Ultra Cloud Core User Plane Function
Introduction
This Release Notes identifies changes and issues related to this software release.
Release Lifecycle Milestones
|
Release Lifecycle Milestone |
Milestone |
Date |
|---|---|---|
|
First Customer Ship |
FCS |
30-Apr-24 |
|
End of Life |
EoL |
30-Apr-24 |
|
End of Software Maintenance |
EoSM |
29-Oct-25 |
|
End of Vulnerability and Security Support |
EoVSS |
31-Oct-25 |
|
Last Date of Support |
LDoS |
31-Oct-26 |
These milestones and the intervals between them are defined in the Cisco Ultra Cloud Core (UCC) Software Release Lifecycle Product Bulletin available on cisco.com.
Release Package Version Information
|
Software Packages |
Version |
|---|---|
|
companion-vpc-21.28.m21.tgz.SPA.tar.gz |
21.28.m21 |
|
qvpc-si-21.28.m21.bin.SPA.tar.gz |
21.28.m21 |
|
qvpc-si-21.28.m21.qcow2.tgz.SPA.tar.gz |
21.28.m21 |
|
NED package |
ncs-6.1.3-cisco-staros-5.52 |
|
NSO |
6.1.3 |
Descriptions for the various packages provided with this release are available in the Release Package Descriptions section.
Verified Compatibility
|
Products |
Version |
|---|---|
|
ADC Plugin |
2.73.9.2019 |
|
RCM |
2024.01.1 |
|
Ultra Cloud Core SMI |
2024.01.1 |
|
Ultra Cloud Core SMF |
2024.01.2 |
What's New in this Release
New in Documentation
This version of Release Notes includes a new section titled What’s New in this Release comprising all new features, enhancements, and behavior changes applicable for the release.
This section will be available in all the 5G release notes and will supersede content in the Release Change Reference (RCR) document. Effective release 2024.01, the RCR document will be deprecated.
Features and Enhancements
This section covers a brief description of the features and enhancements introduced in this release. It also includes links to detailed documentation, where available.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
|
The number of QERs per PDR supported in UPF is increased from two to three in this release. All rules and filters are sent to UPF through PDRs. SMF sends an additional QER for dynamic rules installed on default QFI/bearer. The Gate Status IE indicates whether the gate is open or closed. Default Setting: Not Applicable |
|
|
Liveliness Check between UPF and RCM using Heartbeat Communication |
The application-level heartbeat mechanism allows you to monitor the liveliness of the TCP connection between UPF and RCM. This feature will resolve the half-closed TCP connections between RCM checkpoint managers and UP session managers. RCM sends a heartbeat message every 3 seconds. It checks if it has received the heartbeat message from UPF in the last 60 seconds. RCM will close the TCP connection if it has not received the message. This behavior is applicable for both Active UP to RCM and RCM to Standby UP communication. UPF also behaves similarly where it sends a heartbeat message every 3 seconds. UPF checks if it has received the heartbeat from RCM in the last 60 seconds. If UPF has not received the message, then it will close the TCP connection. The heartbeat functionality is configurable on RCM and UPF using the following commands:
The following show commands on RCM and UPF display the total number of heartbeat messages received and sent:
Default Setting: Disabled – Configuration required to enable |
Behavior Changes
This section covers a brief description of behavior changes introduced in this release.
| Behavior Change | Description |
|---|---|
|
Accurate Correlation of Application Instance IDs for Traffic Optimization |
When you configure the adc app-notification once-per-app CLI in ACS Rulebase, UPF optimizes the reporting once per application. Upon detecting traffic for an application, UPF sends an APP-START notification to SMF with an Application Instance ID. This ID is the flow-id for the first data flow of an application. Previous Behavior: When the last data flow of the application gets terminated, the flow-id of that data flow is used as the Application Instance ID in APP-STOP notification. This causes issues for PCF to correlate the APP-START and APP-STOP notifications. New Behavior: UPF caches the Application Instance ID from the first data flow. When the last data flow of an application terminates, UPF sends the cached Instance ID with the APP-STOP notification. This behavior enables PCF to correlate the APP-START and APP-STOP notifications and identify the application traffic appropriately. |
|
LCI Reporting to Control Plane |
UPF sends the load control information (LCI) to the control plane, to inform the operating status of its resources at the node level. The control plane uses this information to augment UPF selection procedures. Previous Behavior: UPF reported only one LCI per session manager to the control plane because of which some associated CPs did not receive the LCI. New Behavior: UPF reports one LCI to each PFCP peer per session manager. The control plane will be able to distribute calls evenly over multiple UPFs.
Customer Impact: Each CP that supports LCI reporting will now receive multiple messages with the same LCI value from a UPF. |
|
Redirected Packet Drop Statistics |
Previous Behavior: The drop counters were not incremented for redirected packets when the flow action redirect-url CLI was configured. New Behavior: The drop counter is incremented for redirected packets with the flow action redirect-url configuration. The new Redirect-URL field under Flow apply action in the output of the show user-plane-service statistics drop-counter command displays the number of redirected packets that are dropped. Customer Impact: For each redirected packet, you can view the incremented packet drop counter. |
|
SxDemux Stops IP Pool Deregistration Request towards VPNmgr on Standby UPF |
Previous Behavior: After receiving the Sx peer delete checkpoint, SxDemux initiated the IP pool deregistration request towards VPNMgr on a standby UPF. This behavior led to IP chunk deletion resulting in call preallocation failure on a standby UPF. New Behavior: SxDemux does not initiate the IP pool deregistration request towards VPNMgr on a standby UPF, after receiving the Sx peer delete checkpoint. This behavior prevents call preallocation failure on a standby UPF. |
Installation and Upgrade Notes
This Release Note does not contain general installation and upgrade instructions. Refer to the existing installation documentation for specific installation and upgrade considerations.
Software Integrity Verification
To verify the integrity of the software image you have from Cisco, you can validate the SHA512 checksum information against the checksum identified by Cisco for the software.
Image checksum information is available through Cisco.com Software Download Details. To find the checksum, hover the mouse pointer over the software image you have downloaded.
The following screenshot is an example of a UPF release posted in the Software Download page.
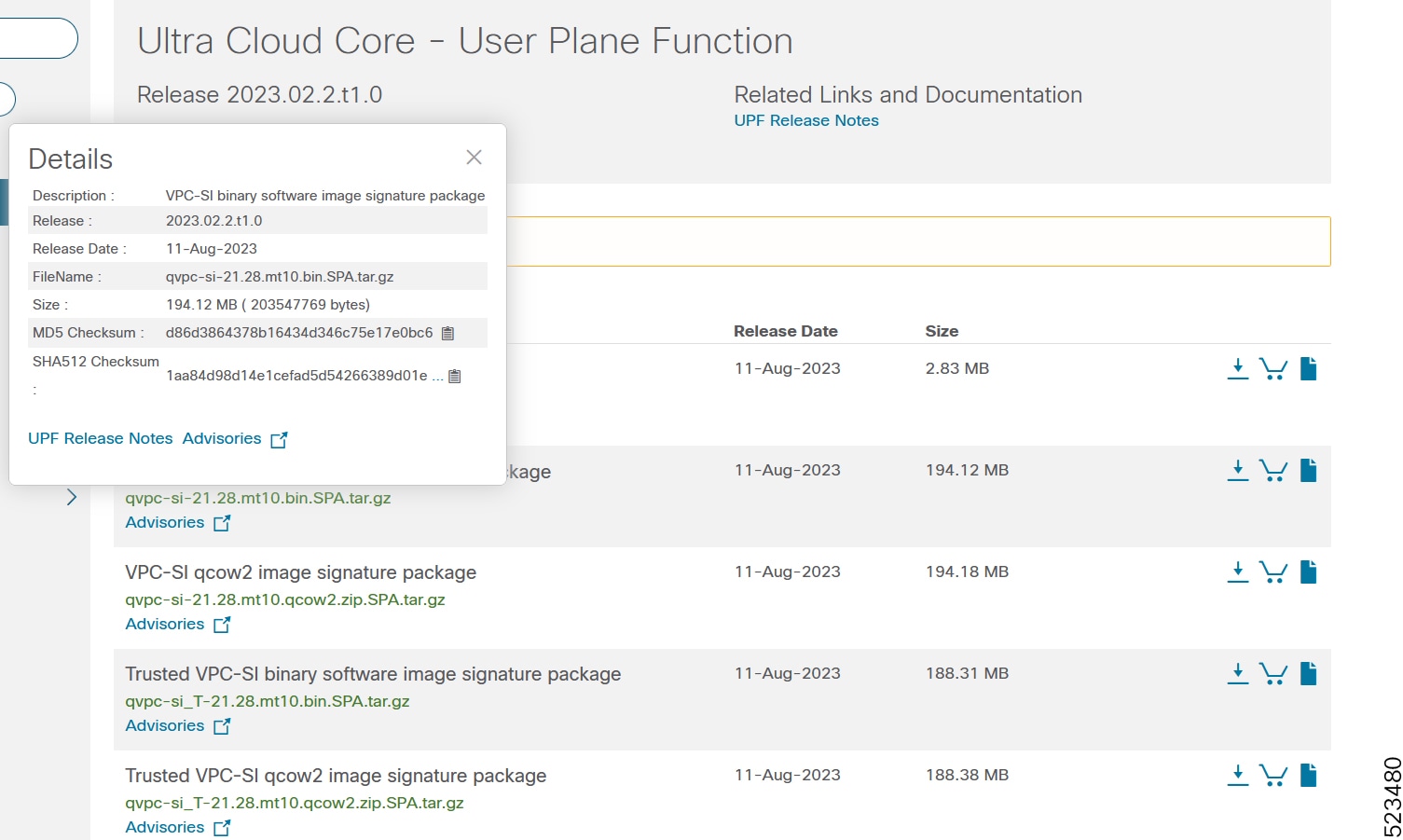
At the bottom you find the SHA512 checksum, if you do not see the whole checksum you can expand it by pressing the "..." at the end.
To validate the information, calculate a SHA512 checksum using the information in Table 1 and verify that it matches either the one provided on the software download page.
To calculate a SHA512 checksum on your local desktop, refer to the following table.
|
Operating System |
SHA512 checksum calculation command examples |
|---|---|
|
Microsoft Windows |
Open a command line window and type the following command: |
|
Apple MAC |
Open a terminal window and type the following command: |
|
Linux |
Open a terminal window and type the following command: OR |
|
NOTES: filename is the name of the file. extension is the file extension (for example, .zip or .tgz). |
|
If the SHA512 checksum matches, you can be sure that no one has tampered with the software image or the image has not been corrupted during download.
If the SHA512 checksum does not match, we advise you to not attempt upgrading any systems with the corrupted software image. Download the software again and verify the SHA512 checksum again. If there is a constant mismatch, please open a case with the Cisco Technical Assistance Center.
Certificate Validation
UPF software images are signed via x509 certificates. Please view the .README file packaged with the software for information and instructions on how to validate the certificates.
Open Bugs for this Release
There are no open bugs in this specific software release.
Resolved Bugs for this Release
The following table lists the resolved bugs in this specific software release.
 Note |
This software release may contain bug fixes first introduced in other releases. Additional information for all resolved bugs for this release are available in the Cisco Bug Search Tool. |
|
Bug ID |
Headline |
Behavior Change |
|---|---|---|
|
Some of non-std QCI bulkstats counters are zero |
No |
|
|
First-Packet-Time is wrongly set for RB URR whn recal measmnt IE is receivd & data sent again |
No |
|
|
Data drop is seen on UPF, when Pure p call (using cnPGW) attached with Dual stack cli |
No |
|
|
Need to stop IP chunk deregistration reqest on sxdemux on standby chassis |
Yes |
|
|
Application instance identifier correlation is incorrect with ADC optimization |
Yes |
|
|
UPF needs to send LCI to all supported CP |
Yes |
|
|
UPF behavior not correct to flip the byte order in ID field |
No |
Operator Notes
StarOS Version Numbering System
The output of the show version command displays detailed information about the version of StarOS currently running on the ASR 5x00 or Cisco Virtualized Packet Core platform.
The Version Build Number for releases 21.1 and later include a major and emergency release number, for example, "21.1.1".
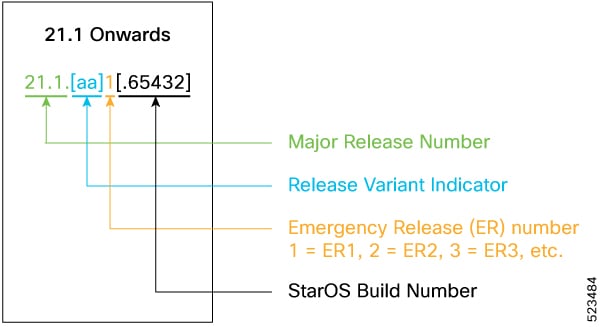
The appropriate version number field increments after a version has been released. The new version numbering format is a contiguous sequential number that represents incremental changes between releases. This format facilitates identifying the changes between releases when using Bug Search Tool to research software releases.
 Note |
The 5G UPF software is based on StarOS and implements the version numbering system described in this section. However, as a 5G network function (NF), it is posted to Cisco.com under the Cloud Native Product Numbering System as described in Cloud Native Product Version Numbering System. |
Cloud Native Product Version Numbering System
The show helm list command displays detailed information about the version of the cloud native product currently deployed.
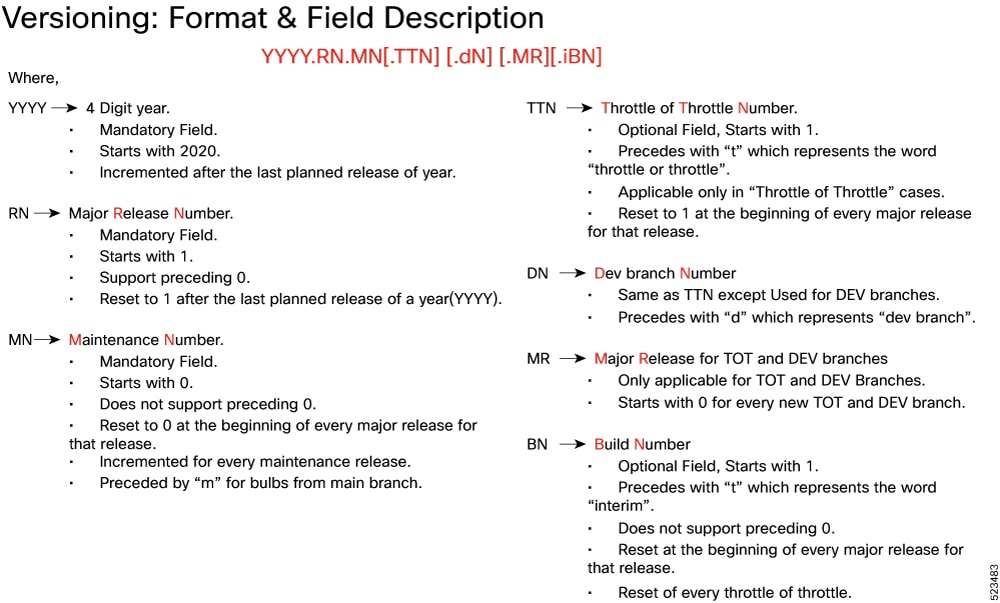
The appropriate version number field increments after a version has been released. The new version numbering format is a contiguous sequential number that represents incremental changes between releases. This format facilitates identifying the changes between releases when using Bug Search Tool to research software releases.
Release Package Descriptions
The following table provides descriptions for the packages that are available with this release.
|
Software Packages |
Description |
|---|---|
|
companion-vpc-<staros_version>.zip.SPA.tar.gz |
Contains files pertaining to VPC, including SNMP MIBs, RADIUS dictionaries, ORBEM clients, etc. These files pertain to both trusted and non-trusted build variants. The VPC companion package also includes the release signature file, a verification script, the x.509 certificate, and a README file containing information on how to use the script to validate the certificate. |
|
qvpc-si-<staros_version>.bin.SPA.tar.gz |
The UPF release signature package. This package contains the VPC-SI deployment software for the UPF as well as the release signature, certificate, and verification information. Files within this package are nested under a top-level folder pertaining to the corresponding StarOS build. |
|
qvpc-si-<staros_version>.qcow2.zip.SPA.tar.gz |
The UPF release signature package. This package contains the VPC-SI deployment software for the UPF as well as the release signature, certificate, and verification information. Files within this package are nested under a top-level folder pertaining to the corresponding StarOS build. |
|
qvpc-si_T-<staros_version>.bin.SPA.tar.gz |
The trusted UPF release signature package. This package contains the VPC-SI deployment software for the UPF as well as the release, signature, certificate, and verification information. Files within this package are nested under a top-level folder pertaining to the corresponding StarOS build. |
|
qvpc-si_T-<staros_version>.qcow2.zip.SPA.tar.gz |
The trusted UPF release signature package. This package contains the VPC-SI deployment software for the UPF as well as the release, signature, certificate, and verification information. Files within this package are nested under a top-level folder pertaining to the corresponding StarOS build. |
|
ncs-<nso_version>-cisco-staros-<version>.signed.bin |
The NETCONF NED package. This package includes all the files that are used for NF configuration. Note that NSO is used for NED file creation. |
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, using the Cisco Bug Search Tool (BST), submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, refer to https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/index.html.
 Feedback
Feedback