Introduction
This document describes the best practices to relocate a Tetration (CSW) cluster with steps for a smooth transition and to minimize potential issues.
Precheck Procedures
Upload a Classic Snapshot
Before you start the relocation process, you must upload a classic snapshot to the TAC case. This snapshot helps you document the current status of the cluster and assess the health of the hardware and services. If any issues with services or hardware issues are observed from the snapshot, create a Return Materials Authorization (RMA) and fix the hardware issues and services.
Execute the Cluster Health Checks Through Upgrade Precheck
Upgrade prechecks verify the operational status of services and the condition of hardware components.
-
Navigate to Upgrade Precheck.
Navigate to the Tetration UI and follow these steps:
Wait a few minutes for the output of the upgrade prechecks. If everything is successful, then you can proceed with the next action plan for the cluster relocation.
Cluster Shutdown Procedure
Shut Down the Cluster
Before relocating the Tetration (CSW) cluster, it is crucial to shut it down properly.
-
Access the Shutdown Option.
Navigate to the Tetration UI:
-
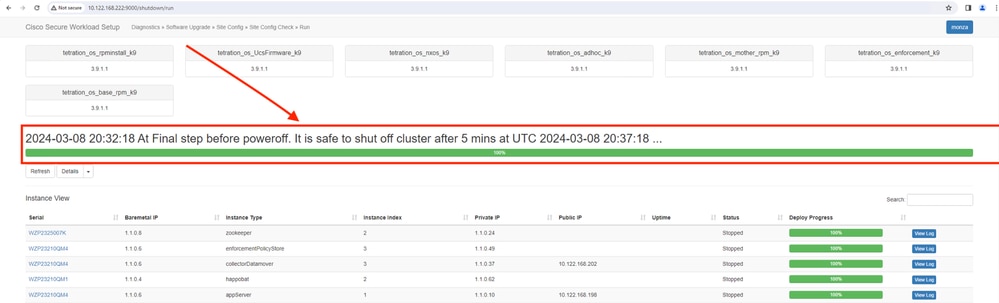
Importance of Proper Shutdown. Shutting down the cluster correctly helps to prevent data loss and ensures a clean stop of all active services.
After completion of cluster shutdown through UI as shown in this image, wait for 5 mins and then power off all the UCS servers and move the entire rack to the new datacenter.
Relocation Procedures
Subnet and IP Addresses Remain Unchanged
When you move the cluster to a new data center rack, it is important to ensure that the subnet, IP addresses, and network configurations remain the same on the new data center uplink router or uplink switch. This avoids network issues and maintains connectivity for all services.
These ports and traffic must be allowed through the firewall when deploying Cisco Secure Workload (Tetration) behind a firewall. Proper configuration of firewall rules is essential to ensure uninterrupted functionality.
|
Source
|
Destination
|
Protocol
|
Port
|
Components
|
Direction
|
Priority
|
|
All Agents
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
TCP
|
443
|
All Sensors
|
Inbound
|
H
|
|
Deep Visibility Agents
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
TCP
|
5640
|
Software sensors
|
Inbound
|
H
|
|
Enforcement Agents
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
TCP
|
5660
|
Enforcement Sensors
|
Inbound
|
H
|
|
Hardware Sensors
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
UDP
|
5640
|
Hardware Sensors
|
Inbound
|
H
|
|
Tetration operator PC/Laptop
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
TCP
|
443
|
for GUI access
|
Inbound
|
H
|
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
SMTP Server
|
TCP
|
25
|
Cluster Management (EMAIL)
|
Outbound
|
H
|
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
NTP Server
|
UDP
|
123
|
Cluster Management (NTP)
|
Outbound
|
H
|
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
DNS server
|
TCP, UDP
|
53
|
Cluster Management (DNS)
|
Outbound
|
H
|
|
Tetration operator PC/Laptop
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
TCP
|
22
|
Cluster Management (SSH)
|
Inbound
|
H
|
|
Tetration operator PC/Laptop
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
TCP
|
9000
|
Cluster Upgrades
|
Inbound
|
H
|
|
Tetration operator PC/Laptop
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
TCP
|
8901-8936
|
CIMC Tunnel
|
Inbound
|
H
|
|
Tetration operator PC/Laptop
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
TCP
|
8001-8036
|
CIMC Tunnel
|
Inbound
|
H
|
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
syslog server
|
UDP
|
514
|
Cluster Management (Syslog)
|
Outbound
|
H
|
|
Tetration Server Subnet
|
LDAP Server
|
TCP
|
389/636
|
Cluster Management (LDAP)
|
Outbound
|
H
|
Ensure Cabling Integrity
Make sure that the cabling remains undisturbed during the relocation. If you are moving the entire Tetration rack, ensure all cables are accounted for so that nothing gets disconnected or damaged.
Post-Relocation Steps
Powering On the Servers
After you power on the server in the new location, log into the Tetration UI. You notice that many Tetration services show up as unhealthy (red).
Handling Unhealthy Services
If you see that some services are unhealthy, contact the Technical Assistance Center (TAC) for support in resolving these issues. Quick engagement with TAC can help restore full functionality.
To fix the unhealthy services, the TAC engineer can restart some of the services or VMs,s and, in some cases, the TAC engineer can reboot the cluster through the Tetration UI.
It is strongly recommend running the Cluster Upgrade Precheck to make sure your cluster has no hardware failures before proceeding with a reboot.
Access the Reboot Option in the Tetration UI:
Conclusion
Summary of Best Practices
The successful relocation of a Tetration (CSW) cluster requires careful planning and execution of the outlined prechecks, shutdown procedures, and post-relocation steps. Using these best practices can help prevent issues and ensure the cluster runs smoothly after the move.


 Feedback
Feedback