Introduction
This document describes migrating a Site-to-Site VPN from one FTD to another, managed by the same FMC, while keeping the VPN connection to router.
Prerequisites
Requirements
To effectively carry out the migration process, Cisco recommends familiarity with the given topics:
• FTD Registration with FMC: Understanding how to register Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) devices with the Firepower Management Center (FMC).
• Site-to-Site VPN Configuration: Experience in configuring site-to-site VPNs on FTD devices managed by FMC.
Components Used
This document is based on the given software and hardware versions:
• Firepower Threat Defense Virtual (FTDv): Two instances running version 7.3.1.
• Firepower Management Center (FMC): Version 7.4.0.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Configure
Procedure
1. Register the New FTD with FMC:
• Begin by registering the new Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) device within the Firepower Management Center (FMC) under Devices > Device Management.
• In this example, The new device registered is named "sadks2."
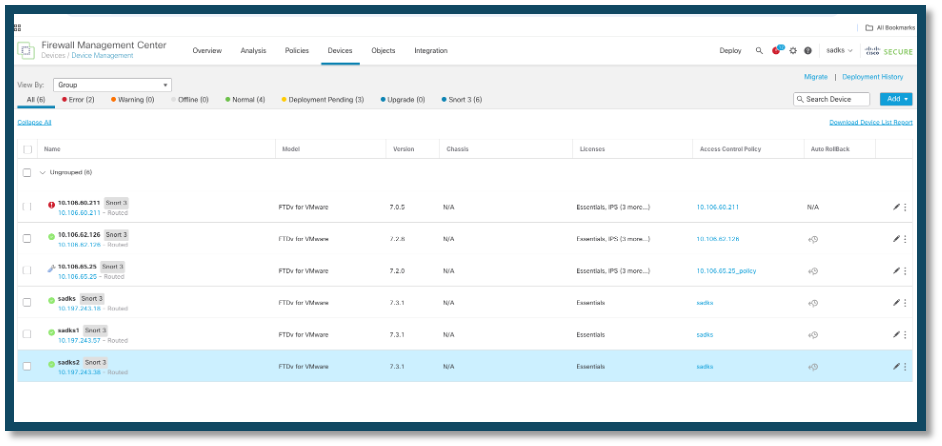 New FTD Registered
New FTD Registered
2. Access the Site-to-Site Tunnel Configuration:
• Navigate to the site-to-site tunnel settings by going to Devices > Site to Site in the FMC interface.
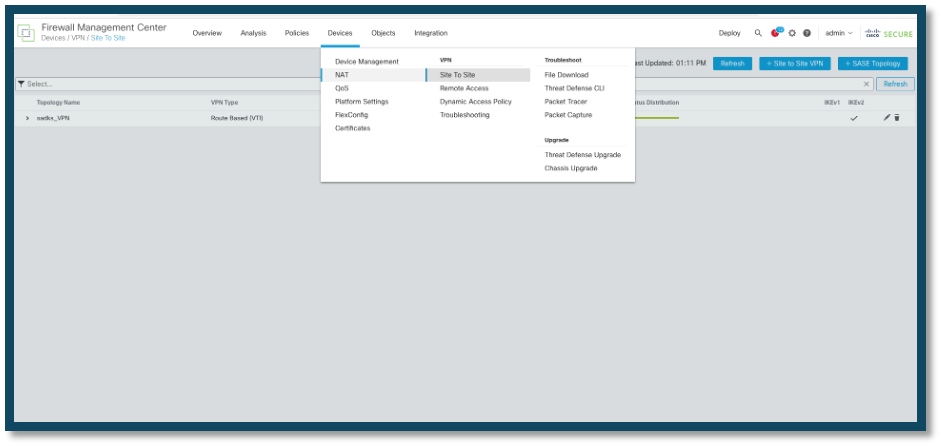 Navigate to VPN Config
Navigate to VPN Config
3. Modify the VPN Configuration:
• Select the VPN configuration that you intend to update.
• Example: In this scenario, the VPN configuration involves an FTD device and a router. Here, Node B represents the FTD device, and the configuration has been updated to change the device association from "sadks" to "sadks2."
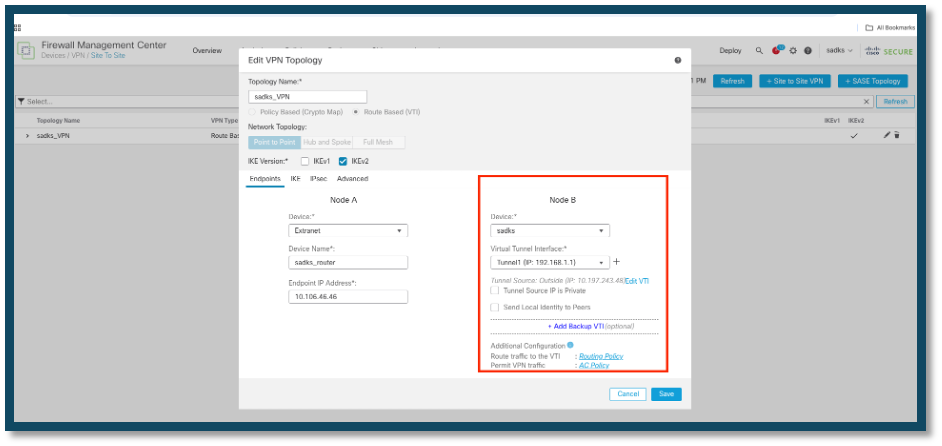 Old FTD Device
Old FTD Device
TO
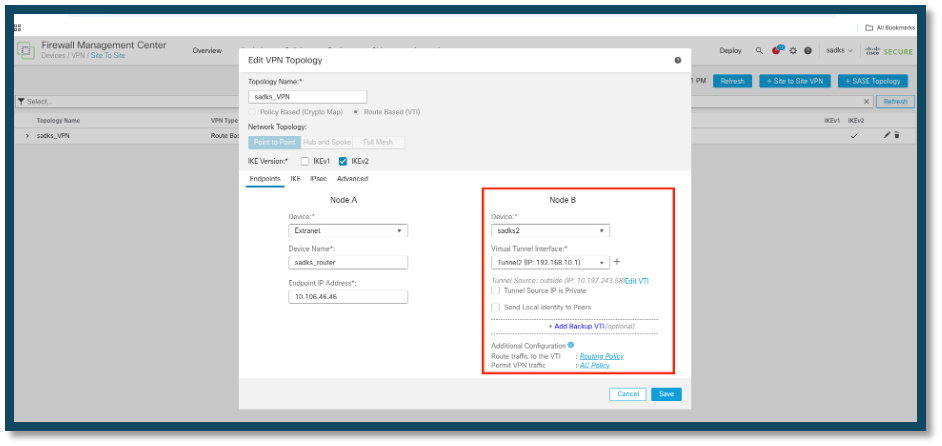 New FTD Device
New FTD Device
4. Save and Deploy the Configuration:
• After making the necessary changes, save the configuration and deploy it to activate the updates.
Verify
The tunnel comes up once deployed.
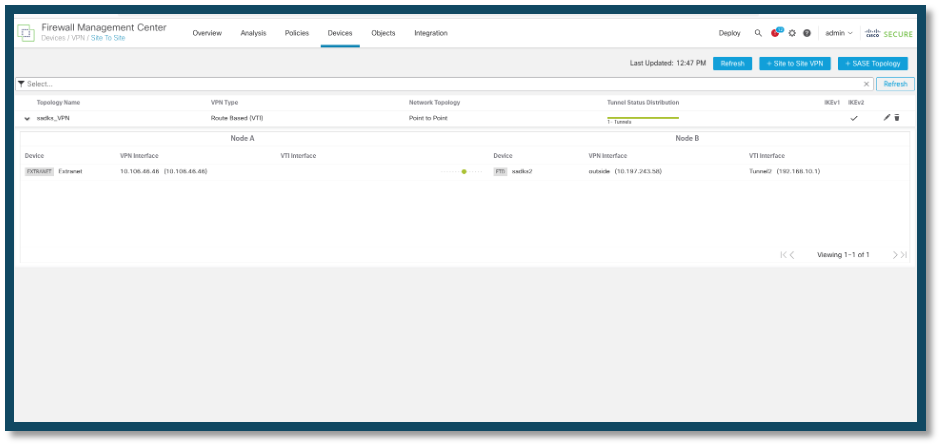 Tunnel Status
Tunnel Status
Troubleshoot
Initial Connectivity Issues
When building a VPN there are two sides negotiating the tunnel. Therefore, it is best to get both sides of the conversation when you troubleshoot any type of tunnel failure. A detailed guide on how to debug IKEv2 tunnels can be found here: How to debug IKEv2 VPNs
The most common cause of tunnel failures is a connectivity issue. The best way to determine this is to take packet captures on the device. Use this command to take packet captures on the device:
capture capout interface outside match ip host 10.106.46.46 host 10.197.243.58
Once the capture is in place, try to send traffic over the VPN and check for bi-directional traffic in the packet capture.
Review the packet capture with this command:
show cap capout
Traffic-Specific Issues
Common traffic issues that you experience are:
- Routing issues behind the FTD -- internal network unable to route packets back to the assigned IP addresses and VPN clients.
- Access control lists blocking traffic.
- Network Address Translation not being bypassed for VPN traffic.
For further information regarding VPNs on the FTD managed by FMC, you can find the full configuration guide here: FTD managed by FMC configuration guide






 Feedback
Feedback