Introduction
This document describes the Configure Customer Voice Portal (CVP) Call Studio Database Element, Tomcat Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI), for SQL Database.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Cisco Unified Contact Center Enterprise (UCCE) Release 12.6.2
- Cisco Package Contact Center Enterprise (PCCE) Release 12.6.2
- CVP Release 12.6.2
- CVP Call Studio 12.6.2
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software versions:
- Cisco PCCE Release 12.6.2
- CVP Release 12.6.2
- CVP Call Studio 12.6.2
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
The database element provides the ability to run an Structured Query Language (SQL) command on external databases within a voice application call flow. The element requires JNDI to be configured in the Java application server in order to handle database connections. Only a single SQL statement can be run per element. There are four types of commands that can be made, but in this document only the single command is used:
Single – This is used to run a SQL query that returns only a single row. Element data will be created with the variable names being the names of the columns returned and the value of that column as the element data value (as a string). If no row is returned, no element data will be set.
More Information can be found in the CVP VXML Element guide.
Configuration
This section explains how to create a new JNDI database connection in Tomcat.
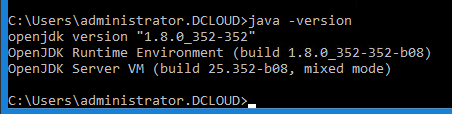
Step 1. Determine the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) Version on your CVP Server.
- Click the Start button (left button corner on your desktop bar)
- Click the Run... option
- Type in CMD and click OK in order to bring up the DOS prompt
- Then type in java-version
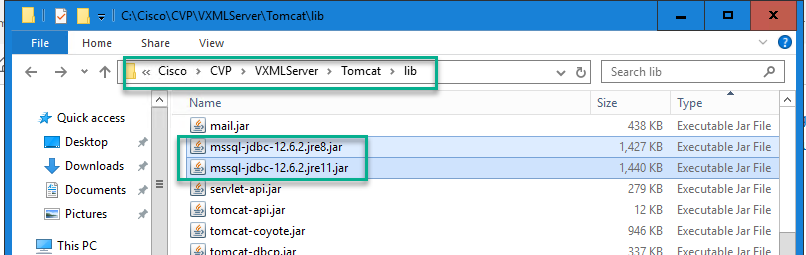
Step 2. Install a compatible Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) driver with the SQL Version. In order to enable database access on your application server, a compatible JDBC driver must be installed. These drivers, typically packaged as JAR files, must be placed in a directory accessible to the application server classpath (on Tomcat, for example, place in %CVP_HOME%\VXMLServer\Tomcat\lib).
Different drivers can be found here.
An example from the MS supported list:
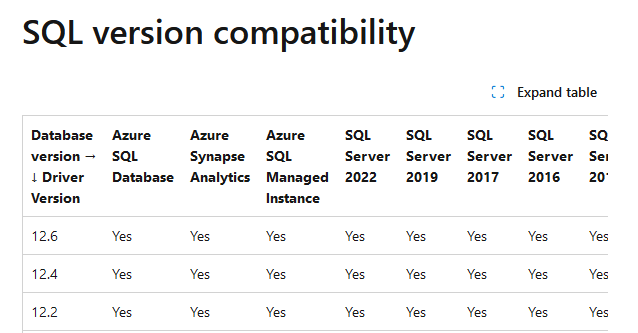
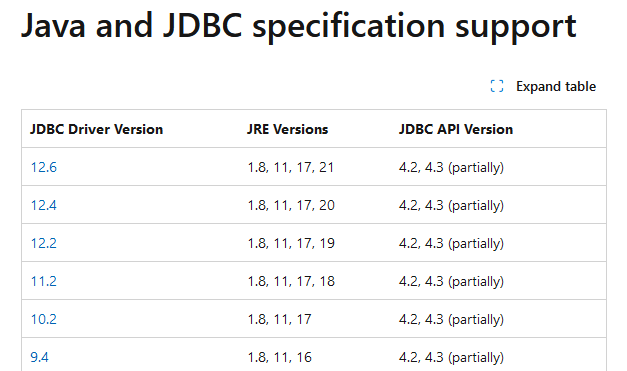

Note: The database must exist for this connection to work. CVP Voice XML (VXML) Server will not create the database for you. In this document the UCCE AW database is used as an example and the JDBC driver version 12.6 is the one installed.
Step 2. Add a Tomcat Context for the database connection so that the CVP VXML Server knows how to communicate with your database. For more information, see https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/jndi-datasource-examples-howto.html.
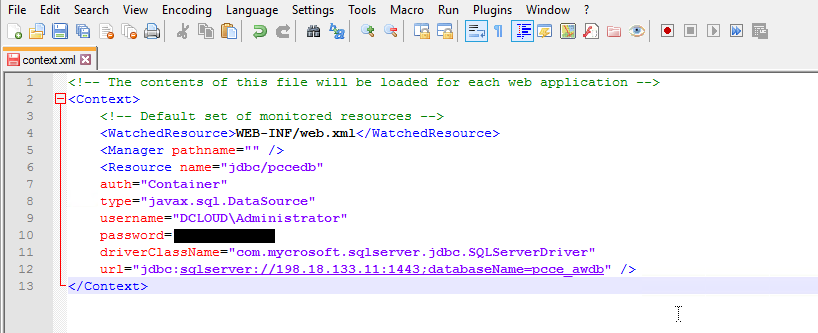
Here is an example that uses SQL (edit context.xml from AUDIUM_HOME\Tomcat\conf folder where AUDIUM_HOME is usually Cisco\CVP\VXMLServer):
<Context>
<Resource name="jdbc/<LABEL_YOU_CHOOSE>"
auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSource"
username="USER_NAME"
password="USER_PW"
driverClassName="com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver"
url="jdbc:sqlserver://HOSTNAME_OR_IP:PORT;DatabaseName=< DB_NAME>" />
</Context>
The default port number for MS SQL is 1433. An example url for the earlier context will be 'jdbc: sql://localhost:1433;databaseName=pcce_awdb'.

Note: Alternately, the <Resource> can be configured in the server.xml file under <GlobalNamingResources>, and a <ResourceLink> created in context.xml under <Context>.
For enhanced security, it is recommended to set the username or password using the element and manually delete the username and password fields from the context.xml file.
If the username and password is provided in the element, the username and password in the context.xml file will be ignored.
Step 3. Under heavy load conditions, enable Database Connection Pooling.
A database connection pool creates and manages a pool of connections to a database. Recycling and reusing already existing connections to a database is more efficient than opening a new connection. For further information on Tomcat Database Pooling, see https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/jndi-datasource-examples-howto.html.

Note: Tomcat 8.0 has two connection pool libraries: commons-dbcp and tomcat-jdbc-pool. Due to a known issue with tomcat-jdbc-pool connection pool library, if the connection between the CVP VXML server and the remote SQL server goes down, the connections are not re-established automatically. The connections can be re-established only after the VXMLServer tomcat service is restarted.
The commons-dbcp connection pool library does not have this problem. The commons-dbcp library is used by default, and the tomcat-jdbc-pool is only used if the tomcat context.xml file contains this line:
factory="org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSourceFactory"
Due to this issue, Cisco does not recommend using the tomcat-jdbc-pool library.
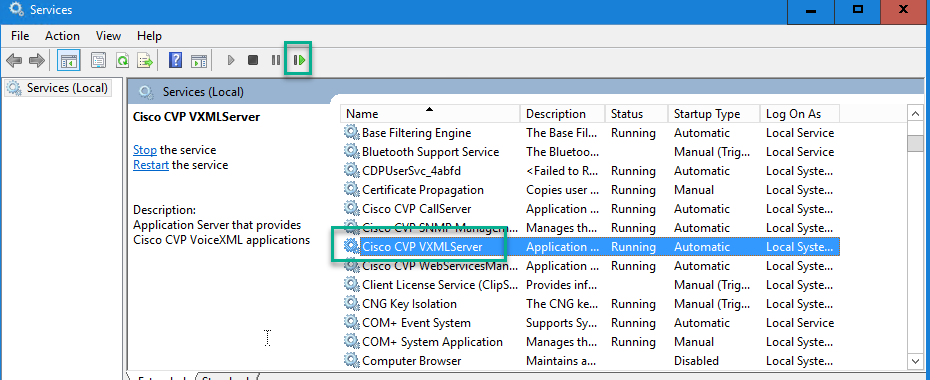
Step 4. Restart the CVP VXML Service.
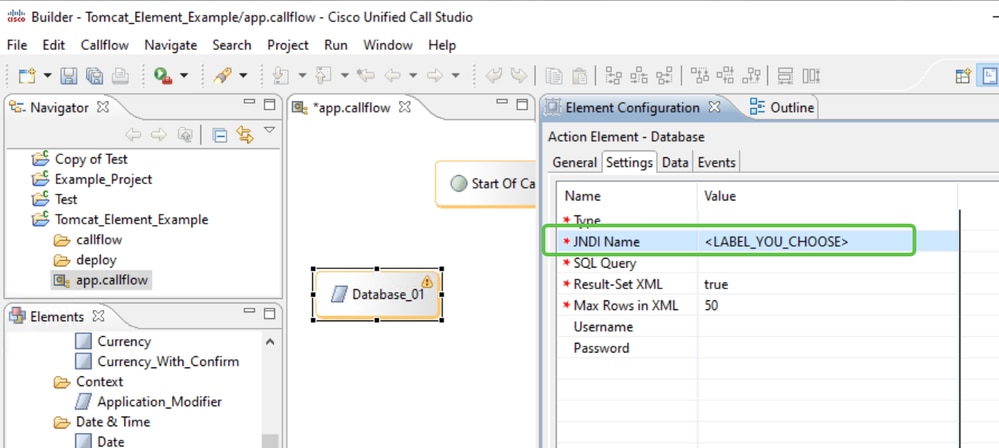
Step 5. In CVP Call Studio, edit the configuration of the Database element in question. Enter the string you entered in <LABEL_YOU_CHOOSE> from the Tomcat Context into the JNDI Name property of the Settings tab of your Database element.

Note: Do not include the jdbc/portion here.
Step 6. Save, Deploy, and Update the application on the VXML server.
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration.
Related Information









 Feedback
Feedback