Table Of Contents
Step 2: Configure a RADIUS AAA Client
Step 3: Configure the Logging Level
Step 4: Install and Set Up an ACS Security Certificate
Obtain Certificates and Copy Them to the ACS Host
Run the Windows Certificate Import Wizard to Install the Certificate (ACS for Windows)
Enable Security Certificates on the ACS Installation
Step 5: Configure Remote Web Access
Step 6: Enable Downloadable ACLs and Network Access Filters
Step 7: Configure ACS for PEAP
Step 8: Configure ACS for EAP-FAST
Step 9: Configure Network Access Filtering
Step 10: Configure Logs and Reports
Step 11: Set Up Network Access Profiles
Step 12: Configure Profile-Based Policies
Create an Authorization Policy
Step 13: Configure Posture Validation for NAC
Configure Internal Posture Validation Policies
Configure External Posture Validation Policies
Configure an External Posture Validation Audit Server
Add the Posture Attribute to the ACS Dictionary
Configure the External Posture Validation Audit Server
Authorization Policy and NAC Audit
Step 14: Set Up Templates to Create NAPs
Sample NAC Layer 3 Profile Template
Protocols Policy for the NAC Layer 3 Template
Sample Posture Validation Rule
Sample Posture Validation Rule
Sample NAC Layer 2 802.1x Template
Sample Posture Validation Rule
Sample Wireless (NAC L2 802.1x) Template
Sample Posture Validation Rule
Using a Sample Agentless Host Template
Step 15: Map Posture Validation Components to Profiles
Step 16: Map an Audit Server to a Profile
Step 17 (Optional): Configure GAME Group Feedback
Import an Audit Vendor file Using CSUtil
Import a Device-Type Attribute File Using CSUtil
Import NAC Attribute-Value Pairs
Configure Database Support for Agentless Host Processing
Configure an External Audit Server
NAC Configuration Scenario
This chapter describes how to set up Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.1, hereafter referred to as ACS, to work in a Cisco Network Admission Control (NAC) environment. This chapter contains the following sections:
•
Step 2: Configure a RADIUS AAA Client
•
Step 3: Configure the Logging Level
•
Step 4: Install and Set Up an ACS Security Certificate
•
Step 5: Configure Remote Web Access
•
Step 6: Enable Downloadable ACLs and Network Access Filters
•
Step 7: Configure ACS for PEAP
•
Step 8: Configure ACS for EAP-FAST
•
Step 9: Configure Network Access Filtering
•
Step 10: Configure Logs and Reports
•
Step 11: Set Up Network Access Profiles
•
Step 12: Configure Profile-Based Policies
•
Step 13: Configure Posture Validation for NAC
•
Step 14: Set Up Templates to Create NAPs
•
Step 15: Map Posture Validation Components to Profiles
•
Step 16: Map an Audit Server to a Profile
•
Step 17 (Optional): Configure GAME Group Feedback
Step 1: Install ACS
This section describes the installation process that you perform to run ACS, which runs on a Windows 2000 Server, Windows 2003, or on a Cisco Secure ACS Solution Engine (ACS SE).
For detailed information on ACS installation, refer to the:
•
Installation Guide for Cisco Secure ACS for Windows Release 4.1
•
Installation Guide for Cisco Secure ACS Solution Engine Release 4.1
To install ACS:
Step 1
Start the ACS installation.
During the installation process, you are prompted to enter a password for encrypting the internal database.
Step 2
Enter a password that is at least 8 characters long, and contains letters and numbers.
The ACS installation process for ACS for Windows automatically creates a shortcut to the ACS administrative GUI on your desktop.
Note
If you are installing ACS on the ACS SE, you must manually create an administrative GUI user by using the add-guiadmin command from the CLI to create a GUI account. For information on this command, see Appendix A of the Installation Guide for Cisco Secure ACS Solution Engine 4.1, "Command Reference." You can then access the administrative GUI through a supported browser. For a list of supported browsers, see Supported and Interoperable Devices and Software Tables for Cisco Secure ACS Release 4.1, which is available at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps2086/
products_device_support_tables_list.htmlStep 3
Double-click the icon to open a browser window to the ACS administrative GUI.
Step 4
If you do not see the icon on the desktop, open your browser from the machine on which you installed ACS and go to one of these addresses:
•
http://IP_address:2002
•
http://hostname:2002
where IP_address is the IP address of the host that is running ACS and hostname is the hostname of the host that is running ACS.
Step 2: Configure a RADIUS AAA Client
Before you can configure agentless host support, you must configure a RADIUS AAA client.
To configure a RADIUS AAA client:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Network Configuration.
The Network Configuration page opens.
Step 2
Do one of the following:
•
If you are using Network Device Groups (NDGs), click the name of the NDG to which you want to assign the AAA client. Then, click Add Entry below the AAA Clients table.
•
To add AAA clients when you have not enabled NDGs, click Add Entry below the AAA Clients table.
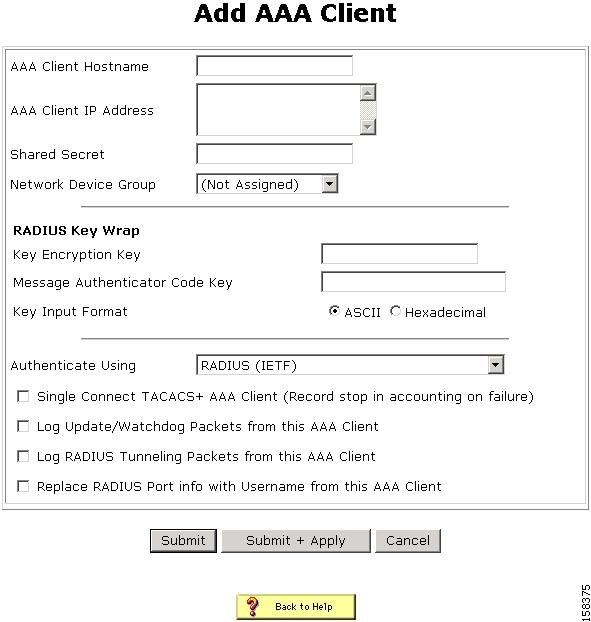
The Add AAA Client page opens, shown in Figure 7-1.
Figure 7-1 Add AAA Client Page
Step 3
In the AAA Client Hostname box, type the name assigned to this AAA client (up to 32 alphanumeric characters).
Step 4
In the AAA Client IP Address box, type the AAA client IP address or addresses.
Step 5
In the Shared Secret box, type the shared secret key for the AAA client. The shared secret must be identical on the AAA client and ACS. Keys are case sensitive. If the shared secrets do not match, ACS discards all packets from the network device.
Step 6
If you are using NDGs, from the Network Device Group list, select the name of the NDG to which this AAA client should belong, or, select Not Assigned to set this AAA client to be independent of NDGs.
Step 7
Type the shared secret keys for RADIUS Key Wrap in EAP-TLS authentications.
Each key must be unique, and must also be distinct from the RADIUS shared key. You can configure these shared keys for each AAA Client, as well as for each NDG. The NDG key configuration overrides the AAA Client configuration. If the key entry is null, ACS uses the AAA client key. You must enable the Key Wrap feature in the NAP Authentication Settings page to implement these shared keys in EAP-TLS authentication:
a.
Key Encryption Key (KEK)—Used for encryption of the Pairwise Master Key (PMK). The maximum length is 20 characters.
b.
Message Authenticator Code Key (MACK)—Used for the keyed hashed message authentication code (HMAC) calculation over the RADIUS message. The maximum length is 16 characters.
c.
Key Input Format—Click the format of the key, ASCII or hexadecimal strings (the default is ASCII).
Step 8
From the Authenticate Using list, select RADIUS (IOS/PIX).
Step 9
Specify additional AAA client settings as required.
Step 10
Click Submit + Apply.
Step 3: Configure the Logging Level
To set ACS to full logging capabilities:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click System Configuration.
The System Configuration page opens.
Step 2
Click Service Control.
Step 3
Under Level of Detail, click the Full radio button.
Step 4
Check the Manage Directory check box and choose how many days of logging to keep. (Select the number of days based on how much space you have on your hard drive: We recommend that you specify seven days.)
Step 5
Click Restart to restart ACS. (Wait until the browser's progress bar shows that the page has reloaded completely.)
Step 4: Install and Set Up an ACS Security Certificate
This section describes a simplified procedure for the ACS for Windows platform. For detailed information on installing certificates and for information on how to install certificates on the Cisco Secure ACS Solution Engine platform, see Chapter 9 of the User Guide for Cisco Secure ACS 4.1, "Advanced Configuration: Authentication and Certificates."
Obtain Certificates and Copy Them to the ACS Host
To copy a certificate to the ACS host:
Step 1
Obtain a security certificate.
Step 2
Create a \Certs directory on the ACS server.
a.
Open a DOS command window.
b.
To create a certificates directory, enter:
mkdir <selected_drive>:\Certs
where selected_drive is the currently selected drive.
Step 3
Copy the following files to the \Certs directory:
•
server.cer (server certificate)
•
server.pvk (server certificate private key)
•
ca.cer (CA certificate)
Run the Windows Certificate Import Wizard to Install the Certificate (ACS for Windows)
To run the Windows Certificate Import wizard to install the certificate on the server:
Step 1
Open Windows Explorer.
Step 2
Go to <selected_drive>:\Certs.
Step 3
Double-click the \Certs\ca.cer file.
The Certificate dialog appears.
Step 4
Select Install Certificate.
The Windows Certificate Import wizard starts.
Step 5
To install the certificate, follow the instructions that the wizard displays.
Step 6
Accept the default options for the wizard.
Note
Only perform this process once on a Windows 2000 Server.
Enable Security Certificates on the ACS Installation
To enable security certificates on the ACS installation:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click System Configuration.
The System Configuration page opens.
Step 2
Click ACS Certificate Setup.
Step 3
Click Install ACS Certificate.
Step 4
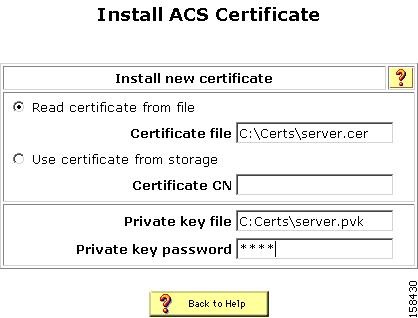
The Install ACS Certificate page opens, as shown in Figure 7-2.
Figure 7-2 Install ACS Certificate Page
Step 5
Click the Read certificate from file radio button.
Step 6
In the Certificate file text box, enter the server certificate location (path and name); for example: c:\Certs\server.cer.
Step 7
In the Private key file text box, type the server certificate private key location (path and name); for example: c:\Certs\server.pvk.
Step 8
In the Private Key password text box, type 1111.
Step 9
Click Submit.
Step 10
ACS displays a message indicating that the certificate has been installed and instructs you to restart the ACS services.
Step 11
Do not restart the services at this time.
Restart the services later, after you have completed the steps for adding a trusted certificate. See Add a Trusted Certificate.
Install the CA Certificate
To install the CA Certificate:
Step 1
Choose System Configuration > ACS Certificate Setup > ACS Certification Authority Setup.
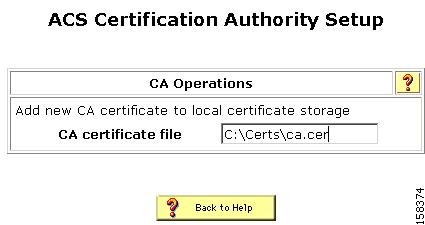
Step 2
The ACS Certification Authority Setup page appears, shown in Figure 7-3.
Figure 7-3 ACS Certification Authority Setup Page
Step 3
In the CA certificate file box, type the CA certificate location (path and name); for example: c:\Certs\ca.cer.
Step 4
Click Submit.
Add a Trusted Certificate
To add a trusted certificate:
Step 1
Choose System Configuration > ACS Certificate Setup > Edit Certificate Trust List.
The Edit Certificate Trust List appears.
Step 2
Locate the trusted certificate that you want to install and check the corresponding check box by the certificate name. For example, find the Stress certificate and check the corresponding check box.
Step 3
Click Submit.
Step 4
To restart ACS, choose System Configuration > Service Control, and then click Restart.
Step 5: Configure Remote Web Access
To prepare ACS for remote administration:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Administration Control.
The System Configuration page opens.
Step 2
Click Add Administrator.
The Administration Control page opens, as shown in Figure 7-4.
Figure 7-4 Administration Control Page
Step 3
To add an administrator, click Add Administrator.
The Add Administrator page opens.
Step 4
In the Administrator Details area:
Step 5
Click Grant All.
This grants all privileges to the new administrator; or, specifies to which groups or actions this administrator is granted access.
Note
For more information on administrative privileges, see the "Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages" section in Chapter 11 of the User Guide for Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.1, "Administrators and Administrative Policy."
Step 6
Click Submit.
After performing these steps, from a remote host, you can open a browser in which to administer ACS.
The URLs for remote access are:
•
http://IP_address:2002
•
http://hostname:2002
Step 6: Enable Downloadable ACLs and Network Access Filters
To enable downloadable access control lists (dACLs) and Network Access Filters (NAFs), which are required to create Network Access Profiles (NAPs):
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Interface Configuration.
The Interface Configuration page opens.
Step 2
Click ACS Certificate Setup.
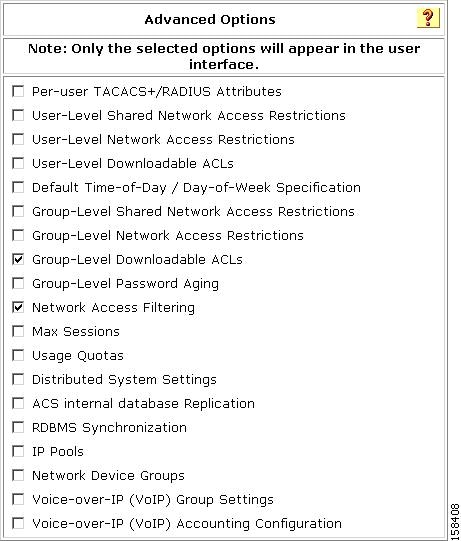
The Advanced Options page appears, shown in Figure 7-5.
Figure 7-5 Advanced Options Required to Enable Network Access Profiles
Step 3
Check the check boxes for:
•
Group-Level Downloadable ACLs
•
Network Access Filtering
Step 4
Click Submit.
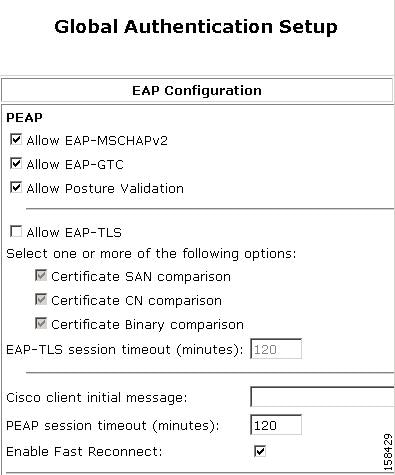
Step 7: Configure ACS for PEAP
To configure ACS so that PEAP will work properly with NAC posture validation:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click System Configuration.
The System Configuration page opens.
Step 2
Click Global Authentication Setup.
The Global Authentication Setup Page appears, as shown in Figure 7-6.
Figure 7-6 Global Authentication Setup Page
Step 3
Check the check box for Allow EAP-MSCHAPv2 or Allow EAP-GTC; or, check both check boxes.
Step 4
In the PEAP section, check the Allow Posture Validation check box.
Step 5
Click Submit + Restart.
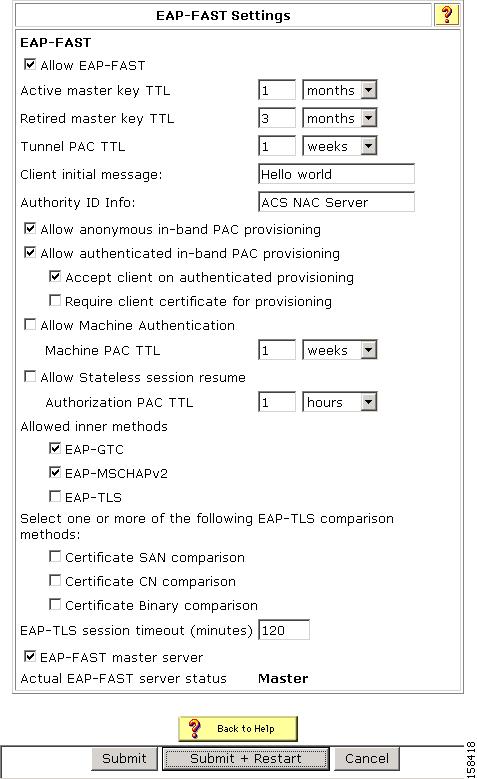
Step 8: Configure ACS for EAP-FAST
To configure ACS to work with NAC and use EAP-FAST will with posture validation:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click System Configuration.
The System Configuration page opens.
Step 2
Click Global Authentication Setup.
The Global Authentication Setup Page appears, as shown in Figure 7-6.
Step 3
Click EAP-FAST Configuration.
The EAP FAST Configuration page appears, as shown in Figure 7-7.
Figure 7-7 EAP-FAST Configuration Page
Step 4
Check the Allow EAP-FAST check box.
Step 5
In the Client Initial Message text box, enter a message, for example, Welcome.
Step 6
In the Authority ID Info field, enter ACS NAC Server.
Step 7
Check the Allow authenticated in-band PAC provisioning check box.
Step 8
Check the Accept client on authenticated provisioning check box.
Step 9
Check the check boxes for the EAP-GTC and EAP-MSCHAPv2 inner methods.
The EAP-FAST Master Server check box is automatically checked (enabled).
Step 10
Click Submit + Restart.
Step 9: Configure Network Access Filtering
To use ACS in a NAC environment, configure network access filtering (NAF).
NAF is an ACS feature that groups several devices into one group. The devices can be ACS clients, ACS servers, ACS network device groups (NDGs), or a specific IP address. NAFs are particularly useful for defining Network Access Profiles (NAPs).
To configure ACS to use NAFs:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Interface Configuration.
The Interface Configuration page opens.
Step 2
Click Advanced Options.
Step 3
Check the Network Access Filtering check box.
Click Submit.
Step 4
In the navigation bar, click Shared Profile Components.
The Shared Profile Components page opens.
Step 5
Click Network Access Filtering.
The Network Access Filtering table appears. Initially, this table does not contain shared profile components.
Step 6
Click Add.
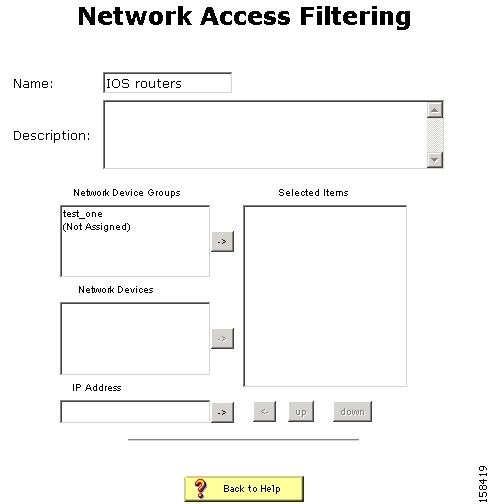
The Edit Network Access Filtering page opens, as shown in Figure 7-8.
Figure 7-8 Edit Network Access Filtering Page
Step 7
In the Name text box, enter a name for the network access filter.
Step 8
Move any devices or device groups to the Selected Items list.
To move a device or device group, select the item to move and then click the right arrow button to move it to the Selected Items list.
Step 9
Click Submit.
Step 10: Configure Logs and Reports
ACS logs records of users who gain network access or are refused network access. The ACS reports summarize these logs, and provide useful information for debugging and tracking problems.
The Passed Authentications report is particularly useful in NAC-enabled networks; because, it shows the group mapping for each posture validation request. By default, the Passed Authentication report is unchecked (disabled).
To enable the Passed Authentication report:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click System Configuration.
The System Configuration page opens.
Step 2
Click Logging.
The Logging Configuration page opens.
Step 3
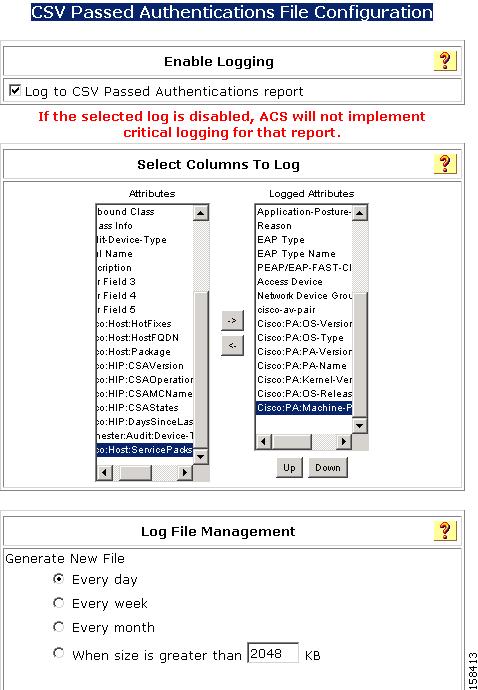
In the ACS Reports table, click the Configure link for the CSV Passed Authentications report.
The CSV Passed Authentications File Configuration page opens, as shown in Figure 7-9.
Figure 7-9 CSV Passed Authentications File Configuration Page
Step 4
Check the Log to CSV Passed Authentications Report check box.
Step 5
Move the attributes that you want to log from the Attributes list to Logged Attributes list.
Some useful attributes to log are:
•
cisco-av-pair attributes starting with PA and A
•
Profile Name
•
Reason
•
System-posture-token
•
Application-posture-token
Step 6
Click Submit.
Step 11: Set Up Network Access Profiles
A NAP, also known as a profile, is a way to classify access requests according to the AAA clients' IP addresses, membership in a network device group, protocol types, or other specific RADIUS attribute values sent by the network device through which the user connects.
If you configure NAPs, ACS traverses the ordered list of active profiles, and maps a RADIUS transaction to a profile by using a first-match strategy on the first access-request of the transaction.
After you set up a profile, you associate a set of rules or policies with it, to reflect your organization's security policies. These associations are called profile-based policies. Configuring a profile-based policy includes creating rules for:
•
Protocols
•
Authentication
•
Posture validation
•
Authorization
A profile is a classification of network access requests for applying a common policy.
You can create a profile in two ways:
•
Manually, by selecting options in the NAP configuration pages.
•
By using the sample NAC templates provided with ACS 4.1 to start a profile and then editing the profile as required for your installation.
When you set up a NAP, you can configure:
•
Profile name
•
Description
•
The Active flag, which determines whether this profile is active or inactive
•
Classification by NAF selection
•
Classification by protocol selection
•
Classification by advanced filtering (Boolean expression that comprises RADIUS attributes and values)
ACS uses three conditions to determine how an access request is classified and mapped to a profile. ACS selects the profile when all three conditions match. For each condition, you can substitute the value Any to always match the condition.
You can classify (filter) a user request by choosing a NAF from the list of existing NAFs. You configure NAF objects in the Shared Profile Components pages.
You can use protocol types to choose one or more protocol types as a filter. The protocol types are a subset of the vendor-specific attributes (VSAs) that a network access server supports. ACS 4.1 does not support the TACACS+ protocol for NAPs.
You can use Advanced Filtering to create a specific rule that contains one or more RADIUS attributes and values. The Advanced Filtering rules are based on a Boolean AND expression that uses RADIUS attributes to examine the request packet.
Each NAP contains a name, description, active flag and a set of classifications that you use to rank an access request based on different parameters.
Create a NAP
To create a NAP:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Network Access Profiles.
The Network Access Profiles page opens. Initially, the list of Network Access Profiles is empty.
Step 2
Click Add.
The Profile Setup page opens, as shown in Figure 7-10.
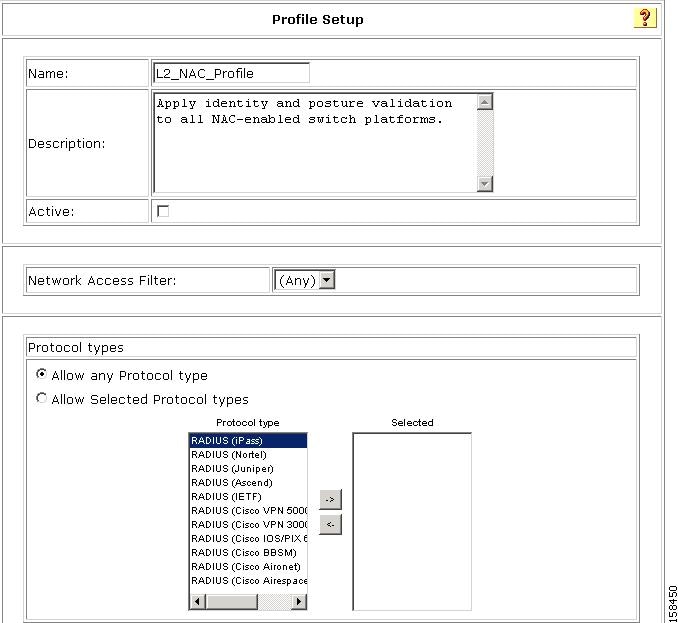
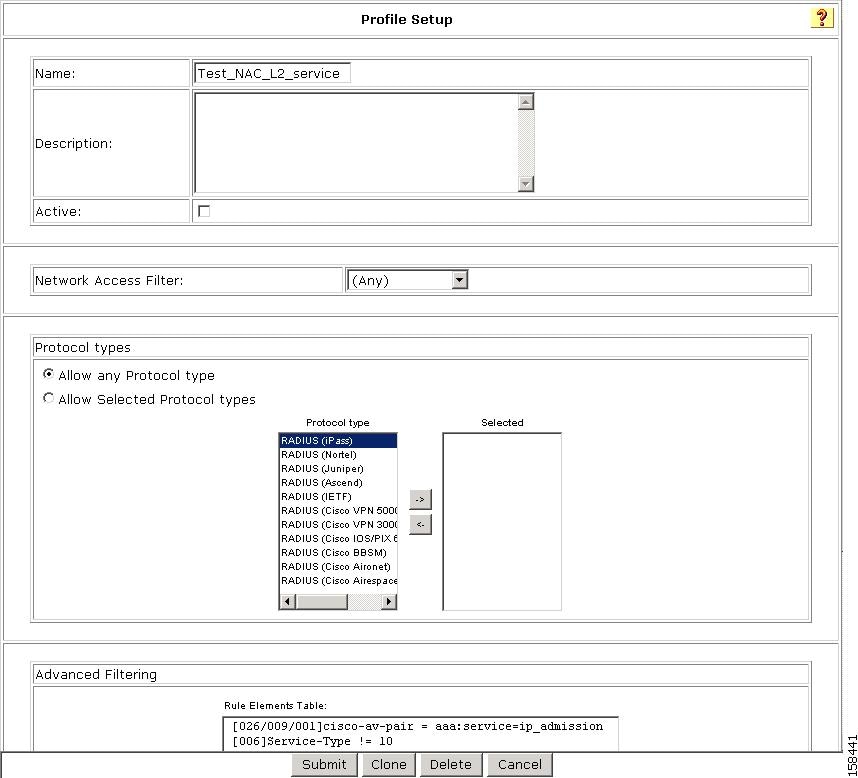
Figure 7-10 Profile Setup Page
Step 3
Enter a name for the profile.
Step 4
If you want to activate the profile now, check the Active check box.
Step 5
To select the protocols that the profile will be used with, click the Allow Selected Protocol types radio button, and then move one or more protocols to the Selected area.
Step 6
Click Submit.
Step 12: Configure Profile-Based Policies
After you create a profile, configure the policies to associate with that profile. The available policies are:
•
Protocols—The protocols with which the selected profile is used.
•
Authentication—The set of configuration policies that are related to authentication mechanisms.
•
Posture Validation —Settings that define how posture validation will be performed.
•
Authorization —An optional set of authorization rules. If you do not specify authorization policies, ACS defaults to the global configuration setting of authorizing by user-groups.
To configure profile-based policies:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Network Access Profiles.
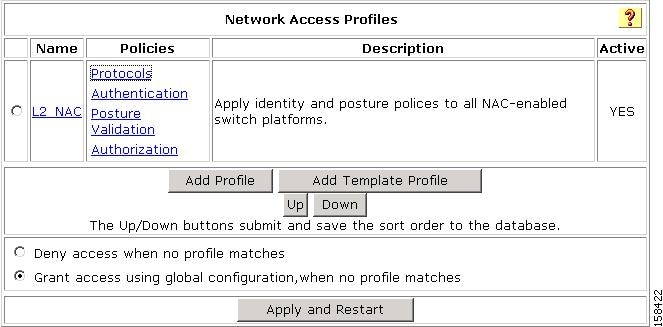
The Edit Network Access Profiles page opens, as shown in Figure 7-11.
Figure 7-11 Edit Network Access Profiles Page
Step 2
Click a a profile option to configure.
•
Protocols—To configure protocol settings, see Configure Protocol Settings.
•
Authentication—To configure authentication settings, see Configure Authentication.
•
Posture Validation—To configure posture validation, see Configure Posture Validation.
•
Authorization—To configure authorization, see Configure Authorization.
Configure Protocol Settings
To configure protocol settings:
Step 1
On the Network Access Profiles page, click Protocols.
The Protocols Settings page for the selected profile opens.
Step 2
In the EAP section, check the Allow Posture Validation check box.
Step 3
Check the Enable EAP-FAST check box.
Step 4
If you are using agentless host processing, check the Allow Agentless Host Processing check box.
Step 5
Click Submit.
Configure Authentication
The Authentication page for a specified profile controls how a profile authenticates matched requests and which user-validation databases ACS uses for authentication.
The Authentication page list the databases that were configured in the External User Databases section. These databases are mapped to ACS user groups based on the mapping rules defined in External User Databases > Databases Group Mapping.
To configure profile authentication settings:
Step 1
In the Edit Network Access Profiles page for the profile that you want to edit, click Authentication.
The Edit Authentication page for the selected profile opens. Figure 7-12 shows an example.
Figure 7-12 Edit Authentication Page for a Selected Profile
Step 2
Select one or more databases from the list of Available Databases and click the right arrow button to move them to the list of Selected databases.
Step 3
If you are configuring a MAC authentication bypass (MAB), see Configure MAB, page 4-20 for instructions on configuring MAB.
Configure Posture Validation
Posture validation rules define how ACS performs posture validation. Each posture validation rule specifies a condition and associated actions. The condition contains a set of required credential types, and the action contains a list of external posture validation servers (optional) and internal posture validation polices.
Posture Validation rules also contain:
•
The name for the rule.
•
A mandatory credential that defines the mandatory credential types that activate this rule.
•
Local policies.
•
A list of external servers that ACS queries for information that it uses to calculate a posture token.
•
Posture Agent (PA) messages that return the client for each token.
•
URL redirect information that is sent to the network access device for each token.
ACS evaluates posture rules by using a first-match strategy. ACS calculates the "worst" token that is returned based on the selected internal policies and information that the external posture servers send.
If the client is a nonresponsive host (NRH), ACS uses a specified audit server to audit the client.
Audit Servers are Cisco and third-party servers that determine posture information about a host without relying on the presence of a PA. These types of hosts are also called agentless hosts. The Cisco PA is called the Cisco Trust Agent. ACS uses audit servers to assess posture validation based on an organization's security policy.
Configure Authorization
A profile-based authorization policy is a set of conditions that ACS uses to authenticate users to the network. ACS associates the conditions that you specify in the authorization policy with actions that determine which RAC and downloadable ACLs are returned to the network device.
When you configure an authorization policy, you can also specify whether access to the network is denied for a specific user group; or, in a NAC network, denied based on a returned posture token. Authorization policies are tied not only to the user identity, but also to the profile type to which a user is mapped and the posture of the machine used to access the network.
Note
In a non-NAC network, leave the assessment result simply as Any (the default).
An authorization rule has this form:
If (user-group = selected-user-group and posture-token = selected-posture-token),
then provision (selected-RAC and selected-dACL)
You can also use the authorization rules to explicitly deny (send an access-reject) as an action. If you check the Include RADIUS attributes from user-group/user check box, ACS merges the RADIUS attributes defined in the user configuration, user-groups, and RAC. This process is:
1.
ACS adds all nonconflicting attributes from all sources.
2.
If a conflict occurs between the RADIUS attributes, ACS uses the attribute from the highest priority sources, where priority is assigned (from high to low):
a.
User
b.
RAC
c.
User-group
Create an Authorization Policy
To create an authorization policy for a profile:
Step 1
On the Network Access Profiles page, click Authorization.
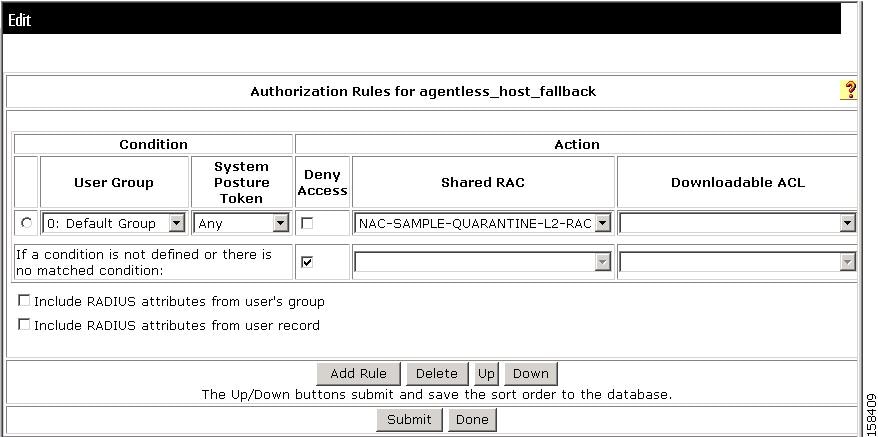
The Edit Authorization Rules page for the selected profile opens. Figure 7-13 shows an example.
Figure 7-13 Edit Authorization Policy Page
Step 2
Click Add Rule to add a line.
Step 3
Choose a User Group, System Posture Token, Shared RAC, and Downloadable ACL.
Note
You must edit the default authorization rule if you do not check the Include RADIUS attributes from user's group and Include RADIUS attributes from user record check boxes.
Step 4
Add additional authorization rules as required.
Step 5
Click Submit.
Step 6
Click Apply and Restart.
Define ACLs
In ACS 4.1, you can download access lists to specific devices or device groups.
You can define an access list that contains one or more ACLs and later download the list to network devices, based on their assignments to user groups. Before you define ACLS, enable downloadable ACLs.
To define an ACL:
Step 1
Choose Shared Profile Components > Downloadable IP ACLs.
A list of downloadable IP ACLs appears, as shown in Figure 7-14:
Figure 7-14 Downloadable IP ACL List
Step 2
Click Add.
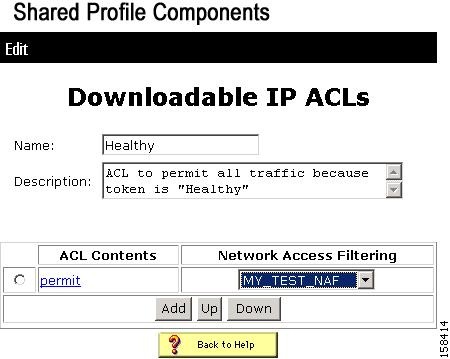
The Edit Downloadable IP ACLs page opens, as shown in Figure 7-15.
Figure 7-15 Downloadable IP ACLs Page
Each Assessment Result (system posture token), according to its definition, should have its own ACL, which contains one or more Access Control Entries (ACEs) that will instruct the NAC network device (router) to block packets from going to a specific destination or allow packets to reach a specific destination.
Step 3
On the Downloadable IP ACLs page, enter a Name and optional Description for the ACL.
Note
Do not use spaces in the name of the ACL. IOS does not accept ACL names that include spaces.
Step 4
Click Add (below the ACL table of contents) to add a new Access Control Entry (ACE) to the ACL and assign it to a NAF.
The Downloadable IP ACL Content page opens, as shown in Figure 7-16.
Figure 7-16 Downloadable IP ACL Content Page
Step 5
In the Name text box, type the ACL name.
Step 6
In the ACL Definitions input box, type definitions for the ACL.
ACL definitions consist of a series of permit and deny statements that permit or deny access for specified hosts. For information on the syntax for ACL definitions, see the "Downloadable ACLs" section of Chapter 4 of the User Guide for Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.1, "Shared Profile Components."
Step 7
Click Submit.
Note
Before configuring the ACL on ACS, you should test the syntax on the device to ensure that each ACE is valid.
The Downloadable ACL page appears with the new ACL in the ACL Contents list, as shown in Figure 7-17.
Figure 7-17 Downloadable ACL Contents List with New Content
Step 8
From the drop-down list in the Network Access Filtering column of the ACL Contents table, choose the correct NAF for this ACL.
You perform this action to enable the downloading of different ACEs for different devices or a group of devices. For example, the syntax of an ACE on routers differs from the syntax on a Project Information Exchange (PIX) firewall. By using a NAF, you can assign the same ACL to a PIX and a router, even though the actual ACE that is downloaded is different.
Step 9
Click Submit.
The new ACL appears on the list of downloadable ACLs.
Create a RAC
Shared RADIUS Authorization Components (RACs) contain groups of RADIUS attributes that you can dynamically assign to user sessions based on a policy. For example, you can create a RAC that gathers RADIUS attributes to define a VLAN. By using NAP configuration, you can define a policy that ACS uses to apply conditions specified in Network Access Filters (grouped NDGs), and in posture assessment rules to the shared RAC.
To define RACs:
Step 1
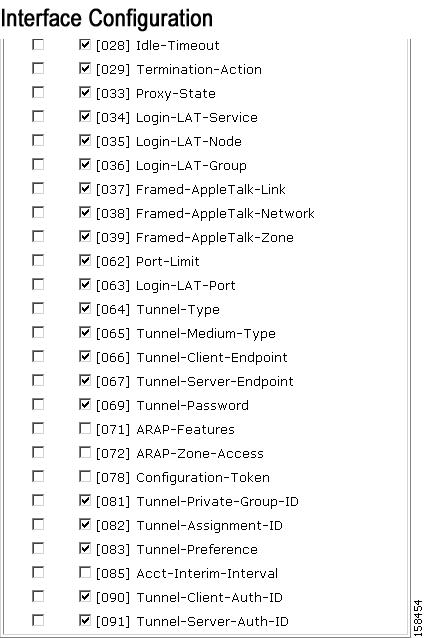
Select the appropriate Tunneling RADIUS attributes in the Advanced Options page:
a.
Choose Interface Configuration > RADIUS (IETF).
b.
Choose the Tunnel attributes as shown in Figure 7-19.
Figure 7-18 Tunnel Attributes for RACs Used in NAC Configuration:
c.
Click Submit.
d.
Restart ACS to enable the new settings.
To restart the system, choose System Configuration > Service Control and then click Restart.
Step 2
To add a RAC:
a.
Choose Shared Profile Components > RADIUS Authorization Components.
The RADIUS Authorization Components page for Tunnel type (64) opens, as shown in Figure 7-19.
Figure 7-19 RADIUS Authorization Components Page
b.
Enter a Name and Description in the RADIUS Authorization Components page.
c.
From the IETF lists, select Tunnel type (64) and click Add.
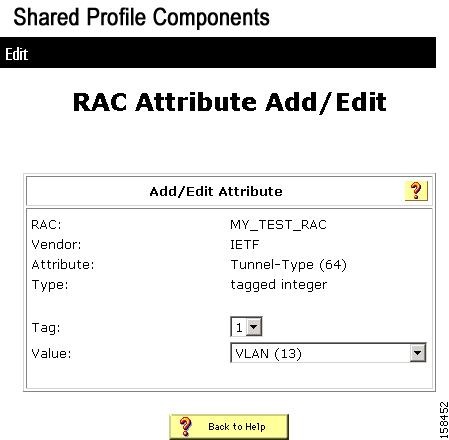
The RAC Attribute Add/Edit page opens, as shown in Figure 7-20.
Figure 7-20 RAC Attribute Add/Edit Page
d.
Click Submit.
Step 3
Add Tunnel-Medium-Type = 802(6), Tunnel-Prate-Group-ID = <vlan name>, or any other attribute that is required to define a VLAN.
Step 4
Click Submit.
Step 13: Configure Posture Validation for NAC
This section describes how to set up simple posture validation for a NAC-enabled network. You can create internal policies that ACS uses to validate the posture data or you can configure ACS to send the posture data to an external posture validation server.
Configure Internal Posture Validation Policies
An internal posture validation policy is an internal attribute policy that you can use in more then one profile. The result of an internal posture validation policy returns a Posture Assessment (token) according to rules that you set.
To create an internal posture validation policy:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Posture Validation.
The Posture Validation Components Setup page opens.
Step 2
Click Internal Posture Validation Setup.
The Posture Validation page opens, which lists any existing posture validation policies.
Step 3
Choose Add Policy.
The Edit Posture Validation page opens.
Step 4
Enter a name for the policy.
Step 5
Enter a Description (optional).
Step 6
Click Submit.
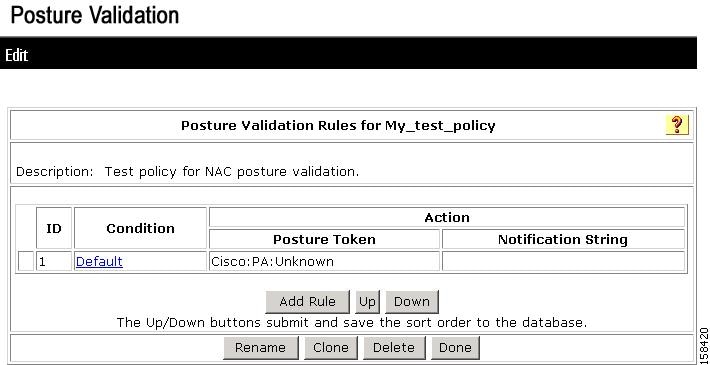
A new internal policy is created with a default rule. Figure 7-21 shows an example policy.
Figure 7-21 Creating a New Posture Validation Policy
Step 7
To edit the default rule:
a.
Click on the Default link.
b.
Choose a new Posture Assessment and Notification String for the default rule.
Step 8
To add a new rule:
a.
Click Add Rule.
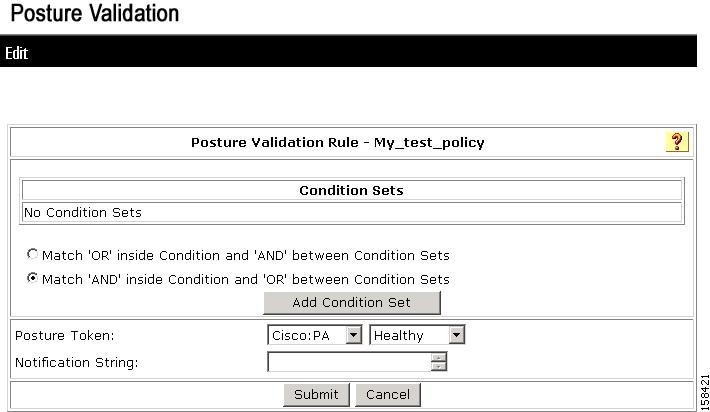
The Edit Posture Rule page appears, as shown in Figure 7-22. Initially no conditions are available for the rule.
Figure 7-22 Edit Posture Validation Rule Page
b.
Click Add Condition Set.
c.
The Add/Edit Condition page appears, as shown in Figure 7-23.
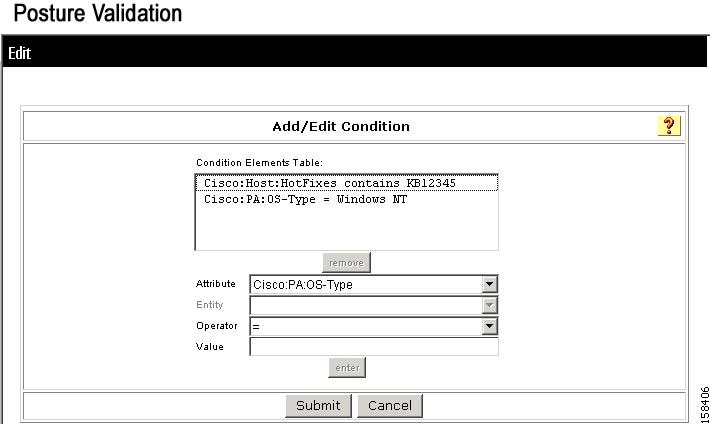
Figure 7-23 Add/Edit Condition Page
d.
From the Attribute drop-down list, choose an Attribute value.
e.
From the Operator drop-down list, choose a condition.
f.
In the Value text box, enter a value for the condition.
g.
Click Enter.
The specified rule appears in Add/Edit Condition page appears, as shown in Figure 7-23.
h.
Enter additional conditions as required.
i.
Click Submit.
j.
Click Apply and Restart to apply the new posture validation rule(s).
For information on creating advanced rules, see Configure Posture Validation.
Configure External Posture Validation Policies
An external posture validation policy uses an external server that returns a posture assessment (token) to ACS according to data that the ACS forwards to this server.
To set up an external posture validation server:
Step 1
In the Posture Validation Components Setup page, click External Posture Validation Setup.
Step 2
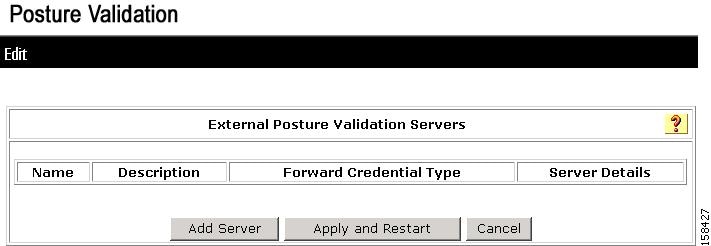
The Edit External Posture Validation Servers page opens, as shown in Figure 7-24.
Figure 7-24 Edit External Posture Validation Servers Page
Initially, the list of external posture validation servers is empty.
Step 3
Click Add Server.
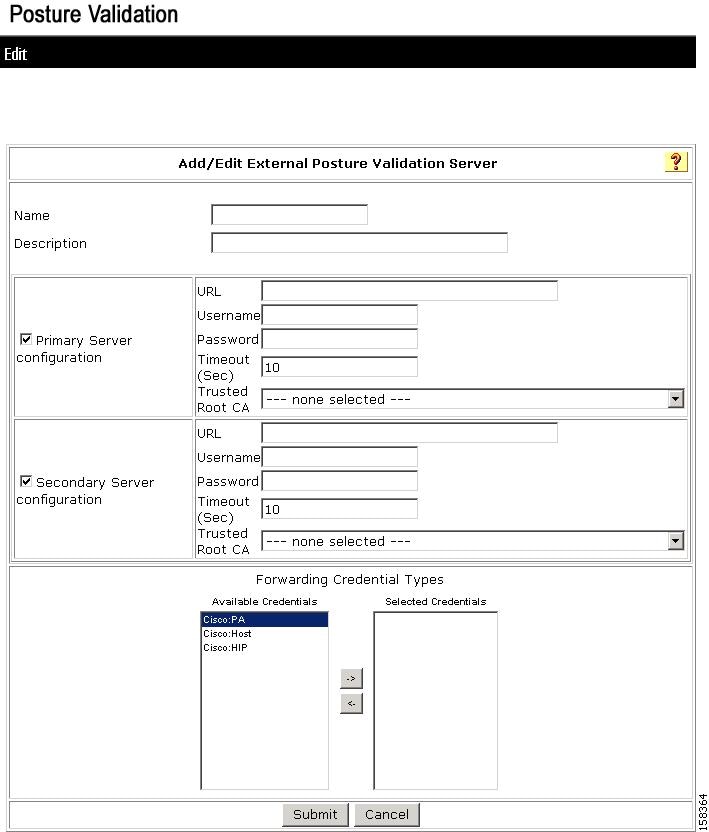
The Add/Edit External Posture Validation Server page appears, as shown in Figure 7-25.
Figure 7-25 Add/Edit External Posture Validation Server Page
Step 4
Enter a Name and Description (optional).
Step 5
Enter the server details, URL, User, Password, Timeout, and certificate (if required by the antivirus server).
Step 6
Click Submit.
Configure an External Posture Validation Audit Server
A NAC-enabled network might include agentless hosts that do not have the NAC client software. ACS can defer the posture validation of the agentless hosts to an audit server. The audit server determines the posture credentials of a host without relying on the presence of a PA.
Configuring an external audit server involves two stages:
•
Adding the posture attribute to the ACS internal dictionary.
•
Configuring an external posture validation server (audit server).
Add the Posture Attribute to the ACS Dictionary
Before you can create an external posture validation server, you must add one or more vendor attributes to the ACS internal data dictionary. To do this, you use the bin\CSUtil tool, which is located in the ACS installation directory.
To add the posture attributes:
Step 1
Create a text file in the \Utils directory with the following format:
[attr#0]vendor-id=[your vendor id]vendor-name=[The name of you company]application-id=6application-name=Auditattribute-id=00003attribute-name=Dummy-attrattribute-profile=outattribute-type=unsigned integerYour vendor ID should be the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)-assigned number that is the first section of the posture token attribute name, [vendor]:6:
Step 2
To install the attributes specified in the text file:
a.
Open a DOS command window.
b.
Enter the following command:
\<ACS_Install_Dir>\bin\CSUtil -addAVP [file_name]
where ACS_Install_Dir is the name of the ACS installation directory and file_name is the name of the text file that contains vendor attributes.
Step 3
Restart the CSAdmin, CSLog, and CSAuth services.
Configure the External Posture Validation Audit Server
You can configure an audit server once, and then use it for other profiles.
To configure an audit server:
Step 1
In the Posture Validation Components Setup page, click External Posture Validation Audit Setup.
Step 2
Click Add Server.
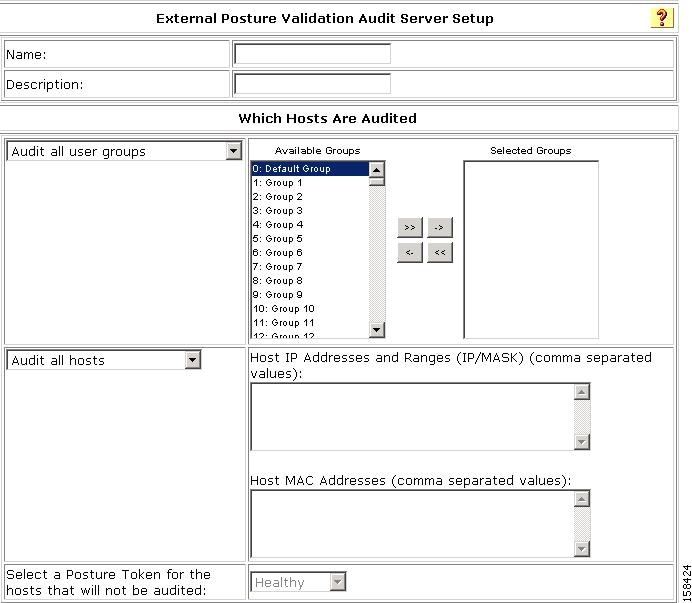
The External Posture Validation Audit Server Setup page appears, as shown in Figure 7-26.
Figure 7-26 External Posture Validation Audit Server Setup Page
Step 3
To configure the audit server:
a.
Enter a Name and Description (optional).
b.
In the Which Hosts Are Audited section, choose what hosts you want to audit. You can enter the host IP or MAC addresses for the hosts that you want to audit or for a host that you do not want to audit.
c.
For the hosts that will not be audited, choose a posture token from the drop-down list.
d.
Scroll down to the Use These Audit Servers section.
Figure 7-27 shows the Use These Audit Servers section of the External Posture Validation Server Setup page.
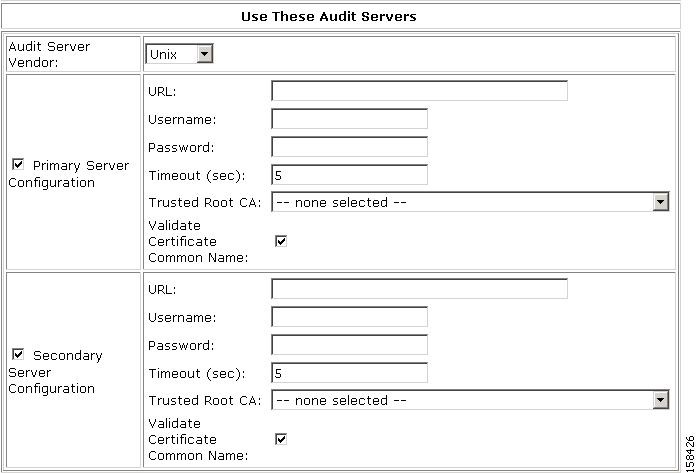
Figure 7-27 Use These Audit Servers Section
e.
In the Use These Audit Servers section, enter the Audit Validation Server information, Audit Server vendor, URL, and password.
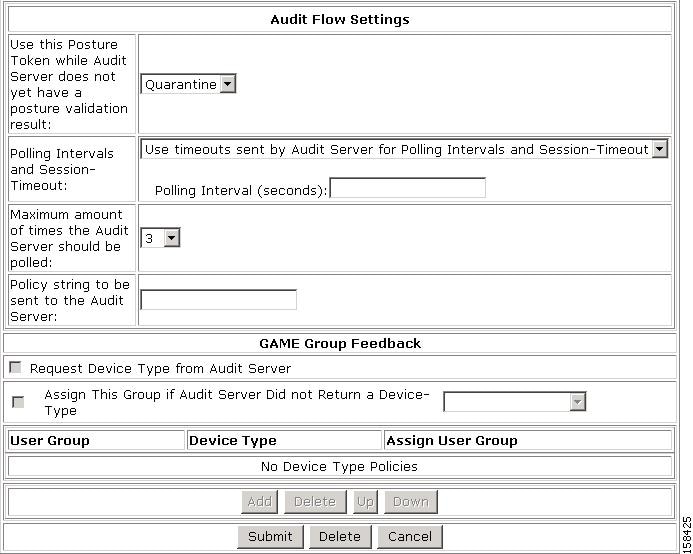
Figure 7-28 shows the Audit Flow Settings and the GAME Group Feedback section.
Figure 7-28 Audit Flow Settings and GAME Group Feedback Sections
f.
If required, in the Audit Flow Setting section, set the audit-flow parameters.
g.
If you are configuring GAME group feedback to support agentless host configuration in the NAC environment, configure the settings in the GAME Group Feedback section.
For information on configuring GAME Group Feedback settings, see Enable GAME Group Feedback.
h.
Click Submit.
Authorization Policy and NAC Audit
Audit servers define two types of posture assessments (tokens). A:
•
Temporary posture assessment is used as the in progress assessment. ACS grants the in progress posture assessment to the agentless host while the audit server is processing the auditing on the host and does not have a final result.
•
Final posture assessment is the posture assessment that the audit server returns after it completes the auditing process.
Note
To configure the authorization policy to work with the audit server, at least two RACs or downloadable ACLs are required: one for the in progress posture assessment and one for the final posture assessment. You should use a separate RAC or downloadable ACL for each token.
Step 14: Set Up Templates to Create NAPs
ACS 4.1 provides several profile templates that you can use to configure common usable profiles. In NAC-enabled networks, you can use these predefined profile templates to configure commonly used profiles. This section describes the templates provided in ACS 4.1.
Sample NAC Profile Templates
ACS 4.1 provides the following sample profile templates for NAC. A:
•
NAC Layer 3 profile template (NAC L3 IP)
•
NAC Layer 2 profile template (NAC L2 IP)
•
NAC Layer 2 802.1x template (NAC L2 802.1x)
•
Wireless (NAC L2 802.1x) template
In addition to these templates, ACS 4.1 provides two templates for agentless host processing that you can use in NAC installations:
•
Agentless Host for Layer 3 profile template
•
Agentless Host for Layer 2 (802.1x) profile template
Sample NAC Layer 3 Profile Template
This template creates a profile for Layer 3 NAC requests. Before you use this template, you should choose System Configuration > Global Authentication Setup and check the Enable Posture Validation check box.
To create a Layer 3 NAC profile template:
Step 1
Check the check boxes for the following options in the Global Authentication Setup page:
•
Allow Posture Validation
•
EAP-FAST
•
EAP-FAST MS-CHAPv2
•
EAP-FAST GTC
Step 2
In the navigation bar, click Network Access Profiles.
The Network Access Profiles page opens.
Step 3
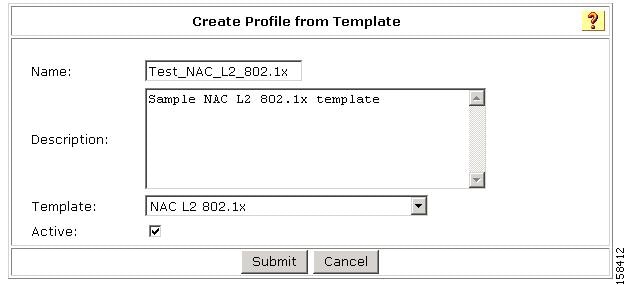
Click Add Template Profile.
The Create Profile from Template page opens, as shown in Figure 7-29.
Figure 7-29 Create Profile From Template Page
Step 4
Enter a Name and Description (optional).
Step 5
From the Template drop-down list, choose NAC L3 IP.
Step 6
Check the Active check box.
Step 7
Click Submit.
If no error appears, then you have created a profile that can authenticate Layer 3 NAC hosts.
The Edit Network Access Profile page opens, and the new profile appears in the Name column.
The predefined values for the Layer 3 NAC template include:
•
Profile Setup options
•
Protocols
•
A sample posture validation policy
•
Authentication policy
Step 8
To select a predefined set of values, click on one of the configuration options:
•
The profile name (to select the profile setup page for the profile)
•
Protocols
•
Authentication Policy
•
Sample Posture Validation Rules
Profile Setup
To use the Profile Setup settings from the template:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the profile that you created.
Step 3
The Profile Setup page appears, as shown in Figure 7-30.
Figure 7-30 Profile Setup Page for Layer 3 NAC Template
The default settings for the profile are:
•
Any appears in the Network Access Filter field, which means that this profile has no IP filter.
You can choose NAFs from the drop-down list, so that only specific host IPs match this profile.
•
In the Protocol types list, Allow any Protocol type appears in the Protocol types list, which means that no protocol type filter exists for this profile.
•
You can click the Allow Selected Protocol types option to specify a protocol type for filtering.
•
Two rules are configured in Advanced Filtering:
[026/009/001]Cisco-av-pair = aaa:service=ip admission[006]Service-Type != 10These rules specify that the associated profile policies authenticate and authorize each RADIUS request that matches the attribute's rules. You can change the advanced filter, and add, remove, or edit any RADIUS attribute that the RADIUS client sends.
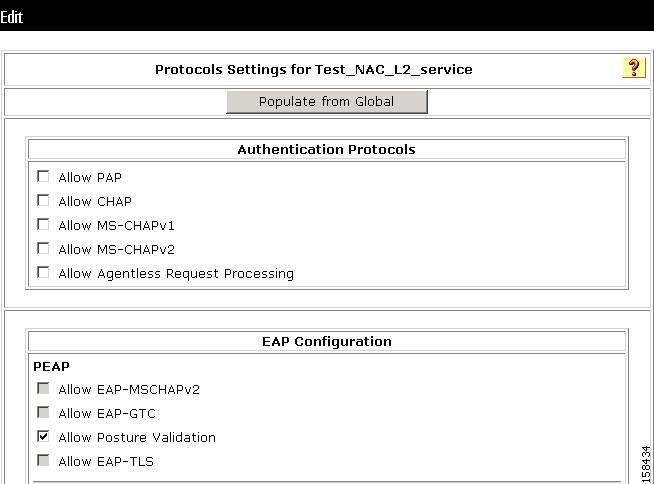
Protocols Policy for the NAC Layer 3 Template
Figure 7-31 shows the Protocols settings for the NAC Layer 3 template.
Figure 7-31 Protocols Setting for NAC Layer 3 Template
In the EAP Configuration section, Posture Validation is enabled.
Authentication Policy
To configure authentication policy:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, select Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the Authentication link from the Policies column.
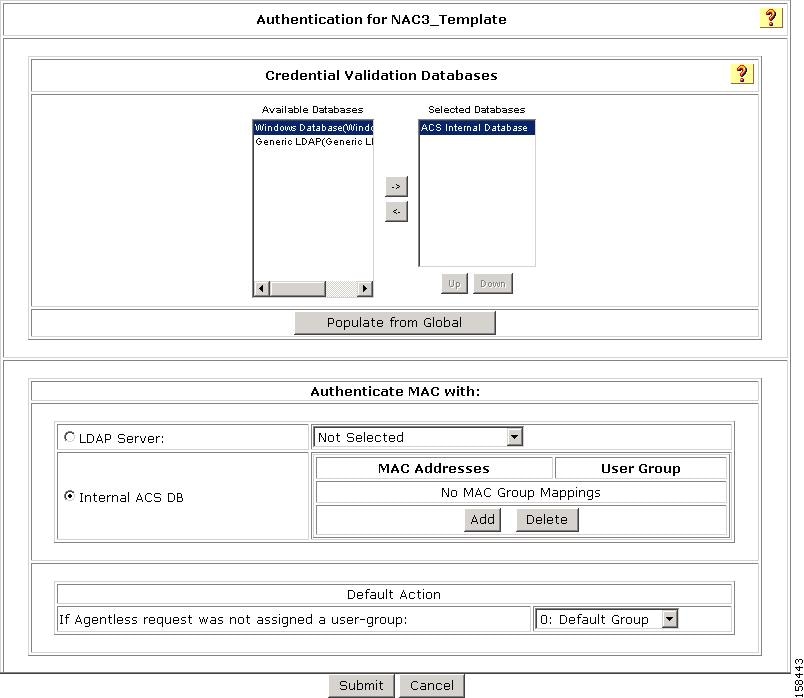
The Authentication page for the profile opens, as shown in Figure 7-32.
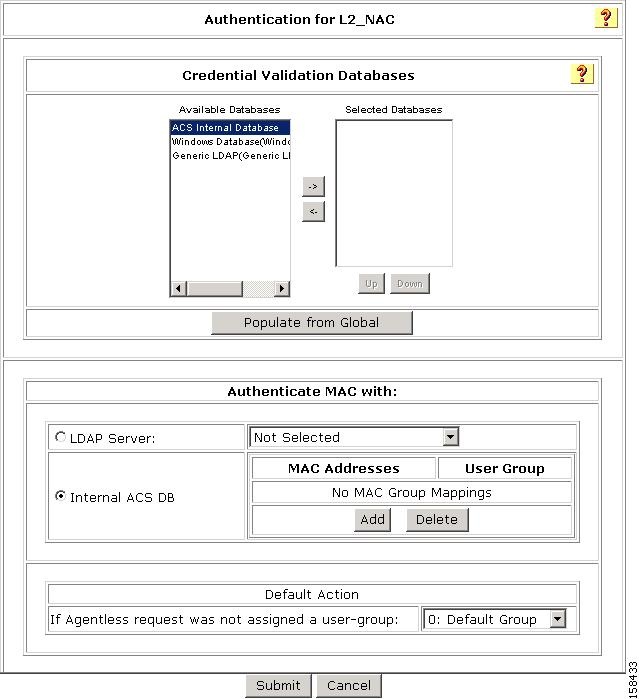
Figure 7-32 Authentication Page for Layer 3 NAC Profile Template
On this page, you can see the Layer 3 NAC template configuration for authentication:
Step 3
Specify the external database that ACS uses to perform authentication:
a.
To keep the default setting (ACS uses its internal database), click the Internal ACS DB radio button.
b.
To specify a LDAP server, click the LDAP Server radio button and then, from the drop-down list, choose an LDAP server.
c.
From the If Agentless request was not assigned a user-group drop-down list, choose a user group to which ACS assigns a host that is not matched to a user group.
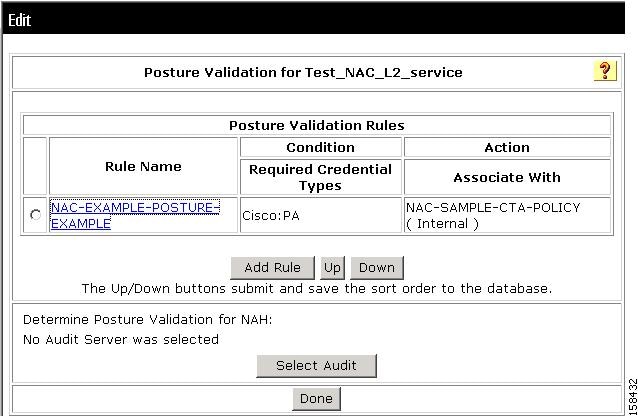
Sample Posture Validation Rule
Figure 7-33 shows the sample posture validation policy provided with the NAC Layer 3 template.
Figure 7-33 Sample Posture Validation Policy for NAC Layer 3 Template
Sample NAC Layer 2 Template
This template creates a profile for Layer 2 NAC requests.
Before you use the Layer 2 NAC profile template:
1.
Select EAP-FAST Configuration in Global Authentication Settings.
2.
Check (enable) the Allow authenticated in-band PAC provisioning.
3.
Check (enable) EAP-GTC and EAP-MSCHAPv2.
To create a Layer 2 NAC profile template:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Network Access Profiles.
The Network Access Profiles page opens.
Step 2
Click Add Template Profile.
Step 3
Enter a Name and Description (optional).
Step 4
From the Template drop-down list, choose NAC L2 IP.
Step 5
Check the Active check box.
Step 6
Click Submit.
If no error appears, then you have created a Profile that can authenticate Layer 2 NAC hosts and the Profile Setup page for the NAC Layer 2 template appears.
The predefined values for the Layer 2 NAC template include:
•
Profile Setup
•
Protocols settings
•
Authentication policy
•
A sample posture validation rule
The name of this policy is NAC-EXAMPLE-POSTURE-EXAMPLE.
Step 7
To select a configuration option, click the option name.
Profile Setup
To enable the profile setup:
Step 1
Go to Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the Profile that you created.
The Profile Setup page appears, as shown in Figure 7-34.
Figure 7-34 Profile Setup Page for NAC Layer 2 Template
The default settings for the profile are:
•
Any appears in the Network Access Filter field, which means that this profile has no IP filter.
You can choose NAFs from the drop-down list, so that only specific host IPs match this profile.
•
Allow any Protocol type appears in the Protocol types list, which means that no protocol type filter exists for this profile.
•
You can select the Allow Selected Protocol types option to specify a protocol type for filtering.
•
Two rules are configured in Advanced Filtering:
[026/009/001]Cisco-av-pair = aaa:service=ip admission[006]Service-Type != 10These rules specify that the associated profile policies authenticate and authorize each RADIUS request that matches the attribute's rules. You can change the advanced filter, and add, remove, or edit any RADIUS attribute that the RADIUS client sends.
This template automatically sets Advanced Filtering and Authentication properties with NAC Layer 2 IP Configuration.
ACS and Attribute-Value Pairs
When you enable NAC Layer 2 IP validation, ACS provides NAC AAA services by using RADIUS. ACS gets information about the antivirus credentials of the endpoint system and validates the antivirus condition of the endpoint.
You can set these Attribute-Value (AV) pairs on ACS by using the RADIUS cisco-av-pair vendor- specific attributes (VSAs).
•
Cisco Secure-Defined-ACL—Specifies the names of the downloadable ACLs on the ACS. The switch gets the ACL name from the Cisco Secure-Defined-ACL AV pair in this format:
#ACL#-IP-name-number
where name is the ACL name and number is the version number, such as 3f783768.
ACS uses the Auth-Proxy posture code to check if the switch has downloaded access-control entries (ACEs) for the specified downloadable ACL. If the switch has not downloaded the ACES, ACS sends an AAA request with the downloadable ACL name as the username so that the switch downloads the ACEs. The downloadable ACL is then created as a named ACL on the switch. This ACL has ACEs with a source address of Any and does not have an implicit Deny statement at the end. When the downloadable ACL is applied to an interface after posture validation is complete, the source address is changed from any to the host source IP address. The ACEs are prepended to the downloadable ACL that is applied to the switch interface to which the endpoint device is connected.
If traffic matches the Cisco Secure-Defined-ACL ACEs, ACS takes appropriate actions required by NAC.
•
url redirect and url-redirect-acl—Specifies the local URL policy on the switch. The switches use these cisco-av-pair VSAs:
— url-redirect = <HTTP or HTTPS URL>
— url-redirect-acl = switch ACL name
These AV pairs enable the switch to intercept an HTTP or Secure HTTP (HTTPS) request from the endpoint device and forward the client web browser to the specified redirect address from which the latest antivirus files can be downloaded. The url-redirect AV pair on the ACS contains the URL to which the web browser will be redirected. The url-redirect-acl AV pair contains the name of an ACL which specifies the HTTP or HTTPS traffic to be redirected. The ACL must be defined on the switch. Traffic which matches a permit entry in the redirect ACL will be redirected.
If the host's posture is not healthy, ACS might send these AV pairs.
For more information about AV pairs that Cisco IOS software supports, see the documentation about the software releases that run on the AAA clients.
Default ACLs
If you configure NAC Layer 2 IP validation on a switch port, you must also configure a default port ACL on a switch port. You should also apply the default ACL to IP traffic for hosts that have not completed posture validation.
If you configure the default ACL on the switch and the ACS sends a host access policy to the switch, the switch applies the policy to traffic from the host that is connected to a switch port. If the policy applies to the traffic, the switch forwards the traffic. If the policy does not apply, the switch applies the default ACL. However, if the switch gets a host access policy from the ACS, but the default ACL is not configured, the NAC Layer 2 IP configuration does not take effect.
When ACS sends the switch a downloadable ACL that specifies a redirect URL as a policy-map action, this ACL takes precedence over the default ACL that is already configured on the switch port. The default ACL also takes precedence over the policy that is already configured on the host. If the default port ACL is not configured on the switch, the switch can still apply the downloadable ACL from ACS.
You use this template for access requests from Layer 2 devices that do not have the 802.1x client installed. The Authentication Bypass (802.1x fallback) template is used for access requests to bypass the nonclient authentication process. Users are mapped to a User Group based on their identity.
Note
Do not click the Populate from Global button; otherwise, the settings for this authentication field will be inherited from the settings in the Global Authentication Setup in System Configuration.
Protocols Settings
Figure 7-35 shows the Protocols settings for the NAC Layer 2 template.
Figure 7-35 Protocols Setting for NAC Layer 2 Template
On this page, you can see the Layer 2 NAC template configuration for protocols. The default settings are:
•
In the EAP Configuration area, posture validation is enabled.
•
Allow EAP-Fast Configuration is checked, which means that this profile allows EAP-FAST authentication.
Authentication Policy
To set the authentication policy:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the Authentication link from the Policies column.
The Authentication Settings page for the NAC Layer 2 template opens, as shown in Figure 7-36.
Figure 7-36 Authentication Settings for NAC Layer 2 Template
Step 3
Specify the external database that ACS uses to perform authentication:
a.
To keep the default setting (ACS uses its internal database), click the Internal ACS DB radio button.
b.
To specify a LDAP server, click the LDAP Server radio button and then, from the drop-down list, choose an LDAP server.
c.
From the If Agentless request was not assigned a user-group drop-down list, choose a user group to which ACS assigns a host that is not matched to a user group.
Sample Posture Validation Rule
Figure 7-37 shows the sample posture validation rule provided with the NAC Layer 2 template.
Figure 7-37 Sample Posture Validation Policy for NAC Layer 2 Template
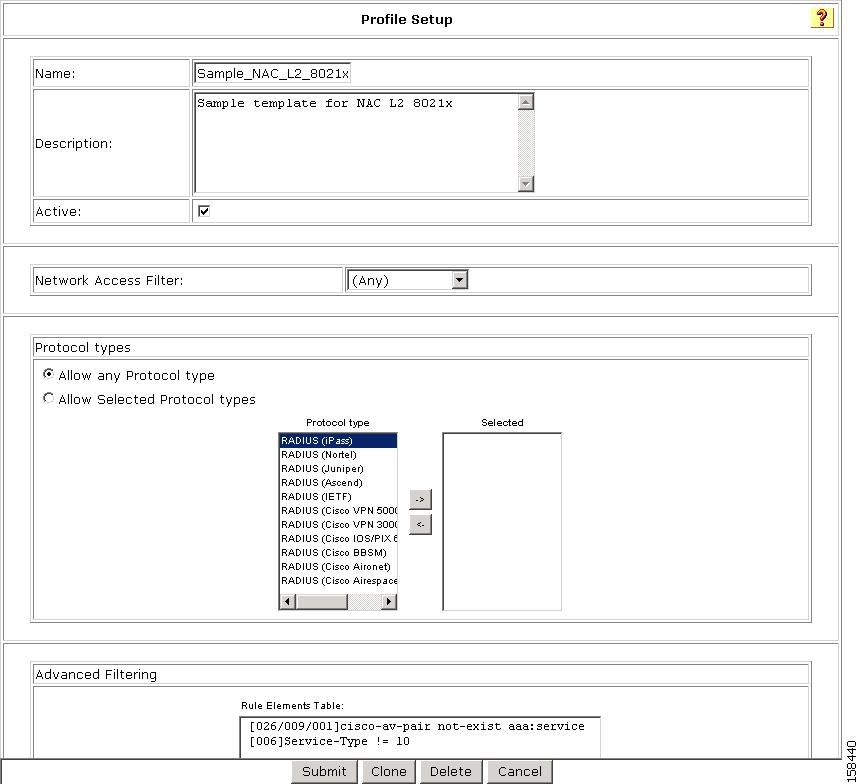
Sample NAC Layer 2 802.1x Template
This template creates a profile for Layer 2 NAC 802.1x requests. Before you use this template, you should choose System Configuration > Global Authentication Setup and check the Enable Posture Validation check box.
To create a Layer 2 NAC 802.1x profile template:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Network Access Profiles.
The Network Access Profiles page opens.
Step 2
Click Add Template Profile.
The Create Profile from Template page opens, as shown in Figure 7-38.
Figure 7-38 Create Profile From Template Page
Step 3
Enter a Name and Description (optional).
Step 4
From the Template drop-down list, choose NAC L2 802.1x.
Step 5
Check the Active check box.
Step 6
Click Submit.
If no error appears, then you have created a Profile that can authenticate Layer 2 NAC hosts.
The Edit Network Access Profile page opens, and the new profile appears in the Name column.
The predefined values for the Layer 2 NAC 802.1x template include:
•
Profile Setup
•
Protocols
•
A sample posture validation policy
•
Authentication policy
Step 7
To select a predefined set of values, click on one of the configuration options:
•
The profile name (to select the profile setup page for the profile)
•
Protocols
•
Authentication Policy
•
Sample Posture Validation Rules
Profile Setup
To use the Profile Setup settings from the template:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the profile that you created.
Step 3
The Profile Setup page appears, as shown in Figure 7-30.
Figure 7-39 Profile Setup Page for NAC Layer 2 802.1x Template
The default settings for the profile are:
•
Any appears in the Network Access Filter field, which means that this profile has no IP filter.
You can choose NAFs from the drop-down list, so that only specific host IPs match this profile.
•
Allow any Protocol type appears in the Protocol types list, which means that no protocol type filter exists for this profile.
•
You can select the Allow Selected Protocol types option to specify a protocol type for filtering.
•
Two rules are configured in Advanced Filtering:
[026/009/001]Cisco-av-pair = aaa:service=ip admission[006]Service-Type != 10These rules specify that the associated profile policies authenticate and authorize each RADIUS request that matches the attribute's rules. You can change the advanced filter, and add, remove, or edit any RADIUS attribute that the RADIUS client sends.
Protocols Policy
Figure 7-40 shows the Protocols settings for the NAC Layer 2 802.1x template.
Figure 7-40 Protocols Setting for NAC Layer 802.1x Template
In the EAP Configuration section, Posture Validation is enabled.
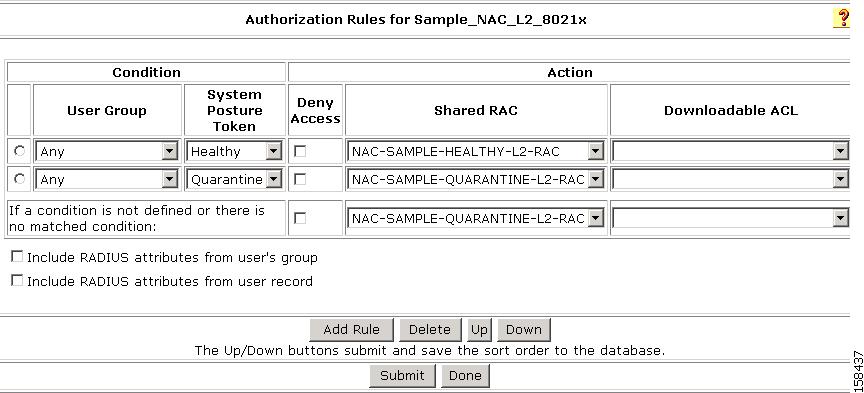
Authorization Policy
To configure an authorization policy for the NAC Layer 2 802.1x template:
Step 1
Go to Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the Authorization link from the Policies column.
The Authentication page for the NAC Layer 2 802.1x template profile appears, as shown in Figure 7-41.
Figure 7-41 Authentication Page for NAC Layer 2 802.1x Profile Template
On this page, you can see the Layer 2 NAC 802.1x template configuration for authorization.
Step 3
Specify the external database that ACS uses to perform authentication:
a.
To keep the default setting (ACS uses its internal database), click the Internal ACS DB radio button.
b.
To specify a LDAP server, click the LDAP Server radio button and then, from the drop-down list, choose an LDAP server.
c.
From the If Agentless request was not assigned a user-group drop-down list, choose a user group to which ACS assigns a host that is not matched to a user group.
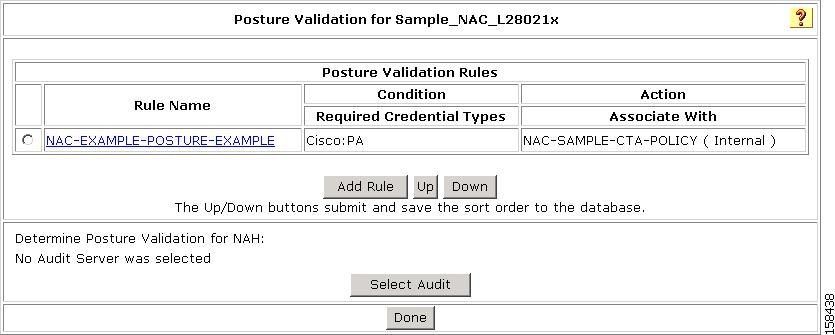
Sample Posture Validation Rule
Figure 7-42 shows the sample posture validation policy provided with the NAC Layer 2 802.1x template.
Figure 7-42 Sample Posture Validation Policy for NAC Layer 2 802.1x Template
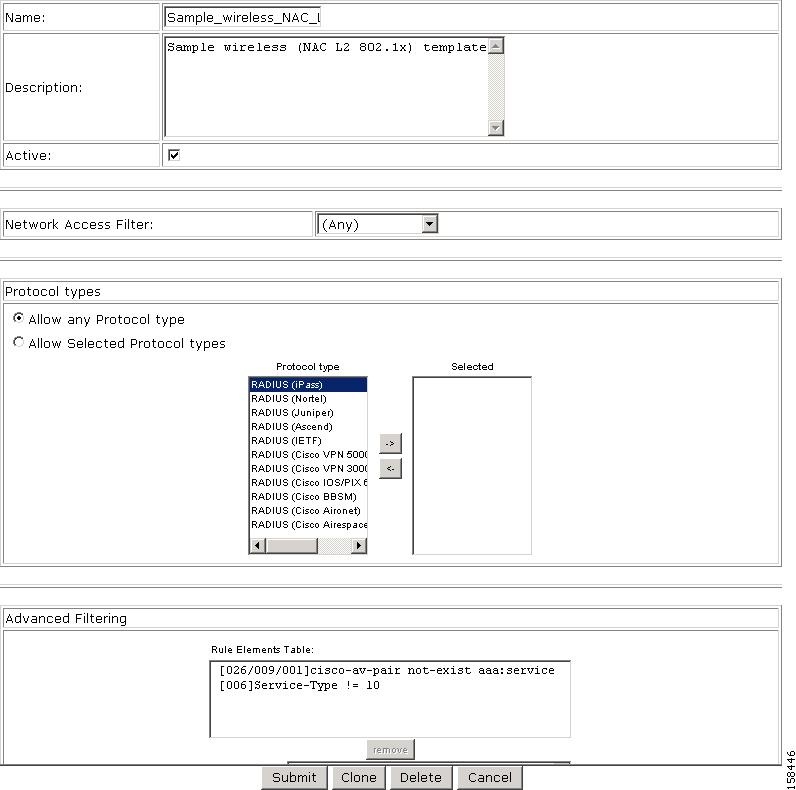
Sample Wireless (NAC L2 802.1x) Template
This template creates a profile for Layer 2 NAC 802.1x requests in wireless networks. Before you use this template, you should choose System Configuration > Global Authentication Setup and check the Enable Posture Validation check box.
To create a wireless (NAC L2 802.1x) NAC profile template:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Network Access Profiles.
The Network Access Profiles page opens.
Step 2
Click Add Template Profile.
The Create Profile from Template page opens, as shown in Figure 7-43.
Figure 7-43 Create Profile From Template Page
Step 3
Enter a Name and Description (optional).
Step 4
From the Template drop-down list, choose Wireless (NAC L2 802.1x).
Step 5
Check the Active check box.
Step 6
Click Submit.
If no error appears, then you have created a Profile that can authenticate wireless NAC Layer 2 802.1x hosts.
The Edit Network Access Profile page opens, and the new profile is listed in the Name column.
The predefined values for the NAC Layer 2 802.1x template include:
•
Profile Setup
•
Protocols
•
A sample posture validation policy
•
Authentication policy
Step 7
To select a predefined set of values, click on one of the configuration options:
•
The profile name (to select the profile setup page for the profile)
•
Protocols
•
Authentication Policy
•
Sample Posture Validation Rules
Profile Setup
To use the Profile Setup settings from the template:
Step 1
Go to Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the profile that you created.
Step 3
The Profile Setup page appears, as shown in Figure 7-44.
Figure 7-44 Profile Setup Page for Wireless (NAC L2 802.1x)Template
The default settings for the profile are:
•
Any appears in the Network Access Filter field, which means that this profile has no IP filter.
You can choose NAFs from the drop-down list, so that only specific host IPs match this profile.
•
In the Protocol types list, Allow any Protocol type appears in the Protocol types list, which means that no protocol type filter exists for this profile.
•
You can click the Allow Selected Protocol types option to specify a protocol type for filtering.
•
Two rules are configured in Advanced Filtering:
[026/009/001]Cisco-av-pair = aaa:service=ip admission[006]Service-Type != 10These rules specify that the associated profile policies authenticate and authorize each RADIUS request that matches the attribute's rules. You can change the advanced filter, and add, remove, or edit any RADIUS attribute that the RADIUS client sends.
Protocols Policy
Figure 7-45 shows the Protocols settings for the Wireless (NAC L2 802.1x) template.
Figure 7-45 Protocols Setting for Wireless NAC 802.1x Template
In the EAP Configuration section, Posture Validation is enabled.
Authorization Policy
To configure an authorization policy for the Wireless NAC Layer 2 802.1x template:
Step 1
Go to Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the Authorization link from the Policies column.
The Authentication page for the profile appears, as shown in Figure 7-46.
Figure 7-46 Authorization Page for Wireless (NAC L2 802.1x) Profile Template
On this page, you can see the Wireless (NAC L2 802.1x) template configuration for authentication:
Step 3
Specify the external database that ACS uses to perform authentication:
a.
To keep the default setting (ACS uses its internal database), click the Internal ACS DB radio button.
b.
To specify a LDAP server, click the LDAP Server radio button and then, from the drop-down list, choose an LDAP server.
c.
From the If Agentless request was not assigned a user-group drop-down list, choose a user group to which ACS assigns a host that is not matched to a user group.
Sample Posture Validation Rule
Figure 7-47 shows the sample posture validation policy provided with the Wireless (NAC L2 802.1x) template.
Figure 7-47 Sample Posture Validation Policy for Wireless (NAC L2 802.1x) Template
Note
The posture validation policy for the wireless NAC L2 802.1x template is the same as for the NAC L2 802.1x template.
Using a Sample Agentless Host Template
ACS 4.1 provides two sample templates for agentless host processing:
•
Agentless Host for L3
•
Agentless Host for L2 (802.1x fallback)
These two templates are almost identical. This section documents the steps for using the Agentless Host for Layer 3 template.
Note
You can use the Agentless Host for L2 (802.1x Fallback) profile template to create a profile that matches a RADIUS request a switch sends. Once the profile is created, an analysis of the RADIUS packet that comes from the Catalyst 6500 must be done to create an accurate match for the profile. The RADIUS request from the switch has a Service Type value of 10, just like NAC-L2-IP; but does not have a Cisco Attribute Value Pair (AV pair) that contains the keyword service. Therefore, the template enables two entries in the Advanced Filtering section.
The Agentless Host for Layer 3 template creates a profile for Layer 3 requests that involve agentless host processing. Before you use this template, you should choose System Configuration > Global Authentication Setup and check the Enable Posture Validation check box.
To create an agentless host for Layer 3 profile template:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Network Access Profiles.
The Network Access Profiles page opens.
Step 2
Click Add Template Profile.
The Create Profile from Template page opens, as shown in Figure 7-48.
Figure 7-48 Create Profile From Template Page
Step 3
Enter a Name and Description (optional).
Step 4
From the Template drop-down list, choose Agentless Host for L3.
Step 5
Check the Active check box.
Step 6
Click Submit.
If no error appears, then you have created a profile that can authenticate Layer 3 NAC hosts.
The Edit Network Access Profile page opens, and the new profile is listed in the Name column.
The predefined values for the Agentless Host for Layer 3 template include:
•
Profile Setup
•
Protocols
•
A sample posture validation policy
•
Authentication policy
Step 7
To select a predefined set of values, click on one of the configuration options.
•
The profile name (to select the profile setup page for the profile)
•
Protocols
•
Authentication Policy
•
Sample Posture Validation Rules
Profile Setup
To use the Profile Setup settings from the template:
Step 1
Go to Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the profile that you created.
Step 3
The Profile Setup page appears, as shown in Figure 7-49.
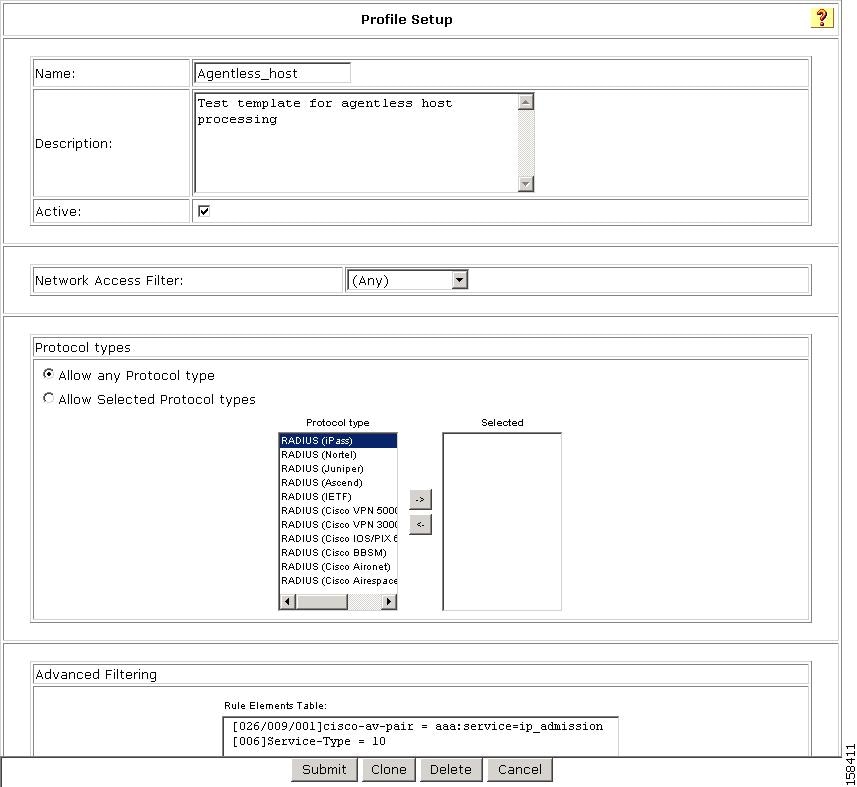
Figure 7-49 Profile Setup Page for Agentless Host for Layer 3 Template
The default settings for the profile are:
•
Any appears in the Network Access Filter field, which means that this profile has no IP filter.
You can choose NAFs from the drop-down list, so that only specific host IPs match this profile.
•
In the Protocol types list, Allow any Protocol type appears in the Protocol types list, which means that no protocol type filter exists for this profile.
•
You can click the Allow Selected Protocol types option to specify a protocol type for filtering.
•
Two rules are configured in Advanced Filtering:
[026/009/001]Cisco-av-pair = aaa:service=ip admission[006]Service-Type != 10These rules specify that the associated profile policies authenticate and authorize each RADIUS request that matches the attribute's rules. You can change the advanced filter, and add, remove, or edit any RADIUS attribute that the RADIUS client sends.
Protocols Policy
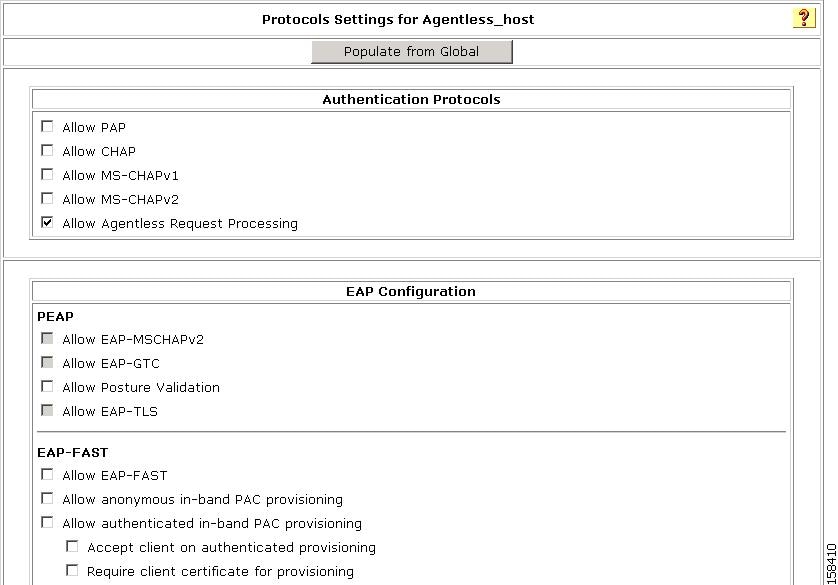
Figure 7-50 shows the Protocols settings for the Agentless Host for Layer 3 template.
Figure 7-50 Protocols Setting for Agentless Host for Layer 3 Template
In the Authentication Protocols section, check Agentless Host processing.
Authentication Policy
To configure an authentication policy for the Agentless Host for Layer 3 template:
Step 1
Go to Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the Authentication link from the Policies column.
The Authentication page for the profile appears, as shown in Figure 7-51.
Figure 7-51 Authentication Page for Agentless Host for Layer 3 Profile Template
On this page, you can see the Agentless Host for Layer 3 template configuration for authentication:
Step 3
Specify the external database that ACS uses to perform authentication:
a.
To keep the default setting (ACS uses its internal database), click the Internal ACS DB radio button.
b.
To specify a LDAP server, click the LDAP Server radio button and then, from the drop-down list, choose an LDAP server.
c.
From the If Agentless request was not assigned a user-group drop-down list, choose a user group to which ACS assigns a host that is not matched to a user group.
Step 15: Map Posture Validation Components to Profiles
To add an internal posture validation policy, external posture validation server, or both, to a profile:
Step 1
Choose Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Choose the relevant profile Posture Validation policy.
Step 3
Click Add Rule.
Step 4
Enter a Name for the rule.
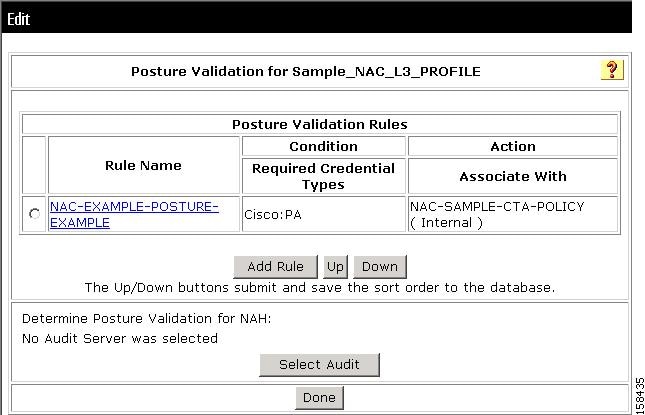
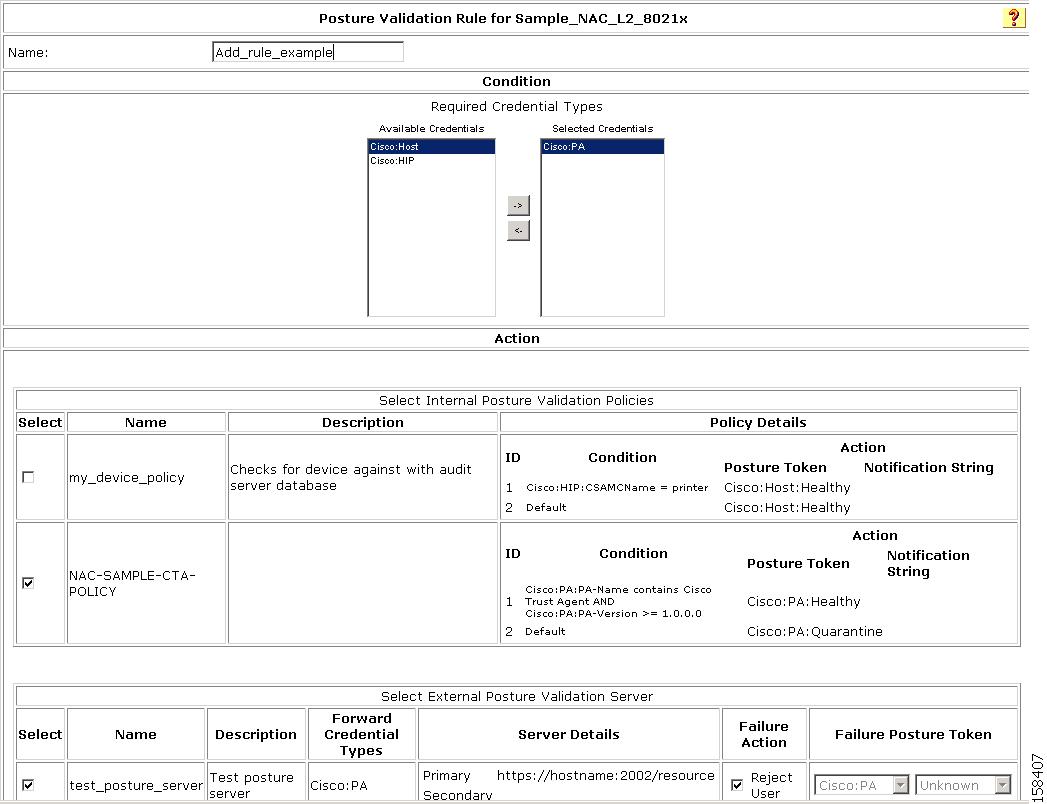
The Add/Edit Posture Validation Rule page for the specified rule appears, as shown in Figure 7-52.
Figure 7-52 Add/Edit Posture Validation Rule Page
Step 5
Choose the Required Credential Types.
Step 6
In the Select External Posture Validation Sever section, select the policies or server that you want to map to this profile. To select a:
•
Posture Server, check the check box next to the server name.
•
Policy, check the check box next to a policy in the Failure Action column.
Step 7
Click Submit.
Step 8
Click Back to return to the Posture Validation policy.
Step 9
Click Apply + Restart.
Step 16: Map an Audit Server to a Profile
To add an external posture validation audit server to a profile:
Step 1
Choose Network Access Profiles.
Step 2
Click the Protocols link for the relevant Posture Validation Policy.
The Protocols Settings page for the selected policy opens.
Step 3
Check the Allow Agentless Request Processing check box.
Step 4
Click Submit.
Step 5
Click the Posture Validation link for the relevant profile Posture Validation policy.
Step 6
Click Select Audit.
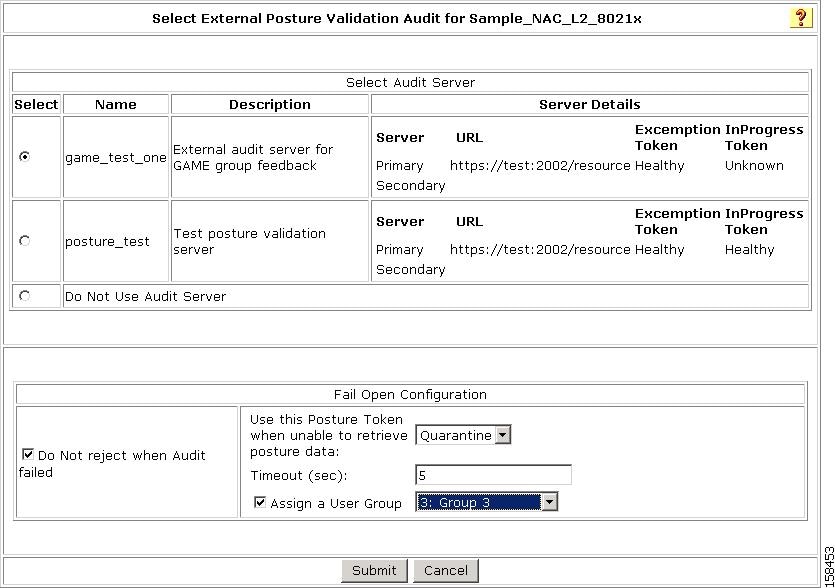
The Select External Posture Validation Audit Server page opens, as shown in Figure 7-53.
Figure 7-53 Select External Validation Audit Server Page
Step 7
Select the audit server to use.
Step 8
To specify a Fail Open configuration to use if the audit fails:
a.
Check the Do not reject when Audit failed check box.
b.
From the Use this Posture Token when unable to retrieve posture data drop-down list, choose a posture token to apply if the audit fails.
c.
Enter a timeout value in seconds.
d.
If you want to specify a user group to which to assign the supplicant if the audit fails, check the Assign a User Group check box and then from the Assign a User Group drop-down list, choose a user group.
Step 9
Click Submit.
Step 10
Click Done.
Step 11
Click Apply and Restart.
Step 17 (Optional): Configure GAME Group Feedback
If you are using ACS in a NAC environment with agentless hosts, then you must configure GAME group feedback.
To configure GAME group feedback:
Step 1
Import an audit vendor file by using CSUtil.exe.
See Import an Audit Vendor file Using CSUtil for details.
Step 2
Import a device-type attribute file by using CSUtil.exe.
See Import a Device-Type Attribute File Using CSUtil for details.
Step 3
Import NAC attribute-value pairs.
See Import NAC Attribute-Value Pairs for details.
Step 4
Configure database support for agentless host processing.
The database that you use can be an external LDAP database (preferred) or the ACS internal database. See Configure Database Support for Agentless Host Processing for details.
Step 5
Enable Posture Validation.
See Enable Posture Validation for details.
Step 6
Configure an external audit server.
See Configure an External Audit Server for details.
Step 7
Enable GAME Group feedback.
To enable GAME Group feedback, in the external audit server posture validation setup section, configure:
•
Which hosts are audited
•
GAME group feedback
•
Device-type retrieval and mapping for vendors who have a device attribute in the RADIUS dictionary
See Enable GAME Group Feedback for details.
Step 8
Set up a device group policy.
See Enable GAME Group Feedback for details.
Import an Audit Vendor file Using CSUtil
For information on importing an audit vendor file by using CSUtil.exe, see the "Adding a Custom RADIUS Vendor and VSA Set" section in Appendix D of the User Guide for Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.1, "CSUtil Database Utility."
Import a Device-Type Attribute File Using CSUtil
Before you can configure GAME group feedback, you must import an attribute file that contains a device-type attribute.
The format of a text file to set up a device-type attributes is:
[attr#0]vendor-id=<the vendor identifier number>vendor-name=<the name of the vendor>application-id=6application-name=Auditattribute-id=00012attribute-name=Device-Typeattribute-profile=in outatribute-type=stringTo import the file:
Step 1
Save the text file that sets up the device-type attribute in an appropriate directory.
Step 2
Open a DOS command window.
Step 3
Enter:
CSUtil -addAVP <device-type filename>where device-type filename is the name of the text file that contains the device-type attribute.
Step 4
Restart ACS:
a.
In the navigation bar, click System Configuration.
b.
Click Service Control.
c.
Click Restart.
Import NAC Attribute-Value Pairs
To import NAC attribute-value pairs:
Step 1
Obtain a NAC attribute-value pairs file.
Step 2
Import the file by using CSUtil.exe.
a.
Start a DOS command window.
b.
Enter:
CSUtil -addAVP <NAC AV-pair filename>
where NAC AV-pair filename is the name of the text file that contains the device-type attribute.
Step 3
Restart ACS:
a.
In the navigation bar, click System Configuration.
b.
Click Service Control.
c.
Click Restart.
Configure Database Support for Agentless Host Processing
The database that you use can be an external LDAP database (preferred) or the ACS internal database.
For information on configuring database support for agentless host processing, see Step 4: Configure LDAP Support for MAB, page 4-9 in Chapter 4, "Agentless Host Support Configuration Scenario".
Enable Posture Validation
You must enable posture validation in two places. In the:
•
Global Authentication Page, as part of the configuration for PEAP.
•
EAP configuration section of the Protocols page for the Network Access Profile that enables agentless host support.
Configure an External Audit Server
For detailed instructions on configuring an external audit server, see Configure an External Posture Validation Audit Server.
Enable GAME Group Feedback
To enable GAME Group feedback:
Step 1
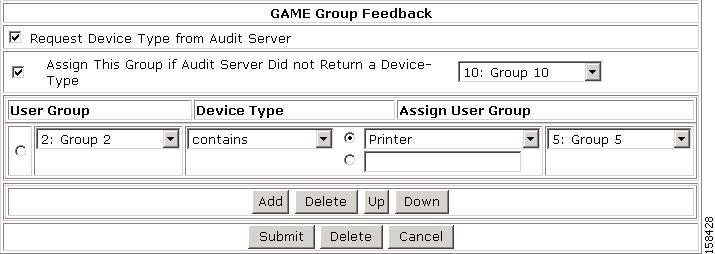
On the External Posture Validation Audit Server Setup page, in the GAME Group Feedback section, check the Request Device Type from Audit Server check box.
If this check box is not available, define an audit device type attribute for the vendor in the internal ACS dictionary.
ACS for Windows:
With ACS for Windows, you use the CSUtil.exe command. For detailed information, see "Posture Validation Attributes" in Appendix D of the User Guide for Cisco Secure ACS.
ACS Solution Engine:
With ACS Solution Engine, you use the NAC Attributes Management page in the web interface. See "NAC Attribute Management (ACS Solution Engine Only)" in Chapter 8 of the User Guide for Cisco Secure ACS for more information.
Step 2
If you want to configure a default destination group that ACS uses if the audit server does not return a device type, check the Assign This Group if Audit Server Did not Return a Device-Type check box.
You should now add entries to the group assignment table. The group assignment table is a list of rules that set conditions that determine the user group to which to assign a particular device type that is returned from the audit server.
Step 3
Click Add to display the group assignment table and add a device-type feedback rule.
The group assignment table appears, as shown in Figure 7-54.
Figure 7-54 GAME Group Feedback Section with Group Assignment Table
Step 4
Specify the following in the group assignment table:
•
User Group—Lists all user groups, including Any. The device type that the MAC authentication returns is initially compared with this list of device types.
•
Match Condition—Valid values for the operator are:
–
match-all
–
=
–
! =
–
contains
–
starts-with
–
regular-expression
•
Device Type—Defines the comparison criteria for the User Group by using an operator and device type. Valid values for the device type drop-down list include:
–
Printer
–
IP Phone
–
Network Infrastructure
–
Wireless Access Point
–
Windows
–
UNIX
–
Mac
–
Integrated Device
–
PDA
–
Unknown
Note
Type a device type in the text box if the device type drop-down does list not contain a particular device.
•
Assign User Group—A drop-down list of administrator-defined user groups. If the comparison of the initial User Group with the Device Type succeeds, ACS will assign this user group.
Step 5
To add additional policies, click Add.
Step 6
To delete a policy, select the policy and click Delete.
Step 7
To move the policies up and down in the group assignment table, click the Up and Down buttons.
Step 8
When you finish setting up policies for group assignment, click Submit.
Step 9
Click Apply and Restart.

 Feedback
Feedback