Prerequisites for Configuring Multicast Routing over GRE Tunnel
Before configuring multicast routing over GRE, you should be familiar with the concepts of IP Multicast Routing Technology and GRE Tunneling.
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Before configuring multicast routing over GRE, you should be familiar with the concepts of IP Multicast Routing Technology and GRE Tunneling.
The following are the restrictions for configuring multicast routing over GRE tunnel:
IPv6 multicast over GRE tunnel is not supported.
The total number of supported multicast routes (mroutes) is 32000, across all tunnels.
Use the formula 8000/(((Number of tunnels)/4) + 1) to derive the number of mroutes.
Bidirectional PIM is not supported.
Multicast routing should be configured on the first hop router (FHR), the rendezvous point (RP) and the last hop router (LHR) to support multicast over the GRE tunnel.
On Catalyst 9000 Series Switches, the tunnel source can be a loopback, physical, or L3 EtherChannel interface.
No feature interactions such as IPSec, ACL, Tunnel counters, Crypto support, Fragmentation, Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), QoS, GRE keepalive, Multipoint GRE, etc. are supported on the GRE Tunnel.
This chapter describes how to configure a Generic Route Encapsulation (GRE) tunnel to tunnel IP multicast packets between non-IP multicast areas. The benefit is that IP multicast traffic can be sent from a source to a multicast group, over an area where IP multicast is not supported. Multicast Routing over GRE Tunnel supports sparse mode and pim-ssm mode; and supports static RP and auto-RP. See Rendevous Point and Auto-RP for information on configuring static RP and auto-RP.
If the path between a source and a group member (destination) does not support IP multicast, a tunnel between them can transport IP multicast packets.
This section provides steps for configuring multicast routing over GRE tunnel.
You can configure a GRE tunnel to transport IP multicast packets between a source and destination that are connected by a medium that does not support multicast routing.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
|
Step 3 |
ip multicast-routing Example: |
Enables IP multicast routing. |
|
Step 4 |
interface tunnel number Example: |
Enters tunnel interface configuration mode. |
|
Step 5 |
ip address ip_address subnet_mask Example: |
Configures IP address and IP subnet. |
|
Step 6 |
ip pim sparse-mode Example: |
Enables sparse mode of operation of Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) on the tunnel interface with one of the following mode of operation: |
|
Step 7 |
tunnel source { ip-address | interface-name } Example: |
Configures the tunnel source. |
|
Step 8 |
tunnel destination { hostname | ip-address } Example: |
Configures the tunnel destination. |
|
Step 9 |
end Example: |
Ends the current configuration session and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
|
Step 10 |
show interface type number Example: |
Displays tunnel interface information. |
The following example shows multicast-routing between a Catalyst switch through a GRE tunnel.
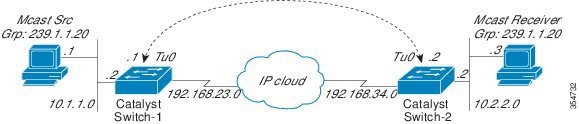
In the figure above, the multicast source (10.1.1.1) is connected to Catalyst Switch-1 and is configured for multicast group 239.1.1.20. The multicast receiver (10.2.2.3) is connected to Catalyst Switch-2 and is configured to receive multicast packets for group 239.1.1.20. Separating Switch-1 and Switch-2 is an IP cloud, which is not configured for multicast routing.
A GRE tunnel is configured between Switch-1 to Switch-2 sourced with their loopback interfaces. Multicast-routing is enabled on Switch-1 and Switch-2. The ip pim sparse-mode command is configured on tunnel interfaces to support PIM in the sparse mode. Sparse mode configuration on the tunnel interfaces allows sparse-mode packets to be forwarded over the tunnel depending on rendezvous point (RP) configuration for the group.
Device(config)# ip multicast-routing
Device(config)# interface Loopback0 //Tunnel source interface
Device(config-if)# ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
Device(config)# interface Tunnel 10 //Tunnel interface configured for PIM traffic
Device(config-if)# ip address 192.168.24.1 255.255.255.252
Device(config-if)# ip pim sparse-mode
Device(config-if)# ip nhrp map 192.168.24.3 4.4.4.4 //NHRP may optionally be configured to dynamically discover tunnel end points.
Device(config-if)# ip nhrp map multicast 4.4.4.4
Device(config-if)# ip nhrp network-id 1
Device(config-if)# ip nhrp nhs 192.168.24.3
Device(config-if)# tunnel source Loopback0
Device(config-if)# tunnel destination 4.4.4.4
Device(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0 //Source interface
Device(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
Device(config-if)# ip pim sparse-mode
Device(config)# ip multicast-routing
Device(config)# interface Loopback0 //Tunnel source interface
Device(config-if)# ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
Device(config)# interface Tunnel 10 //Tunnel interface configured for PIM traffic
Device(config-if)# ip address 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.252
Device(config-if)# ip nhrp map 192.168.24.4 2.2.2.2 //NHRP may optionally be configured to dynamically discover tunnel end points.
Device(config-if)# ip nhrp map multicast 2.2.2.2
Device(config-if)# ip nhrp network-id 1
Device(config-if)# ip nhrp nhs 192.168.24.4
Device(config-if)# ip pim sparse-mode
Device(config-if)# tunnel source Loopback0
Device(config-if)# tunnel destination 2.2.2.2
Device(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0 //Receiver interface
Device(config-if)# ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
Device(config-if)# ip pim sparse-mode
| Related Topic | Document Title |
|---|---|
|
For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter. |
See the IP Multicast Routing Commands section of the Command Reference (Catalyst 9600 Series Switches) . |
This table provides release and related information for the features explained in this module.
These features are available in all the releases subsequent to the one they were introduced in, unless noted otherwise.
|
Release |
Feature |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS XE Gibraltar 16.11.1 |
Multicast Routing over GRE Tunnel |
Multicast routing over GRE tunnel allows IP multicast traffic to be sent from a source to a multicast group, over an area where IP multicast is not supported |