- Preface
- Overview
- Installing the Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG-Quick Start
- Installing the Cisco Prime Network Services Controller
- Installing the Cisco VSG
- Registering Devices with the Cisco Prime NSC
- Installing the Cisco VSG on a Cisco Cloud Service Platform Virtual Services Appliance
- Upgrading the Cisco VSG and the Cisco Prime NSC
- Index
Cisco VSG for Microsoft Hyper-V, Release 5.2(1)VSG2(1.1a) and Cisco Prime NSC, Release 3.2 Installation and Upgrade Guide
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Chapter: Installing the Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG-Quick Start
- Information About Installing Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG
Installing the Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG-Quick Start
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Information About Installing Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG
- Task 1: Installing the Cisco Prime NSC from an ISO Image
- Task 2: On the VSM, Configuring Cisco Prime NSC Policy Agent
- Task 3: On the VSM, Preparing Cisco VSG Port Profiles
- Task 4: On the VSM, Configuring Virtual Network Adapters on the Hosts
- Task 5: Installing Cisco VSG from an ISO Image
- Task 6: On the VSG, Configuring the Cisco Prime NSC Policy Agent
- Task 7: On Cisco VSG, Cisco VSM, and Cisco Prime NSC, Verifying the NSC Policy-Agent Status
- Task 8: On Cisco Prime NSC, Configuring a Tenant, Security Profile, Compute Firewall, and Assigning Cisco VSG to the Compute Firewall
- Task 9: On the Prime NSC, Configuring a Permit-All Rule
- Task 10: On Cisco VSG, Verifying the Permit-All Rule
- Task 11: Enabling Logging
- Task 12: Enabling the Traffic VM Port-Profile for Firewall Protection and Verifying the Communication Between the VSM, VEM, and VSG
- Task 13: Installing Microsoft Service Provider Foundation
- Task 14: Sending Traffic Flow and on Cisco VSG Verifying Statistics and Logs
Information About Installing Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG
This chapter describes how to install and set up a basic working configuration of Cisco Prime Network Services Controller (Cisco Prime NSC) and Cisco Virtual Security Gateway (Cisco VSG). The example in this chapter uses the ISO files of the software for installation. The steps assume that Cisco Nexus 1000V Series switch is operational, and endpoint VMs are already installed.
Cisco VSG and Cisco Prime NSC Installation Planning Checklists
Planning the arrangement and architecture of your network and equipment is essential for a successful operation of Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG.
- Basic Hardware and Software Requirements
- License Requirements
- VLAN Configuration Requirements for VSG
- Required Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG Information
- Tasks and Prerequisites Checklist
- Host Requirements
- Obtaining Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG Software
Basic Hardware and Software Requirements
The following table lists the basic hardware and software requirements for Cisco VSG and Cisco Prime NSC installation.
| Requirement | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Virtual CPUs |
|||||
|
Memory |
|||||
|
Disk Space |
Cisco VSG: 3 GB Cisco Prime NSC: Without InterCloud functionality, 40 GB on shared NFS or SAN, and configured on two disks as follows: |
||||
|
Processor |
x86 Intel or AMD server with a 64-bit processor. |
||||
|
Network Interfaces |
|||||
|
Microsoft SCVMM |
SCVMM 2012 SP1 or SCVMM 2012 R2 |
||||
|
Browser |
Any of the following browsers:
|
||||
|
Ports |
Access to the Cisco Prime NSC application using a web browser and the following ports (if the deployment uses a firewall, make sure to permit the following ports): |
||||
|
Flash Player |
Adobe Flash Player plugin 11.2 or higher |
 Note | The Cisco VSG software is available for download at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps13095/index.html and the Cisco Prime NSC software is available for download at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps13213/index.html. |
License Requirements
 Note | If you try to access VSG services with VSM in essential mode, an error message is generated on VSM console indicating that the Nexus1000V Multi-Hypervisor License is required for VSG. |
- Default: The Nexus 1000v switch may be configured in Essential or Advanced mode.
- Essential Mode: Not Supported.
- Advanced Mode: After upgrade to Software Release 5.2(1)SM(5.2) - Nexus1000V Multi-Hypervisor License is available with 1024 Socket Count and expires in 60 days.

Note
You must install either the evaluation or the permanent (MSFT PKG) license prior to upgrading to the Software Release 5.2(1)SM(5.2). - Evaluation: The Nexus 1000V switch should be in Advanced mode. After upgrading to Software Release 5.2(1)SM (5.2) - Nexus1000V Multi-Hypervisor License is available with1024 Socket Count and expires in 60 days.
- Permanent: The Nexus 1000V switch should be in Advanced mode. After upgrading to Software Release 5.2(1)SM(5.2) - Nexus1000V Multi-Hypervisor License is available with 1024 Socket Count and expires in 60 days.
 Note | You have to request for an evaluation or permanent Nexus1000V Multi-Hypervisor License. |
For more information about the Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V licenses, see the Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V License Configuration Guide.
VLAN Configuration Requirements for VSG
Required Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG Information
The following information can be used during the Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG installation.
| Type | Your Information | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cisco VSG name—Unique within the inventory folder and up to 80 characters |
|||
|
Hostname—Where the Cisco VSG will be installed in the inventory folder |
|||
|
ISOs—Managed within SCVMM library, if stored at C:\ProgramData\Virtual Machine Manager Library Files\ISO to manage. Refresh the SCVMM library after saving the ISO file to the specified location. |
|||
|
Cisco VSG management IP address |
|||
|
VSM management IP address |
|||
|
Cisco Prime NSC instance IP address |
|||
|
Mode for installing the Cisco VSG |
|||
|
Cisco VSG VLAN number |
|||
|
Cisco VSG port profile name
|
|||
|
HA pair ID (HA domain ID) |
|||
|
Cisco VSG admin password |
|||
|
Cisco Prime NSC admin password |
|||
|
Cisco VSM admin password |
|||
|
Shared secret password (Cisco Prime NSC, Cisco VSG policy agent, Cisco VSM policy agent) |
|||
| NSC DNS IP address | |||
| NSC NTP IP address |
Tasks and Prerequisites Checklist
|
Tasks |
Prerequisites | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task 1: Installing the Cisco VNMC from an ISO image. |
|
||||
| Task 2: On the VSM, Configuring Cisco Prime NSC Policy Agent |
|
||||
| Task 3: On the VSM, Preparing Cisco VSG Port Profiles |
|
||||
| Task 4: On the VSM, Configuring Virtual Network Adapters on the Hosts |
|
||||
| Task 5: Installing Cisco VSG from an ISO Image |
|
||||
| Task 6: On the VSG, Configuring the Cisco Prime NSC Policy Agent |
|
||||
| Task 7: On Cisco VSG, Cisco VSM, and Cisco Prime NSC, Verifying the NSC Policy-Agent Status | — | ||||
| Task 8: On Cisco Prime NSC, Configuring a Tenant, Security Profile, Compute Firewall, and Assigning Cisco VSG to the Compute Firewall |
|
||||
| Task 13: Installing Microsoft Service Provider Foundation | — | ||||
| Task 9: On Cisco Prime NSC, Assigning Cisco VSG to the Compute Firewall | — | ||||
| Task 9: On the Prime NSC, Configuring a Permit-All Rule | — | ||||
| Task 10: On Cisco VSG, Verifying the Permit-All Rule | — | ||||
| Task 11: Enabling Logging | — | ||||
| Task 12: Enabling the Traffic VM Port-Profile for Firewall Protection and Verifying the Communication Between the VSM, VEM, and VSG |
|
||||
| Task 14: Sending Traffic Flow and on Cisco VSG Verifying Statistics and Logs | — |
Host Requirements
Obtaining Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG Software
Cisco VSG software is available for download at the following URL:
http://software.cisco.com/download/navigator.html
Cisco Prime NSC software is available for download at the following URL:
http://software.cisco.com/download/navigator.htmlTask 1: Installing the Cisco Prime NSC from an ISO Image
Ensure that you have:
- Verified that the Hyper-V host on which to deploy Cisco Prime NSC VM is available in SCVMM.
- Copied the Cisco Prime NSC 3.2 ISO image to the SCVMM library location on the file system. To make this image available in SCVMM, choose , right-click the library location, and then refresh.
- NTP server information.
Task 2: On the VSM, Configuring Cisco Prime NSC Policy Agent
Once Cisco Prime NSC is installed, you must register the VSM with Cisco Prime NSC.
Ensure that you have:
-
Cisco Prime NSC policy-agent image on the
VSM (for example, vsmhv-pa.3.2.1c.bin)

Note
The string vsmhv-pa must appear in the image name as highlighted.
- The IP address of Cisco Prime NSC
- The shared secret password you defined during Cisco Prime NSC installation
-
IP
connectivity between the VSM and
Cisco Prime NSC is working

Note
If you upgrade your VSM, you must also copy the latest Cisco VSM policy agent image. This image is available in Cisco Prime NSC image bundle to boot from a flash drive and to complete registration with Cisco Prime NSC.
 Note | VSM clock should be synchronized with Cisco Prime NSC clock. |
1. On the VSM, enter the following commands:
2. Check the status of the NSC policy agent configuration to verify that you have installed Cisco Prime NSC correctly and it is reachable by entering the show nsc-pa status command. This example shows that Cisco Prime NSC is reachable and the installation is correct:
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | On the VSM,
enter the following commands:
vsm# configure terminal vsm(config)# nsc-policy-agent vsm(config-nsc-policy-agent)# registration-ip 10.193.75.95 vsm(config-nsc-policy-agent)# shared-secret Example_Secret123 vsm(config-nsc-policy-agent)# policy-agent-image vsmhv-pa.3.2.1c.bin vsm(config-nsc-policy-agent)# exit vsm(config)# copy running-config startup-config vsm(config)# exit |
| Step 2 | Check the status
of the NSC policy agent configuration to verify that you have installed Cisco Prime NSC correctly and it is reachable by
entering the
show nsc-pa
status command. This example shows that Cisco Prime NSC is reachable and the installation is
correct:
vsm# show nsc-pa status NSC Policy-Agent status is - Installed Successfully. Version 3.2(1)-vsm vsm The VSM is now registered with Cisco Prime NSC. |
This example shows that Cisco Prime NSC is unreachable or an incorrect IP is configured:
vsm# show nsc-pa status
nsc Policy-Agent status is - Installation Failure
Cisco Prime NSC not reachable.
vsm#
This example shows that the NSC policy-agent is not configured or installed:
vsm# show nsc-pa status NSC Policy-Agent status is - Not Installed
Task 3: On the VSM, Preparing Cisco VSG Port Profiles
To prepare Cisco VSG port profiles, you must create the VLANs and use the VLANs in Cisco VSG data port profile and the Cisco VSG-ha port profile.
Ensure that you have:
1. Create a Cisco VSG data port profile and a Cisco VSG-ha port profile by first enabling the Cisco VSG data port-profile configuration mode. Cisco VSG data interface should be in the system VLAN. To configure VSG data interface in the system VLAN, you need a system network segment, a system port-profile, and an uplink configured as a system uplink. Use the configure command to enter global configuration mode.
2. Create Network Uplink port-profile and use it in the Logical Switch.
3. Create the network segment and port-profile for the Data VLAN.
4. Create the network segment and port-profile for the HA VLAN.
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | Create a
Cisco
VSG data port
profile and a
Cisco VSG-ha port
profile by first enabling the
Cisco
VSG data
port-profile configuration mode. Cisco VSG data interface should be in the system VLAN. To configure VSG data interface in the system VLAN, you need a system network segment, a system port-profile, and an uplink configured as a system uplink. Use the
configure command to enter global configuration mode.
vsm# configure |
| Step 2 | Create Network
Uplink port-profile and use it in the Logical Switch.
vsm(config)# nsm logical network vsm_LogicalNet vsm(config-logical-net)# exit vsm(config)# nsm network segment pool vsm_NetworkSite vsm(config-net-seg-pool)# member-of logical network vsm_LogicalNet vsm(config-net-seg-pool)# exit vsm(config)# nsm ip pool template VM_IP_Pool vsm(config-ip-pool-template)# ip address 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.255 vsm(config-ip-pool-template)# network 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.1 vsm(config-ip-pool-template)# exit vsm(config)#port-profile type ethernet sys-uplink vsm(config-port-prof)#channel-group auto vsm(config-port-prof)#no shutdown vsm(config-port-prof)#system port-profile vsm(config-port-prof)#state enabled vsm(config-port-prof)#exit vsm(config)# nsm network uplink vsm_Uplink vsm(config-uplink-net)# allow network segment pool vsm_NetworkSite vsm(config-uplink-net)# import port-profile sys_Uplink vsm(config-uplink-net)# system network uplink vsm(config-uplink-net)# publish uplink-network vsm(config-uplink-net)# exit |
| Step 3 | Create the
network segment and port-profile for the Data VLAN.
vsm(config)# nsm network segment VMAccess_502 vsm(config-net-seg)# member-of network segment pool vsm_NetworkSite vsm(config-net-seg)# system network segment vsm(config-net-seg)# switchport access vlan 502 vsm(config-net-seg)# ip pool import template VM_IP_Pool vsm(config-net-seg)# publish network-segment vsm(config-net-seg)# exit vsm(config)# port-profile type vethernet VSG_Data vsm(config-port-prof)# no shutdown vsm(config-port-prof)# state enabled vsm(config-port-prof)# system port-profile vsm(config-port-prof)# publish port-profile vsm(config-port-prof)# exit |
| Step 4 | Create the
network segment and port-profile for the HA VLAN.
vsm(config)# nsm network segment VMAccess_503 vsm(config-net-seg)# member-of network segment pool vsm_NetworkSite vsm(config-net-seg)# switchport access vlan 503 vsm(config-net-seg)# ip pool import template VM_IP_Pool vsm(config-net-seg)# publish network-segment vsm(config-net-seg)# exit vsm(config)# port-profile type vethernet VSG_HA vsm(config-port-prof)# no shutdown vsm(config-port-prof)# state enabled vsm(config-port-prof)# publish port-profile vsm(config-port-prof)# exit |
Task 4: On the VSM, Configuring Virtual Network Adapters on the Hosts
Now that you have prepared Cisco VSG port profiles on VSM, you should configure virtual network adapters on the hosts.
This task includes the following subtasks:
Ensure that you have:
Create Port-profile for the Virtual Network Adapter
You need to log in to VSM to create port-profile for the virtual network adapter.
1. Create port-profile for the virtual network adapter in VSM.
DETAILED STEPS
Example: vsm#configure terminal vsm(config)#port-profile type vethernet Virtual-Net-PP vsm(config-port-prof)#capability l3-vservice vsm(config-port-prof)#no shutdown vsm(config-port-prof)#state enabled vsm(config-port-prof)#publish port-profile vsm(config-port-prof)#exit vsm#copy running-config startup-config |
Creating Virtual Network Adapter
Make sure that you know the following:
| Step 1 | Launch SCVMM. |
| Step 2 | In the VMs and Services tab, click All Hosts. |
| Step 3 | Choose the host on which you want to add the virtual network adapter. |
| Step 4 | Right-click the host and choose Properties from the pop-up menu. |
| Step 5 | In the Properties window, click Virtual Switches. |
| Step 6 | On the Virtual Switches tab, click New Virtual Network Adapter. |
| Step 7 | In the Name field, enter name of virtual network adapter. |
| Step 8 | Under the Connectivity, in the VM Network field, choose an appropriate VM network. |
| Step 9 | Under Port profile, select L3 service enabled port-profile that you created from the Classification drop-down list. |
| Step 10 | Under IP address configuration, check Static radio-button and do the following: |
| Step 11 | Click Ok. |
| Step 12 | The VM manager warning message appears, click Ok. |
What to Do Next
Add a physical router between VSG and virtual network adapter.
Task 5: Installing Cisco VSG from an ISO Image
 Note | Cisco VSG is supported as VSB on Nexus Cloud Services platform only. |
Ensure that you have:
- Installed Microsoft SCVMM SP1 or SCVMM R2.
- Downloaded the Cisco VSG ISO image and uploaded it to the server (C:\ProgramData\Virtual Machine Manager Library Files\ISO). Refresh the library server under the Library tab.
- Cisco VSG-Data port profile: VSG-Data.
- Cisco VSG-ha port profile: VSG-ha.
- HA ID.
- IP/subnet mask/gateway information for Cisco VSG
- Administrator password
- Minimum of 2 GB RAM and 2 GB hard disk space, recommended space is 4 GB RAM and 4 GB hard disk.
- Cisco Prime NSC IP address.
- The shared secret password.
- IP connectivity between Cisco VSG and Cisco Prime NSC is okay.
- Cisco VSG NSC-PA image name (vsghv-pa.2.1.1e.bin) is available.
| Step 1 | Launch SCVMM. |
| Step 2 | On the VMs and Services tab, click Create Virtual Machine. |
| Step 3 | In the Create Virtual Machine Wizard, in the Select Source screen, check the Create the new virtual machine with a blank virtual hard disk radio button, and click Next. |
| Step 4 | In the
Specify
Virtual Machine Identity screen, enter the name for the Cisco VSG in
the
Virtual machine name field and click
Next.
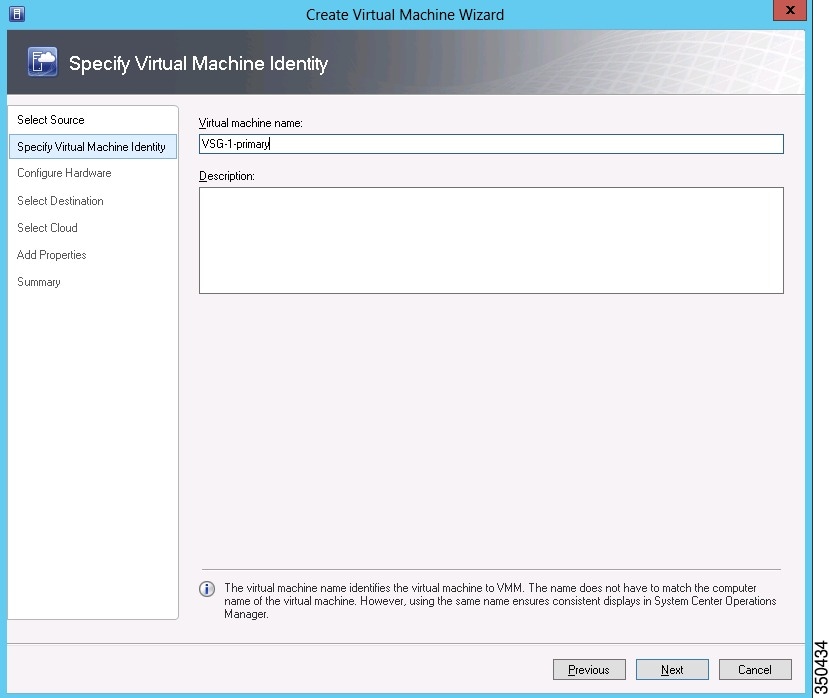 |
| Step 5 | In the
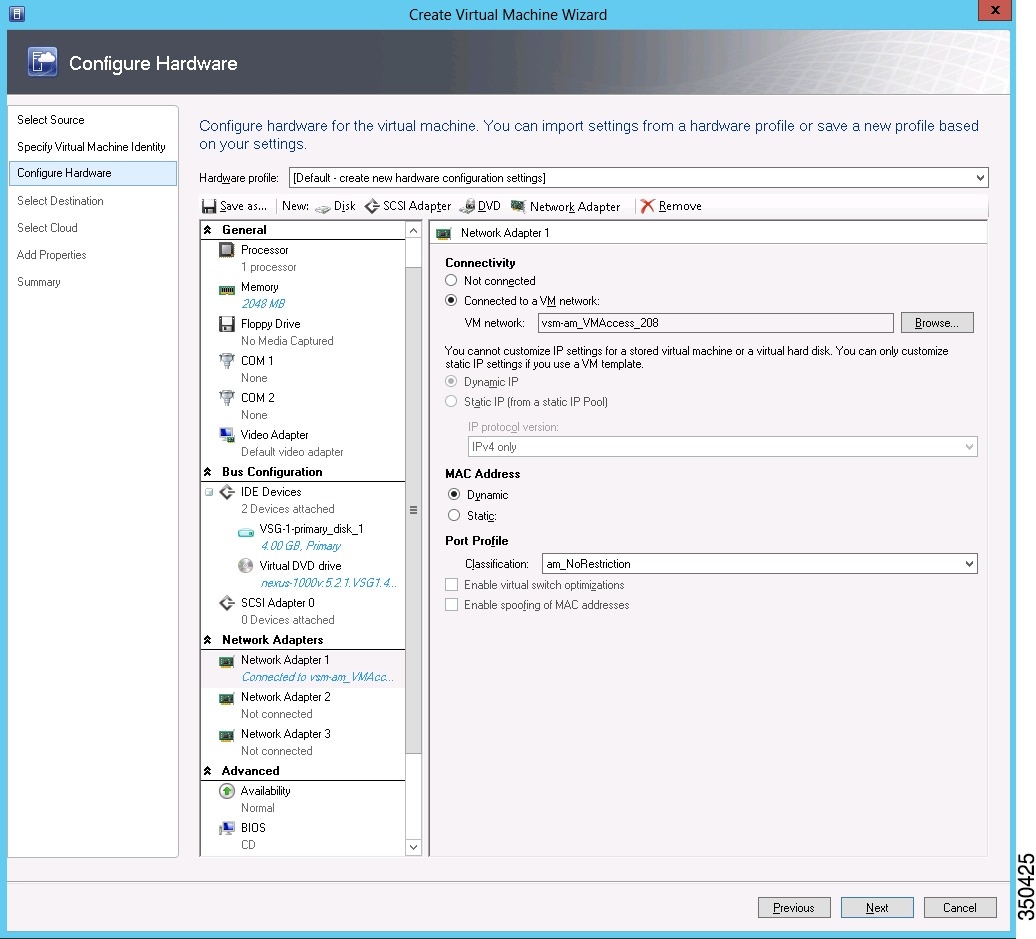
Configure Hardware section, do the following:
|
| Step 6 | In the Select Destination section, choose Place the virtual machine in a host, choose the host group on which you want to store the VSG from the drop-down list, and click Next. |
| Step 7 | In the Select Host section, choose the host that you want to place the VSG on and click Next. |
| Step 8 | In the Configure Settings section, review the virtual machine settings to ensure they are correct, and click Next. |
| Step 9 | (Optional) In the Add Properties section, choose the Other Linux (64-bit) from the Operating System from the drop-down list, and then click Next. |
| Step 10 | In the Summary section, click Create. |
| Step 11 | Once the VSG is successfully installed, choose the VSG on the VMs and Services tab, and click Power On. |
| Step 12 | Connect to the VSG using . |
Task 6: On the VSG, Configuring the Cisco Prime NSC Policy Agent
Once Cisco Prime NSC is installed, you must register Cisco VSG with Cisco Prime NSC.
Ensure that you have:
-
The
Cisco Prime NSC policy-agent image on Cisco VSG (for example, vsghv-pa.2.1.1e.bin).

Note
The string vsghv-pa must appear in the image name as highlighted.
- IP address of the Cisco Prime NSC.
- Shared secret password you defined during the Cisco Prime NSC installation.
-
IP
connectivity between the VSG and the
Cisco Prime NSC.

Note
If you upgrade your VSG, you must also copy the latest Cisco VSG policy agent image. This image is available in Cisco Prime NSC image bundle to boot from a flash drive and to complete registration with Cisco Prime NSC.
 Note | VSG clock should be synchronized with Cisco Prime NSC clock. |
1. On Cisco VSG, configure the NSC policy agent:
2. Check the status of the NSC policy agent configuration to verify that you have installed Cisco Prime NSC correctly and it is reachable by entering the show nsc-pa status command. This example shows that Cisco Prime NSC is reachable and the installation is correct:
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | On Cisco VSG,
configure the NSC policy agent:
VSG-Firewall# configure Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. VSG-Firewall(config)# nsc-policy-agent VSG-Firewall(config-nsc-policy-agent)# registration-ip 10.193.72.242 VSG-Firewall(config-nsc-policy-agent)# shared-secret Sgate123 VSG-Firewall(config-nsc-policy-agent)# policy-agent-image vnmc-vsgpa.2.1.1b.bin VSG-Firewall(config-nsc-policy-agent)# copy running-config startup-config [########################################] 100% Copy complete, now saving to disk (please wait)... VSG-Firewall(config-nsc-policy-agent)# exit |
| Step 2 | Check the status
of the NSC policy agent configuration to verify that you have installed
Cisco Prime NSC correctly and it is reachable by
entering the
show nsc-pa
status command. This example shows that
Cisco Prime NSC is reachable and the installation is
correct:
VSG-Firewall(config)# show nsc-pa status NSC Policy-Agent status is - Installed Successfully. Version 2.1(1b)-vsgCisco VSG is now registered with Cisco Prime NSC. |
This example shows that Cisco Prime NSC is unreachable or an incorrect IP is configured:
vsg# show nsc-pa status
NSC Policy-Agent status is - Installation Failure
Cisco Prime NSC not reachable.
vsg#
This example shows that the NSC policy-agent is not configured or installed:
vsg# show nsc-pa status NSC Policy-Agent status is - Not Installed
Task 7: On Cisco VSG, Cisco VSM, and Cisco Prime NSC, Verifying the NSC Policy-Agent Status
You can use the show nsc-pa status command to verify the nsc policy-agent status on Cisco VSG, Cisco VSM, and Cisco Prime NSC (which can indicate that you have installed the policy-agent successfully).
1. Log in to the Cisco VSG.
2. Check the status of NSC-PA configuration by entering the following command:
3. Log in to the Cisco VSM.
4. Check the status of NSC-PA configuration by entering the following command:
5. Log in to Cisco Prime NSC.
6. Click Resource Management and then click Resources.
7. In the navigation pane, click VSMs and verify the VSM information in the VSMs pane.
8. In the navigation pane, click VSGs and verify the VSG information in the VSGs pane.
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | Log in to the Cisco VSG. |
| Step 2 | Check the status
of NSC-PA configuration by entering the following command:
vsg# show nsc-pa status NSC Policy-Agent status is - Installed Successfully. Version 2.0(1a)-vsg vsg# |
| Step 3 | Log in to the Cisco VSM. |
| Step 4 | Check the status of NSC-PA configuration by entering the following
command:
VSM# show nsc-pa status NSC Policy-Agent status is - Installed Successfully. Version 2.0(0.22)-vsm VSM# |
| Step 5 | Log in to Cisco Prime NSC. |
| Step 6 | Click Resource Management and then click Resources. |
| Step 7 | In the navigation pane, click VSMs and verify the VSM information in the VSMs pane. |
| Step 8 | In the navigation pane, click VSGs and verify the VSG information in the VSGs pane. |
Task 8: On Cisco Prime NSC, Configuring a Tenant, Security Profile, Compute Firewall, and Assigning Cisco VSG to the Compute Firewall
Now that you have Cisco Prime NSC and Cisco VSG successfully installed with the basic configurations, you should configure the basic security profiles and policies.
This task includes the following subtasks:
Configuring a Tenant on Cisco Prime NSC
Tenants are entities (businesses, agencies, institutions, and so on) whose data and processes are hosted on VMs on the virtual data center. To provide firewall security for each tenant, the tenant must first be configured in Cisco Prime NSC.
1. From the Cisco Prime NSC toolbar, click the Tenant Management tab.
2. In the Navigation pane directory tree, right-click root, and from the drop-down list, choose Create Tenant.
3. In the Create Tenant dialog box, do the following:
4. Click OK.
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | From the Cisco Prime NSC toolbar, click the Tenant Management tab. |
| Step 2 | In the Navigation pane directory tree, right-click root, and from the drop-down list, choose Create Tenant. |
| Step 3 | In the Create Tenant dialog box, do the following: |
| Step 4 | Click
OK.
Notice that the tenant that you have just created is listed in the left-side pane under root. |
What to Do Next
Configuring a Security Profile on the Cisco Prime NSC
You can configure a security profile on Cisco Prime NSC.
| Step 1 | In the Cisco Prime NSC toolbar, click the Policy Management>Service Profiles. |
| Step 2 | In the Root navigation window, from the directory path, choose . |
| Step 3 | Right-click
Compute
Security Profile and choose
Add Compute Security Profile.
The Add Compute Security Profile dialog box opens. |
| Step 4 | In the Add Compute Security Profile dialog box, do the following: |
| Step 5 | Click OK |
What to Do Next
See Configuring a Compute Firewall and Assigning Cisco VSG to Cisco Prime NSC
Configuring a Compute Firewall and Assigning Cisco VSG to Cisco Prime NSC
The compute firewall is a logical virtual entity that contains the device profile that you can bind (assign) to Cisco VSG VM. The device policy in the device profile is then pushed from Cisco Prime NSC to Cisco VSG. Once this is complete, the compute firewall is in the applied configuration state on Cisco Prime NSC.
| Step 1 | From Cisco Prime NSC, choose . |
| Step 2 | On the left-pane directory tree, navigate to choose a tenant. |
| Step 3 | Click the Action drop-down list, choose Add Compute Firewall. The Add Compute Firewall dialog box opens. |
| Step 4 | In the Add Compute Firewall dialog box, do the following: |
| Step 5 | Click
Next.
The new Compute Firewall pane displays with the information that you provided. |
| Step 6 | In the Select Service Devices pane, choose Assign VSG radio button, from the VSG Devices drop-down, choose a VSG. then and click Next. |
| Step 7 | In the Interface tab, Configure Data Interface pane, enter data interface (data0) IP address and subnet mask, and click Next. |
| Step 8 | Verify the configuration in Summary tab and click Finish. |
| Step 9 | Click and verify the status of the firewall. |
Task 9: On the Prime NSC, Configuring a Permit-All Rule
You can configure a permit-all rule in the Cisco Prime NSC.
| Step 1 | Log in to the Cisco Prime NSC. |
| Step 2 | Choose . |
| Step 3 | Choose , and then select a security profile. |
| Step 4 | In the right pane, click Add ACL Policy Set. |
| Step 5 | In the Add ACL Policy dialog box, do the following: |
| Step 6 | In the Add ACL Policy dialog-box, enter the policy name, enter policy description, and then click Add Rule. |
| Step 7 | In the
Add
Rule dialog box, do the following:
|
| Step 8 | In the
Add
Policy dialog box, click
OK.
The newly created policy is displayed in the Assigned field. |
| Step 9 | In the Add Policy Set dialog box, click OK. |
| Step 10 | In the Service Profile window, click Save. |
Task 10: On Cisco VSG, Verifying the Permit-All Rule
You can verify the rule presence in Cisco VSG, by using the Cisco VSG CLI and the show commands.
vsg# show running-config rule rule POL-DEMO/R-DEMO@root/Tenant/VDC cond-match-criteria: match-allaction permit rule POL1/R1@root/Tenant/VDC cond-match-criteria: match-allaction permit rule default/default-rule@root cond-match-criteria: match-allaction drop vsg#
Task 11: Enabling Logging
To enable logging follow these procedures:
Enabling Logging level 6 for Policy-Engine Logging
Logging enables you to see what traffic is going through your monitored virtual machine. This logging is helpful for verifying that you have a proper configuration and to help in troubleshooting. You can enable Logging Level 6 for policy-engine logging in a monitor session.
| Step 1 | Log in to Cisco Prime NSC. |
| Step 2 | Choose . |
| Step 3 | In the Navigation pane, choose , and then click Edit. |
| Step 4 | In the
Edit
Syslog dialog box, do the following:
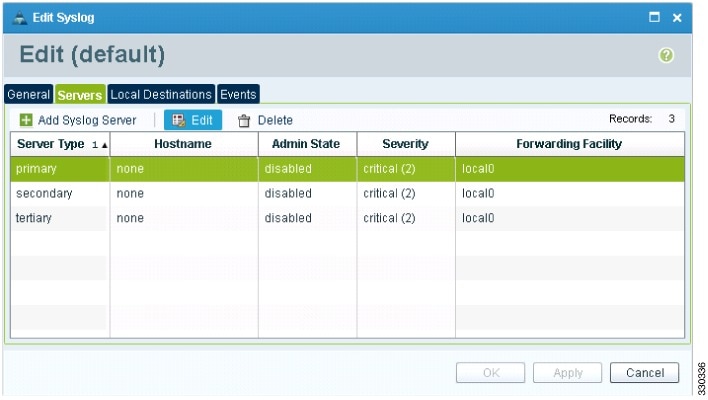 |
| Step 5 | In the Edit Syslog Client dialog box, do the following: |
| Step 6 | Click OK. |
What to Do Next
Enabling Global Policy-Engine Logging
Logging enables you to see what traffic is going through your monitored VM. This logging is helpful for verifying that you have a proper configuration and to help in troubleshooting.
Task 12: Enabling the Traffic VM Port-Profile for Firewall Protection and Verifying the Communication Between the VSM, VEM, and VSG
Ensure that you have:
- Server VM that runs with an access port profile (for example, web server)
- Cisco VSG data IP address (for example, 10.10.10.200) and VLAN ID (for example, 100)
- Set up the Virtual Network Adapter
- Security profile name (for example, sp-web)
- Organization (Org) name (for example, root/Tenant-A)
- Port profile that you would like to edit to enable firewall protection
Enabling Traffic VM Port-Profile for Firewall Protection
You can enable a traffic VM port profile for traffic protection.
1. Create VSG node.
2. Create the network segment and Traffic VM Port-Profile for Firewall Protection.
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | Create VSG node.
vsm#configure terminal vsm (config)# vservice node VSG type vsg vsm (config-vservice-node)# ip address 10.10.10.200 vsm (config-vservice-node)# adjacency l3 vsm (config-vservice-node)# exit vsm (config)# copy running-config startup-config |
| Step 2 | Create the
network segment and Traffic VM Port-Profile for Firewall Protection.
vsm(config)# nsm network segment VMAccess_400 vsm(config-net-seg)# member-of network segment pool vsm_NetworkSite vsm(config-net-seg)# switchport access vlan 400 vsm(config-net-seg)# ip pool import template VM_IP_Pool vsm(config-net-seg)# publish network-segment vsm(config-net-seg)# exit vsm(config)# port-profile type vethernet pp-webserver vsm(config-port-prof)# org root/Tenant-A vsm(config-port-prof)# vservice node VSG profile sp-web vsm(config-port-prof)# no shutdown vsm(config-port-prof)# state enabled vsm(config-port-prof)# publish port-profile vsm(config-port-prof)# exit vsm(config)# show port-profile name pp-webserver |
What to Do Next
Verifying the VSM or VEM for Cisco VSG Reachability
Ensure that you have assigned the traffic VM port profile with firewall protection to the traffic VM.

This example shows how to verify the communication between the VEM and the VSG:
VSM# show vservice brief
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Node Information
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ID Name Type IP-Address Mode State Module
1 VSG-1 vsg 192.161.0.85 l3 Alive 3,4,
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Path Information
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port Information
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PortProfile:PP-VSERVICE
Org:root/Tenant1
Node:VSG-1(192.161.0.85) Profile(Id):SP1(6)
Veth Mod VM-Name vNIC IP-Address
4 4 traffic-vm-win-22 192.163.0.53,
8 3 traffic-vm-win-12 192.163.0.76
10 3 traffic-vm-ubuntu-61 192.163.0.80,
11 3 traffic-vm-ubuntu-52 192.163.0.52,
A display showing the IP-ADDR Listing and Alive state verifies that the VEM can communicate with the Cisco VSG.
Checking the VM Virtual Ethernet Port for Firewall Protection
This example shows how to verify the VM Virtual Ethernet port for firewall protection:
VSM(config)# show vservice port brief port-profile VSGDemo-WEB-FW
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port Information
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PortProfile:VSGDemo-WEB-FW
Org:root/Demo
Node:VSG(153.1.1.13) Profile(Id):Demo-Default-Security-Profile(6)
Veth Mod VM-Name vNIC IP-Address
1 3 web-server1 152.1.1.11,
 Note | Make sure that your VNSP ID value is greater than 1. |
Task 13: Installing Microsoft Service Provider Foundation
| SCVMM Version | SPF Version |
|---|---|
System Center 2012 Service Pack 1 |
7.1.3117.0 |
System Center 2012 R2 |
7.2.379.0 |
This task includes the following subtasks:
Installing Service Provider Foundation
For detailed information about installing Service Provider Foundation, see How to Install Service Provider Foundation for System Center 2012 R2 available at: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn266007.aspx
Ensure that you have:
- Downloaded install system center 2012 R2 orchestrator.
- Verified the system requirements for Service Provider Foundation (SPF). For information on system requirements, refer to System Requirements for Service Provider Foundation for System Center 2012 SP1, available at: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj642899.aspx.
- NTP server information.
Configuring Service Provider Foundation
After the Service Provider Foundation (SPF) is successfully installed, you need to a create stamp ID (stampId) and associate it with the Microsoft SCVMM server. For more information about configuring SPF, see http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj613915.aspx.
Verifying Service Provider Foundation Installation
To check if the SPF installation is successful and functional, launch the following VMM REST interface web link:
https://<spf_host>:8090/SC2012R2/VMM/Microsoft.Management.Odata.Svc
where <spf_host> is the IP address for the Microsoft SCVMM VM.
Use the following link to launch the Virtual Machines REST URL:
https://<spf_host>:8090/SC2012R2/VMM/Microsoft.Management.Odata.Svc/VirtualMachines
where <spf_host> is the IP address for the SCVMM VM.
Creating VM Manager on Cisco Prime NSC
You need to create a VM manager to enable Prime NSC to retrieve VM information from Microsoft SCVMM.
Task 14: Sending Traffic Flow and on Cisco VSG Verifying Statistics and Logs
This section includes the following topics:
Sending Traffic Flow
You can send traffic flow through the Cisco VSG to ensure that it is functioning properly.
| Step 1 | Ensure that you
have the VM (Server-VM) that is using the port profile (pp-webserver)
configured for firewall protection.
 |
| Step 2 | Log in to any of your client virtual machine (Client-VM). |
| Step 3 | Send traffic (for example, HTTP) to your Server-VM.
[root@]# wget http://172.31.2.92/ --2010-11-28 13:38:40-- http://172.31.2.92/ Connecting to 172.31.2.92:80... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 258 [text/html] Saving to: `index.html' 100%[=======================================================================>] 258 --.-K/s in 0s 2010-11-28 13:38:40 (16.4 MB/s) - `index.html' saved [258/258] [root]# |
| Step 4 | Check the policy-engine statistics and log in to Cisco VSG. |
What to Do Next
See Verifying Policy-Engine Statistics and Logs on Cisco VSG.
Verifying Policy-Engine Statistics and Logs on Cisco VSG
Log in to Cisco VSG and check the policy-engine statistics and logs.
This example shows how to check the policy-engine statistics and logs:
vsg# show policy-engine stats Policy Match Stats: default@root : 0 default/default-rule@root : 0 (Drop) NOT_APPLICABLE : 0 (Drop) PS_web@root/Tenant-A : 1 pol_web/permit-all@root/Tenant-A : 1 (Log, Permit) NOT_APPLICABLE : 0 (Drop) vsg# terminal monitor vsg# 2010 Nov 28 05:41:27 firewall %POLICY_ENGINE-6-POLICY_LOOKUP_EVENT: policy=PS_web@root/Tenant-A rule=pol_web/permit-all@root/Tenant-A action=Permit direction=egress src.net.ip-address=172.31.2.91 src.net.port=48278 dst.net.ip-address=172.31.2.92 dst.net.port=80 net.protocol=6 net.ethertype=800

 Feedback
Feedback