Why Don't RIPv1 and IGRP Support Variable-Length Subnet Mask?
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
The ability to specify a different subnet mask for the same network number on different subnets is called Variable-Length Subnet Mask (VLSM). RIPv1 and IGRP are classful protocols and are incapable of carrying subnet mask information in their updates. Before RIPv1 or IGRP sends out an update, it performs a check against the subnet mask of the network that is about to be advertised and, in case of VLSM, the subnet gets dropped.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Example
This section provides an example. In this figure, Router 1 has three subnets with two different masks (/24 and /30):
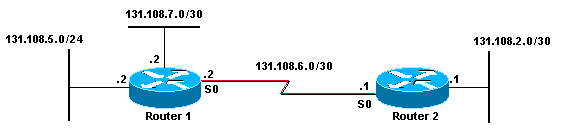
Router 1 goes through these steps before sending an update to Router 2. Refer to Behavior of RIP and IGRP When Sending or Receiving Updates for more information on these steps.
-
Router 1 checks to see whether 131.108.5.0/24 is part of the same major net as 131.108.6.0/30, which is the network assigned to the interface that will be sourcing the update.
-
It is, and now Router 1 checks whether 131.108.5.0 has the same subnet mask as 131.108.6.0/30.
-
Because it does not, Router 1 drops the network, and does not advertise the route.
-
Router 1 now checks whether 131.108.7.0/30 is part of the same major net as 131.108.6.0/30, which is the network assigned to the interface that will be sourcing the update.
-
It is, and now Router 1 checks whether 131.108.7.0/30 has the same subnet mask as 131.108.6.0/30.
-
Because it does, Router 1 advertises the network.
These checks determined that Router 1 only includes 131.108.7.0 in its update that is sent to Router 2. When the debug ip rip command is issued, you can actually see the update sent by Router 1. This is how it looks:
RIP: sending v1 update to 255.255.255.255 via Serial0 (131.108.6.2) subnet 131.108.7.0, metric 1
Notice that in the previous output only one subnet is included in the update. This results in this entry in Router 2's routing table, which is displayed using the show ip route command:
131.108.0.0/30 is subnetted, 3 subnets R 131.108.7.0 [120/1] via 131.108.6.2, 00:00:08, Serial0 C 131.108.6.0 is directly connected, Serial0 C 131.108.2.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0
In order to avoid having subnets eliminated from routing updates, either use the same subnet mask over the entire RIPv1 network or use static routes for networks with different subnet masks.
Related Information
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback