-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Storage Media Encryption Configuration Guide
-
Index
-
New and Changed Information
-
Preface
-
Cisco SME Overview
-
Cisco SME Getting Started
-
Cisco SME Cluster Management
-
Cisco SME Interface Configuration
-
Cisco SME Tape Management
-
Cisco SME Key Management
-
Using the CLI to Configure Cisco SME
-
Cisco SME Best Practices
-
Cisco SME Troubleshooting
-
Cisco SME CLI Commands
-
Offline Data Restore Tool
-
Creating Self-sign certificates
-
Database Backup and Restore
-
Planning for Cisco SME Installation
-
Table Of Contents
Enabling Clustering Using Fabric Manager
Enabling Clustering Using Device Manager
Enabling Cisco SME Using Fabric Manager
Enabling Cisco SME Using Device Manager
Enabling SSH Using Device Manager
Enabling SSH Using Fabric Manager
sme.useIP for IP Address or Name Selection
IP Access Lists for the Management Interface
Creating and Assigning Cisco SME Roles and Cisco SME Users
Creating and Assigning Cisco SME Roles Using Fabric Manager
Creating and Assigning Cisco SME Roles Using the CLI
Installing Fabric Manager, Fabric Manager Client, and Enabling HTTPS
Adding a Fabric and Changing the Fabric Name
Obtaining and Installing Licenses
Java Cryptography Extension Requirement
Cisco SME Configuration Overview
Initial Cisco SME Configuration
Saving Cisco SME Cluster Configurations
Cisco SME Configuration Restrictions
Cisco SME Configuration Limits
Getting Started
This chapter includes information about Cisco SME installation and the preliminary tasks that you must complete before configuring Cisco SME. It includes the following:
•
Cisco SME Configuration Restrictions
Note
To check for additional information about this release, and to determine if this release supports SME, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Release Notes available at the following Cisco Systems website:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps5989/prod_release_notes_list.html
Cisco SME Installation
Cisco SME has the following installation requirements:
•
Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 3.3(3) or later must be installed on the Cisco MDS 9222i switch or the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch with an MSM-18/4 module.
To determine if the release supports SME, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Release Notes and the Cisco Data Center Interoperability Matrix.
•
Cisco Fabric Manager Server must be installed on a computer that you want to use to provide centralized MDS management services and performance monitoring. The Cisco Key Management Center (Cisco KMC) is on this server.
Note
Although you need to install Fabric Manager Server, you do not need a Fabric Manager Server license to use Cisco SME. Additional Fabric Manager Server capabilities are not enabled by default with Cisco SME, so there is no free performance monitoring or other functionality.
•
Fabric Manager Web Client can be used to configure and manage Cisco SME using a web browser.
Cisco Fabric Manager is installed using the Fabric Manager Installation CD-ROM included with your switch, or you can download Fabric Manager. For information on installing Fabric Manager, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide. For information on installing Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 3.2(2), see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide.
You can use one of two configuration management tools to configure Cisco Storage Media Encryption.
•
Cisco MDS 9000 Fabric Manager
Cisco MDS 9000 Fabric Manager
The Cisco Fabric Manager is a set of network management tools that supports Secure Simple Network Management Protocol version 3 (SNMPv3). It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that displays real-time views of your network fabrics, and lets you manage the configuration of Cisco MDS 9000 Family devices and third-party switches. The Cisco Fabric Manager applications are:
•
Fabric Manager Web Client—Provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that displays real-time views of your network fabric, and lets you manage the configuration of Cisco MDS 9000 Family devices and third-party switches.
Note
Cisco SME configuration is supported in Fabric Manager Web Client only.
•
Fabric Manager Server—Must be started before running the Fabric Manager Client. It can be accessed by up to 16 Fabric Manager Clients at a time.
•
Device Manager—Presents two views of a switch.
–
Device View displays a continuously updated physical representation of the switch configuration, and provides access to statistics and configuration information for a single switch.
–
Summary View presents real-time performance statistics of all active interfaces and channels on the switch for Fibre Channel and IP connections.
Note
During the Fabric Manager installation, the use_ip flag in the smeserver.properties file is set to FALSE by default. If you choose to use IP addresses, the DNS server should not be configured on any switch in the fabric and the use_ip flag in the smeserver.properties file must be set to TRUE.
The Cisco Fabric Manager applications are an alternative to the CLI for most switch configuration commands.
For more information on configuring the Cisco MDS switch using the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager.
Command Line Interface
With the CLI, you can type commands at the switch prompt, and the commands are executed when you press the Enter key. The CLI parser provides command help, command completion, and keyboard sequences that allow you to access previously executed commands from the buffer history.
For more information on configuring the Cisco MDS switch using the CLI, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 CLI Configuration Guide.
Before You Begin
This section describes the required tasks that must be completed before you configure Cisco SME. It includes the following:
•
Creating and Assigning Cisco SME Roles and Cisco SME Users
•
Installing Fabric Manager, Fabric Manager Client, and Enabling HTTPS
•
Adding a Fabric and Changing the Fabric Name
•
Installing Smart Card Drivers
•
Obtaining and Installing Licenses
•
Cisco SME Configuration Overview
Before configuring Cisco SME, you must explicitly enable clustering, Cisco SME, SSH, and DNS on the MDS switch with an installed MSM-18/4 module or on the MDS 9222i switch. By default, these are disabled. The configuration and verification operations for Cisco SME are only available when these are enabled on a switch.
Enabling Clustering
You can enable clustering on the Cisco MDS 9000 switch with an installed MSM-18/4 module using Fabric Manager and Device Manager 3.2(2).
Note
Be sure to enable clustering first, then enable Cisco SME.
This section includes the following topics:
•
Enabling Clustering Using Fabric Manager
•
Enabling Clustering Using Device Manager
Enabling Clustering Using Fabric Manager
To enable clustering using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
In the Physical Attributes pane, select End Devices > SME Clusters.
Figure 2-1 Physical Attributes Pane
Step 2
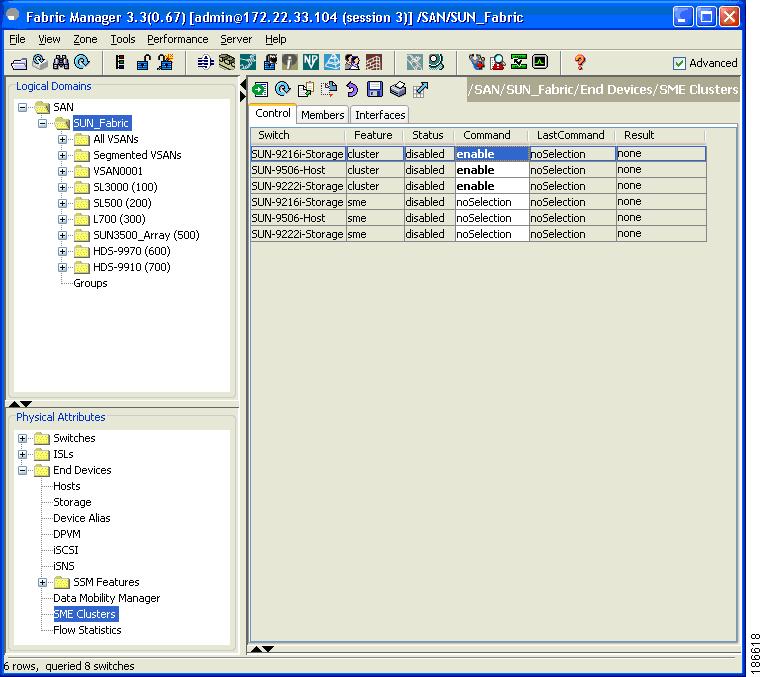
From the Control tab in the information pane, locate the switch.
Step 3
From the dropdown menu in the Command column, select enable. The default is noSelection.
Note
You can select enable on multiple switches and then click Apply.
Figure 2-2 Information Pane
Step 4
Click the Apply icon.
Enabling Clustering Using Device Manager
To enable clustering using Device Manager, do the following for a specific switch:
Step 1
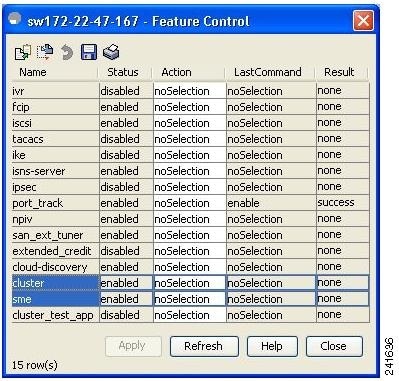
From the Admin menu in the device screen, select Feature Control..
Step 2
Select cluster.
Step 3
From the Action column drop-down menu, select enable.
Figure 2-3 Device Manager Feature Control Window
Step 4
Click the Apply icon.
Enabling Cisco SME
You can enable Cisco SME using Fabric Manager or Device Manager.
Note
Be sure to enable clustering first then enable Cisco SME.
This section includes the following topics:
•
Enabling Cisco SME Using Fabric Manager
•
Enabling Cisco SME Using Device Manager
Enabling Cisco SME Using Fabric Manager
To enable Cisco SME using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
In the Physical Attributes pane, select End Devices > SME Clusters.
Figure 2-4 Physical Attributes Pane
Step 2
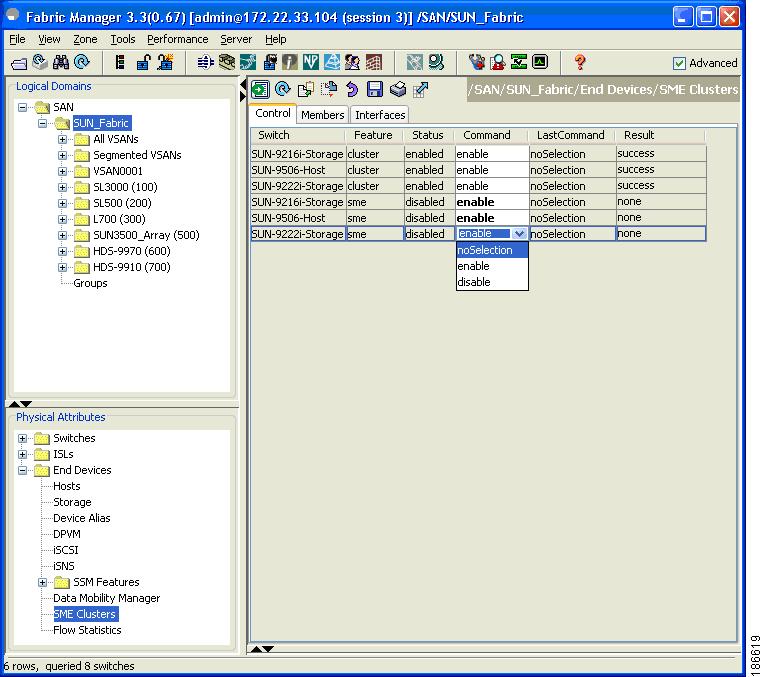
From the Control tab in the information pane, locate the switch.
Step 3
From the dropdown menu in the Command column, select enable. The default is noSelection.
Note
You can select enable on multiple switches and then click Apply.
Figure 2-5 Information Pane
Step 4
Click the Apply icon.
Enabling Cisco SME Using Device Manager
To enable Cisco SME using Device Manager, do the following for a specific device:
Step 1
From the Admin menu in the device screen, select Feature Control...
Step 2
Select sme.
Step 3
From the Action column drop-down menu, select enable.
Figure 2-6 Device Manager Feature Control Window
Step 4
Click the Apply icon.
Enabling SSH
Before using Cisco SME, you need to generate an SSH server key-pair SSH on the MDS switch with the MSM-18/4 modules installed. By default, the SSH service is disabled.
This section includes the following:
•
Enabling SSH Using Device Manager
•
Enabling SSH Using Fabric Manager
Enabling SSH Using Device Manager
Before using Cisco SME, you need to generate an SSH server key-pair SSH on the MDS switch with the MSM-18/4 modules installed.By default, the SSH service is disabled.
To enable SSH using Device Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
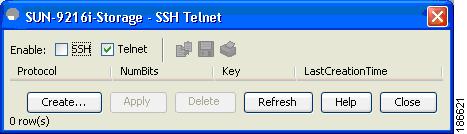
From the Security menu in the device screen, select SSH/Telnet.
Step 2
Check SSH and then click Create.
Figure 2-7 Device Manager SSH Telnet Window
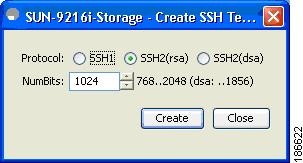
Step 3
Click Create again.
Figure 2-8 Device Manager Create SSH Window
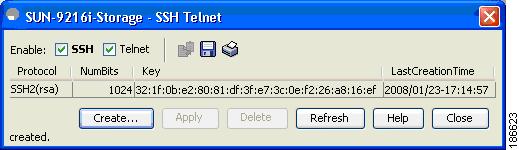
Step 4
Close both the windows. Repeat these steps for each switch.
Figure 2-9 Device Manager Final Window
Step 5
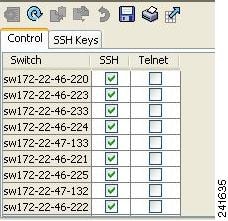
Go to Fabric Manager Web Client and enable SSH on the switches that have Cisco SME configured.
Figure 2-10 Enabling SSH on Cisco SME configured switches
Enabling SSH Using the CLI
Before using Cisco SME, you need to generate an SSH server key-pair SSH on the MDS switch with the MSM-18/4 modules installed.
Be sure to have an SSH server key-pair with the appropriate version before enabling the SSH service. Generate the SSH server key-pair according to the SSH client version used. The number of bits specified for each key-pair ranges from 768 to 2048.
Note
For additional information on enabling SSH, refer to the Cisco 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide.
Generating the SSH Server Key-Pair
The SSH service accepts three types of key-pairs for use by SSH versions 1 and 2.
•
The dsa option generates the DSA key-pair for the SSH version 2 protocol.
•
The rsa option generates the RSA key-pair for the SSH version 2 protocol.
Note
RSA1 is not supported for Cisco SME; use the rsa or dsa option.
If you delete all of the SSH keys, you cannot start a new SSH session.
To generate the SSH server key-pair, follow these steps:
To enable or disable the SSH service using the CLI, follow these steps
:
Enabling SSH Using Fabric Manager
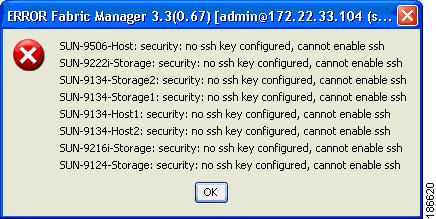
You must first generate the SSH keys using either the Device Manager or the CLI. If you try to enable SSH in the Fabric Manager Web Client before generating the SSH keys, you will get an error message. See Figure 2-11.
Figure 2-11 Error Message in Fabric Manager
After generating the keys, enable SSH in Fabric Manager as follows:
Step 1
Log in to Fabric Manager.
Step 2
In the Physical Attributes pane, select Switch>Security > SSH/Telnet.
Figure 2-12 Physical Attributes Pane
Step 3
Select SSH or Telnet for all switches in the fabric.
Figure 2-13 Information Pane
Step 4
Click the Apply icon.
Enabling DNS
DNS offers services to map a host name to an IP address in the network through a DNS server. When you configure DNS on the switch, you can substitute the host name for the IP address with all IP commands, such as ping, telnet, upload, and download.
You must decide to use DNS completely or to use IP addresses fully in your fabric. A combination of these will not work with the Cisco SME feature.
If you chose to use DNS, the following requirements apply:
•
All switches should be configured using DNS.
•
The domain-name (or the domain list), and the IP name server must be configured to reach remote switches.
•
The DNS server should be configured on the Fabric Manager server.
If you choose to use IP addresses, the DNS server should not be configured on any switch in the fabric and the use_ip flag in the smeserver.properties must be set to TRUE.
For information on configuring DNS, refer to the Configuring IP Services chapter in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide.
To verify that DNS is enabled everywhere in the cluster, ping between the Fabric Manager server and the MDS switches and also between the MDS switches with DNS names.
sme.useIP for IP Address or Name Selection
If you do not have DNS configured on all switches in the cluster, you can use sme.useIP. For information about sme.useIP, see Chapter 9, "Cisco SME Troubleshooting".
IP Access Lists for the Management Interface
Cluster communication requires the user of the Management interface. IP ACL configurations must allow UDP and TCP traffic on ports 9333, 9334, 9335, and 9336.
Creating and Assigning Cisco SME Roles and Cisco SME Users
The Cisco SME feature provides two primary roles: Cisco SME Administrator and the Cisco SME Recovery Officer. Be default, Cisco SME assigns both the Cisco SME Administrator and the Cisco SME Recovery Officer to the same user. This assignment works well for small scale deployments of Cisco SME.
Note
For Basic and Standard security modes, one user should hold the Cisco SME Administrator and the Cisco SME Recovery Officer roles.
Table 2-1 shows a description of the Cisco SME roles and the number of users that should be considered for each role.
Configuring the AAA Roles
For information on configuring the AAA roles for the Cisco SME Administrator and the Cisco SME Recovery Officer, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide.
Creating and Assigning Cisco SME Roles Using Fabric Manager
For detailed information on creating and assigning roles, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
Note
Cisco SME role names must begin with "sme". For example, valid role names could be "sme-admin", "sme-recovery", or "sme-admin-vsan1".
You need to create a Cisco SME role and then assign users to the Cisco SME role. To create a Cisco SME role, follow these steps:
Step 1
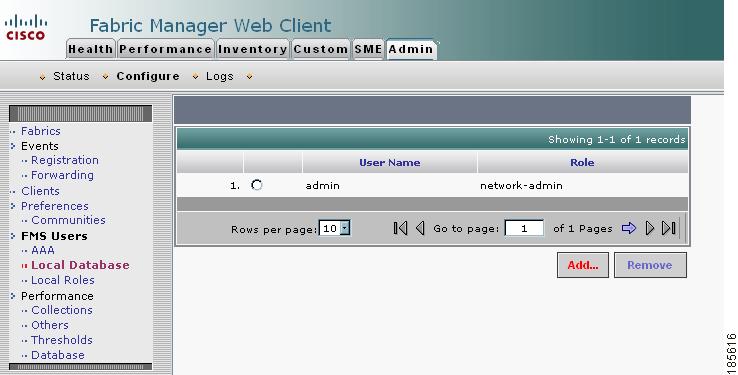
In the Admin tab, click on Configure > Local Database.
Step 2
Click the Add... button.
Figure 2-14 Creating and Assigning Cisco SME Roles
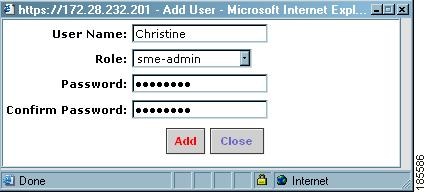
Step 3
Type in the user name and password.
Step 4
For the user role, select sme-admin or sme-recovery from the roles drop-down menu.
Step 5
Click Add.
Creating and Assigning Cisco SME Roles Using the CLI
For detailed information on creating and assigning roles, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide.
To create a Cisco SME role or to modify the profile for an existing Cisco SME role, follow these steps:
Note
Only users belonging to the network-admin role can create roles.
Note
The two security roles required by Cisco SME can be implicitly created by using the setup sme command. For VSAN based access control, you must create the custom roles.
Installing Fabric Manager, Fabric Manager Client, and Enabling HTTPS
To be able to manage Cisco SME, you need to install Fabric Manager Server Enterprise edition. For information on installing Cisco Fabric Manager, refer to the installation chapters of the .
Note
To configure Cisco SME, the Fabric Manager user credentials must be the same as the switch user.
Note
To configure Cisco SME in a dual fabric environment, all the switches in the cluster should have the same credentials for SME user.
Cisco SME requires the HTTPS protocol on the Cisco MDS 9000 switch with an MSM-18/4 module installed. You must enable HTTPS during the Fabric Manager installation. To enable HTTPS, refer to the installation information in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
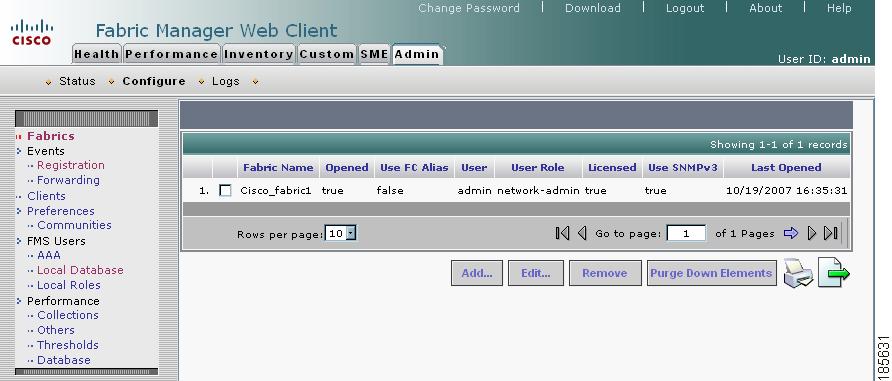
Adding a Fabric and Changing the Fabric Name
You need to add the fabric that includes the Cisco MDS switch with the MSM-18/4 module installed. Or you also can add a fabric that includes an MDS 9222i switch.
Note
Cisco SAN-OS Release 3.2(2) supports one cluster per switch. You will want to consider this during your planning.
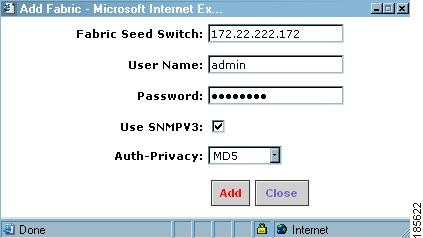
To add a fabric using Fabric Manager Web Server, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to Fabric Manager Web Client.
Step 2
Click the Admin tab.
Step 3
Click Configure.
Step 4
Click Add.
Figure 2-15 Fabric Manager Admin Screen
The Add Fabric seed switch screen displays fields to log in to the fabric seed switch.
Step 5
Enter the fabric seed switch name or IP address and enter the community.
Step 6
Click Add.
Figure 2-16 Fabric Seed Switch Login
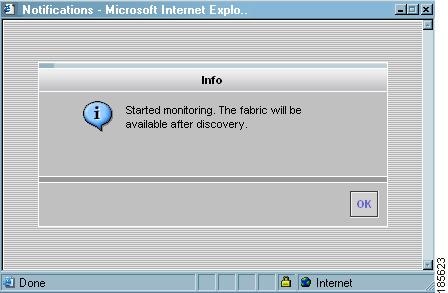
Note
It takes a few minutes after you click Add connect to the seed switch.
A notification window indicates that monitoring has started and that the fabric will be available after discover is complete.
Figure 2-17 Monitoring Notification
Step 7
Click Ok to return to the main screen.
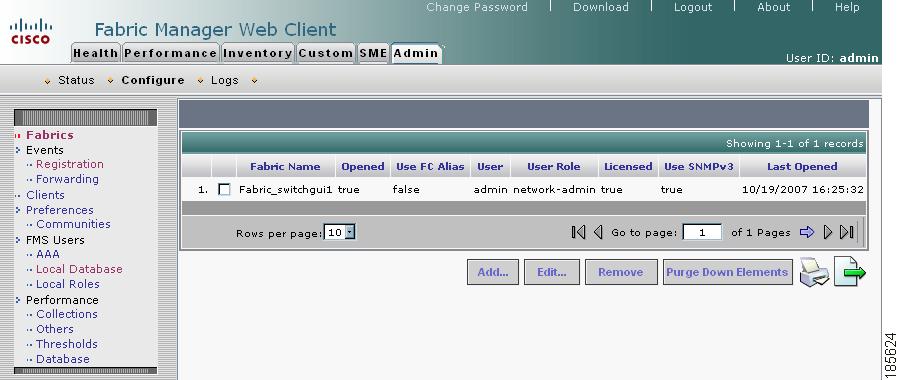
Note
The fabric name is identified as the fabric plus the switch name. You need to manually change the fabric name so that if you reopen the fabric with a different seed switch, the fabric name will remain the same. If you do not manually change the fabric name and you reopen the fabric with a different seed switch, the fabric may be renamed to show the new switch name. Choose a unique name that is easily identifiable.
Figure 2-18 New Fabric Added
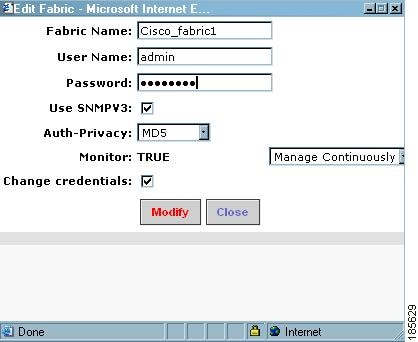
Step 8
Select the fabric and click Edit.
Step 9
Enter a unique fabric name, user name, and password.
Step 10
Select Manage Continuously and click Modify.
Note
Cisco SME requires that you select Manage Continuously to receive continuous updates from the switches.
Figure 2-19 Enter a Unique Fabric Name
Step 11
Click Close to return to the main screen and view the new fabric name.
Figure 2-20 Viewing the New Fabric Name
Installing Smart Card Drivers
The smart card reader must be connected to a management workstation that is used to configure Cisco SME. The smart card driver and the smart card drivers library file must be installed in the workstation. These are found on the Fabric Manager Installation CD.
When connecting a new smart card reader after the installation of smart card drivers, you may be required to restart the computer. If the card reader is not recognized on your workstation, you may need to install the latest smart card drivers. You can find the Download link on the Fabric Manager Web Client.
Note
The smart card reader is only supported on Windows platforms.
Obtaining and Installing Licenses
To use the Cisco SME feature, you need the appropriate Cisco SME license; however, enabling Cisco SME without a license key starts a counter on the grace period. You then have 120 days to install the appropriate license keys or disable the use of Cisco SME. If at the end of the 120-day grace period the switch does not have a valid license key for Cisco SME, it will be automatically disabled.
To identify if the Cisco SME feature is active, use the show license usage license-name command.
Note
You can not use a Cisco SME interface if the Cisco SME licenses are not installed.
The following three Cisco SME licenses are available:
To obtain and install Cisco SME licenses, refer to the licensing chapter in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide.
Cisco SME Requirements
This section describes the following requirements:
•
Java Cryptography Extension Requirement
Java Cryptography Extension Requirement
Cisco SME requires Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy Files 5C0 (for JRE 1.5). You will need to extract and copy the local_policy.jar and the US_export_policy.jar files to the $JAVA_HOME\jre\lib\security\ directory. You can obtain these files from the Fabric Manager Installation CD.
Zoning Requirement
Zoning requirements include the following:
•
Internal virtual N-ports are created by Cisco SME in the default zone. The default zone must be set to deny and these virtual N-ports must not be zoned with any other host or target.
For information on zoning, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide.
FC-Redirect Requirements
FC-Redirect requirements include the following:
•
The MDS switch with the MSM-18/4 module installed or the 9222i switch needs to be running SAN-OS Release 3.2(2).
•
The target must be connected to an MDS 95XX/9216/9222i switch running SAN-OS 3.2(2).
•
32 targets per MSM-18/4 module can be FC-redirected.
•
Each FC-redirected target can be zoned to 16 hosts or less.
•
CFS should be enabled on all required switches for FC-redirect.
•
Cisco SME servers and tape devices should not be part of an IVR zone set.
Cisco SME Configuration Overview
Before configuring Cisco SME on your switch, it is important to become familiar with the Cisco SME configuration process. This section provides an overview of the Cisco SME configuration process and includes the following topics:
•
Initial Cisco SME Configuration
•
Saving Cisco SME Cluster Configurations
Initial Cisco SME Configuration
Note
For information about what you need to do before you initially configure Cisco SME, see the "Before You Begin" section.
Cisco SME configuration tasks listed below provide an overview of the basic Cisco SME configuration process. Complete the Cisco SME configuration tasks on the switch with an installed MSM-18/4 module or on a Cisco MDS 9222i switch.
Cisco SME basic configuration tasks include the following:
•
Create the Cisco SME interface (Chapter 4, "Cisco SME Interface Configuration")
•
Create a cluster for Cisco SME (Chapter 3, "Cisco SME Cluster Management")
•
Add the interfaces to the cluster (Chapter 3, "Cisco SME Cluster Management")
•
Create a tape group (including selecting the backup server and discovering backup libraries) (Chapter 5, "Cisco SME Tape Configuration")
For details about configuration procedures using the CLI, see Chapter 7, "Using the Command Line Interface to Configure SME."
Saving Cisco SME Cluster Configurations
CautionConfiguration changes must be saved on all switches in the cluster for correct cluster operation. This must be done after the initial cluster creation and after all subsequent changes are made to the cluster configuration.
You must save configuration changes whenever switches or interfaces are added or deleted from a cluster.
Cisco SME Configuration Restrictions
This section includes information on Cisco SME configuration limitations and restrictions. It contains the following:
•
Cisco SME Configuration Limits
FICON Restriction
Cisco SME is not supported on FICON devices and Cisco SME cluster devices can not be part of a FICON VSAN.
iSCSI Restriction
You can not configure Cisco SME and iSCSI on the same Cisco MDS MSM-18/4 module as SME uses the iSCSI port indices.
FC-Redirect Restrictions
FC-Rredirect is not supported on the following switches:
•
Cisco MDS 9124 switch
•
Cisco MDS 9134 switch
•
Cisco MDS 9020 switch and the Cisco MDS 9040 switch
Cisco SME Configuration Limits
Table lists the Cisco SME configurations and the corresponding limits.

 Feedback
Feedback