Configuring NetFlow
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Information About NetFlow
- Guidelines and Limitations for NetFlow
- Default Settings for NetFlow
- Enabling the NetFlow Feature
- Configuring Netflow
- Verifying the NetFlow Configuration
- NetFlow Example Configuration
- Related Documents for NetFlow
- Feature History for NetFlow
Information About NetFlow
NetFlow allows you to evaluate IP and Ethernet traffic and understand how and where it flows. NetFlow gives you visibility into traffic that transits the virtual switch by characterizing traffic based on its source, destination, timing, and application information. You can use this information to assess network availability and performance, assist in meeting regulatory requirements (compliance), and help with troubleshooting. NetFlow gathers data that you can use for accounting, network monitoring, and network planning.
- What Is a Flow
- Flow Record Definition
- Accessing NetFlow Data
- Exporting Flows to the NetFlow Collector Server
- What NetFlow Data Looks Like
- High Availability for NetFlow
What Is a Flow
You create a flow using a flow record to define the criteria for your flow. All criteria must match for the packet to count in the given flow. Flows are stored in the NetFlow cache. Flow information tells you the following:
-
Source address tells you who is originating the traffic.
-
Destination address tells who is receiving the traffic.
-
Ports characterize the application that uses the traffic.
-
Class of service examines the priority of the traffic.
-
The device interface tells how traffic is being used by the network device.
-
Tallied packets and bytes show the amount of traffic.
Flow Record Definition
A flow record defines the information that NetFlow gathers, such as the packets in the flow and the types of counters gathered per flow. You can define new flow records or use the predefined Cisco Nexus 1000V flow record.
Predefined flow records use 32-bit counters and are not recommended for data rates above 1 Gbps. For data rates that are higher than 1 Gbps, Cisco recommends that you manually configure the records to use 64-bit counters.
The following table describes the criteria defined in a flow record.
Predefined Flow Records
Cisco Nexus 1000V Predefined Flow Record: Netflow-Original
switch# show flow record netflow-original
Flow record netflow-original:
Description: Traditional IPv4 input NetFlow with origin ASs
No. of users: 0
Template ID: 0
Fields:
match ipv4 source address
match ipv4 destination address
match ip protocol
match ip tos
match transport source-port
match transport destination-port
match interface input
match interface output
match flow direction
collect routing source as
collect routing destination as
collect routing next-hop address ipv4
collect transport tcp flags
collect counter bytes long
collect counter packets long
collect timestamp sys-uptime first
collect timestamp sys-uptime last
switch#
 Note | Although the following lines appear in the output of the show flow record command, the commands they are based on are not currently supported in Cisco Nexus 1000V. The use of these commands has no affect on the configuration. collect routing source as collect routing destination as collect routing next-hop address ipv4 |
Cisco Nexus 1000V Predefined Flow Record: Netflow IPv4 Original-Input
switch# show flow record netflow ipv4 original-input
Flow record netflow ipv4 original-input:
Description: Traditional IPv4 input NetFlow
No. of users: 0
Template ID: 0
Fields:
match ipv4 source address
match ipv4 destination address
match ip protocol
match ip tos
match transport source-port
match transport destination-port
match interface input
match interface output
match flow direction
collect routing source as
collect routing destination as
collect routing next-hop address ipv4
collect transport tcp flags
collect counter bytes long
collect counter packets long
collect timestamp sys-uptime first
collect timestamp sys-uptime last
switch#
Cisco Nexus 1000V Predefined Flow Record: Netflow IPv4 Original-Output
switch# show flow record netflow ipv4 original-output
Flow record netflow ipv4 original-output:
Description: Traditional IPv4 output NetFlow
No. of users: 0
Template ID: 0
Fields:
match ipv4 source address
match ipv4 destination address
match ip protocol
match ip tos
match transport source-port
match transport destination-port
match interface input
match interface output
match flow direction
collect routing source as
collect routing destination as
collect routing next-hop address ipv4
collect transport tcp flags
collect counter bytes
collect counter packets
collect timestamp sys-uptime first
collect timestamp sys-uptime last
switch#
Cisco Nexus 1000V Predefined Flow Record: Netflow Protocol-Port
switch# show flow record netflow protocol-port
Flow record netflow protocol-port:
Description: Protocol and Ports aggregation scheme
No. of users: 0
Template ID: 0
Fields:
match ip protocol
match transport source-port
match transport destination-port
match interface input
match interface output
match flow direction
collect counter bytes
collect counter packets
collect timestamp sys-uptime first
collect timestamp sys-uptime last
switch#
Accessing NetFlow Data
You can use two methods to access NetFlow data:
CLI for NetFlow
You can use the CLI to access NetFlow data and to view what is happening in your network.
The CLI uses a flow monitor and a flow exporter to capture and export flow records to the NetFlow collector. Cisco Nexus 1000V supports the NetFlow Version 9 export format.
 Note | The Cisco Nexus 1000V supports UDP as the transport protocol for exporting data, up to two exporters per monitor. |
Flow Monitor
A flow monitor creates an association between the following NetFlow components:
-
Flow record—Consists of matching and collection criteria
-
Flow exporter—Consists of the export criteria
This flow monitor enables a set, which consists of a record and an exporter. You can define this set once and reuse it multiple times. You can create multiple flow monitors for different needs. A flow monitor is applied to a specific interface or port profile in a specific direction.
Flow Exporter
The flow exporter is used to define the source and destination of the flow records. The source is from the VEM module and the destination is the reporting server, called the Netflow Collector. An IP packet is sent from the source to the destination with the collected information. The packet originates from the VEM, but you can configure which IP address is placed in the source field of the IP packet. The destination requires an IP address as well as a UDP port number for which the Netflow collector listens for packets.
An exporter definition includes the following:
NetFlow Collector
The NetFlow data reporting process is as follows:
-
You configure NetFlow records to define the information that NetFlow gathers.
-
You configure Netflow monitor to capture flow records to the NetFlow cache.
-
You configure NetFlow export to send flows to the collector.
-
The Cisco Nexus 1000V searches the NetFlow cache for flows that have expired and exports them to the NetFlow collector server.
-
Flows are bundled together based on space availability in the UDP export packet and based on an export timer.
-
The NetFlow collector software creates real-time or historical reports from the data.
Exporting Flows to the NetFlow Collector Server
Timers determine when a flow is exported to the NetFlow collector server. See the following figure where a flow is ready for export when one of the following occurs:
-
The flow is inactive for a certain amount of time, during which no new packets are received for the flow.
-
The flow has lived longer than the active timer, such as a long FTP download.
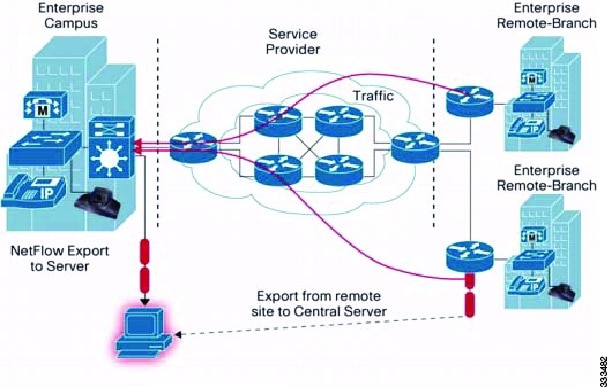
What NetFlow Data Looks Like
The following figure shows an example of NetFlow data.
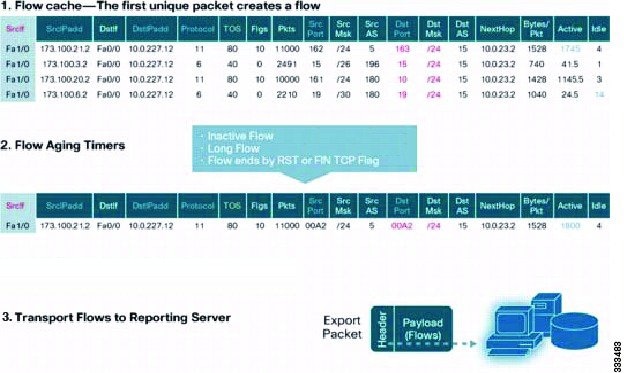
High Availability for NetFlow
The Cisco Nexus 1000V supports stateful restarts for NetFlow. After a reboot or supervisor switchover, the Cisco Nexus 1000V applies the running configuration.
Guidelines and Limitations for NetFlow
-
In Cisco Nexus 1000V, the mgmt0 interface IP address of the VSM is configured by default as the source IP address for an exporter.
-
Predefined flow records use 32-bit counters, which are recommended for data rates above 1 Gbps. For data rates that are higher than 1 Gbps, Cisco recommends that you manually configure the records to use 64-bit counters.
-
The Cisco Nexus 1000V includes the following predefined flow records:
-
netflow-original—The Cisco Nexus 1000V predefined traditional IPv4 input NetFlow with origin ASs

Note
The routing-related fields in this predefined flow record are ignored.
-
netflow ipv4 original-input—The Cisco Nexus 1000V predefined traditional IPv4 input NetFlow
-
netflow ipv4 original-output—The Cisco Nexus 1000V predefined traditional IPv4 output NetFlow
-
netflow protocol-port—The Cisco Nexus 1000V predefined protocol and ports aggregation scheme
-
-
Up to 8,000 NetFlow instances are allowed per Distributed Virtual Switch (DVS).
-
Up to 300 NetFlow instances are allowed per host.
-
A maximum of one flow monitor per interface per direction is allowed.
-
Up to two flow exporters are allowed per monitor.
-
Up to 64 NetFlow monitors, exporters, or records are allowed per DVS.
-
NetFlow is not supported on port channels or interfaces in a port channel.
Default Settings for NetFlow
| Parameters | Default |
|---|---|
|
NetFlow version |
9 |
|
Source |
Line card export with spoofed mgmt0 IP address of the VSM |
|
Match |
Direction and interface (incoming/outgoing) |
|
Flow monitor active timeout1 |
1800 |
|
Flow monitor inactive timeout 2 |
45 |
|
DSCP |
Default/best-effort (0) |
|
VRF |
Management (1) |
Enabling the NetFlow Feature
You are logged in to the CLI in EXEC mode.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | switch(config)# feature netflow | Enables the NetFlow feature. |
| Step 3 | switch(config)# show feature | (Optional) Displays the available features and whether or not they are enabled. |
| Step 4 | switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to enable the NetFlow feature:
switch# configure terminal switch(config)# feature netflow switch(config)#
Configuring Netflow
Defining a Flow Record
-
You know which of the options you want this flow record to match.
-
You know which options you want this flow record to collect.
 Note | Although the following lines appear in the output of the show flow record command, the commands they are based on are not currently supported in Cisco Nexus 1000V. The use of these commands has no effect on the configuration. collect routing source as collect routing destination as collect routing next-hop address ipv4 |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 2 | switch(config)# flow record name |
Creates a flow record by name, and places you in the CLI Flow Record Configuration mode for that specific record. | ||
| Step 3 | switch(config-flow-record)# description string |
(Optional) Adds a description of up to 63 characters to the flow record and saves it to the running configuration. | ||
| Step 4 | switch(config-flow-record)# match {ip {protocol | tos} | ipv4 {destination | source} | transport {destination-port | source-port} | datalink {{mac {source-address | destination-address}} | ethertype | vlan | vxlan }} |
Defines the flow record to match one of the following and saves it in the running configuration.
| ||
| Step 5 | switch(config-flow-record)# collect {counter {bytes [long] | packets [long]} | timestamp sys-uptime{first | last} | transport tcp flags} |
Specifies a collection option to define the information to collect in the flow record and saves it in the running configuration.
| ||
| Step 6 | switch(config-flow-record)# show flow record [name] | (Optional)
Displays information about flow records. | ||
| Step 7 | switch(config-flow-record)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
The following example shows how to create a flow record:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# flow record RecordTest
switch(config-flow-record)# description Ipv4flow
switch(config-flow-record)# match ipv4 destination address
switch(config-flow-record)# collect counter packets
switch(config-flow-record)# show flow record RecordTest
Flow record RecordTest:
Description: Ipv4flow
No. of users: 0
Template ID: 0
Fields:
match ipv4 destination address
match interface input
match interface output
match flow direction
collect counter packets
switch(config-flow-record)#
Defining a Flow Exporter
A flow exporter defines where and how flow records are exported to the NetFlow collector server.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | switch(config)#flow exporter name |
Creates a flow exporter, saves it in the running configuration, and places you in CLI Flow Exporter Configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | switch(config-flow-exporter)# description string |
Adds a description of up to 63 characters to this flow exporter and saves it in the running configuration. |
| Step 4 | switch(config-flow-exporter)# destination ipv4-address |
Specifies the IP address of the destination interface for this flow exporter and saves it in the running configuration. |
| Step 5 | switch(config-flow-exporter)# dscp value |
Specifies the differentiated services codepoint value for this flow exporter, between 0 and 63, and saves it in the running configuration. |
| Step 6 | switch(config-flow-exporter)# source lc-exp ipv4-address/subnet-mask | (Optional)
Specifies the IP address to spoof, from which the flow records are sent to the NetFlow collector server, and saves it in the running configuration. |
| Step 7 | switch(config-flow-exporter)# transport udp port-number |
Specifies the destination UDP port, between 1 and 65535, used to reach the NetFlow collector, and saves it in the running configuration. |
| Step 8 | switch(config-flow-exporter)# version {9} |
Specifies NetFlow export version 9, saves it in the running configuration, and places you in the export version 9 configuration mode. |
| Step 9 | switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# option {exporter-stats | interface-table} timeout value |
|
| Step 10 | switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# template data timeout seconds |
Sets the template data resend timer and its value, between 1 and 86400 seconds, and saves it in the running configuration. |
| Step 11 | switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# show flow exporter [name] |
(Optional) Displays information about the flow exporter. |
| Step 12 | switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# copy running-config startup-config |
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
The following example shows how to create a flow exporter:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# flow exporter ExportTest
switch(config-flow-exporter)# description ExportHamilton
switch(config-flow-exporter)# destination 192.0.2.1
switch(config-flow-exporter)# dscp 2
switch(config-flow-exporter)# source lc-exp 192.0.2.2/24
switch(config-flow-exporter)# transport udp 200
switch(config-flow-exporter)# version 9
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# option exporter-stats timeout 1200
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# template data timeout 1200
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# show flow exporter ExportTest
Flow exporter ExportTest:
Description: ExportHamilton
Destination: 192.0.2.1
VRF: management (1)
Destination UDP Port 200
Source IP Address 192.0.2.2
Export from Line Card
DSCP 2
Export Version 9
Exporter-stats timeout 1200 seconds
Data template timeout 1200 seconds
Exporter Statistics
Number of Flow Records Exported 0
Number of Templates Exported 0
Number of Export Packets Sent 0
Number of Export Bytes Sent 0
Number of Destination Unreachable Events 0
Number of No Buffer Events 0
Number of Packets Dropped (No Route to Host) 0
Number of Packets Dropped (other) 0
Number of Packets Dropped (LC to RP Error) 0
Number of Packets Dropped (Output Drops) 1
Time statistics were last cleared: Never
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# copy running-config startup-config
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)#
Defining a Flow Monitor
A flow monitor is associated with a flow record and a flow exporter.
A maximum of one flow monitor per interface or port profile per direction is permitted.
-
You know the name of an existing flow exporter to associate with this flow monitor.
-
You know the name of an existing flow record to associate with this flow monitor. You can use either a flow record you previously created, or one of the following Cisco Nexus 1000V predefined flow records:
 Note | Cisco recommends that you use the predefined flow records for systems with a lower data rate. For systems operating at a higher data rate of more than 1 Gbps, Cisco recommends that you manually configure the flow record and use the 64-bit long counters. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | switch(config)# flow monitor name |
Creates a flow monitor by name, saves it in the running configuration, and places you in the CLI Flow Monitor Configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | switch(config-flow-monitor)# description string |
(Optional) For the specified flow monitor, adds a descriptive string of up to 63 alphanumeric characters, and saves it in the running configuration. |
| Step 4 | switch(config-flow-monitor)# exporter name |
For the specified flow monitor, adds an existing flow exporter and saves it in the running configuration. |
| Step 5 | switch(config-flow-monitor)# record { [name | netflow {ipv4}] | netflow-original | original-input |original-output |protocol-port} |
|
| Step 6 | switch(config-flow-monitor)# show flow monitor [name] |
(Optional) Displays information about existing flow monitors. |
| Step 7 | switch(config-flow-monitor)# copy running-config startup-config |
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
The following example shows how to create a flow exporter:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# flow monitor MonitorTest
switch(config-flow-monitor)# description Ipv4Monitor
switch(config-flow-monitor)# exporter ExportTest
switch(config-flow-monitor)# record RecordTest
switch(config-flow-monitor)# show flow monitor MonitorTest
Flow Monitor MonitorTest:
Use count: 0
Flow Record: RecordTest
Flow Exporter: ExportTest
switch(config-flow-monitor)#
Assigning a Flow Monitor to an Interface
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | switch(config)# interface interface-type interface-number |
Places you in the CLI Interface Configuration mode for the specified interface. |
| Step 3 | switch(config-if)# ip flow monitor name {input | output} |
For the specified interface, assigns a flow monitor for input or output packets and saves it in the running configuration. |
| Step 4 | switch(config-if)# show flow interface interface-type interface-number | (Optional)
For the specified interface, displays the NetFlow configuration. |
| Step 5 | switch(config-if)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
The following example shows how to assign a flow monitor to an interface:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface veth 2
switch(config-if)# ip flow monitor MonitorTest output
switch(config-if)# show flow interface veth 2
Interface Vethernet2:
Monitor: MonitorTest
Direction: Output
switch(config-if)#
Adding a Flow Monitor to a Port Profile
-
You are logged in to the CLI in EXEC mode.
-
You have already created the flow monitor.
-
If using an existing port profile, you have already created the port profile and you know its name.
-
If creating a new port profile, you know the type of interface (Ethernet or vEthernet), and you know the name you want to give it.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | switch(config)# port-profile [type {ethernet | vethernet}] name |
Enters port profile configuration mode for the named port profile. |
| Step 3 | switch(config-port-prof)# ip flow monitor name {input | output} |
Applies a named flow monitor to the port profile for either incoming (input) or outgoing (output) traffic. |
| Step 4 | switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [expand-interface] [name profile-name] | (Optional)
Displays the configuration for verification. |
| Step 5 | switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional)
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to add a flow monitor to a port profile:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# port-profile AccessProf
switch(config-port-prof)# ip flow monitor access4 output
switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile name AccessProf
port-profile AccessProf
type: vethernet
status: disabled
capability l3control: no
pinning control-vlan: -
pinning packet-vlan: -
system vlans: none
port-group:
max ports: 32
inherit:
config attributes:
ip flow monitor access4 output
evaluated config attributes:
ip flow monitor access4 output
assigned interfaces:
switch(config-port-prof)#
Verifying the NetFlow Configuration
Use one of the following commands to verify the configuration:
| Command | Purpose | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
show flow cache |
Displays information about NetFlow flow cache. |
||
|
show flow exporter [name] |
Displays information about NetFlow flow exporter. |
||
|
show flow interface [interface-type number] |
Displays information about NetFlow interfaces. |
||
|
show flow monitor [name [cache module number | statistics module number] ] |
Displays information about NetFlow flow monitors.
|
||
|
show flow record [name] |
Displays information about NetFlow flow records. |
||
|
show flow timeout |
Displays the NetFlow flow timeout setting. |
Example: show flow exporter
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# show flow exporter ExportTest
Flow exporter ExportTest:
Description: ExportHamilton
Destination: 192.0.2.1
VRF: management (1)
Destination UDP Port 200
Source IP address 192.0.2.2
Export from Line Card
DSCP 2
Export Version 9
Exporter-stats timeout 1200 seconds
Data template timeout 1200 seconds
Exporter Statistics
Number of Flow Records Exported 0
Number of Templates Exported 0
Number of Export Packets Sent 0
Number of Export Bytes Sent 0
Number of Destination Unreachable Events 0
Number of No Buffer Events 0
Number of Packets Dropped (No Route to Host) 0
Number of Packets Dropped (other) 0
Number of Packets Dropped (LC to RP Error) 0
Number of Packets Dropped (Output Drops) 1
Time statistics were last cleared: Never
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)#
Example: show flow interface
switch(config-if)# show flow interface veth2
Interface Vethernet2:
Monitor: MonitorTest
Direction: Output
switch(config-if)#
Example: show flow monitor
switch(config-flow-monitor)# show flow monitor
Flow Monitor MonitorTest:
Use count: 1
Flow Record: test
Flow Exporter: ExportTest
Flow Monitor MonitorIpv4:
Use count: 70
Flow Record: RecordTest
Flow Exporter: ExportTest
switch(config-flow-monitor)#
Example: show flow monitor cache module
switch(config-port-prof)# show flow monitor mDocs cache module 5
Cache type: Normal
Cache size (Bytes): 224
Active Flows: 8
Flows added: 8
Packets added: 228
Flows aged: 0
- Watermark aged 0
- Inactive timeout 0
- Active timeout 0
- Event aged 0
- Emergency aged 0
- Permanent 0
- Immediate aged 0
- Session aged 0
- Fast aged 0
- Counters Overflow 0
* Denotes interface no longer exists, so just the IF Handle is displayed
IPV4 SRC ADDR IPV4 DST ADDR INTF INPUT INTF OUTPUT FLOW DIRN bytes pkts
=============== =============== ==================== ==================== ========= ========== ==========
192.168.0.15 192.168.0.11 Veth4 Veth6 Input 5390 55
192.168.0.11 192.168.0.15 Veth6 Veth4 Input 5390 55
192.168.0.14 192.168.0.10 Veth1 Veth5 Input 5292 54
192.168.0.10 192.168.0.14 Veth5 Veth1 Input 5292 54
Example: show flow monitor statistics module
switch(config)# show flow monitor m1 statistics module 3
Cache type: Normal
Cache size: 0
Active Flows: 1
Flows added: 149
Packets added: 350
Flows aged: 148
- Watermark aged 0
- Active timeout 0
- Inactive timeout 148
- Event aged 0
- Emergency aged 0
- Permanent 0
- Immediate aged 0
- Session aged 0
- Fast aged 0
- Counters Overflow 0
switch(config)#
Example: show flow record
switch(config-flow-record)# show flow record RecordTest
Flow record RecordTest:
Description: Ipv4flow
No. of users: 0
Template ID: 0
Fields:
match ipv4 destination address
match interface input
match interface output
match flow direction
collect counter packets
switch(config-flow-record)#
NetFlow Example Configuration
The following example shows how to configure flow monitor using a new flow record and apply it to an interface:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# flow record RecordTest
switch(config-flow-record)# description Ipv4flow
switch(config-flow-record)# match ipv4 destination address
switch(config-flow-record)# collect counter packets
switch(config-flow-record)# exit
switch(config)# flow exporter ExportTest
switch(config-flow-exporter)# description ExportHamilton
switch(config-flow-exporter)# destination 192.0.2.1
switch(config-flow-exporter)# dscp 2
switch(config-flow-exporter)# source lc-exp 192.0.2.2/24
switch(config-flow-exporter)# transport udp 200
switch(config-flow-exporter)# version 9
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# option exporter-stats timeout 1200
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# template data timeout 1200
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# exit
switch(config-flow-exporter)# exit
switch(config)# flow monitor MonitorTest
switch(config-flow-monitor)# description Ipv4Monitor
switch(config-flow-monitor)# exporter ExportTest
switch(config-flow-monitor)# record RecordTest
switch(config-flow-monitor)# exit
switch(config)# interface veth 2
switch(config-if)# ip flow monitor MonitorTest output
switch(config-if)# show flow interface veth 2
Interface Vethernet2:
Monitor: MonitorTest
Direction: Output
switch(config-if)#
The following example shows how to configure flow monitor using a predefined record and apply it to an interface:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# flow exporter ExportTest
switch(config-flow-exporter)# description ExportHamilton
switch(config-flow-exporter)# destination 192.0.2.1
switch(config-flow-exporter)# dscp 2
switch(config-flow-exporter)# source lc-exp 192.0.2.2/24
switch(config-flow-exporter)# transport udp 200
switch(config-flow-exporter)# version 9
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# option exporter-stats timeout 1200
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# template data timeout 1200
switch(config-flow-exporter-version-9)# exit
switch(config-flow-exporter)# exit
switch(config)# flow monitor MonitorTest
switch(config-flow-monitor)# description Ipv4Monitor
switch(config-flow-monitor)# exporter ExportTest
switch(config-flow-monitor)# record netflow-original
switch(config-flow-monitor)# exit
switch(config)# interface veth 2
switch(config-if)# ip flow monitor MonitorTest output
switch(config-if)# show flow interface veth 2
Interface Vethernet2:
Monitor: MonitorTest
Direction: Output
switch(config-if)#
Related Documents for NetFlow
| Related Topic | Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco NetFlow Overview |
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/ios-nx-os-software/ios-netflow/index.html |
Feature History for NetFlow
This table includes only the updates for those releases that have resulted in additions or changes to the feature.
| Feature Name | Releases | Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
NetFlow |
2.2(1) |
Distributed NetFlow was introduced. |
 Feedback
Feedback