LAN automation
LAN automation is a network management process that
-
simplifies network operations,
-
eliminates manual, repetitive network configuration tasks, and
-
establishes a standard, error-free underlay network.
LAN automation accelerates the creation of the underlay network without the traditional network planning and implementation process.
This guide is based on Catalyst Center Release 2.3.3; however, an additional topic in the guide provides some information on the LAN automation process based on Catalyst Center Release 2.3.5 and later.
 Note |
Cisco DNA Center has been rebranded as Catalyst Center. During the rebranding process, you will see both names used in different collaterals, but both names refer to the same product. |
The steps and examples may vary based on your Catalyst Center version. For more information on configuring LAN automation and related features, see Cisco Catalyst Center User Guide.
LAN automation workflow
Cisco LAN automation provides these key benefits:
-
Zero-touch provisioning: Network devices are dynamically discovered, onboarded, and automated from their factory default state to fully integrated state in the network.
-
End-to-end topology: You can model and program dynamic discovery of new network systems and their physical connectivity. These new systems can be automated with Layer 3 IP addressing and routing protocols to dynamically build end-to-end routing topologies.
-
Resilience: Cisco LAN automation integrates system and network configuration parameters that optimize forwarding topologies and redundancy. Cisco LAN automation enables system-level redundancy and automates best practices to ensure resiliency during planned or unplanned network outages.
-
Security: The network access and infrastructure protection parameters recommended by Cisco are automated, providing security from the initial deployment.
-
Compliance: LAN automation helps eliminate errors, misconfigurations, and inconsistent rules and settings that drain IT resources. LAN automation provides compliance across the network infrastructure during new system onboarding by automating globally managed parameters from Catalyst Center.
The Cisco LAN automation workflow helps enterprise IT administrators prepare, plan, and automate greenfield networks in four main steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Plan:
|
|
Step 2 |
Design:
|
|
Step 3 |
Discover:
|
|
Step 4 |
Provision:
|
Planning LAN automation
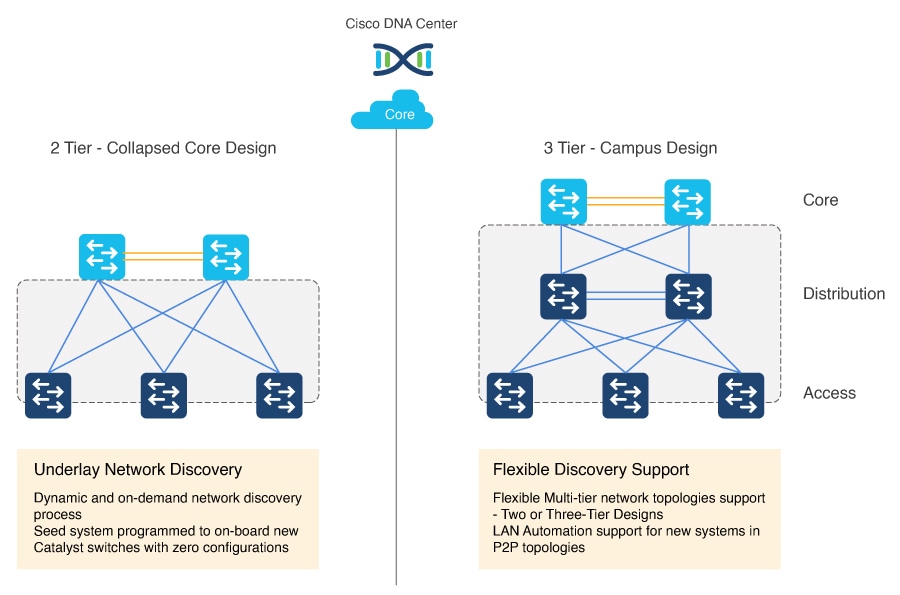
LAN automation planning is the first step in successfully building the underlay network. This section explains the aspects you must consider to ensure that the Cisco LAN automation support matrix aligns with the targeted underlay network environment.
System roles and network topologies
This section describes the device roles and the supported network topologies for LAN automation.
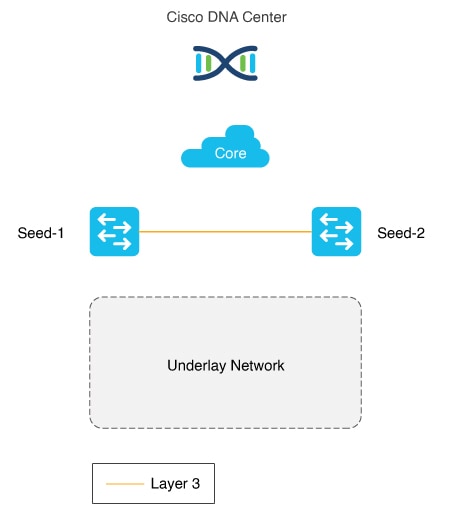
Seed device
The seed device is a predeployed system in the network and is the initial point through which LAN automation discovers and onboards new switches downstream. The seed device can be automated through technologies such as Plug and Play (PnP) and zero-touch provisioning or configured manually. Device discovery happens only on the primary seed device interfaces.
The figure illustrates the network boundaries of the seed device from the Catalyst Center connection in the IP core to the underlay network that LAN automation will discover. The peer seed (Seed-2) can also be automated through LAN automation. However, only one seed device is required.
PnP agent
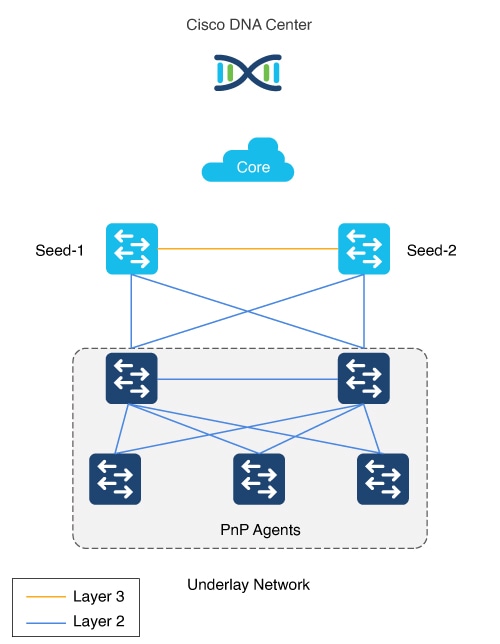
The PnP agent is a Cisco Catalyst switch with factory default settings. The switch uses the built-in day-0 mechanism to communicate with Catalyst Center and support the integrated PnP server function. Catalyst Center dynamically builds the PnP profile and configuration sets that enable complete day-0 automation.
The figure shows the PnP agent physical connection to the seed device.
Automation boundary
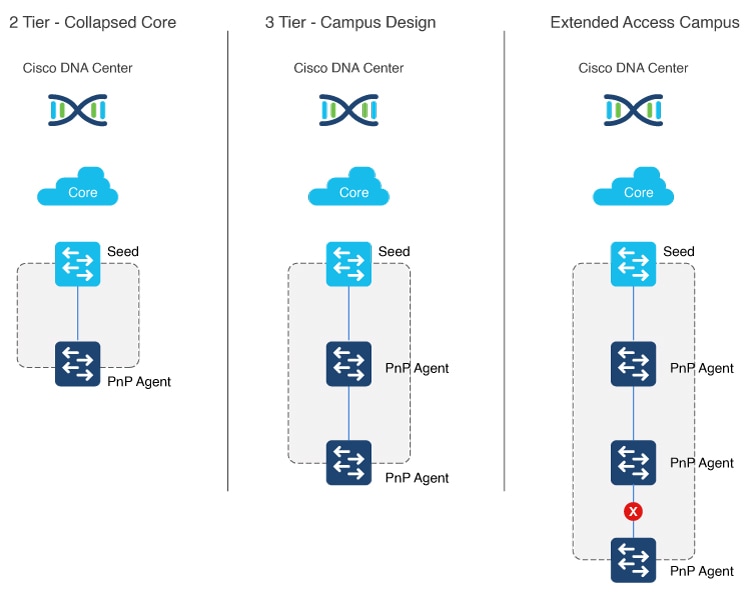
In general, we recommend building structured and hierarchical network designs in enterprise networks to provide scalability and redundancy at every network tier. While the three-tier architecture is proven in large-scale enterprise campus networks, the network design varies based on the overall network size and physical connections. As part of the initial planning, the network admin must determine the physical topology to automate with Cisco LAN automation.
LAN automation in Catalyst Center supports a maximum of two hops from the initial automation boundary point device. To build the underlay network up to the access layer, the network admin must start the automation boundary from the core or distribution layer. Any additional network devices beyond two hops might be discovered but cannot be automated.
LAN automation initiates only on directly connected neighbors.
These two scenarios illustrate the LAN automation process in a three-tier network:
-
Scenario 1: You have a three-tier network and you want to LAN automate distribution- and access-layer switches. Because distribution-layer switches (which are directly connected to the seed) participate in LAN automation, both distribution- and access-layer switches will be discovered and LAN automated.
-
Scenario 2: You have a three-tier network and you want to LAN automate distribution- and access-layer switches. You already LAN automated the distribution layer. Later, you add access-layer switches to your network and you want to LAN automate these switches. Because the distribution switches are already LAN automated and links converted to Layer 3, Tier 1 switches cannot be used as the seed. You must choose distribution as the seed in this scenario.
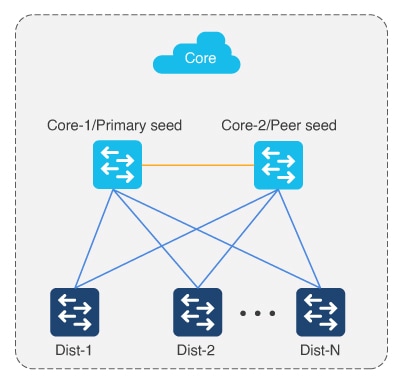
Multistep LAN automation for large topologies: First pass
Large topologies are brought up by performing LAN automation multiple times. During the first pass, core devices are chosen as seed devices to bring up the distribution switches as new devices.
 Note |
N is 50 devices or fewer at a time. All switches in the group can be booted in parallel or in a staggered fashion. |
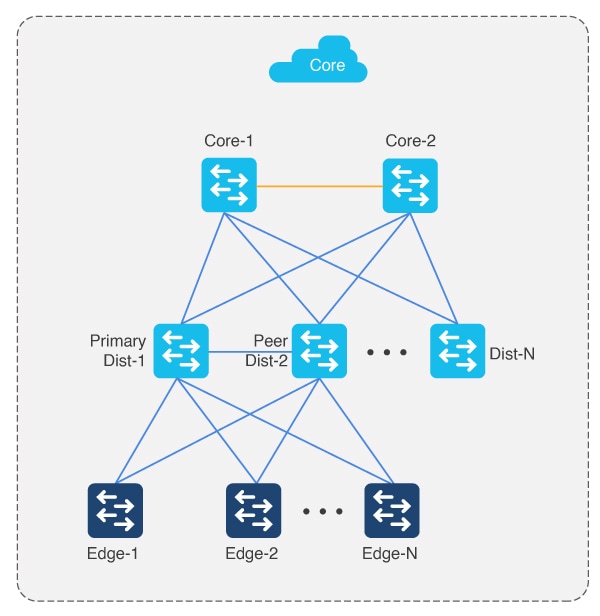
Multistep LAN automation for large topologies: Second pass with first group
During the second pass, two of the distribution switches act as seed devices to bring up the edge devices as new devices. All new devices in this session must connect directly to the two distribution switches that act as seed devices. Repeat this process for the remaining set of distribution switches, two at a time.
-
Repeat the second pass for each set of distribution to bring up the access/edge switches (where N is 50 devices or fewer at a time).
-
Connect uplinks from edges to the primary and peer distribution switches only.
-
Power down IOT/extended devices during the LAN automation session.
-
Distribution switches can be connected to other distribution switches.
-
There can be two tiers of devices below the seeds.
-
Always connect new devices to the primary seed device. Connection to the peer seed device is optional.
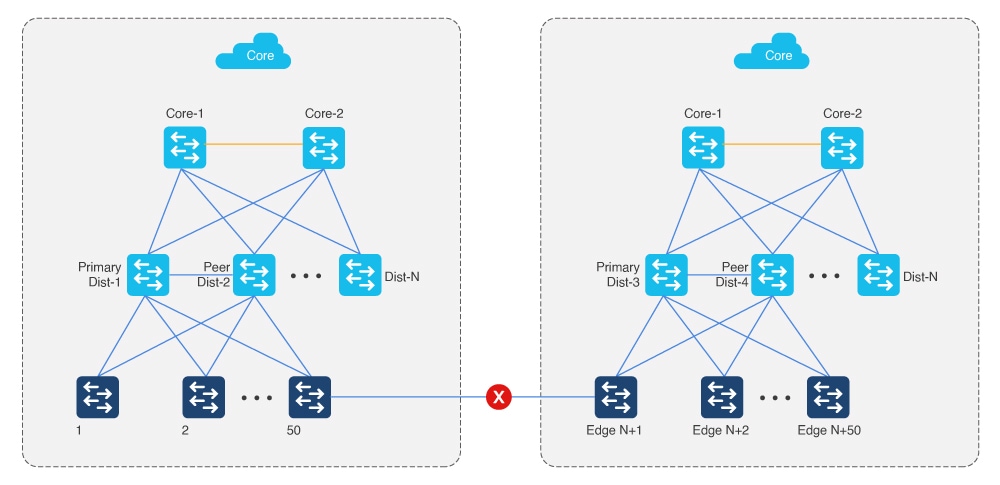
Multistep LAN Automation for large topologies: Second pass with second group
Edge devices in one group cannot be connected to edge devices in another group. Newly discovered PnP devices in the LAN automation session cannot be connected to existing nonseed inventory devices.
 Note |
In Catalyst Center 2.3.5 and later, you can establish links between the devices after LAN automation stops using the Add Link feature. For more information, see Create a link between interfaces. |
Constraints
-
LAN automation does not automate the onboarding of a StackWise Virtual (SVL) switch through PnP. SVL switch can only be used as a seed device.
-
LAN automation does not support stack renumbering.
-
For platform support, see Supported switches for each role at different layers.
Layer 3 link configuration
After all devices are added to the Catalyst Center inventory, you can stop the LAN automation session on the GUI to begin the Layer 3 link configuration process.
If you accidentally stop the LAN automation process before all PnP devices are added to the Catalyst Center inventory, links are not configured on in-progress devices. You must delete the in-progress devices from the inventory, begin a new LAN automation session, bring the in-progress devices to the factory-default state, and reload the devices to rediscover them and get their links configured.
Catalyst Center Release 2.3.5 and later provide the support for day-n link configurations (add and delete link). For more information, see Create a link between interfaces.
Layer 3 link configuration process
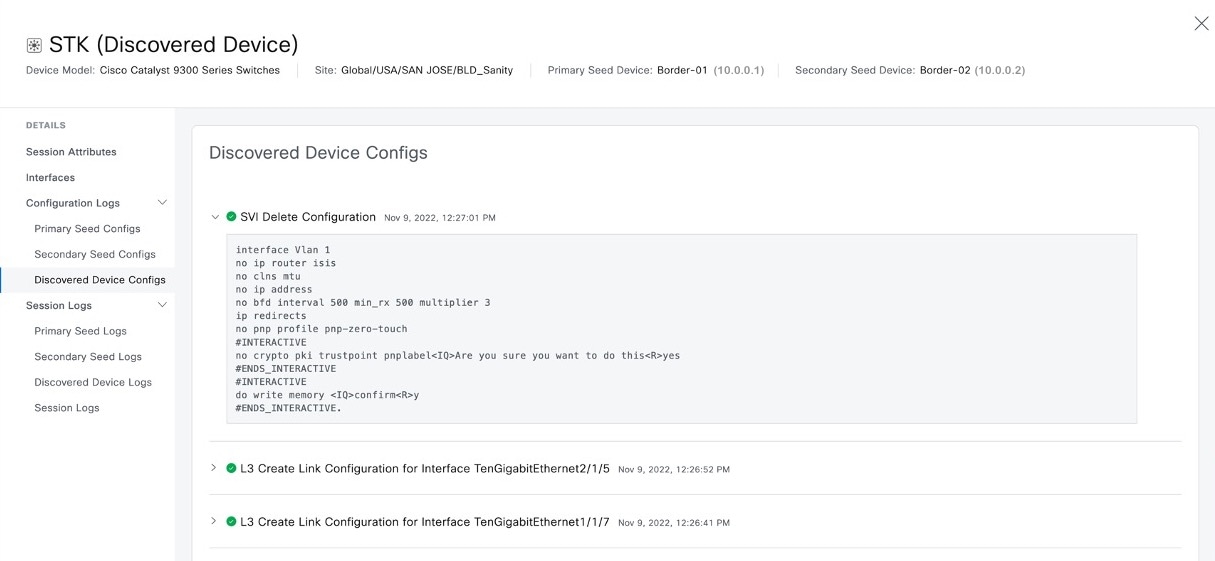
The Layer 3 link configuration process starts by converting Layer 2 links to Layer 3 links, which is done by traversing the network graph built during new device onboarding. First, the lower device link is converted to a Layer 3 IP address. Next, the upper device link is converted to a Layer 3 IP address. Router IS-IS configuration is also performed during this step in the connecting links. During this phase, there might be a temporary loss of connectivity to the lower-tier device until the upper-tier link is configured. This phase can also result in an STP topology change when the Layer 2 links are converted to Layer 3.
The process follows an algorithm that begins with the tier-three devices, followed by the tier-two devices, and completes with the tier-one devices.
It is important to note that only the links between devices that participate in the current LAN automation session are converted to Layer 3 links. Links between the newly discovered PnP device and the existing nonseed inventory device are not converted to Layer 3.
Link configuration use cases
Link configuration process when a LAN-automated device is deleted from the inventory:
-
Use case 1: The edge device is single-homed—connected to only one intermediate node and the intermediate node is deleted from the inventory.
In this case, the /31 point-to-point link IP address is deleted from Catalyst Center (IPAM) but may not be unconfigured from the edge device, which is still in the inventory. This is because the edge device can become unreachable from Catalyst Center due to the point-to-point interface between the intermediate node and the fabric border being unconfigured before the one on the edge device. In this case, log in to the edge device CLI and set the interface connected to the deleted device to default configuration. This avoids duplicate IP address assignment during LAN automation workflows later due to the released IP addresses still being present on the device. Use the LAN automation workflow to add the intermediate nodes or edge devices again instead of manual point-to-point link configurations. Ensure to delete the edge device from the inventory before adding again using LAN automation.
-
Use case 2: The edge device is dual-homed—connected to two intermediate nodes and one of the intermediate nodes is deleted from the inventory.
In this case, the /31 point-to-point link IP address is deleted from Catalyst Center (IPAM) and is unconfigured from the edge device as well. There is no manual configuration required on the edge devices.
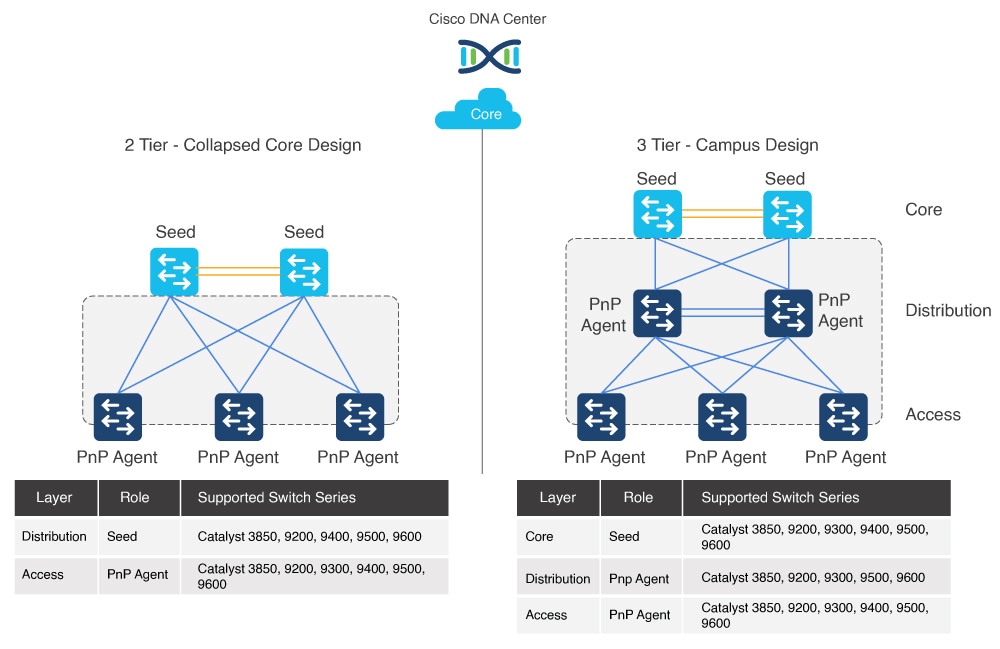
Supported switches for each role at different layers
The figure shows supported device families for the seed and PnP agent at different layers.
LAN automation product support matrix
| Role1 | Product model2 | Network module34 |
|---|---|---|
|
Seed or PnP agent |
C9606R C9600-SUP-1 C9600-SUP-1/2 C9600X-SUP-2 |
Seed: Any uplinks and module ports are supported. PnP agent: 100G interfaces are not supported. |
|
Seed or PnP agent |
C9500-32C C9500-32QC C9500-24Y4C C9500-48Y4C C9500X-28C8D |
— |
|
Seed or PnP agent |
C9500-12Q C9500-24Q C9500-40X C9500-16X |
Any front-panel ports5 |
|
Seed or PnP agent |
C9404R C9407R C9410R |
Sup-16 Sup-1XL3 Sup-1XL-Y3 Any line card |
|
Seed or PnP agent |
C9400-SUP-1 C9400-SUP-1XL C9400-SUP-1XL-Y C9400X-SUP-2XL C9400X-SUP-2 |
— |
|
Seed or PnP agent |
C9300-24S C9300-24T C9300-24P C9300-24U C9300-24H C9300-48S C9300-48T C9300-48P C9300-48U C9300-48H C9300-24UX C9300-24UXB C9300-24UB C9300-48UXM C9300-48UN C9300-48UB C9300L-48UXG C9300L-24UXG C9300L-24P C9300L-48P C9300L-48T C9300L-24T C9300LM-48UX-4Y C9300LM-48U-4Y C9300LM-24U-4Y C9300LM-48T-4Y C9300X-12Y C9300X-24Y C9300X-24HX C9300X-48HXN C9300X-48HX C9300X-48TX |
Any uplinks and module ports |
|
Seed or PnP agent |
C9200-24T C9200-24P C9200-24PB C9200-48T C9200-48P C9200-48PB C9200-48PL C9200-24PXG C9200-48PXG C9200L-24T C9200L-24P C9200L-48T C9200L-48P C9200L-48PL C9200L-24PXG C9200L-48PXG C9200CX-12T-2X2G C9200CX-12P-2X2G C9200CX-8P-2X2G |
Any uplinks and module ports |
|
Seed or PnP agent |
WS-C3850-24T WS-C3850-48T WS-C3850-24P WS-C3850-48P WS-C3850-48F WS-C3850-24U WS-C3850-48U WS-C3850-24XU WS-C3850-12X48U WS-C3850-12S WS-C3850-24S WS-C3850-12XS WS-C3850-24XS WS-C3850-48XS |
Any uplinks and module ports |
|
Seed or PnP agent |
IE-9310-26S2C IE-9320-26S2C |
Any uplinks and module ports |
Site planning
Use the Catalyst Center Design feature to create the required sites, buildings, and floors. Consider how the primary seed and peer seed will be connected to the new devices—for example, will they all belong to the same site or follow a hierarchy? Also consider how to share IP pools across different sites, buildings, and floors. One option is to have a pool specific to a site. Another option is to share a common LAN pool for all sites in the hierarchy. If the devices are onboarded across multiple LAN automation sessions, ensure that the required IP pools are available across the sites within the hierarchy.
 Note |
You cannot change the site after provisioning the devices. For this reason, we recommend that you complete LAN automation before you provision devices. |
IP pool planning
To create IP pools for LAN automation, begin with creating a global pool in Catalyst Center, followed by a site-specific LAN IP pool, which LAN automation allocates internally.
LAN IP pool allocation
-
One part of the IP pool is reserved for a temporary DHCP server. The size of this pool depends on the size of the parent LAN pool. For example, if the parent pool is 192.168.10.0/24, a /26 subpool is allocated for the DHCP server. If the pool size is larger than /24, the DHCP pool size is increased up to a maximum of /23 subpool (512 IP addresses). Therefore, a /24 pool reserves 64, a /23 pool reserves 128, a /22 pool reserves 256, and larger pools reserve 512 IP addresses for the DHCP server. To start LAN automation, the pool size must be atleast /25, which reserves a /27 pool or 32 IP addresses for the DHCP pool. This IP pool is reserved temporarily for the duration of the LAN automation discovery session. After the LAN automation discovery session completes, the DHCP pool is released, and the IPs are returned to the LAN pool. Because the DHCP pool is usually the largest contiguous segment of IPs required, the pool should have at least one such segment available. If the pool is too fragmented, it cannot allocate the DHCP pool and the LAN automation session ends with an IP pool allocation error.
-
Another part of the IP pool is reserved internally with a subpool size of /27. This subpool is for allocating single IPs for Loopback0 and Loopback60000 always. Also, two consecutive IPs for point-to-point L3 links are allocated from this subpool if no separate overlapping IP pool is provided. This internally reserved subpool is used throughout the LAN automation sessions for providing IPs as long as it has IPs available. If exhausted, a new /27 subpool is created for allocating IPs. These subpools are released only when all the allocated IPs are released as part of the devices being deleted from Catalyst Center. Otherwise, the subpools remain throughout the process and are not allowed to be removed. Due to this internal subpool allocation logic, the IP pool usage in IPAM counts the subpools instead of the actual IPs allocated to the devices.
-
If a shared or link overlapping IP pool is provided for the point-to-point Layer 3 links, then the subpool of size /27 is reserved internally from the shared pool instead of the main IP pool. The subpools are automatically deleted when all the allocated IPs from the pool are released.
Single and shared IP pool
When a dedicated (single) IP pool is used to build the underlay networks, each of the devices discovered via LAN automation gets a unique /31 per interface for point-to-point connection, and a unique /32 for Loopback0 and the underlay multicast.
A link overlapping IP pool or shared IP pool is used to optimize the IPv4 addressing in the underlay network by allowing overlapping /31 IP addresses for a multisite deployment. Hosts in different sites can get duplicate IP addresses on the /31 links. The /31s in the underlay are not advertised outside of the fabric site and hence there is no need for them to be unique. However, the /32 loopback needs to be unique to every device, and should be advertised to the global routing table to identify the device in the entire network.
IP pool roles
The LAN IP pool can have these two valid roles:
-
Link Overlapping IP Pool: This pool role is optional for a LAN automation session. If provided, the allocation of IP addresses is only on the point-to-point Layer 3 links.
-
Main IP Pool (Principal IP Address Pool in Catalyst Center Release 2.3.5 and later): This pool role is mandatory for every LAN automation session. This is the pool that is used for all management-related IP addressing such as loopbacks, multicast, and DHCP. If the Link Overlapping IP Pool is not provided, then the Main IP Pool is the default fallback pool for the Layer 3 links IP addressing.

IP address allocation in Catalyst Center Release 2.3.7.x and later
In Catalyst Center Release 2.3.7.x and later, IP address allocation from LAN pool is based on IP address range instead of subnet allocation. This approach helps in minimizing the issue of IP address loss during subnet creation and in effective management of the IP addresses. Instead of creating a subnet, IP address range is blocked for both DHCP pool allocation and IP address assignment for point-to-point links, loopback, and multicast. The LAN automation workflow supports assignment of IP address pools with /27, /28, and /29 subnet masks.
IP pool usage example
Imagine you want to LAN automate 10 devices using the same pool, where each device has one link to the primary seed and another link to the secondary.
Consider a 192.168.199.0/24 pool. When LAN automation starts, a /26 pool is reserved for the DHCP addresses. In this example, 192.168.199.1 to 192.168.199.63 are reserved and assigned to VLAN 1 for the 10 devices.
Next, a /27 pool is reserved for loopback addresses. If there is no shared IP pool, then this pool is used for point-to-point links as well. Because there are 10 devices with two links each, a total of 2*10*2 = 40 IP addresses are reserved for point-to-point links, and 10 loopback addresses are reserved.
In total, 60 IP addresses are reserved for the 10 devices: 10 for each VLAN 1, 10 for each loopback, and 40 for the point-to-point links between devices and seeds.
After LAN automation stops, the VLAN 1 IP addresses are released back to the pool, and 90 addresses are allocated for the LAN automation session.
Guidelines for IP pool allocation
-
The same IP pool can be used for multiple discovery sessions. For example, you can run one discovery session and discover the first set of devices. After discovery completes, you can provide the same IP pool for a subsequent LAN automation session. Similarly, you can choose one LAN pool for one discovery session and another LAN pool for a second discovery session.

Note
When the seed device for LAN automation session is in a different site than the discovered device site, then the same shared IP pool cannot be used with the same seed and different discovered device site. This is to avoid the allocation of duplicate IP to the same seed device.
-
Every time you start LAN automation, it checks for 64 available IP addresses in the IP pool. If you decide to run LAN automation multiple times with the same pool, use at least a /24 pool. If you plan to LAN automate only once for the IP pool, a /25 pool suffices.
-
Avoid using an address pool that is already utilized elsewhere in the network, such as an address pool that belongs to the loopback or to other addresses configured on the device.
Site-specific CLI and SNMP configuration
To start LAN automation, a site-specific CLI and SNMPv2 read or SNMPv3 configuration is required. Use the Catalyst Center Design feature to configure the site-specific CLI and SNMP configurations. Save the site configuration used for LAN automation. When you configure credentials globally, they become visible at the site level. You must click the radio button for the specific site and then save the configuration to make it available for LAN automation.
 Note |
SNMPv2 write credentials are not required. If they are configured, they will not be pushed to the device during LAN automation. |
Configuration on seed devices
Follow these guidelines when configuring the seed devices:
-
Ensure that the system MTU (maximum transmission unit) value is at least 9100.
-
Turn on IP routing on the seed devices.
-
Set up routing between the seed service and Catalyst Center so that Catalyst Center has IP reachability to the LAN IP pool subnet.
-
We recommend that you use the default interfaces connected to PnP agents. If the peer seed device has IP interfaces configured on the interfaces connected to PnP agents, those links are not configured. If you want to configure the peer device interfaces connected to PnP agents, use the default interfaces and perform an inventory synchronization on the peer seed device. LAN automation works only when the ports are Layer 2. The ports on the Cisco Catalyst 6000 Series Switches are Layer 3 by default. Convert the ports to Layer 2 before starting LAN automation.
-
Configure device credentials and SNMP credentials on the seed devices.
-
If the seed devices have Layer 3 interfaces configured, ensure that there are no conflicts with any of the IP pools provided in Catalyst Center. Check the IP addresses which are configured manually.
-
Ensure that the seed devices don't have any other interfaces connected to another DHCP server running in VLAN 1.
-
LAN automation configures loopback on the seed devices if they are not configured.
-
If you change configuration on the seed devices before running LAN automation, synchronize the seed devices with the Catalyst Center inventory.
-
Assign the seed devices to a site. (It is not necessary to provision the seed devices for LAN automation.)
-
Ensure that shell processing full command is not enabled on the seed devices because this can lead to LAN automation failure.
Additional recommended configurations on seed devices
If you plan to run multiple discovery sessions to onboard devices across different buildings and floors connected to the same seed devices, we recommend that you block the ports for PnP agents that do not participate in the upcoming discovery session.
For example, imagine seed devices in Building-23 connected to PnP agents on Floor-1 and Floor-2. Floor-1 devices are connected on interfaces Gig 1/0/10 through Gig 1/0/15. Floor-2 devices are connected on interfaces Gig 1/0/16 through Gig 1/0/20. For the discovery session on Floor-1, we recommend that you shut down ports connected to Gig 1/0/16 through Gig 1/0/20. Otherwise, the PnP agents connected to Floor-2 might also get DHCP IPs from the server running on the primary seed device. Because these interfaces aren't selected for the discovery session, they remain as stale entries in the PnP database. When you run the discovery session for Floor-2, the discovery doesn't function correctly until these devices are deleted from the PnP application and write erase/reloaded. Therefore, we recommend that you shut down other discovery interfaces.
For Catalyst Center Release 1.2.8 and earlier, if clients are connected to a switch being discovered, they may contend for DHCP IP and exhaust the pool, causing LAN automation to fail. Therefore, we recommend that you connect the client after LAN automation is complete.
This endpoint/client integration restriction does not apply to Catalyst Center Release 1.2.10 and later. Clients can remain connected while the switch is undergoing LAN automation.
PnP agent initial state
Ensure that the device that you want to LAN automate is running the Advantage license level. Otherwise, you cannot execute certain commands.
 Note |
Catalyst Center 2.3.5 and later support automatic license upgrade for C9000 and C3850 series switches. |
New PnP agents have factory defaults and are ready to start LAN automation.
If you are reusing existing network devices, follow these steps:
-
Ensure that PnP agents have the required license to execute LISP, IS-IS routing, and CTS-related CLI commands. Use the show license command to view the current license level. If required, upgrade the license.
-
Ensure that PnP agents do not have stale certificates or keys from the previous runs.
-
Use these commands to restore the switch configurations to factory default:
-
For Cisco IOS XE 16.11 and earlier, use:
[CLI config mode] no pnp profile pnp-zero-touch no crypto pki certificate pool Also remove any other crypto certs shown by "show run | inc crypto" crypto key zeroize config-register 0x2102 or 0x0102 (if not already) do write end[CLI exec mode] delete /force nvram:*.cer delete /force stby-nvram:*.cer (if a stack) delete /force flash:pnp-reset-config.cfg write erase reload (enter no if asked to save) -
For Cisco IOS XE 16.12.x or later, use:
[CLI exec mode] pnpa service reset no-prompt
-
Network design
The design phase is the second step in LAN automation. It involves these steps:
-
Design and build global sites
-
Configure the global and local network services
-
Configure global device credentials
-
Design the global IP address pool and assign the LAN automation pool for the required site from the global pool
Design your network
Use this procedure to create your network, configure device credentials, and add IP address pools for LAN automation.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Set up a network hierarchy. |
|
Step 2 |
Configure the device credentials. |
|
Step 3 |
Configure IP address pools. |
Device discovery
Device discovery is the third step in building the underlay network. It scans the devices within a network and sends the list of discovered devices to the inventory.
Review the underlay configuration of the seed device before creating and running a discovery profile.
Create discovery profile
This section explains how to create a discovery profile.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Catalyst Center home page, click the menu icon and choose . |
||
|
Step 2 |
In the Discovery window, click Add Discovery. |
||
|
Step 3 |
In the New Discovery window, enter the following details:
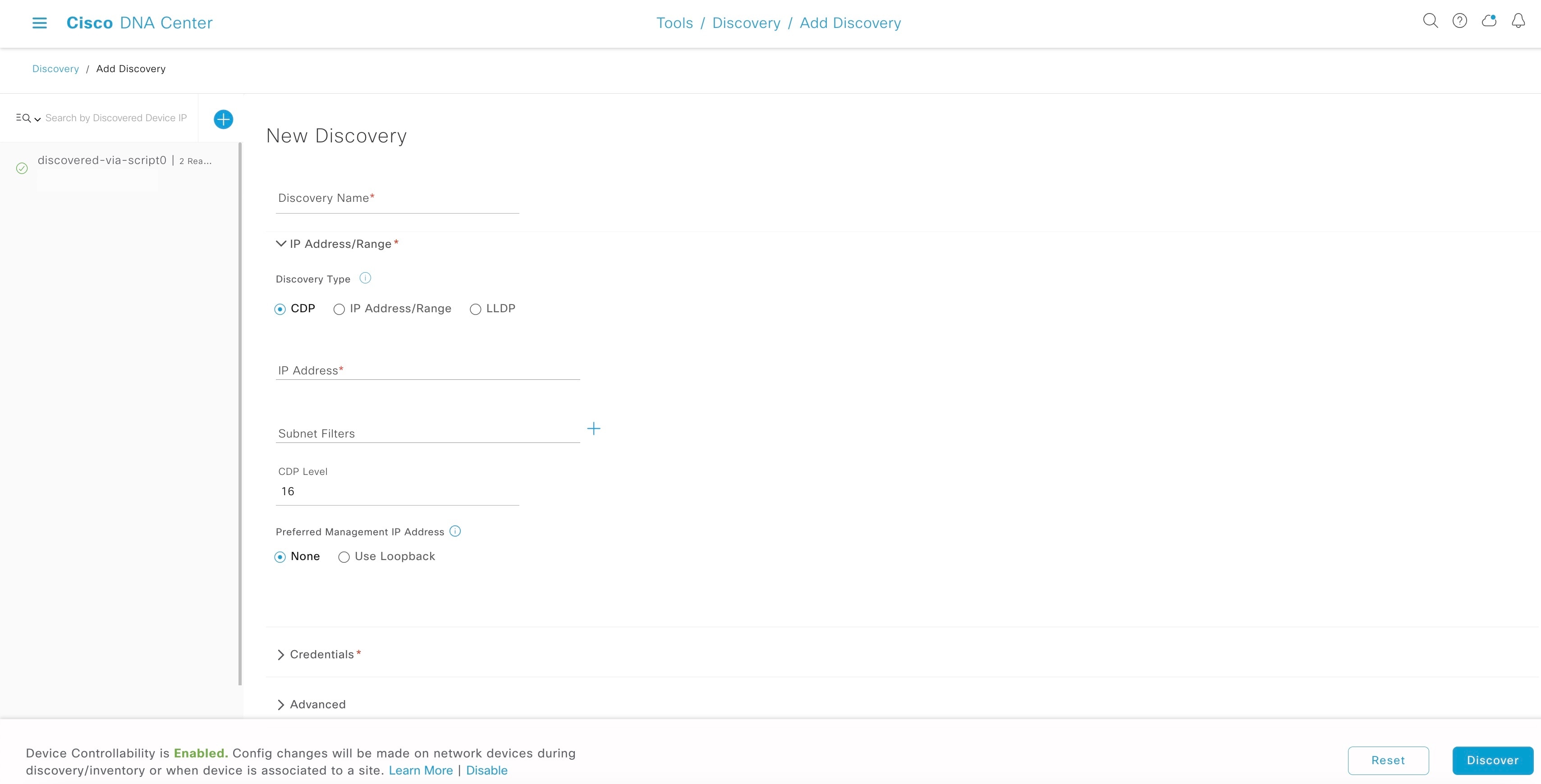
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Click Discover. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Choose a discovery schedule and click Start. You can view the status and results of the scan in the Discoveries window.
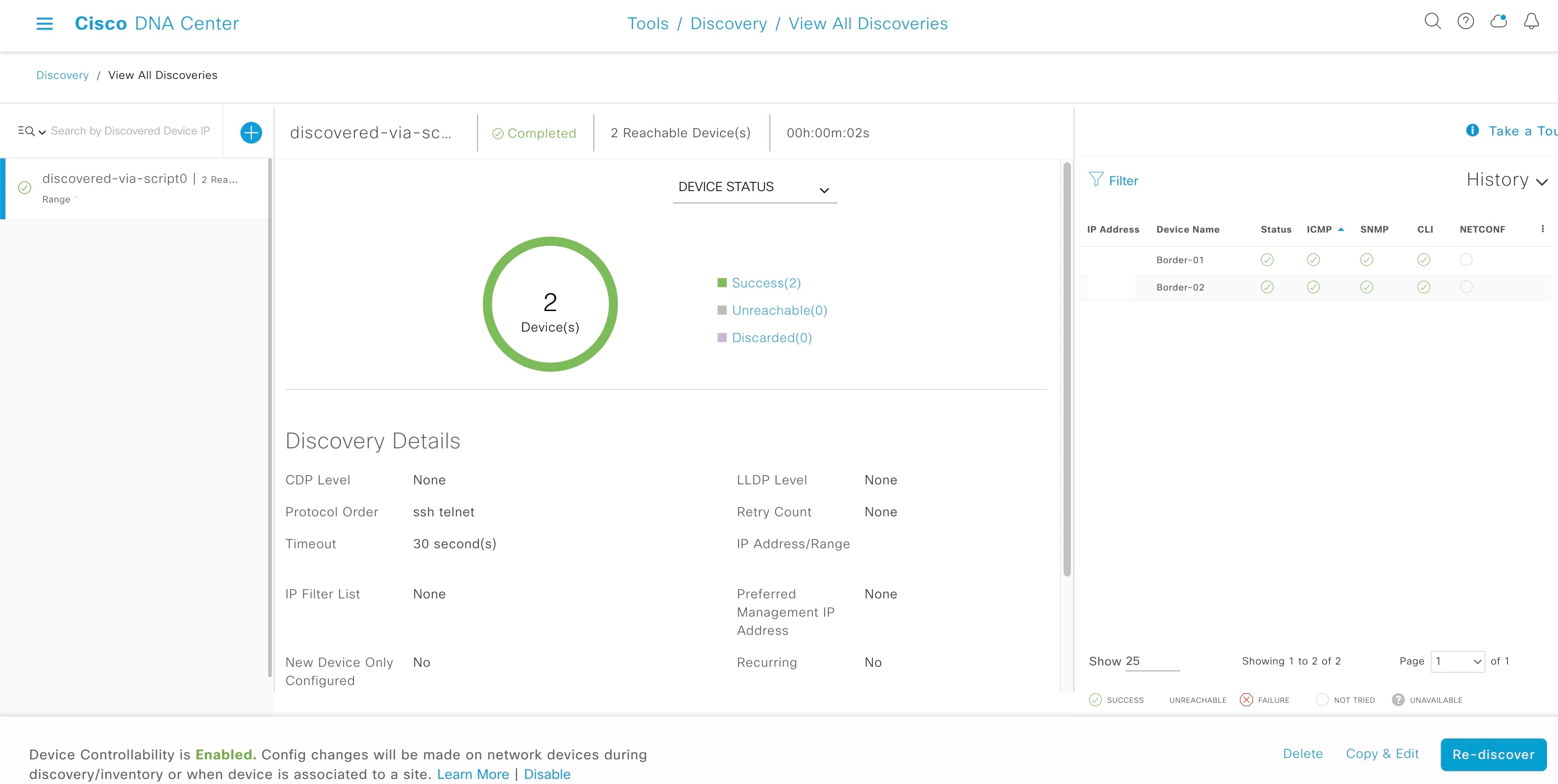
|
||
|
Step 6 |
Verify that the discovered device is added to the inventory.
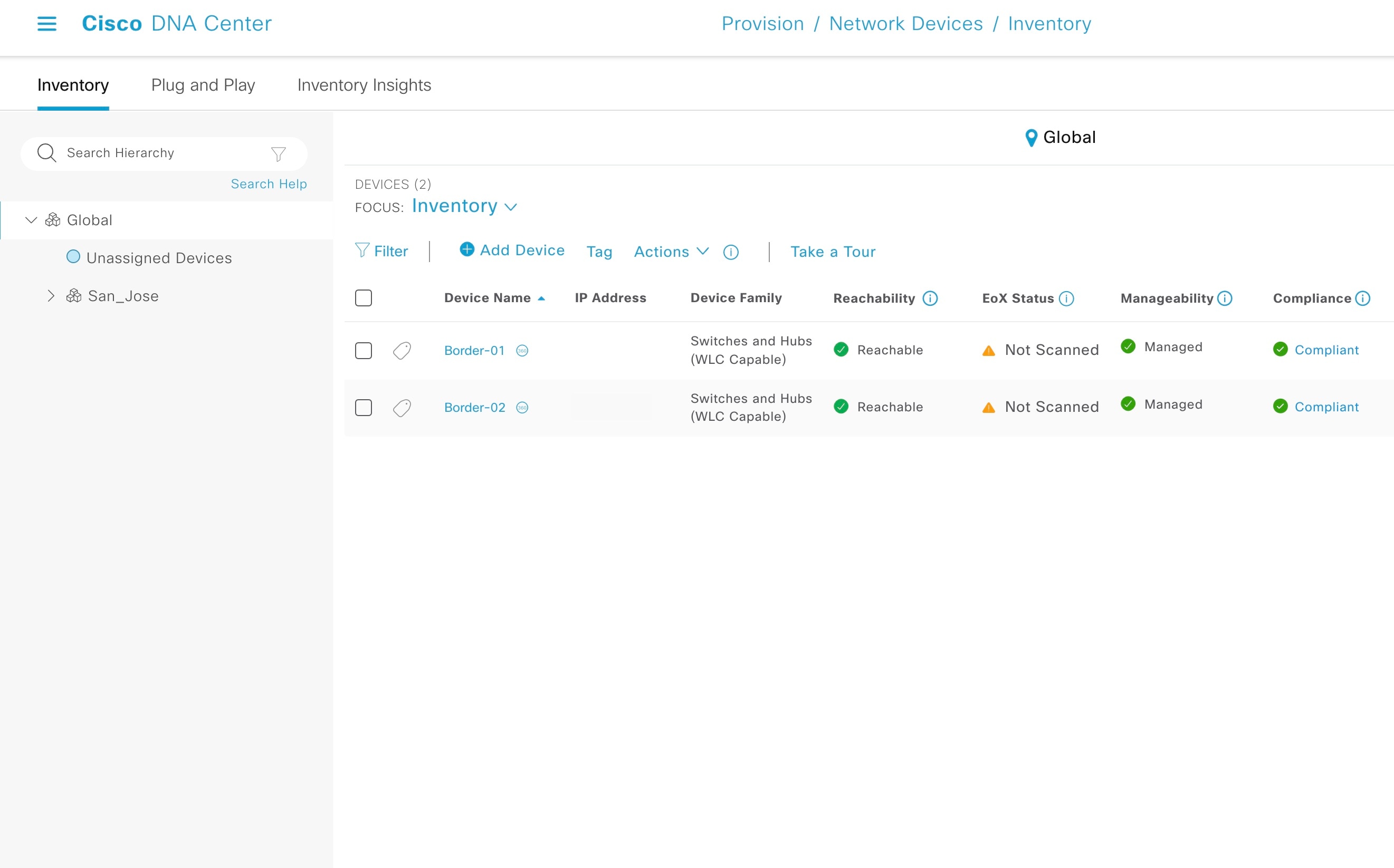
|
||
|
Step 7 |
Check the check box next to the device and choose to assign the device to a site. 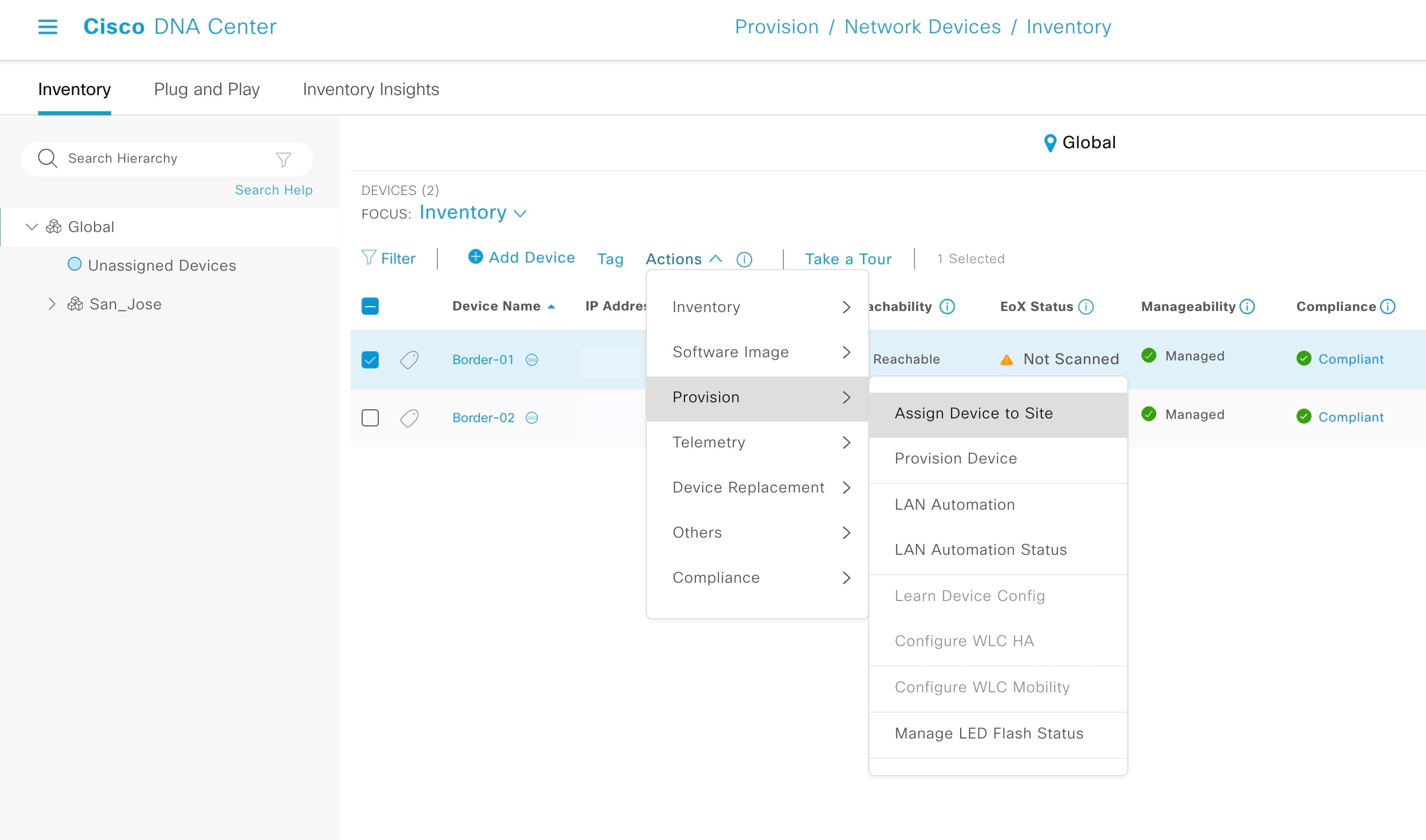
|
||
|
Step 8 |
In the Assign Device to Site window, choose a site and click Apply. For Catalyst Center 1.2.6 and earlier, ensure that both the primary and peer seeds are in the same site and same floor (although they can be physically on different floors). The discovered device is added to the selected site.
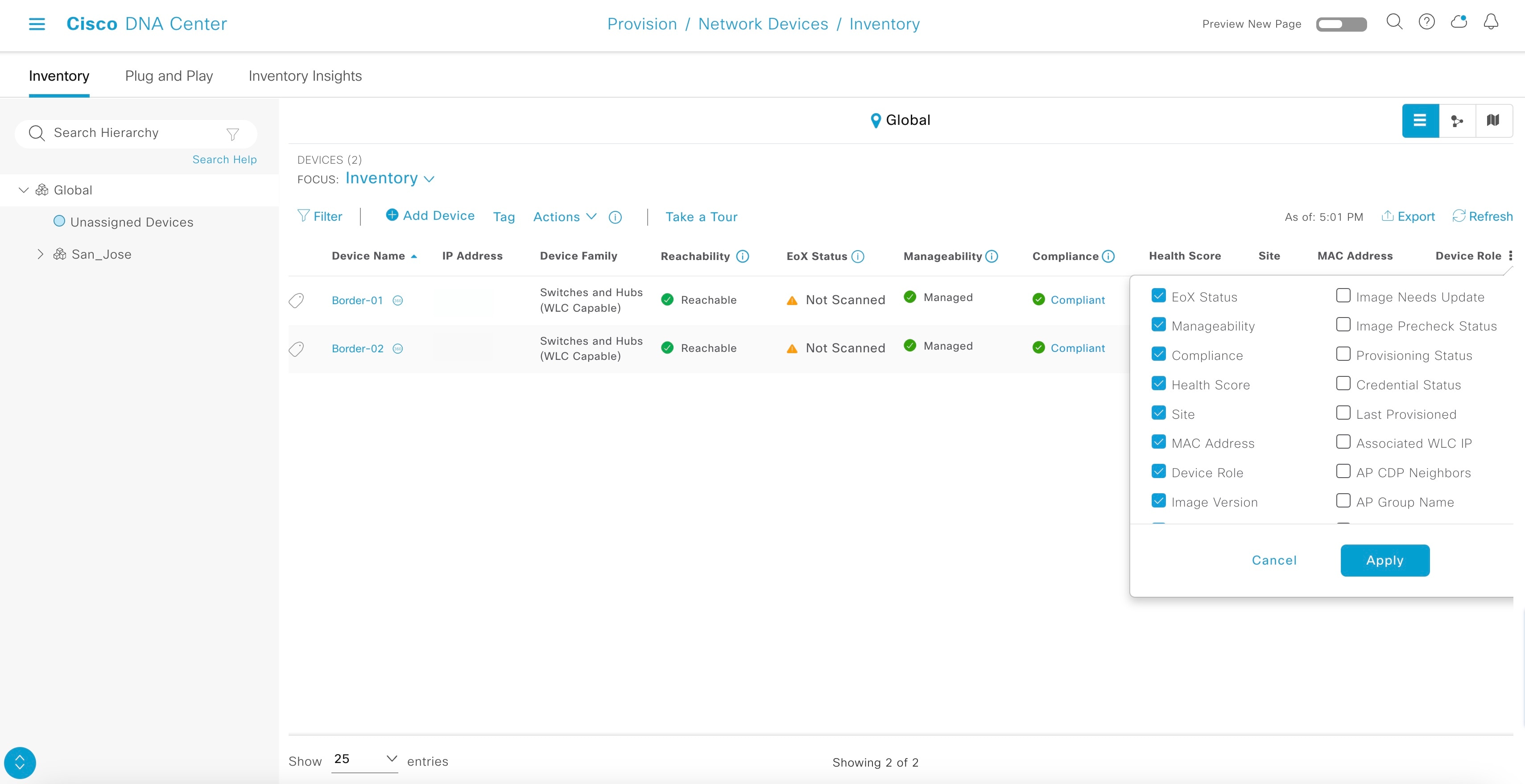
|
Provisioning LAN automation
Provisioning is the final step in the LAN automation process. It is divided into two stages:
-
Device discovery and onboarding (starting LAN automation)
When LAN automation starts, Catalyst Center
-
pushes the loopback and IS-IS configuration to the primary and peer seed devices and the temporary configuration to the primary seed device, enabling discovery and onboarding of the PnP agent.

Note
Catalyst Center Release 2.3.3 and later support
is-type level-2-onlyas part of IS-IS configurations.
-
discovers new devices.
-
upgrades the device software image and pushes the configuration to discovered devices.

Note
The image is updated only if a golden image is marked for that switch type in Catalyst Center under .
When LAN automation starts, the temporary configuration is pushed to the primary seed device. This allows the device to discover and onboard the PnP agent. Next, the PnP agent image is upgraded and basic configurations such as loopback address, system MTU, and IP routing are pushed to the PnP agent.
-
-
Interface configuration (stopping LAN automation)
When the LAN automation process stops,
-
the discovery phase ends, and all point-to-point links between the seed and discovered devices and between the discovered devices (maximum of two hops) are converted to Layer 3.
-
all temporary DHCP and VLAN 1 configurations on the seed and discovered devices are removed. The DHCP subpool is returned to the LAN automation pool.
-
Steps to consider before starting LAN automation
This section describes the necessary prechecks before starting the LAN automation process.
IP pool subnet reachability
A LAN pool is an IP address pool that is used for IP address allocation during LAN automation. LAN automation discovery uses the LAN pool to reach PnP agents.
Before starting LAN automation, make sure that Catalyst Center can reach the IP addresses allocated from the LAN pool.
Example
For example, if the LAN pool is 192.168.10.0, Catalyst Center should have the correct route to reach this subnet.
Refer to this sample code to test IP pool reachability:
-
Create an SVI (VLAN 1 interface) on the primary seed device.
[On seed device]Switch(config)#interface vlan1 Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 Switch(config-if)#end -
From the Catalyst Center console, ping the seed device.
[On Catalyst Center CLI console][Sat Jun 23 05:55:18 UTC] maglev@10.195.192.157 $ ping 192.168.99.1 PING 192.168.99.1 (192.168.99.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.99.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=252 time=0.579 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.99.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=252 time=0.684 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.99.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=252 time=0.541 ms -
Reset the SVI configuration on the seed device when finished.
[On seed device]Switch(config)#default int vlan 1 Interface Vlan1 set to default configuration
If the ping test fails, check the route configuration on Catalyst Center.
Add a static route for LAN pool
Catalyst Center hardware includes multiple physical interfaces. Each interface serves a different communication category. See the Cisco Digital Network Architecture Center Appliance Installation Guide for recommended interface connections, IP routing, and static assignment. In a single-home design, Catalyst Center performs the host function with the default gateway providing IP routing. In a multi-home design, Catalyst Center must have a static route to the LAN automation networks through the enterprise-facing interface.
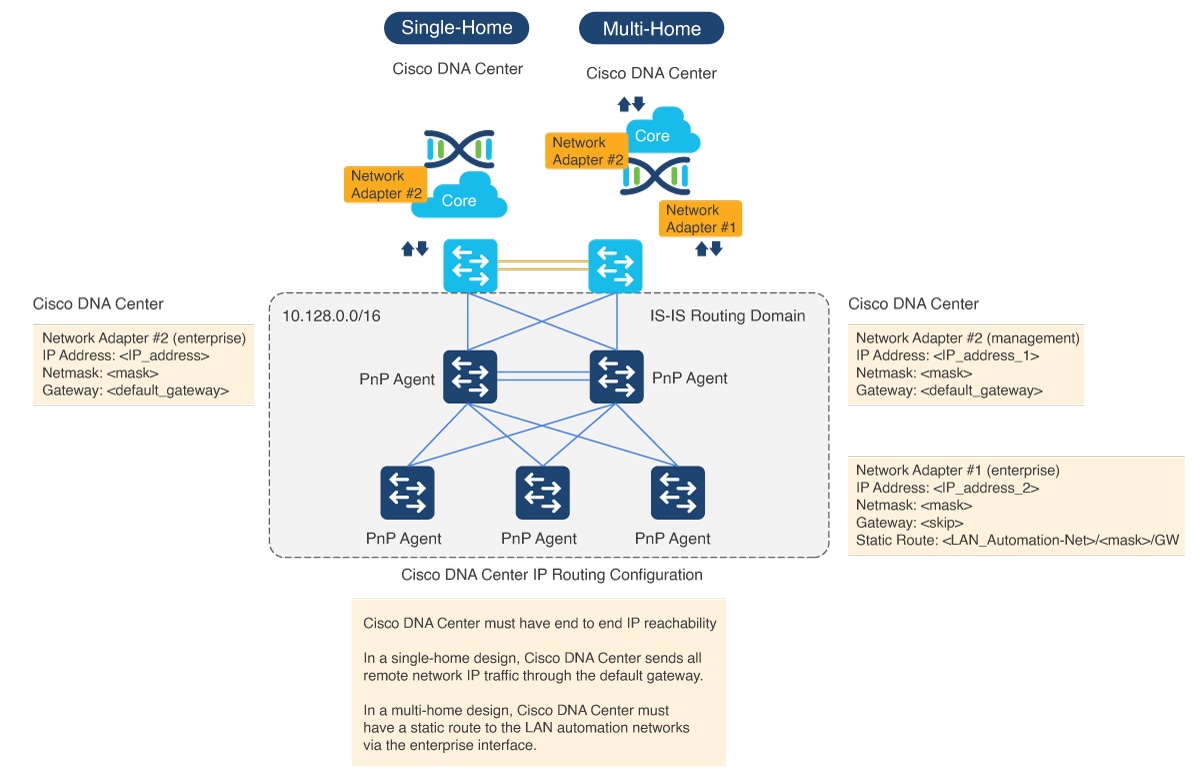
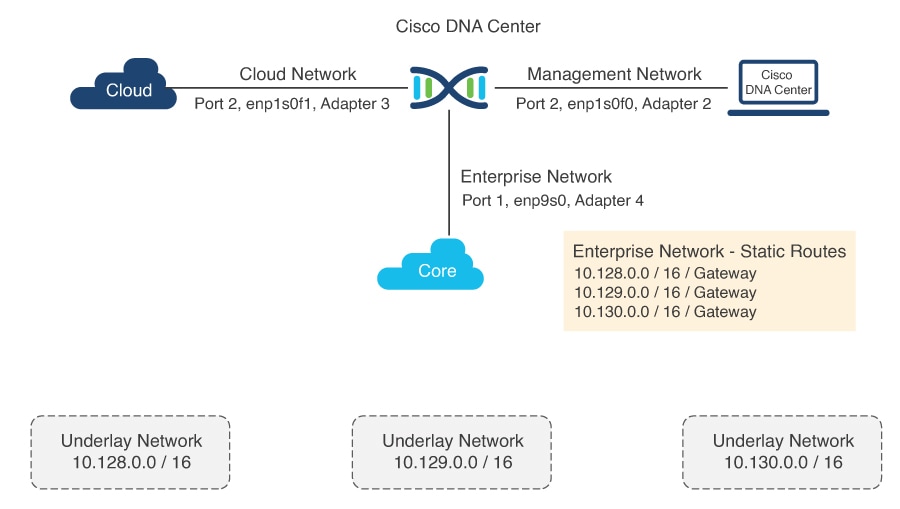
For a multi-home design, add a static route on Catalyst Center to resolve the IP reachability issue. You can add a static route during the initial Catalyst Center configuration or later using a maglev command. Do not use the Linux route command, because maglev APIs might not retrieve the correct information if the route is modified using the route command.
For a single-home design, verify routing between the seed device and Catalyst Center.
Follow these steps to add a static route on Catalyst Center:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
On the Catalyst Center console, enter the command The configuration wizard opens. 
|
|
Step 2 |
Enter the static route and click Next. The config wizard validates and configures host networking. |
|
Step 3 |
Ensure that you select the correct interface to add the static route. If the correct interface is not displayed, click Next until it appears. |
|
Step 4 |
Leave the Network Proxy field blank. If proxy validation fails, skip the proxy settings. |
|
Step 5 |
To apply the changes to the controller, click Proceed. Adding a static route takes five to six minutes (5-6 minutes). Ignore any warning messages.
|
Verify the PnP agent initial state
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Before starting LAN automation, make sure that the PnP agent is in System Configuration Dialog state. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Do not press Yes or No. Leave the device in the same state.
|
||
|
Step 3 |
Follow the same steps (Step 1 and Step 2) for stack switches.
|
Port connections and license levels
Before starting LAN automation, verify the port connections and the license level on the devices.
-
Connect PnP agents directly to seed devices. Do not connect PnP agents to any other network (for example, the management network) or any network that can provide DHCP through another server on VLAN 1.
-
Ensure that the seed ports connected to the PnP agents use Layer 2 and are in the default state. For example, ports on Cisco Catalyst 6500 and 9500H switches use Layer 3 by default.
-
Ensure that the port on the primary seed that connects to the PnP agents does not block STP.
-
Ensure that the PnP agent is running the Advantage license level.
Remove a device from inventory
This section applies to devices that were discovered or LAN automated at any point.
If the devices to discover in an upcoming LAN automation session are already present in the inventory, remove them from inventory.
Before you begin
If a device was provisioned and added to the fabric, remove it from the fabric and unprovision it. Then, remove it from the inventory.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Catalyst Center home page, click the menu icon and choose . |
|
Step 2 |
Filter the devices by Serial Number. |
|
Step 3 |
Choose a device and from the Actions drop-down list, choose . 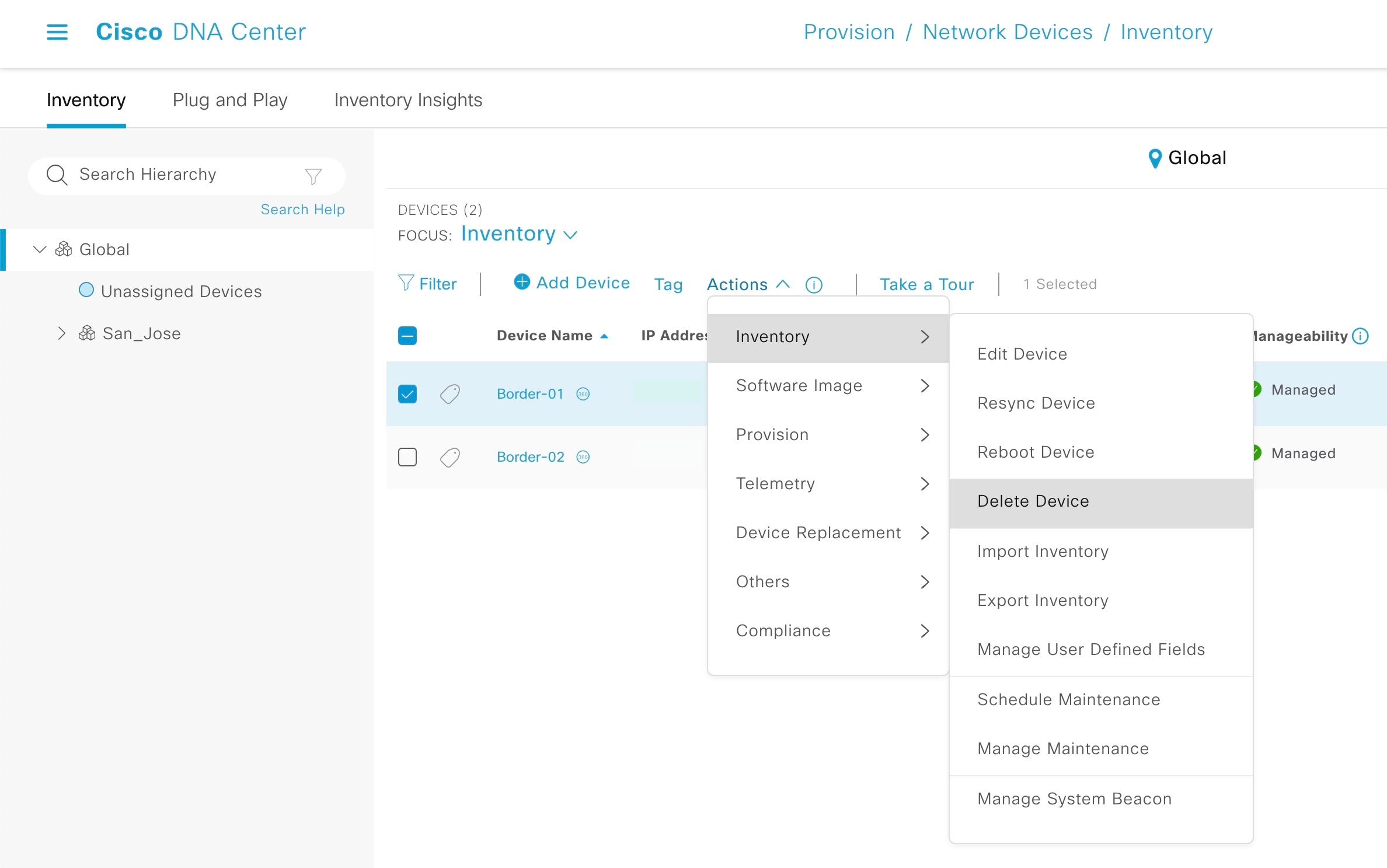
|
Remove devices from PnP before discovery
Before starting a LAN automation session, check whether the devices you want to discover are already listed in PnP. Remove them from PnP so that device discovery works as intended.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Catalyst Center home page, click the menu icon and choose . |
|
Step 2 |
From the Device Status filter, choose Unclaimed. Make sure that the device (Serial Number) being discovered is not available under Unclaimed. 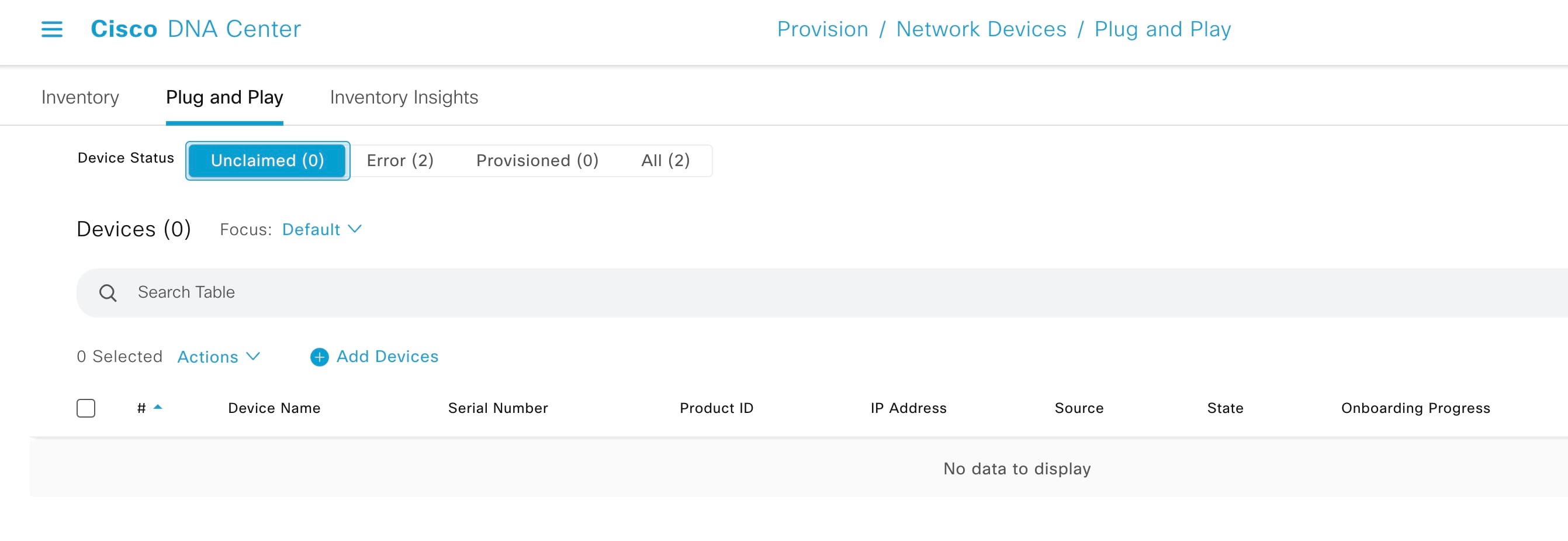
|
|
Step 3 |
If the device is available, log in to the device console and remove the PnP profile. For Cisco IOS XE 16.12.x or later, use this command: |
|
Step 4 |
Check the check box next to the device in the Unclaimed section and choose . |
Verify the PnP agent mode
The PnP agent must be in INSTALL mode for image upgrade during LAN automation.
Image upgrade through LAN automation occurs in the background.
 Note |
For modular switch platforms (Catalyst 9400 and 9600 series) with chassis plus supervisor, day-zero image upgrade is not supported. Instead, use day-n SWIM for image upgrade for these series of modular chassis. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Under , check whether a golden image is selected for the discovered device. After PnP discovers the device, Catalyst Center checks if a golden image is marked for the switch family (Cisco Catalyst 9300 or 3850). If the golden image is marked and the discovered device is not running it, LAN automation upgrades the discovered device to the golden image. If not, Catalyst Center skips the image upgrade and pushes the initial device configuration. |
|
Step 2 |
Ensure that the discovered device is running in INSTALL mode to allow LAN automation to upgrade the image. If the device is in BUNDLE mode, LAN automation will not upgrade the image. |
|
Step 3 |
If the device is in BUNDLE mode and you want to proceed with LAN automation, remove the golden image for the relevant switch family under . |
Configuring LAN automation attributes
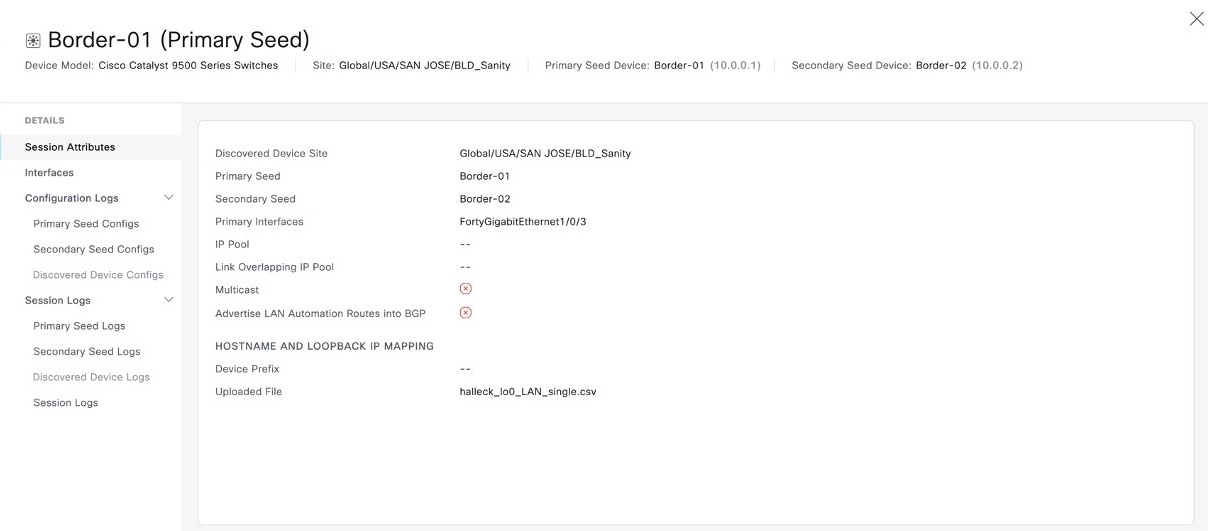
To set up LAN automation, select the primary seed device, peer seed device, site for seed device, a LAN IP pool, and an interface. Optionally, select the device prefix, hostname CSV file, and a configurable IS-IS password.
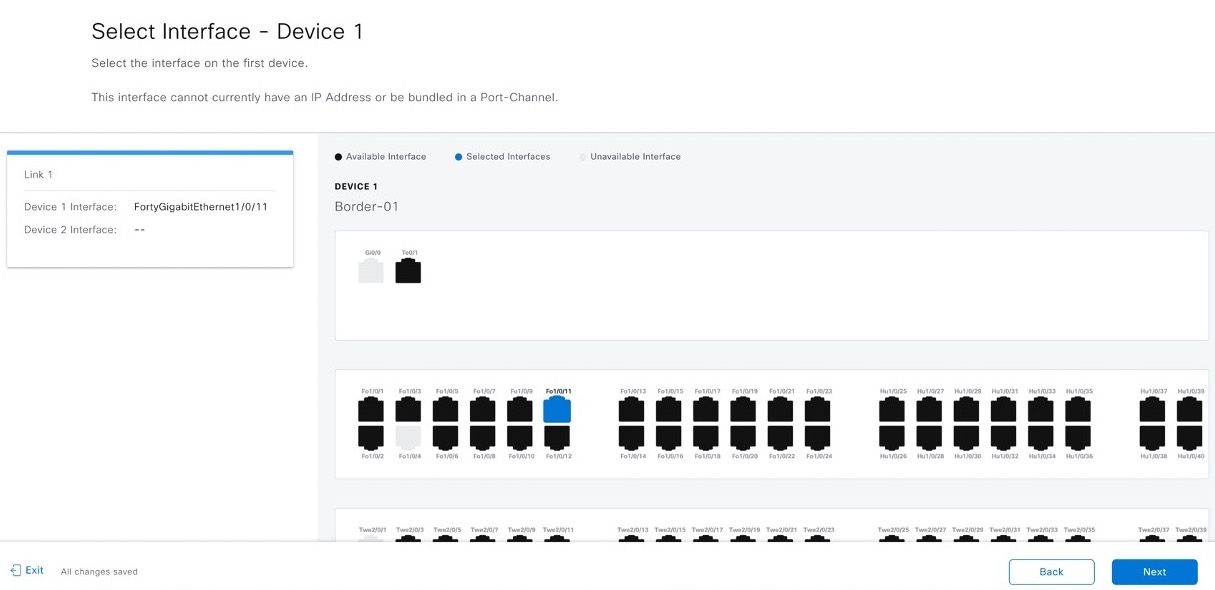
Interface selection
The interfaces on the primary seed device are used for new device discovery and Layer 3 configuration. The interfaces on seed devices provide a filter to directly connect PnP agents that can be onboarded through the LAN automation session. For example, consider four directly connected PnP agents: device 1 is connected through Gig1/0/10, device 2 through Gig 1/0/11, device 3 through Gig 1/0/12, and device 4 through Gig 1/0/13. If you choose Gig 1/0/11 and Gig 1/0/12 as discovery interfaces, LAN automation discovers only device 1 and device 2. If device 3 and device 4 try to initiate the PnP flow, LAN automation filters them because they connect through unselected interface. You can use this mechanism to restrict the discovery process.
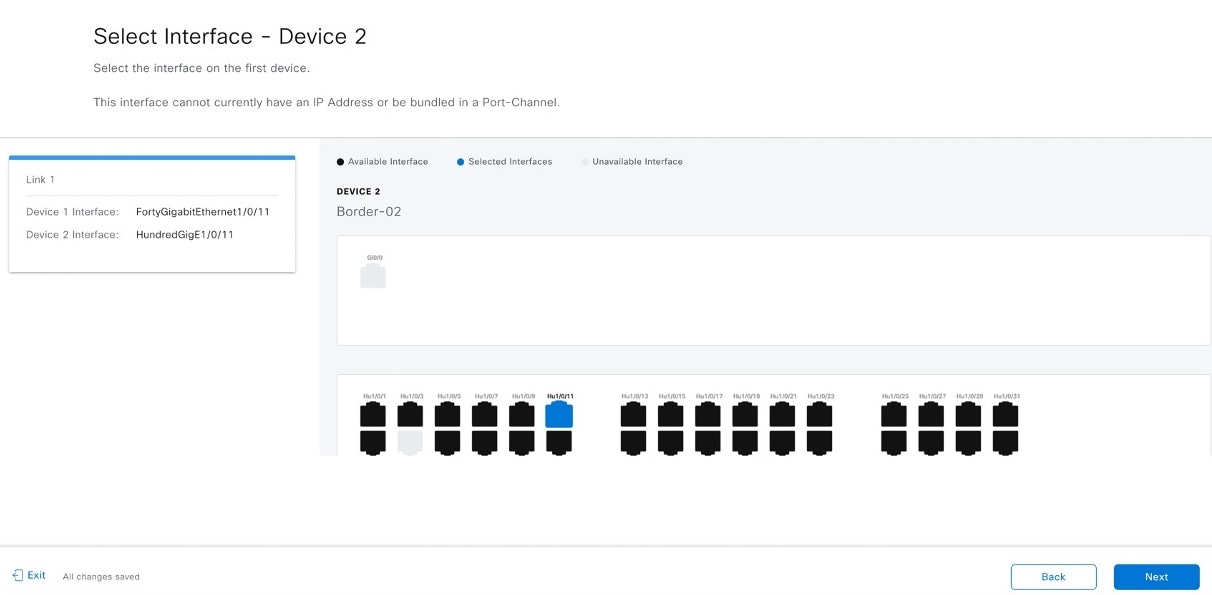
You can also choose interfaces between the primary seed and the peer seed to configure with Layer 3 links. If there are multiple interfaces between the primary and peer seeds, you can choose to configure any set of these interfaces with Layer 3 links. If no interfaces are chosen, they aren't configured with Layer 3 links.
The option to choose a peer seed interface is not available. Interfaces between peer seed and PnP agents are automatically identified based on the topology information gathered from the device. The topology information is derived from the CDP data available on the device.
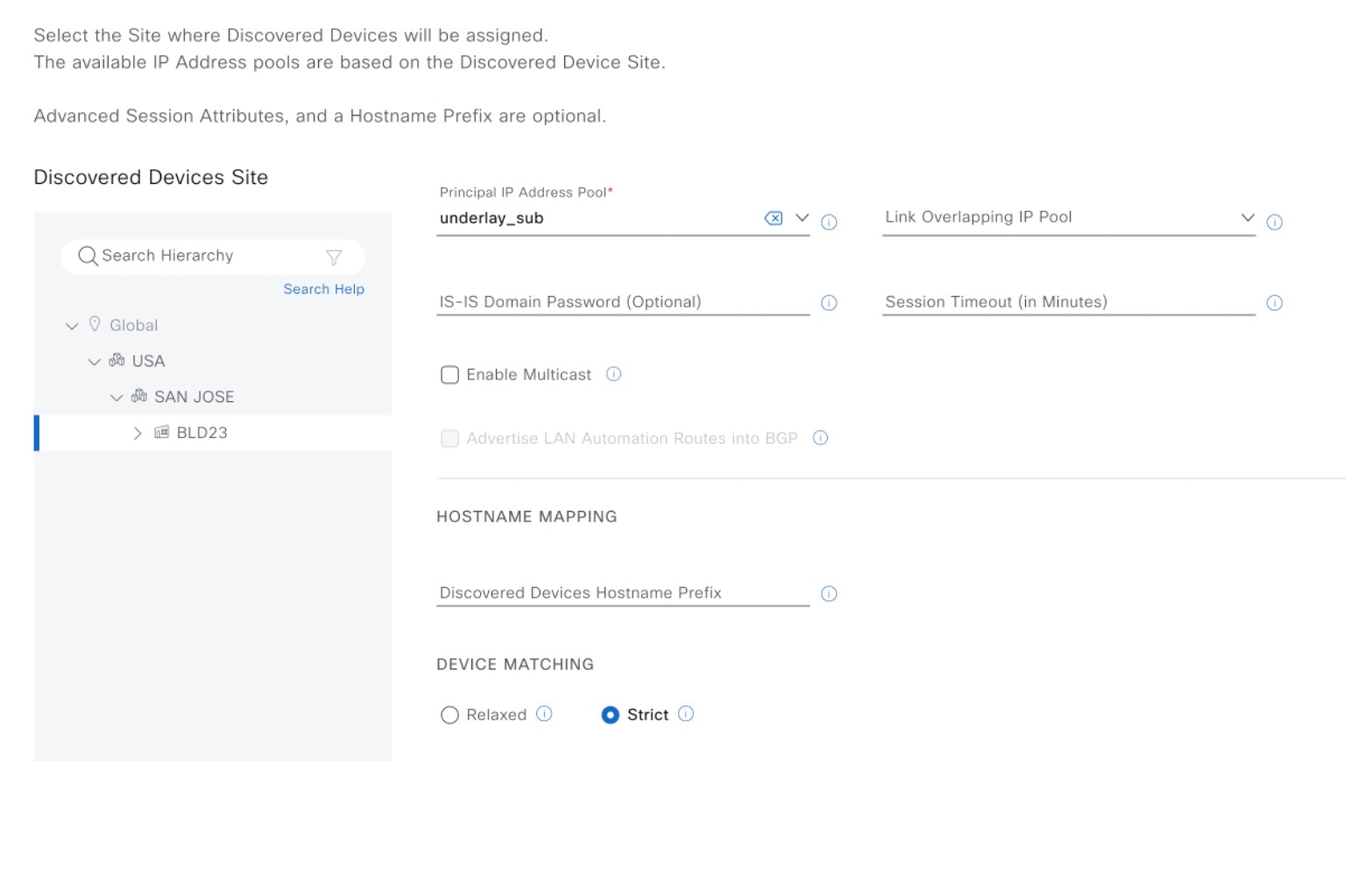
Site selection
You can select sites for both seed devices and PnP agents. Currently, one site is designated for seed devices and one site for PnP agents.
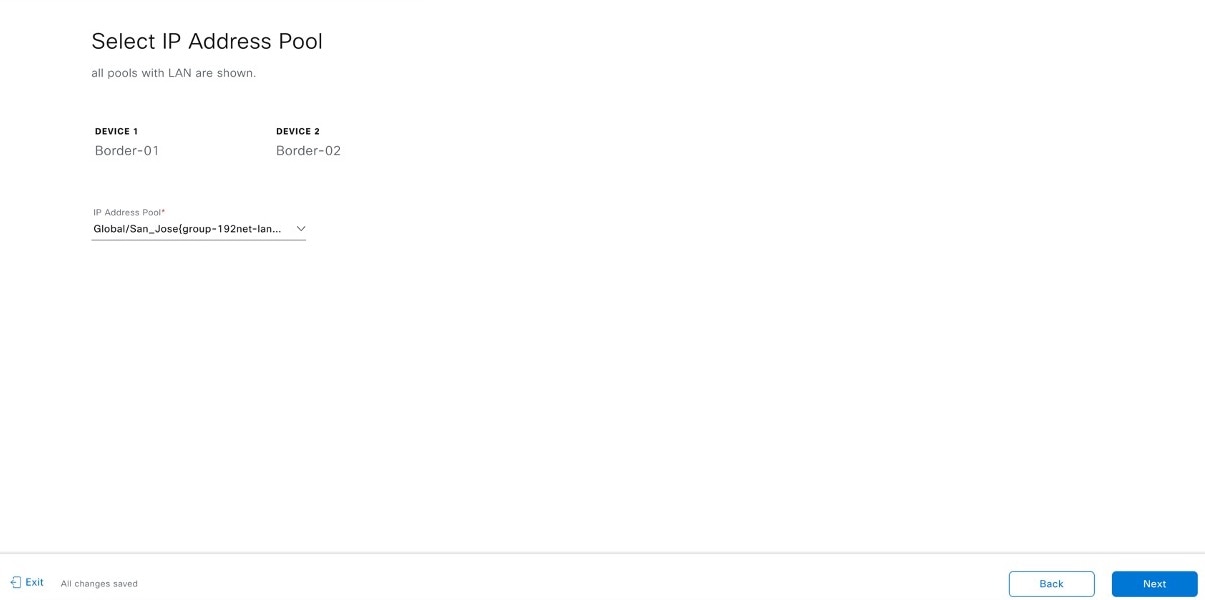
LAN pool selection
The LAN pool is selected based on PnP agent site information. To start LAN automation, select a LAN pool from the list of pools available for a particular site. You can reuse the same LAN pool for multiple LAN automation sessions. For example, you can run a discovery session to find the initial set of devices. After the session completes, you can provide the same IP pool for subsequent LAN automation sessions. Similarly, you can choose a different LAN pool for other discovery sessions. Make sure the LAN pool you select has enough capacity.
IS-IS password
-
If you enter a password, make sure it matches the password configured on the seed. If the entered value does not match the password on the primary and peer seeds, an error is returned.
-
If the password on the primary and peer seeds does not match, an error is returned.
If you enter a value in the IS-IS Password field:
-
If the primary seed has an IS-IS password configured, LAN automation configures the primary seed's IS-IS password on the PnP devices (and on the peer seed, if it doesn't already have the password).
-
If the primary seed doesn't have an IS-IS password but the peer does, LAN automation configures the peer seed's IS-IS password on the PnP devices and on the primary seed.
-
If the primary and peer seeds don't have an IS-IS password configured and you enter a value in the password field, LAN automation configures the user-entered password on the PnP devices and on the primary and peer seeds.
If you leave the IS-IS Password field blank:
-
If the primary seed has an IS-IS password configured, LAN automation configures the primary seed's IS-IS password on the PnP devices (and on the peer seed, if it doesn't already have the password).
-
If the primary seed doesn't have an IS-IS password but the peer does, LAN automation configures the peer seed's IS-IS password on the PnP devices and on the primary seed.
-
If the primary and peer seeds don't have an IS-IS password configured, LAN automation uses the default value "cisco" for the PnP devices and for both seeds.
Hostname mapping
-
Default: If no value is entered, LAN automation sets the hostname as Switch, followed by the loopback address. Example: Switch-192-168-199-100.
-
Device Name Prefix: The device prefix is used to generate hostnames for discovered devices. LAN automation maintains the site counter and generates the name using the prefix and the current site counter. For example, if the device prefix is Building-23-First-Floor, LAN automation generates device names such as Building-23-First-Floor-1, and Building-23-First-Floor-2.
-
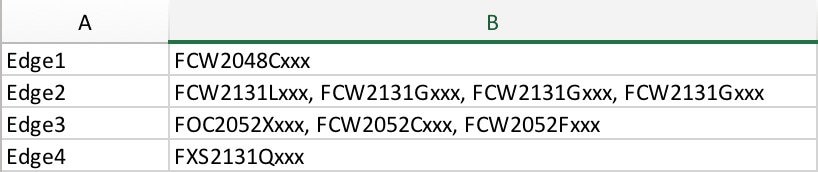
Hostname Map File Format: Catalyst Center expects a CSV file with the hostname and serial number (hostname,serial number) as shown in the example. For stack LAN automation, the CSV file lets you enter one hostname and multiple serial numbers per row. Use commas to separate serial numbers.

Note
If both a device name prefix and a hostname map file are used, the hostname map file takes precedence, and the device name prefix is not used.
Start LAN automation
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Catalyst Center GUI, click the menu icon and choose . |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
In the Inventory window, choose . |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
Enter the required details and click Start. For more information on the attributes, see Configuring LAN automation attributes. 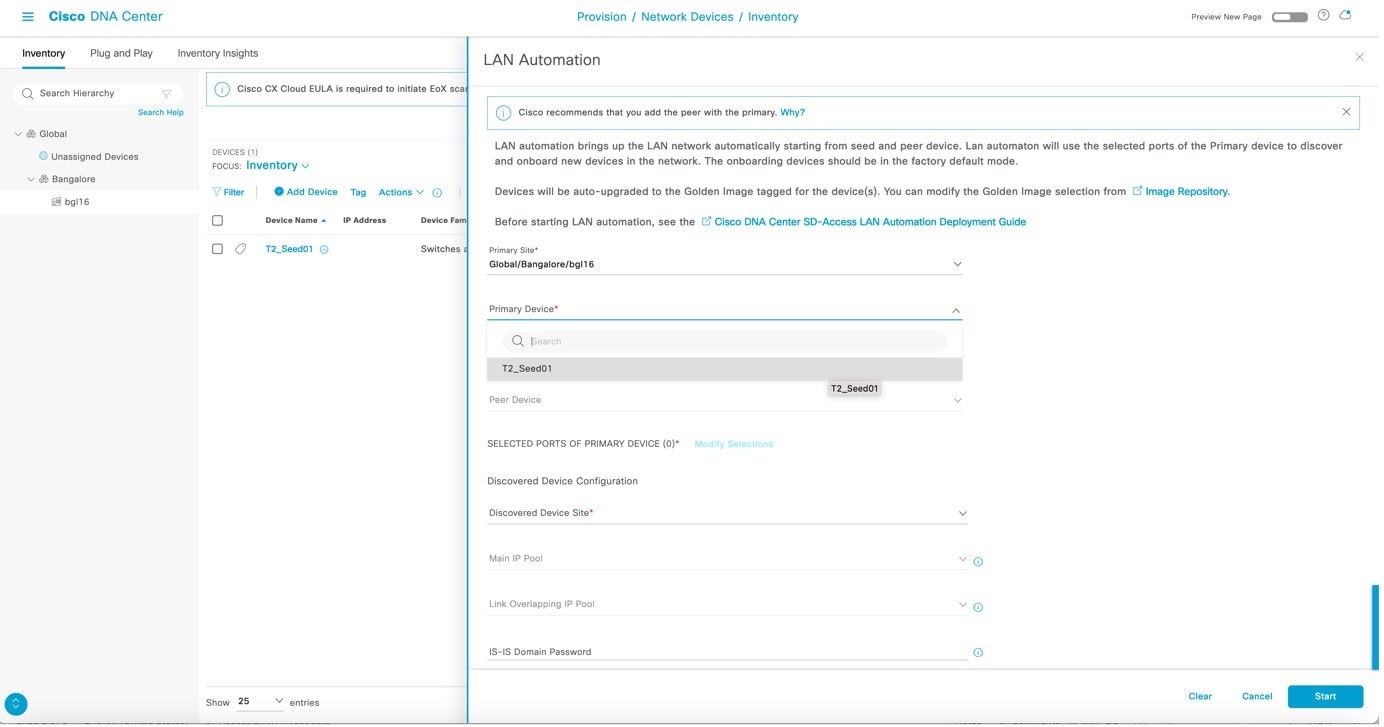
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
After LAN automation starts, click LAN Automation Status to monitor the progress. 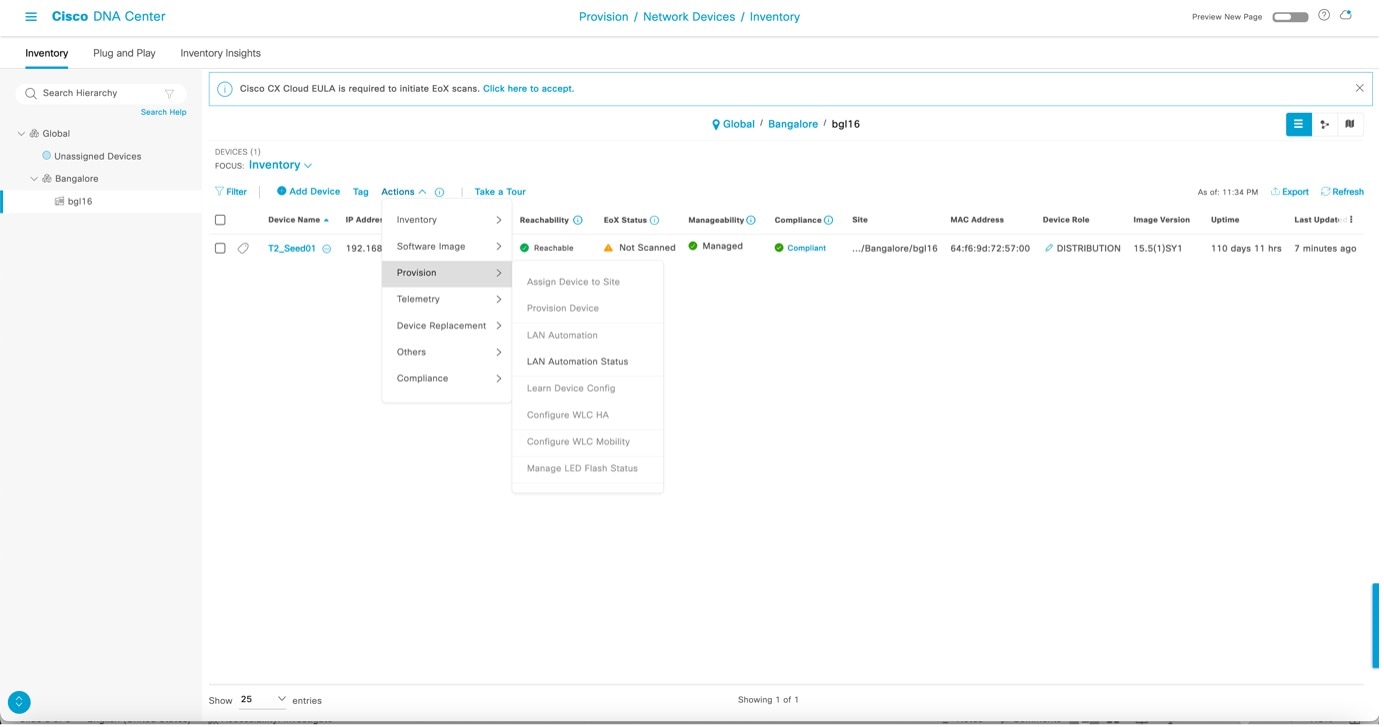
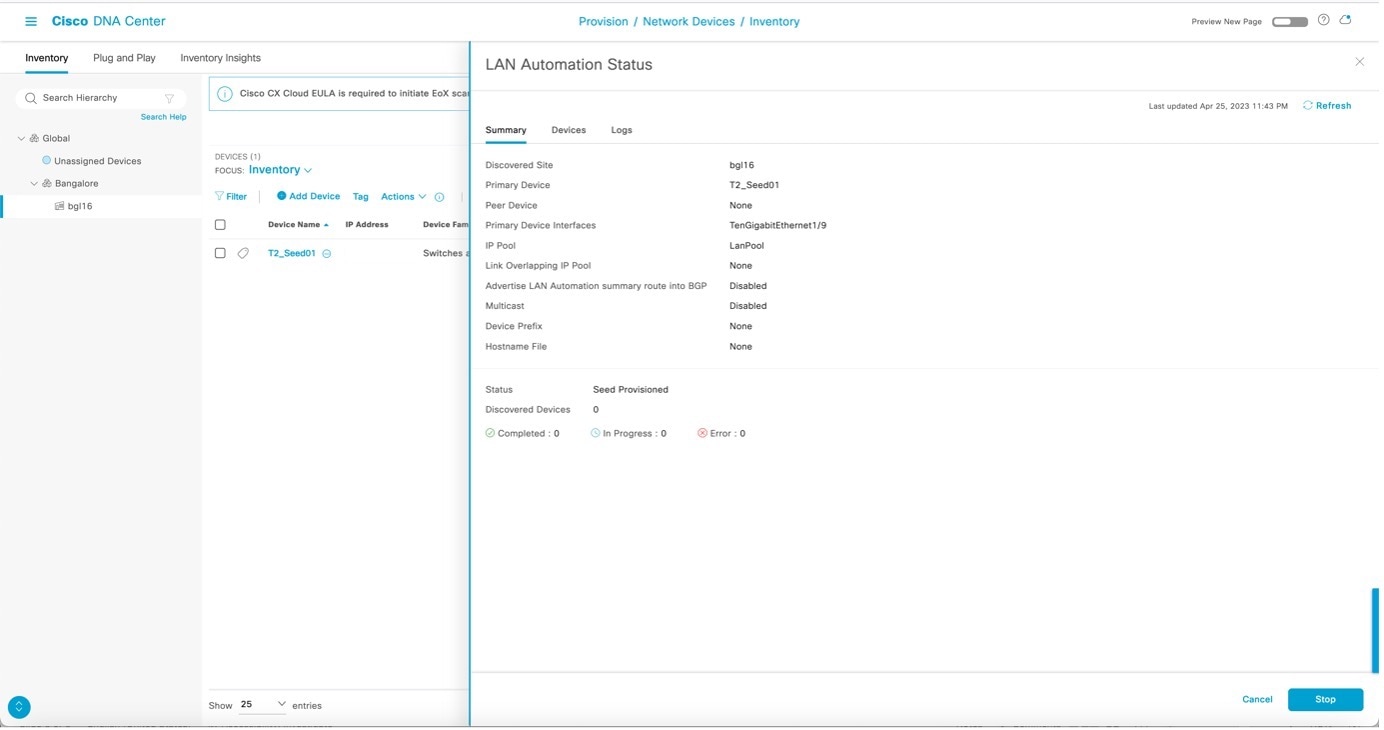
Sample configuration for seed devices
After LAN automation starts, the loopback and IS-IS configuration is pushed to the seed devices. This table lists sample configurations for the primary seed device.
This table lists sample configurations for the secondary seed device.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
After device discovery starts, view the logs on the PnP agent.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
After the device is discovered, Catalyst Center checks if a golden image is marked for the switch family of the discovered device. If a golden image is marked and the discovered device is not running it, LAN automation first upgrades the discovered device to the golden image. If not, Catalyst Center skips the image upgrade and pushes the initial device configuration. Sample logs for image upgrade: Catalyst Center pushes part of the configuration, allowing the devices to be onboarded and managed by Catalyst Center. In the LAN Automation Status window,
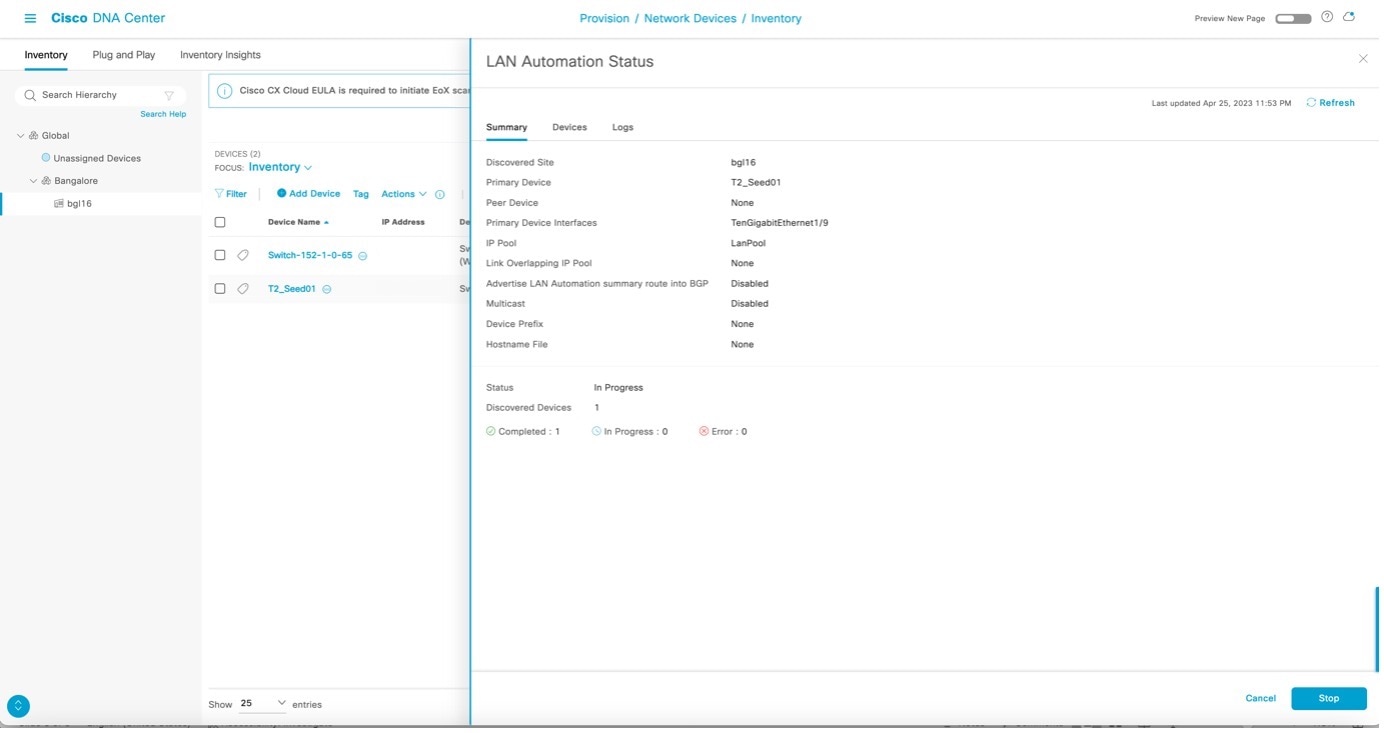
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
View the logs on the PnP agent, as shown in the example. It is safe to press return on the console if you want to. When you press return, the hostname changes to the value entered in the Hostname Mapping field when you started LAN automation. After all devices are discovered, the Discovered Devices status changes to Completed and the discovered devices are added to the inventory.
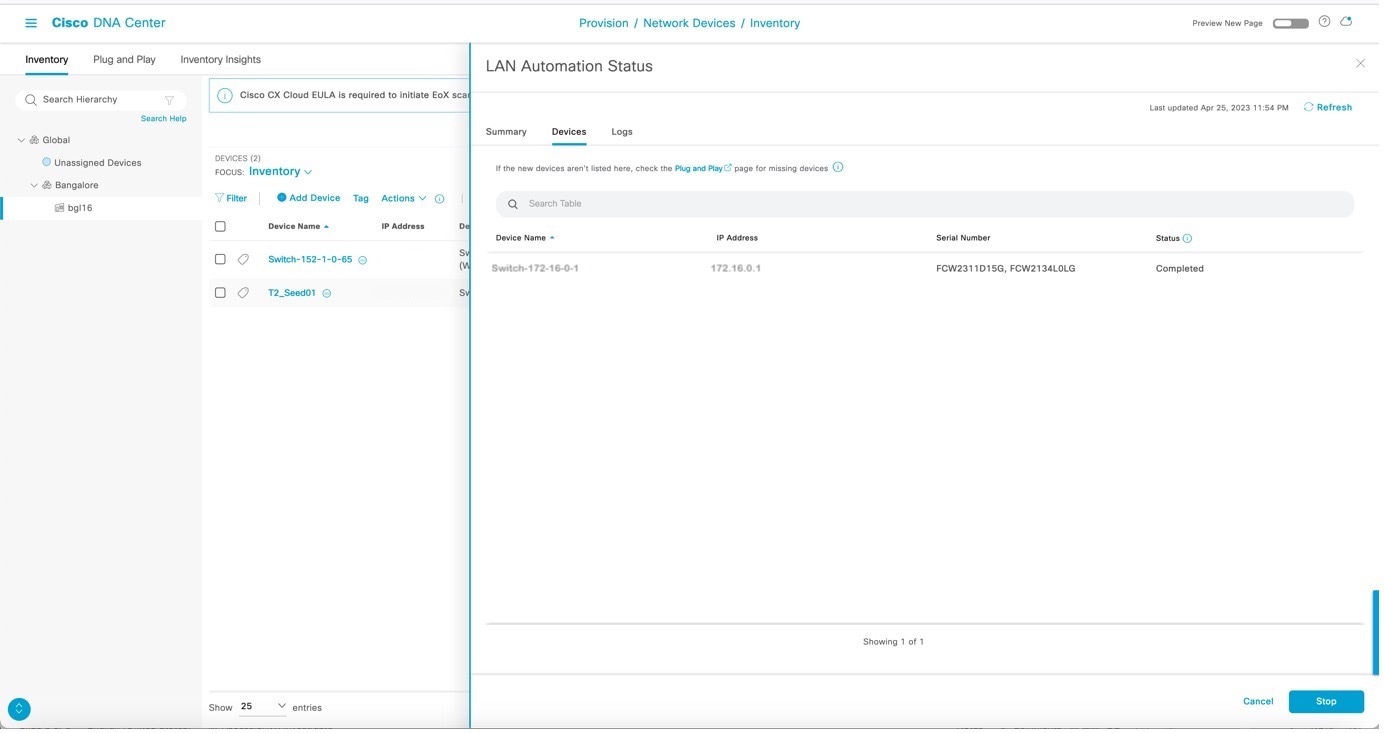
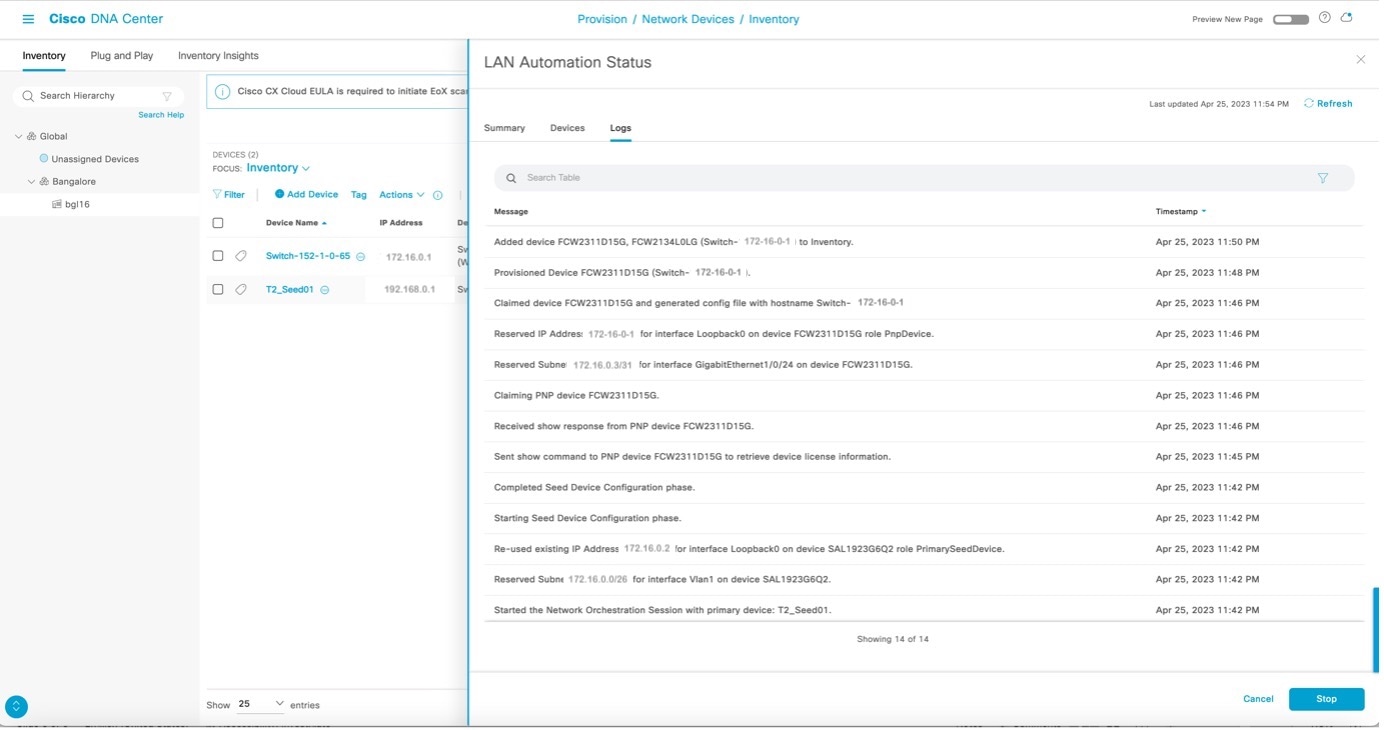
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
From the Catalyst Center home page, click the menu icon and choose and filter the devices by serial number. The newly discovered switches appear as Managed. The example shows a sample configuration pushed to the discovered devices.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
After the Discovered Devices status changes to Completed and all discovered devices are displayed in the inventory as Managed, you can stop LAN automation. However, before stopping LAN automation, check the Topology page to make sure that the links between the discovered device and primary and peer seed are displayed. Choose and click the physical links between the seed and discovered device. Make sure that the interfaces are correct. If the physical links are not visible, resynchronize the seed device where the physical links connect. After resynchronization, check the Topology window again to make sure that the links are visible before stopping LAN automation. |
Stop LAN automation
Stop LAN automation to finish discovering required devices and to prevent inadvertent discovery of additional devices.
When LAN automation stops, these actions occur:
-
The remainder of the configuration is pushed to network devices, which includes converting the point-to-point links from Layer 2 to Layer 3.
-
The configuration for VLAN 1 is removed, and the IP addresses for VLAN 1 are returned to the LAN automation pool.
-
The device is onboarded in Catalyst Center and assigned to the site.
Stop LAN automation process
-
In the LAN Automation Status window, click Stop.
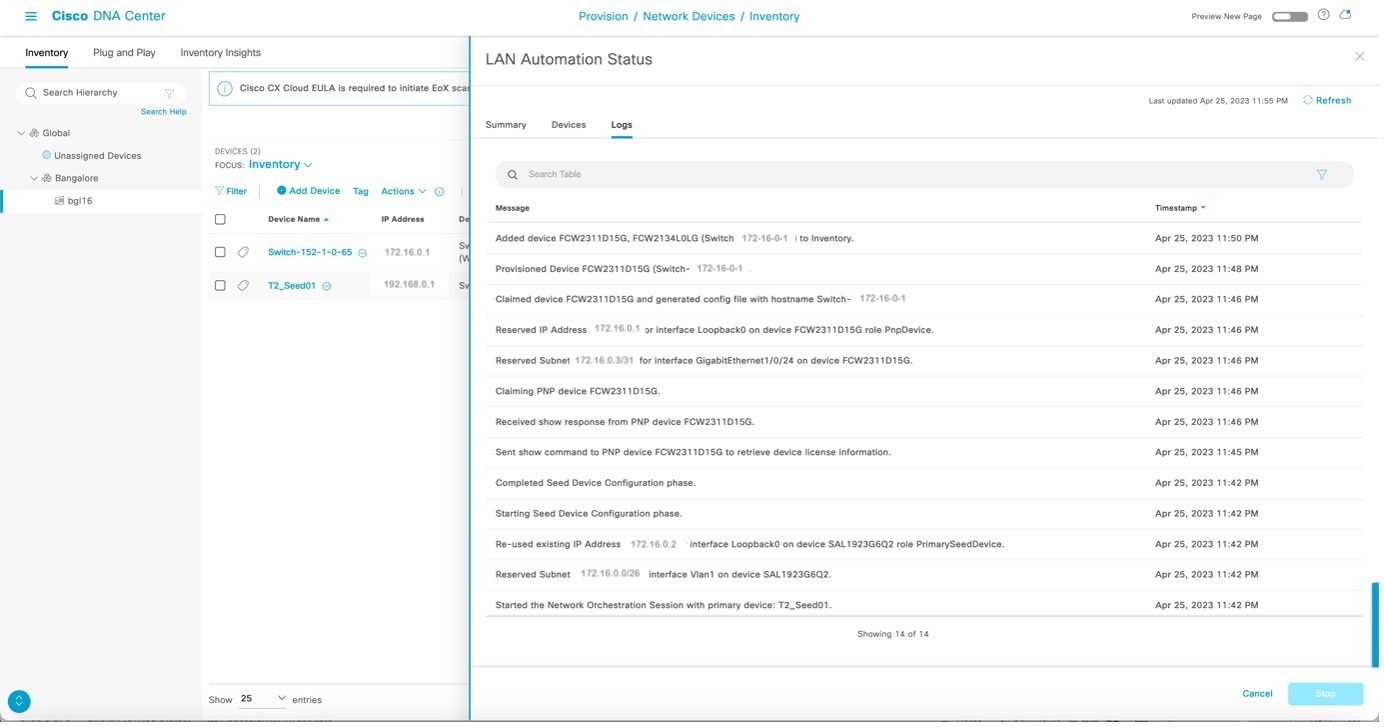
-
After the LAN automation stop process starts, the LAN Automation Status changes to STOP in Progress.
-
The network orchestration service issues a synchronization operation (RESYNC) for seed and PnP devices to retrieve the state of all links. After the initial RESYNC completes, the service pushes the Layer 3 configuration on all Layer 2 links. It then reissues RESYNC to resynchronize the cluster's link state.
The Layer 3 link configuration is pushed when network orchestration stops. Each interface pair receives its configuration.
For example, here is a sample configuration:
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13 description Fabric Physical Link no switchport dampening ip address 192.168.2.97 255.255.255.252 ip router isis logging event link-status load-interval 30 bfd interval 500 min_rx 50 multiplier 3 no bfd echo isis network point-to-point -
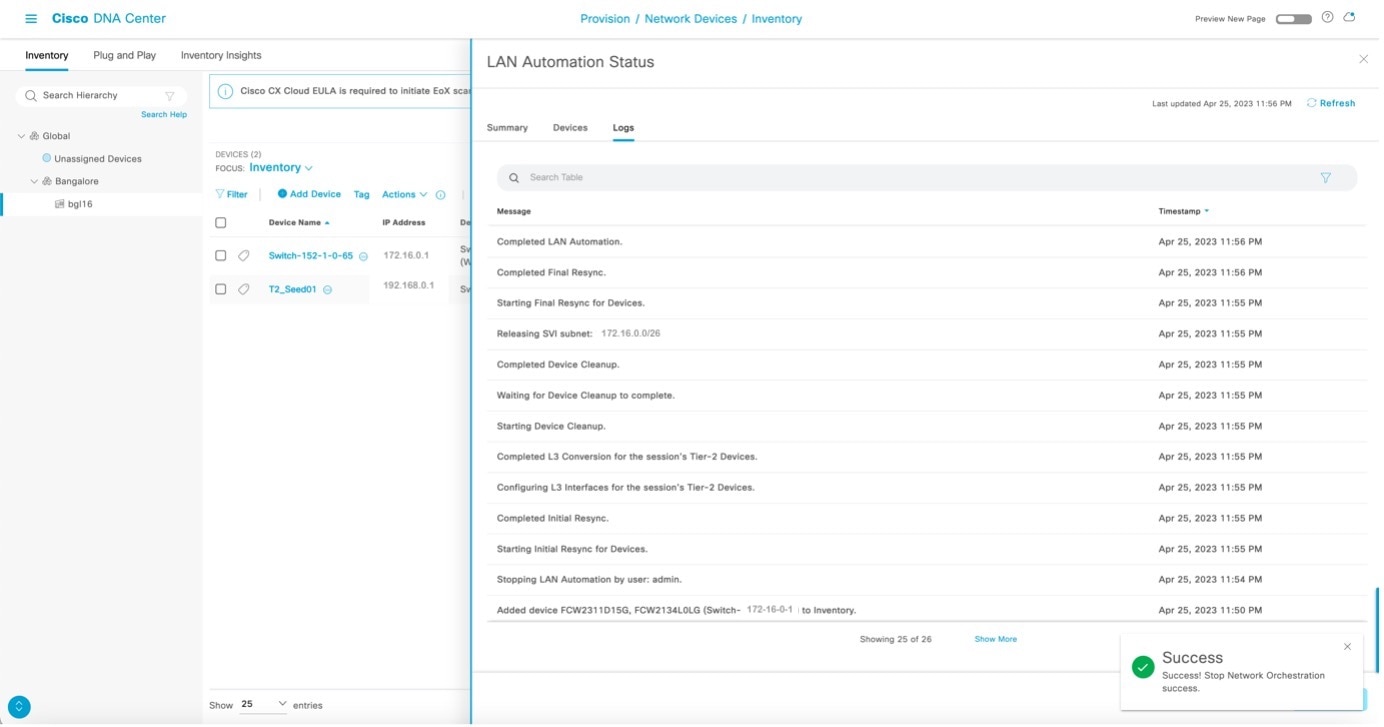
After all the point-to-point links between the seeds and discovered devices, including links between peer seed and discovered devices, are configured, the devices are added to the site and synced to Catalyst Center.
-
The LAN automation process completes and the LAN Automation Status changes to Completed.
-
Check the LAN automation logs to verify the status.
Add switches and links to an existing LAN-automated stack
This section describes how to add a new switch, add an existing switch, or configure a link in a LAN-automated stack.
Add a new switch
This section explains how to add a brand new switch that has never been present in Catalyst Center.
You can add switches to a stack that is already LAN automated and in a provisioned state without LAN automating or discovering the new switch.
Before you begin
Ensure that these conditions are met:
-
The switch is not discovered and not present in the Catalyst Center inventory.
-
The switch has the same image and license version as the provisioned standalone or stack. Verify the image and license version by using the
show verandshow license right-to-usecommands. -
The switch is in the same boot mode as the stack: INSTALL (preferred) or BUNDLE mode.
Sample configuration to verify the boot mode:
9300_Edge_1#show ver | inc INSTALL * 1 62 C9300-48U 16.6.3 CAT9K_IOSXE INSTALL 2 62 C9300-48U 16.6.3 CAT9K_IOSXE INSTALL 3 62 C9300-48U 16.6.3 CAT9K_IOSXE INSTALL 4 62 C9300-48U 16.6.3 CAT9K_IOSXE INSTALL
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Use the stack cable to connect the new switch to the stack, and then power it on. After two to three minutes, the new switch is added to the stack as a standby if one switch is already present in the stack, or as a member if two or more switches are present. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Use the commands |
||
|
Step 3 |
After adding the switch to the stack, open the Catalyst Center Inventory, choose the original provisioned switch or stack, and resynchronize. |
||
|
Step 4 |
After the synchronization completes, the new serial number is displayed in the inventory. This completes the addition process.
This image displays the serial number before adding the new switch. 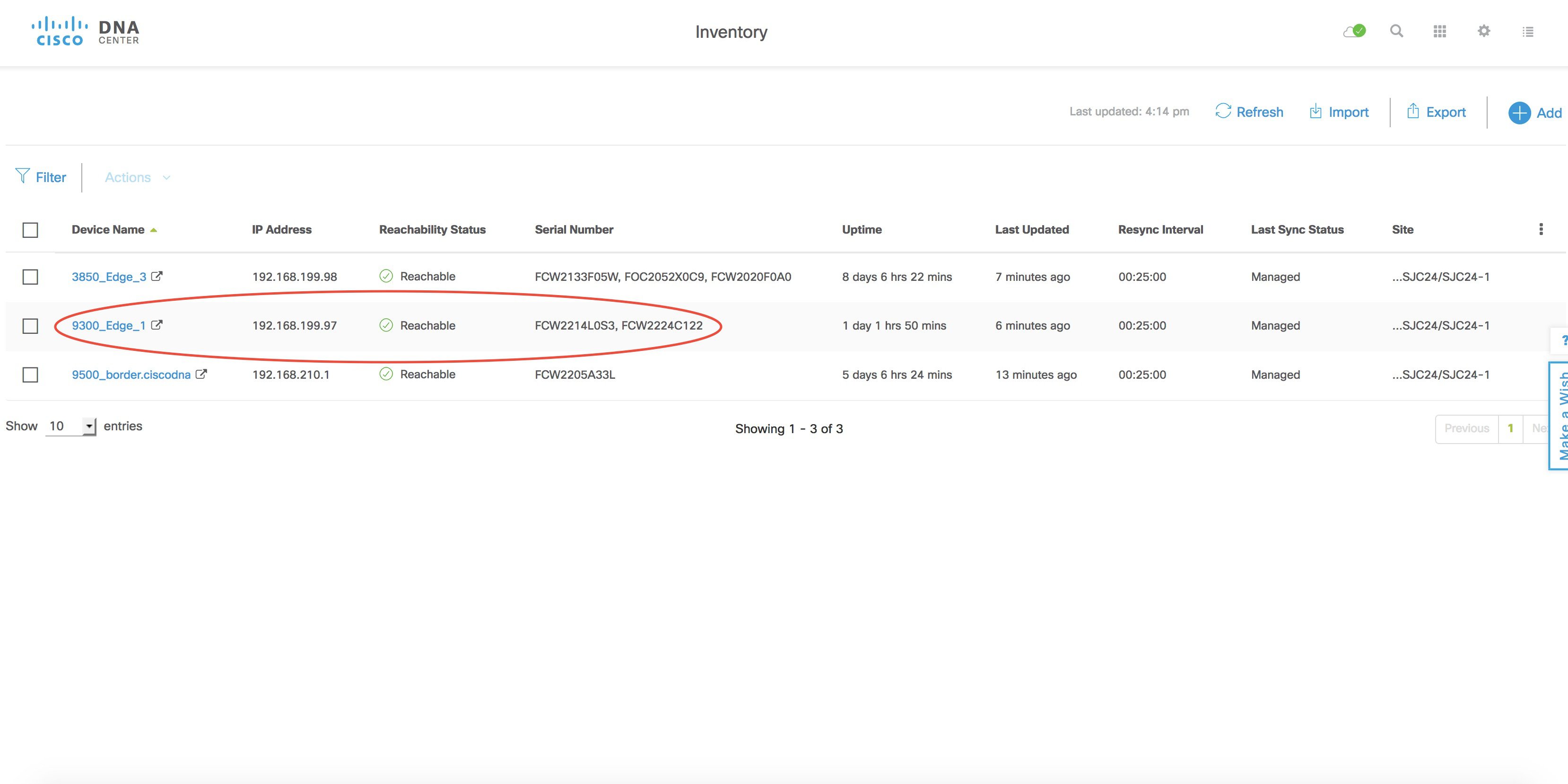
This image displays the serial number after adding the new switch. 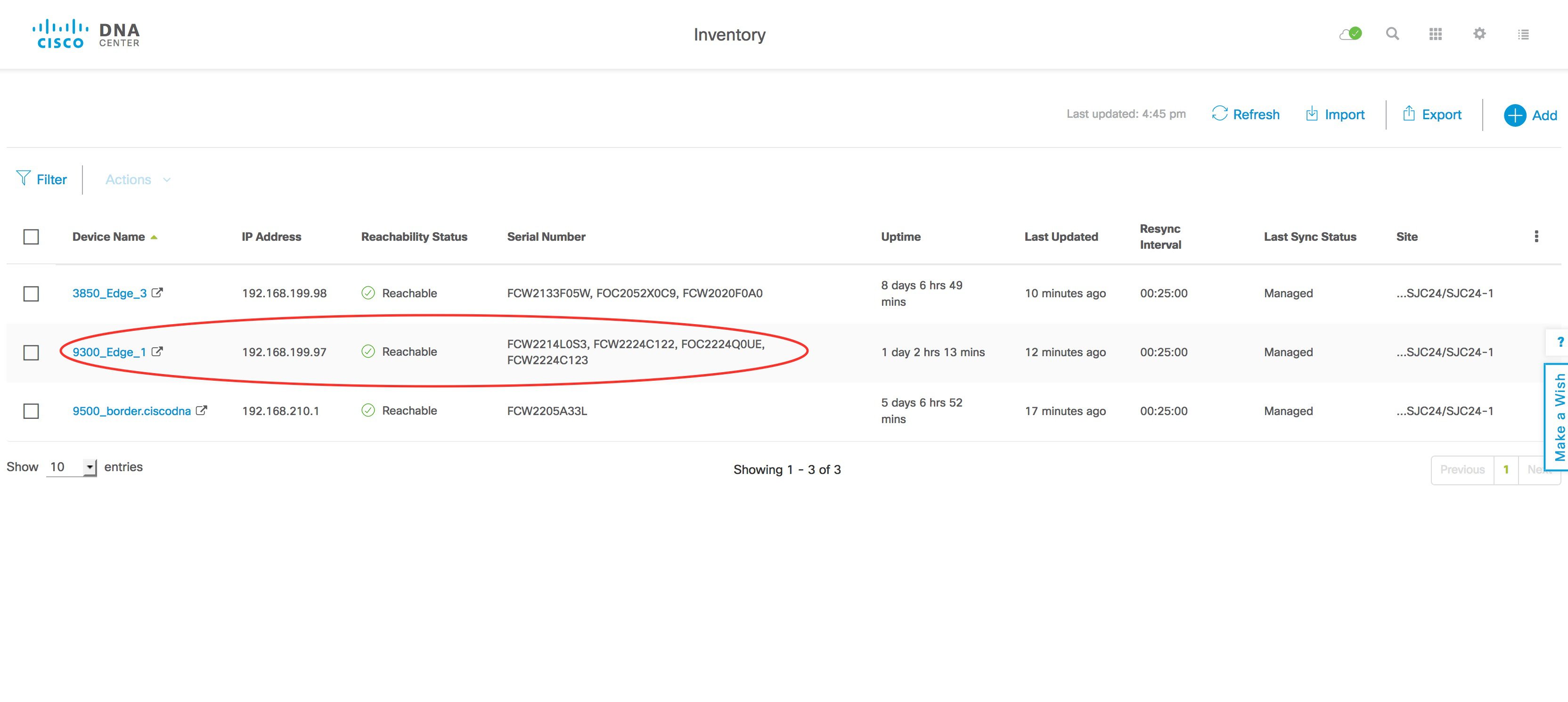
|
Add an existing switch
This section shows how to add an existing switch that was already present in Catalyst Center.
If the switch was previously LAN-automated, either as part of another stack or as a standalone device, or was discovered by PnP, remove the switch physically before adding it. Next, remove its entry from the inventory, and from the PnP application or database
Remove the switch from inventory
|
If the switch is... |
Then... |
|---|---|
|
standalone |
|
|
part of a stack |
|
Remove the switch from PnP
|
If the switch is... |
Then... |
|---|---|
|
standalone |
|
|
part of a stack |
|
Configure additional links after LAN automation stops
Use this procedure to configure
-
additional links between the primary and peer seed devices or between distribution devices after LAN automation stops, and
-
uplinks from the newly added stack switch to the primary and peer seed devices.
If you chose the Enable Multicast option the first time LAN automation ran on the device, do not choose Enable Multicast when you configure additional links.
Follow these steps to configure the Layer 3 links using LAN automation. When LAN automation stops, go to the newly configured Layer 3 ports and manually configure ip pim sparse-mode under the interface.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Run the show cdp neighbors command to ensure that the neighbor connected to the new link is displayed. For example, a new link connects the Ten 4/1/5 port on switch 9300_Edge-7 to the For 1/0/1 port on switch 9500_border-6 as shown in this sample configuration. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Ensure that both ports to which the link is connected (Ten 4/1/5 and For 1/0/1) do not have any Layer 3 configurations on them. If Layer 3 configurations exist, use the default interfaces for the new uplink and resynchronize both devices. |
||
|
Step 3 |
From the Catalyst Center home page, choose . |
||
|
Step 4 |
In the Primary Device field, enter the switch (for example, 9500_border-6) to which the new link is connected. |
||
|
Step 5 |
In the Peer Device field, enter the switch (for example, 9300_Edge-7) where you want to configure the new link. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Select the port on the primary device where the uplink connects; that is, the port where the PnP device is connected (for example, For 1/0/1). |
||
|
Step 7 |
Use the same LAN automation pool that was used to provision the original stack. |
||
|
Step 8 |
Start LAN automation. Wait for two minutes, and then stop LAN automation. Because no new device discovery is necessary, skip the full LAN automation process. After you stop LAN automation, both ports connected to the uplink are configured with an IP address from the same LAN automation pool. |
||
|
Step 9 |
As shown in the example, after LAN automation stops and completes, both ports are configured for Layer 3 from the LAN pool.
|
Move an uplink to the newly added switch
You cannot move an uplink from a stack that is already provisioned to a newly added switch in a LAN-automated stack.
 Note |
In Catalyst Center Release 2.3.5 and later, you can move an uplink to a newly added switch using the Add Link and Delete Link workflows.
|
40-G interface on the Cisco Catalyst 9400 Series Switches
For Cisco IOS XE 16.11.1 and later, Cisco IOS enables the 40-G port on bootup if these conditions are met:
-
The switch must have its day-0, factory-default configuration. For information about how to bring a device back to its day-0 configuration, see PnP agent initial state.
-
For a single supervisor, a 10-G/1-G SFP cannot be inserted in any of the SUP ports (ports 1 to 8). A 40-G QSFP must be inserted in ports 9 or 10.
-
For a dual supervisor, a 10-G/1-G SFP cannot be inserted in any of the SUP ports (ports 1 to 8). A 40-G QSFP must be inserted in port 9 only.
Troubleshoot LAN automation
If you encounter any problems, collect the root cause analysis (RCA) file. This file helps troubleshoot the issue. Log in
to the Catalyst Center CLI and run the $ sudo rca command to generate the RCA file.
For a three-node cluster, collect the RCA file for each cluster.
Additional information: LAN automation in Catalyst Center Release 2.3.5 and later
This topic provides information on the LAN automation process based on Catalyst Center Release 2.3.5. Steps and examples may differ in later versions.
To learn more about LAN automation and related features for your Catalyst Center version, see Cisco Catalyst Center User Guide.
Provision LAN automation
Follow these steps to discover and provision devices using LAN automation.
Before you begin
This topic describes the LAN automation procedure in Catalyst Center 2.3.5 and later. Steps may vary depending on your Catalyst Center version.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
|
Step 2 |
In the LAN Automation window, click Start LAN Automation. 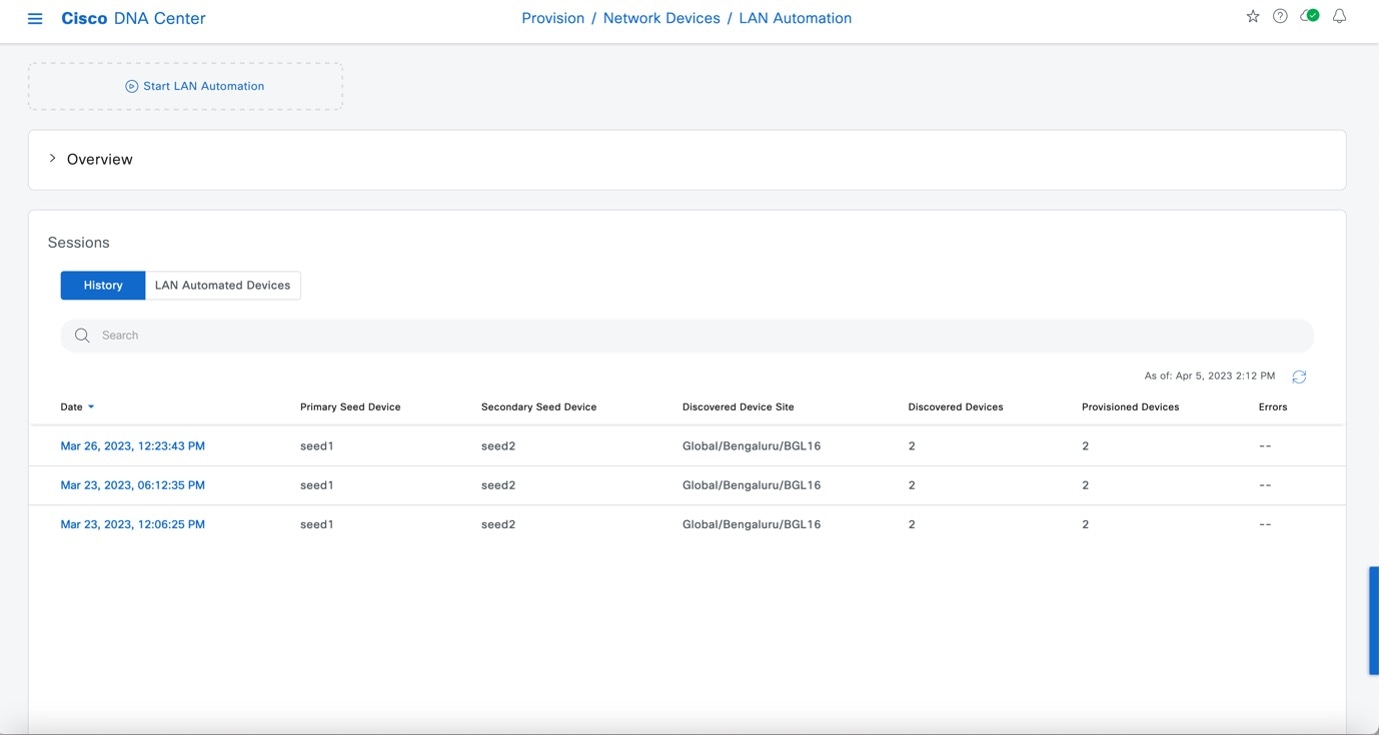
|
|
Step 3 |
Configure the Seed Devices.
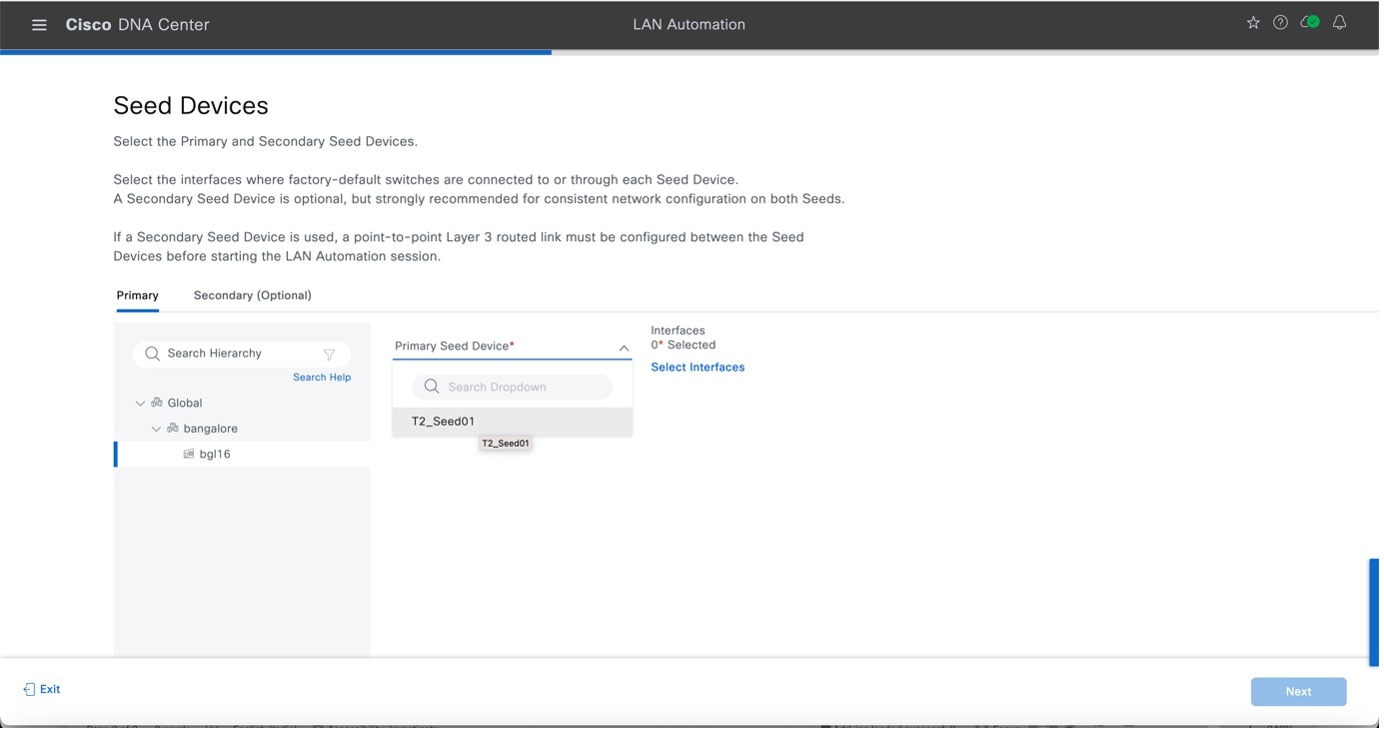
In Catalyst Center Release 2.3.7.5 and later, you can add a discovery depth level for LAN automation. Devices are LAN automated up to the specified level under the primary seed device. The default value for Discovery Depth is 2, and the maximum value is 5. Review the discovery depth in the summary window and see its value in the session details window after the LAN automation starts.
In the Select Interfaces window, choose the interfaces and click Add Selected. 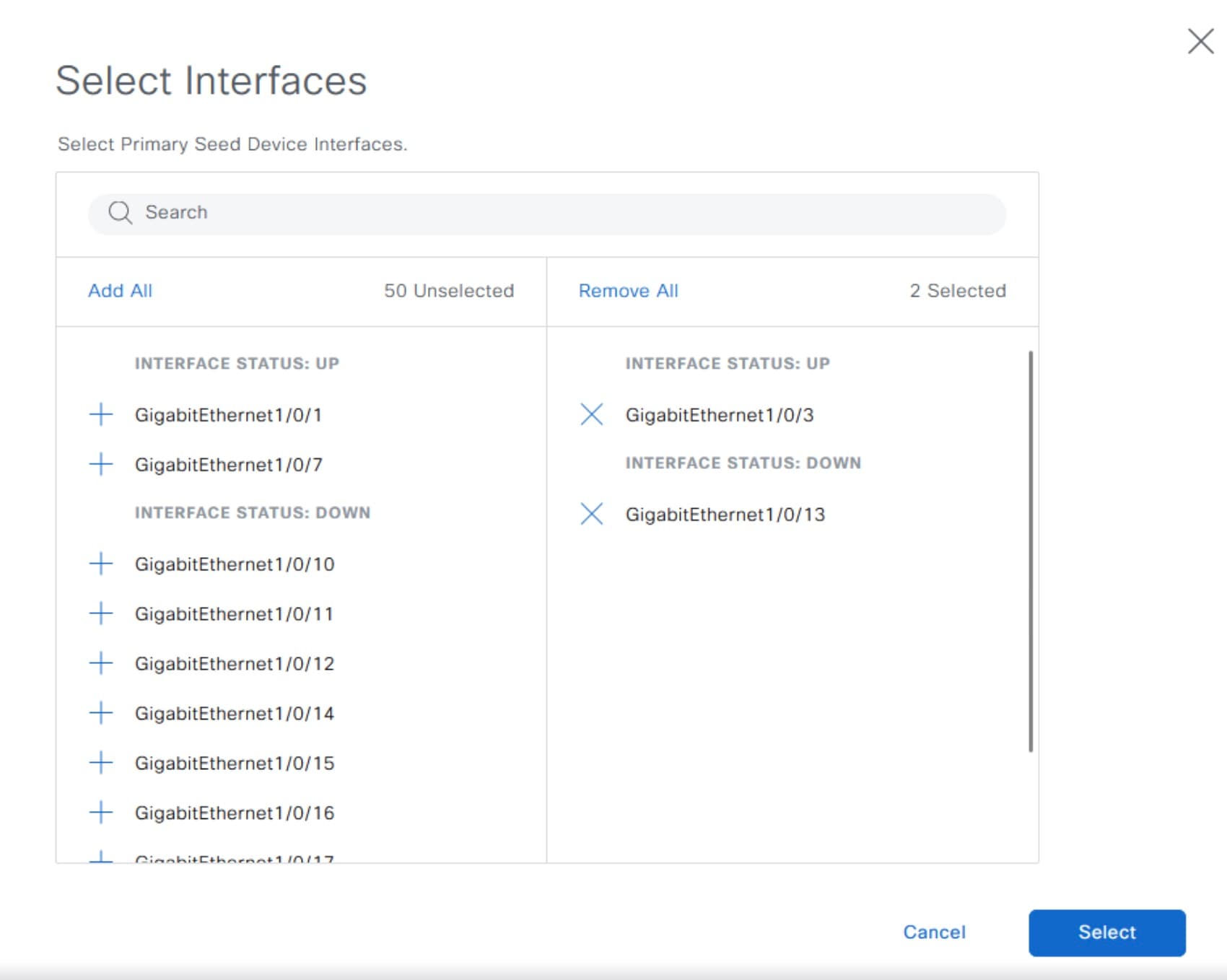
|
|
Step 4 |
In the Session Attributes window, select the Principal IP Address Pool and add the other details as required. 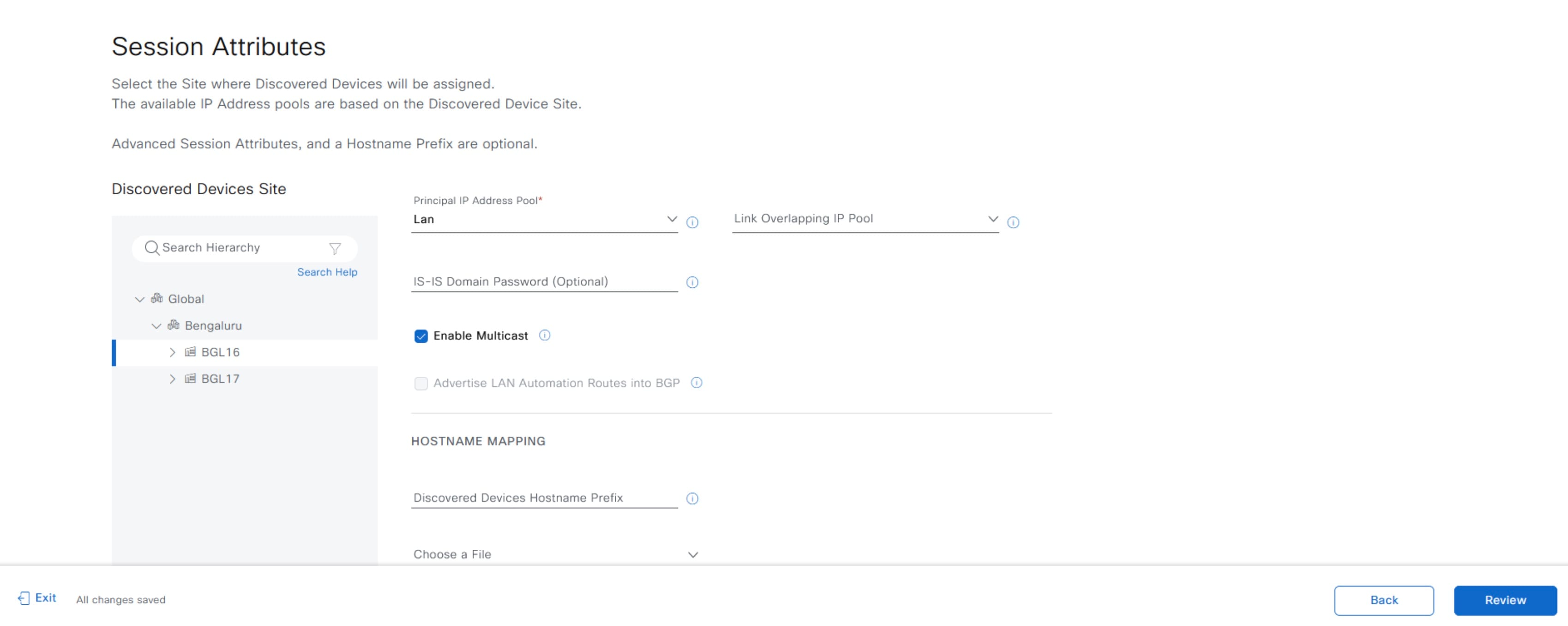
In Catalyst Center Release 2.3.7.5 and later, you can specify these additional session attributes:
You can review the session attributes in the summary window and view them in the device details window after the LAN automation is complete. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Review. |
|
Step 6 |
After reviewing the configurations, click Start to begin the LAN automation. 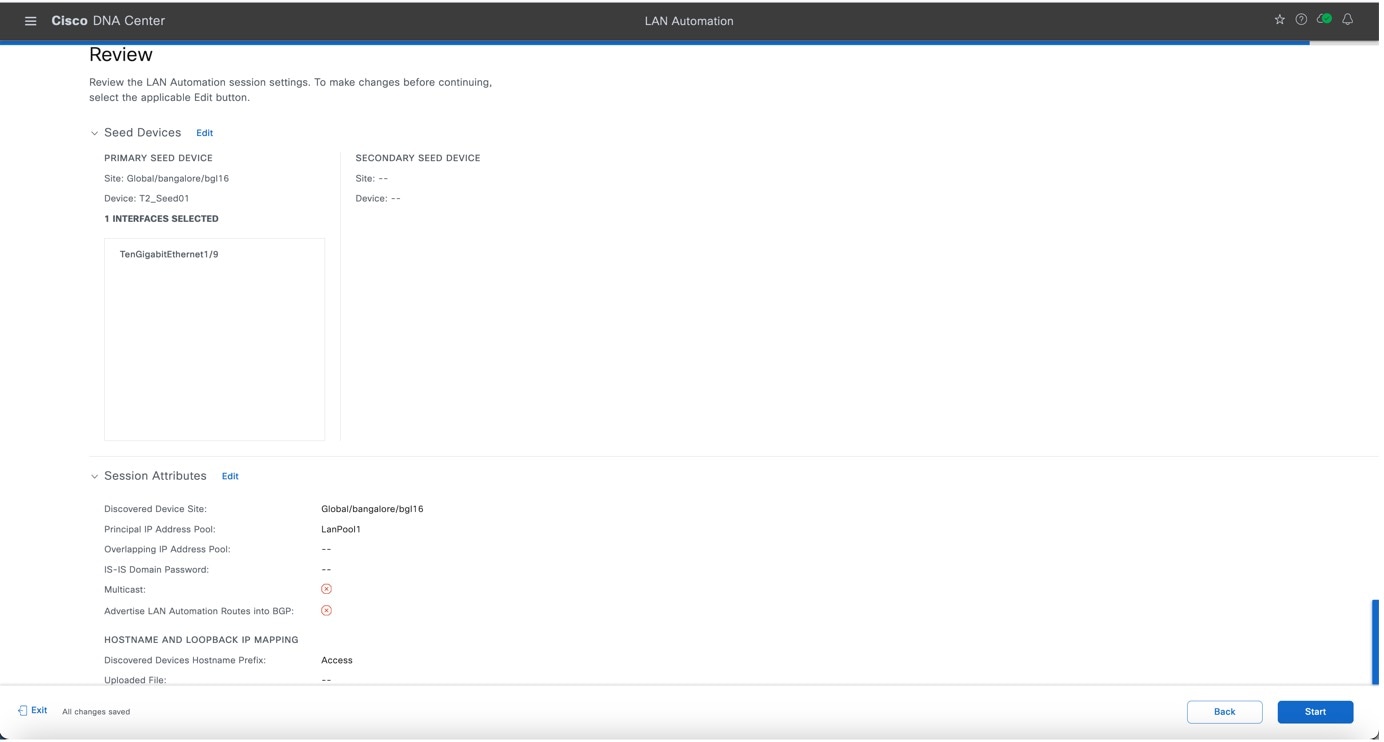
The LAN automation session is created and a tile for the session is displayed in the LAN Automation window. 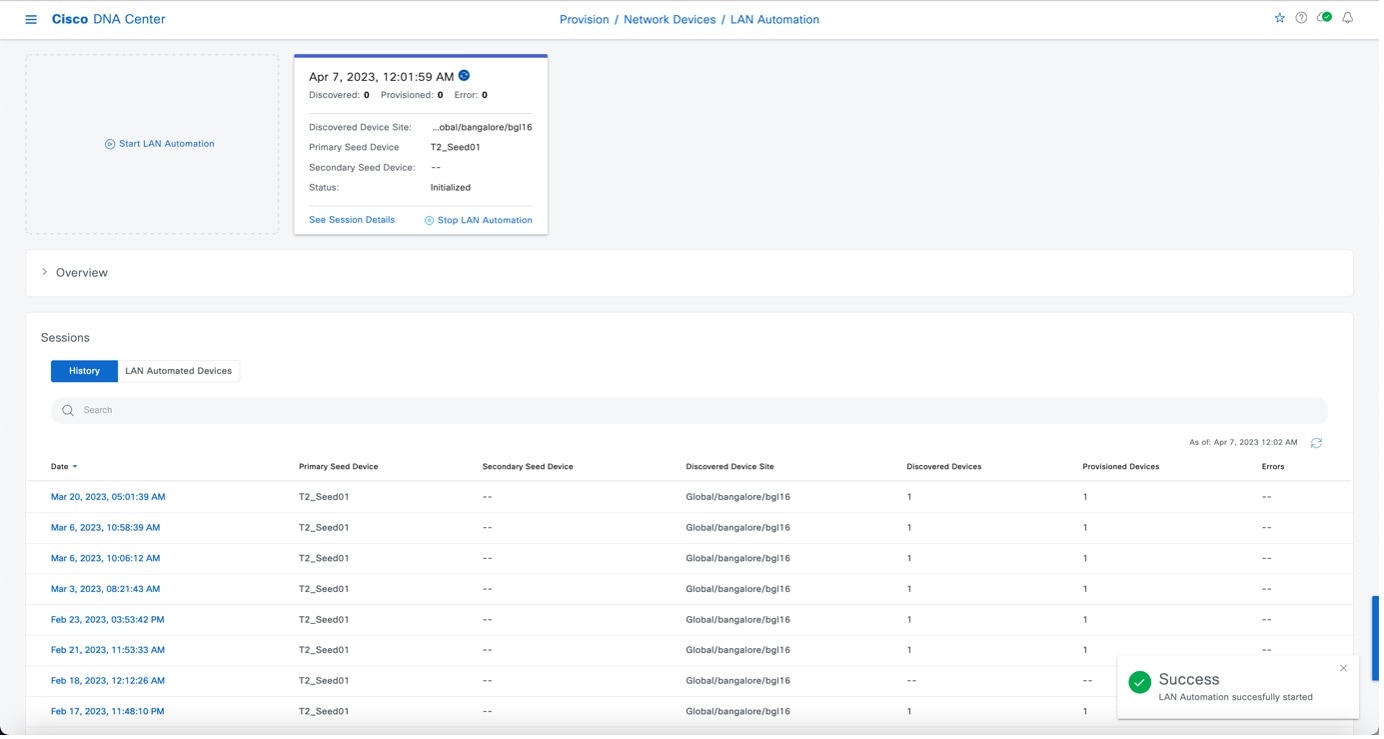
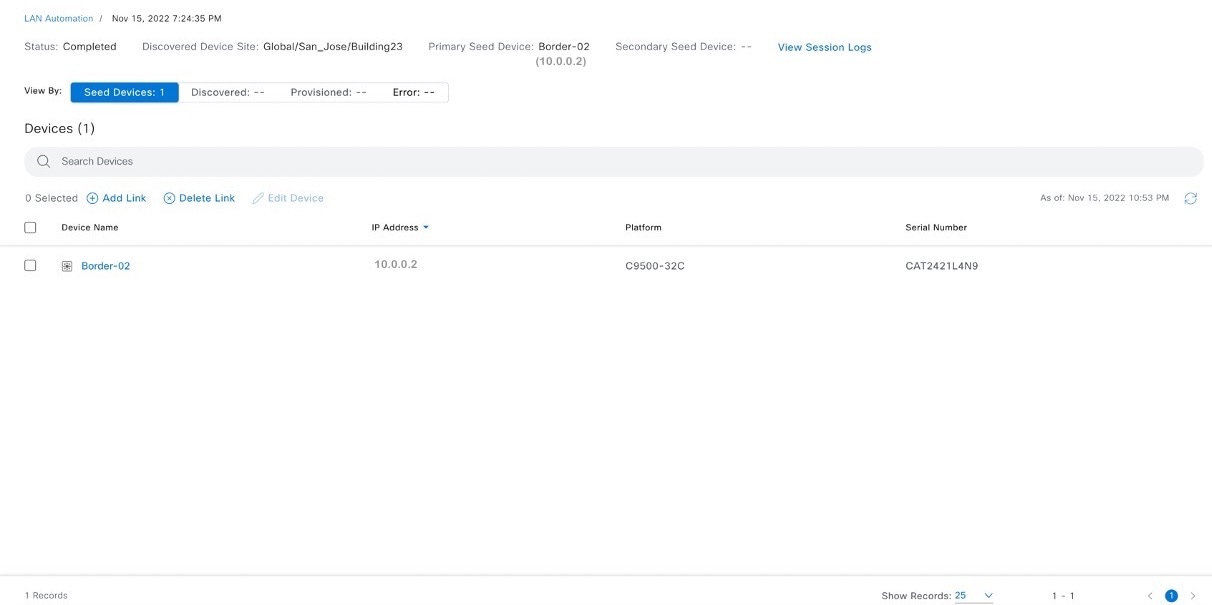
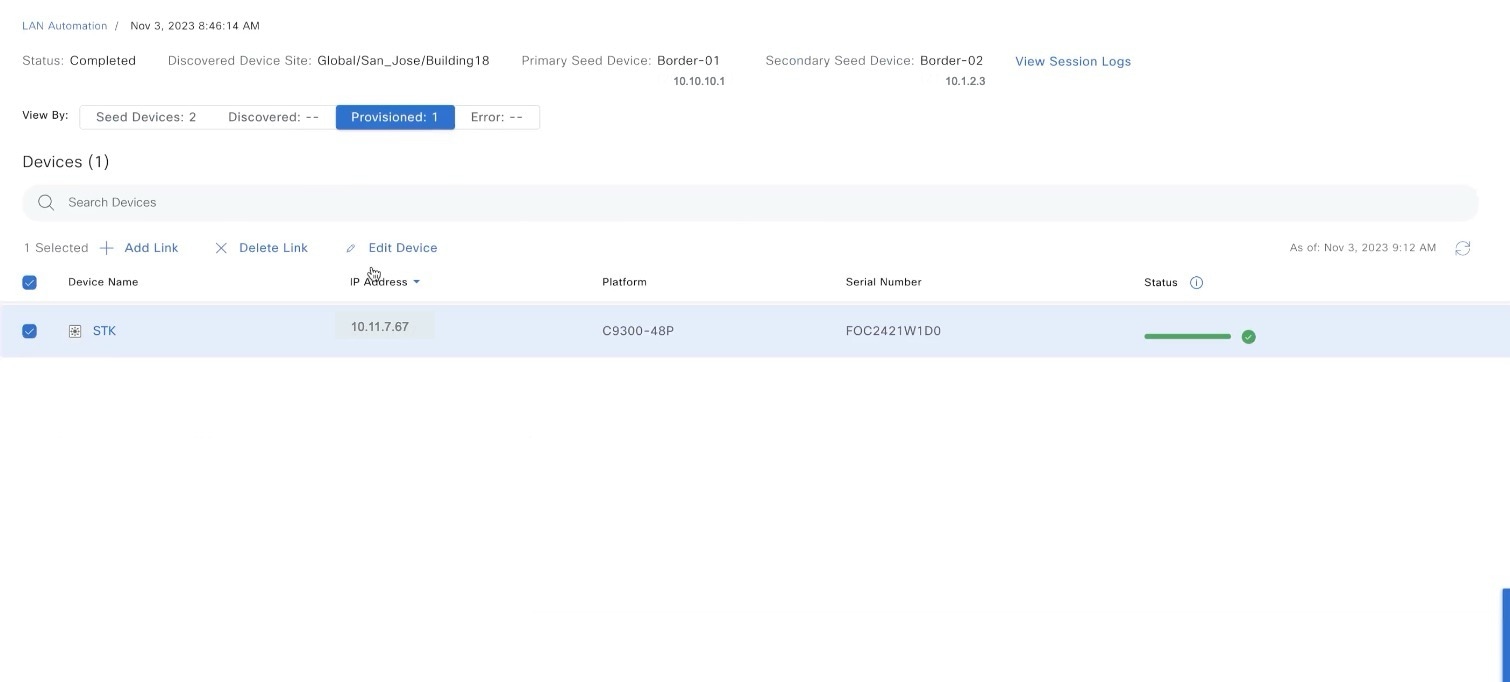
Click See Session Details in the tile to view session details. In the session details window, click View Session Logs to see session logs. The session details window shows the status of the LAN automation session and lists the devices that are in the LAN automation process. You can filter the data and see details of the seed devices, discovered devices, provisioned devices, or the error messages. Stop the LAN automation process after all devices are provisioned and the progress bar in the Status column shows complete. 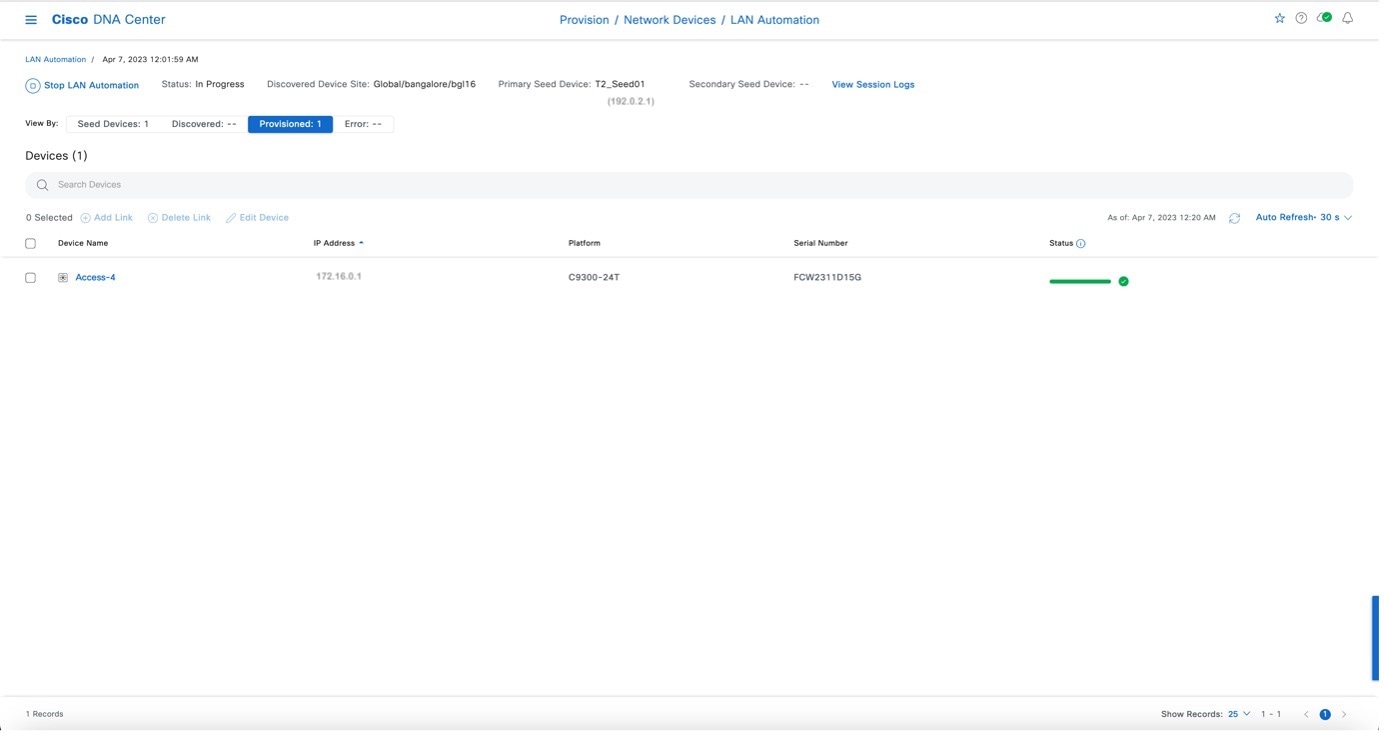
To stop LAN automation for the session, click Stop LAN Automation in the session details window or in the session tile. The LAN automation status changes to STOP in Progress. 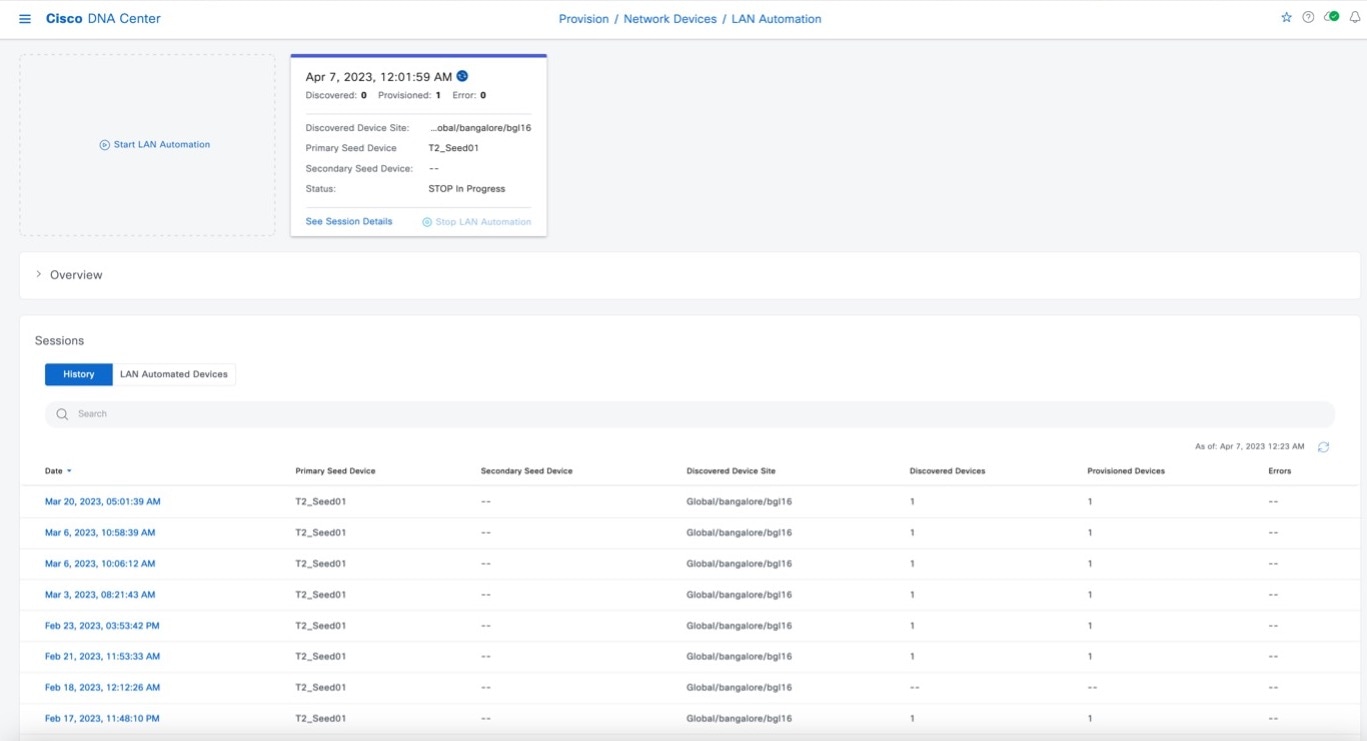
Use the History tab to view LAN automation session history. Search for specific text using the search field. Click a date link to view session details. Use the LAN Automated Devices tab to see details of LAN automated devices. Filter data using the search field. Click a toggle button to filter results by device status:
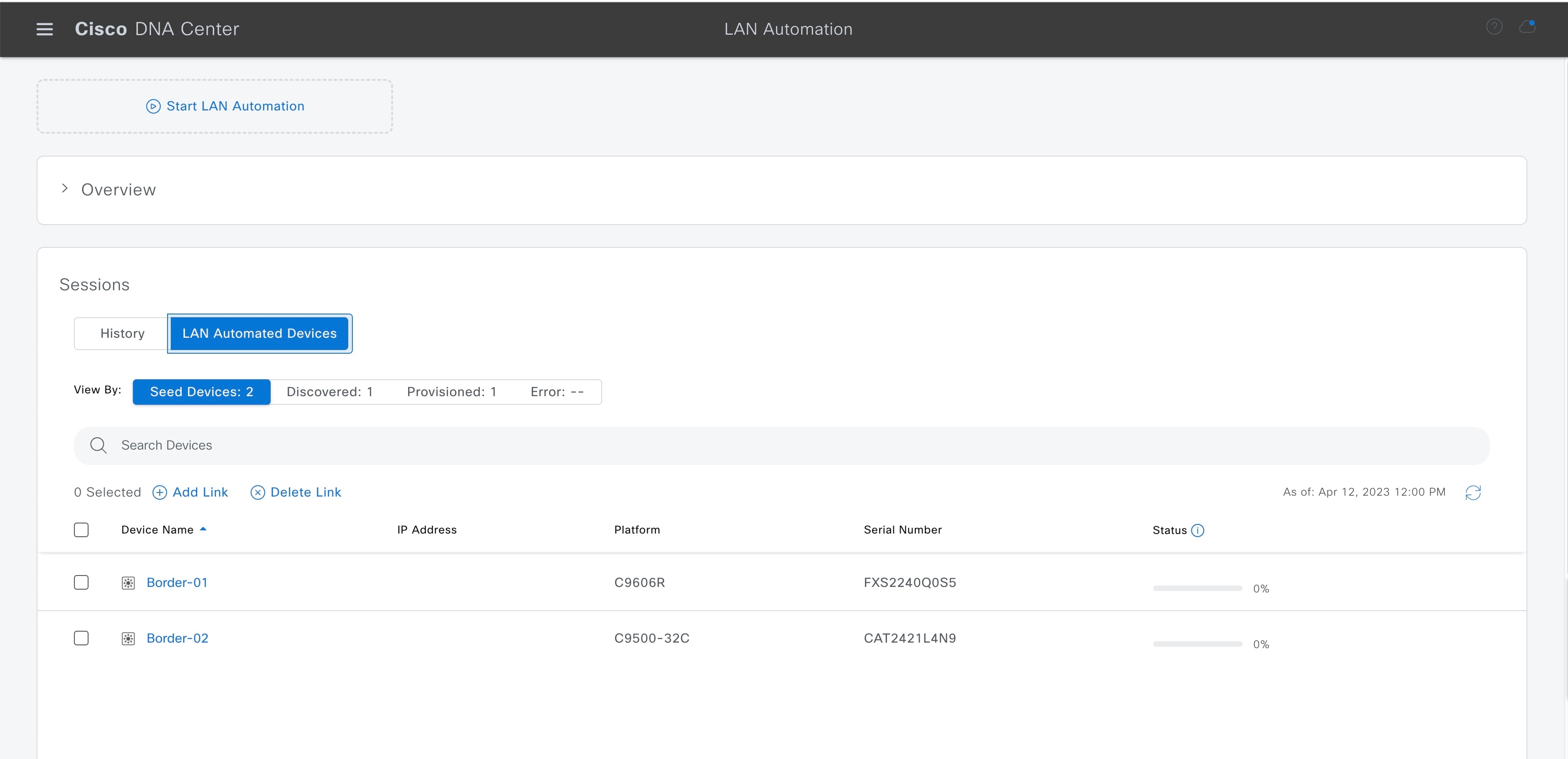
|
View device logs and configurations
Access and review the LAN automation session logs, device-specific logs, and device configurations.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the LAN Automation window, click the History tab in the Sessions area and click the hyperlinked date to view the session details. 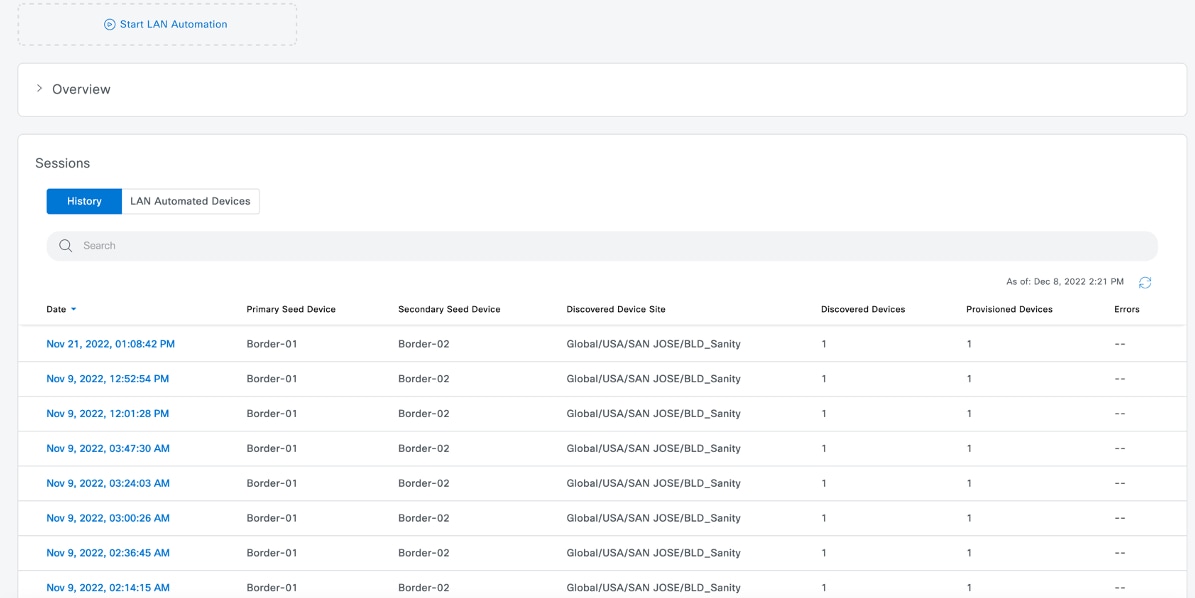
|
|
Step 2 |
In the session details window, click View Session Logs. 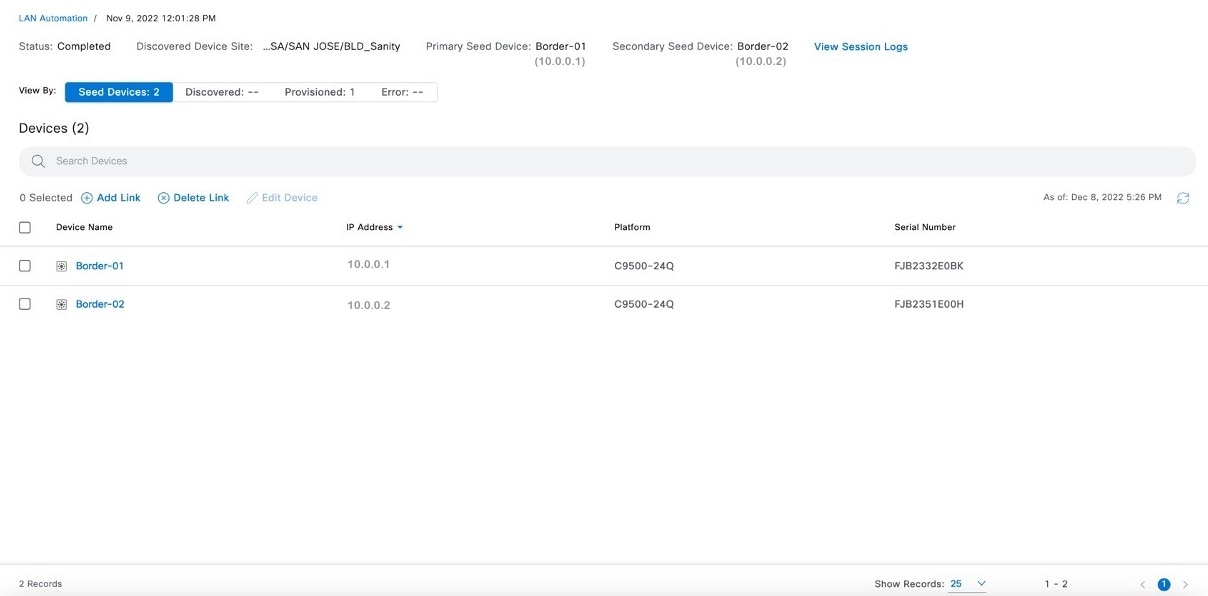
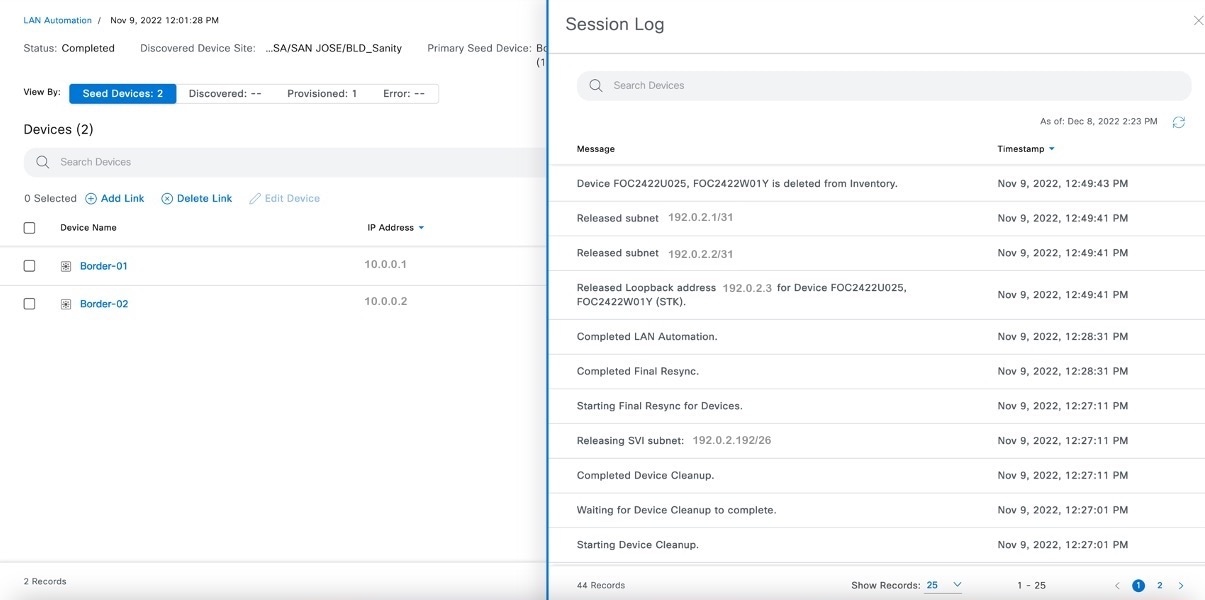
|
|
Step 3 |
Click the device name to view device-specific logs and configurations. Use the toggle button to filter the devices. 
|
|
Step 4 |
In the left pane of the device details window, expand Configuration Logs to view the device configurations. 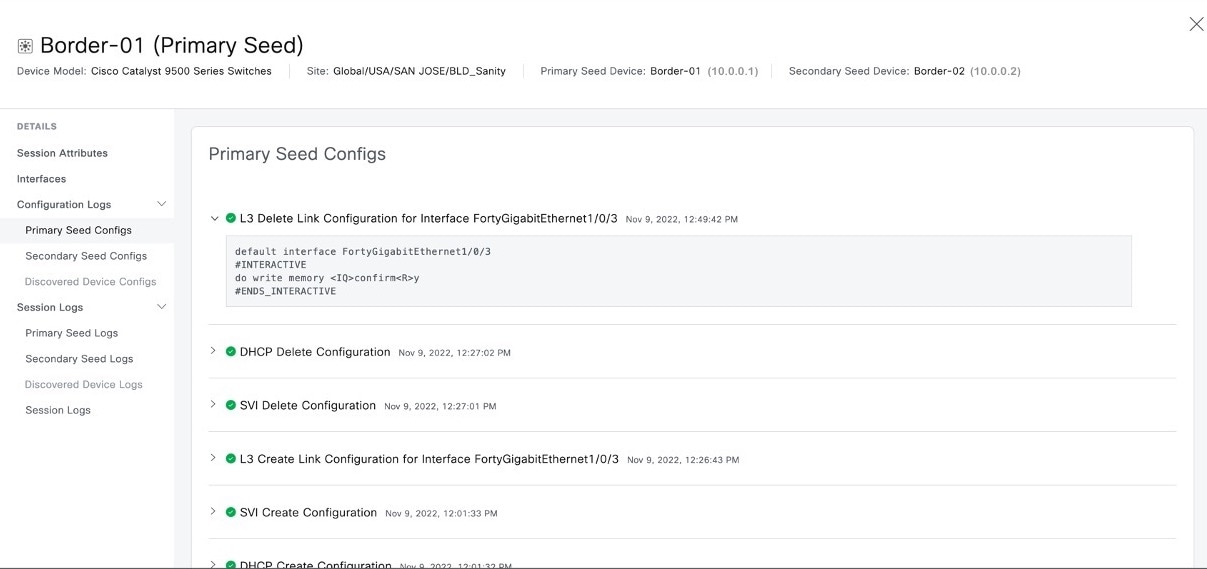
|
|
Step 5 |
Expand Session Logs to view the device-specific logs. 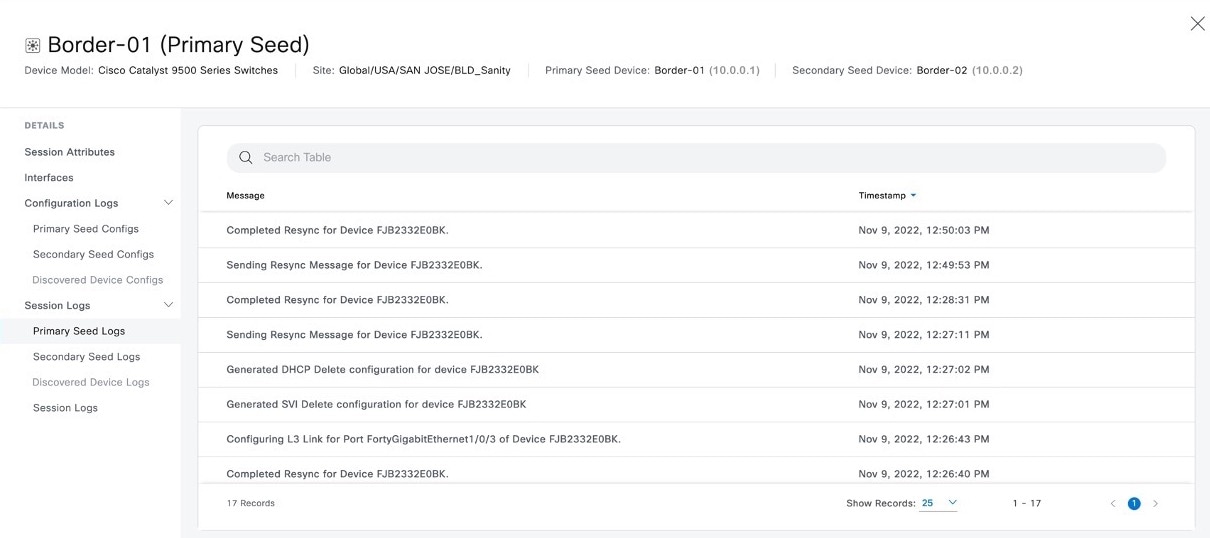
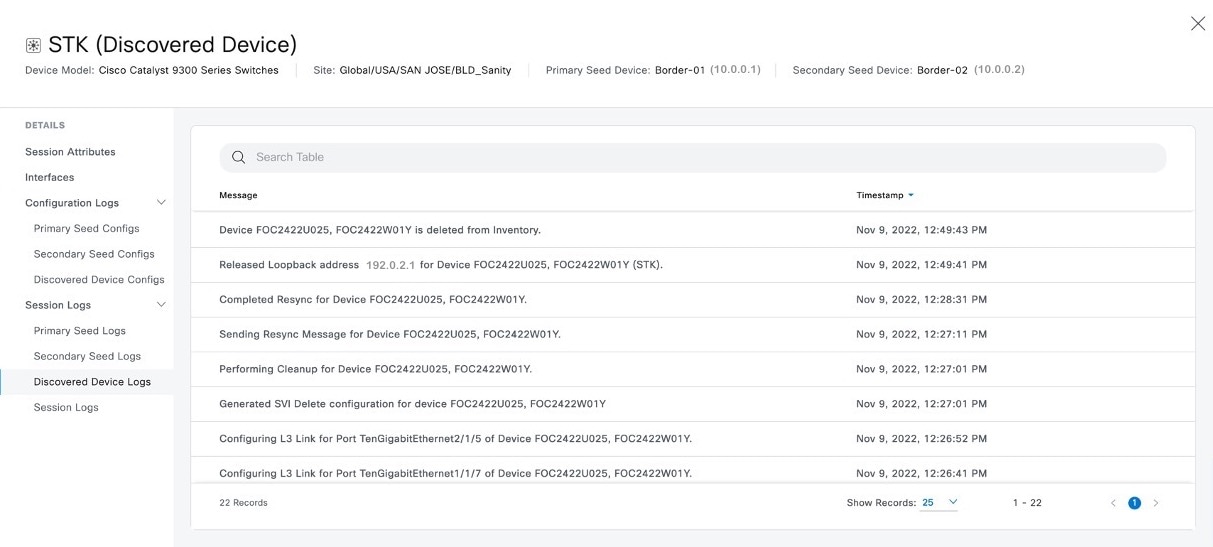
|
Create a link between interfaces
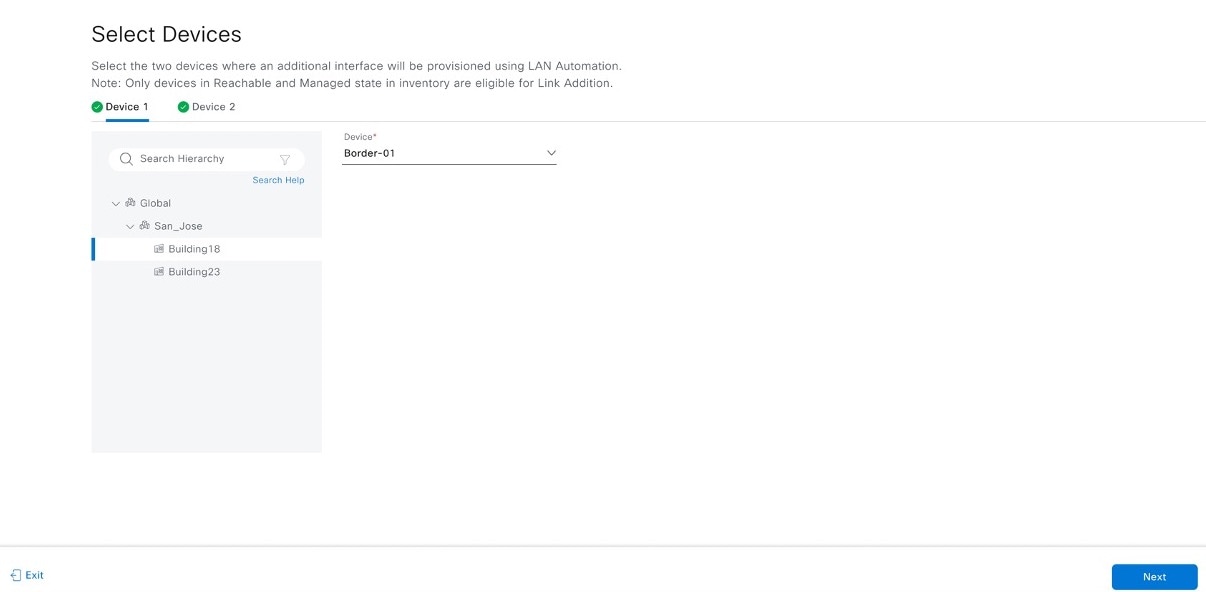
Configure additional links between interfaces after LAN automation stops.
Before you begin
This topic describes how to configure additional links between interfaces using Catalyst Center 2.3.5. Steps might differ depending on your Catalyst Center version.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
|
Step 2 |
Choose one of these options.
|
|
Step 3 |
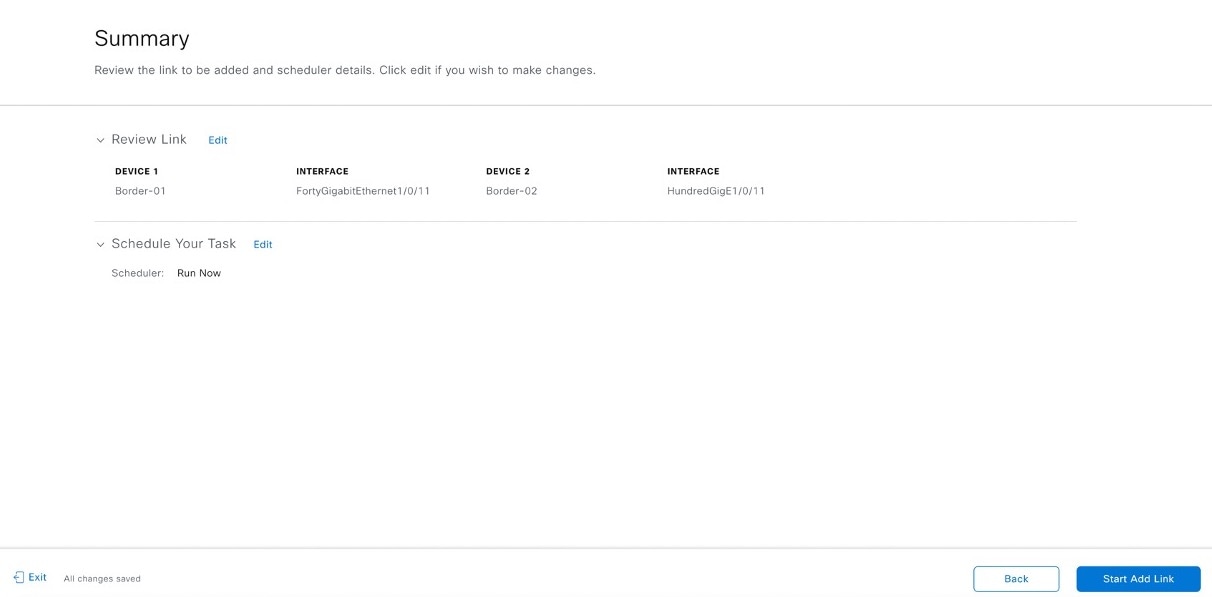
Follow these steps in the Add Link workflow: |
|
Step 4 |
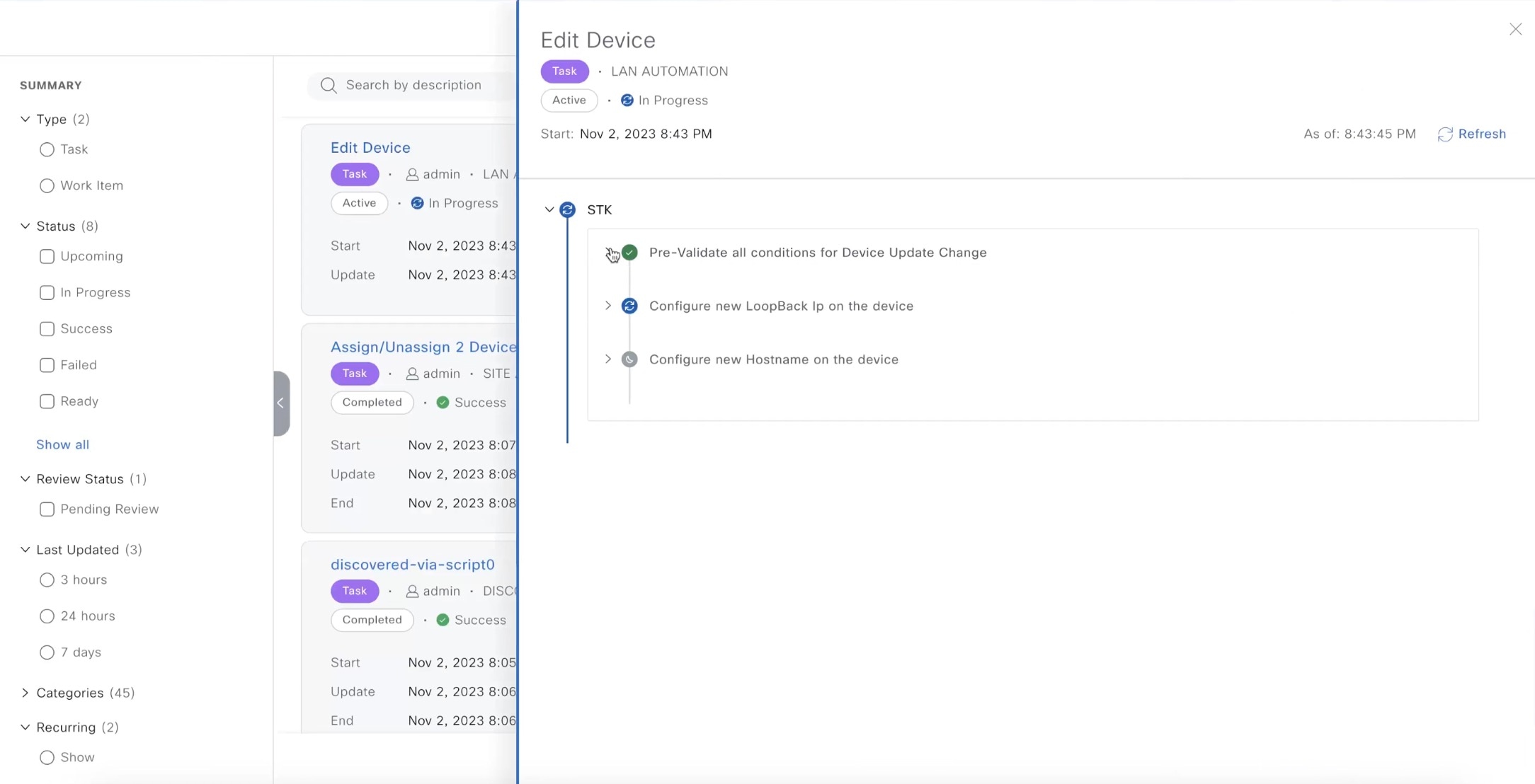
To see the status of the configuration, click View Status in Activities. |
What to do next
-
Click Delete link.
-
Select the devices and the interfaces.
-
Click Start Delete Link.
Edit LAN automated devices
Use this procedure to edit the hostname and Loopback0 interface IP address of a LAN automated device in Catalyst Center Release 2.3.7.5 and later.
Before you begin
Reserve LAN IP pools and discover the devices through LAN automation.
 Note |
|
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
|
Step 2 |
In the LAN Automation window, click the LAN Automated Devices tab. |
|
Step 3 |
Check the check box next to the device that you want to edit and click Edit Device.
|
|
Step 4 |
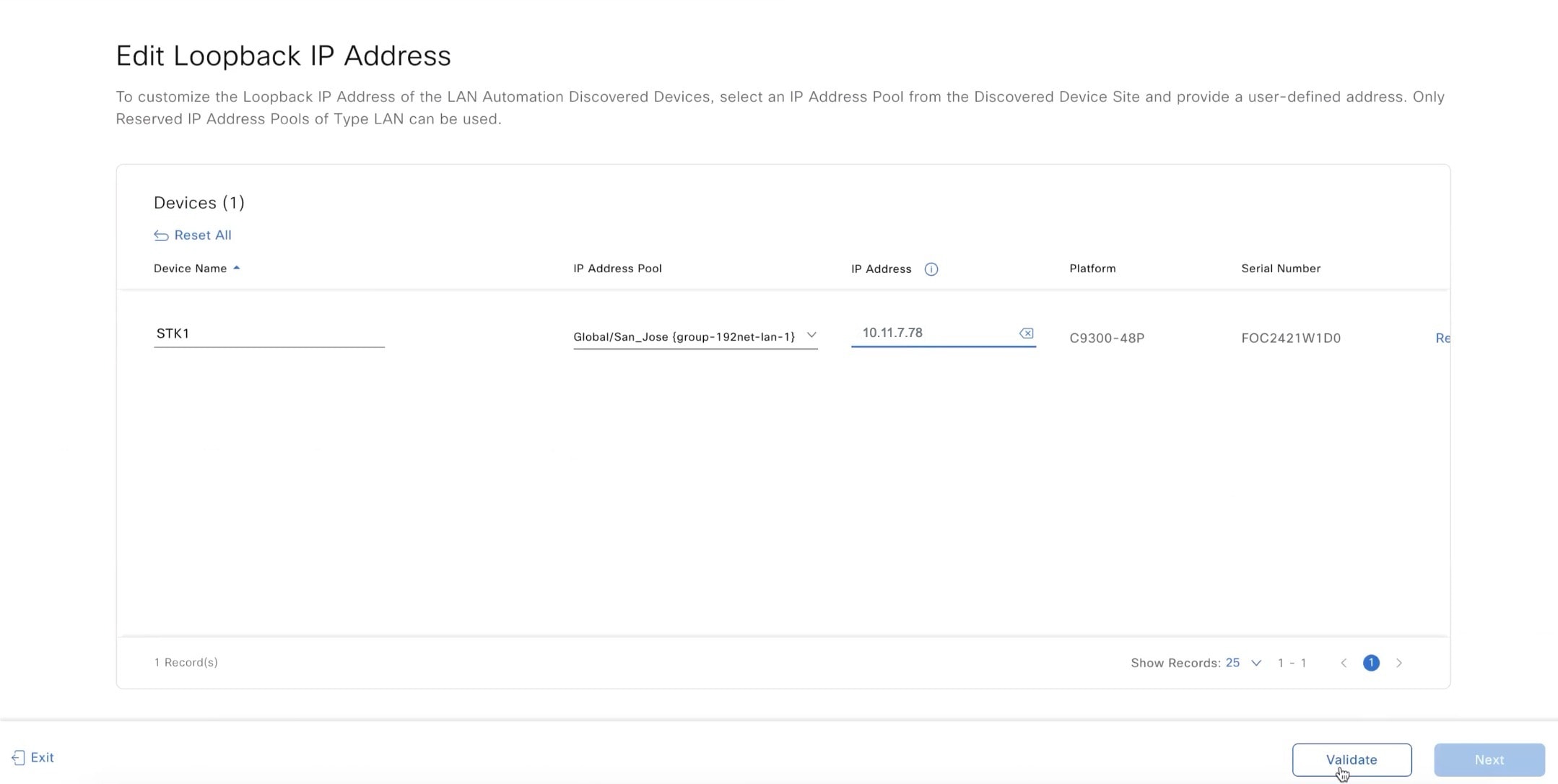
In the Edit Devices window, edit the Device Name, IP Address Pool, and IP Address fields, as required. Enter the IP address without a subnet mask. Ensure that the IP address is within the range of the selected IP address pool.
|
|
Step 5 |
Click Validate to validate the IP address allocation. |
|
Step 6 |
After validation, click Next. |
|
Step 7 |
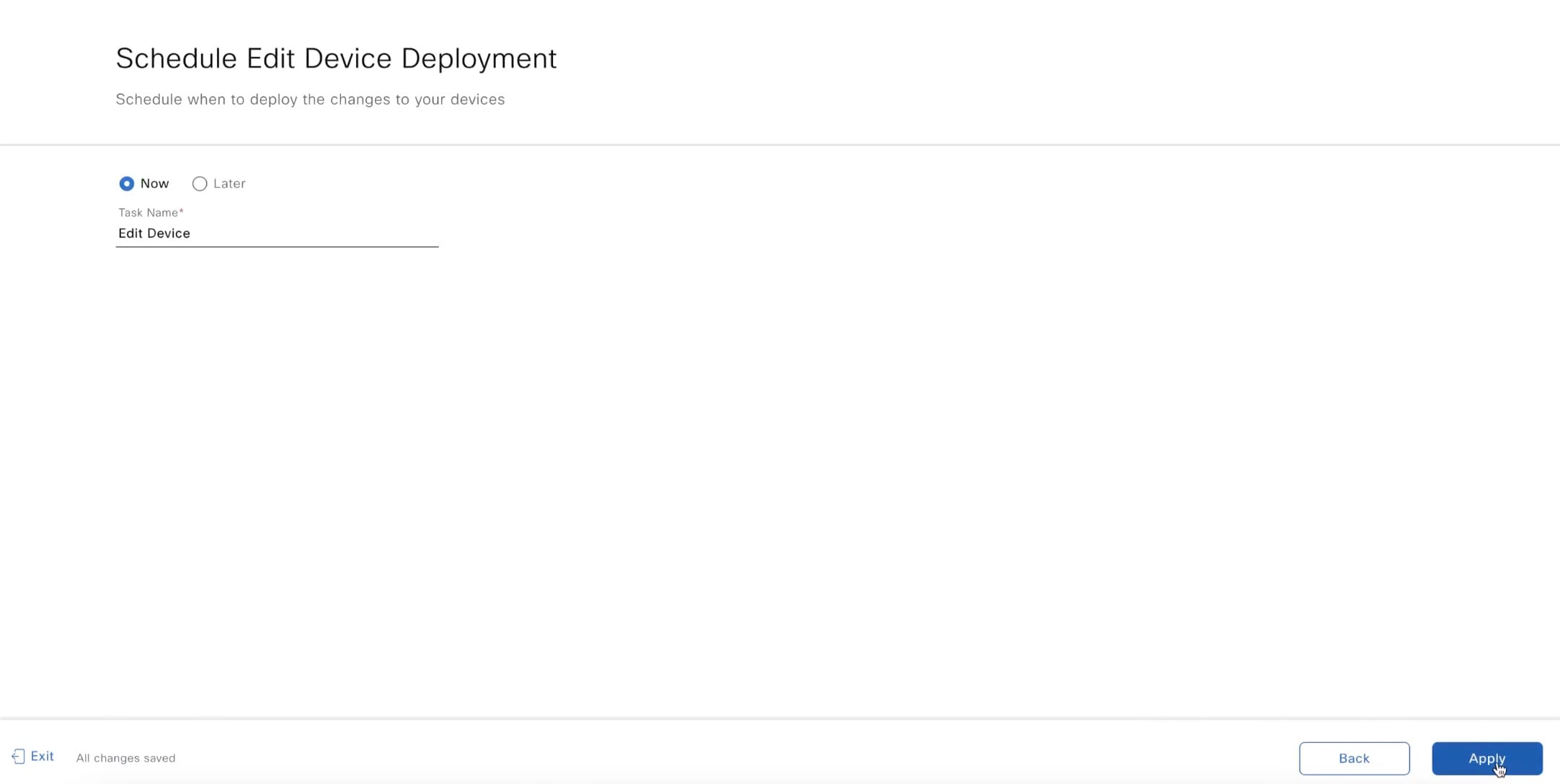
Choose Now or Later to schedule the edit device deployment and click Apply.
|
What to do next
You can view the status of the edit task under the window.
Manage devices in strict discovery mode
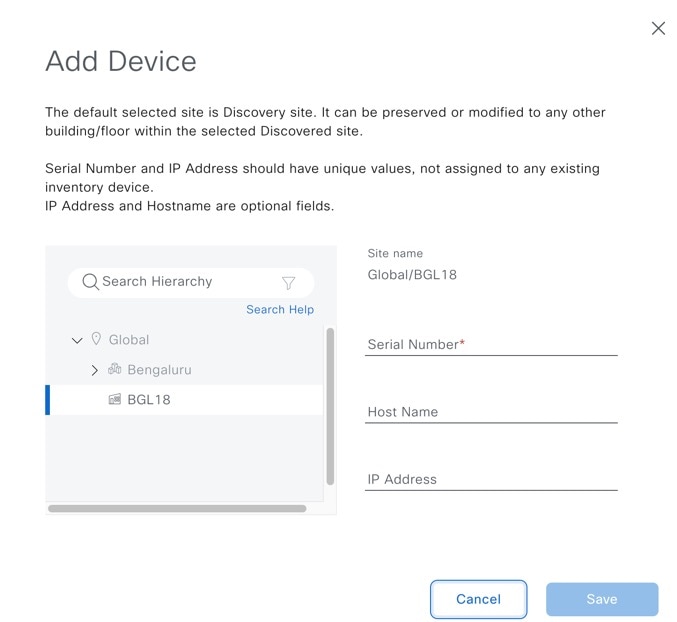
With Catalyst Center Release 2.3.7.5 and later, you can choose either Relaxed mode or Strict mode for device matching during discovery. Strict mode limits device discovery to a defined list. Follow these steps to add, edit, or delete devices in the discovery list.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the LAN Automation window, click Start LAN Automation. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Add the seed devices and click Next. |
||
|
Step 3 |
In the Session Attributes window, in the left pane, select a building or a floor. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Under Device Matching, select the Strict option. 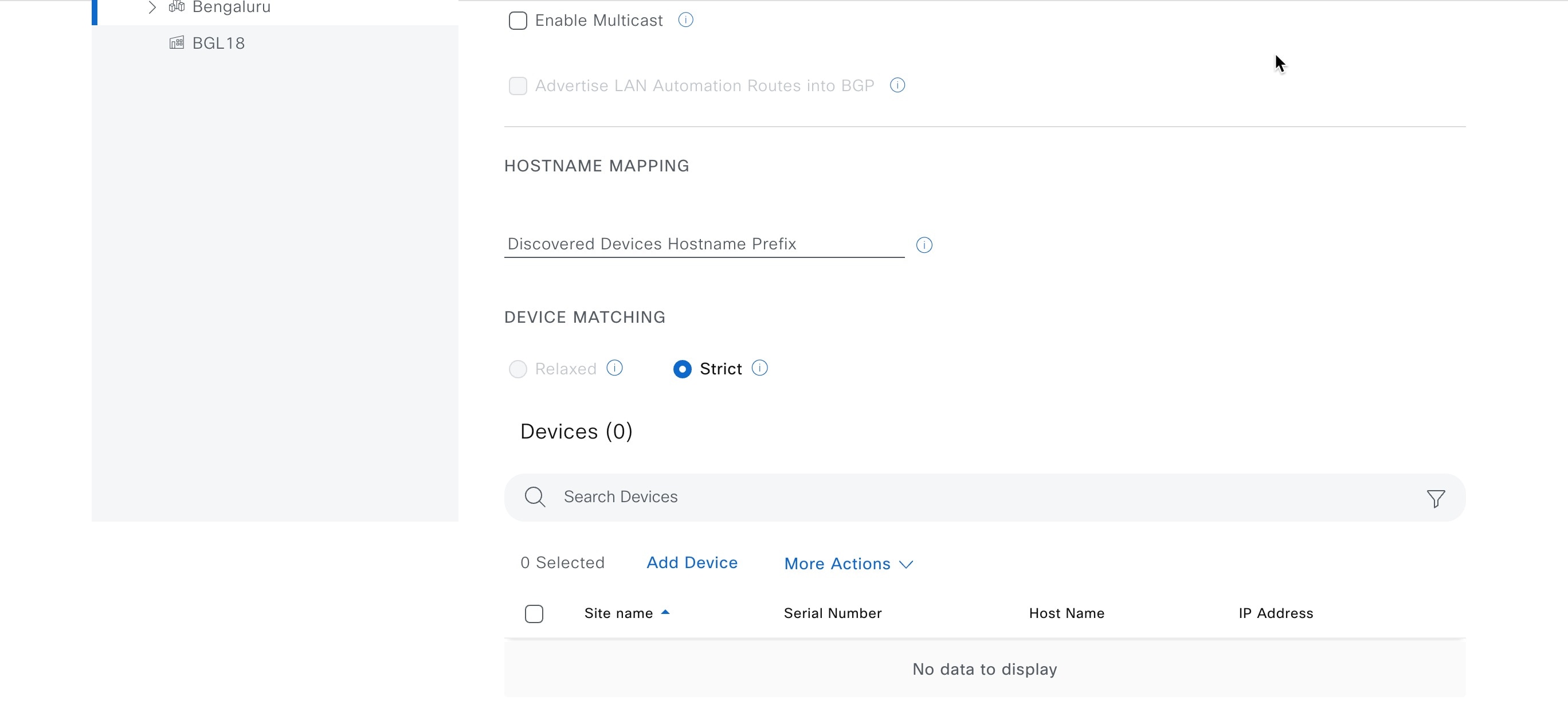
|
||
|
Step 5 |
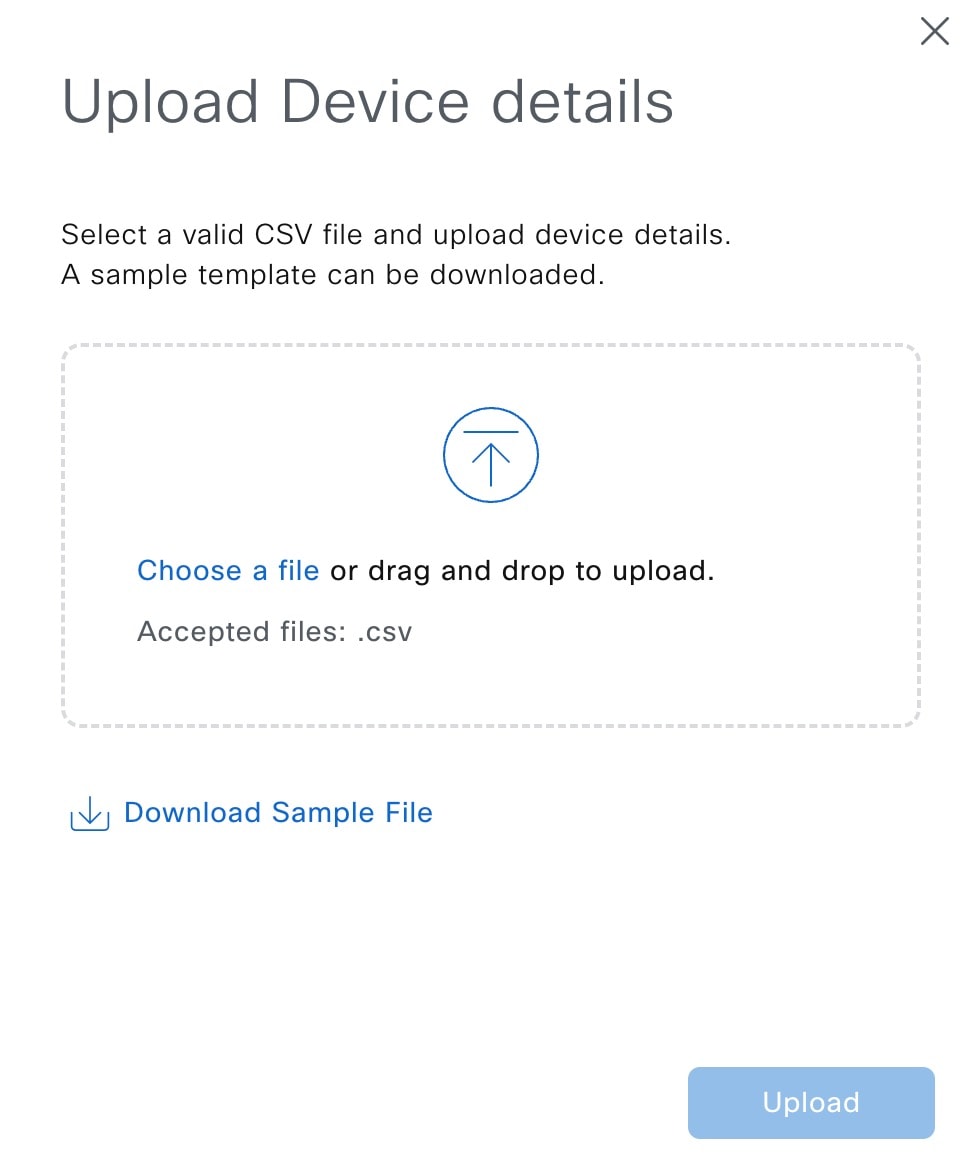
Add devices using one of these options for your discovery list:
|
||
|
Step 6 |
Follow these steps to edit a device from the discovery list: |
||
|
Step 7 |
Follow these steps to delete a device from the discovery list: |
 , check the
, check the 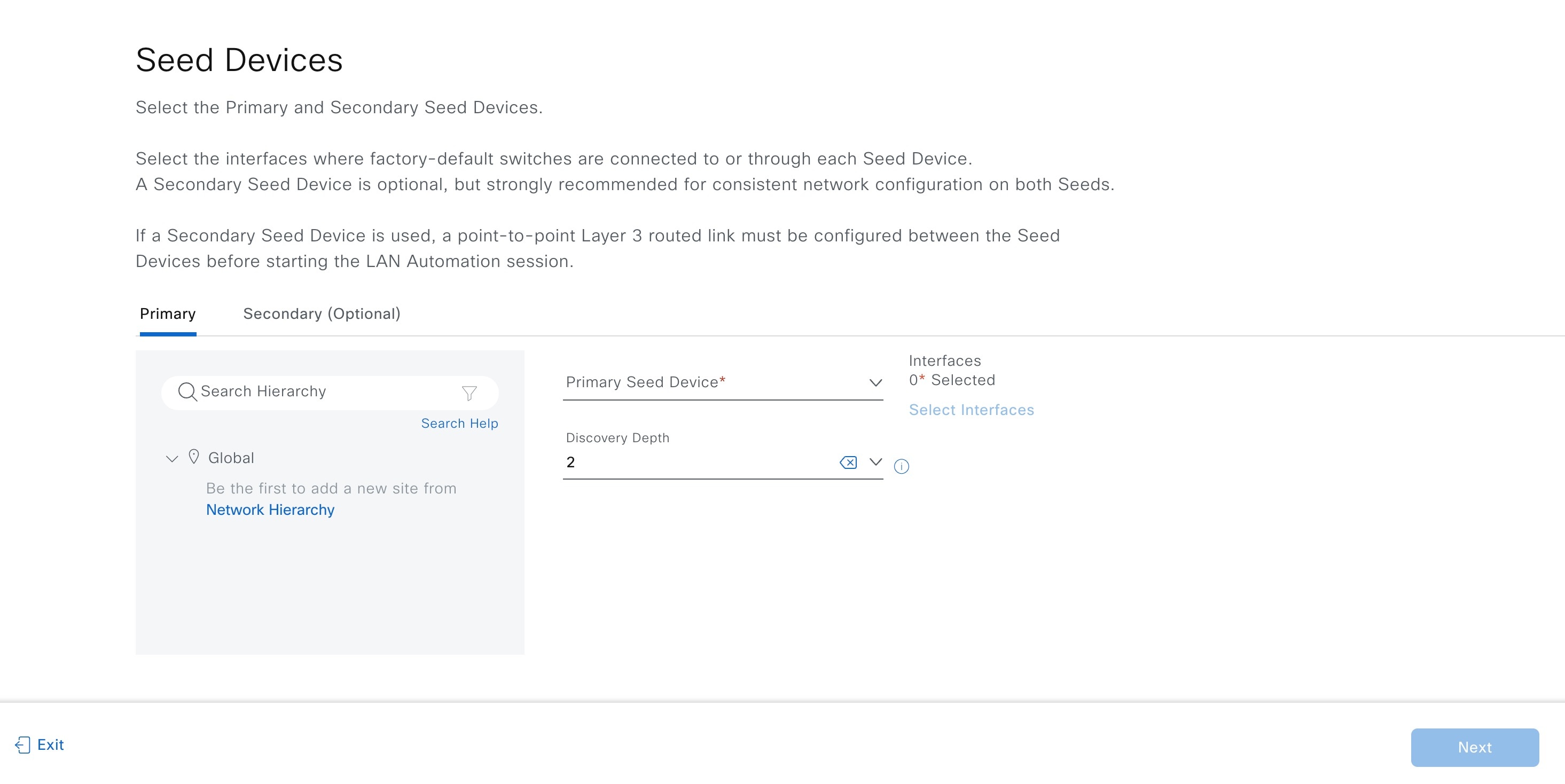
 Feedback
Feedback