3, port adapter slot 0, and interface port 0:
Router(config)# interface tokenring 3/0/0Step 3
If IP routing is enabled on the system, you can assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface with the ip address configuration subcommand as follows:
Router(config-int)# ip address 1.1.1.10 255.255.255.0
CautionEach Token Ring port must be configured for the same ring speed as the ring to which it is connected; either 4 or 16 Mbps. If the port is set for a different speed, it will cause the ring to beacon, which effectively brings the ring down and makes it inoperable.

Note
Token Ring ports operate at either 4 or 16 Mbps. The default speed for the 4R-FDX port adapter's Token Ring ports is 4 Mbps, which you can change to 16 Mbps on any port using the configuration ring-speed n command, where n is the speed (4 or 16) in Mbps. Before you enable the Token Ring interfaces, ensure that each is set for the correct speed, or you risk bringing down the ring.
Step 4
Change the default shutdown state to up and enable the interface as follows:
Router(config-int)# no shutdownWhen you enable the interface by using the no shutdown command, the LED for 4 Mbps or 16 Mbps is turned on after about 5 seconds. The In Ring LED for that interface is turned on about 5 to 18 seconds later, when the port is initialized and connected to the ring.
Step 5
Either accept the default ring speed of 4 Mbps, or enable the Token Ring interface speed for 16-Mbps operations as follows:
Router(config-int)# ring-speed 16Step 6
Enter any additional configuration subcommands required to enable routing protocols and set the interface characteristics.
Step 7
Repeat Step 2 through Step 6 for each new interface.
Step 8
When all new interfaces are configured, press Ctrl-Z (hold the Control key down and press the Z key) to exit configuration mode.
Step 9
Write the new configuration to nonvolatile memory by entering the following:
Router# copy running-config startup-config[OK]Router#Step 10
Enter quit to exit configuration mode:
Router# quit
You have completed configuring the Token Ring interfaces. To check the configuration, proceed to the following section "Checking the Configuration."

Note
If you require full-duplex operation, verify that you are using a 4R-FDX port adapter and that you have the correct minimum Cisco IOS release for full-duplex compatibility; refer to the sections "Software and Hardware Requirements" section and "Verifying Full-Duplex Token Ring Port Adapter Capability in Your Router" section, then proceed to the following section "Configuring Full-Duplex Operation" section.
Configuring Full-Duplex Operation
Full-duplex operation requires a 4R-FDX port adapter and a host router running a specific level of Cisco IOS software. (Refer to the section "Software and Hardware Requirements" section.)
Full-duplex operation is not the default configuration and must be turned on using the full-duplex command. To turn off full-duplex operation and reset the interface, use the no full-duplex or half-duplex command.
Following is an example of configuring a 4R-FDX interface for full-duplex operation using the full-duplex command:
Router# conf tEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.Router(config)# int tokenring 3/0/0Router(config-if)# full-duplexCtrl-zRouter#
Note
If the port adapter does not support full-duplex operation, the following error message appears: "%TokenRing3/0/0 interface does not support full-duplex."
The output of the show interfaces tokenring slot/port-adapter/port command displays the state of the Token Ring port adapter interface and the state of full-duplex operation. Following is a partial sample output of this command from a 4R-FDX interface with full-duplex operation enabled:
Router# show int tokenring 3/0/0TokenRing3/0/0 is up, line protocol is upHardware is cxBus Token Ring, address is 0000.0000.0000 (bia 0000.0000.0000)Internet address is 14.0.0.2/8MTU 4464 bytes, BW 1600 Kbit, DLY 630 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255Encapsulation SNAP, loopback not set, keepalive not setARP type: SNAP, ARP Timeout 04:00:00Ring speed: 16 Mbps, operating in full-duplex[display text omitted]
Note
When full-duplex operation is turned off using the no full-duplex or half-duplex commands, the last line of the preceding display includes the following information: operating in half-duplex.
Checking the Configuration
After configuring the new interface, use the show commands to display the status of the new interface or all interfaces, and the ping command to check connectivity.
Using show Commands to Verify the VIP2 Status
The following steps use show commands to verify that the new interfaces are configured and operating correctly.
Step 1
Display the system software and hardware configuration with the show version command. Ensure that the list includes the new interfaces and that your system is running the appropriate Cisco IOS software for your configuration.
Step 2
Display all the current interface processors and their interfaces with the show controllers cbus command. Verify that the new VIP2 appears in the correct slot.
Step 3
Specify one of the new Token Ring interfaces with the show interfaces type slot/port adapter/interface command and verify that the first line of the display specifies the interface with the correct slot number. Also verify that the interface and line protocol are in the correct state: up or down.
Step 4
Display the protocols configured for the entire system and specific interfaces with the show protocols command. If necessary, return to configuration mode to add or remove protocol routing on the system or specific interfaces.
Step 5
Display the running configuration file with the show running-config command. Display the configuration stored in NVRAM using the show startup-config command. Verify that the configuration is accurate for the system and each interface.
If the interface is down and you configured it as up, or if the displays indicate that the hardware is not functioning properly, ensure that the network interface is properly connected and terminated. If you still have problems bringing up the interface, contact a customer service representative for assistance.
To display information about a specific interface, use the show interfaces command with the interface type, chassis slot, port adapter, and interface port address in the format show interfaces [type slot/port adapter/port]. To display information about all interfaces installed in the system, use the show interfaces command without arguments.
The following example of the show interfaces tokenring [slot/port adapter/port] command shows information specific to the first 4R-FDX interface port (port 0) in chassis slot 3 and port adapter slot 0:
Router# sh int tokenring 3/0/0TokenRing3/0/0 is up, line protocol is upHardware is cxBus Token Ring, address is 0000.0000.0000 (bia 0000.0000.0000)Internet address is 14.0.0.2/8MTU 4464 bytes, BW 1600 Kbit, DLY 630 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255Encapsulation SNAP, loopback not set, keepalive not setARP type: SNAP, ARP Timeout 04:00:00Ring speed: 16 Mbps, operating in full-duplex[display text omitted]The show version (or show hardware) command displays the configuration of the system hardware (the number of each interface processor type installed), the software version, the names and sources of configuration files, and the boot images. Following is an example of the show version command used with a Cisco 7500 series system:
Router# show versionCisco Internetwork Operating System SoftwareIOS (tm) GS Software (RSP-A), Version 11.1(8)CA [amcrae 125]Copyright (c) 1986-1996 by cisco Systems, Inc.Compiled Sat 10-Aug-96 17:56 by biffImage text-base: 0x600108A0, data-base: 0x60952000ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 5.3(16645) [szhang 571], INTERIM SOFTWAREROM: GS Software (RSP-BOOT-M), Version 11.1(8)CA, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)Router uptime is 5 days, 4 minutesSystem restarted by reloadSystem image file is "rsp-jv-mz", booted via slot0cisco RSP2 (R4600) processor with 16384K bytes of memory.R4600 processor, Implementation 32, Revision 2.0Last reset from power-onG.703/E1 software, Version 1.0.Channelized E1, Version 1.0.SuperLAT software copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp).Bridging software.X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant.TN3270 Emulation software (copyright 1994 by TGV Inc).Primary Rate ISDN software, Version 1.0.Chassis Interface.1 EIP controller (6 Ethernet).1 TRIP controller (4 Token Ring).2 MIP controllers (4 E1).1 VIP2 controller (2 E1)(4 Token Ring).6 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interfaces.8 Token Ring/IEEE 802.5 interfaces.3 Serial network interfaces.6 Channelized E1/PRI ports.125K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.8192K bytes of Flash PCMCIA card at slot 0 (Sector size 128K).8192K bytes of Flash internal SIMM (Sector size 256K).No slave installed in slot 7.Configuration register is 0x0To determine which type of port adapter is installed on a VIP2 in your system, use the show diag slot command. Specific port adapter information is displayed, as shown in the following example of two 4R-FDX port adapters in chassis slot 3:
Router# show diag 3Slot 3:Physical slot 3, ~physical slot 0x7, logical slot 3, CBus 0Microcode Status 0x4Master Enable, LED, WCS LoadedBoard is analyzedPending I/O Status: NoneEEPROM format version 1VIP2 controller, HW rev 2.2, board revision UNKNOWNSerial number: 03341418 Part number: 73-1684-02Test history: 0x00 RMA number: 00-00-00Flags: cisco 7000 board; 7500 compatibleEEPROM contents (hex):0x20: 01 15 02 02 00 32 FC 6A 49 06 94 02 00 00 00 000x30: 07 2B 00 2A 1A 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00Slot database information:Flags: 0x4 Insertion time: 0x3188 (01:20:53 ago)Controller Memory Size: 8 MBytesPA Bay 0 Information:Token Ring PA, 4 portsEEPROM format version 1HW rev 1.1, Board revision 0Serial number: 02827613 Part number: 73-1390-04PA Bay 1 Information:Token Ring PA, 4 portsEEPROM format version 1HW rev 1.1, Board revision 88Serial number: 02023786 Part number: 73-1390-04Using the ping and loopback Commands
The ping and loopback commands allow you to verify that an interface port is functioning properly and to check the path between a specific port and connected devices at various locations on the network, after the system has booted successfully and is operational. This section provides brief descriptions of these commands. Refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section, for detailed command descriptions and examples.
The ping command sends echo request packets out to a remote device at an IP address that you specify. After sending an echo request, the command waits a specified time for the remote device to reply. Each echo reply is displayed as an exclamation point (!) on the console terminal; each request that is not returned before the specified timeout is displayed as a period (.). A series of exclamation points (!!!!!) indicates a good connection; a series of periods (.....) or the messages [timed out] or [failed] indicate that the connection failed.
Following is an example of a successful ping command to a remote server with the address 1.1.1.10:
Router# ping 1.1.1.10 <Return>Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echoes to 1.1.1.10, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/15/64 msRouter#If the connection fails, verify that you have the correct IP address for the destination and that the device is active (powered on), and repeat the ping command.
The loopback test allows you to detect and isolate equipment malfunctions by testing the connection between the 4R-FDX port adapter interface and a remote device such as a MAU, MSAU, or Token Ring switch. The loopback subcommand places an interface in loopback mode, which enables test packets that are generated from the ping command to loop through a remote device or interface cable. If the packets complete the loop, the connection is good. If not, you can isolate a fault to the remote device or interface cable in the path of the loopback test.

Note
You must configure a clock rate on the port before performing a loopback test. However, if no cable is attached to the port, the port is administratively up, and the port is in loopback mode, you do not have to configure a clock rate on the port before performing a loopback test.
When no interface cable is attached to a 4R-FDX port adapter interface, issuing the loopback controller command tests the path between the VIP2 and the interface port only (without leaving the VIP2 and port adapter).
For complete descriptions of interface subcommands and the configuration options available for Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7500 series-related interfaces, refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section.
Cisco 7200 Series and the 4R-FDX Port Adapter
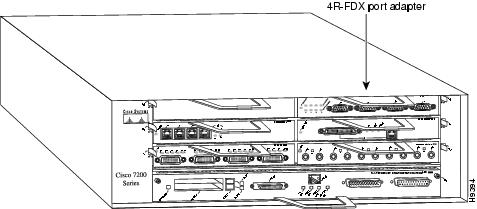
The 4R-FDX port adapter can be installed in any available port adapter slot in Cisco 7200 series routers (which consists of the 2-slot Cisco 7202, 4-slot Cisco 7204, and the 6-slot Cisco 7206). Figure 17 shows a 4R-FDX port adapter installed in port adapter slot 6 of a Cisco 7206.
Figure 17 Cisco 7206 with a 4R-FDX Port Adapter in Port Adapter Slot 6
The following sections include information specific to the 4R-FDX port adapter and its use in the Cisco 7200 series routers:
•
Installing or Replacing a Port Adapter in Cisco 7200 Series Routers
•
Attaching 4R-FDX Port Adapter Interface Cables
•
Configuring 4R-FDX Interfaces
Installing or Replacing a Port Adapter in Cisco 7200 Series Routers
Depending on your circumstances, you might need to install a new port adapter in a Cisco 7200 series router or replace a failed port adapter in the field. In either case no tools are necessary; all port adapters available for the Cisco 7200 series connect directly to the router midplane and are locked into position by a port adapter lever. When removing and replacing a port adapter, you will need an antistatic mat onto which you can place a removed port adapter and an antistatic container into which you can place a failed port adapter for shipment back to the factory.

Note
The Cisco 7200 series routers support OIR; therefore, you do not have to power down the Cisco 7200 series routers when removing and replacing a 4R-FDX port adapter.
When a port adapter slot is not in use, a blank port adapter must fill the empty slot to allow the router to conform to EMI emissions requirements and to allow proper air flow across the port adapters. If you plan to install a new port adapter in a slot that is not in use, you must first remove a blank port adapter.
Removing a Port Adapter
Following is the procedure for removing a port adapter from a Cisco 7200 series router:
Step 1
Attach an ESD-preventative wrist strap between you and an unfinished chassis surface.
Step 2
Place the port adapter lever for the desired port adapter slot in the unlocked position. The port adapter lever remains in the unlocked position. (Refer to Figure 18Figure 18.)
Figure 18 Placing the Port Adapter Lever in the Unlocked Position (Cisco 7206 Shown)
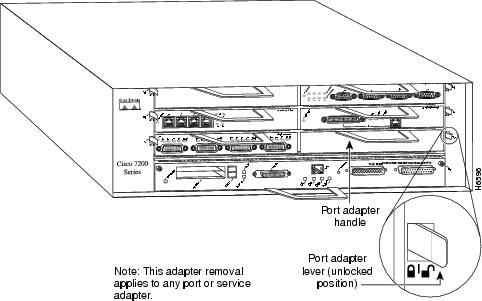
Step 3
Grasp the handle on the port adapter and pull the port adapter from the midplane, about half way out of its slot. If you are removing a blank port adapter, pull the blank port adapter from the chassis slot.

Note
As you disengage the port adapter from the router midplane, OIR administratively shuts down all active interfaces on the port adapter.
Step 4
With the port adapter half way out of the slot, disconnect all cables from the port adapter.
Step 5
After disconnecting the cables, pull the port adapter from its chassis slot.

CautionAlways handle the port adapter by the carrier edges and handle; never touch the port adapter's components or connector pins. (Refer to Figure 19 Figure 19.)
Figure 19 Handling a Port Adapter
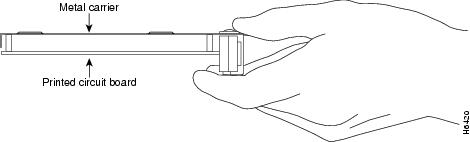
Step 6
Place the port adapter on an antistatic surface with its components facing upward, or in a static shielding bag. If the port adapter will be returned to the factory, immediately place it in a static shielding bag.
This completes the procedure for removing a port adapter from a Cisco 7200 series router.
Replacing a Port Adapter
Following is the procedure for installing a new port adapter in a Cisco 7200 series router:
Step 1
Attach an ESD-preventative wrist strap between you and an unfinished chassis surface.
Step 2
Use both hands to grasp the port adapter by its metal carrier edges and position the port adapter so that its components are downward. (Refer to Figure 19).
Step 3
Align the left and right edge of the port adapter metal carrier between the guides in the port adapter slot.Figure 20
Figure 20 Aligning the Port Adapter Metal Carrier Between the Slot Guides
(Cisco 7206 Shown)

Step 4
With the metal carrier aligned in the slot guides, gently slide the port adapter half way into the slot.

CautionDo not slide the port adapter all the way into the slot until you have connected all required cables. Trying to do so will disrupt normal operation of the router.
Step 5
With the port adapter half way in the slot, connect all required cables to the port adapter.
Step 6
After connecting all required cables, carefully slide the port adapter all the way into the slot until you feel the port adapter's connectors seat in the midplane.
Step 7
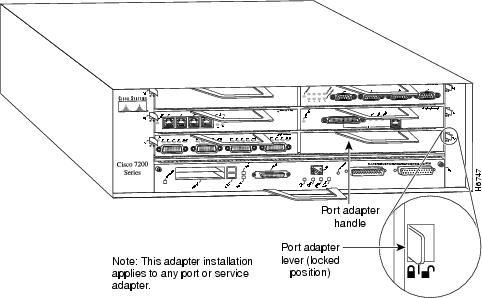
Move the port adapter lever to the locked position. Figure 21 shows the port adapter lever in the locked position.

Note
If the port adapter lever does not move to the locked position, the port adapter is not completely seated in the midplane. Carefully pull the port adapter halfway out of the slot, reinsert it, and move the port adapter lever to the locked position.
Figure 21 Placing the Port Adapter Lever in the Locked Position (Cisco 7206 Shown)
This completes the procedure for installing a new port adapter in a Cisco 7200 series router.
Attaching 4R-FDX Port Adapter Interface Cables
You need one Token Ring interface cable for each 4R-FDX port adapter interface you want to use. Token Ring interface cables are not available from Cisco Systems, but are commercially available through outside cable vendors.
Use the following procedure to attach Token Ring cables to the 4R-FDX port adapter:
Step 1
Determine which 4R-FDX port adapter ports you want to use.

Note
The IBM Token Ring specifies a star topology, with all end stations connected through a device called an MSAU or Token Ring switch. IEEE 802.5 does not specify any topology, although most implementations are based on a star configuration with end stations attached to a device called an MAU or Token Ring switch. Also, IBM Token Ring specifies twisted-pair cabling, whereas IEEE 802.5 does not specify media type. Most Token Ring networks use shielded twisted-pair (STP) cabling; however, some networks that operate at 4 Mbps use UTP cable.
Step 2
Attach the port adapter end of a Token Ring interface cable, or other connection equipment, to the interface portFigure 22.

Note
Port adapters have a handle but this handle is not shown in Figure 22 to allow a full view of detail on the 4R-FDX port adapter's faceplate.
Figure 22 Token Ring Interface Cable Connections


CautionEach 4R-FDX port adapter interface must be configured for the same ring speed as the ring to which it is connected; either 4 or 16 Mbps. If the 4R-FDX port adapter interface is set for a different speed, it will cause the ring to beacon, which effectively brings the ring down and makes it inoperable.
Step 3
Attach the network end of the Token Ring interface cable to the appropriate Token Ring equipment at your site: a MAU, MSAU, or Token Ring switch.
This completes the procedure for attaching port adapter interface cables.
Configuring 4R-FDX Interfaces
If you installed a new 4R-FDX port adapter or if you want to change the configuration of an existing interface, you must use the privileged-level configure command. If you replaced a 4R-FDX port adapter that was previously configured, the system will recognize the new 4R-FDX port adapter interfaces and bring each of them up in their existing configuration.

Note
Configuration commands are executed from the privileged level of the EXEC command interpreter, which usually requires password access. Contact your system administrator, if necessary, to obtain access.
After you verify that the new 4R-FDX port adapter is installed correctly (the enabled LED goes on), use the configure command to configure the new interfaces. Be prepared with the information you will need, such as the following:
•
Protocols you plan to route on each new interface
•
Internet protocol (IP) addresses if you plan to configure the interfaces for IP routing
•
Whether the new interfaces will use bridging or source route bridging (SRB)

Note
The 4R-FDX interfaces on a Cisco 7200 series router can be configured for 16-Mbps full-duplex operation but are configured for 4-Mbps half-duplex operation as a default.
For complete descriptions of interface subcommands and the configuration options available for Cisco 7200 series-related interfaces, refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section.
Selecting Port Adapter Slot and Token Ring Interface Port Numbers
This section describes how to identify port adapter slot and Token Ring interface port numbers. In the router, physical port addresses specify the actual physical location of each interface port on the router. (See .) This address is composed of a two-part number in the format port adapter slot number/interface port number:
•
The first number identifies the chassis slot in which the 4R-FDX port adapter is installed.
•
The second number identifies interface ports on each 4R-FDX port adapter and are always numbered in sequence as interface 0 through 3.
Interface ports on the 4R-FDX port adapter maintain the same address regardless of whether other port adapters are installed or removed. However, when you move a port adapter to a different slot, the first number in the address changes to reflect the new slot number.
In the Cisco 7200 series routers, port adapter slots are numbered from the lower left to the upper right, beginning with port adapter slot 1 and continuing through port adapter slot 2 for the Cisco 7202, slot 4 for the Cisco 7204, and slot 6 for the Cisco 7206. Port adapter slot 0 is reserved for the optional Fast Ethernet port on the I/O controller—if present. Figure 23 shows the port adapter slots and interface ports of a Cisco 7206.

Note
The I/O controller is available with or without a Fast Ethernet port. You can install both I/O controller types in all Cisco 7200 series routers; however, when you install an I/O controller with a Fast Ethernet port in a Cisco 7202, the system software automatically disables the port.
The individual interface port numbers always begin with 0. The number of additional ports depends on the number of ports on a port adapter. For example, the addresses of the interface ports on the 4R-FDX port adapter in slot 6 are 6/0 through 6/3 (chassis slot 6 and interface ports 0 through 3). If the 4R-FDX port adapter were installed in port adapter slot 4, the interface addresses would be 4/0 through 4/3.
Figure 23 4R-FDX Token Ring Interface Port Number Example
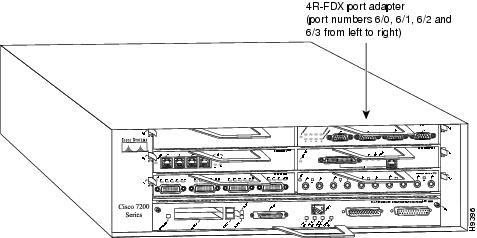
You can identify interface ports by physically checking the slot/interface port location on the back of the router or by using software commands to display information about a specific interface or all interfaces in the router.
Shutting Down an Interface
Before you replace an interface cable, replace port adapters, or remove an interface that you will not replace, use the shutdown command to shut down (disable) the interfaces. Doing so prevents anomalies from occurring when you reinstall the new or reconfigured port adapters. You can shut down individual interfaces by specifying the chassis slot number, port adapter number, and the interface port number. When you shut down an interface, it is designated administratively down in the show command displays.
Follow these steps to shut down an interface:
Step 1
Enter the privileged level of the EXEC command interpreter.
Step 2
At the privileged-level prompt, enter configuration mode and specify that the console terminal will be the source of the configuration subcommands as follows:
Router# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.Router(config)#Step 3
Specify the slot/port address of the controller that you want shut down by entering the subcommand controller, followed by the type (tokenring) and port adapter slot number/interface port number The example that follows is for a 4R-FDX port adapter in chassis slot 3:
Router(config)# controller tokenring 3/0Step 4
Enter the shutdown command as follows:
Router(config-cont)# shutdownStep 5
Write the new configuration to memory as follows:
Router# copy running-config startup-config[OK]Router#The system displays an OK message when the configuration has been stored.
Step 6
To verify that new interfaces are now in the correct state (shutdown), use the show interface tokenring port adapter slot number/interface port number command to display the specific interface.
Router# show int tokenring 3/0TokenRing3/0 is down, line protocol is downHardware is IBM2692, address is 0000.0000.0000 (bia 0000.0000.0000)[display text omitted]Step 7
To reenable the interfaces, repeat the previous steps, but use the no shutdown command in Step 5; then write the new configuration to memory as follows:
Router(config)# int tokenring 3/0Router(config-int)# no shutdownCtrl-ZRouter#Router# copy running-config startup-config[OK]Router# show int tokenring 3/0TokenRing3/0 is up, line protocol is upHardware is IBM2692, address is 0000.0000.0000 (bia 0000.0000.0000)[display text omitted]
For complete descriptions of software configuration commands, refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section.
Configuring Interfaces
Following are instructions for a basic interface configuration using the configure command: enabling an interface, setting interface ring speed, and specifying IP routing. You might also need to enter other configuration subcommands depending upon the requirements for your system configuration. For complete descriptions of configuration subcommands and the configuration options available, refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section.
Press the Return key after each step unless otherwise noted. At any time you can exit the privileged level and return to the user level by entering disable at the prompt as follows:
Router# disableRouter>Following is an example of a basic configuration procedure:
Step 1
At the privileged-level prompt, enter configuration mode and specify that the console terminal will be the source of the configuration subcommands, as follows:
Router# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.Step 2
Specify the first Token Ring interface to configure by entering the subcommand interface followed by tokenring and port adapter slot number/interface port number. The example that follows is for the first interface of the port adapter in port adapter slot 6:
Router(config)# interface tokenring 6/0Step 3
If IP routing is enabled on the system, you can assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface with the ip address configuration subcommand as follows:
Router(config-int)# ip address 1.1.1.10 255.255.255.0
CautionEach Token Ring port must be configured for the same ring speed as the ring to which it is connected; either 4 or 16 Mbps. If the port is set for a different speed, it will cause the ring to beacon, which effectively brings the ring down and makes it inoperable.

Note
Token Ring ports operate at either 4 or 16 Mbps. The default speed for the 4R-FDX port adapter's Token Ring ports is 4 Mbps, which you can change to 16 Mbps on any port using the configuration ring-speed n command, where n is the speed (4 or 16) in Mbps. Before you enable the Token Ring interfaces, ensure that each is set for the correct speed, or it can bring down the ring.
Step 4
Change the shutdown state to up and enable the interface as follows:
Router(config-int)# no shutdownWhen you enable the interface by using the no shutdown command, the LED for 4 Mbps or 16 Mbps is turned on after about 5 seconds. The In Ring LED for that interface is turned on about 5 to 18 seconds later, when the port is initialized and connected to the ring.
Step 5
Either accept the default ring speed of 4 Mbps, or enable the Token Ring interface speed for 16-Mbps operation as follows:
Router(config-int)# ring-speed 16Step 6
Enter any additional configuration subcommands required to enable routing protocols and set the interface characteristics.
Step 7
Repeat Step 2 through Step 6 for each new interface.
Step 8
When all new interfaces are configured, press Ctrl-Z (hold the Control key down and press the Z key).
Step 9
Write the new configuration to nonvolatile memory by entering the following:
Router# copy running-config startup-config[OK]Router#
You have completed configuring the Token Ring interfaces. To check the configuration, proceed to the following section "Checking the Configuration" section.

Note
If you require full-duplex operation, verify that you are using a 4R-FDX port adapter and that you have the correct minimum Cisco IOS release for full-duplex compatibility; refer to the sections "Software and Hardware Requirements" section and "Verifying Full-Duplex Token Ring Port Adapter Capability in Your Router" section; then proceed to the following section "Configuring Full-Duplex Operation" section.
Configuring Full-Duplex Operation
Full-duplex operation requires a 4R-FDX port adapter and a host router running a specific level of Cisco IOS software. (Refer to the section "Software and Hardware Requirements" section.)
Full-duplex operation is not the default configuration and must be turned on using the full-duplex command. To turn off full-duplex operation and reset the interface, use the no full-duplex or half-duplex command.
Following is an example of configuring a 4R-FDX interface for full-duplex operation using the full-duplex command:
Router# conf tEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.Router(config)# int tokenring 6/0Router(config-if)# full-duplexCtrl-zRouter#
Note
If the port adapter does not support full-duplex operation, the following error message appears: "%TokenRing6/0 interface does not support full-duplex."
The output of the show interfaces tokenring port adapter slot/interface port command displays the state of the Token Ring port adapter interface and the state of full-duplex operation. Following is a partial sample output of this command from a 4R-FDX interface with full-duplex operation enabled:
Router# show int tokenring 6/0TokenRing6/0 is up, line protocol is upHardware is IBM2692, address is 0000.0000.0000 (bia 0000.0000.0000)Internet address is 14.0.0.2/8MTU 4464 bytes, BW 1600 Kbit, DLY 630 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255Encapsulation SNAP, loopback not set, keepalive not setARP type: SNAP, ARP Timeout 04:00:00Ring speed: 16 Mbps, operating in full-duplex[display text omitted]
Note
When full-duplex operation is turned off using the no full-duplex or half-duplex commands, the last line of the preceding display includes the following information: operating in half-duplex.
Checking the Configuration
After configuring the new interface, use the show commands to display the status of the new interface or all interfaces, and the ping command to check connectivity.
Using show Commands to Verify the Status of the New Interfaces
The following steps use show commands to verify that the new interfaces are configured and operating correctly.
Step 1
Display the system hardware configuration with the show version command. Ensure that the list includes the new Token Ring interfaces.
Step 2
Display all the current interfaces with the show controllers command. Verify that the new 4R-FDX port adapter appears in the correct slot.
Step 3
Specify one of the new Token Ring interfaces with the show interfaces type port adapter slot/interface port command and verify that the first line of the display specifies the interface with the correct slot number. Also verify that the interface and line protocol are in the correct state: up or down.
Step 4
Display the protocols configured for the entire system and specific interfaces with the show protocols command. If necessary, return to configuration mode to add or remove protocol routing on the system or specific interfaces.
Step 5
Display the running configuration file with the show running-config command. Display the configuration stored in NVRAM using the show startup-config command. Verify that the configuration is accurate for the system and each interface.
If the interface is down and you configured it as up, or if the displays indicate that the hardware is not functioning properly, ensure that the network interface is properly connected and terminated. If you still have problems bringing up the interface, contact a customer service representative for assistance.
To display information about a specific interface, use the show interfaces command with the interface type, port adapter slot, and interface port address in the format show interfaces [type port adapter slot/interface port]. To display information about all interfaces installed in the system, use the show interfaces command without arguments.
Following is an example of the show interfaces tokenring [port adapter slot/interface port] command shows information specific to the first 4R-FDX interface port (port 0) in port adapter slot 6:
Router# sh int tokenring 6/0TokenRing6/0 is up, line protocol is upHardware is IBM2692, address is 0000.0c0c.4444 (bia 0060.3e47.4360)Internet address is 14.0.0.2/8MTU 4464 bytes, BW 1600 Kbit, DLY 630 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255Encapsulation SNAP, loopback not set, keepalive not setARP type: SNAP, ARP Timeout 04:00:00Ring speed: 16 Mbps, operating in full-duplex[display text omitted]The show version (or show hardware) command displays the configuration of the system hardware (the number of each interface type installed), the software version, the names and sources of configuration files, and the boot images. Following is an example of the show version command:
Router# show versionCisco Internetwork Operating System SoftwareIOS (tm) 7200 Software (C7200-J-M), Version 11.1(8)CA [rmontino 105]Copyright (c) 1986-1996 by cisco Systems, Inc.Compiled Sun 04-Aug-96 06:00 by rmontinoImage text-base: 0x600088A0, data-base: 0x605A4000ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 11.1(8)CA RELEASED SOFTWAREROM: 7200 Software (C7200-BOOT-M), RELEASED SOFTWARE 11.1(8)CA [gstovall 1]Router uptime is 4 hours, 22 minutesSystem restarted by reloadSystem image file is "c7200-j-mz", booted via slot0cisco 7206 (NPE150) processor with 12288K/4096K bytes of memory.R4700 processor, Implementation 33, Revision 1.0 (Level 2 Cache)Last reset from power-onBridging software.Channelized E1, Version 1.0.SuperLAT software copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp.X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant.TN3270 Emulation software (copyright 1994 by TGV INC).Primary Rate ISDN software, Version 1.0.Chassis Interface.4 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interfaces.1 FastEthernet/IEEE 802.3 interface.4 Token Ring /IEEE802.5 interfaces.12 Serial network interfaces.2 Channelized E1/PRI ports.125K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.1024K bytes of packet SRAM memory.20480K bytes of Flash PCMCIA card at slot 0 (Sector size 128K).8192K bytes of Flash internal SIMM (Sector size 256K).Configuration register is 0x2To determine which type of port adapter is installed in your Cisco 7200 series router, use the show diag slot command. Specific port adapter information is displayed, as shown in the following example of a 4R-FDX port adapter in port adapter slot 6:
Router# show diag 6Slot 6:Token-ring Full Duplex port adapter, 4 portsPort adapter is analyzedPort adapter insertion time 1d18h agoHardware revision 1.0 Board revision A0Serial number 2023868 Part number 73-1390-04Test history 0x0 RMA number 00-00-00EEPROM format version 1EEPROM contents (hex):0x20: 01 4A 01 01 00 1E E1 71 49 05 6E 04 00 00 00 000x30: 58 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00For complete command descriptions and examples for the Cisco 7200 series routers, refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section.
Using the ping and loopback Commands
The ping and loopback commands allow you to verify that an interface port is functioning properly and to check the path between a specific port and connected devices at various locations on the network, after the system has booted successfully and is operational. This section provides brief descriptions of these commands. Refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section, for detailed command descriptions and examples.
The ping command sends echo request packets out to a remote device at an IP address that you specify. After sending an echo request, the command waits a specified time for the remote device to reply. Each echo reply is displayed as an exclamation point (!) on the console terminal; each request that is not returned before the specified timeout is displayed as a period (.). A series of exclamation points (!!!!!) indicates a good connection; a series of periods (.....) or the messages [timed out] or [failed] indicate that the connection failed.
Following is an example of a successful ping command to a remote server with the address 1.1.1.10:
Router# ping 1.1.1.10 <Return>Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echoes to 1.1.1.10, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/15/64 msRouter#If the connection fails, verify that you have the correct IP address for the destination and that the device is active (powered on), and repeat the ping command.
The loopback test allows you to detect and isolate equipment malfunctions by testing the connection between the 4R-FDX port adapter interface and a remote device such as a MAU, MSAU, or Token Ring switch. The loopback subcommand places an interface in loopback mode, which enables test packets that are generated from the ping command to loop through a remote device or interface cable. If the packets complete the loop, the connection is good. If not, you can isolate a fault to the remote device or interface cable in the path of the loopback test.

Note
You must configure a clock rate on the port before performing a loopback test. However, if no cable is attached to the port, the port is administratively up, and the port is in loopback mode, you do not have to configure a clock rate on the port before performing a loopback test.
When no interface cable is attached to a 4R-FDX port adapter interface, issuing the loopback controller command tests the path between the network processing engine and the interface port only (without leaving the network processing engine and port adapter).
For complete descriptions of interface subcommands and the configuration options available for Cisco 7200 series-related interfaces, refer to the publications listed in the section "Related Documentation" section.
Related Documentation
The documentation listed below is available online, on the Documentation CD-ROM, or as printed documents.
Your router, switch, or gateway and the Cisco IOS software running on it contain extensive features and functionality, which are documented in the following resources:
•
Cisco IOS software:
–
For configuration information and support, refer to the modular configuration and modular command reference publications in the Cisco IOS software configuration documentation set that corresponds to the software release installed on your Cisco hardware.
–
To check the minimum software requirements of Cisco IOS software with the hardware installed on your router, Cisco maintains the Software Advisor tool on Cisco.com: http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/CompNav/Index.pl. You must be a registered user on Cisco.com to access this tool.

Note
You can access Cisco IOS software configuration and hardware installation and maintenance documentation on the World Wide Web at http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml.
•
Cisco 7000 series routers:
For hardware installation and maintenance information, refer to the following publications:
–
Cisco 7000 Hardware Installation and Maintenance that shipped with your router.
–
Second-Generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2) Installation and Configuration
•
Cisco 7200 series routers:
–
For port adapter hardware and memory configuration guidelines, refer to the Cisco 7200 Series Port Adapter Hardware Configuration Guidelines.
–
For hardware installation and maintenance information (including the Cisco 7206 or Cisco 7206VXR as a router shelf in a Cisco AS5800 Universal Access Server), refer to the installation and configuration guide that shipped with your Cisco 7200 series router.
–
For information on network processing engines or network services engines, refer to the Network Processing Engine and Network Services Engine Installation and Configuration publication.
–
For information on the router boot images, refer to the Cisco 7200 Series Routers Boot Images Information publication.
•
Cisco 7500 series routers:
For hardware installation and maintenance information, refer to the following publications:
–
Cisco 7500 Installation and Configuration or the quick start guide that shipped with your router
–
Second-Generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2) Installation and Configuration
•
For international agency compliance, safety, and statutory information for WAN interfaces:
–
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco 7000 Series Routers
–
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco 7200 Series Routers
–
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco 7500 Series Routers
–
Site Preparation and Safety Guide
•
To view Cisco documentation or obtain general information about the documentation, refer to the following sections:
–
Obtaining Technical Assistance
–
Customer service at 800 553-6387 or 408 526-7208. Customer service hours are 5:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. Pacific time, Monday through Friday (excluding Cisco-observed holidays). You can also send e-mail to cs-rep@cisco.com.
Obtaining Documentation
These sections explain how to obtain documentation from Cisco Systems.
World Wide Web
You can access the most current Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at this URL:
Translated documentation is available at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Documentation CD-ROM
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a Cisco Documentation CD-ROM package, which is shipped with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM is updated monthly and may be more current than printed documentation. The CD-ROM package is available as a single unit or through an annual subscription.
Ordering Documentation
You can order Cisco documentation in these ways:
•
Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order Cisco product documentation from the Networking Products MarketPlace:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/order/order_root.pl
•
Registered Cisco.com users can order the Documentation CD-ROM through the online Subscription Store:
http://www.cisco.com/go/subscription
•
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by calling Cisco Systems Corporate Headquarters (California, U.S.A.) at 408 526-7208 or, elsewhere in North America, by calling 800 553-NETS (6387).
Documentation Feedback
You can submit comments electronically on Cisco.com. In the Cisco Documentation home page, click the Fax or Email option in the "Leave Feedback" section at the bottom of the page.
You can e-mail your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
You can submit your comments by mail by using the response card behind the front cover of your document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Document Resource Connection
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883We appreciate your comments.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance. Customers and partners can obtain online documentation, troubleshooting tips, and sample configurations from online tools by using the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) Web Site. Cisco.com registered users have complete access to the technical support resources on the Cisco TAC Web Site.
Cisco.com
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that provides immediate, open access to Cisco information, networking solutions, services, programs, and resources at any time, from anywhere in the world.
Cisco.com is a highly integrated Internet application and a powerful, easy-to-use tool that provides a broad range of features and services to help you with these tasks:
•
Streamline business processes and improve productivity
•
Resolve technical issues with online support
•
Download and test software packages
•
Order Cisco learning materials and merchandise
•
Register for online skill assessment, training, and certification programs
If you want to obtain customized information and service, you can self-register on Cisco.com. To access Cisco.com, go to this URL:
Technical Assistance Center
The Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) is available to all customers who need technical assistance with a Cisco product, technology, or solution. Two levels of support are available: the Cisco TAC Web Site and the Cisco TAC Escalation Center.
Cisco TAC inquiries are categorized according to the urgency of the issue:
•
Priority level 4 (P4)—You need information or assistance concerning Cisco product capabilities, product installation, or basic product configuration.
•
Priority level 3 (P3)—Your network performance is degraded. Network functionality is noticeably impaired, but most business operations continue.
•
Priority level 2 (P2)—Your production network is severely degraded, affecting significant aspects of business operations. No workaround is available.
•
Priority level 1 (P1)—Your production network is down, and a critical impact to business operations will occur if service is not restored quickly. No workaround is available.
The Cisco TAC resource that you choose is based on the priority of the problem and the conditions of service contracts, when applicable.
Cisco TAC Web Site
You can use the Cisco TAC Web Site to resolve P3 and P4 issues yourself, saving both cost and time. The site provides around-the-clock access to online tools, knowledge bases, and software. To access the Cisco TAC Web Site, go to this URL:
All customers, partners, and resellers who have a valid Cisco service contract have complete access to the technical support resources on the Cisco TAC Web Site. The Cisco TAC Web Site requires a Cisco.com login ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a login ID or password, go to this URL to register:
http://www.cisco.com/register/
If you are a Cisco.com registered user, and you cannot resolve your technical issues by using the Cisco TAC Web Site, you can open a case online by using the TAC Case Open tool at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen
If you have Internet access, we recommend that you open P3 and P4 cases through the Cisco TAC Web Site.
Cisco TAC Escalation Center
The Cisco TAC Escalation Center addresses priority level 1 or priority level 2 issues. These classifications are assigned when severe network degradation significantly impacts business operations. When you contact the TAC Escalation Center with a P1 or P2 problem, a Cisco TAC engineer automatically opens a case.
To obtain a directory of toll-free Cisco TAC telephone numbers for your country, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
Before calling, please check with your network operations center to determine the level of Cisco support services to which your company is entitled: for example, SMARTnet, SMARTnet Onsite, or Network Supported Accounts (NSA). When you call the center, please have available your service agreement number and your product serial number.
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the "Related Documentation <required for IOS - optional for other>" section.

Copyright © 1997-2002, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)

 Feedback
Feedback