-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Switch-to-Switch Interoperability Configuration Guide
-
Index
-
Preface
-
Interoperability Overview
-
Interoperability Limitations
-
MDS 9000 Core with Brocade Edge Topology (Interop Mode 1)
-
MDS 9000 Core with Brocade and McData Edge Topology (Interop Mode 1)
-
MDS 9000 Switch and McData Dual Core Topology (Interop Mode 1)
-
MDS 9000 Core with Brocade 3900/12000 Edge Toplogy
-
MDS 9000 Legacy Switch Interop Mode 2
-
MDS 9000 Legacy Switch Interop Mode 3
-
MDS 9000 Legacy Switch Interop Mode 4
-
MDS 9020 Switch Interoperability
-
Interoperability with Inter-VSAN Routing
-
IBM BladeCenter
-
Standards Perspectives
-
Caveats
-
Table Of Contents
MDS 9000 Legacy Switch Interop Mode 4
MDS 9000 Legacy Switch Interop Mode 4
This chapter covers legacy switch interop mode 4 for connecting MDS9000 switches to McData switches running in McData Fabric 1.0 mode. It includes the following sections:
Specifications
Legacy switch interoperability mode 4, introduced in Cisco SAN-OS Release 3.0(1), provides the means to non-disruptively connect a McData switch running in McData Fabric 1.0 mode with an MDS 9000 switch.
While in this mode, the MDS VSAN emulates the behavior of a McData switch, including the use of offsets when referring to domain IDs and FC IDs, and in its ability to only establish an Inter-Switch Link (ISL) with another switch that uses McData's OUI (08:00:88).
Note
•
If an MDS 9000 switch is using IVR to provide access between McData connected devices and devices in other VSANs, all zoning should be done from the MDS switch.
•
Cisco Fabric Manager running Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 3.0(1) or higher must be used to manage fabrics containing interop mode 4 VSANs.
VSAN World Wide Name
A VSAN running in interop mode 4 must be configured to use a WWN that follows a specific set of rules regarding the following format:
2y:yy:08:00:88:zz:zz:zz
•
Mandatory: The first byte must begin with 2.
•
Mandatory: y = 0:00 or hex representation of the VSAN number. (For example, 0:0a for VSAN 10.)
•
Mandatory: 3rd, 4th and 5th bytes of the WWN must be 08:00:88 (McData OUI).
•
Recommended: z = last three bytes of the switch WWN.
•
Mandatory: The chosen WWN must be unique across the fabric.
Note
Because the WWN has a McData OUI, the WWN can conflict only with McData switches or other MDS switches with VSANs running in interop mode 4.
Tip
The easiest method to obtain a WWN that meets these conditions is to use the system assigned Local switch WWN and replace the OUI. Notice that 0xbc0 is 3008 in decimal.
switch# show fcdomain vsan 3008The local switch is the Principal Switch.Local switch run time information:State: StableLocal switch WWN: 2b:c0:00:0c:85:e9:d2:c1Running fabric name: 2b:c0:00:0c:85:e9:d2:c1Running priority: 128Current domain ID: 0x0a(10)The VSAN WWN cannot be configured unless the VSAN is in a suspended state. Set the WWN using the following command:
switch# conf tEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.switch(config)# wwn vsan <VSAN #> vsan-wwn <wwn>Domain and FC IDs
A McData switch refers to domain IDs in the range of 1 to 31, while FC IDs are used within the range 97 to 127, with an offset of 96. The interop mode 4 VSAN emulates the same behavior as the McData switch. Therefore, when configuring static domain IDs on an MDS switch, the range 1 to 31 should be used; however, devices that log into the VSAN (even physically located on the MDS switch) receive an FC ID whose domain ID is 97-127.
Note
If a static domain ID is configured on the MDS switch, it must be in the range 1 to 31 for the interop mode 4 VSAN. However, persistent FC IDs must be configured in the range 97 to 127.
For example, in the following output, a device in VSAN 3008 is assigned an FC ID that contains domain ID 0x6a (106), but upon examining the domain-list, domain ID 10 is displayed. McData's offset of 96 is the difference between the device's FC ID and the domain ID within the domain-list.
switch# show flogi database vsan 3008---------------------------------------------------------------------------INTERFACE VSAN FCID PORT NAME NODE NAME---------------------------------------------------------------------------fc2/5 3008 0x6a0000 50:06:0e:80:04:27:e0:46 50:06:0e:80:04:27:e0:46Total number of flogi = 1.switch# show fcdomain domain-list vsan 3008Number of domains: 2Domain ID WWN--------- -----------------------0x06(6) 10:00:08:00:88:a0:ee:f7 [Principal]0x0a(10) 2b:c0:08:00:88:e9:d2:c1 [Local]
Note
If IVR-1 is configured, the domain that is in non-interop mode 4 must have a domain ID in the range 97 to 127 because IVR-1 does not modify the domain ID or FC ID unlike, IVR-2 (NAT).
No modifications to the McData switch are required to connect to the MDS switch. A short procedure is required on the MDS switch prior to establishing the ISL. Cisco Fabric Manager running Cisco SAN-OS Release 3.0(1) or higher should be used to manage an MDS based fabric that contains an interop mode 4 VSAN.
Configuration
To establish connectivity between the McData switch and an MDS switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Create the VSAN.
switch# conf tEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.switch(config)# vsan databaseswitch(config-vsan-db)# vsan 3008Step 2
Record the Local switch WWN:
switch(config-vsan-db)# do show fcdomain vsan 3008The local switch is the Principal Switch.Local switch run time information:State: StableLocal switch WWN: 2b:c0:00:0c:85:e9:d2:c1Running fabric name: 2b:c0:00:0c:85:e9:d2:c1Running priority: 128Current domain ID: 0x0a(10)Step 3
Suspend the VSAN.
switch(config-vsan-db)# vsan 3008 suspendStep 4
Configure interop mode 4 for the VSAN.
switch(config-vsan-db)# vsan 3008 interop 4Step 5
Configure the VSAN WWN for the VSAN according to the rules specified in VSAN World Wide Name.
switch(config-vsan-db)# do show wwn switchSwitch WWN is 20:00:00:0c:85:e9:d2:c0switch(config-vsan-db)# wwn vsan 3008 vsan-wwn 2b:c0:08:00:88:e9:d2:c1switch(config)#Step 6
Unsuspend the VSAN.
switch(config)# vsan databaseswitch(config-vsan-db)# no vsan 3008 suspendStep 7
Add the ISL to the VSAN and verify connectivity.
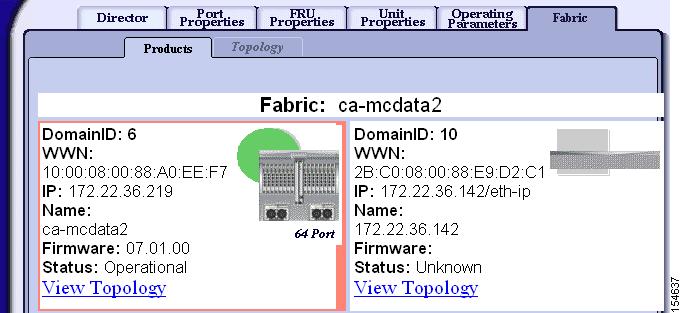
switch# show fcdomain domain-list vsan 3008Number of domains: 2Domain ID WWN--------- -----------------------0x06(6) 10:00:08:00:88:a0:ee:f7 [Principal]0x0a(10) 2b:c0:08:00:88:e9:d2:c1 [Local]switch# show topology vsan 3008FC Topology for VSAN 3008 :--------------------------------------------------------------------Interface Peer Domain Peer Interface Peer IP Address--------------------------------------------------------------------fc2/15 0x06(6) Port 63 ::Figure 9-1 show how the McData GUI displays the MDS switch and the domain IDs of 6 and 10.
Figure 9-1 McData GUI Displaying an MDS Switch in Interop Mode 4
At this point, devices within the VSAN can be zoned using either the Cisco SAN-OS command-line interface, Cisco Fabric Manager, or the McData GUI.

 Feedback
Feedback