Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder Line Card Data Sheet
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
The Cisco® Network Convergence System (NCS) 2000 400 Gbps XPonder line card dramatically enhance Dense Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (DWDM) transmission. The XPonder provides 400 Gbps of Client, and 400 Gbps of Trunk capacity on a single, two-slot wide line card capable of mapping Client traffic to either of two 200 Gbps Trunk ports, or into a 400G dual-wavelength super-channel, all while leveraging software configurable Coherent modulation schemes.
Three Coherent modulation formats are supported to best suit network requirement:
● 100 Gbps Coherent polarization-multiplexed Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK)
● 150 Gbps Coherent polarization 8-state quadrature amplitude modulation (8-QAM)
● 200 Gbps Coherent polarization 16-state quadrature amplitude modulation (16-QAM)
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder Card (Figure 1) simplifies the integration and transport of 10 Gigabit, 40 Gigabit and 100 Gigabit Ethernet and Optical Transport Unit Level 4 (OTU-4) interfaces and services into enterprises and service provider optical networks.

Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder
The bandwidth carried on core and metropolitan DWDM networks is growing exponentially, while operators’ revenues struggle to keep pace. Internet traffic continues to grow at exponential rates, mainly due to demand for next-generation services such as quadruple play (data, voice, video, and mobility), video distribution, Internet Protocol Television (IPTV), and other high-bandwidth services. Complicating the issue is the varying state of migration between legacy and Packet services that operators find themselves within, causing them to find creative ways to support a variety of service types.
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder solution can dramatically lower the cost to carry bandwidth, helping to maintain and improve customers’ profitability with advanced modulation schemes, the ability to transmit 200 Gbps wavelengths on existing or new DWDM systems for both metro and Long Haul distances, improves return on investment by increasing the overall capacity per fiber pair without impacting the unregenerated transmission distance supported by the system.
The 200 Gbps 16QAM solution enables 25.4 Tbps capacity transmission over a single Fiber Pair.
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder Card also supports an embedded OTN switching functionality capable of supporting ODU-2/4 switching between Clients and Trunk Ports.
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder Card provides compelling benefits in the areas of Efficiency, Performance, Flexibility and Density improvements.
Efficiency
In a single, 2-slot wide line card, the 400 Gbps XPonder supports any mix of 40x 10G, 8x 40GE+8x10GE and 4x 100G signals up to a maximum bandwidth of 400 Gbps, while providing the ability to selectively groom these services into 2 wavelengths capable of 200 Gbps each.
Performance improvement
The latest generation of Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) provide a dramatic boost to the optical performance of 100 Gbps QPSK and 200 Gbps 16-QAM. Availability of 8-QAM Modulation format further enhance the Long Haul capability of the system, allowing to take advantage of additional transport capacity for all cases where 100 Gbps reach is not needed.
Flexibility
The service type of both Client and Trunk optics are based on pluggable modules, allowing a true pay-as-you-grow investment profile where card personality is defined and redefined at the pluggable level. Due to the port-by-port service type flexibility, this also radically reduces the variety of line cards an operator is required to inventory.
Density
Thanks to the adoption of the QSFP+ and QSFP28 form factors for the client interfaces, the Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder is able to double the slot density compared with previous generation of Transponder card.
The NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder (Figure 2) is a 2-slots wide line card that provides two high speed CFP2-based DWDM ports capable of transmitting 100 Gbps, 150 Gbps and 200 Gbps over a single carrier.
The high speed Trunk ports provides:
● 100 Gbps coherent DWDM transmission with QPSK modulation
● 150 Gbps coherent DWDM transmission with 8-QAM modulation
● 200 Gbps coherent DWDM transmission with 16-QAM modulation
The transmission rate is software configurable and the line card provides high gain SD-FEC with 15% and 25% overhead.
The NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder supports six QSFP+ based client ports that can be equipped with 40 Gbps or 4x 10 Gbps optics and four QSFP28/QSFP+ based client ports that can be equipped with 100 Gbps QSFP28, 40 Gbps QSFP+ and 4x 10 Gbps QSFP+.
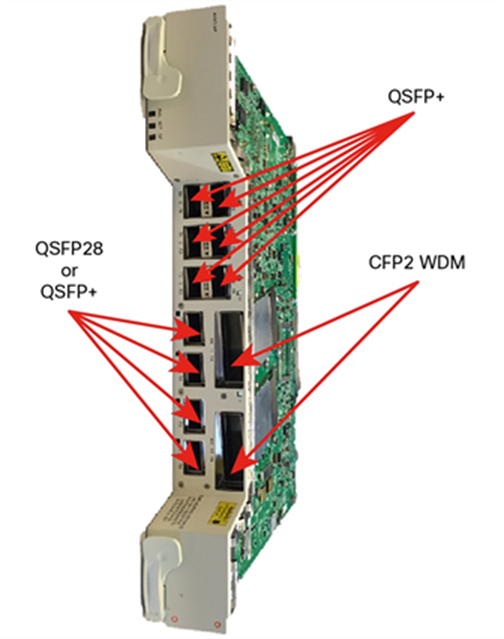
Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder
Advanced modulation scheme
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder line card features multiple software configurable modulation schemes to cope with tradeoffs between reach and transport capacity per wavelength. The primary modulation schemes leveraged today for DWDM transmission are QPSK, 8-QAM and 16-QAM. The constellation diagrams for these modulation types are illustrated in Figure 3.

Constellation diagrams for QPSK, 8-QAM, and 16-QAM
While higher order modulation formats provide higher spectral efficiency, they are limited by reach.
Figure 4 shows variation of reach vs. spectral efficiency for QPSK, 8-QAM and 16-QAM using SMF and LEAF fiber for various channel spacing.
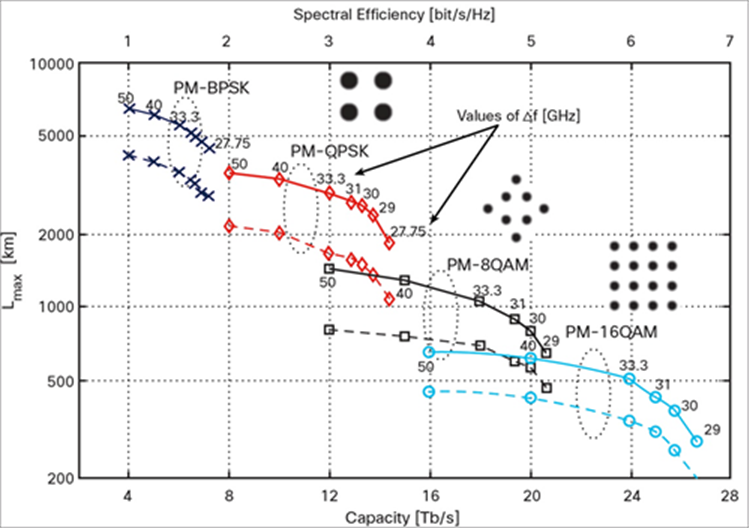
The chart provides capacity (Tbps) and spectral efficiency (bit/s/Hz) VS maximum reach (Lmax) for different modulation schemes. SMF Is represented in solid lines and LEAF Is represented in dashed lines.
Cisco Coherent Transmission technology greatly enhances the reach and reliability of transport performance while providing the flexibility to select the optimal modulation scheme for a specific application. The primary benefits of Cisco Coherent technology are:
● Strong optical signal-to-noise ratio performance
● Outstanding chromatic dispersion robustness, avoiding any additional cost related to optical chromatic dispersion compensation equipment
● Extended polarization mode dispersion robustness
● Very high spectral efficiency, allowing wavelengths to be transmitted across a large number of ROADMs with negligible penalty
Trunk CFP2 WDM pluggables
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder Trunk ports supports Analog Coherent Optical (ACO) CFP2 WDM with software-provisionable tuneability across the full C-Band, covering 96 Nyquist shaped channels on the 50GHz grid or gridless with 100MHz tuning granularity per channel. Different modulation schemes are also software configurable as described earlier.
Client ports
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder provides the following client services:
● 10 Gbps through 4x 10 Gbps QSFP+, the following client protocols are available: 10GE LAN-PHY, OC-192, STM-64, OTU2/2e, 8/10/16G FC.
● 40GE through QSFP+ supported and hardware readiness for OTU-3 service with software upgrade in future
● 100 Gbps through 100 Gbps QSFP28, the following client protocols are available: 100GE and OTU4
Software configurable FEC option
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder features the ability to select between two overhead configurations from the management interface for Software Defined Forward Error Correction (SD FEC): 25% overhead for maximum performances, 15% overhead to minimize filtering impairment.
10 Port 10 Gbps line card pairing configuration
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder can be coupled with the 10-Port 10 Gbps line card to support 10-port 10 Gbps Muxponder capabilities. The XPonder can be connected through the Cisco Network Convergence System (NCS) 2006 or NCS 2015 backplane (no client required) with the 10-Port 10 Gbps line card to provide OTN multiplexing of 10 ports of 10GE LAN-PHY data streams into a single 100 Gbps or 200 Gbps DWDM wavelength generated from the NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder. The configuration is supported with the Line module configured in Muxponder mode. A common application is to leverage the ability of the 10-Port 10 Gbps line card to support optics with over 10km of reach using SFP+ pluggables.
Management
The Cisco NCS 2000 system provides comprehensive management capabilities to support Operations, Administration, Maintenance, and Provisioning (OAM&P) capabilities through the integrated Cisco Transport Controller (CTC) craft interface with support from the Cisco Evolved Programmable Network Manager (EPN-M) network management system. The 400 Gbps XPonder line card features digital wrapper (G.709) functionality, providing per-wavelength performance management capabilities, especially for services transported transparently across networks. Without the digital wrapper functions, a carrier transporting a service transparently would be unable to identify network impairments that may degrade the transported signal and violate the SLA agreements. The digital wrapper’s Generic Communication Channel (GCC) provides a separate communications channel on a per-wavelength basis to be used when transparent signals are transported. GCC allows the Cisco NCS 2000 system to extend its advanced network auto discovery capabilities to DWDM-based services.
Licensing
The Cisco NCS 4000 400-Gbps XPonder features a licensing scheme allowing users to purchase only the functions they require.
The line card is available in two versions: an unlicensed version that includes all functions, and a licensed version that includes a subset of functions and bandwidth and is upgradable with feature-specific licenses.
The licensed version of the card supports the following functions:
● 100Gbps of client bandwidth (can be 100G or 10x10G or 2x40GE + 2 x 10GE or 6x16GFC)
● Capability to use one trunk CFP2 WDM with 100G QPSK modulation scheme (no limitation of FEC usage or CD or any optical performance)
Additional functions are offered through feature licenses; for example:
● Additional 100G client bandwidth (up to reach total of 400G maximum available client bandwidth)
● Capability to have the wavelength at 200G 16-QAM
● Capability to turn on second WDM port
Performance monitoring
The Trunk ports on the Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder line card provides support for transparent signal performance monitoring. The digital wrapper channel is monitored according to G.709 Optical Transport Network (OTN) and G.8021 standards. Performance monitoring of optical parameters on the client and DWDM interfaces include Loss Of Signal (LOS), laser bias current, transmit optical power, and receive optical power. Calculation and accumulation of the performance monitoring data are supported in 15-minute and 24-hour intervals as per G.7710.
Physical system parameters measured at the wavelength level, such as mean polarization mode dispersion, accumulated chromatic dispersion, or received optical signal to noise ratio, are also included in the set of performance monitoring parameters. These can greatly simplify troubleshooting operations and enhance the set of data that can be collected directly from the equipment. A detailed list of performance monitors is given in Table 8.
The XPonder card incorporates faceplate-mounted LEDs to provide a quick visual check of the operational status of the card. An orange circle is printed on the faceplate, indicating the shelf slot in which you can install the card.
Network applications: Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder
200 Gbps Muxponder application (Metro, Long Haul)
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder line card with QSFP28 provides a very efficient two-slot solution to transport on a single wavelengths 16-QAM 200 Gbps traffic by using both 100 Gbps optical client ports, directly managed by the QSFP28 (both LR4 or SR4) pluggable interface.
Cisco 100 Gbps SR4 or LR4 2xTransponder application (Ultra Long Haul)
By leveraging QSFP28 pluggable Client transceivers and the two Coherent DWDM Trunk ports on the Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder line card, operators can leverage a very efficient two slot solution to transport two 100 Gbps client services on to two QPSK 100 Gbps wavelengths directly managed by the QSFP28 (both LR4 or SR4) pluggable interface.
10 Gbps, 40 Gbps Muxponder
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder line card can directly accept both LR and SR 10G clients, via QSFP+ 4x 10 Gbps and 40 Gbps via QSFP+. Muxponder function can be done over both 100 Gbps and 200 Gbps transmission.
10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, and 100 Gbps Muxponder
The client ports of the NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder can be configured with a mix of 10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, and 100 Gbps inputs limited only by the 400 Gbps capacity of the line card.
10/40/100 Gbps Encryption over 100/150/200G DWDM
NCS 2000 400 Gbps Xponder card supports Encryption at ODU4 level providing encryption in both Muxponder and Xponder mode of operation.
OTN switching
The Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder line card embeds an OTN Switching engine capable to provide ODUk level switching among any of the ports (Client and Trunks).
Provided switching capacity is 800 Gbps and supported ODUk containers are ODU-2 and ODU-4. Integrated OTN switching capabilities allows to optimize wavelength usage across multiple locations in the network by efficiently grooming Client services on a single 100 Gbps or 200 Gbps wavelength as represented in Figure 5.
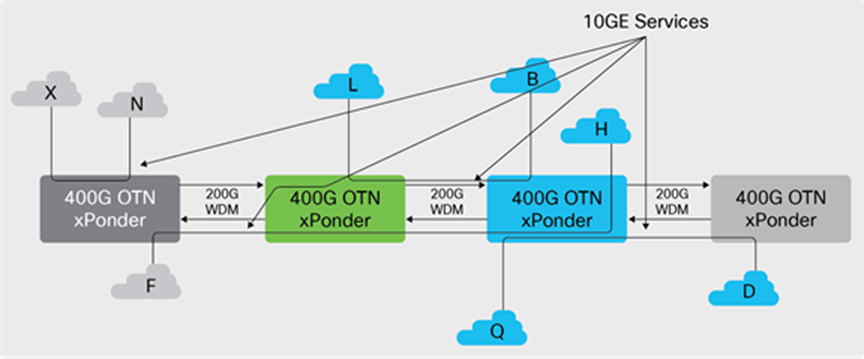
400 Gbps XPonder OTN Switching Application: Distributed Aggregation
Compact design
● Dual-slot card design for high-density, 100/150/200 Gbps solutions
● Up to 3 cards per Cisco NCS 2006 shelf assembly, or 7 cards per NCS 2015 shelf assembly
Regulatory compliance
Table 1 lists regulatory compliance information for the Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder line card. Note that all compliance documentation may not be completed at the time of product release. Please check with your Cisco sales representative for countries other than Canada, the United States, and the European Union.
Table 1. Regulatory compliance
| ETSI System |
|
| Countries and Regions Supported |
|
|
● Canada
● United States
● Korea
● Japan
● European Union
|
● European Union
● Africa
● CSI
● Australia
● New Zealand
● China
● Korea
● India
● Saudi Arabia
● South America
|
| EMC (Class A) |
|
|
● ICES-003, 2004
● FCC 47CFR15, 2007
|
● ETSI EN 300 386 V1.4.1 (2008-04) Telecommunication network equipment EMC requirements (Note: EMC-1)
● CISPR22:2008 and EN55022:2006/A1:2007 Information Technology Equipment (Emissions) (EMC-2)
● CISPR24: 1997/A1:2001/A2:2002 and EN55024:1998/A1:2001/A2:2003: Information Technology Equipment – Immunity characteristics – Limits and Methods of Measurement (test levels)
|
| Safety |
|
|
● CSA C22.2 #60950-1 – Edition 7, March 2007
● UL 60950-1 – Edition 2, March 2007
● GR-1089-CORE Issue 4, NEBS EMC and Safety, June 2006
|
● UL 60950-1 – Edition 2, March 2007
● IEC 60950-1 Information technology equipment Safety Part 1: General requirements – Edition 2, 2005 and National Differences as per CB Bulletin 112A
● IEC/EN 60950-1 (2006/10) with Amendment 11:2004 to EN 60950-1:2001, 1
st Edition and National Differences as per CB Bulletin 112A.
● EN 60950-1, Edition 2 (2006) Information technology equipment – Safety – Part 1: General requirements
● CE Safety Directive: 2006/95/EC
|
| Laser |
|
|
● UL 60950-1 – Edition 2, March 2007
● IEC 60825-1: 2001 Ed.1.2 (incl. am1+am2) Safety of laser products Part 1: Equipment classification, requirements and users guide
● IEC60825-2 Ed.3 (2004) Safety of laser products Part 2: Safety of optical fiber communication systems + A1:2006
|
● IEC 60825-1: 2001 Ed.1.2 (incl. am1+am2) Safety of laser products Part 1: Equipment classification, requirements and users guide
● IEC60825-2 Ed.3 (2004) Safety of laser products Part 2: Safety of optical fibre communication systems + A1:2006
● 21CFR1040 (2008/04) (Accession Letter and CDRH Report) Automatic Laser Shutdown and restart (ALS) according to ITU-T G.664 (03/06). Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff (Laser Notice No. 50), June 2007
● Laser Products: Conformance with IEC 60825-1 and IEC 60601-2-22; Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff (Laser Notice No. 50), June 2007
|
| Environmental |
|
|
● GR-63-CORE Issue 3, Network Equipment Building Standards (NEBS) Physical Protection, March 2006
|
● ETS 300-019-2-1 V2.1.2 (Storage, Class 1.1)
● ETS 300-019-2-2 V2.1.2 (1999-09): Transportation, Class 2.3
● ETS 300-019-2-3 V2.2.2 (2003-04): Operational, Class 3.1E
|
| Optical |
|
|
● GR-253-CORE – Issue 04
● ITU-T G.691
|
● ITU-T G.709
● ITU-T G.975
|
| Quality |
|
|
● TR-NWT-000332, Issue 4, Method 1 calculation for 20-year Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF)
|
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
|
● GR-1089-CORE Issue 4, NEBS EMC and Safety (June 2006) (Note: NEBS-1)
● GR-63-CORE Issue 3, NEBS Physical Protection (March 2006) (Note: NEBS-2)
● ATT-TP-76200: 2008
● ANSI T1.315-2001
● GR-499: 2004 Transport Systems Generic Requirements (TSGR): Common Requirements
|
|
Other specifications
Table 2 lists system requirements for the Cisco NCS 2000 400 Gbps XPonder line card. Table 3 provides the Coherent DWDM specifications, Table 4 details receive-side optical performances, Table 5 lists performance-monitoring parameters, Table 6 provides card specifications, and Table 7 gives ordering information. Refer to CFP2 WDM Datasheet for physical parameters.
Table 2. System requirements
| Component |
Cisco NCS 2000M6 |
| Processor |
TNC-E/TSC-E/TNC-S/TNCS-O/TNCS2/TNCS-2O |
| Shelf assembly |
Cisco NCS2002, NCS2006, NCS2015 |
| System software |
Release 10.6.1 or later |
Table 3. DWDM specifications
| Parameter |
Value |
| Baud rate |
31.3793 Gbaud ±20 ppm (OTU4 with SD-FEC 15% OH) 34.1660 Gbaud ±20 ppm (OTU4 with SD-FEC 25% OH) |
| Automatic laser shutdown and restart |
ITU-T G.664 (06/99) |
| Nominal wavelengths (lTnom) |
Full-tunable between 1528.77 and 1567.13 nm (C-Band) |
| Optical Transmitter |
|
| Type |
CP-QPSK modulation format CP-8QAM modulation format CP-16QAM modulation format |
| Optical Receiver |
|
| Chromatic dispersion tolerance (DLRmax) |
+/– 70,000, ps/nm with CP-QPSK formats +/– 25,000, ps/nm with 16-QAM |
| DGD Tolerance |
100 ps |
| Polarization change rate OSNR Penalty <0.5dB
●
100G QPSK
●
150G 8QAM
●
200G 16QAM
|
300krad/s 100krad/s 100krad/s |
Table 4. DWDM receive-side optical performances
| Modulation |
FEC Type |
Pre-FEC BER |
Post-FEC BER |
Input Power Sensitivity* |
DGD |
B2B OSNR (0.1 nm RWB) |
| CP-QPSK |
SD-FEC (25% OH) |
<4E(-2) |
<10E (–15) |
0 to -14dBm |
– |
11.3 dB |
| CP-QPSK |
SD-FEC (15% OH) |
<4E(-2) |
<10E (–15) |
0 to -14dBm |
– |
11.8 dB |
| CP-8QAM |
SD-FEC (25% OH) |
<3E(-2) |
<10E (–15) |
0 to -14dBm |
– |
16.1 dB |
| CP-8QAM |
SD-FEC (15% OH) |
<3E(-2) |
<10E (–15) |
0 to -14dBm |
– |
16.6 dB |
| CP-16QAM |
SD-FEC (25% OH) |
<3E(-2) |
<10E (–15) |
0 to -14dBm |
– |
19.6 dB |
| CP-16QAM |
SD-FEC (15% OH) |
<3E(-2) |
<10E (–15) |
0 to -14dBm |
– |
20.3 dB |
|
|
* Receiver Sensitivity can be extended down to -20dBm allocating additional OSNR margins |
|||||
Table 5. Performance monitoring parameters
| Area |
Parameter Name |
Description |
|
| OTN |
OTUk SM |
ODUk PM |
|
| BBE-SM |
BBE-PM |
Number of background block errors |
|
| BBER-SM |
BBER-PM |
Background block error ratio |
|
| ES-SM |
ES-PM |
Number of errored seconds |
|
| ESR-SM |
ESR-PM |
Errored seconds ratio |
|
| SES-SM |
SES-PM |
Number of severely errored seconds |
|
| SESR-SM |
SESR-PM |
Severely errored seconds ratio |
|
| UAS-SM |
UAS-PM |
Number of unavailable seconds |
|
| FC-SM |
FC-PM |
Number of failure counts |
|
| FEC |
Bit errors |
Number of corrected bit errors |
|
| Uncorrectable words |
Number of uncorrectable words |
||
| Trunk optical performance monitoring |
OPT |
Transmitter optical power |
|
| LBC |
Transmitter laser bias current |
||
| OPR |
Receiver optical power |
||
| RCD |
Residual chromatic dispersion |
||
| PMD |
Mean polarization mode dispersion |
||
| OSNR |
Optical signal-to-noise ratio, calculated with 0.5 nm RBW |
||
| SOPMD |
Second Order PMD (SOPMD) Estimation |
||
| SOPCR |
Polarization Change Rate Estimation |
||
| PDL |
Polarization Dependent Loss (PDL) Estimation |
||
Table 6. Card specifications
| Management |
|
| Card LEDs Failure (FAIL) Active/standby (ACT/STBY) Signal Fail (SF) |
Red Green/yellow Yellow |
| Client port LEDs (per port) Active input signal |
Green |
| DWDM port LEDs Active input signal Output wavelength |
Green Green |
| Power (including pluggable) |
|
| Typical Maximum |
330 W 385 W |
| Physical |
|
| Dimensions |
Occupies 2 slot |
| Weight |
6.8 lb (3.1 kg) |
| Reliability and availability |
|
| Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) |
272,380 hrs |
| Latency (end to end) |
|
| 100GE SD – FEC 15% |
28 microseconds |
| Storage temperature |
-40°C to 70°C (-40°F to 158°F) |
| Operating temperature Normal Short-term1 |
0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F) -5°C to 55°C (23°F to 131°F) |
| Relative humidity Normal Short-term1 |
5% to 85%, noncondensing 5% to 90% but not to exceed 0.024 kg water/kg of dry air |
| 1 Short-term refers to a period of not more than 96 consecutive hours and a total of not more than 15 days in 1 year (a total of 360 hours in any given year, but no more than 15 occurrences during that 1-year period). The values shown are valid for M6 or M2 chassis. |
|
Table 7. Ordering information
| Part Number |
Description |
| NCS2K-400G-XP= |
400G CFP2 MR xponder |
| NCS2K-400GXP-L-K9= |
400G CFP2 MR XP licensed 100G client bandwidth + 1 port WDM |
| L-NCS2K-100G-LIC= |
100G bandwidth client license |
| L-NCS2K-WDM-LIC= |
WDM port license |
| L-NCS2K-8QAM= |
WDM port license - upgrade to 8QAM (150G) |
| L-NCS2K-16QAM= |
WDM port license - upgrade to 16QAM (200G) |
| ONS-CFP2-WDM= |
100G QPSK/200G 16-QAM - WDM CFP2 pluggable |
| ONS-QSFP28-LR4= |
100Gbps multirate QSFP28, LR |
| ONS-QSFP-4X10-MLR= |
4x10Gbps multirate QSFP+, LR |
| QSFP-100G-FR-S |
100GBASE FR QSFP Transceiver, 2km over SMF |
| QSFP-100G-LR4-S= |
100GBASE LR4 QSFP transceiver, LC, 10km over SMF |
| QSFP-40G-LR4 |
40GBASE-LR4, 1310 nm, SMF |
| QSFP-100G-SR4-S= |
100GBASE SR4 QSFP transceiver, MPO, 100m over OM4 MMF |
| QSFP-4X10G-LR-S= |
QSFP 4x10G transceiver module, SM MPO, 10KM, enterprise class |
| QSFP-100G-SM-SR= |
100GBASE CWDM4 Lite QSFP Transceiver, 2km over SMF, 10 - 60C |
| QSFP-40G-SR4= |
40GBASE-SR4 QSFP Transceiver Module with MPO Connector |
| ONS-QC-16GFC-LW= |
4 X 16G/8G Fiber Channel QSFP+, SM, C Temp |
| ONS-QC-16GFC-SW= |
4 X 16G Channel QSFP+, MM, C Temp |
| QSFP-40G-SR-BD |
Cisco 40GBASE-SR Bi-Directional QSFP Module for Duplex MMF |
| QSFP-40/100-SRBD |
100G and 40GBASE SR-BiDi QSFP Transceiver, LC, 100m OM4 MMF |
| NCS2K-MF-8X10G-FO= |
2x4x10G QSFP+ to 10G fan out |
| ONS-12MPO-MPO-2= |
Multifiber patchcord - MPO to MPO 12 fibers - 2m |
| ONS-12MPO-MPO-4= |
Multifiber patchcord - MPO to MPO 12 fibers - 4m |
| ONS-12MPO-MPO-6= |
Multifiber patchcord - MPO to MPO 12 fibers - 6m |
| ONS-12MPO-MPO-8= |
Multifiber patchcord - MPO to MPO 12 fibers - 8m |
The following warranty terms apply to the Cisco NCS 2002, NCS 2006 and NCS 2015, as well as services you may use during the warranty period. Your formal warranty statement appears in the Cisco Information Packet that accompanies your Cisco product.
● Hardware warranty duration: 5 years
● Software warranty duration: 1 year
● Hardware replacement, repair, or refund procedure: Cisco or our service center will use commercially reasonable efforts to ship a replacement part for delivery within 15 working days after receipt of the defective product at Cisco’s site. Actual delivery times of replacement products may vary depending on customer location.
Product warranty terms and other information applicable to Cisco products are available at: https://www.cisco.com/go/warranty.
Cisco Services for Migrating Converged IP + Optical Solutions
Services from Cisco and our partners help you get the most value from your investments in the Cisco converged IP + Optical solution quickly and cost-effectively. We can help you design, implement, and validate your solution to speed migration and cutover. Coordinate every step through to interworking. Strengthen your team. And make the most of tomorrow’s opportunities. Learn more at https://www.cisco.com/go/spservices.
Flexible payment solutions to help you achieve your objectives
Cisco Capital® financing makes it easier to get the right technology to achieve your objectives, enable business transformation, and help you stay competitive. We can help you reduce the total cost of ownership, conserve capital, and accelerate growth. In more than 100 countries, our flexible payment solutions can help you acquire hardware, software, services, and complementary third-party equipment in easy, predictable payments. Learn more.
For more information about the Cisco NCS 2000, visit https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/optical-networking/network-convergence-system-2000-series/index.html.