Cisco RADKit Data Sheet
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- US/Canada 800-553-2447
- Worldwide Support Phone Numbers
- All Tools
 Feedback
Feedback
Cisco Remote Automation Development Kit (RADKit) is a Software Development Kit (SDK) that offers a set of ready-to-use tools and Python modules, providing efficient and scalable interactions with local or remote equipment. It enables manual device access and automation, and allows users to capture data, monitor states, deploy configurations, or administer network devices. RADKit comprises of the following components:
● RADKit Service
● RADKit Client
● RADKit Cloud
RADKit Service is an on-premise part that must be deployed on the target network. Managed by the network owner, RADKit Service:
● Maintains an inventory of network devices managed by RADKit, including their credentials
● Maintains Administrator accounts for managing the RADKit Service and local operations on the network devices
● Maintains a list of users authorized to remotely operate on some or all the network devices to assist Network Administrators
● Connects to network devices and executes the requests from local and remote users
RADKit Client is any application consuming the RADKit Application Programming Interface (API) to execute device operations through RADKit Service. The RADKit Client can be in the same network as the RADKit Service or it can operate remotely. A RADKit User (human or automated) uses a Remote Client to request data collections or command execution through RADKit Service.
RADKit Cloud is a cloud-based service connecting RADKit Clients and RADKit Services without a direct IP connection. RADKit Cloud eliminates the need for a Virtual Private Network (VPN) while offering end-to-end encryption, ensuring that Cisco or any third-party does not have access to customer data.
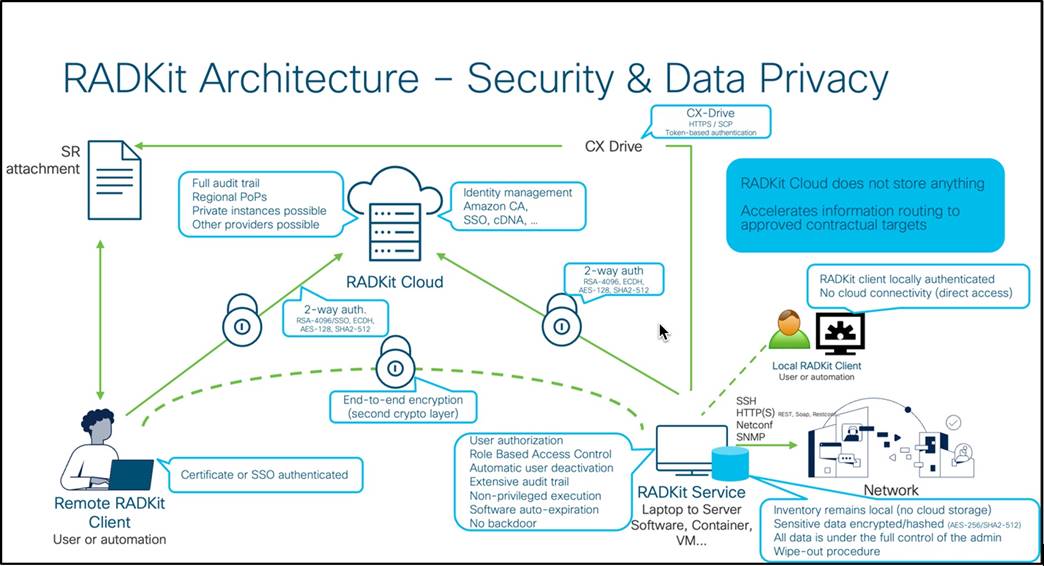
Connection Security
Traffic is encrypted end-to-end (the dashed connection represents an overlay Transport Layer Security (TLS)-1.3 session with its ephemeral keys). RADKit Cloud has restricted visibility over the messages in transit, having just enough information to transfer data with no access to the content. A key advantage of RADKit Cloud is that both the RADKit Service and RADKit Client can interface without inbound firewall rules.
Each entity opens an egress TLS channel to RADKit Cloud, simplifying the deployment, reducing customer risk (no open ingress port or protocol), and ensuring that only cloud-authenticated traffic can reach the RADKit Service. RADKit Service can then proceed with remote peer validation and authorization, independent of the cloud for end-to-end security.
Each action performed by a RADKit Service Administrator or Remote User is logged by RADKit Service. The audit trail is stored on customer premises and is accessible only to Administrators, ensuring that Cisco personnel cannot access or modify it.
API Security
The RADKit SDK provides all necessary APIs and libraries to collect data or automated actions. The dependencies are highly scrutinized to keep RADKit libraries current, ensuring a strong security foundation for the application. In addition, the RADKit SDK minimizes or eliminates the need to manage device credentials, reducing the risk of credential leaks and proliferation.
RADKit consumes significantly less CPU, RAM, and disk space compared to other solutions. By default, it places minimal load on network devices and systems and can be tuned to balance performances with impact.
With the RADKit Client, an entity (human or automated) can perform various actions on local or remote network devices.
RADKit Network Console (radkit-network-console) is a Command Line Utility (CLI) tool that is easy to understand and can be quickly learned. It enables Network Engineers to utilize key RADKit features without prior programming experience or Python code writing.
RADKit Client SDK
RADKit Client SDK is a suite of Python modules that remote users can leverage to write powerful automations like data capture, device configuration, upgrades, etc. Both RADKit Client and RADKit Network Console can manage network devices exclusively through the API, demonstrating the power of RADKit's API.
RADKit Client Read, Evaluate, Print, and Loop (REPL) (radkit-client) is a Python REPL where all key RADKit Client SDK modules are pre-loaded. The REPL offers auto-completion and syntax highlighting, serving as a powerful tool for learning the API. It is also used by power users as an advanced shell in production.
Local or Remote Connection to a RADKit Service
The first operation a RADKit Client typically performs is establishing a connection with the RADKit Service. RADKit Client provides the ability to connect to a:
● Local RADKit Service: The service can be on the same process, same machine, or across networks, assuming IP connectivity
● Remote RADKit Service: When the client and service have no direct IP connectivity, RADKit Cloud can be used as an intermediate
Integrated Secure Password Management
RADKit Client can deliver its high value features without managing applications or device credentials. Once RADKit Client is authenticated and authorized with a RADKit Service, RADKit Access Management allows scripters and developers to focus on core business activities without concern of mishandling credentials during the development, testing, and deployment phases.
RADKit Client and Network Console offer interactive terminals to devices managed by a RADKit Service. This capability is enabled by the RADKit Client API, allowing developers and scripters to remotely control a device through Secure Shell (SSH) or Teletype Network (Telnet) protocol connections.
The web User Interface (UI) of devices managed by RADKit Service are accessible through RADKit Client.
RADKit Service offers Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) proxy for RADKit Client to expose, enabling low-level troubleshooting and remote access to TCP services like Windows Remote Desktop, Virtual Network Computing, and X-Window.
Remote users can upload and download files from network devices, such as logs, core dumps, software images, and configurations.
RADKit Client can control RADKit Service to upload and attach network device outputs and files to a Technical Assistance Center (TAC) service request.
RADKit Client and RADKit Service support all major management protocols such as SSH, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), Open API, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), and Netconf. The RADKit Client API provides powerful APIs for each protocol, enabling automatic development or manual data requests without the need for boilerplate code.
Asynchronous and Parallelized Command Execution
RADKit Client APIs are asynchronous. Programmers of any experience level can effortlessly queue requests to a RADKit Service.
A single API call can request a RADKit Service to collect data across thousands of devices. RADKit Client and RADKit Service schedule, parallelize, and return data asynchronously to maximize efficiency, and minimize the impact on the network.
RADKit Service can be managed from a web UI that is highly responsive and workflow-oriented that supports:
● As-you-type searches on devices, users, and logs (including regular expressions)
● User-friendly bulk operations on devices
● Log navigation and highlighting
RADKit Service can import and store synchronized device inventories from many other platforms, including Catalyst Center, ACI API, Wireless Controllers, Firewall Management Consoles and many others (refer to RADKit documentation for an exhaustive list). In addition, RADKit supports inventory upload in .CSV and .JSON formats and through APIs. RADKit can ingest thousands of devices per second.
RADKit Service Control API and CLI
RADKit Service offers a comprehensive set of APIs and CLI tools, allowing users to control and manage every aspect of a RADKit Service without using a web UI. The web UI is developed based on public APIs. Users can develop custom solutions or contract services to enhance the workflow and import data from a non-natively supported source.
User Management and Role Based Access Control
RADKit includes three user types:
● Super Administrators
● Administrators
● Remote Users
Super Administrators and Administrators have differentiated RADKit Service management rights. Remote Users are restricted to the querying of network equipment to which they are given granular access by Administrators.
RADKit Service logs all activities, including those of Super Administrators, Administrators, and Remote Users in user-readable files. These logs can be viewed from the web UI and are available for archiving or automation. RADKit logs are in user-readable format or JSON format for easy ingestion into log management systems, such as Splunk.
RADKit capabilities are summarized in the following table.
| RADKit Capabilities |
Description |
| Connectivity |
● TLS 1.3 for all RADKit component inter-communication
● End-to-end encryption
● End-to-end authentication
● Direct, VPN, or cloud
|
| Security
|
● Cisco Cisco Secure Development Lifecycle approved
● Certificate / Public-key and Open ID authentication
● Role-based access control
● Password vault support
● Audit trail
|
| Powerful API |
● Control API (manage RADKit)
● Client API (mange network services)
● Local and remote management
● Parallelization (100’s of parallel queries)
● Easy on resources (CPU, RAM)
|
| Terminal and Web UI |
● Terminal interactive mode
● Port forwarding
● Web UI proxying
● File transfer
● Automatic Service Request attachment
|
| Multi-Protocol |
● SSH
● Bidirectional SCP, SFTP
● HTTP (Rest, soap, RESTconf)
● Netconf or Yang
● Swagger or Open API
|
| Multi-Domain |
● Enterprise (SD-WAN, SDA, IOS-XE, etc.)
● Security (Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center (FMC), Cisco Firepower Threat Defense (FTD), Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA), Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) etc.)
● Collaboration (Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM), Expressway etc.)
● Data Center (Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI), Nexus, Storage etc.)
● Service Provider (Crosswork, IOS-XR etc.)
|
RADKit Service
RADKit Service is a lightweight application installed on customer premises that serves as a secure gateway to the customer’s network devices. It supports many standard management protocols such as SSH, Telnet, Netconf, SNMP, HTTP or REST, Swagger or OpenAPI, and Socket Secure (SOCKS) or HTTP proxying. Customers have full control over device access, specifying which Cisco Engineer can access devices, which protocols to use, and the duration of access.
RADKit Client is a Python SDK that enables Cisco Engineers to remotely query or access a customer’s network devices through a RADKit Service. It enables programmatic management, troubleshooting and monitoring, automated retrieval and analysis of device outputs using Cisco internal tools, direct interaction with the devices, and more.
RADKit Cloud acts as a transport between the RADKit Client and RADKit Service. It provides TLS encryption, Certificate Authority and Cisco Online Certificate Status Protocol services, and Cisco Single Sign On (SSO) and certificate-based authentication for clients and services (jointly referred to as “Endpoints”).
In addition, RADKit includes the following utilities for increased usability and manageability:
● RADKit Network Console is a simplified interface to RADKit Client that does not require any knowledge of Python or programming. It gives access to key RADKit features with minimal training.
● RADKit Control is a companion to RADKit Service that can be used either as a CLI tool or as a Python API making it possible to manage one or more RADKit Services remotely over the network (direct IP connectivity is required). Additionally, every operation that can be done through the web UI can be done through RADKit Control.
● RADKit Service Graphical UI is a multi-platform graphical application that allows users to start, stop, and configure the RADKit Service, read logs, and change the logging level.
● RADKit Medic is an application that assists users in supporting, repairing, and resetting RADKit installations to their factory defaults.
Hardware and Operating System Requirements
RADKit Service and RADKit Client applications can be installed on a variety of Operating Systems (OS) and architectures. Refer to the OS and hardware requirements documentation for more information.
The RADKit SDK is built for and tested against many Windows, Linux, and MacOS versions, and most supported Python versions. Click here to view a current version of this table.
The RADKit Service web UI and Client Proxy web UI support all major browsers, including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Chromium, Safari, and Mozilla Firefox.
Note: Browsers must be kept current for compatibility and security. Minor rendering differences may occur across different browsers.
RADKit works across a broad set of network platforms, from controllers to routers, switches, as illustrated in the table below. Click here to view a current list of supported network.
| Technology |
Display Name |
SSH |
SCP/SFTP |
HTTPS |
Import |
Swagger |
Netconf |
SNMP |
| Collaboration |
Broadworks |
yes |
yes |
no |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| CMS |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
yes |
– |
– |
|
| CUCM |
yes1 |
yes |
yes |
no2 |
– |
– |
– |
|
| CVOS |
yes1 |
yes |
no |
no |
– |
– |
– |
|
| CVP |
yes |
yes |
|
– |
yes |
– |
– |
|
| Expressway |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
yes |
– |
– |
|
| UCCE |
yes |
yes |
no |
no |
yes |
– |
– |
|
| CX |
CSPC |
yes |
yes |
no |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
| RADKit Service |
– |
– |
yes |
– |
yes |
– |
– |
|
| Data Center |
APIC |
yes |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
| CIMC |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
| HyperFlex |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
yes |
– |
– |
|
| Intersight |
yes |
yes |
yes |
no |
– |
– |
– |
|
| Nexus Dashboard |
yes |
yes |
yes |
no |
– |
– |
– |
|
| NX-OS |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
yes |
yes |
|
| UCS Manager |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
| Enterprise |
AireOS |
yes |
yes |
no |
no |
– |
– |
yes |
| Catalyst Center |
yes |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
|
| Cisco AP OS |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
| IOS XE |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
yes |
yes |
|
| SD-WAN cEdge |
yes3 |
yes3 |
yes3 |
– |
– |
yes3 |
yes3 |
|
| SD-WAN vManage |
yes |
yes |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
|
| WLC |
yes |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
yes |
yes |
|
| Security |
ASA |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
yes |
| FDM |
yes |
yes |
yes |
no |
– |
– |
– |
|
| FMC |
yes |
no2 |
yes |
no2 |
yes |
– |
– |
|
| FTD |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
yes |
– |
– |
|
| ISE |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
yes |
– |
– |
|
| Secure Email Appliance |
yes |
yes |
no2 |
– |
– |
– |
yes |
|
| Secure Email and Web Manager |
yes |
yes |
no2 |
– |
– |
– |
yes |
|
| Secure Web Appliance |
yes |
yes |
no2 |
– |
– |
– |
yes |
|
| SP |
Crosswork |
yes |
yes |
yes |
no4 |
– |
– |
– |
| IOS XR |
yes |
yes |
no |
– |
– |
yes |
yes |
|
| NCS-2000 |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
| NSO |
yes |
yes |
yes |
no2 |
– |
yes |
– |
|
| Routed PON |
yes |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
| StarOS |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
| UCC 5G AMF Ops-Center |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
| UCC 5G PCF Ops-Center |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
| UCC 5G SMF Ops-Center |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
|
|
Linux |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
|
Generic |
yes |
yes |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
[1] interactive and ExecSequence (no exec)
[2] in progress
[3] using public IP
[4] use Crosswork Application Package (CAPP) instead
Users with a valid support contract can open TAC cases for help troubleshooting issues with RADKit and Cisco-covered devices.
● Email Support at radkit@cisco.com
 Feedback
Feedback