Configure Zero Trust Remote Access Deployment on Secure Firewall
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the process of configuring Clientless Zero Trust Access Remote Access deployment on a Secure Firewall.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends you have knowledge of these topics:
- Secure Firewall Management Center (FMC)
- Basic ZTNA Knowledge
- Basic Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) knowledge
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software versions:
- Secure Firewall version 7.4.1
- Firepower Management Center (FMC) version 7.4.1
- Duo as Identity Provider (IdP)
- Microsoft Entra ID (formerly, Azure AD) as IdP
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Zero Trust Access feature is based on Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) principles. ZTNA is a zero trust security model that eliminates implicit trust. The model grants the least privilege access after verifying the user, the context of the request, and after analyzing the risk if access is granted.
The current requirements and limitations for ZTNA are:
- Supported on Secure Firewall version 7.4.0+ managed by FMC version 7.4.0+ (Firepower 4200 Series)
- Supported on Secure Firewall version 7.4.1+ managed by FMC version 7.4.1+ (All other platforms)
-
Only web applications (HTTPS) are supported. Scenarios requiring decryption exemption are not supported
-
Supports only SAML IdPs
-
Public DNS updates are required for remote access
-
IPv6 is not supported. NAT66, NAT64, and NAT46 scenarios are not supported
-
The feature is available on threat defense only if Snort 3 is enabled
-
All hyperlinks in protected web applications must have a relative path
-
Protected web applications running on a virtual host or behind internal load balancers must use the same external and internal URL
-
Not supported on individual mode clusters
-
Not supported on applications with strict HTTP Host Header validation enabled
-
If the application server hosts multiple applications and serves content based on the Server Name Indication (SNI) header in the TLS Client Hello, the external URL of the zero trust application configuration must match the SNI of that specific application
- Supported only in Routed Mode
- Smart License required (does not work in evaluation mode)
For more information and details about Zero Trust Access in Secure Firewall refer to the Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center Device Configuration Guide, 7.4.
Configure
This document focuses on a Remote Access Deployment of ZTNA.
In this example scenario, remote users require access to the Web User Interfaces (UI) of a test FMC and a Cisco Telemetry Broker (CTB) which are hosted behind a Secure Firewall. Access to these applications is granted by two different IdPs: Duo & Microsoft Entra ID respectively, as shown in the next diagram.
Network Diagram
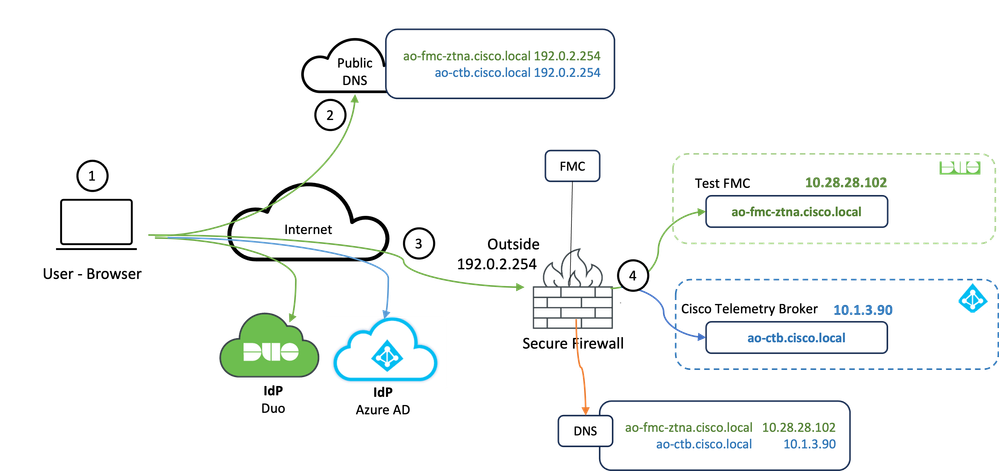 Topology diagram
Topology diagram
- The remote users need to access applications hosted behind the Secure Firewall.
- Each application must have a DNS entry in the public DNS servers.
- These application names must resolve to the IP address of the Secure Firewall Outside interface.
- The Secure Firewall resolves to the real IP addresses of the applications and authenticates each user to each application using SAML authentication.
Prerequisite Configuration
Identity Provider (IdP) and Domain Name Server (DNS)
- The applications or application groups must be configured in a SAML Identity Provider (IdP) such as Duo, Okta, or Azure AD. In this example, Duo and Microsoft Entra ID are used as IdPs.
- The certificate and metadata generated by the IdPs is used when configuring the application on the Secure Firewall
Internal and external DNS servers
- External DNS servers (used by remote users) must have the FQDN entry of the applications, and resolve to the Secure Firewall outside interface IP address
- Internal DNS servers (used by Secure Firewall) must have the FQDN entry of the applications, and resolve to the real IP address of the application
Certificates
The next certificates are required for the ZTNA Policy configuration:
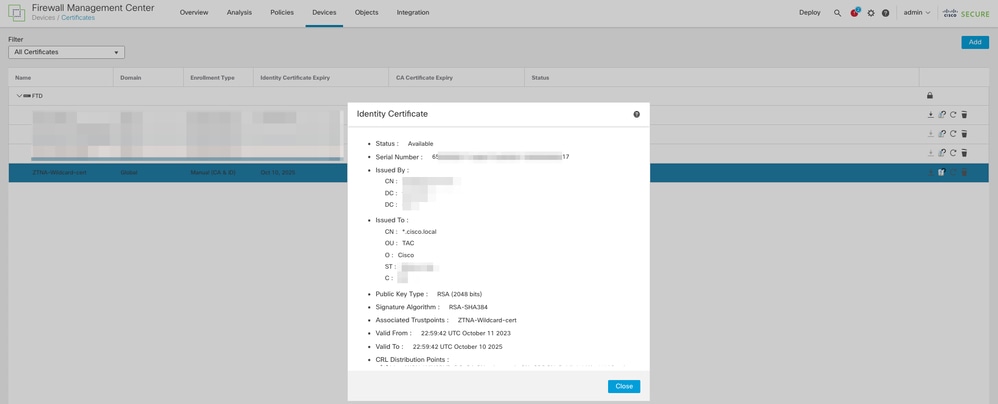
- Identity/Proxy certificate: Used by the Secure Firewall to masquerade the applications. The Secure Firewall here acts as a SAML Service Provider (SP). This certificate must be a wildcard or Subject Alternative Name (SAN) certificate that matches the FQDN of the private applications (a common certificate that represents all the private applications at the pre-authentication stage)
- IdP certificate: The IdP used for authentication provides a certificate for each application or application group defined. This certificate must be configured so that the Secure Firewall
Is able to verify the IdP’s signature on incoming SAML assertions (if this is defined for an application group, the same certificate is used for the entire group of applications) - Application certificate: The encrypted traffic from the remote user to the application needs to be decrypted by the Secure Firewall, therefore, the certificate chain and private key of each application must be added to the Secure Firewall.
General Configurations
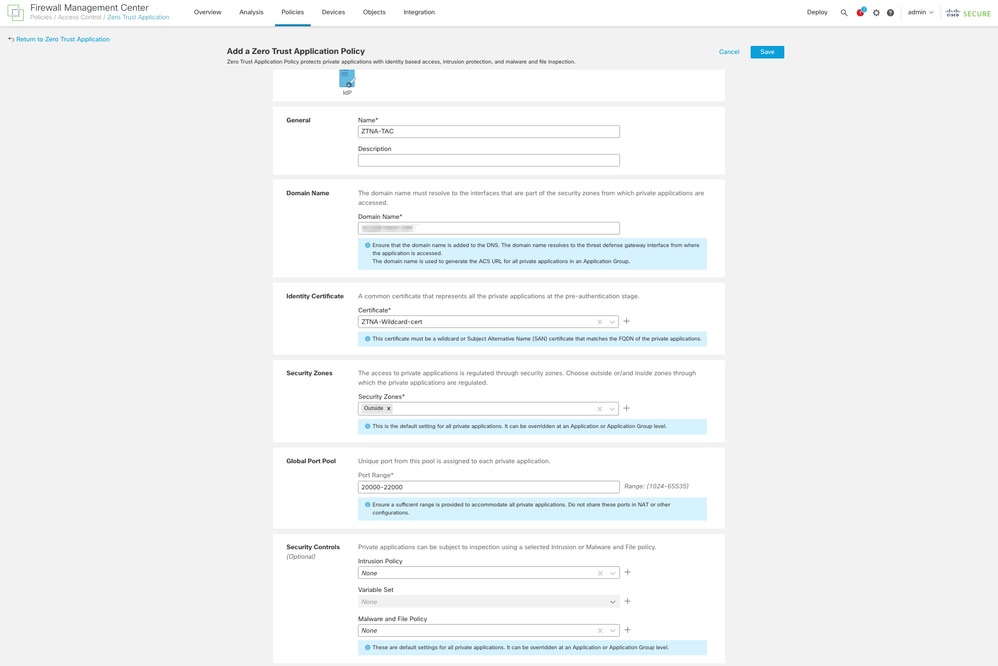
To configure a new Zero Trust Application, perform the next steps:
- Navigate to Policies > Access Control > Zero Trust Application and click on Add Policy.
- Complete the required fields:
a) General: Enter the name and description of the policy.
b) Domain Name: This is the name that is added to the DNS and must resolve to the threat defense gateway interface from where the applications are accessed.
Note: The domain name is used to generate the ACS URL for all private applications in an Application Group.
c) Identity certificate: this is a common certificate that represents all the private applications at the pre-authentication stage.
Note: This certificate must be a wildcard or Subject Alternative Name (SAN) certificate that matches the FQDN of the private applications.
d) Security Zones: Select outside or/and inside zones through which the private applications are regulated.
e) Global Port Pool: Unique port from this pool is assigned to each private application.
f) Security Controls (optional): Select if the private applications are subject to inspection.
In this sample configuration, the next information was entered:
The identity/proxy certificate used in this case is a wildcard certificate to match the FQDN of the private applications:
3. Save the policy.
4. Create the new Application Groups and/or new Applications:
- An Application defines a private web application with SAML authentication, interface access, Intrusion and Malware and File policies.
- An Application Group allows you to group multiple Applications, and share common settings such as SAML authentication, interface access, and security control settings.
In this example, two different application groups and two different applications are configured: one for the application to be authenticated by Duo (test FMC Web UI) & one for the application to be authenticated by Microsoft Entra ID (CTB Web UI).
Configure Application Group
Application Group 1: Using Duo as IdP
a. Enter the Application Group Name and click Next for the SAML Service Provider (SP) Metadata to be displayed.
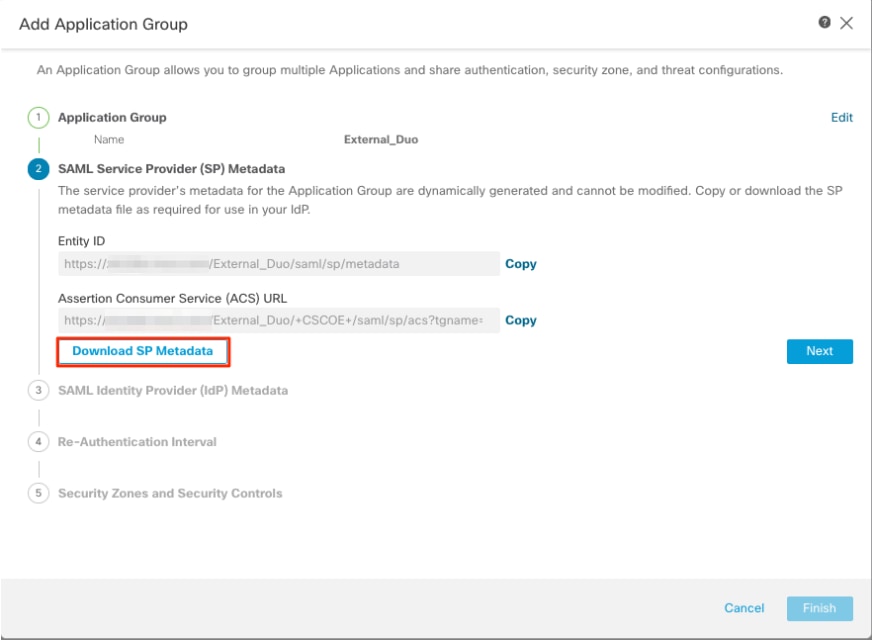
b. Once the SAML SP Metadata is displayed, go to the IdP and configure a new SAML SSO application.
c. Log in to Duo and navigate to Applications > Protect an Application.
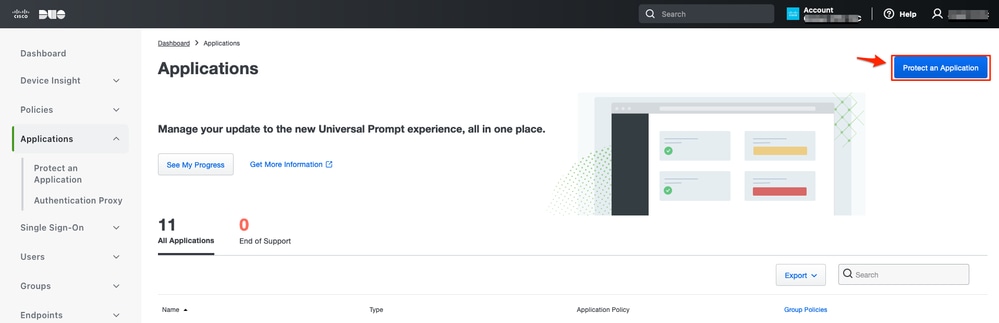
d. Look for Generic SAML Service Provider and click Protect.
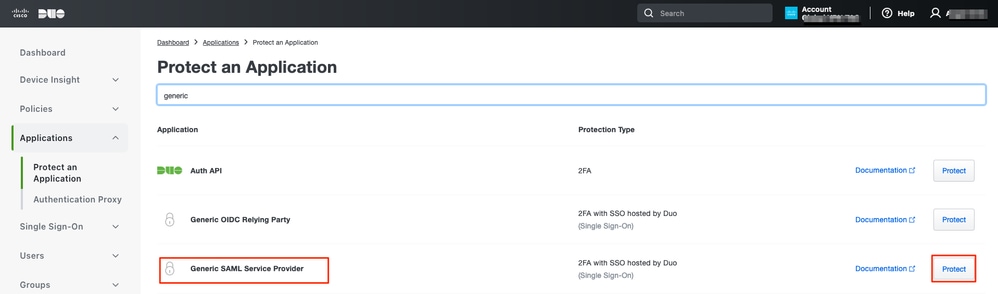
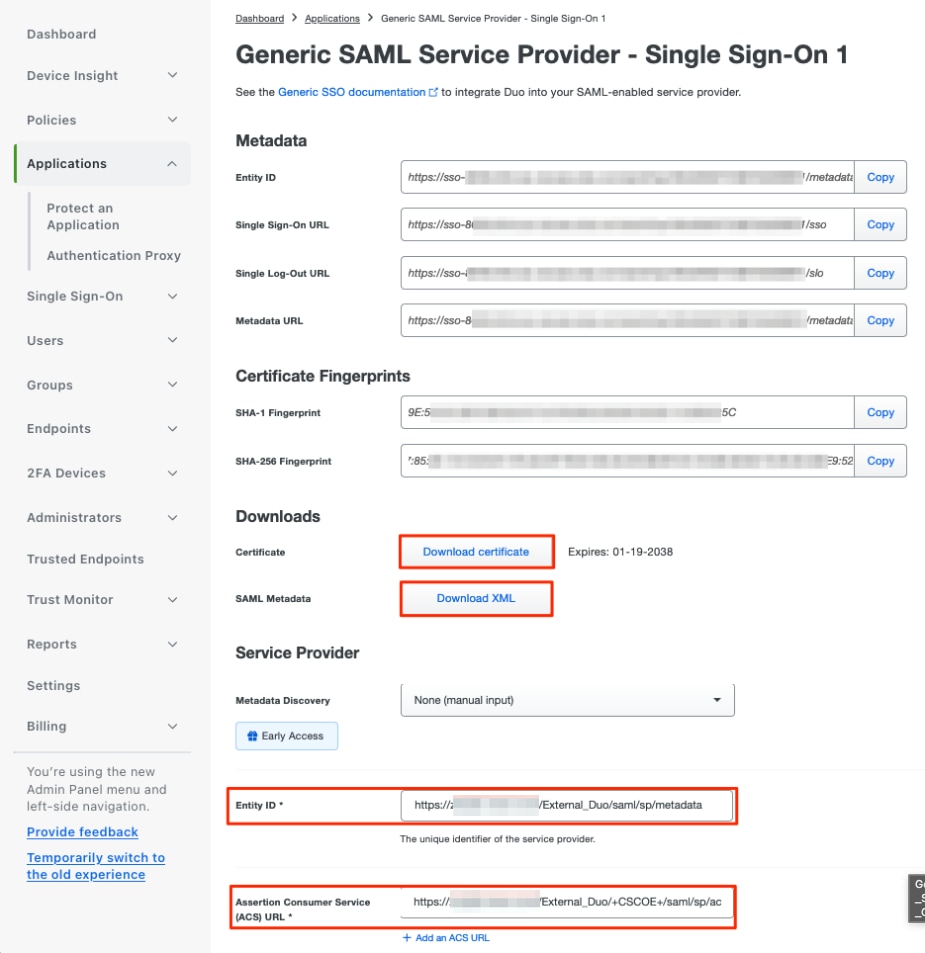
e. Download the Certificate and SAML Metadata from the IdP as it is required to continue the configuration on Secure Firewall.
f. Enter the Entity ID and Assertion Consumer Service (ACS) URL from the ZTNA Application Group (generated in step a).
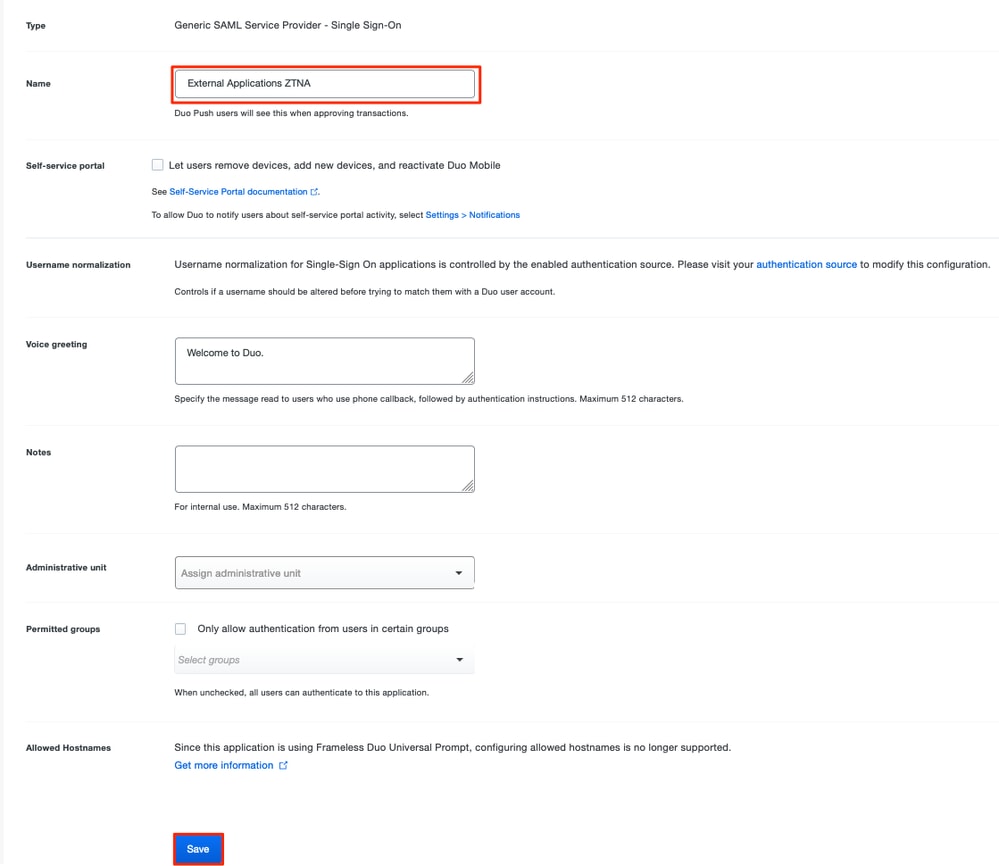
g. Edit the application in accordance to your specific requirements and allow access to the application only to the intended users and click Save.
h. Navigate back to the FMC and add the SAML IdP Metadata to the Application Group, using the files downloaded from the IdP.
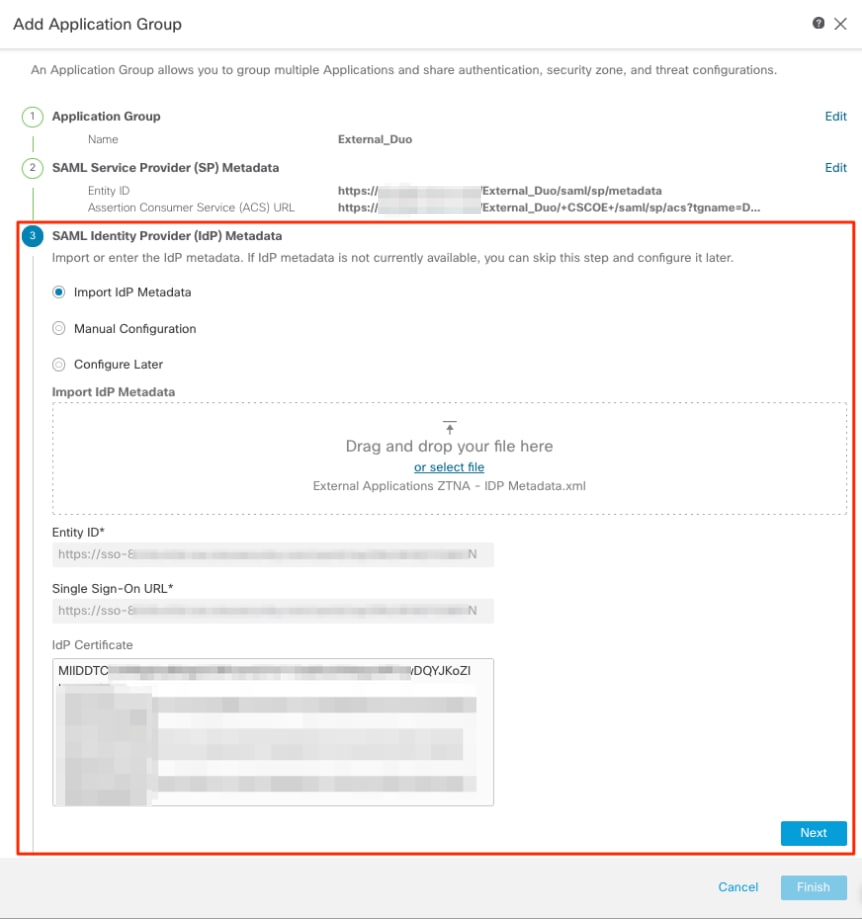
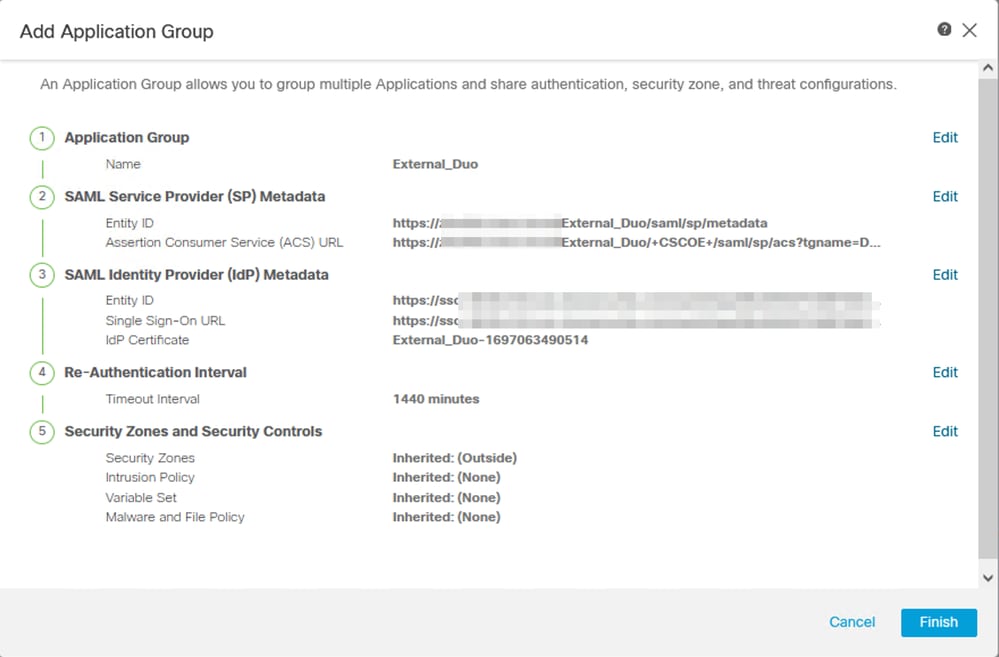
i. Click Next and configure the Re-Authentication Interval and Security Controls as per your requirements. Review the summary configuration and click Finish.
Application Group 2: Using Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) as IdP
a. Enter the Application Group Name and click Next for the SAML Service Provider (SP) Metadata to be displayed.
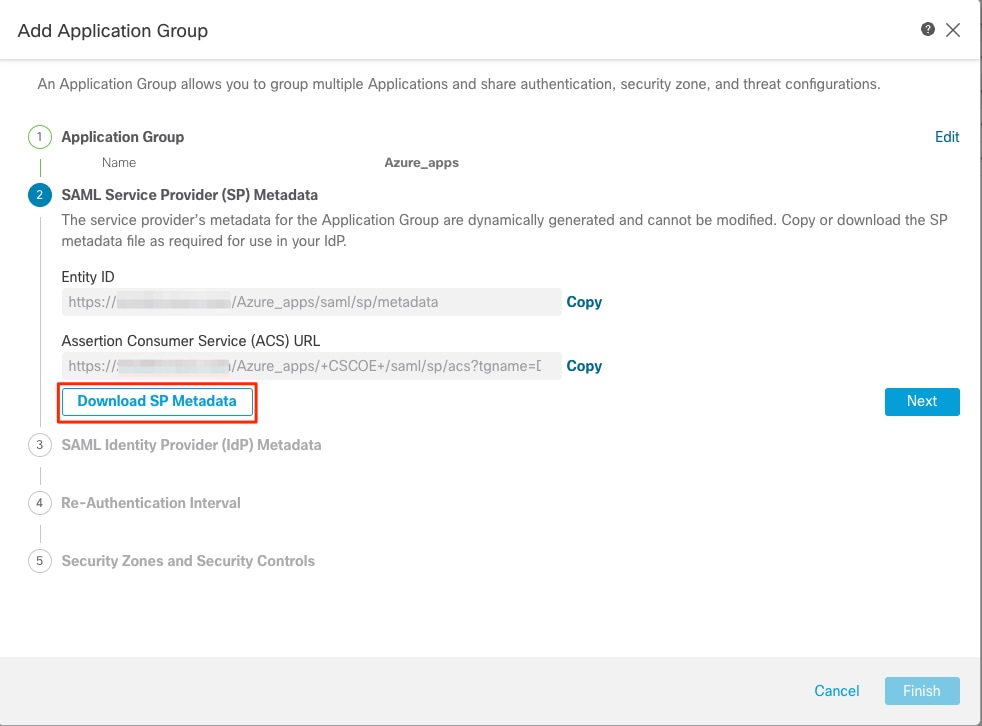
b. Once the SAML SP Metadata is displayed, go to the IdP and configure a new SAML SSO application.
c. Log in to Microsoft Azure and navigate to Enterprise applications > New Application.
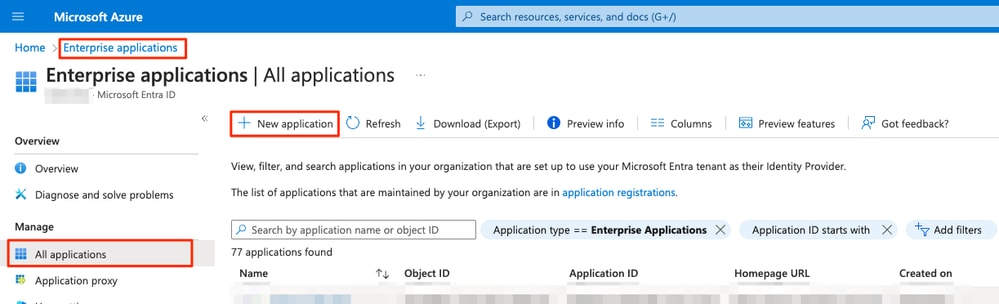
d. Click on Create your own application > Enter the name of the application > Create
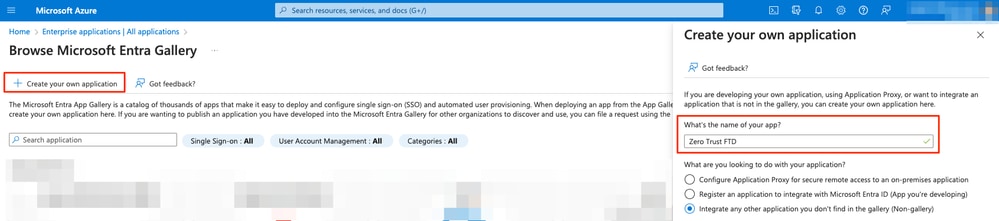
e. Open the application and click on Assign users and groups to define the users and/or groups that are allowed to access the application.
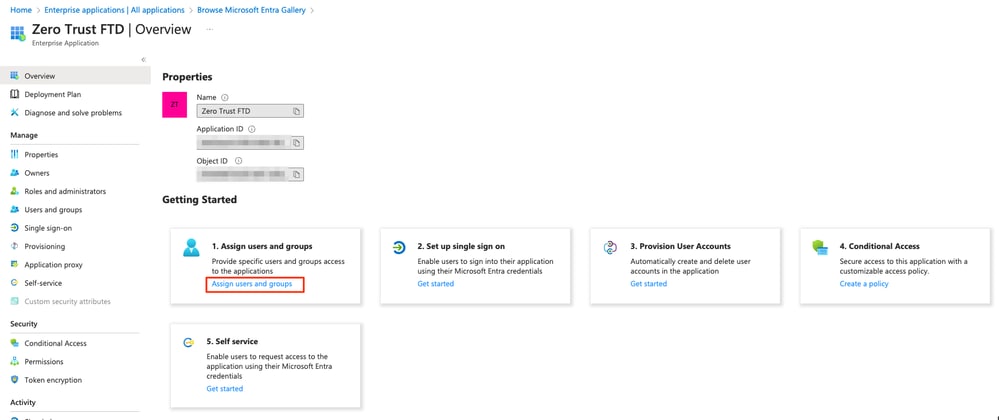
f. Click on Add user/group > Select the necessary users/groups > Assign. Once the correct users/groups have been assigned, click on Single sign-on.
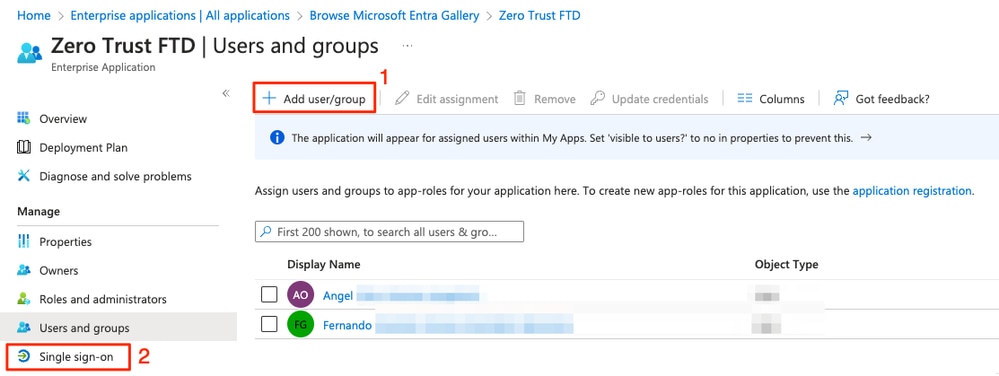
g. Once in the Single sign-on section, click on SAML.
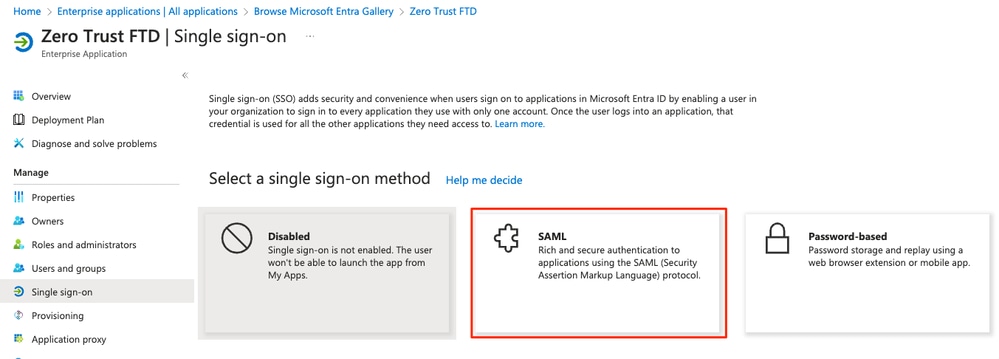
h. Click on Upload metadata file and select the XML file downloaded from the Service Provider (Secure Firewall) or manually enter the Entity ID and Assertion Consumer Service (ACS) URL from the ZTNA Application Group (generated in step a).
Note: Ensure to also download the Federation Metadata XML or individually download the the Certificate (base 64) and copy the SAML Metadata from the IdP (Login & Logout URLs and Microsoft Entra Identifiers) as these are required to continue the configuration on the Secure Firewall.
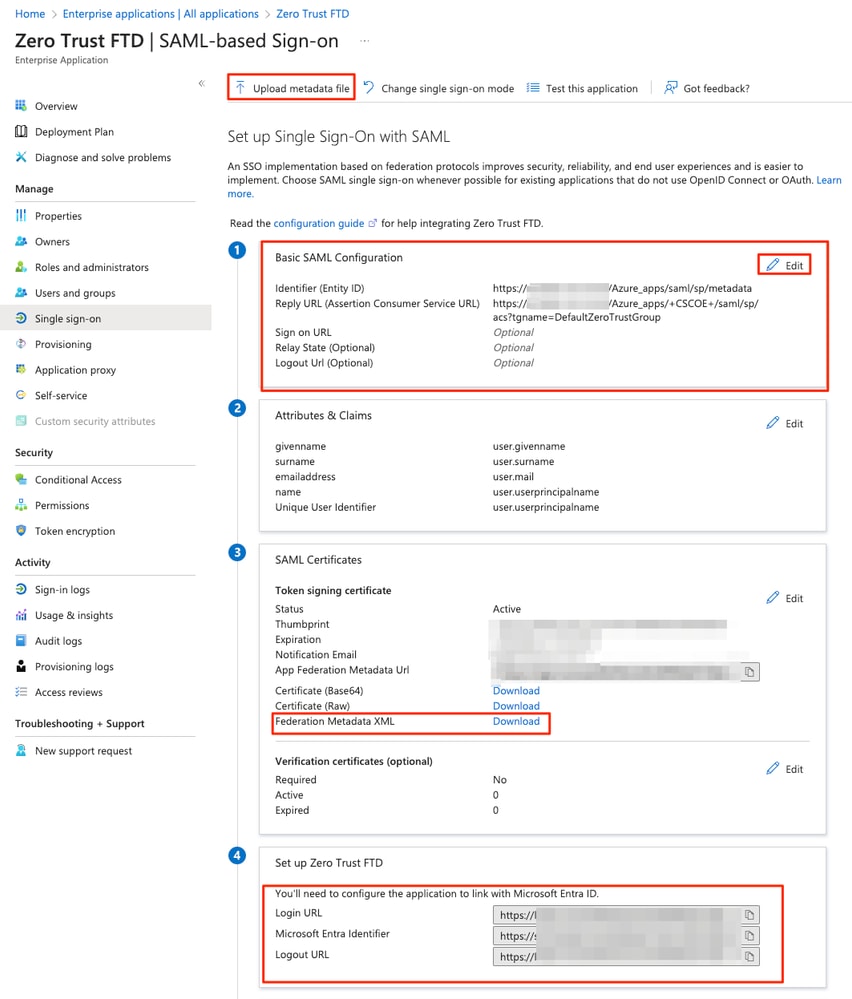
i. Navigate back to the FMC and import the SAML IdP Metadata to the Application Group 2, using the metadata file downloaded from the IdP or manually enter the required data.
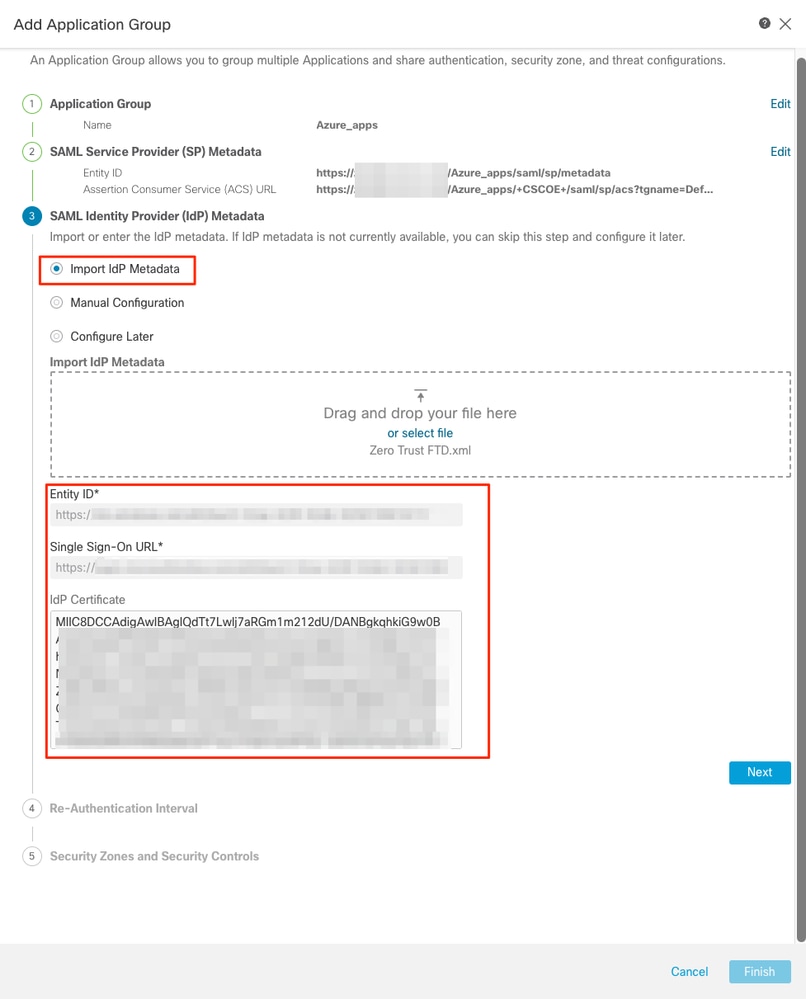
j. Click Next and configure the Re-Authentication Interval and Security Controls as per your requirements. Review the summary configuration and click Finish.
Configure Applications
Now that the Application Groups have been created, click Add Application to define the applications to be protected and accessed remotely.
- Enter the Application Settings:
a) Application Name: Identifier for the configured application.
b) External URL: Published URL of the application in the public/external DNS records. This is the URL used by users to access the application remotely.
c) Application URL: Real FQDN or Network IP of the application. This is the URL used by Secure Firewall to reach the application.
Note: By default, the External URL is used as Application URL. Uncheck the checkbox to specify a different Application URL.
d) Application Certificate: the certificate chain and private key of the application to be accessed (Added from FMC Home Page > Objects > Object Management > PKI > Internal certs)
e) IPv4 NAT Source (optional): The source IP address from the remote user is translated to the selected addresses before forwarding the packets to the application (only Host and Range type network objects/object-groups having IPv4 addresses are supported). This can be configured to ensure that the applications have a route back to the remote users through the Secure Firewall
f) Application Group (optional): Select if this Application is added to an existing Application Group to use the settings configured for it.
In this example, the applications to be accessed using ZTNA are a test FMC Web UI and the Web UI of a CTB located behind the Secure Firewall.
The certificates of the Applications must be added in Objects > Object Management > PKI > Internal certs:
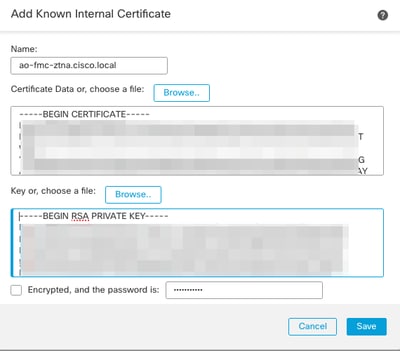
Note: Ensure to add all the certificates for each application to be accessed with ZTNA.
Once the certificates have been added as Internal Certs, continue to configure the remaining settings.
The Application settings configured for this example are:
Application 1: Test FMC Web UI (Member of the Application Group 1)
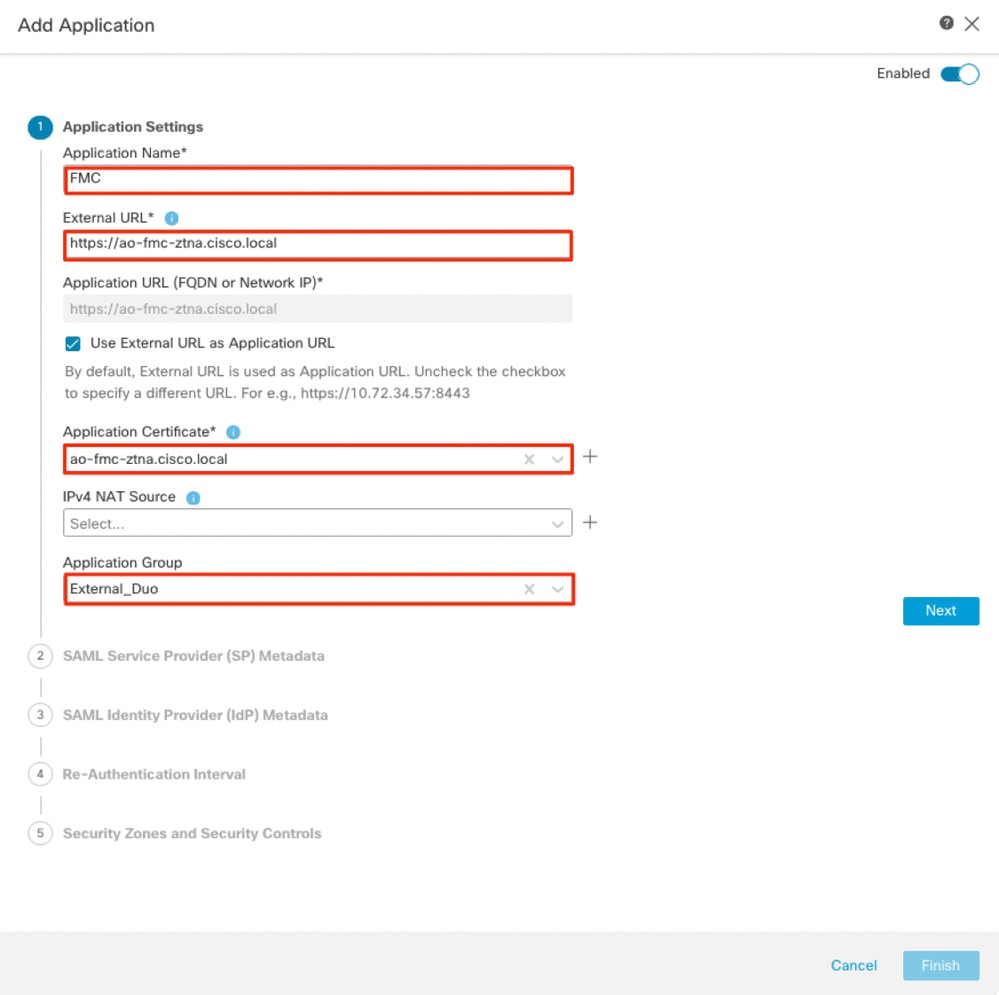
As the Application was added to the Application Group 1, the remaining settings are inherited for this application. You can still override the Security Zones and Security Controls with different settings.
Review the configured Application and click Finish.
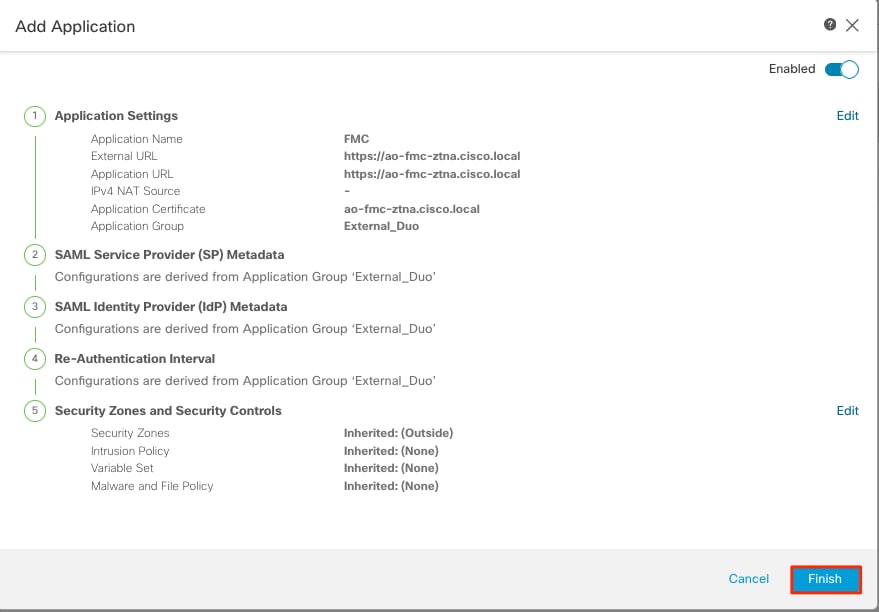
Application 2: CTB Web UI (Member of the Application Group 2)
The configuration summary for this application is the next:

Note: Notice that for this application, a network object "ZTNA_NAT_CTB" was configured as IPv4 NAT Source. With this configuration, the source IP address from the remote users is translated to an IP address within the configured object before forwarding the packets to the application.
This was configured because the application (CTB) default route points to a gateway other than the Secure Firewall, therefore the return traffic was not sent to the remote users. With this NAT configuration, a static route was configured on the application for the subnet ZTNA_NAT_CTB to be reachable through the Secure Firewall.
After the applications have been configured, they are now displayed under the corresponding Application Group.
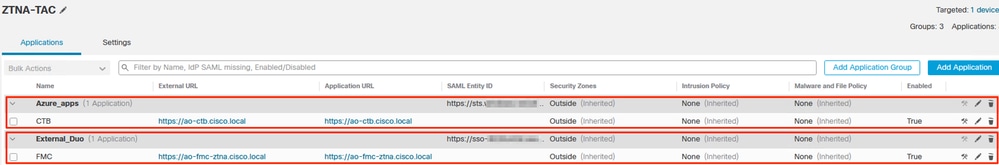
Finally, save the changes and deploy the configuration.
Verify
Once the configuration is in place, remote users can reach the applications through the external URL and if they are allowed by the corresponding IdP, have access to it.
Application 1
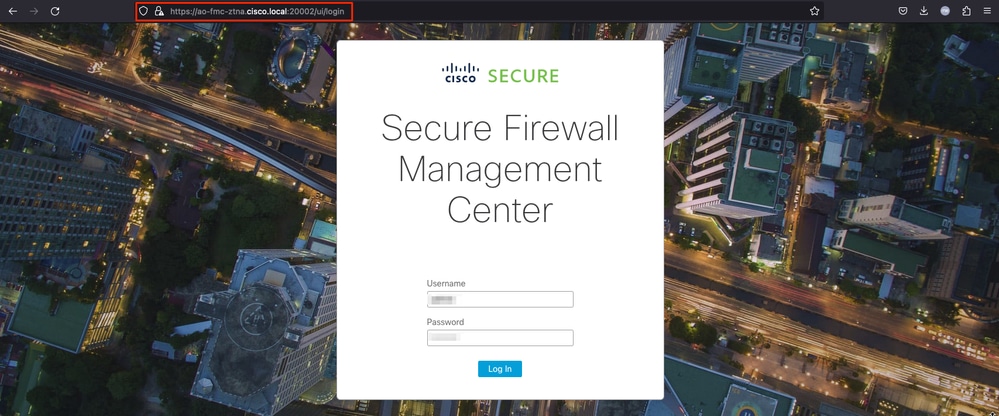
1. The user opens a web browser and navigates to the external URL of the application 1. In this case, the external URL is "https://ao-fmc-ztna.cisco.local/"
Note: The external URL name must resolve to the IP address of the Secure Firewall interface that was configured. In this example, it resolves to the Outside interface IP address (192.0.2.254)
2. As this is a new access, the user is redirected to the IdP login portal configured for the application.
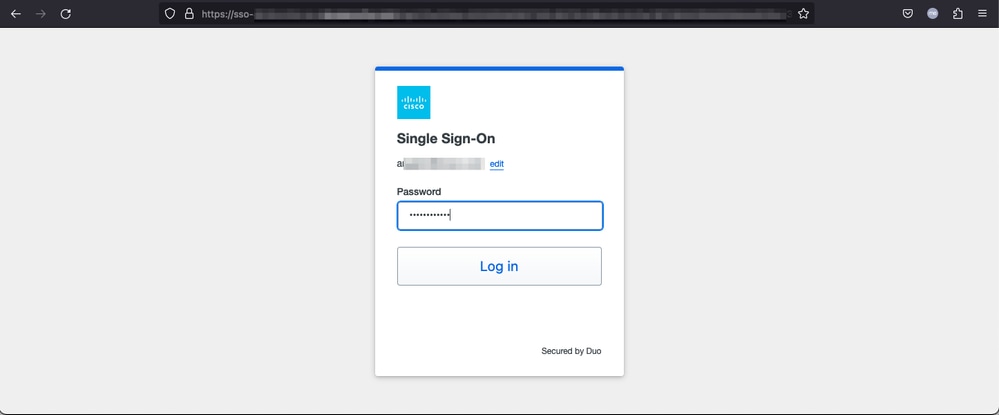
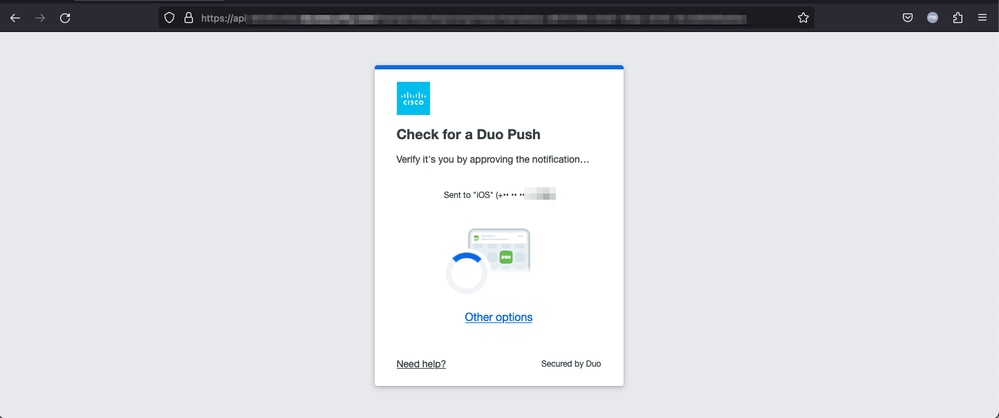
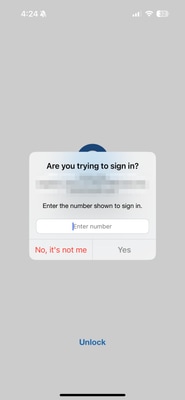
3. The user is sent a Push for MFA (this depends on the MFA method configured on the IdP).
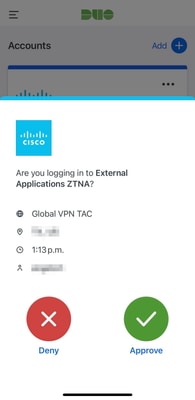
4. Once the user is successully authenticated and authorized by the IdP, it is granted remote access to the application defined in the ZTNA Policy (test FMC Web UI).
Application 2
1. The same steps are performed to access the second application (CTB Web UI), however, authentication is done by Microsoft Entra ID.
The user opens a web browser and navigates to the external URL of the application 2. In this case, the external URL is "https://ao-ctb.cisco.local/ "
Note: The external URL name must resolve to the IP address of the Secure Firewall interface that was configured. In this example, it resolves to the Outside interface IP address (192.0.2.254)
2. As this is a new access, the user is redirected to the IdP login portal configured for the application.
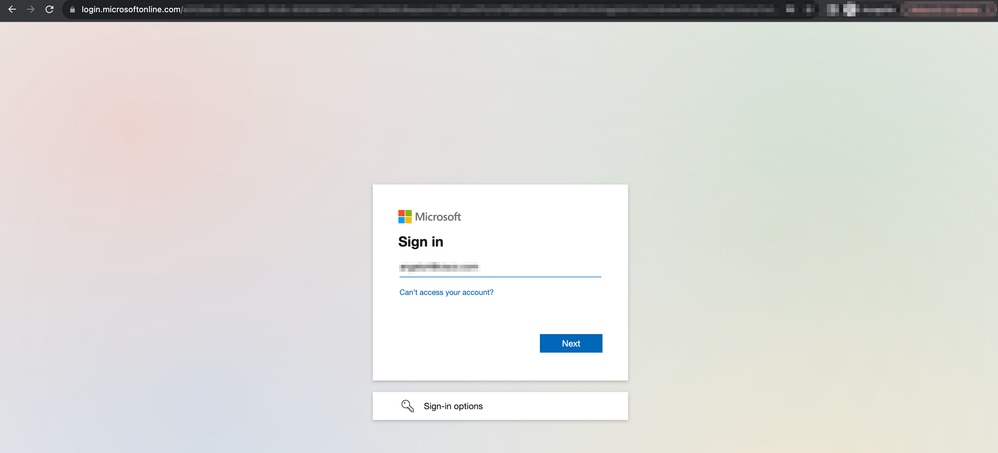
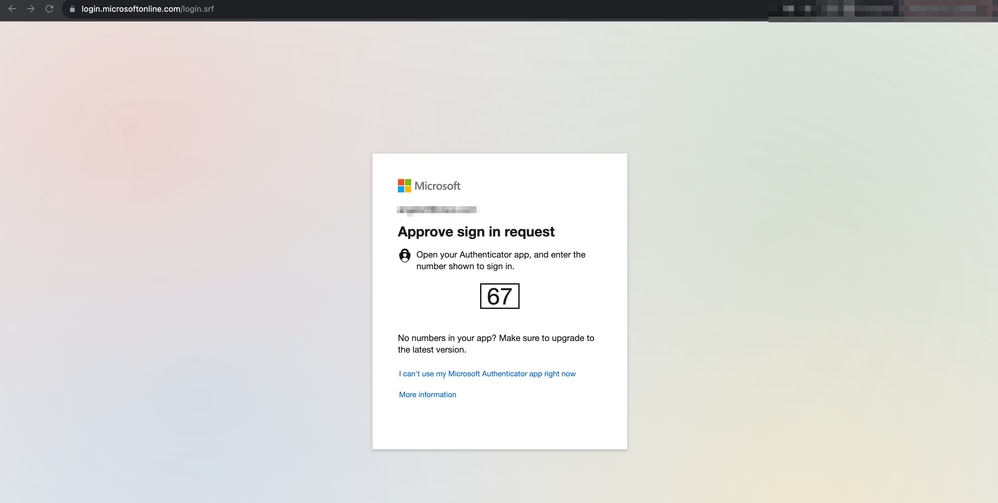
3. The user is sent a Push for MFA (this depends on the MFA method configured on the IdP).
4. Once the user is successully authenticated and authorized by the IdP, it is granted remote access to the application defined in the ZTNA Policy (CTB Web UI).
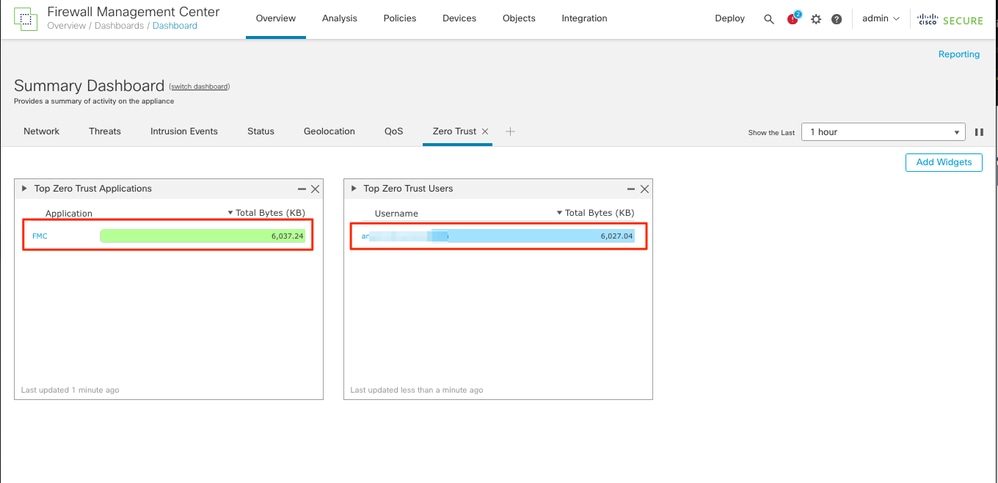
Monitor
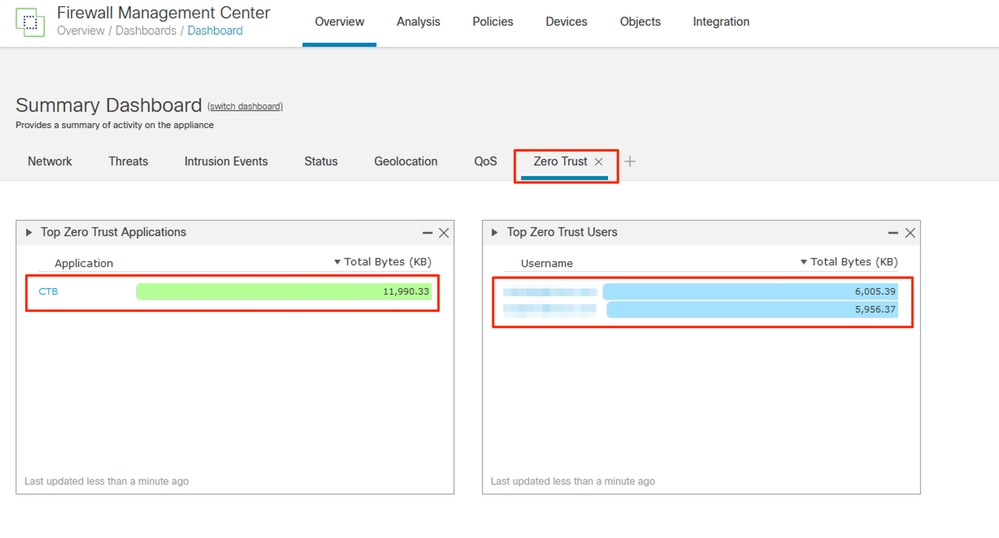
You can monitor the applications and users from the FMC Overview > Dashboard > Zero Trust.
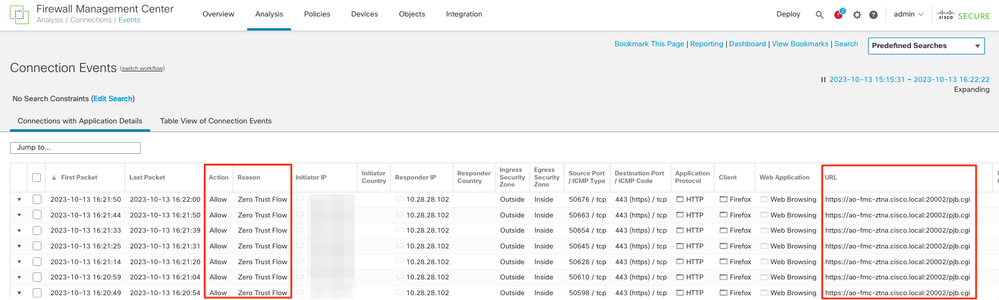
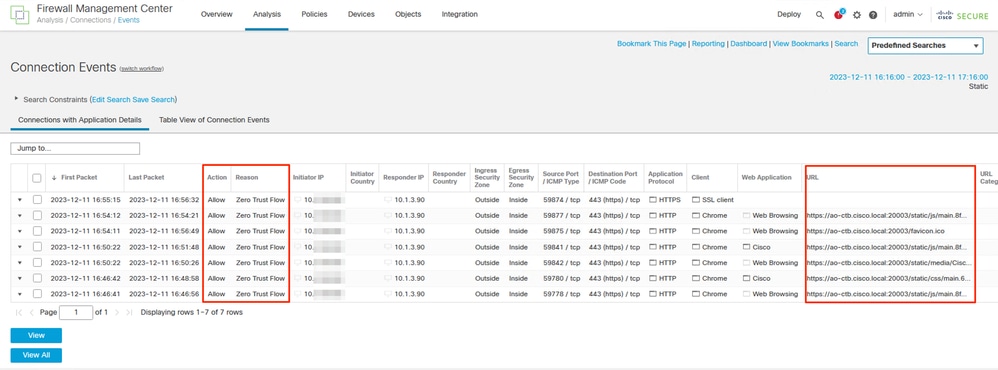
To investigate the connection events, navigate to Analysis > Connections > Events.
Additionally, show and clear commands are available in the FTD CLI to view the zero-trust configuration and display statistics and session information.
firepower# show running-config zero-trust
application Show application configuration information
application-group Show application group configuration
| Output modifiers
<cr>
firepower# show zero-trust
sessions Show zero-trust sessions
statistics Show zero-trust statistics
firepower# show zero-trust sessions
application show zero-trust sessions for application
application-group show zero-trust sessions for application group
count show zero-trust sessions count
user show zero-trust sessions for user
detail show detailed info for the session
| Output modifiers
<cr>
firepower# clear zero-trust
sessions Clear all zero-trust sessions
statistics Clear all zero-trust statistics
firepower# clear zero-trust sessions
application Clear zero-trust sessions for application
user Clear zero-trust sessions for user
<cr>
Troubleshoot
A diagnostics tool has been added to the FMC to troubleshoot ZTNA related issues.
- The Diagnostics feature is designed to ease the troubleshooting process for users by showing at what point in the Zero Trust Access configuration an issues exists
- Diagnostics provide overall analysis (OK or not) and collects detailed logs that can be analysed to solve issues
Application-specific Diagnostics is used to detect:
- DNS-related issues
- Misconfiguration, for example, socket not opened, classification rules, NAT rules
- Issues in Zero Trust Access Policy
- Interface-related issues, for example, interface not configured, or interface is down
Generic Diagnostics to detect:
- If a strong cipher license is not enabled
- If the application certificate is not valid
- If the authentication method is not initialised to SAML in the default tunnel group
- HA and cluster bulk sync issues
- Get insights from snort counters to diagnose issues, such as those related to tokens or decryption
- PAT pool exhaustion issue in source translation.
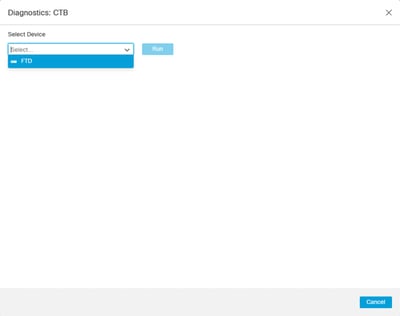
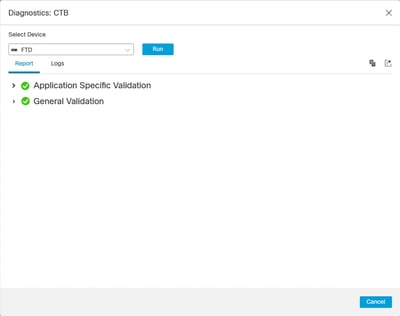
To run the diagnostics:
1. Navigate to the diagnostics icon present for each ZTNA Application.
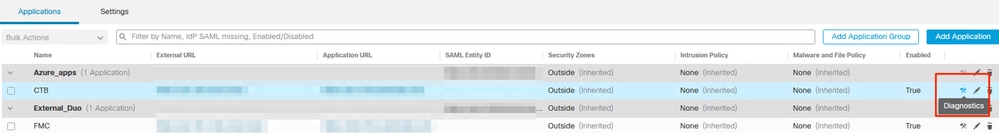
2. Select a device and click Run.
3. View the results in the report.
If you need to work with Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) for troubleshooting purposes, please collect the output of the next debug and show commands:
- show counters protocol zero-trust
- debug zero-trust 255
- debug webvpn request 255
- debug webvpn response 255
- debug webvpn saml 255
Related Information
- For additional assistance, please contact TAC. A valid support contract is required: Cisco Worldwide Support Contacts.
- You can also visit the Cisco VPN Community here.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
14-Dec-2023
|
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Angel OrtizSecurity Technical Leader
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback