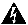

Table Of Contents
Installing and Removing Power Components
Information About Installing and Removing the Power Components
Precautions and Recommendations
Supplemental Unit Bonding and Grounding Guidelines
Before Powering the Chassis Up or Down
Converting from One Power System to Another
How to Install or Remove the Power Components
Installing and Removing Power Components
This chapter provides instructions on how to install and remove the Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System Line Card Chassis power components.
This chapter presents the following topics:
•
Information About Installing and Removing the Power Components
•
How to Install or Remove the Power Components
Information About Installing and Removing the Power Components
This section contains some general information about the power components.
•
Supplemental Unit Bonding and Grounding Guidelines
•
Before Powering the Chassis Up or Down
•
Converting from One Power System to Another
Basic Chassis Power Details
The Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis can be either DC or AC powered. The chassis power system (DC or AC) provides the necessary power for chassis components. A chassis with AC input power requires 8,750 watts to power the chassis. A chassis with DC input power requires 8,000 watts to power the chassis.
For more detailed information on the two power types, see the "DC Power Systems" section and the "AC Power Systems" section.
The line card chassis requires that at least the power distribution units (PDUs) and their power modules be installed to operate properly.
Tip
Be sure to install the PDUs before installing the power modules.
Three types of PDUs exist:
•
AC Wye PDU
•
AC Delta PDU
•
DC PDU
AC PDUs connect to AC rectifiers, while DC PDUs connect to the DC power entry modules (PEMs). Although there are differences among the different PDU types (AC Wye, AC Delta, and DC), they are installed in the same manner. Similarly, the different power modules are also installed in the same manner. For detailed information, see the "How to Install or Remove the Power Components" section.
Note
The PDUs arrive with the power cables preattached.
CautionUse only one type of PDU—AC Wye, AC Delta, or DC—and its mating power module in a chassis at one time.
Precautions and Recommendations
Follow these precautions and recommendations when planning power connections to the router:
•
Check the power at your site before installation and periodically after installation to ensure that you are receiving clean power. Install a power conditioner, if necessary.
•
Properly ground your system to avoid damage from lightning and power surges.
CautionTo ensure electromagnetic compatibility, a Cisco router must be operated with all its power modules always installed.
Note
You must have the chassis horizontal mounting rails installed in the rack to ensure EMI compliance.
Warning
This unit might have more than one power supply connection. All connections must be removed to de-energize the unit. Statement 1028
Supplemental Unit Bonding and Grounding Guidelines
Although the router chassis has a safety earth ground connection as part of the power cabling to the PDUs, the chassis includes an option that allows you to connect the central office ground system or interior equipment ground system to the supplemental bonding and grounding receptacles on the router chassis. Two threaded ground inserts are located on the fan tray door at the rear (MSC) side of the chassis (see Figure 2-1). This ground point is also called the network equipment building system (NEBS) bonding and grounding stud.
Note
These bonding and grounding receptacles satisfy the Telcordia NEBS requirements for supplemental bonding and grounding connections. If you are not installing the router in a NEBS environment, you can choose to bypass these guidelines and rely on the safety earth ground connection for the AC- and DC-input PDUs.
Figure 2-1 NEBS Bonding and Grounding Points (Rear of Chassis)
If you plan to connect the routing system to a network equipment building system (NEBS)-compliant supplemental bonding and grounding system at the site, you must have the following:
•
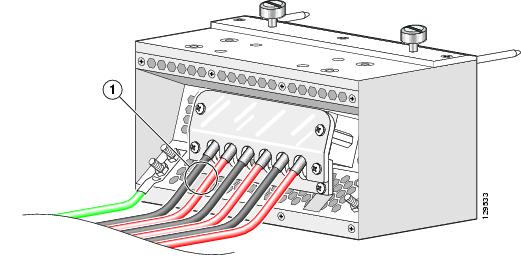
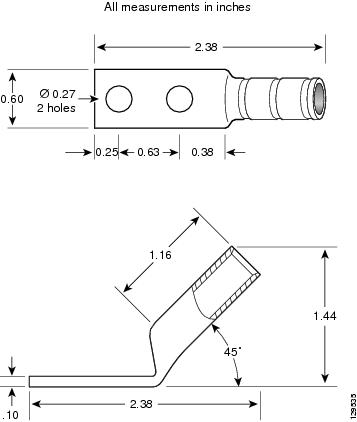
A minimum of one ground lug that has two M6 bolt holes with 0.625-inch (15.86-mm) spacing between them, and a wire receptacle large enough to accept a 6-AWG or larger multistrand copper wire. The lug is similar to the type used for the DC-input power supply leads (see Figure 2-3). This ground lug is not available from Cisco Systems. This type of lug is available from electrical-connector vendors, such as Panduit (see Figure 2-3).
•
Two M6 or equivalent hex-head bolts with locking washers (nickel-plated brass is ideal) and nuts. These bolts, locking washers, and nuts are not available from Cisco Systems; they are available from any commercial hardware vendor.
•
A ground wire. Although we recommend at least 6-AWG multistrand copper wire, the actual wire diameter and length depend on your router location and site environment. This wire is not available from Cisco Systems; it is available from any commercial cable vendor.
CautionThe DC Return of the Cisco CRS-1 8-slot chassis should remain isolated from the system frame and chassis (DC-I: Isolated DC Return).
DC Power Systems
A DC-powered Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis contains two DC-input power distribution units (PDUs) and two DC power entry modules (PEMs). Each DC PDU is connected to three pairs of DC power feeds and powers a single 7500-watt DC PEM that is field replaceable. Input DC power enters the PDU and is passed to the PEM, which provides power to the components in the chassis. Each PEM has its own circuit breaker.
The DC PDU is shipped with a plastic safety cover over the input terminal block (see Figure 2-2). This safety cover is in two parts, each part held on to the PDU with a Phillips screw. We recommend removing the safety cover only when wiring and unwiring the chassis. The safety cover is slotted in such a way that the wires can only come out on the bottom portion of the cover.
Figure 2-2 DC PDU with Plastic Safety Cover
Each PDU requires three DC inputs of -48/-60 VDC (nominal), 60-amp service. The PDU accepts input DC power in the range -40.5 to -75 VDC, and has three sets of double-stud terminals (-48/-60VDC Lines and -48/-60VDC Returns) for connecting to the VDC inputs.
Each DC PDU should be connected to a different central office DC power source:
•
One PDU should be connected to three -48/-60 VDC "A" buses.
•
The other PDU should be connected to three -48/-60 VDC "B" buses.
If DC power to a PDU fails, the other PDU provides enough power for the chassis. This 2N power redundancy enables the routing system to operate in spite of single power failure.
For DC power cables, we recommend that you use commensurately rated, high-strand-count copper wire cable, based on local electrical codes. These wires are not available from Cisco Systems; they are available from any commercial vendor. DC power cables must be terminated by cable lugs at the power shelf end.
Note
All six -48/-60VDC Return input wires for one chassis should have the same wire gauges and the lengths should be matched within 10% of deviation.
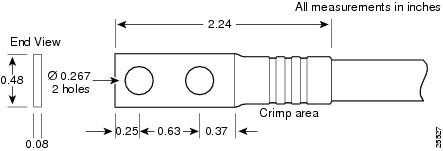
The grounding lugs should be dual-hole and able to fit over M6 terminal studs at 0.63 in (15.88-mm) centers (for example, Panduit part number LCD6-14A-L, or equivalent) (see Figure 2-3).
Figure 2-3 DC Power Grounding Cable Lug
The terminal lugs (in other words, all lugs not used for grounding) should be 45-degree angled, industry-standard dual-hole compressions lugs, and able to fit over M6 terminal studs at 0.63 in (15.88-mm) centers (for example, AWG no. 2 wires, such as Panduit part number LCC2-14AH-Q or equivalent) (see Figure 2-4).
Note
The power wire and ground wire connector screws have a 20 in.-lb (2.26 N-m) torque value. The mounting screws have a 9 in.-lb (1.04 N-m) torque value.
Figure 2-4 DC Power Cable Lug
Note
Be sure to follow all lug insulation instructions provided by the lug manufacturer.
The color coding of the source DC power cable leads depends on the color coding of the site DC power source. Typically, green or green and yellow indicates that the cable is a ground cable. Because there is no color code standard for the source DC wiring, you must ensure that the power cables are connected to the DC-input PDU terminal studs in the proper positive (+) and negative (-) polarity.
In some cases, the source DC cable leads might have a positive (+) or negative (-) label. This is a relatively safe indication of the polarity, but you must verify the polarity by measuring the voltage between the DC cable leads. When making the measurement, the positive (+) lead and negative (-) lead must always match the (+) and (-) labels on the PDU.
CautionNo damage should occur because of reverse polarity, but you should correct a reverse polarity condition immediately.
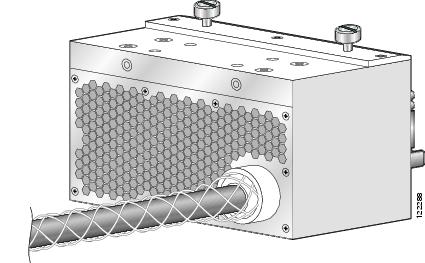
DC PDU Wiring
This section describes how to wire the DC PDU. For more detailed information on chassis DC power systems, see the "DC Power Systems" section.
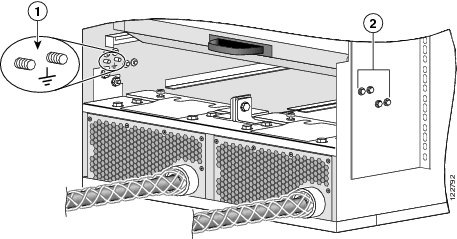
Figure 2-5 DC PDU Power Cable Connections
CautionWhen wiring the PDU, be sure to attach the ground wire first and tighten the nuts to a torque value of 30 in-lb (3.39 N-m). When removing the wiring, be sure to remove the ground wire last.
To wire the DC PDU, follow these steps:
Step 1
Remove the upper plastic terminal block safety cover (leave the lower safety cover in place; see Figure 2-5). Using a standard Phillips screwdriver, remove the four screws holding the upper plastic safety cover to the wiring terminal block.
Step 2
Attach lugs to the DC-input wires. For details on lugs, see the "DC Power Systems" section.
The wire should be sized according to local and national installation requirements. Use only copper wire.
Note
The power supply terminal block lug opening width is 0.62 inch (15.8 mm). The terminal posts are centered 0.625 inches (15.88 mm) apart and are M6-threaded. We recommend that you use an appropriately sized 45-degree angled industry standard 2-hole, standard barrel compression lug. The power supply ground studs, located below the terminal block, are also M6-threaded.
Step 3
Using a 10-mm socket wrench, attach the ground wire to the ground wire terminal.
Step 4
Using the wrench, attach the three negative wires (the red wires as shown in Figure 2-5) to the terminal block.
Step 5
Using the wrench, attach the three positive wires (the black wires as shown in Figure 2-5) to the terminal block.
Step 6
Reattach the upper plastic safety cover: with a phillips screwdriver, insert and tighten the four screws holding the cover to the wiring terminal block.
AC Power Systems
An AC-powered Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis contains two AC power distribution units (PDUs) and two AC rectifier modules. Each AC PDU is connected to a 3-phase (200 to 240) input VAC power source and connects to a single 7500-watt AC rectifier module that is field replaceable. Each AC rectifier module converts input AC power to the 54.5 VDC used by the Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis. Each rectifier has its own circuit breaker.
To provide 2N power redundancy for the Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis, each PDU and AC rectifier pair is connected to a different AC power source. During normal operation when both power sources are operational, both PDUs and rectifiers function together to power the chassis. However, if a power sources fails, the other power source provides the other PDU and rectifier pair with enough input power to power the chassis. This 2N power redundancy enables the routing system to operate despite the power failure.
Two versions of the AC PDU are available to accommodate AC input power in either the Delta or Wye configuration. Each PDU has a different Cisco part number. The PDUs are shipped with AC power cords that are 14 feet (4.3 m) long.
The AC PDUs have the following input VAC power requirements:
•
AC Wye input: 3-phase, 200 to 240 VAC nominal (phase-to-neutral), 50 to 60 Hz, 16 A (International) or 20 A (North America). The PDU is rated for 14-amp service, and accepts AC input of 16 or 20 A.
The Wye power cord has a 5-pin IEC 60309 plug that is rated for 400 VAC, 16 or 20 A, (3W + N + PE). The power cord plugs into a similarly rated IEC 60309 receptacle.
•
AC Delta input: 3-phase, 200 to 240 VAC nominal (phase-to-phase), 50 to 60 Hz, 30 A. The PDU is rated for 24-amp service, and accepts AC input of 30 A.
The Delta power cord has a 4-pin NEMA L15-30P plug that is rated for 250 VAC, 30 A (3W + PE). The power cord plugs into a similarly rated NEMA L15-30R locking-type receptacle.
For additional power details, see Appendix A, "CRS-1 8-Slot Line Card Chassis Specifications," or Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System 8-Slot Line Card Chassis System Description.
Before Powering the Chassis Up or Down
While the line card chassis does not have a single power switch that powers the entire chassis and all its components up and down, the AC rectifier or DC PEM linkage cuts power to the chassis as a whole when both power components are turned off. Most components on the chassis, such as the power modules, MSCs, PLIMs, and fan trays can be removed or installed in the chassis while it is running.
Before you can power the chassis up, you must do the following:
Step 1
Install the PDUs (see the "Installing a PDU" section).
Step 2
Install the power modules (see the "Installing a Power Module" section).
Step 3
Install the route processor (RP) card (see the "Installing an RP or DRP Card" section on page 4-38).
Step 4
Activate your power source.
Step 5
Turn the power module switches to the on position.
To power down the chassis entirely, you must power down each of the two power modules; you move each power switch to the off position by pulling it toward you. Both power modules must be disconnected or the PDUs unplugged to de-energize the chassis completely.
Note
After powering off the AC rectifier, wait a minimum of 20 seconds before powering it on again.
Note
All power cords must be unplugged from wall power to fully remove power from the chassis.
Converting from One Power System to Another
To convert a Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis from AC to DC power, or from DC to AC power, you must:
Step 1
Power down the chassis completely. See the "Before Powering the Chassis Up or Down" section.
Step 2
Remove the power modules. See the "Removing a Power Module" section.
Step 3
Remove the PDUs. See the "Removing a PDU" section.
Step 4
Install the new PDUs. See the "Installing a PDU" section.
If you are converting from AC to DC power, you must wire the PDU properly. See the "DC Power Systems" section.
Step 5
Install the power modules. See the "Installing a Power Module" section.
Step 6
Power the chassis back up. See the "Before Powering the Chassis Up or Down" section.
CautionUse only one type of PDU and power module, either AC or DC, in a chassis at one time.
How to Install or Remove the Power Components
This section contains the following procedures:
Note
Although there are differences among the different PDU types (AC Wye, AC Delta, and DC), they are installed in the same manner.
Note
Although there are differences between the different power module types (AC and DC), they are installed in the same manner.
Installing a PDU
This section describes how to install a PDU in the Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis. For information on the difference between the power types, see the "DC Power Systems" section and the "AC Power Systems" section. For complete information on regulatory compliance and safety, see Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System.
The PDU is installed into the back of the chassis. After the PDU is installed, you can slide the power modules into the chassis and connect them to the PDU to provide power to the chassis (see the "Installing a Power Module" section for details). Although there are differences among the different PDU types (AC Wye, AC Delta, and DC), they are installed in the same manner. (Figure 2-6 shows an AC Wye PDU for reference.)
Figure 2-6 AC Wye PDU
Prerequisites
Before performing this task, remove any front cosmetic covers.
Required Tools and Equipment
You need the following tools and part to perform this task:
•
ESD-preventive wrist strap
•
10-mm socket wrench
•
8-mm socket or open (box end) wrench
•
PDU
–
AC Wye PDU Cisco product number CRS-8-LCC-PDU-ACW=
–
AC Delta PDU Cisco product number CRS-8-LCC-PDU-ACD=
–
DC PDU Cisco product number CRS-8-LCC-PDU-DC=
Steps
To install a PDU, follow these steps:
Step 1
Attach the ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and connect its leash to one of the ESD connection sockets on the rear (MSC) side of the chassis or a bare metal surface on the chassis.
Step 2
Make sure that the PDU is unplugged.
Step 3
Grasp the PDU by the side and set it carefully into place in a PDU slot on the rear (MSC) side of the chassis. Be sure to lift the PDU over the lip on the edge of the chassis, and align the guide pins on the chassis with the guide holes on the PDU.
CautionDo not lift the PDU by the power cord—doing so can damage the PDU or the cord.
Step 4
If needed, put the second PDU into place in the other PDU slot on the chassis.
Note
The PDU holding plate bolts to both PDUs and the side of the interior of the chassis.
Step 5
Install the PDU holding plate.
a.
Slide the holding plate into place on top of the PDU, using the guide bolts on the side of the chassis to place it correctly.
b.
Use the socket wrench to bolt the holding plate to the top of the PDUs with the eight 10-mm bolts (four for each PDU).
c.
Use the socket wrench to bolt the holding plate to the interior of the side of the chassis with the four 8-mm bolts (two for each side)
Step 6
Use the socket wrench to install the 8-mm center holding bolt and the 10-mm nut.
What to Do Next
After performing this task, install the power modules (see the "Installing a Power Module" section), and replace any cosmetic covers.
Removing a PDU
This section describes how to remove a PDU in the Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis. For information on the difference between the power types, see the "DC Power Systems" section and the "AC Power Systems" section. For complete information on regulatory compliance and safety, see Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System.
The PDU is located at the back of the chassis. Although there are differences among the different PDU types (AC Wye, AC Delta, and DC), they are installed in the same manner (see Figure 2-7, which shows an AC Wye PDU for reference).
Figure 2-7 AC Wye PDU for the 8-Slot Chassis
Prerequisites
Before performing this task, remove any front cosmetic covers, power down and remove the power modules, and unplug the PDU. See the "Before Powering the Chassis Up or Down" section, and the "Removing a Power Module" section.
If you are removing a DC PDU, see the "DC Power Systems" section; if you are removing an AC PDU, see the "AC Power Systems" section for more information.
Required Tools and Equipment
You need the following tools to perform this task:
•
ESD-preventive wrist strap
•
10-mm socket wrench
•
8-mm socket or open (box end) wrench
Steps
To remove an AC Wye PDU, follow these steps:
Step 1
Attach the ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and connect its leash to one of the ESD connection sockets on the rear (MSC) side of the chassis or a bare metal surface on the chassis.
Step 2
Turn the power module power switch to the off position.
Step 3
Disconnect the PDU from the power source.
Step 4
Remove the power module of the PDU that you are removing from the chassis (see the "Removing a Power Module" section).
Step 5
On the rear (MSC) side of the chassis, use the socket wrench to remove the 8-mm center holding bolt and 8-mm nut from the PDU holding plate.
Step 6
Remove the PDU holding plate.
a.
Use the socket wrench to unbolt the four 8-mm bolts (two for each side) that attach the holding plate to the interior of the side of chassis.
b.
Use the socket wrench to unbolt the eight 10-mm bolts (four for each PDU) that attach the holding plate to the top of the PDUs.
c.
Carefully remove the holding plate from the top of the PDUs and set it aside.
Step 7
Grasp the PDU and lift it carefully over the lip at the back of the chassis and set it carefully aside.
CautionDo not lift the PDU by the power cord—doing so can damage the PDU or the cord.
What to Do Next
After performing this task, you may install a new PDU, if needed (see the "Installing a PDU" section), and replace any cosmetic covers.
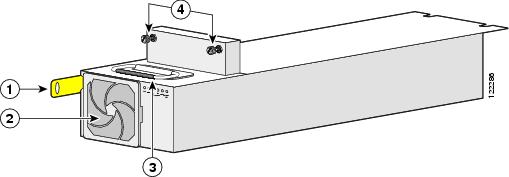
Installing a Power Module
This section describes how to install a power module in the Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis. For information on the difference between the power types, see the "DC Power Systems" section and the "AC Power Systems" section. For complete information on regulatory compliance and safety, see Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System.
The power module is installed into the front of the chassis, and mates with the PDU that is installed on the back of the chassis (see the "Installing a PDU" section for information). Although there are differences among the different power modules (AC Wye, AC Delta, and DC), they are installed in the same manner. (Figure 2-8 shows an AC Wye power rectifier for reference.)
Figure 2-8 AC Power Rectifier
Prerequisites
Before performing this task, make sure that the PDU has been installed (see the "Installing a PDU" section) and remove any cosmetic covers.
Required Tools and Equipment
You need the following tools and part to perform this task:
•
ESD-preventive wrist strap
•
Medium Phillips screwdriver
•
Power module
–
AC rectifier Cisco product number CRS-8-AC-RECT=
–
DC PEM Cisco product number CRS-8-DC-PEM=
Steps
To install a power module, follow these steps:
Step 1
Attach the ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and connect its leash to one of the ESD connection sockets on the front (PLIM) side of the chassis or a bare metal surface on the chassis.
Step 2
Make sure that the power switch is in the off position.
Step 3
Grasp the handle on the top of the module firmly, and lift it partway up.
Step 4
Using two hands to support and guide the power module, slide it into the chassis power bay on the front (PLIM) side of the chassis until the connector on the back of the module meets the connector on the backplane of the PDU.
CautionAn AC rectifier weighs 36 lbs (13.44 kg); a DC PEM weighs 38 lbs (17.24 kg). You should use both hands when handling a power module.
Step 5
Press the power module in firmly to seat it against the PDU.
CautionTo prevent damage to the PDU-to-module connections, do not use excessive force when seating a power module to its PDU.
Step 6
Tighten the two captive screws on the face of the power module to seat it snugly against the PDU.
Step 7
Push the power tab at the bottom front of the module in to the on position.
What to Do Next
After performing this task, you may connect the PDU to the power source (see the "DC Power Systems" section and the "AC Power Systems" section) and power up the chassis (see the "Before Powering the Chassis Up or Down" section).
Removing a Power Module
This section describes how to remove a power module from the Cisco CRS-1 8-slot line card chassis. For information on the difference between the power types, see the "DC Power Systems" section and the "AC Power Systems" section. For complete information on regulatory compliance and safety, see Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System.
The power module is located on the front of the chassis, and mates with the PDU that is installed on the back of the chassis (see the "Installing a PDU" section for information). Although there are differences among the power modules (AC Wye, AC Delta, and DC), they are installed in the same manner. (Figure 2-9 shows an AC Wye power rectifier for reference.)
Figure 2-9 AC Power Rectifier
Prerequisites
Before performing this task, remove any front cosmetic covers.
Required Tools and Equipment
You need the following tools to perform this task:
•
ESD-preventive wrist strap
•
Medium Phillips screwdriver
Steps
To remove a power module, follow these steps:
Step 1
Attach the ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and connect its leash to one of the ESD connection sockets on the front (PLIM) side of the chassis or a bare metal surface on the chassis.
Step 2
On the front side of the chassis, pull the power tab on the bottom front of the power module out to the off position.
Step 3
Use the screwdriver to loosen the two captive screws on the front of the power module.
Step 4
Grasp the power module handle and pull the power module halfway from the bay. Be sure to pull the module by the handle only.
CautionTake care when handling a power module that has recently been in use—it can be hot to the touch.
CautionAn AC rectifier weighs 36 lbs (13.44 kg); a DC PEM weighs 38 lbs (17.24 kg). You should use both hands when handling a power module.
Step 5
Use your free hand to support the power module while you slide the module completely from the bay, then set the module safely aside.
What to Do Next
After performing this task, you may install a new power module, if needed (see the "Installing a Power Module" section), and replace any front cosmetic covers.