Performing a Preinstallation Configuration (Optional)
The following procedures describe the processes to ensure that your AP installation and initial operation go as expected.
 Note |
Performing a preinstallation configuration is an optional procedure. If your network controller is properly configured, you can install your AP in its final location and connect it to the network from there. |
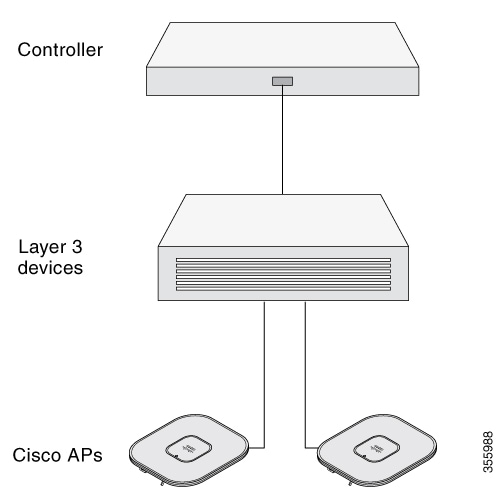
Perform the following steps:
Before you begin
-
Enable Layer 3 connectivity between APs, Cisco Controller Management, and AP-Manager interface.
-
Configure the switch to which your AP has to attach. See the Cisco Wireless Controller Configuration Guide for the release you are using, for additional information.
-
Configure the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller as the primary so that new APs always join it.
-
Ensure that the DHCP is enabled on the network. The AP must receive its IP address through DHCP.

Note
An 802.11ax AP is assigned an IP address from the DHCP server only if a default router (gateway) is configured on the DHCP server (enabling the AP to receive its gateway IP address) and the gateway ARP is resolved.
-
CAPWAP UDP ports must not be blocked in the network.
-
The AP must be able to find the IP address of the controller. This can be accomplished using DHCP, DNS, or IP subnet broadcast. This guide describes the DHCP method to convey the controller IP address. For other methods, see the product documentation.

Note
The AP requires a multi-gigabit Ethernet (5 Gbps) link to prevent the Ethernet port from becoming a bottleneck for traffic.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Power the AP using supported power source.
|
||
|
Step 2 |
(Optional) Configure the AP. Use the controller CLI, GUI, or Cisco DNA Center to customize the access point-specific 802.11ax network settings. |
||
|
Step 3 |
If the preinstallation configuration is successful, the Status LED is green, indicating normal operation. Disconnect the AP and mount it at the location at which you intend to deploy it on the wireless network. |
||
|
Step 4 |
If your AP does not indicate normal operation, turn it off and repeat the preinstallation configuration.
|



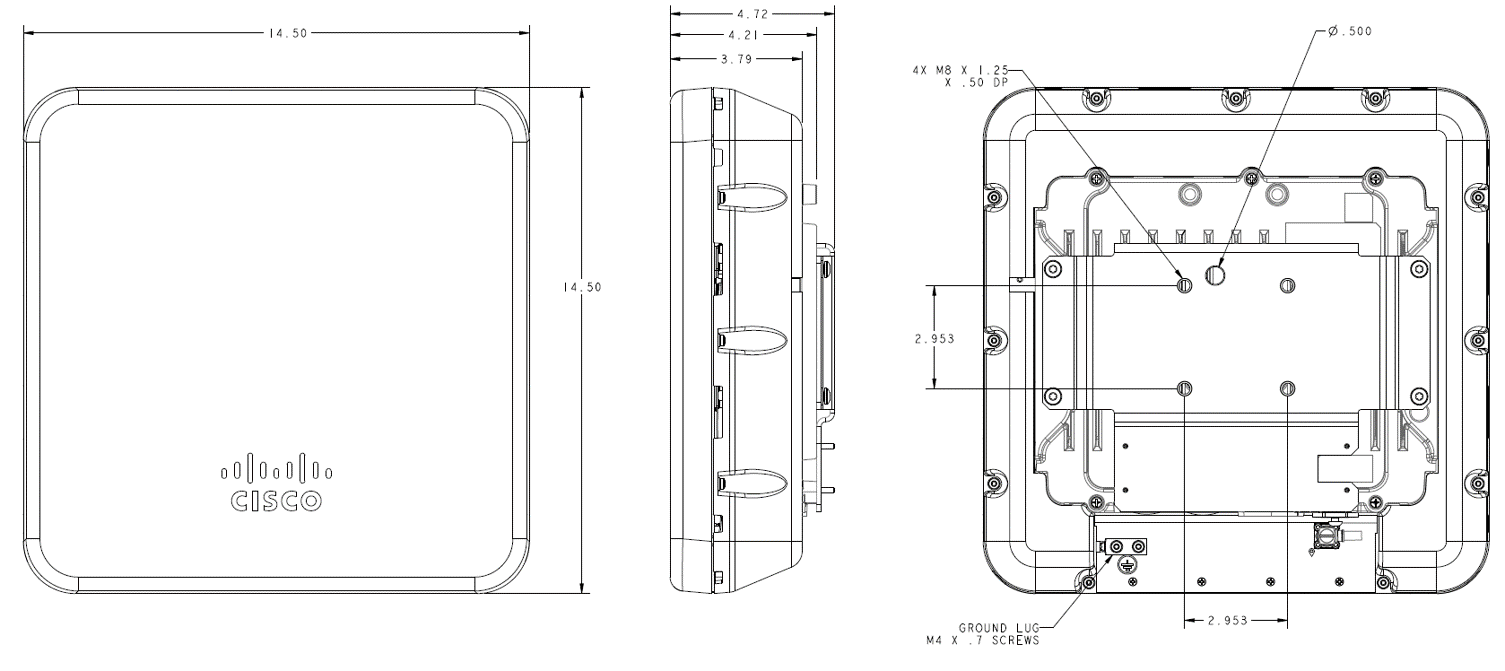
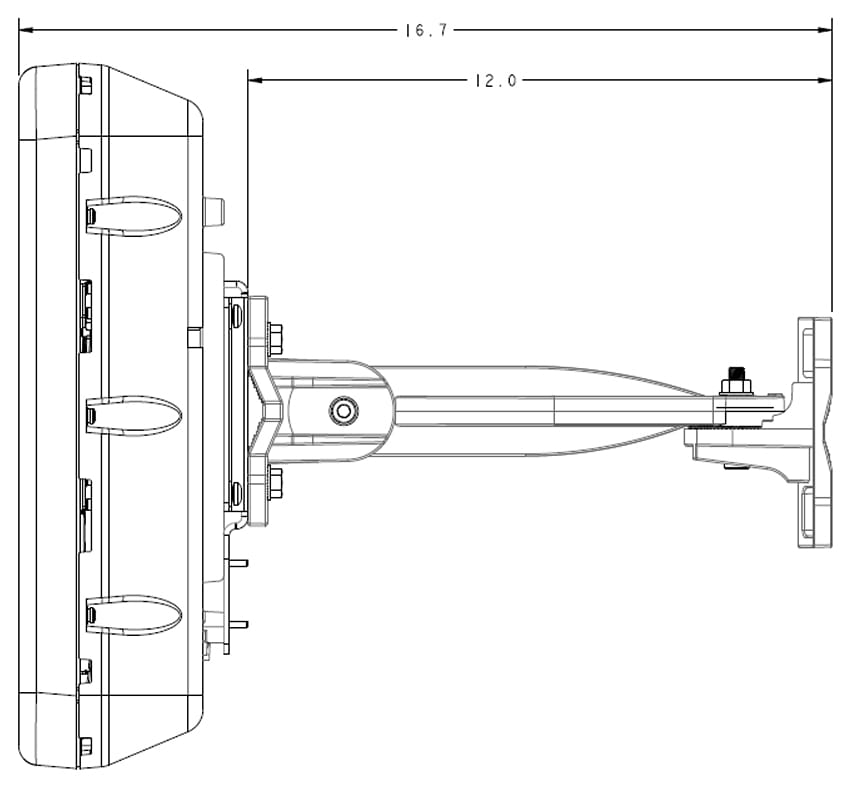
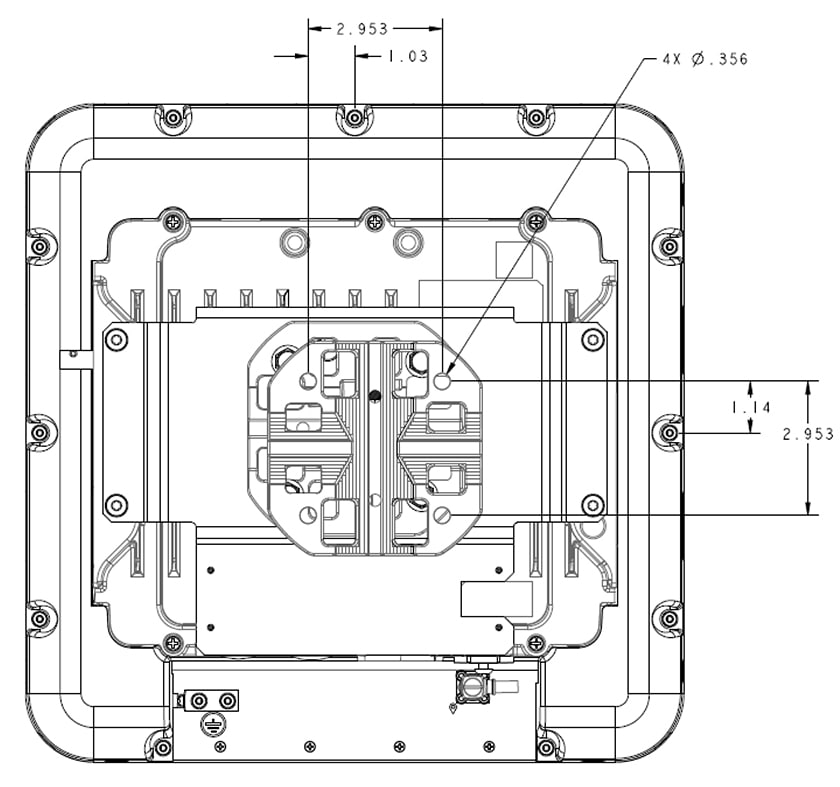




 Feedback
Feedback