- Preface
- New and Changed Information
- Understanding the Carrier Packet Transport System
- Hardware
- Configuring Ethernet Virtual Circuit
- Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching
- Configuring MPLS–Transport Profile
- Configuring Pseudowire
- Configuring Virtual Private LAN Services
- Configuring Quality of Service
- Configuring High Availability
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring Link Aggregation Group and Link Aggregation Control Protocol
- Configuring Span
- Configuring MAC Learning
- Configuring Multicast VLAN Registration
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Configuring Ethernet OAM, Connectivity Fault Management, and Y.1731
- Configuring Synchronous Ethernet
- Configuring Performance Monitoring, RMON, OTN, and Port Provisioning
- Configuring Local Authentication
- Configuring Cisco Discovery Protocol
- Alarm Troubleshooting
- SNMP
- CPT Error Messages
- Support for MSTP Cards
- Network Element Defaults
- Index
Cisco CPT Configuration Guide–CTC and Documentation Release 9.7.0.2 and Cisco IOS Release 15.2(02) SC2
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- February 7, 2015
Chapter: Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching
- Understanding Multiprotocol Label Switching
- NTP-J42 Configure Global Settings for MPLS
- DLP-J108 Create a Loopback Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J109 Create and Edit a Loopback Interface Using CTC
- DLP-J110 Specify the IP Address for Interfaces That Participate in an MPLS Network Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J111 Specify the IP Address for Interfaces That Participate in an MPLS Network Using CTC
- Understanding OSPF and NSF
- NTP-J65 Configure OSPF and OSPF–TE
- DLP-J112 Enable OSPF Protocol on Specific Interfaces Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J113 Enable OSPF on Specific Interfaces Using CTC
- DLP-J209 Configure NSF for OSPF Using CTC
- DLP-J221 Configure Cisco NSF for OSPF Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J222 Configure IETF NSF for OSPF Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J138 Configure OSPF to Support Traffic Engineering Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J139 Enable OSPF-TE Protocol on Specific Interfaces Using CTC
- Understanding LDP
- Understanding MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration
- NTP-J43 Configure MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration
- DLP-J115 Enable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J116 Disable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J117 Verify MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands
- Example of MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration with OSPF
- DLP-J118 Enable or Disable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using CTC
- Understanding MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization
- NTP-J44 Configure MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization
- DLP-J119 Enable MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J120 Disable MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J121 Verify MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization Using Cisco IOS Commands
- Example of MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization
- DLP-J122 Enable MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization Using CTC
- Understanding MPLS LDP Backoff
- Understanding MPLS LDP Session Protection
- NTP-J46 Configure MPLS LDP Session Protection
- DLP-J125 Enable MPLS LDP Session Protection Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J126 Verify MPLS LDP Session Protection Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J127 Enable MPLS LDP Session Protection Using CTC
- DLP-J128 Enable Directly Connected LDP Sessions Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J130 Create Targeted LDP Sessions Using CTC
- DLP-J131 Configure MPLS LDP Discovery Using CTC
- Understanding Explicit Null Label
- DLP-J132 Enable Explicit Null Label Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J133 Enable Explicit Null Label Using CTC
- Understanding LDP Graceful Restart
- Examples of Show MPLS Commands
- Understanding MPLS-TE
- NTP-J48 Configure MPLS-TE Parameters
- DLP-J136 Configure MPLS and RSVP to Support Traffic Engineering Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J137 Enable MPLS-TE on a System and on Specific Interfaces Using CTC
- DLP-J140 Enable RSVP Graceful Restart on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J141 Enable RSVP Graceful Restart on an Interface Using CTC
- DLP-J142 Configure MPLS-TE Parameters for Each Interface Using CTC
- Understanding Periodic Flooding Timer
- NTP-J49 Configure MPLS-TE LSP Attributes
- DLP-J145 Add Attributes to an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J146 Associate an LSP Attribute List with a Path Option for an MPLS TE Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J147 Configure an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J148 Modify an Attribute in an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J149 Remove an Attribute from an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J150 Delete an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J151 Verify Attributes Within an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J152 Verify All LSP Attribute Lists Using Cisco IOS Commands
- NTP-J51 Configure MPLS-TE Path Protection
- DLP-J155 Create a Path Option List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J157 Assign a Secondary Path Option to Protect a Primary Path Option Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J158 Configure Fallback Bandwidth Path Options for TE Tunnels Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J159 Modify the Bandwidth on a Path Option for Bandwidth Override Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J160 Modify a Path Option to Use a Different LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J161 Remove a Path Option for Bandwidth Override Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J162 Remove a Path Option for a LSP in a MPLS TE Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
- NTP-J51 Configure MPLS-TE Tunnels
- DLP-J163 Create a MPLS-TE Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J164 Enable Automatic Bandwidth Adjustment for a Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J165 Configure MPLS–TE–Tunnel Source Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP–J166 Create an MPLS–TE Tunnel Using CTC
- DLP-J167 Edit an MPLS–TE Tunnel Using CTC
Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching
This chapter describes Multiprotocol Label Switching and procedures to configure Multiprotocol Label Switching.
- Understanding Multiprotocol Label Switching
- Understanding OSPF and NSF
- Understanding LDP
- Understanding MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration
- Understanding MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization
- Understanding MPLS LDP Backoff
- Understanding MPLS LDP Session Protection
- Understanding LDP Graceful Restart
- Examples of Show MPLS Commands
- Understanding MPLS-TE
- Understanding MPLS–TE LSP Attributes
- Understanding MPLS–TE Verbatim Path Support
- Understanding MPLS–TE Path Protection
- Understanding MPLS–TE Tunnels
- Understanding Explicit Path
Understanding Multiprotocol Label Switching
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is the technology that scales IP networks for the service providers. MPLS provides mechanisms for IP quality of service (QoS) and IP traffic engineering. MPLS is an industry standard on which label switching is based. MPLS is a switching method that forwards IP traffic using a label. This label instructs the routers and the switches in the network where to forward the packets. The forwarding of MPLS packets is based on preestablished IP routing information.
MPLS enables service providers to offer additional services to their enterprise customers, including VPNs, improved traffic engineering, QoS, Layer 2 tunneling, and multiprotocol support.
There are two ways to set up the MPLS infrastructure—LDP and MPLS–TE. Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) differs from MPLS–TE in terms of the protocol it uses to distribute the labels along the path. LDP uses the Label Distribution Protocol whereas MPLS–TE uses the Resource Reservation Protocol – Traffic Engineering (RSVP–TE) protocol to distribute the labels. However, both LDP and RSVP–TE use the OSPF for the routing protocol.
 Note | Carrier Packet Transport (CPT) supports OSPF and OSPF-TE. |
Understanding Common Terms in MPLS
The following section describes the common terms in MPLS.
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)—This technique allows the forwarding of packets based on labels. In a normal IP network, the packets are switched based on the destination IP address. In an MPLS network, the packets are switched based on the label.
Label Distribution Protocol (LDP)—This protocol (an IETF standard) binds labels to network addresses.
Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)—This protocol distributes labels for traffic engineering.
Resource Reservation Protocol – Traffic Engineering (RSVP–TE)—This protocol reserves network resources to provide quality of service guarantees to application flows, and distributes labels for traffic engineering. RSVP-TE is an extension to RSVP.
Label Switched Path (LSP)—This is the path that the label takes to pass through the network. LSPs are unidirectional. LSP is a sequence of hops where a packet travels from one router to another router through label switching mechanisms. A label switched path can be established dynamically based on normal routing mechanisms, or through configuration.
Label Switch Router (LSR)—This is a device, such as a switch or router, that forwards MPLS packets based on the value of a fixed-length label encapsulated in each packet. LSRs dynamically learn the labels they should use to switch the packets through label distribution protocols, such as LDP and RSVP-TE.
Label Information Base (LIB)—This is the database that the LSR uses to store labels learned from other LSRs and labels assigned by the local LSR.
Traffic Engineering (TE)—This provides a set of techniques and processes that causes routed traffic to travel through the network on a path other than the one that is chosen when standard routing methods are used. TE is the ability to dynamically define routes based on known demand or alternate available routes.
Forwarding Equivalency Class (FEC)—FEC handles a set of packets that can be handled equivalently for the purpose of forwarding to make it suitable for binding to a single label. The set of packets destined for an address prefix is one example of an FEC.
Tunnel—This refers to a secure communication path between two peers, such as two LSRs.
Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP)—This protocol uses the Internet protocol to exchange routing information within an autonomous system. Examples of common IGPs include OSPF and Routing Information Protocol (RIP).
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)—Link-state, hierarchical IGP routing algorithm proposed as a successor to Routing Information Protocol (RIP) in the Internet community. OSPF features include least-cost routing, multipath routing, and load balancing.
Pseudowire—This refers to emulation of services over the MPLS network. It is a technique to transport any kind of payload over the MPLS network.
Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM)— This verifies that the packets associated with a specific FEC are forwarded to the correct LSP and are terminated on a LSR that is an egress for that FEC.
- NTP-J42 Configure Global Settings for MPLS
- DLP-J108 Create a Loopback Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J109 Create and Edit a Loopback Interface Using CTC
- DLP-J110 Specify the IP Address for Interfaces That Participate in an MPLS Network Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J111 Specify the IP Address for Interfaces That Participate in an MPLS Network Using CTC
NTP-J42 Configure Global Settings for MPLS
| Purpose | This procedure configures global settings for MPLS. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J108 Create a Loopback Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure creates a loopback interface that is used as the LDP router ID. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J109 Create and Edit a Loopback Interface Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure creates and edits a loopback interface that is used as the LDP router ID. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
You can create only one loopback interface.
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to create or edit a loopback interface. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click Control Plane. |
| Step 5 | Click the Loopback/IP tab. |
| Step 6 | If you want to create a loopback interface, complete the following: |
| Step 7 | If you want to edit a loopback interface, complete the following: |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J110 Specify the IP Address for Interfaces That Participate in an MPLS Network Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure specifies the IP addresses for interfaces that participate in an MPLS network using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J111 Specify the IP Address for Interfaces That Participate in an MPLS Network Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure specifies the IP addresses for interfaces that participate in an MPLS network. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
All the interfaces participating in the MPLS network must specify the IP address and mask.
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to specify the IP addresses. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click Control Plane. |
| Step 5 | Click the Loopback/IP tab. |
| Step 6 | In the Interfaces/IP Addressing area, enter the IP address and mask for the interfaces that you want to participate in an MPLS network. |
| Step 7 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding OSPF and NSF
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a link–state, hierarchical IGP routing algorithm proposed as a successor to Routing Information Protocol (RIP) in the Internet community. OSPF features include least–cost routing, multipath routing, and load balancing.
LDP and RSVP–TE uses OSPF for the routing protocol. CPT supports OSPF and OSPF–TE.
See Nonstop Forwarding for information on Nonstop Forwarding (NSF).
- NTP-J65 Configure OSPF and OSPF–TE
- DLP-J112 Enable OSPF Protocol on Specific Interfaces Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J113 Enable OSPF on Specific Interfaces Using CTC
- DLP-J209 Configure NSF for OSPF Using CTC
- DLP-J221 Configure Cisco NSF for OSPF Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J222 Configure IETF NSF for OSPF Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J138 Configure OSPF to Support Traffic Engineering Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J139 Enable OSPF-TE Protocol on Specific Interfaces Using CTC
NTP-J65 Configure OSPF and OSPF–TE
| Purpose | This procedure configures OSPF and OSPF–TE protocols. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J112 Enable OSPF Protocol on Specific Interfaces Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure defines the interfaces where OSPF runs and defines the area ID for those interfaces. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J113 Enable OSPF on Specific Interfaces Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure defines the interfaces where OSPF runs and defines the area ID for those interfaces. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | CPT supports OSPF and OSPF-TE. CPT supports only one OSPF instance but multiple OSPF areas. |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to enable the OSPF protocol on specific interfaces. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click Control Plane. |
| Step 5 | Click the OSPF tab. |
| Step 6 | In the OSPF Enabled Interfaces area, click Create. The Create OSPF Entry dialog box appears. |
| Step 7 | Enter the IP address, wildcard, and area ID of the interface where the OSPF runs and click OK. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J209 Configure NSF for OSPF Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures NSF for OSPF using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Non Stop Forwarding (NSF) is required for uninterrupted service of OSPF over SSO.
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to enable the OSPF NSF. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click Control Plane. |
| Step 5 | Click the OSPF tab. |
| Step 6 |
In the OSPF NSF area, check the following check boxes as required:
|
| Step 7 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J221 Configure Cisco NSF for OSPF Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures Cisco NSF for OSPF using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J222 Configure IETF NSF for OSPF Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures IETF NSF for OSPF using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
DLP-J138 Configure OSPF to Support Traffic Engineering Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures OSPF to support traffic engineering. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | MPLS traffic engineering supports only a single IGP instance. MPLS traffic engineering must not be configured in more than one IGP instance. |
DLP-J139 Enable OSPF-TE Protocol on Specific Interfaces Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures a router running OSPF to flood traffic engineering for specific OSPF areas. In other words, this procedure enables MPLS TE for selected OSPF areas. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to enable the OSPF-TE protocol on specific interfaces. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click MPLS TE. |
| Step 5 | Click the OSPF-TE tab. |
| Step 6 | In the OSPF TE Enabled Areas area, select the area IDs where you want to enable OSPF-TE. |
| Step 7 | Check the Autoconfig check box for specific area IDs where you want to enable OSPF-TE. |
| Step 8 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 9 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding LDP
Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) enables peer label switch routers (LSRs) in an MPLS network to exchange label binding information for supporting hop-by-hop forwarding in an MPLS network. Label switching on a router requires the Cisco Express Forwarding to be enabled on that router.
MPLS LDP enables LSRs to request, distribute, and release label prefix binding information to peer routers in a network. LDP enables LSRs to discover potential peers and to establish LDP sessions with those peers for the purpose of exchanging label binding information.
MPLS LDP enables one LSR to inform another LSR of the label bindings it has made. When a pair of routers communicates the LDP parameters, they establish a label switched path (LSP). MPLS LDP enables LSRs to distribute labels along normally routed paths to support MPLS forwarding. This method of label distribution is called hop-by-hop forwarding. With IP forwarding, when a packet arrives at a router, the router checks the destination address in the IP header, performs a route lookup, and forwards the packet to the next hop. With MPLS forwarding, when a packet arrives at a router, the router checks the incoming label, looks up the label in a table, and then forwards the packet to the next hop. MPLS LDP is useful for applications that require hop-by-hop forwarding, such as MPLS VPNs.
MPLS LDP provides the building blocks for MPLS-enabled applications, such as VPNs.
LDP Label Spaces and LDP Identifiers
An LDP label binding is an association between a destination prefix and a label. The label used in LDP label binding is allocated from a set of possible labels called a label space.
LDP supports two types of label spaces:
Interface–specific—An interface–specific label space uses interface resources for labels. Depending on its configuration, an LDP platform may support zero, one, or more interface–specific label spaces.
Platform–wide—An LDP platform supports a single platform–wide label space, which interfaces that share the same labels can use. For Cisco platforms, all interface types, except LC–ATM, use the platform–wide label space.
LDP supports identifiers of 6 bytes that are called LDP Identifiers (LDP ID), which are used to name label spaces. The LDP ID is made up of the following components:
The first four bytes, called the LDP router ID, identify the LSR that owns the label space.
The last two bytes, called the local label space ID, identify the label space within the LSR. For the platform–wide label space, the last two bytes of the LDP ID are always both 0.
The LDP ID takes the following form:
<LDP router ID> : <local label space ID>
The examples of LDP IDs are 209.165.200.225 and 209.165.200.226
LDP Router ID
The mpls ldp router-id command allows you to establish the IP address of an interface as the LDP router ID.
The following steps describe the normal process to determine the LDP router ID:
The router examines the IP addresses of all the operational interfaces.
If these IP addresses include loopback interface addresses, the router selects the largest loopback address. Configuring a loopback address helps ensure a stable LDP ID for the router because the state of loopback addresses does not change. However, configuring a loopback interface and IP address on each router is not required.
If these IP addresses do not include loopback interface addresses, the router selects the largest IP address pertaining to an operational interface as the LDP router ID.
The loopback IP address does not become the router ID of the local LDP ID under the following circumstances:
If the loopback interface has been explicitly shut down.
If the mpls ldp router-id command specifies that a different interface should be used as the LDP router ID.
If you use a loopback interface, ensure that the IP address for the loopback interface is configured with a /32 network mask. In addition, ensure that the routing protocol in use is configured to advertise the corresponding /32 network.
DLP-J114 Specify the LDP Router ID Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure establishes the IP address of an interface as the LDP router ID. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | Ensure that the specified interface is operational before assigning it as the LDP router ID. |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Specify the LDP Router ID
The following example assigns interface TenGigabitEthernet4/1 as the LDP router ID:
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# mpls ip Router(config)# mpls label protocol ldp Router(config)# mpls ldp router-id TenGigabitEthernet4/1
The following example displays the LDP router ID:
Router# show mpls ldp discovery
Local LDP Identifier:
10.15.15.15:0
Discovery Sources:
Interfaces:
Ethernet4 (ldp): xmit/recv
LDP Id: 10.14.14.14:0
Understanding MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration
To enable LDP, you must configure it globally and on each interface where it is needed. Configuring LDP on many interfaces can be time-consuming.
The MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration feature enables you to globally configure LDP on each interface associated with a specific OSPF instance. OSPF IGPs support this feature. The MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration feature blocks LDPs from enabling on interfaces that you want to prevent from being enabled. This feature makes configuration easier, faster, and error–free.
Restrictions
The MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration feature has the following restrictions:
If LDP is disabled globally, the mpls ldp autoconfig command fails and generates a console message explaining that LDP must first be enabled globally by using the global mpls ip command.
If the mpls ldp autoconfig command is configured for the OSPF instance, you cannot use the global no mpls ip command. To disable LDP, you must first use the no mpls ldp autoconfig command.
The MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration feature is not supported on traffic engineering tunnel interfaces.
- NTP-J43 Configure MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration
- DLP-J115 Enable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J116 Disable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J117 Verify MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands
- Example of MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration with OSPF
- DLP-J118 Enable or Disable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using CTC
NTP-J43 Configure MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration
| Purpose | This procedure configures MPLS LDP autoconfiguration. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J115 Enable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure allows you to: |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls ip Example:Router(config)# mpls ip | Globally enables MPLS hop-by-hop forwarding. |
| Step 4 | mpls label protocol ldp Example:Router(config)# mpls label protocol ldp | Specifies LDP as the default label distribution protocol. |
| Step 5 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure, and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | ip address ip-address mask-value Example:Router(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.11 255.255.255.255 | Assigns an IP address and network mask to the interface. |
| Step 7 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 8 | router ospf process-id Example:Router(config)# router ospf 1 | Enables OSPF routing and enters router configuration mode. |
| Step 9 | network ip-address wildcard-mask area area-id Example:Router(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 3 | Specifies the interface where OSPF runs and defines the area ID for that interface. |
| Step 10 | mpls ldp autoconfig [area area-id] Example:Router(config-router)# mpls ldp autoconfig area 3 | Enables the MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration feature. If no OSPF area is specified, the command applies to all the interfaces associated with the OSPF process. If an area ID is specified, then only the interfaces associated with that OSPF area are enabled with LDP. |
| Step 11 | end Example:Router(config-router)# end | Exits router configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 12 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J116 Disable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure disables the MPLS LDP autoconfiguration feature. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure, and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | no mpls ldp igp autoconfig [area area-id] Example:Router(config-if)# no mpls ldp igp autoconfig | Disables LDP for that interface. |
| Step 5 | end Example:Router(config-if)# end | Exits interface configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J117 Verify MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure verifies LDP autoconfiguration. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | show mpls interfaces [type number ] [all] [detail] [internal] Example:Router# show mpls interfaces TenGigabitEthernet4/1 detail | Displays the method used to enable LDP on an interface. The following example shows that LDP was enabled on the interface by both the mpls ip and mpls ldp autoconfig commands:
Interface TenGigabitEthernet4/1:
IP labeling enabled (ldp):
Interface config
IGP config
LSP Tunnel labeling enabled
BGP labeling not enabled
MPLS operational
Fast Switching Vectors:
IP to MPLS Fast Switching Vector
MPLS Turbo Vector
MTU = 1500
|
| Step 3 | show mpls ldp discovery [all] [detail] Example:Router# show mpls ldp discovery detail | Displays how LDP was enabled on the interface. In the following example, LDP was enabled by both the mpls ip and mpls ldp autoconfig commands:
Local LDP Identifier:
10.11.11.11:0
Discovery Sources:
Interfaces:
TenGigabitEthernet4/1 (ldp): xmit/recv
Enabled: Interface config, IGP config;
Hello interval: 5000 ms; Transport IP addr: 10.11.11.11
LDP Id: 10.10.10.10:0
Src IP addr: 10.0.0.1; Transport IP addr: 10.10.10.10
Hold time: 15 sec; Proposed local/peer: 15/15 sec
|
| Step 4 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example of MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration with OSPF
The following configuration commands enable LDP for OSPF process 1 area 3. The mpls ldp autoconfig area 3 command and the OSPF network commands enable LDP on TenGigabitEthernet interfaces 0/0, 0/1, and 1/1. The no mpls ldp igp autoconfig command on TenGigabitEthernet interface 1/0 prevents LDP from being enabled on TenGigabitEthernet interface 1/0, even though OSPF is enabled for that interface.
configure terminal interface TenGigabitEthernet 0/0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 ! interface TenGigabitEthernet 0/1 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.0.0.1 ! interface TenGigabitEthernet 1/1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.0.0 ! interface TenGigabitEthernet 1/0 ip address 10.1.0.1 0.1.0.255 exit ! router ospf 1 network 10.0.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 3 network 10.1.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 3 mpls ldp autoconfig area 3 end interface TenGigabitEthernet 1/0 no mpls ldp igp autoconfig
DLP-J118 Enable or Disable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure allows you to: |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to enable or disable LDP autoconfiguration. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click Control Plane. |
| Step 5 | Click the OSPF tab. |
| Step 6 | In the LDP Autoconfig area, complete one of the following actions:
|
| Step 7 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization
Packet loss can occur because the IGP and LDP are not synchronized. Packet loss can occur in the following situations:
When an IGP adjacency is established, the router begins forwarding packets using the new adjacency before the LDP label exchange process completes between the peers on that link.
If an LDP session closes, the router continues to forward traffic using the link that is associated with the LDP peer rather than an alternate pathway with a fully synchronized LDP session.
The MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization feature performs the following tasks:
Enables LDPs and IGPs to synchronize to minimize MPLS packet loss.
Globally enables LDP–IGP synchronization on each interface that is associated with an IGP OSPF process.
Disables LDP–IGP synchronization on interfaces that you do not want enabled.
Prevents MPLS packet loss due to synchronization conflicts.
Works when LDP is enabled on interfaces using either the mpls ip or mpls ldp autoconfig command or using the CTC procedure DLP-J118 Enable or Disable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using CTC.
If the LDP peer is reachable, the IGP waits indefinitely to synchronize. To limit the length of time an IGP session must wait to synchronize with LDP, enter the mpls ldp igp sync holddown command. If the LDP peer is not reachable, the IGP establishes the adjacency to enable the LDP session to be established.
When an IGP adjacency is established on a link but LDP–IGP synchronization is not yet achieved or is lost, the IGP advertises the max–metric on that link.
MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization with Peers
When the MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization feature is enabled on an interface, LDP determines if any peer connected by the interface is reachable by checking the peer transport address in the routing table. If a routing entry (including the longest match or the default routing entry) for the peer exists, LDP assumes that LDP–IGP synchronization is required for the interface and notifies the IGP to wait for LDP convergence.
LDP–IGP synchronization with peers requires the routing table to be accurate. If the routing table shows there is a route for the peer transport address, that route must be able to reach the peer transport address. However, if the route is a summary route, a default route, or a statically configured route, it may not the correct route for the peer. You must verify that the route in the routing table can reach the peer transport address.
When the routing table has an inaccurate route for the peer transport address, LDP cannot set up a session with the peer. This delay causes the IGP to wait for LDP convergence unnecessarily for the sync hold–down time.
MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization Delay Timer
MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization feature provides the option to configure a delay time for MPLS LDP and IGP synchronization for each interface. Normally, when LDP–IGP synchronization is configured, LDP notifies IGP as soon as LDP is converged. When the delay timer is configured, this notification is delayed.
When LDP is fully established and synchronized, LDP checks the delay timer:
If you configured a delay time, LDP starts the timer. When the timer expires, LDP checks if the synchronization is still valid and notifies the OSPF process.
If you did not configure a delay time or if synchronization is disabled or down or if an interface was removed from an IGP process, LDP stops the timer and immediately notifies the OSPF process.
If you configure a new delay time while a timer is running, LDP saves the new delay time but does not reconfigure the running timer.
MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization Incompatibility with IGP Nonstop Forwarding
The MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization feature is not supported during the startup period if IGP Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) is configured. The MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization feature conflicts with IGP NSF when the IGP is performing NSF during startup. After the NSF startup is complete, the MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization feature is supported.
MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization Compatibility with LDP Graceful Restart
LDP graceful restart protects traffic when an LDP session is lost. If an interface that supports a graceful–restart–enabled LDP session fails, MPLS LDP–IGP synchronization is still achieved on the interface while it is protected by Graceful Restart. MPLS LDP–IGP synchronization is eventually lost under the following circumstances:
- NTP-J44 Configure MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization
- DLP-J119 Enable MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J120 Disable MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J121 Verify MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization Using Cisco IOS Commands
- Example of MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization
- DLP-J122 Enable MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization Using CTC
NTP-J44 Configure MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization
| Purpose | This procedure configures MPLS LDP–IGP synchronization. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J119 Enable MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables LDP-IGP synchronization on each interface that is associated with an OSPF process. This procedure also limits the number of seconds that an IGP session must wait to synchronize with LDP. By default, the IGP session waits indefinitely if the LDP peer is reachable. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J115 Enable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls ip Example:Router(config)# mpls ip | Globally enables MPLS hop-by-hop forwarding. |
| Step 4 | mpls label protocol ldp Example:Router(config)# mpls label protocol ldp | Specifies LDP as the default label distribution protocol. |
| Step 5 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | ip address ip-address mask-value Example:Router(config-if)# ip address 10.25.0.11 255.255.255.255 | Assigns an IP address and network mask to the interface. |
| Step 7 | mpls ip Example:Router(config-if)# mpls ip | Enables hop-by-hop forwarding on the interface. |
| Step 8 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 9 | router ospf process-id Example:Router(config)# router ospf 1 | Enables OSPF routing and enters router configuration mode. |
| Step 10 | network ip-address wildcard-mask area area-id Example:Router(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 3 | Defines an interface on which OSPF runs and defines the area ID for that interface. |
| Step 11 | mpls ldp sync Example:Router(config-router)# mpls ldp sync | Enables MPLS LDP-IGP synchronization for interfaces for an OSPF process. |
| Step 12 | mpls ldp igp sync holddown milliseconds Example:Router(config-router)# mpls ldp igp sync holddown 20 | Specifies the period that an IGP session must wait to synchronize with LDP. |
| Step 13 | end Example:Router(config-router)# end | Exits router configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 14 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J120 Disable MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure disables LDP-IGP synchronization on each interface. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J115 Enable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | no mpls ldp igp sync Example:Router(config-if)# no mpls ldp igp sync | Disables MPLS LDP-IGP synchronization for that interface. |
| Step 5 | end Example:Router(config-if)# end | Exits interface configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J121 Verify MPLS LDP–IGP Synchronization Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure verifies LDP-IGP synchronization on each interface. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J115 Enable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using Cisco IOS Commands |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
After you configure the interfaces for LDP, OSPF, and LDP–IGP synchronization, verify that the configuration is working correctly using the show mpls ldp igp sync and show ip ospf mpls ldp interface commands.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | show mpls ldp igp sync [all | interface type number] Example:Router# show mpls ldp igp sync | Displays the output of this command in the following example shows that MPLS LDP–IGP synchronization is configured correctly, because LDP is configured and the SYNC status shows that synchronization is enabled. TenGigabitEthernet4/1: LDP configured; SYNC enabled. SYNC status: sync achieved; peer reachable. IGP holddown time: infinite. Peer LDP Ident: 10.0.0.1:0 IGP enabled: OSPF 1 |
| Step 3 | show ip ospf [process-id] mpls ldp interface [interface] Example:Router# show ip ospf mpls ldp interface | Displays the output of the show ip ospf mpls ldp interface command in the following example shows that the interfaces are properly configured. TenGigabitEthernet4/1 Process ID 1, Area 0 LDP is configured through LDP autoconfig LDP-IGP Synchronization: Yes Holddown timer is not configured Timer is not running TenGigabitEthernet4/2 Process ID 1, Area 0 LDP is configured through LDP autoconfig LDP-IGP Synchronization: Yes Holddown timer is not configured Timer is not running |
| Step 4 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example of MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization
The following configuration commands enable LDP for OSPF process 1. The mpls ldp sync command and the OSPF network commands enable LDP on interfaces TenGigabitEthernet0/0, TenGigabitEthernet0/1, and TenGigabitEthernet1/1, respectively. The no mpls ldp igp sync command on interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0 prevents LDP from being enabled on interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0, even though OSPF is enabled for that interface.
Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet0/0 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.1 Router(config-if)# mpls ip ! Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet0/1 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.0.1.1 Router(config-if)# mpls ip ! Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet1/1 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1 Router(config-if)# mpls ip ! Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.1.0.1 Router(config-if)# mpls ip ! Router(config)# router ospf 1 Router(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 3 Router(config-router)# network 10.1.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 3 Router(config-router)# mpls ldp sync Router(config-router)# exit Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0 Router(config-if)# no mpls ldp igp sync
DLP-J122 Enable MPLS LDP-IGP Synchronization Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables LDP-IGP synchronization on each interface that is associated with an OSPF process. This procedure also limits the number of seconds that an IGP session must wait to synchronize with LDP. By default, the IGP session waits indefinitely if the LDP peer is reachable. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J118 Enable or Disable MPLS LDP Autoconfiguration Using CTC |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | This feature is supported only on interfaces that are running OSPF processes. |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to enable LDP-IGP synchronization. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click Control Plane. |
| Step 5 | Click the OSPF tab. |
| Step 6 | In the LDP Synchronization area, check the Enabled check box to enable LDP-IGP synchronization on all the interfaces that belong to an OSPF process. |
| Step 7 | Enter the number of seconds in the Holddown field to specify the period that an IGP session must wait to synchronize with LDP. |
| Step 8 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 9 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding MPLS LDP Backoff
The LDP backoff mechanism prevents two LSRs that were configured incompatibly from engaging in an unthrottled sequence of session setup failures. For example, an incompatibility arises when two neighboring routers attempt to perform LC-ATM (label-controlled ATM) when they are using different ranges of VPI/VCI values for labels.
If a session setup attempt fails due to an incompatibility, each LSR delays its next attempt (that is, backs off), increasing the delay exponentially with each successive failure until the maximum backoff delay is reached.
The default settings correspond to the lowest settings for initial and maximum backoff values defined by the LDP protocol specification. You should change the settings from the default values only if such settings result in undesirable behavior.
- NTP-J45 Configure MPLS LDP Backoff
- DLP-J123 Configure MPLS LDP Backoff Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J124 Configure MPLS LDP Backoff Using CTC
NTP-J45 Configure MPLS LDP Backoff
| Purpose | This procedure configures MPLS LDP backoff. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J123 Configure MPLS LDP Backoff Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures the parameters for MPLS LDP backoff mechanism using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls ldp backoff initial-backoff maximum-backoff Example:Router(config)# mpls ldp backoff 10 30 | Configures MPLS LDP backoff mechanism and specifies the period for initial and maximum backoff. |
| Step 4 | end Example:Router(config)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 5 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J124 Configure MPLS LDP Backoff Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures the parameters for MPLS LDP backoff mechanism. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to configure the parameters for LDP backoff. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click LDP. |
| Step 5 | In the Session area, enter the number of seconds in the Holdtime field to specify the period for which an LDP session is maintained in the absence of LDP messages from the session peer. |
| Step 6 | Enter the number of seconds in the Init Backoff field to specify the period for the initial backoff. |
| Step 7 | Enter the number of seconds in the Max Backoff field to specify the period for the maximum backoff. |
| Step 8 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 9 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding MPLS LDP Session Protection
The MPLS LDP Session Protection feature provides faster label distribution protocol convergence when a link recovers following an outage. MPLS LDP Session Protection feature protects an LDP session between directly connected neighbors or an LDP session established for a TE tunnel.
MPLS LDP Session Protection feature maintains LDP bindings when a link fails. MPLS LDP sessions are protected through the use of LDP Hello messages. When you enable MPLS LDP, the LSRs send messages to find other LSRs with which they can create LDP sessions.
LDP graceful restart must be enabled before establishing a LDP session.
Directly Connected MPLS LDP Sessions
If the LSR is one hop from its neighbor, it is directly connected to its neighbor. The LSR sends out LDP Hello messages as User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets to all the routers on the subnet. The hello message is called an LDP Link Hello. A neighboring LSR responds to the hello message and the two routers begin to establish an LDP session. This is called basic discovery.
To initiate an LDP session between routers, the routers determine which router will take the active role and which router will take the passive role. The router that takes the active role establishes the LDP TCP connection session and initiates the negotiation of the LDP session parameters. To determine the roles, the two routers compare their transport addresses. The router with the higher IP address takes the active role and establishes the session.
After the LDP TCP connection session is established, the LSRs negotiate the session parameters, including the method of label distribution to be used. Two methods are available:
- NTP-J46 Configure MPLS LDP Session Protection
- DLP-J125 Enable MPLS LDP Session Protection Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J126 Verify MPLS LDP Session Protection Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J127 Enable MPLS LDP Session Protection Using CTC
- DLP-J128 Enable Directly Connected LDP Sessions Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J130 Create Targeted LDP Sessions Using CTC
- DLP-J131 Configure MPLS LDP Discovery Using CTC
- Understanding Explicit Null Label
- DLP-J132 Enable Explicit Null Label Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J133 Enable Explicit Null Label Using CTC
NTP-J46 Configure MPLS LDP Session Protection
| Purpose | This procedure configures MPLS LDP session protection. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J125 Enable MPLS LDP Session Protection Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables MPLS LDP Session Protection. This procedure enables LDP sessions to be protected during a link failure. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures |
|
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ip cef [distributed] Example:Router(config)# ip cef | Configures Cisco Express Forwarding. |
| Step 4 | interface loopbacknumber Example:Router(config)# interface loopback0 | Configures a loopback interface and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 5 | ip address ip-address mask-value Example:Router(config-if)# ip address 10.25.0.11 255.255.255.255 | Assigns an IP address and network mask to the loopback interface. |
| Step 6 | interface type number Example:Router(config-if)# interface TenGigabitEthernet4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 7 | mpls ip Example:Router(config-if)# mpls ip | Configures MPLS hop-by-hop forwarding for a specified interface. |
| Step 8 | mpls label protocol ldp Example:Router(config-if)# mpls label protocol ldp | Configures the use of LDP on a specific interface. |
| Step 9 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Exits interface configuration mode and enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 10 | mpls ldp session protection [for acl] [duration {infinite | seconds}] Example:Router(config)# mpls ldp session protection | Enables MPLS LDP Session Protection. |
| Step 11 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J126 Verify MPLS LDP Session Protection Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure verifies MPLS LDP Session Protection. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | show mpls ldp discovery [all] [detail] Example:Router# show mpls ldp discovery | Use this command and check that the output contains xmit/recv to the peer router.
Local LDP Identifier:
10.0.0.5:0
Discovery Sources:
Interfaces:
TenGigabitEthernet4/1 (ldp): xmit/recv
LDP Id: 10.0.0.1:0
Targeted Hellos:
10.0.0.5 -> 10.0.0.3 (ldp): active, xmit/recv
LDP Id: 10.0.0.3:0
|
| Step 2 | show mpls ldp neighbor [all] [address | interface] [detail] [graceful-restart] Example:Router# show mpls ldp neighbor | Use this command to check that the targeted hellos are active. Peer LDP Ident: 10.0.0.3:0; Local LDP Ident 10.0.0.5:0 TCP connection: 10.0.0.3.646 - 10.0.0.5.11005 State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 1453/1464; Downstream Up time: 21:09:56 LDP discovery sources: Targeted Hello 10.0.0.5 -> 10.0.0.3, active Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 10.3.104.3 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.3 |
| Step 3 | show mpls ldp neighbor [all] [address | interface] [detail] [graceful-restart] Example:Router# show mpls ldp neighbor detail | Use this command to check that the MPLS LDP Session Protection state is Ready or Protecting. If the second last line of the output shows Incomplete, the Targeted Hello Adjacency is not up yet.
Peer LDP Ident: 10.16.16.16:0; Local LDP Ident 10.15.15.15:0
TCP connection: 10.16.16.16.11013 - 10.15.15.15.646
State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 53/51; Downstream; Last TIB rev sent 74
Up time: 00:11:32; UID: 1; Peer Id 0;
LDP discovery sources:
Targeted Hello 10.15.15.15 -> 10.16.16.16, active, passive;
holdtime: infinite, hello interval: 10000 ms
Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident:
10.0.0.2 10.16.16.16 10.101.101.101 11.0.0.1
Peer holdtime: 180000 ms; KA interval: 60000 ms; Peer state: estab
Clients: Dir Adj Client
LDP Session Protection enabled, state: Protecting
duration: infinite
|
| Step 4 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J127 Enable MPLS LDP Session Protection Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables MPLS LDP session protection and configures its parameters. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J135 Configure MPLS LDP Graceful Restart Using CTC |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to configure MPLS LDP session protection. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click LDP. |
| Step 5 | In the Protection area, check the Enabled check box to enable MPLS LDP session protection. |
| Step 6 | Click the Infinite radio button to enable session protection for infinite duration or enter the number of seconds in the Duration field to specify the period for which the LDP Targeted Hello Adjacency must be retained after a link is lost. |
| Step 7 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
DLP-J128 Enable Directly Connected LDP Sessions Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures MPLS LDP sessions between two directly connected routers. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls ip Example:Router(config)# mpls ip | Configures MPLS hop-by-hop forwarding globally. |
| Step 4 | mpls label protocol ldp Example:Router(config)# mpls label protocol ldp | Configures the use of LDP on all the interfaces. |
| Step 5 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | mpls ip Example:Router(config-if)# mpls ip | Configures MPLS hop-by-hop forwarding on the interface. |
| Step 7 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Exits interface configuration mode and enters the global configuration mode. |
| Step 8 | exit Example:Router(config)# exit | Exits global configuration mode and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 9 | show mpls interfaces [interface] [all] [detail] [internal] Example:Router# show mpls interfaces | Verifies that the interfaces have been configured to use LDP. |
| Step 10 | show mpls ldp discovery [all] | [detail] Example:Router# show mpls ldp discovery | Verifies that the interface is up and is sending Discovery Hello messages. |
| Step 11 | show mpls ldp neighbor [all] [address | interface] [detail] [graceful-restart] Example:Router# show mpls ldp neighbor | Displays the status of LDP sessions. |
| Step 12 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J130 Create Targeted LDP Sessions Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure creates targeted LDP sessions using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to create targeted LDP sessions. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click LDP. |
| Step 5 | In the Targeted LDP Sessions area, click Create. The Create Targeted LDP Session dialog box appears. |
| Step 6 | Enter the IP address of the neighboring router in the IP Address field and click OK. |
| Step 7 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J131 Configure MPLS LDP Discovery Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures the holdtime and interval between transmission of consecutive LDP discovery hello messages or discovery targeted hello messages between LSRs. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to configure holdtime and interval for LSRs that are directly connected and indirectly connected. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click LDP. |
| Step 5 | In the Hello area, enter the number of seconds in the Holdtime field to specify the period a discovered LDP neighbor must wait without receiving a LDP hello message from the neighbor. |
| Step 6 | Enter the number of seconds in the Interval field to specify the period between the sending of consecutive hello messages. |
| Step 7 | In the Targeted Hello area, enter the number of seconds in the Holdtime field to specify the period a discovered LDP neighbor must wait without receiving a LDP targeted hello message from the neighbor. |
| Step 8 | Enter the number of seconds in the Interval field to specify the period between the sending of consecutive targeted hello messages. |
| Step 9 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 10 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding Explicit Null Label
Normally, LDP advertises an implicit null label for directly connected routes. The implicit null label causes the second last (penultimate) LSR to remove the MPLS header from the packet. In this case, the penultimate LSR and the last LSR do not have access to the quality of service (QoS) values that the packet carried before the MPLS header was removed. To preserve the QoS values, you can configure the LSR to advertise an explicit null label (a label value of zero). The LSR at the penultimate hop forwards MPLS packets with a null label instead of forwarding IP packets.
 Note | An explicit null label is not needed when the penultimate hop receives MPLS packets with a label stack that contains at least two labels and penultimate hop popping (PHP) is performed. In that case, the inner label can still carry the QoS value needed by the penultimate and edge LSR to implement their QoS policy. |
DLP-J132 Enable Explicit Null Label Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables explicit null label using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls ip Example:Router(config)# mpls ip | Configures MPLS hop-by-hop forwarding globally. |
| Step 4 | mpls label protocol ldp Example:Router(config)# mpls label protocol ldp | Configures the use of LDP on all the interfaces. |
| Step 5 | interface type number Example: Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet 4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | mpls ip Example:Router(config-if)# mpls ip | Configures MPLS hop-by-hop forwarding on the interface. |
| Step 7 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Exits interface configuration mode and enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 8 | mpls ldp explicit-null [for prefix-acl | to peer-acl | for prefix-acl to peer-acl] Example:Router(config)# mpls ldp explicit-null | Advertises an explicit null label in situations where it would normally advertise an implicit null label. |
| Step 9 | exit Example:Router(config)# exit | Exits global configuration mode and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 10 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J133 Enable Explicit Null Label Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables explicit null label using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to enable the explicit null label. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click LDP. |
| Step 5 | In the Explicit Null Label area, check the Enabled check box to advertise an explicit null label in situations where it would normally advertise an implicit null label. |
| Step 6 | Click Apply to save the changes. |
| Step 7 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding LDP Graceful Restart
LDP graceful restart protects traffic when a LDP session is lost. If an interface that supports a graceful-restart-enabled LDP session fails, MPLS LDP-IGP synchronization is still achieved on the interface while it is protected by graceful restart.
LDP graceful restart must be enabled in the following scenarios:
- NTP-J47 Configure MPLS LDP Graceful Restart
- DLP-J134 Configure MPLS LDP Graceful Restart Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J135 Configure MPLS LDP Graceful Restart Using CTC
NTP-J47 Configure MPLS LDP Graceful Restart
| Purpose | This procedure configures MPLS LDP graceful restart. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J134 Configure MPLS LDP Graceful Restart Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures the parameters for MPLS LDP graceful restart using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls ldp graceful-restart Example:Router(config)# mpls ldp graceful-restart | Enables MPLS LDP graceful restart. |
| Step 4 | mpls ldp graceful-restart timers forwarding-holding seconds Example:Router(config)# mpls ldp graceful-restart timers forwarding-holding 10 | Specifies the period the MPLS forwarding state must hold after the control plane restarts. |
| Step 5 | mpls ldp graceful-restart timers max-recovery seconds Example:Router(config)# mpls ldp graceful-restart timers max-recovery 20 | Specifies the period a LSR must hold stale label-forward error correction (FEC) bindings after an LDP session has been reestablished. |
| Step 6 | mpls ldp graceful-restart timers neighbor-liveness seconds Example:Router(config)# mpls ldp graceful-restart timers neighbor-liveness 15 | Specifies the period a LSR must wait for an LDP session to be reestablished. |
| Step 7 | end Example:Router(config)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J135 Configure MPLS LDP Graceful Restart Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures the parameters for MPLS LDP graceful restart. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to configure the parameters for MPLS LDP graceful restart. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click LDP. |
| Step 5 | In the Graceful Restart area, check the Enabled check box to enable MPLS LDP graceful restart. |
| Step 6 | Enter the number of seconds in the Forwarding holding field to specify the period the MPLS forwarding state must hold after the control plane restarts. |
| Step 7 | Enter the number of seconds in the Max recovery field to specify the period a LSR must hold stale label-FEC bindings after an LDP session has been reestablished. |
| Step 8 | Enter the number of seconds in the Neighbor liveliness field to specify the period a LSR must wait for an LDP session to be reestablished. |
| Step 9 | Click Apply to save the configuration. Enable OSPF NSF for LDP graceful restart to effectively minimize traffic hits. See DLP-J209 Configure NSF for OSPF Using CTC. |
| Step 10 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Examples of Show MPLS Commands
show mpls interfaces
The following show mpls interfaces command output shows that the interfaces TenGigabitEthernet4/1 and TenGigabitEthernet4/2 have been configured to use LDP:
Router# show mpls interfacesInterface IP Tunnel BGP Static Operational TenGigabitEthernet4/1 Yes (ldp) No No No Yes TenGigabitEthernet4/2 Yes No No No Yes
show mpls ldp discovery
The following show mpls ldp discovery command output shows that the interface is up and is sending LDP Discovery Hello messages.
Router# show mpls ldp discovery
Local LDP Identifier:
172.16.12.1:0
Discovery Sources:
Interfaces:
TenGigabitEthernet4/1 (ldp): xmit
show mpls ldp neighbor
The following show mpls ldp neighbor command output shows that the LDP session between routers is successfully established:
Router# show mpls ldp neighborPeer LDP Ident: 10.1.1.2:0; Local LDP Ident 10.1.1.1:0 TCP connection: 10.1.1.2.18 - 10.1.1.1.66 State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 12/11; Downstream Up time: 00:00:10 LDP discovery sources: TenGigabitEthernet4/1, Src IP addr: 10.20.10.2 Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 10.1.1.2 10.20.20.1 10.20.10.2
Understanding MPLS-TE
Traffic Engineering is a set of techniques and processes used to cause routed traffic to travel through the network on a path other than the one that is chosen if standard routing methods were used. Traffic Engineering is the ability to dynamically define routes based on known demand or alternate available routes.
MPLS Traffic Engineering (MPLS–TE) is the use of label switching to improve traffic performance along with an efficient use of network resources. MPLS–TE is the process of adjusting bandwidth allocations to ensure that enough bandwidth is left for high priority traffic. In MPLS–TE, the upstream router creates a network tunnel for a particular traffic stream and sets the bandwidth available for that tunnel.
CPT supports OSPF and OSPF-TE in this release.
You can specify the IP address assigned to an interface as the source IP address for control packets. The default behavior is to use the router ID configured in the Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) using the mpls traffic-eng router-id command.
When you configure an MPLS TE tunnel, the address specified in the tunnel source command is used as the source IP address for control traffic to signal the tunnel. The source IP address overrides the default IP address taken from the IGP mpls traffic-eng router-id command.
The traffic engineering router ID for the node is the IP address associated with the loopback interface. The router ID is not editable.
- NTP-J48 Configure MPLS-TE Parameters
- DLP-J136 Configure MPLS and RSVP to Support Traffic Engineering Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J137 Enable MPLS-TE on a System and on Specific Interfaces Using CTC
- DLP-J140 Enable RSVP Graceful Restart on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J141 Enable RSVP Graceful Restart on an Interface Using CTC
- DLP-J142 Configure MPLS-TE Parameters for Each Interface Using CTC
- Understanding Periodic Flooding Timer
NTP-J48 Configure MPLS-TE Parameters
| Purpose | This procedure configures the parameters for MPLS–TE tunnel. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J136 Configure MPLS and RSVP to Support Traffic Engineering Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures MPLS and Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) to support traffic engineering on the routers. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ip cef Example:Router(config)# ip cef | Enables Cisco Express Forwarding. |
| Step 4 | mpls traffic-eng tunnels Example:Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng tunnels | Enables MPLS traffic engineering tunnel signaling on a device. |
| Step 5 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet4/1 | Specifies the interface and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | ip address ip-address mask-value Example:Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.10 255.255.255.255 | Assigns an IP network address and network mask to the interface. |
| Step 7 | ip rsvp bandwidth or ip rsvp bandwidth value or ip rsvp bandwidth percent value Example:Router(config-if)# ip rsvp bandwidth 100 | Enables RSVP for IP on an interface to support traffic engineering. |
| Step 8 | end Example:Router(config-if)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 9 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J137 Enable MPLS-TE on a System and on Specific Interfaces Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables MPLS-TE tunnel signaling globally on a system and on the desired interfaces. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to enable MPLS-TE. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click MPLS TE. |
| Step 5 | Click the Link TE Attrs tab. |
| Step 6 | Check the Enabled check box at the top to globally enable MPLS-TE tunnel signaling on the system. |
| Step 7 | In the Interfaces area, check the Enabled check box for interfaces that you want to enable MPLS-TE tunnel signaling. |
| Step 8 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 9 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J140 Enable RSVP Graceful Restart on an Interface Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables RSVP graceful restart on an interface using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | You must repeat this procedure for each interface in the neighboring router. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet4/1 | Specifies the interface to configure and enters interface configuration mode. Repeat this step as needed to configure the additional interfaces. | ||
| Step 4 | ip rsvp signalling hello graceful-restart neighbor ip-address Example:Router(config-if)# ip rsvp signalling hello graceful-restart neighbor 10.0.0.0 | Enables support for RSVP graceful restart on routers helping their neighbors recover TE tunnels following Stateful Switchover (SSO). Repeat this step as needed to configure additional IP addresses on the interfaces of the neighboring router.
| ||
| Step 5 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J141 Enable RSVP Graceful Restart on an Interface Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure enables RSVP graceful restart on an interface using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J209 Configure NSF for OSPF Using CTC |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to enable RSVP graceful restart on an interface. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click MPLS-TE. |
| Step 5 | Click the RSVP-TE tab. |
| Step 6 | Enter the number of seconds in the Frequency field. |
| Step 7 | In the Graceful Restart area, complete the following: |
| Step 8 | Click Apply to enable RSVP graceful restart on the desired interfaces. |
| Step 9 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J142 Configure MPLS-TE Parameters for Each Interface Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure configures MPLS-TE parameters for each interface. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP-J137 Enable MPLS-TE on a System and on Specific Interfaces Using CTC |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to configure MPLS-TE parameters for each interface. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click MPLS TE. |
| Step 5 | Click the Link TE Attrs tab. |
| Step 6 | For interfaces that you have enabled MPLS-TE tunnel signaling: |
| Step 7 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding Periodic Flooding Timer
When a threshold is crossed, the MPLS traffic engineering link management advertises updated link information. If no thresholds are crossed, changes can be flooded periodically unless periodic flooding is disabled.
Changes in the MPLS TE topology database are flooded by the link state IGP. Some changes, such as those to link status (up or down) or configured parameters, trigger immediate flooding. Other changes are considered less urgent and are flooded periodically. For example, changes to the amount of link bandwidth allocated to TE tunnels are flooded periodically unless the change causes the bandwidth to cross a configurable threshold.
- DLP-J143 Change the Periodic Flooding Timer Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J144 Change the Periodic Flooding Timer Using CTC
DLP-J143 Change the Periodic Flooding Timer Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure sets the interval for periodic flooding of traffic engineering topology information using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls traffic-eng link-management timers periodic-flooding interval Example:Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng link-management timers periodic-flooding 25 | Changes the interval used for periodic flooding. The default value is 180 seconds. The range is from 0 to 3600 seconds. A value of 0 turns off periodic flooding. If you set this value anywhere in the range from 1 to 29, it is treated as 30. |
| Step 4 | end Example:Router(config)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 5 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J144 Change the Periodic Flooding Timer Using CTC
| Purpose | This procedure sets the interval for periodic flooding of traffic engineering topology information. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to change the periodic flooding timer. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the fabric or line card and choose Open Packet Transport System View. The Packet Transport System View dialog box appears. |
| Step 3 | Click the Provisioning tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click MPLS TE. |
| Step 5 | Click the Link TE Attrs tab. |
| Step 6 | Enter the value in seconds, in the Periodic Flooding field to change the interval used for periodic flooding. The default value is 180 seconds. The range is 0 to 3600 seconds. A value of 0 turns off periodic flooding. If you set this value anywhere in the range from 1 to 29 seconds, it is treated as 30 seconds. |
| Step 7 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding MPLS–TE LSP Attributes
The MPLS Traffic Engineering—LSP Attributes provides an LSP Attribute List feature and a Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature. These features have the following benefits:
The LSP Attributes List feature provides the ability to configure values for several LSP–specific path options for TE tunnels.
One or more TE tunnels can specify specific path options by referencing an LSP attribute list.
The Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature provides a single command that allows a TE tunnel to fall back temporarily to path options that can reduce bandwidth constraints.
 Note | You can configure LSP attributes for path options associated with MPLS TE tunnels only through Cisco IOS commands and not through CTC. |
Several LSP attributes can be applied to path options for TE tunnels using an LSP attribute list. If bandwidth is the only LSP attribute you require, then you can configure a path option for bandwidth override.
Prerequisites
Before configuring either an LSP Attribute List or a Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature, you must configure a MPLS TE tunnel.
Traffic Engineering Bandwidth and Bandwidth Pools
MPLS TE allows constraint–based routing (CBR) of IP traffic. One of the constraints satisfied by CBR is the availability of required bandwidth over a selected path. Regular TE tunnel bandwidth is called the global pool.
You can configure the LSP Attributes bandwidth path option to use the global pool bandwidth. The bandwidth value for the path option may be any valid value and the pool does not have to be the same as that configured on the tunnel.
Autobandwidth and Path Option for Bandwidth Override
If Traffic Engineering automatic bandwidth (autobandwidth) adjustment is configured for a tunnel, traffic engineering automatically adjusts the bandwidth allocation for the traffic engineering tunnel based on its measured usage of the bandwidth of the tunnel.
Traffic engineering autobandwidth samples the average output rate for each tunnel marked for automatic bandwidth adjustment. For each marked tunnel, it periodically adjusts the allocated bandwidth for the tunnel to be the largest sample for the tunnel since the last adjustment. The default reoptimization setting in the MPLS AutoBandwidth feature is every 24 hours.
The frequency at which the tunnel bandwidth is adjusted and the allowable range of adjustments is configured on a per–tunnel basis. In addition, the sampling interval and the interval over which to average tunnel traffic to obtain the average output rate is user–configurable on a per–tunnel basis.
The automatic bandwidth feature allows you to configure and monitor the bandwidth for MPLS TE tunnels. If automatic bandwidth is configured for a tunnel, TE automatically adjusts the tunnel bandwidth.
The Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature allows you to override the bandwidth configured on a TE tunnel. This feature also overrides bandwidth configured or recalculated by automatic bandwidth adjustment if the path option in effect has bandwidth override enabled.
Constraint–Based Routing and Path Option Selection
MPLS traffic engineering automatically establishes and maintains LSPs across the network by using the RSVP. The path that an LSP uses is determined by the LSP resource requirements and network resources, such as bandwidth. Traffic engineering tunnels are calculated at the LSP head based on a fit between required and available resources (constraint–based routing).
Without the Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature, a TE tunnel establishes an LSP based on dynamic or explicit path options in order of preference. However, the bandwidth and other attributes configured on the TE tunnel allow the setup of an LSP only if LSP path options satisfy the constraints. If a path that satisfies the configured path options cannot be found, then the tunnel is not set up.
The Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature provides a fallback path option that allows overriding the bandwidth configured on the TE tunnel interface. For example, you can configure a path option that sets the bandwidth to zero effectively removing the bandwidth constraint imposed by the constraint–based routing calculation.
Tunnel Reoptimization and Path Option Selection
Reoptimization occurs when a device with traffic engineering tunnels periodically examines tunnels with established LSPs to learn if better LSPs are available. If a better LSP is available, the device attempts to signal the better LSP. If the signaling is successful, the device replaces the older LSP with the new LSP.
Reoptimization can be triggered by a timer, the mpls traffic–eng reoptimize command, or a configuration change that requires the resignalling of a tunnel. The MPLS AutoBandwidth feature, for example, uses a timer to set the frequency of reoptimization based on the bandwidth path option attribute. The Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature allows for the switching between bandwidth configured on the TE tunnel interface and bandwidth configured on a specific path option. This increases the success of signaling an LSP for the TE tunnel.
With bandwidth override configured on a path option, traffic engineering attempts to reoptimize the bandwidth every 30 seconds to reestablish the bandwidth configured on the tunnel.
Path Option Selection with Bandwidth Override
The Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature allows you to configure bandwidth parameters on a specific path option using the bandwidth keyword in the tunnel mpls traffic–eng path–option command. When an LSP is signaled using a path option with a configured bandwidth, the bandwidth associated with the path option is signaled instead of the bandwidth configured directly on the tunnel.
This feature provides you with the ability to configure multiple path options that reduce the bandwidth constraint each time the headend of a tunnel fails to establish an LSP.
Explicit and Dynamic Path Options
You can configure multiple path options for a single tunnel. For example, there can be several explicit path options and a dynamic option for one tunnel.
If you specify the dynamic keyword, the physical bandwidth of the interface and the available TE bandwidth are checked to ensure that the requested amount of bandwidth does not exceed the physical bandwidth of any link. To oversubscribe links, you must specify the explicit keyword. If you use the explicit keyword, the amount of bandwidth that is available on the link for TE is only checked; the amount of bandwidth you configure is not limited to how much physical bandwidth is available on the link.
- NTP-J49 Configure MPLS-TE LSP Attributes
- DLP-J145 Add Attributes to an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J146 Associate an LSP Attribute List with a Path Option for an MPLS TE Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J147 Configure an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J148 Modify an Attribute in an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J149 Remove an Attribute from an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J150 Delete an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J151 Verify Attributes Within an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J152 Verify All LSP Attribute Lists Using Cisco IOS Commands
NTP-J49 Configure MPLS-TE LSP Attributes
| Purpose | This procedure configures LSP attributes for MPLS–TE. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J145 Add Attributes to an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure adds attributes to an LSP attribute list using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
LSP Attributes configuration mode is used to display the specific LSP attributes list and to add or change the required path option attribute.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes string Example:Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1 | Configures an LSP attribute list and enters LSP Attributes configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | affinity value [mask value] Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# affinity 0 mask 0 | (Optional) Specifies attribute flags for links comprising an LSP. |
| Step 5 | bandwidth global kbps Example: Router(config-lsp-attr)# bandwidth global 1000 | Specifies an LSP bandwidth. |
| Step 6 | priority setup-priority [hold-priority] Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# priority 2 2 | Specifies the LSP priority.
|
| Step 7 | list Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# list | (Optional) Displays the contents of the LSP attribute list. |
| Step 8 | exit Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit | (Optional) Exits LSP Attributes configuration mode. |
| Step 9 | end Example:Router(config)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 10 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Add Attributes to an LSP Attribute List
The following example shows how to add the protection attributes to the LSP attribute list identified with the numeral 1:
Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# affinity 7 7 Router(config-lsp-attr)# bandwidth 1000 Router(config-lsp-attr)# priority 1 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit
DLP-J146 Associate an LSP Attribute List with a Path Option for an MPLS TE Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure associates an LSP attribute list with a path option for an MPLS TE tunnel. This procedure is required if you want to apply the LSP attribute list that you configured to path options for your MPLS TE tunnels. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Based on your requirements, you can configure LSP attributes lists with different sets of attributes for different path options. LSP attribute lists also provide an easy way to configure multiple TE tunnels to use the same LSP attributes. You can reference the same LSP attribute list to configure LSP–specific parameters for one or more TE tunnels.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 | Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | tunnel destination {hostname | ip-address} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 209.165.200.225 | Specifies the destination of the tunnel for this path option. |
| Step 5 | tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng | Sets the encapsulation mode for the tunnel for MPLS TE. |
| Step 6 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce | (Optional) Specifies that the IGP should use the tunnel (if the tunnel is up) in its enhanced shortest path first (SPF) calculation. |
| Step 7 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth kbps Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng global bandwidth 1000 | Configures the bandwidth required for a MPLS TE tunnel and assigns it to the global pool. The kbps argument is the bandwidth, in kilobits per second, set aside for the MPLS TE tunnel. The valid range is from 1 to 4294967295 kbps. |
| Step 8 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority setup-priority [hold-priority] Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 1 1 | Sets the priority to be used when the system determines which existing tunnels are eligible to be preempted.
|
| Step 9 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option number {dynamic | explicit {name path-name | path-number} [verbatim]} [attributes string] [bandwidth global] kbps] [lockdown] Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 dynamic attributes 1 | Adds an LSP attribute list to specify LSP-related parameters for path options for an MPLS TE tunnel.
|
| Step 10 | end Example: Router(config)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 11 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Associate an LSP Attribute List with a Path Option for an MPLS TE Tunnel
The following example shows how to associate the LSP attribute list identified by the numeral 3 with path option 1:
Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 3 Router(config-lsp-attr)# bandwidth 1000 Router(config-lsp-attr)# priority 2 2 Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit ! ! Router(config)# interface Tunnel 1 Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered TenGigabitEthernet4/1 Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 10.112.0.12 Router(config-if)# tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng affinity 1 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 5000 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 dynamic attributes 3
DLP-J147 Configure an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures a label switched path (LSP) attribute list with the desired attributes to be applied on a path option. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Based on your requirements, you can configure LSP attributes lists with different sets of attributes for different path options.
LSP attribute lists also provide an easy way to configure multiple TE tunnels to use the same LSP attributes. That is, you can reference the same LSP attribute list to configure LSP–specific parameters for one or more TE tunnels.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes string Example:Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1 | Configures an LSP attribute list and enters LSP Attributes configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | affinity value [mask value] Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# affinity 0 mask 0 | (Optional) Specifies the attribute flags for links comprising an LSP. |
| Step 5 | auto-bw [frequency secs] [max-bw kbps] [min-bw kbps] [collect-bw] Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# auto-bw | (Optional) Specifies the automatic bandwidth configuration.
|
| Step 6 | bandwidth global kbps Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# bandwidth global 5000 | (Optional) Specifies the LSP bandwidth. |
| Step 7 | list Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# list | (Optional) Displays the contents of the LSP attribute list. |
| Step 8 | lockdown Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# lockdown | (Optional) Disables reoptimization of the LSP. |
| Step 9 | priority setup-priority [hold-priority] Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# priority 1 1 | (Optional) Specifies the LSP priority.
|
| Step 10 | record-route Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# record-route | (Optional) Records the route used by the LSP. |
| Step 11 | no sub-command Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# no record-route | (Optional) Removes a specific attribute from the LSP attributes list. |
| Step 12 | exit Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit | (Optional) Exits from LSP attributes configuration mode. |
| Step 13 | end Example:Router(config)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 14 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Configure an LSP Attribute List
This example shows how to configure the affinity, bandwidth, and priority LSP-related attributes in an LSP attribute list identified with the numeral 1:
Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# affinity 7 7 Router(config-lsp-attr)# bandwidth 1000 Router(config-lsp-attr)# priority 1 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit
DLP-J148 Modify an Attribute in an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure modifies an attribute in an LSP attribute list. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
The LSP attribute list provides a flexible user interface that can be extended or modified an any time to meet the requirements of your MPLS TE tunnel traffic. LSP Attributes configuration mode is used to display the specific LSP attributes list and to modify the required path option attribute.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes string Example:Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1 | Configures an LSP attribute list and enters LSP Attributes configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | affinity value [mask value] Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# affinity 1 mask 1 | Specifies the attribute flags for links comprising an LSP. |
| Step 5 | list Example: Router(config-lsp-attr)# list | (Optional) Displays the contents of the LSP attribute list. |
| Step 6 | exit Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit | (Optional) Exits LSP Attributes configuration mode. |
| Step 7 | end Example:Router(config)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Modify an Attribute in an LSP Attribute List
The following example shows how to modify the bandwidth in an LSP attribute list identified by the numeral 5:
Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 5 Router(config-lsp-attr)# bandwidth 1000 Router(config-lsp-attr)# priority 1 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# list
LIST 5 bandwidth 1000 priority 1 1
Router(config-lsp-attr)# bandwidth 500 Router(config-lsp-attr)# list
LIST 5 bandwidth 500 priority 1 1
Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit
DLP-J149 Remove an Attribute from an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure removes an attribute from an LSP attribute list. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
The LSP attributes list provides a means to easily remove a path option attribute that is not required for your MPLS TE tunnel traffic. The LSP Attributes configuration mode is used to display the specific LSP attribute list and for the no sub-command command, which is used to remove the specific attribute from the list. Replace the sub-command argument with the command that you want to remove from the list.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes string Example:Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1 | Configures an LSP attribute list and enters LSP Attributes configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | no sub-command Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# no priority | Removes a specific attribute from the LSP attribute list. |
| Step 5 | list Example: Router(config-lsp-attr)# list | (Optional) Displays the contents of the LSP attribute list. |
| Step 6 | exit Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit | (Optional) Exits LSP Attributes configuration mode. |
| Step 7 | end Example:Router(config)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Remove an Attribute from an LSP Attribute List
The following example shows how to remove the priority attribute from the LSP attribute list identified by the string simple:
Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes simple Router(config-lsp-attr)# priority 1 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# list
LIST simple priority 1 1 ! Router(config-lsp-attr)# no priority Router(config-lsp-attr)# list
LIST simple
!
Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit
DLP-J150 Delete an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure deletes an LSP attribute list. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Perform this task when you no longer require the LSP attribute path options specified in the LSP attribute list for an MPLS TE tunnel.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | no mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes string Example:Router(config)# no mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1 | Removes a specified LSP attribute list from the device configuration. |
| Step 4 | end Example:Router(config)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 5 | show mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes [name string] [internal] Example: Router# show mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes | (Optional) Displays information about configured LSP attribute lists. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Delete an LSP Attribute List
The following example shows how to delete an LSP attribute list identified by numeral 1:
Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# affinity 7 7 Router(config-lsp-attr)# bandwidth 1000 Router(config-lsp-attr)# priority 1 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit ! Router(config)# no mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1
DLP-J151 Verify Attributes Within an LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure verifies the attributes within an LSP attribute list. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes stringlist Example:Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1 list | Enters LSP Attributes configuration mode for a specific LSP attribute list and verifies that the contents of the attributes list are as expected. |
| Step 4 | exit Example:Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit | Exits LSP Attributes configuration mode. |
| Step 5 | end Example: Router(config)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J152 Verify All LSP Attribute Lists Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure verifies all the configured LSP attribute lists. Use this procedure to display all LSP attribute lists to verify that the attributes lists that you configured are in operation. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | show mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes [name string] [internal] Example:Router# show mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes | Verifies that all the configured LSP attribute lists are as expected. |
| Step 3 | show running-config | begin text-string Example:Router# show running-config | begin mpls traffic-eng lsp | Verifies that all the configured LSP attribute lists are as expected. Use the begin command modifier with the mpls traffic-eng lsp text-string to locate the LSP attributes information in the configuration file. |
| Step 4 | exit Example:Router# exit | Exits user EXEC mode. |
| Step 5 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Understanding MPLS–TE Verbatim Path Support
The MPLS Traffic Engineering–Verbatim Path Support feature allows network nodes to support RSVP extensions without supporting IGP extensions for TE, thereby bypassing the topology database verification process.
MPLS TE LSPs usually require that all the nodes in the network are TE aware, meaning they have IGP extensions to TE in place. However, some network administrators want the ability to build TE LSPs to traverse nodes that do not support IGP extensions to TE, but that do support RSVP extensions to TE.
Verbatim LSPs are helpful when all or some of the intermediate nodes in a network do not support IGP extensions for TE.
When this feature is enabled, the IP explicit path is not checked against the TE topology database. Because the TE topology database is not verified, a Path message with IP explicit path information is routed using the shortest path first (SPF) algorithm for IP routing.
- NTP-J50 Configure MPLS-TE Verbatim Path Support
- DLP-J153 Configure MPLS TE–Verbatim Path Support Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J154 Verify Verbatim LSPs for MPLS TE Tunnels Using Cisco IOS Commands
NTP-J50 Configure MPLS-TE Verbatim Path Support
| Purpose | This procedure configures verbatim path support for MPLS–TE tunnels. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J153 Configure MPLS TE–Verbatim Path Support Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures MPLS traffic engineering–verbatim path support. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | interface tunnel number Example:Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 | Enters interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 4 | ip unnumbered loopback number Example: Router(config–if)# ip unnumbered loopback 1 | Configures an unnumbered IP interface, which enables IP processing without an explicit address. A loopback interface is usually configured with the router ID.
| ||
| Step 5 | tunnel destination {host–name | ip–address} Example:Router(config–if)# tunnel destination 10.100.100.100 | Specifies the destination for a tunnel. | ||
| Step 6 | tunnel mode mpls traffic–eng Example: Router(config–if)# tunnel mode mpls traffic–eng | Sets the tunnel encapsulation mode to MPLS traffic engineering. | ||
| Step 7 | tunnel mpls traffic–eng bandwidth kbps Example:Router(config–if)# tunnel mpls traffic–eng bandwidth 1000 | Configures the bandwidth required for an MPLS TE tunnel and assigns it to the global pool. | ||
| Step 8 | tunnel mpls traffic–eng autoroute announce Example:Router(config–if)# tunnel mpls traffic–eng autoroute announce | Specifies that IGP must use the tunnel (if the tunnel is up) in its enhanced SPF calculation. | ||
| Step 9 | tunnel mpls traffic–eng priority setup–priority [hold–priority] Example:Router(config–if)# tunnel mpls traffic–eng priority 1 1 | Configures the setup and reservation priority for a tunnel.
| ||
| Step 10 |
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option {number {dynamic [attributes lsp-attributes | bandwidth kbps] [lockdown] | lockdown [bandwidth kbps] | explicit {identifier path-number | name path-name} [attributes lsp-attributes [verbatim]] | bandwidth kbps [lockdown] [verbatim]] | lockdown bandwidth kbps [verbatim] | verbatim bandwidth kbps [lockdown]}} Example: Router(config–if)# tunnel mpls traffic–eng path–option 1 explicit name test verbatim | Specifies LSP–related parameters, including the verbatim keyword used with an explicit path option, for a MPLS TE tunnel. | ||
| Step 11 | end Example:Router(config)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 12 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Configure MPLS TE—Verbatim Path Support
The following example shows how to configure a tunnel with an explicit path option using verbatim.
interface tunnel 1 ip unnumbered loopback 1 tunnel destination 10.10.100.100 tunnel mode mpls traffic–eng tunnel mpls traffic–eng bandwidth 1000 tunnel mpls traffic–eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic–eng priority 1 1 tunnel mpls traffic–eng path–option 1 explicit name path1 verbatim
DLP-J154 Verify Verbatim LSPs for MPLS TE Tunnels Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure verifies the verbatim option that is configured for the LSPs for MPLS TE tunnels. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel-interfacenumber [brief] Example:Router# show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel1 | Displays information about tunnels including those configured with an explicit path option using verbatim. |
| Step 3 | disable Example:Router# disable | (Optional) Exits to user EXEC mode. |
| Step 4 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Verify Verbatim LSPs for MPLS TE Tunnels
In the following example, the show mpls traffic-eng tunnels command displays tunnel information, including whether the explicit path option is using verbatim, and the Active Path Options parameters that show the status of verbatim.
Router# show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel100
Name: R259_t5 (Tunnel100) Destination: 192.168.30.1
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 1, type explicit (verbatim) path1 (Basis for Setup, path weight 0)
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 100 kbps (Global) Priority: 1 1 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: explicit path option 1 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: enabled
Understanding MPLS–TE Path Protection
Path protection provides an end–to–end failure recovery mechanism (that is, full path protection) for MPLS–TE tunnels. A secondary LSP is established to provide failure protection for the protected LSP that is carrying a tunnel TE traffic. When there is a failure on the protected LSP, the headend router immediately enables the secondary LSP to temporarily carry the tunnel traffic. If there is a failure on the secondary LSP, the tunnel does not have the path protection until the failure along the secondary path is cleared.
The failure detection mechanisms that trigger a switchover to a secondary tunnel include the following:
Path error from RSVP signaling
Notification from the RSVP hello that a neighbor is lost
Notification from the IGP that the adjacency is down
Local teardown of the LSP of the protected tunnel due to preemption to signal higher priority LSPs, online insertion and removal (OIR), and so forth
Presignaling a secondary LSP is faster than configuring a secondary primary path option or allowing the tunnel headend router to dynamically recalculate a path. The actual recovery time is topology dependent, and affected by delay factors such as propagation delay or switch fabric latency.
Prerequisites
Ensure that your network supports MPLS TE, Cisco Express Forwarding, or OSPF.
Enable MPLS.
Configure TE on the routers.
Configure a TE tunnel with a primary path option by using the tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option command.
If your router supports stateful switchover (SSO), configure RSVP Graceful Restart in full mode on the routers.
If your router supports SSO, you must have configured SSO on the device for Cisco Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) operation.
Restrictions
Enhanced Path Protection
Enhanced path protection provides support of multiple backup path options for each primary path option. You can configure up to eight backup path options for a given primary path option. Only one of the configured backup path options is actively signaled at any time.
After you enter the mpls traffic-eng path-option list command, you can enter the backup path priority in the number argument of the path-option command. A lower identifier represents a higher priority. Priorities are configurable for each backup path option. Multiple backup path options and a single backup path option cannot coexist to protect a primary path option.
Benefits of MPLS-TE Protection
The following sections describe the benefits of MPLS-TE protection.
Multiple Backup Tunnels Protecting the Same Interface
There is no limit (except memory limitations) to the number of backup tunnels that can protect a given interface. In many topologies, support for node protection requires supporting multiple backup tunnels per protected interface.
The multiple backup tunnels provides the following benefits:
Redundancy—If one backup tunnel is down, other backup tunnels protect LSPs.
Increased backup capacity—If the protected interface is a high-capacity link and no single backup path exists with an equal capacity, multiple backup tunnels can protect that one high-capacity link. The LSPs using this link will fail over to different backup tunnels, allowing all of the LSPs to have adequate bandwidth protection during failure (rerouting). If bandwidth protection is not desired, the router spreads LSPs across all available backup tunnels (that is, load balancing is available across the backup tunnels).
RSVP Hello
RSVP Hello allows a router to detect when its neighbor has gone down but its interface to that neighbor is still operational. When Layer 2 link protocols are unable to detect that the neighbor is unreachable, hellos provide the detection mechanism; this allows the router to switch LSPs onto its backup tunnels and avoid packet loss.
- NTP-J51 Configure MPLS-TE Path Protection
- DLP-J155 Create a Path Option List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J157 Assign a Secondary Path Option to Protect a Primary Path Option Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J158 Configure Fallback Bandwidth Path Options for TE Tunnels Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J159 Modify the Bandwidth on a Path Option for Bandwidth Override Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J160 Modify a Path Option to Use a Different LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J161 Remove a Path Option for Bandwidth Override Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J162 Remove a Path Option for a LSP in a MPLS TE Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
NTP-J51 Configure MPLS-TE Path Protection
| Purpose | This procedure configures path protection for MPLS–TE tunnels. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J155 Create a Path Option List Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure creates a path option list of backup paths for a primary path option. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | To use a secondary path instead, see the DLP-J169 Configure Explicit Paths for Secondary Paths Using Cisco IOS Commands. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | mpls traffic-eng path-option list [name pathlist-name | identifier pathlist-number] Example:Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng path-option list name pathlist-01 | Configures a path option list, and enters path-option list configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | path-option number explicit [name pathoption-name | identifier pathoption-number]
Example:Router(cfg-pathoption-list)# path-option 10 explicit identifier 200 | (Optional) Specifies the name or identification number of the path option to add, edit, or delete. The pathoption-number value range is from 1 to 65535. |
| Step 5 | list Example: Router(cfg-pathoption-list)# list | (Optional) Lists all the path options. |
| Step 6 | no [pathoption-name | pathoption-number] Example:Router(cfg-pathoption-list)# no 10 | (Optional) Deletes a specified path option. |
| Step 7 | exit Example:Router(cfg-pathoption-list)# exit | (Optional) Exits path-option list configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Create a Path Option List
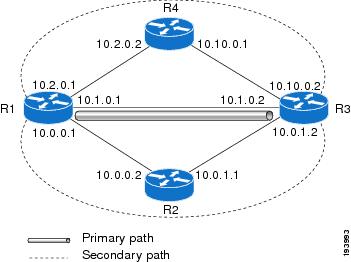
The following example shows how to configure two explicit paths named secondary1 and secondary2.
Router(config)# ip explicit-path name secondary1 Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# index 1 next 10.0.0.2 Explicit Path name secondary1: 1: next-address 10.0.0.2 Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# index 2 next 10.0.1.2 Explicit Path name secondary1: 1: next-address 10.0.0.2 2: next-address 10.0.1.2 Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# ip explicit-path name secondary2 Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# index 1 next 10.2.0.2 Explicit Path name secondary2: 1: next-address 10.2.0.2 Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# index 2 next 10.10.0.2 Explicit Path name secondary2: 1: next-address 10.2.0.2 2: next-address 10.10.0.2 Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# exit
The following example shows how to create a path option list of backup paths. You can define the path option list by using the explicit paths.
Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng path-option list name pathlist-01 Router(cfg-pathoption-list)# path-option 10 explicit name secondary1 path-option 10 explicit name secondary1 Router(cfg-pathoption-list)# path-option 20 explicit name secondary2 path-option 10 explicit name secondary1 path-option 20 explicit name secondary2 Router(cfg-pathoption-list)# exit
DLP-J157 Assign a Secondary Path Option to Protect a Primary Path Option Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure assigns a secondary path option to protect a primary path option using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Assign a secondary path option if there is a link or node failure along a path and all the interfaces in the network are not protected.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface tunnelnumber Example:Router(config)# interface tunnel500 | Configures a tunnel interface and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 |
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option protect {number {dynamic [attributes lsp-attributes | bandwidth kbps] [lockdown] | lockdown [bandwidth kbps] | explicit {identifier path-number | name path-name} [attributes lsp-attributes [verbatim]] | bandwidth kbps [lockdown] [verbatim]] | lockdown bandwidth kbps [lockdown] [verbatim] | verbatim [lockdown]]} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option protect 10 explicit name path344 | Configures a secondary path option for a MPLS TE tunnel. |
| Step 5 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | (Optional) Exits interface configuration mode and enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Assign a Secondary Path Option to Protect a Primary Path Option
The following example shows how to configure a traffic engineering tunnel.
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config-if)# interface tunnel500 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option protect 10 explicit name path344
The following show running interface command output shows that path protection has been configured. Tunnel 500 has path option 10 using path344 and protected by path3441, and path option 20 using path345 and protected by path348.
Router# show running interface tunnel500
Building configuration... Current configuration : 497 bytes ! interface Tunnel500 ip unnumbered Loopback0 tunnel destination 10.0.0.9 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 7 7 tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 100 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit name path344 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 20 explicit name path345 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option protect 10 explicit name path3441 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option protect 20 explicit name path348 end
DLP-J158 Configure Fallback Bandwidth Path Options for TE Tunnels Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures the fallback bandwidth path options for a TE tunnel. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Use this procedure to configure path options that reduce the bandwidth constraint each time the headend of a tunnel fails to establish an LSP.
Configuration of the Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature can reduce bandwidth constraints on path options temporarily and improve the chances to set up an LSP for the TE tunnel. When a TE tunnel uses a path option with bandwidth override, the traffic engineering attempts every 30 seconds to reoptimize the tunnel to use the preferred path option with the original configured bandwidth. The Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature is designed as a temporary reduction in bandwidth constraint. To force immediate reoptimization of all traffic engineering tunnels, you can use the mpls traffic-eng reoptimize command. You can also configure the lockdown command with bandwidth override to prevent automatic reoptimization.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 | Configures the interface type and enters the interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | tunnel destination {hostname | ip-address} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 209.165.200.225 | Specifies the destination of the tunnel for this path option. |
| Step 5 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option number {dynamic | explicit {name path-name | path-number} [verbatim] [attributes string] [bandwidth global] kbps] }[lockdown] Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 dynamic bandwidth 500 | Adds a path option for bandwidth override to specify a bandwidth fallback for a path option for an MPLS TE tunnel.
|
| Step 6 | end Example:Router(config-if)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 7 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Configure Fallback Bandwidth Path Options for TE Tunnels
The following example shows how to configure the multiple path options with the tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option command:
interface Tunnel 1 ip unnumbered Loopback0 tunnel destination 10.10.10.12 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 1 1 tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 1000 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit name path1 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 2 explicit name path2 bandwidth 500 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 3 dynamic bandwidth 0 end
The device selects a path option for an LSP in the following order of preference:
The device attempts to signal an LSP using path options starting with path-option 1.
The device attempts to signal an LSP with the 1000 kbps bandwidth configured on the tunnel interface because path-option 1 has no bandwidth configured.
If 1000 kbps bandwidth is not available over the network, the device attempts to establish an LSP using path-option 2.
Path-option 2 has a bandwidth of 500 kbps configured. This reduces the bandwidth constraint from the original 1000 kbps configured on the tunnel interface.
If 500 kbps is not available, the device attempts to establish an LSP using path-option 3.
Path-option 3 is configured as dynamic and has bandwidth 0. The device establishes the LSP if an IP path exists to the destination and all other tunnel constraints are met.
DLP-J159 Modify the Bandwidth on a Path Option for Bandwidth Override Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure modifies the bandwidth on a path option for bandwidth override. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
You might need to further reduce or modify the bandwidth constraint for a path option to ensure that the headend of a tunnel establishes an LSP.
The Path Option for Bandwidth Override feature is designed as a temporary reduction in bandwidth constraint. To force immediate reoptimization of all traffic engineering tunnels, you can use the mpls traffic-eng reoptimize command. You can also configure the lockdown command with bandwidth override to prevent automatic reoptimization.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 | Configures the interface type and enters the interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | tunnel destination {hostname | ip-address} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 209.165.200.225 | Specifies the destination of the tunnel for this path option. |
| Step 5 |
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option {number {dynamic [attributes lsp-attributes | bandwidth kbps] [lockdown] | lockdown [bandwidth kbps] | explicit {identifier path-number | name path-name} [attributes lsp-attributes [verbatim]] | bandwidth kbps [lockdown] [verbatim]] | lockdown bandwidth kbps [verbatim] | verbatim bandwidth kbps [lockdown]}} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 2 dynamic bandwidth 500 | Adds a path option for bandwidth override to specify a bandwidth fallback for a path option for an MPLS TE tunnel. |
| Step 6 | end Example:Router(config-if)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 7 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Modify the Bandwidth on a Path Option for Bandwidth Override
The following example shows how to modify the bandwidth on a path option for bandwidth override. Path-option 3 is changed to an explicit path with a bandwidth of 100 kbps. Path-option 4 is configured with bandwidth 0.
interface Tunnel 1 ip unnumbered Loopback0 tunnel destination 10.10.10.12 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 1 1 tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 1000 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit name path1 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 2 explicit name path2 bandwidth 500 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 3 dynamic bandwidth 0 ! ! Router(config)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 3 explicit name path3 bandwidth 100 Router(config)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 4 dynamic bandwidth 0
DLP-J160 Modify a Path Option to Use a Different LSP Attribute List Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure modifies the path option to use a different LSP attribute list. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Based on your requirements, you can configure LSP attributes lists with different sets of attributes for different path options or change the set of attributes associated with a path option. Use the tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option number dynamic attributes string command in interface configuration mode to modify the path option to use a different LSP attribute list. The attributes keyword and string argument combination names the new LSP attribute list for the path option specified.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 | Configures the interface type and enters the interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | tunnel destination {hostname | ip-address} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 209.165.200.225 | Specifies the destination of the tunnel for this path option. |
| Step 5 |
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option {number {dynamic [attributes lsp-attributes | bandwidth kbps] [lockdown] | lockdown [bandwidth kbps] | explicit {identifier path-number | name path-name} [attributes lsp-attributes [verbatim]] | bandwidth kbps [lockdown] [verbatim]] | lockdown bandwidth kbps [verbatim] | verbatim bandwidth kbps [lockdown]}} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 dynamic attributes 1 | Adds an LSP attribute list to specify LSP-related parameters for a path options for an MPLS TE tunnel. |
| Step 6 | end Example:Router(config-if)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 7 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Modify a Path Option to Use a Different LSP Attribute List
The following example shows how to modify the path option 1 to use an LSP attribute list identified by the numeral 1:
Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# affinity 7 7 Router(config-lsp-attr)# bandwidth 500 Router(config-lsp-attr)# priority 1 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit
Router(config)# mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes 2 Router(config-lsp-attr)# bandwidth 1000 Router(config-lsp-attr)# priority 1 1 Router(config-lsp-attr)# exit
Router(config)# interface Tunnel 1 Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered TenGigabitEthernet4/1 Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 10.112.0.12 Router(config-if)# tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng affinity 1 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 5000 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 dynamic attributes 1
DLP-J161 Remove a Path Option for Bandwidth Override Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure removes the bandwidth on the path option for bandwidth override. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 | Configures the interface type and enters the interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | tunnel destination {hostname | ip-address} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 209.165.200.225 | Specifies the destination of the tunnel for this path option. |
| Step 5 |
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option {number {dynamic [attributes lsp-attributes | bandwidth kbps] [lockdown] | lockdown [bandwidth kbps] | explicit {identifier path-number | name path-name} [attributes lsp-attributes [verbatim]] | bandwidth kbps [lockdown] [verbatim]] | lockdown bandwidth kbps [verbatim] | verbatim bandwidth kbps [lockdown]}} Example:Router(config-if)# no tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 2 dynamic bandwidth 500 | Removes a path option for bandwidth override that specifies a bandwidth fallback for a path option for an MPLS TE tunnel. |
| Step 6 | end Example:Router(config-if)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 7 | show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel-interface [brief] Example:Router# show mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel1 | (Optional) Displays information about tunnels. |
| Step 8 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Remove a Path Option for Bandwidth Override
The following example shows how to remove a path option for bandwidth override:
Router(config)# interface Tunnel 1 Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered loopback0 Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 10.10.10.12 Router(config-if)# tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 1 1 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 1000 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit name path1 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 2 explicit name path2 bandwidth 500 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 3 explicit name path3 bandwidth 100 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 4 dynamic bandwidth 0 ! Router(config-if)# no tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 3 explicit name path3 bandwidth 100
DLP-J162 Remove a Path Option for a LSP in a MPLS TE Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure removes a path option for a LSP in a MPLS TE tunnel. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Use this task to remove a path option for a LSP when your MPLS TE tunnel traffic requirements change.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 | Configures the interface type and enters the interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | tunnel destination {hostname | ip-address} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 209.165.200.225 | Specifies the destination of the tunnel for this path option. |
| Step 5 | no tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option number {dynamic | explicit {name path-name | path-number} [verbatim]} [attributes string] [bandwidth global] kbps] [lockdown] Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 dynamic attributes 1 | Removes an LSP attribute list that specifies LSP-related parameters for a path option for an MPLS TE tunnel. |
| Step 6 | end Example:Router(config-if)# end | (Optional) Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 7 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Remove a Path Option for a LSP in a MPLS TE Tunnel
The following example shows how to remove the path option 1 for an LSP in a TE tunnel:
Router(config)# interface Tunnel 1 Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered TenGigabitEthernet4/1 Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 10.112.0.12 Router(config-if)# tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng affinity 1 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 5000 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit path1 attributes 1 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 2 explicit path2 attributes 2 ! ! Router(config-if)# no tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit path1 attributes 1
Understanding MPLS–TE Tunnels
MPLS TE enables you to build LSPs across your network for forwarding traffic.
MPLS TE LSPs let the headend of a TE tunnel control the path its traffic takes to a particular destination. This method is more flexible than forwarding traffic based only on a destination address.
Interarea tunnels allow you to build:
TE tunnels between areas (interarea tunnels).
TE tunnels that start and end in the same area, on multiple areas on a router (intra–area tunnels).
Some tunnels are more important than others. For example, you may have tunnels carrying VoIP traffic and tunnels carrying data traffic that are competing for the same resources. You may have certain data tunnels that are more important than others. MPLS TE allows you to have some tunnels preempt others. Each tunnel has a priority, and more important tunnels take precedence over less important tunnels.
- NTP-J51 Configure MPLS-TE Tunnels
- DLP-J163 Create a MPLS-TE Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J164 Enable Automatic Bandwidth Adjustment for a Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J165 Configure MPLS–TE–Tunnel Source Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP–J166 Create an MPLS–TE Tunnel Using CTC
- DLP-J167 Edit an MPLS–TE Tunnel Using CTC
NTP-J51 Configure MPLS-TE Tunnels
| Purpose | This procedure configures MPLS–TE tunnels. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J163 Create a MPLS-TE Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure creates a MPLS-TE tunnel using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | interface tunnel number Example: Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 | Configures a tunnel interface and enters interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 4 | ip unnumbered interface-type interface-number Example:Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered loopback 0 | Gives the tunnel interface an IP address that is the same as that of interface loopback0. An MPLS TE tunnel interface must be unnumbered because it represents a unidirectional link. This command is not effective until loopback0 has been configured with an IP address. | ||
| Step 5 | tunnel destination ip-address Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 209.165.200.225 | Specifies the destination for a tunnel. The destination must be the MPLS TE router id of the destination device. | ||
| Step 6 | tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng | Sets the encapsulation mode of the tunnel to MPLS TE. | ||
| Step 7 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth kbps Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 250 | Configures the bandwidth for the MPLS TE tunnel.
| ||
| Step 8 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option [protect] preference-number {dynamic | explicit | {name path-name | path-number}} [lockdown] Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 explicit test | Configures the tunnel to use a named IP explicit path or a path dynamically calculated from the TE topology database. A dynamic path is used if an explicit path is currently unavailable. | ||
| Step 9 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Exits to global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 10 | exit Example:Router(config)# exit | Exits to privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 11 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J164 Enable Automatic Bandwidth Adjustment for a Tunnel Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure enables automatic bandwidth adjustment for a tunnel and constrains the range of automatic bandwidth adjustments applied to the tunnel. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example: Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface tunnel-number Example:Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 | Configures a tunnel interface and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng auto-bw [collect-bw] [frequency seconds] [max-bw kbps] [min-bw kbps] Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng auto-bw max-bw 2000 min-bw 1000 | Enables automatic bandwidth adjustment for the tunnel and controls the manner in which the bandwidth for a tunnel is adjusted. |
| Step 5 | exit Example:Router(config-if)# exit | Exits to global configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | exit Example:Router(config)# exit | Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 7 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Tunnel Configuration for Automatic Bandwidth
The following example shows how to use the tunnel mpls traffic-eng auto-bw command to enable automatic bandwidth adjustment for Tunnel 1. The command specifies a maximum allowable bandwidth of 2000 kbps, a minimum allowable bandwidth of 1000 kbps, and the default automatic bandwidth adjustment frequency of once a day, be used.
interface tunnel1 ip unnumbered loopback 0 tunnel destination 192.168.17.17 tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 1500 tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 1 1 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 dynamic tunnel mpls traffic-eng auto-bw max-bw 2000 min-bw 1000
DLP-J165 Configure MPLS–TE–Tunnel Source Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure specifies a tunnel source for an MPLS TE tunnel using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
You can configure the tunnel source as an IP address or as an interface. If you configure the tunnel source as an interface, then you must configure an IP address for the interface.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface type number Example:Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 | Configures a tunnel interface and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | ip unnumbered interface-name interface-number Example:Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered loopback0 | Configures an unnumbered IP interface, which enables IP processing without an explicit address. An MPLS TE tunnel interface must be unnumbered because it represents a unidirectional link. |
| Step 5 | no ip directed-broadcast Example:Router(config-if)# no ip directed-broadcast | Disables the translation of a directed broadcast to physical broadcasts. |
| Step 6 | tunnel source {ip-address | interface-type interface-number} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel source loopback1 | Configures the tunnel source. |
| Step 7 | tunnel destination {host-name | ip-address} Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 192.168.2.1 | Specifies the destination for a tunnel. The destination must be the MPLS TE router ID of the destination device. |
| Step 8 | tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng Example: Router(config-if)# tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng | Sets the encapsulation mode of the tunnel to MPLS TE. |
| Step 9 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority setup-priority [hold-priority] Example: Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 1 1 | Sets the priority to be used when the system determines which existing tunnels are eligible to be preempted.
|
| Step 10 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth bandwidth Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 5000 | Configures the bandwidth for the MPLS traffic engineering tunnel. |
| Step 11 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng affinity affinity-value mask mask-value Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng affinity 0x0 mask 0x0 | Configures the properties an MPLS TE tunnel requires in its links. |
| Step 12 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option number explicit name explicit-path-name Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit name best-way | Configures a path option for an MPLS TE tunnel. |
| Step 13 | tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce Example:Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce | Causes the IGP to use the tunnel in its enhanced shortest path first (SPF) calculation. |
| Step 14 | end Example:Router(config-if)# end | Exits interface configuration modes and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 15 | show ip rsvp sender Example:Router# show ip rsvp sender | Displays the IP address used as the source for tunnel control traffic. |
| Step 16 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Configure MPLS TE–Tunnel Source
The output of the show running-config command displays the tunnel source configuration. If the tunnel source command is not configured, the IP address specified in the IGP command mpls traffic-eng router-id is used.
Router# show running-configBuilding configuration... Current configuration: 3969 bytes ! !
Router(config)# interface Tunnel1 Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered loopback0 Router(config-if)# tunnel source loopback1 Router(config-if)# tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 192.168.2.1 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 1 1 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 5000 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng affinity 0x0 mask 0x0 Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit name BEST-WAY Router(config-if)# tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce
DLP–J166 Create an MPLS–TE Tunnel Using CTC
| Purpose |
This procedure creates an MPLS–TE tunnel using CTC. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | You cannot create an MPLS–TE tunnel and an MPLS–TP tunnel on the same interface. |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to create an MPLS–TE tunnel. |
| Step 2 | From the View menu, choose Go to Network View. |
| Step 3 | Click the Layer2+ tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click Circuits. |
| Step 5 | Click the MPLS TE Tunnels tab. |
| Step 6 | Click Create. The Circuit Creation wizard appears. |
| Step 7 | In the Circuit
Attributes screen of the wizard:
|
| Step 8 | In the Source screen of the wizard, choose the source node from the Node drop–down list. |
| Step 9 | In the Tunnel
Attributes area of the Source screen:
|
| Step 10 | Click the
Path
Option Configuration link. The Path Options dialog box appears. To
configure a primary path for an MPLS TE tunnel:
|
| Step 11 | In the Path
Protection area of the Source screen, specify the following to configure a
secondary path for a MPLS TE tunnel:
|
| Step 12 | In the Destination
screen of the Circuit Creation wizard, specify the following:
|
| Step 13 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
DLP-J167 Edit an MPLS–TE Tunnel Using CTC
| Purpose |
This procedure edits an MPLS–TE tunnel. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | DLP–J166 Create an MPLS–TE Tunnel Using CTC |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to edit an MPLS–TE tunnel. |
| Step 2 | From the View menu, choose Go to Network View. |
| Step 3 | Click the Layer2+ tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click Circuits. |
| Step 5 | Click the MPLS TE Tunnels tab. The list of MPLS–TE tunnels appear. |
| Step 6 | Select a tunnel to edit. |
| Step 7 | Click
Edit. The Tunnel Edit dialog box appears that
displays the network map.
The nodes in the network map are the nodes, the ports are the ports, links between the nodes are L2 PPC or OchTrail tunnel links. The unmanaged nodes are not displayed in the network map. |
| Step 8 | Click the General tab. |
| Step 9 | Modify the values of parameters such as name, description, and admin state as required. |
| Step 10 | Click Apply to save the configuration. |
| Step 11 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
Understanding Explicit Path
You can configure multiple path options for a single tunnel. For example, there can be several explicit path options and a dynamic option for one tunnel.
If you specify the dynamic keyword, the software checks both the physical bandwidth of the interface and the available TE bandwidth to be sure that the requested amount of bandwidth does not exceed the physical bandwidth of any link. To oversubscribe links, you must specify the explicit keyword. If you use the explicit keyword, the software only checks how much bandwidth is available on the link for TE; the amount of bandwidth you configure is not limited to how much physical bandwidth is available on the link.
- NTP-J52 Configure Explicit Paths
- DLP-J168 Create an Explicit Path Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J169 Configure Explicit Paths for Secondary Paths Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J170 Create an Explicit Path Using CTC
NTP-J52 Configure Explicit Paths
| Purpose | This procedure configures explicit paths. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
Stop. You have completed this procedure. |
DLP-J168 Create an Explicit Path Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure creates an explicit path using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ip explicit-path {name path-name | identifier number} [enable | disable] Example:Router(config)# ip explicit-path name path-tunnel1 | Enters IP explicit path configuration mode and creates or modifies the specified path. |
| Step 4 | next-address [loose | strict] ip-address Example:Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# next-address loose 192.168.40.40 | Specifies the next IP address in the explicit path. |
| Step 5 | end Example:Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
DLP-J169 Configure Explicit Paths for Secondary Paths Using Cisco IOS Commands
| Purpose | This procedure configures the explicit paths for secondary paths using Cisco IOS commands. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite or remote |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
This procedure configures an explicit path. Use this procedure to specify a secondary path that does not include common links or nodes associated with the primary path in case those links or nodes go down.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example:Router> enable | Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example:Router# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ip explicit-path {name path-name | identifier number} [enable | disable] Example:Router(config)# ip explicit-path name path3441 enable | Creates or modifies the explicit path and enters IP explicit path configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | index index next-address [loose | strict] ip-address Example:Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# index 1 next-address 10.0.0.1 | Inserts or modifies a path entry at a specific index. The IP address represents the node ID. |
| Step 5 | exit Example: Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# exit | Exits IP explicit path configuration mode and enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). | — |
Example: Configure Explicit Paths for Secondary Paths
In the following example, the explicit path is named path3441. There is an index command for each router. If there is failure, the secondary path is used.
Router(config)# ip explicit-path name path3441 enable Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# index 1 next 10.0.0.1 Explicit Path name path3441: 1: next-address 10.0.0.1 Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# index 2 next 10.0.0.2 Explicit Path name path3441: 1: next-address 10.0.0.1 2: next-address 10.0.0.2 Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# index 3 next 10.0.1.1 Explicit Path name path3441: 1: next-address 10.0.0.1 2: next-address 10.0.0.2 3: next-address 10.0.1.1 Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# index 4 next 10.0.1.2 Explicit Path name path3441: 1: next-address 10.0.0.1 2: next-address 10.0.0.2 3: next-address 10.0.1.1 4: next-address 10.0.1.2 Router(cfg-ip-expl-path)# exit
DLP-J170 Create an Explicit Path Using CTC
| Purpose |
This procedure creates an explicit path. |
| Tools/Equipment | None |
| Prerequisite Procedures | None |
| Required/As Needed | As needed |
| Onsite/Remote | Onsite |
| Security Level | Provisioning or higher |
 Note | The secondary path for an MPLS TE tunnel can be only an explicit path and not a dynamic path. |
| Step 1 | Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node on the network where you want to create an explicit path. |
| Step 2 | From the View menu, choose Go to Network View. |
| Step 3 | Click the Layer2+ tab. |
| Step 4 | From the left pane, click Provisioning. |
| Step 5 | Click Explicit Paths. |
| Step 6 | Click Create. The Create Explicit Path dialog box appears that displays the network map. |
| Step 7 | Enter the name for the explicit path in the Name field. |
| Step 8 | Specify one of the
following options for the explicit path type:
|
| Step 9 | If you want to include nodes in the explicit path: |
| Step 10 | If you want to
include an unmanaged node (non
node) in the explicit path:
|
| Step 11 | Click Apply in the Create Explicit Path dialog box and close the dialog box. |
| Step 12 | Return to your originating procedure (NTP). |
 Feedback
Feedback