5G Converged Core Session Management Function
Introduction
This Release Notes identifies changes and issues related to this software release.
Release Lifecycle Milestones
|
Release Lifecycle Milestone |
Milestone |
Date |
|---|---|---|
|
First Customer Ship |
FCS |
30-Apr-2025 |
|
End of Life |
EoL |
30-Apr-2025 |
|
End of Software Maintenance |
EoSM |
29-Oct-2026 |
|
End of Vulnerability and Security Support |
EoVSS |
29-Oct-2026 |
|
Last Date of Support |
LDoS |
31-Oct-2027 |
These milestones and the intervals between them are defined in the Cisco Ultra Cloud Core (UCC) Software Release Lifecycle Product Bulletin available on cisco.com.
Release Package Version Information
|
Software Packages |
Version |
|---|---|
| ccg-2025.02.0.SPA.tgz |
2025.02.0 |
| NED package |
ncs-6.4.3-ccg-nc-2025.02.0 ncs-6.1.14-ccg-nc-2025.02.0 |
| NSO |
6.4.3 6.1.14 |
Descriptions for the various packages provided with this release are available in the Release Package Descriptions section.
Verified Compatibility
|
Products |
Version |
|---|---|
|
Ultra Cloud Core SMI |
2025.02.1.17 |
|
Ultra Cloud CDL |
1.12.1 |
|
Ultra Cloud Core UPF |
2025.02.0 |
|
Ultra Cloud cnSGWc |
2025.02.0 |
For information on the Ultra Cloud Core products, refer to the documents for this release available at:
What's New in this Release
Features and Enhancements
This section covers a brief description of the features and enhancements introduced in this release. It also includes links to detailed documentation, where available.
| Feature | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
This feature adds support to the SMF for managing attach and detach functions originating from S4-SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node). This allows the consolidation of 2G/3G and 4G/5G network control within a single converged core. By integrating the networks, you can simplify the network management and reduce the operational costs. Commands Introducted: profile converged-core activated-features 2g3g —This CLI command enables S4-SGSN support for 2G and 3G RAT type in SMF. Default Settings:Disabled - Configuration Required to Enable |
|||
|
This feature allows the SMF to blocklist a specific UPF node when it continuously rejects session establishment requests. The UPF may reject these requests from the SMF due to various errors, such as licensing issues. However, without information on the issues at the UPF, the SMF might repeatedly select the same UPF, leading to an increased number of session creation failures. By enabling this feature, the network operators can prevent the SMF from repeatedly selecting the same UPF for a defined time interval. Commands Introduced:
Default Setting: Disabled—Configuration Required to Enable |
|||
|
The enterprises with large and complex 5G networks require centralized IP address allocation and management. This feature helps achieve centralization of IPAM by allowing the SMF to allocate IPs through a DHCP server. Commands Introduced:
Default Settings: Disabled—Configuration Required to Enable |
|||
| NF Discovery based on Preferred Locality |
SMF includes the "3gpp-Sbi-Discovery-preferred-locality" HTTP header when communicating with the SCP. By populating this header, SMF enables more efficient NF selection based on locality during peer NF discovery, resulting in optimized network function interactions and improved service delivery.
|
Behavior Changes
This section covers a brief description of behavior changes introduced in this release.
| Behavior Change | Description |
|---|---|
|
Encode quotaManagementIndicator in the charging request |
Previous Behavior: The offline converted rating group SMF did not send the quotaManagementIndicator to the CHF in charging requests. New Behavior: The offline converted rating group SMF now sends the quotaManagementIndicator as CONVERTED_OFFLINE to the CHF in charging requests. |
|
Explicit TEID setting in GTPv2 messages for Context Not Found scenario |
Previous Behavior: SMF did not explicitly set the Tunnel Endpoint Identifier (TEID) flag to 0 in certain GTPv2 messages when sending a response with the Cause IE set to "Context Not Found (64)." This led to stale TEID values being used inadvertently. New Behavior: SMF explicitly sets the TEID flag to 0 in the GTPv2 header for the following messages when the Cause IE is "Context Not Found (64)":
This update ensures compliance with GTPv2 specifications and aligns with 3GPP standards, providing improved handling for error scenarios. |
|
Handling of FQDN in smContextStatusUri |
Previous Behavior: Receiving an FQDN in the smContextStatusUri within the N11CreateSmContextReq led to service restart, as only IPv4 and IPv6 addresses were correctly processed. New Behavior: The system now properly decodes FQDNs in the smContextStatusUri, integrating them into the nfFqdn IE within the ServingNetworkFunctionInformation IE in ChargingDataReq. This ensures seamless handling alongside IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. Customer Impact: Customers can now use FQDNs in the smContextStatusUri, which will be accurately processed and included in the relevant information elements, enhancing network configuration flexibility and functionality |
|
Implement RPC limits to prevent CLI timeouts |
Previous Behavior: Previously, there were no limits on the number of Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs) collected from each pod instance and included in the response, which could result in a CLI timeout. New Behavior: The system now limits the number of RPCs received per pod instance to 50,000 and the total number of RPCs from all pod instances to 200,000. The show rpc all command displays a maximum of 200,000 lines in its output. |
|
Interface type display for overload information |
Previous Behavior: The interface type was incorrectly displayed in the output of the show overload-info peer all command. For instance, the peer type "MME" was shown as "S5" instead of its correct interface type. New Behavior: The interface type is now correctly assigned based on the peer type:
This correction aligns the command output with expected network behavior, ensuring precise representation of interface types. Customer Impact: The update rectifies the interface type display errors in the command output, improving the clarity and accuracy of the system's overload information. |
|
Load Control Information Calculation Update |
Previous Behavior: For active and standby types of pods, such as protocol, GTPC, LI, UDP-proxy, GTPP, and Diameter, the Load Control Information (LCI) was calculated by taking the average of loads of the pods. Due to this calculation, the system did not detect overload even though the active pod was heavily loaded. New Behavior: The Load Control Information (LCI) is now calculated by taking the maximum load among the standby and active pods. This behavior helps the system to correctly identify the overloaded active pod. |
|
Name change for RAN Cause IE on N7 interface |
Previous Behavior: In 3GPP standard releases 15.4.0 and 16.0, certain Information Elements (IEs) on the N7 interface were sent with an invalid prefix "_". The affected IEs included _5gSmCause, _5gMmCause, and _3gppPsDataOffStatus. New Behavior: The invalid prefix "_" has been removed from the IEs on the N7 interface. Customer Impact: Customers will observe a change in the naming of a few IEs on the N7 interface. This change ensures consistency and compliance with standard naming practices. |
|
NF Discovery based on Preferred Locality |
Previous Behavior: The 3gpp-sbi-discovery-preferred-locality header was not sent to the SCP, even if the following conditions were met:
New Behavior: The 3gpp-sbi-discovery-preferred-locality header is sent to the SCP when the following conditions are met:
|
|
Retry-Terminate mechanism for HSMF roaming |
Previous Behavior: In HSMF roaming scenarios, the retry-terminate mechanism was not functional. The system failed to apply the retry-terminate
action as part of N4 failure handling even when the following configurations are available:
New Behavior: The retry-terminate mechanism is now effectively implemented for HSMF roaming scenarios. This update provides the necessary retry procedures during the UPF setup, ensuring that roaming cases are managed accurately and efficiently. |
|
Updated Cause Code for Rejected N11 Retrieve Message during Disabled Interworking |
Old behavior: Previously, during the EPS fallback scenario, if the IWK is marked as disabled the SMF rejected N11 retrieve message with a failure cause code 403 forbidden- 'UPIP_REQ_DENIED_IN_RAT'. New behavior: With this enhancement, during the EPS fallback scenario, if the IWK is marked as disabled the SMF rejects N11 retrieve message with a failure cause code 403 forbidden with an updated cause code as "SUBSCRIPTION_DENIED". |
|
Enhancements in UPIP Functionality to Support Roaming, Session Modification, and N16 Interface |
Old Behavior: During the resource setup process at gNB, such as idle-active, N2 ho, xn ho, the SMF recalculated UPIP for existing sessions and updated the latest UPIP values to the gNB. The dynamic configuration change for UPIP under the DNN configuration was applicable for the existing sessions. Also, previously the UPIP feature did not support roaming and session modification functionalities. New behavior: As part of the UPIP enhancement process, the SMF decides to enable UPIP based on UDM SM data, UE data rates, and the local configuration during the 5G session create processes or handover to 5G. The SMF does not recalculate the UPIP values again during handovers, it uses the UPIP values decided during session create time. The dynamic configuration change for UPIP under the DNN configuration does not apply to the existing session. Also, the UPIP functionality is enhanced to support roaming and UE init modification for UPIP data rate change. |
Related Documentation
Installation and Upgrade Notes
This Release Note does not contain general installation and upgrade instructions. Refer to the existing installation documentation for specific installation and upgrade considerations.
Software Integrity Version
To verify the integrity of the software image you have from Cisco, you can validate the SHA512 checksum information against the checksum identified by Cisco for the software.
Image checksum information is available through Cisco.com Software Download Details. To find the checksum, hover the mouse pointer over the software image you have downloaded.

At the bottom you find the SHA512 checksum, if you do not see the whole checksum you can expand it by pressing the "..." at the end.
To validate the information, calculate a SHA512 checksum using the information in the following table and verify that it matches either the one provided on the software download page.
To calculate a SHA512 checksum on your local desktop, refer to the table below.
|
Operating System |
SHA512 checksum calculation command examples |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Microsoft Windows |
Open a command line window and type the following command:
|
||
|
Apple MAC |
Open a terminal window and type the following command:
|
||
|
Linux |
Open a terminal window and type the following command:
OR
|
||
|
|||
If the SHA512 checksum matches, you can be sure that no one has tampered with the software image or the image has not been corrupted during download.
If the SHA512 checksum does not match, we advise you to not attempt upgrading any systems with the corrupted software image. Download the software again and verify the SHA512 checksum again. If there is a constant mismatch, please open a case with the Cisco Technical Assistance Center.
Certificate Validation
SMF software images are signed via x509 certificates. Please view the .README file packaged with the software for information and instructions on how to validate the certificates.
Open Bugs for this Release
The following table list an open bug in this specific software release.
 Note |
This software release may contain open bugs first identified in other releases. Additional information for all open bugs for this release are available in the Cisco Bug Search Tool. |
|
Bug ID |
Headline |
|---|---|
|
Show subs file writing with failed-open option returning "Unable to perform Subscriber Search" |
Resolved Bugs for this Release
The following table lists the resolved bugs in this specific software release.
 Note |
This software release may contain bug fixes first introduced in other releases. Additional information for all resolved bugs for this release is available in the Cisco Bug Search Tool. |
|
Bug ID |
Headline |
Behavior Change |
|---|---|---|
|
SMF |
||
| create_bearer_request procedures failed without a reason label being pegged |
No |
|
|
Enhancements in UPIP (User plane integrity protection) feature |
Yes |
|
|
Nodemgr dumps continuous errors when issued the command to clear the taps |
No |
|
| CSCwn59558 |
show rpc all shows no entries with log "Read timed out" in product-confd-callback logs |
Yes |
| CSCwn80324 |
LCI value is not calculated correctly for active/standby type of pods like gtpc-ep |
Yes |
|
Not hitting the START_OF_SERVICE_DATA_FLOW; multiple predefined sharing CA |
No |
|
|
Create over create with SLA timeout |
No |
|
| Not handling smContextStatusUri value as fqdn, svc crashes while creating n40req |
Yes |
|
| rest-ep-nx-x stopped sending HB post crash |
No |
|
|
CCG is forwarding the RAN NAS cause code within the _5gSmCause AVP in the N7 update |
Yes |
|
| SMF wrongly considers SGW as Overload MME Peer |
Yes |
|
| ops-center pods crashed due to concurrent commands executed | No | |
| nodemgr restart - Failed to read System Up Time from cache maxRetry:30 | No | |
|
Not restricting the PCO length when slice present |
No |
|
|
slice sst matching for three digit not working |
No |
|
|
Not restricting the PCO length when slice present |
No |
|
| CSCwo83066 | Back to back FOP sessions file writing is taking SMF into overload state | Yes |
|
IoT |
||
| CSCwn80092 | Handling N4 failure during UPF Association | No |
Operator Notes
Cloud Native Product Version Numbering System
The show helm list command displays detailed information about the version of the cloud native product currently deployed.
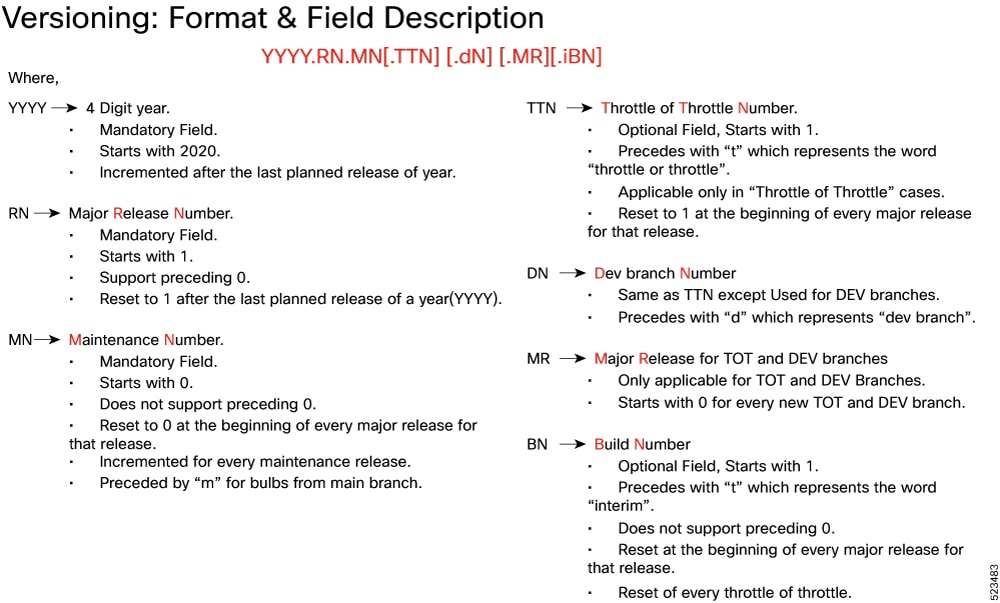
The appropriate version number field increments after a version has been released. The new version numbering format is a contiguous sequential number that represents incremental changes between releases. This format facilitates identifying the changes between releases when using Bug Search Tool to research software releases.
Release Package Descriptions
The following table provides descriptions for the packages that are available with this release.
|
Software Packages |
Description |
|---|---|
|
ccg.<version>.SPA.tgz |
The SMF offline release signature package. This package contains the SMF deployment software, NED package, as well as the release signature, certificate, and verification information. |
|
ncs-<nso_version>-ccg-nc-<version>.tar.gz |
The NETCONF NED package. This package includes all the yang files that are used for NF configuration. Note that NSO is used for the NED file creation. |
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, using the Cisco Bug Search Tool (BST), submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, refer to https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/index.html.
 Feedback
Feedback