Table of Contents
Cisco V.150.1 Minimum Essential Requirements Configuration Guide
Contents
Feature Information for Cisco V.150.1 Minimum Essential Requirements
Prerequisites for Cisco V.150.1 MER
Restrictions for Cisco V.150.1 MER
Information About Cisco V.150.1 MER
Cisco Legacy V.150.1
Differences Between Cisco V.150.1 MER and Cisco Legacy V.150.1
Advantages of Modem Relay Over Modem Pass-through
SCIP—EI, Modem over IP, and Fax over IP Interfaces
Cisco V.150.1 MER Network Architecture
Configuration Task Flow
Configure Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Configure Line-side Functionality of Gateway
Configuring SCCP on Cisco IOS Gateways
Configuring Modem Transport Methods for STCAPP Devices
Configuring Modem Pass-through Calls
Configuring V.150.1 Modem Relay Parameters
Configure Trunk-side Functionality of the Gateway
Configuring the T1 Controller and Operating Parameters
Configuring MGCP for Compatibility with Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Configuring MGCP Parameters for Modem Relay
Troubleshooting Tips
Verifying and Troubleshooting the Cisco V.150.1 MER Configuration
Symptoms and Possible Solutions for Cisco V.150.1 MER
Cisco V.150.1 Minimum Essential Requirements Configuration Guide
First Published: March 25, 2011
Last Updated: April 06, 2017
The Cisco V.150.1 Minimum Essential Requirements feature complies with the requirements of the National Security Agency (NSA) SCIP-216 Minimum Essential Requirements (MER) for V.150.1 recommendation. The SCIP-216 recommendation has simplified the existing V.150.1 requirements. Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 15.6(2)T and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 10.5(2), Cisco V.150.1 MER feature is enhanced to support interoperability with third-party devices.
The support for Cisco V.150.1 MER is available from Cisco IOS Release 15.1(4)M and Cisco Communications Manager Release 8.6, where in the negotiation support is added to the following interfaces:
-
Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) for analog gateway endpoints and Secure Communication Interoperability Protocol—End Instruments (SCIP—EI)
-
Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) T1 (PRI and channel-associated signaling [CAS]) and E1 (PRI) trunks
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified Communications Manager) Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunks
This feature also provides support for Unified Capability Requirement (UCR) 2008 Modem over IP (MoIP) and Fax over IP (FoIP).
The V.150.1 is an ITU recommendation for using a modem over IP networks that support dialup modem calls for large installed bases of modems and telephony devices operating on a traditional public switched telephone network (PSTN). The V.150.1 recommendation specifically defines how to relay data from modems and telephony devices on a PSTN into and out of an IP network via a modem.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.4(4)T, Cisco developed the Secure Communication Between IP Secure Endpoint and Trunk-Side Secure Terminal Equipment (STE) Endpoint feature, and in Cisco IOS Release 12.4(9)T, the Secure Communication Between IP Secure Endpoint and Line-Side STE Endpoint feature to meet the requirements of this standard. In this document, these features are referred to as “Cisco Legacy V.150.1.”
Note This document focuses primarily on the capabilities of the Cisco V.150.1 MER feature but also provides some information for the Cisco Legacy V.150.1 feature. For more detailed information about the original feature, see the Secure Communication Between IP-STE Endpoint and Line-Side STE Endpoint document.
Feature Information for Cisco V.150.1 Minimum Essential Requirements
Table 1
lists the release history for this feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to
http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn
. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Note Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Table 1 Feature Information for the Cisco V.150.1 Minimum Essential Requirements Feature
|
|
|
|
Cisco V.150.1 Minimum Essential Requirements (MER)
|
Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.4.1
|
This feature was introduced in the Cisco 4000 series ISR.
|
Cisco V.150.1 MER Enhancement
|
15.6(2)T
|
This feature was enhanced to provide interoperability with third-party equipment in a network.
In Cisco IOS Release 15.6(2)T, this feature was implemented only on the following platforms: Cisco 1921, Cisco 1941, Cisco 2901, Cisco 2911, Cisco 2921, Cisco 2951, Cisco 3925, Cisco 3925E, Cisco 3945, Cisco 3945E, VG 310, VG 350, and VG20xXM platforms.
|
Cisco V.150.1 (MER)
|
15.1(4)M
|
This feature was renamed and enhanced to provide:
-
V.150.1 MER modem relay support
-
RFC 2833 support for Events 32-35
-
T.38 Annex F support
-
No-Audio Codec Support
-
Backward compatibility to existing V.150.1 implementation
|
Secure Communication Between IP-STE Endpoint and Line-Side STE Endpoint
|
12.4(4)T
12.4(9)T
|
This feature was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.4(4)T.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.4(9)T, this feature was implemented on the following platforms: Cisco 2801, Cisco 2811, Cisco 2821, Cisco 2851, Cisco 3825, Cisco 3845, Cisco VG224.
|
Prerequisites for Cisco V.150.1 MER
-
For Cisco V.150.1 MER with third-party equipment interoperability -
– You must have Cisco IOS Release 15.6(2)T or later and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 10.5(2) or later.
– You must have universalk9-mz image installed and running on ISR Generation 2s (ISR G2s) or VG350 and VG20xXM platforms
– UC and security feature licenses are needed for ISR G2s
-
For Cisco V.150.1 MER (without third-party equipment interoperability) -
– You must have Cisco IOS Release 15.1(4)M or later and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 8.6 or later
– You must have adventerprisek9-mz installed on ISRG1 (28xx/38xx) or advipservicesk9-mz installed on VG22x platforms.
Restrictions for Cisco V.150.1 MER
-
V.90 and V.92 are not supported in Cisco Legacy V.150.1 or in Cisco V.150.1 MER modem relay.
-
Cisco V.150.1 MER cannot operate with modem relay that is supported on C542 or C549 DSP technology.
-
FoIP implementation cannot interoperate with the non-State Signaling Event (SSE)-based T.38 fax relay protocol.
-
RFC 2833 support for modem events is limited to the Cisco V.150.1 MER implementation.
-
The Cisco VGD-1T3 platform has Cisco Unified Communications Manager MGCP support, but Cisco V.150.1 MER SCCP Telephony Control Application (STCAPP) support is not available.
Information About Cisco V.150.1 MER
Cisco Legacy V.150.1
In Cisco IOS Release 12.4(4)T, the Secure Communication Between IP Secure Endpoint and Line-Side STE Endpoint feature enabled V.150.1 for STCAPP-control voice ports and allowed an on-network secure terminal equipment (STE), connected directly to a Cisco IOS gateway, to establish a secure call to an IP secure endpoint. Figure 1 shows a basic topology for the V.150.1 standard.
Figure 1 Standard Topology for the V.150.1 Standard
In Cisco IOS Release 12.4(9)T, the Secure Communication Between IP Secure Endpoint and Trunk-Side STE Endpoint feature implemented V.150.1 for the Cisco IOS gateway. The capability was implemented only on MGCP gateways for placing secure calls between the IP secure endpoints and off-network STE devices via MGCP-controlled time-division multiplexing (TDM) trunks.
STE utilizes both modem pass-through and modem relay for secure phone calls. Cisco and another company implemented V.150.1 to carry SCIP (formerly known as Future Narrow Band Digital Terminal [FNBDT]) data to meet the DoD requirements of STE. There is also a VoIP STE that uses only modem relay for secure phone calls.
Cisco’s Legacy V.150.1 implementation contains the following features:
-
Cisco Legacy V.150.1 supports registration of device capabilities to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
-
Cisco Legacy V.150.1 enables either V.150.1 modem relay or passthrough on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager-controlled line-side and trunk-side gateway endpoints. Modem relay and modem pass-through using g.711 and g.729, is implemented as nonstandard codecs in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
-
Cisco Legacy V.150.1 falls back to modem pass-through when the Cisco Unified Communications Manager does not provide modem transport directive, allowing compatibility with earlier Cisco IOS releases. (Secure Communication Between IP Secure Endpoint and Line-Side STE Endpoint analog/BRI only).
-
With Cisco Legacy V.150.1, STU devices do not use FNBDT. STU devices use a proprietary STUIII signaling/datapump that is not compatible with Cisco Legacy V.150.1. A STU cannot be used to place a secure call to an IP secure endpoint.
Differences Between Cisco V.150.1 MER and Cisco Legacy V.150.1
Table 2
summarizes the differences and advantages of Cisco V.150.1 MER over the Cisco Legacy V.150.1.
Table 2 Differences Between Cisco Legacy V.150.1 and Cisco V.150.1 MER
|
|
Cisco V.150.1 MER Modem Relay (SCIP-216 Compliant)
|
Simple Packet Relay Transport (SPRT) (but not all SPRT messages)
|
New SPRT Cleardown MR (CM) messages.
|
Uses SSE for ANSwering tone/ANSwering tone with amplitude modulation (ANS/ANSam)
|
Move from a proprietary Modem Relay transition to standards-based modem relay transition, using RFC 2833 ANS/ANSam signaling.
|
|
Proprietary SSE messages
|
New Reason Identifier Codes (RICs) and SSEs.
Call setup protocol requirements for negotiating specific V.150.1 capabilities.
|
T.38 (non-SSE)
|
T.38 fax relay SSE version 3.
|
Audio codec support only
|
Both Audio codec and “NoAudio” codec support for interworking with Modem Relay Preferred Devices plus audio codec.
|
Requires configuration on the gateway to turn on V.150.1 modem relay line-side parameters
|
Autoconfiguration of V.150.1 controlled at the Cisco Unified Communications Manager device configuration page for SCCP gateway analog phone ports.
|
No support for MoIP
|
MoIP—Modem Relay and audio passthrough.
|
H.323/SIP/TI/E1
|
V.150.1 MER can be used over SIP and T1/E1 trunks. V.150.1 MER is not supported over H.323 trunks (only Cisco Legacy V.150.1 is supported over H.323 trunks).
|

Note When endpoints are capable of both modem relay and modem pass-through, Cisco Unified Communications Manager uses MER modem relay as first preference.
Table 3
summarizes the hardware and software compatibility information for Cisco Legacy V.150.1 and Cisco V.150.1 MER.
Table 3 Compatibility Matrix Contrasting Cisco Legacy V.150.1 and Cisco V.150.1 MER
|
|
|
Digital Signal Processor (DSP)/DSP Module
|
Original Software Releases for Legacy V.150.1
|
Original Software Releases for V.150.1 MER
|
|
NM-HD-2V
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/384
|
PVDM2s
(Built-in DSP)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
2911/2921/2951
3925/3945/3925E/3945E
|
PVDM2s
(Built-in DSP)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 15.0(1)M
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
|
NM-HD-2VE
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
PVDM2s
(Built-in DSP)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
2911/2921/2951
3925/3945/3925E/3945E
|
PVDM2s
(Built-in DSP)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 15.0(1)M
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
|
NM-HDV2
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
PVDM2s
(Built-in DSP)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
2911/2921/2951
3925/3945/3925E/3945E
|
PVDM2
(Onboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 15.0(1)M
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
|
NM-HDV2-2T1/E1
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
PVDM2
(Onboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
2911/2921/2951
3925/3945/3925E/3945E
|
PVDM2
(Onboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 15.0(1)M
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
|
NM-HDV2-1T1/E1
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
PVDM2
(Onboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
2911/2921/2951
3925/3945/3925E/3945E
|
PVDM2
(Onboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 15.0(1)M
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
VIC-4FXS/DID
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
PVDM2
(Onboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
VIC2-2FXS
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
PVDM2
(Onboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
|
VIC3-2FXS/DID
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
NMs 5510/PVDM2
PVDM2
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS15.1(4)M
|
2901/2911/2921/2951
3925/3945/3925E/3945E
|
NMs 5510/PVDM2
PVDM3
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 15.0(1)M
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
|
VIC3-4FXS/DID
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
NMs 5510/PVDM2
PVDM2
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
2901/2911/2921/2951
3925/3945/3925E/3945E
|
NMs 5510/PVDM2
PVDM3
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 15.0(1)M
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
|
VWIC2-1MFT-T1/E1
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
NMs 5510/PVDM2
PVDM2
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
2901/2911/2921/2951
3925/3945/3925E/3945E
|
NMs 5510/PVDM2
PVDM3
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 15.0(1)M
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
|
VWIC2-2MFT-T1/E1
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
NMs 5510/PVDM2
PVDM2
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
2901/2911/2921/2951
3925/3945/3925E/3945E
|
NMs 5510/PVDM2
PVDM3
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 15.0(1)M
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
EVM-HD-8FXS/DID
|
2821/2851
3825/3845
|
PVDM2
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
|
EM3-HDA-8FXS
|
2911/2921/2951
3925/3945/3925E/3945E
|
PVDM3
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 15.0(1)M
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
2811/2821/2851
3825/3845
|
PVDM2
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 4.2
Cisco IOS 12.4(4)T
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
Built in
|
VG 202/204/224
|
PVDM2
(Motherboard DSP Slot)
|
Cisco UCM 6.1.3, 7.0.1 or higher
Cisco IOS 12.4(22)T or later
|
Cisco UCM 8.6
Cisco IOS 15.1(4)M
|
NM-2FXS / NIM-4FXS / NIM-2FXS/4FXO
|
ISR 4000 Series
|
DM8147 DSP
|
|
Cisco UCM 11.5 and higher
Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.4.1
|
NIM-1MFT-T1/E1/ NIM-2MFT-T1/E1 / NIM-4MFT-T1/E1 / NIM-8MFT-T1/E1/ NIM-1CE1T1-PRI / NIM-2CE1T1-PRI / NIM-8CE1T1-PRI
|
ISR 4000 Series
|
PVDM4
|
|
Cisco UCM 11.5 and higher
Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.4.1
|
Advantages of Modem Relay Over Modem Pass-through
The advantages of modem relay over modem pass-through are:
-
Consumes less bandwidth
-
Uses error correction mechanism rather than redundancy
-
Specifically designed to transport modem communication over IP whereas modem pass-through adapts a voice codec
-
More efficient and robust in maintaining transmissions over IP
For more information, see
Fax/Modem over IP
.
SCIP—EI, Modem over IP, and Fax over IP Interfaces
The following interfaces are supported for SCIP and MoIP:
-
MGCP T1 (PRI and CAS) and E1 PRI endpoints subtending MGCP Cisco IOS gateways.
-
SCCP Analog FXS SCIP-compliant endpoints subtending SCCP Cisco IOS gateways.
-
SCIP-EI V.150 IP endpoints running the SCCP protocol version 21 and later.
-
AS-SIP Trunk and SIP ICT.
The following interfaces are supported for FoIP:
-
MGCP T1 (PRI and CAS) and E1 PRI endpoints subtending MGCP Cisco IOS gateways.
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager AS-SIP Trunk and Cisco UCM SIP ICT.
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager FoIP is not supported on SCCP analog FXS ports in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(4)M and Cisco Unified Communications Manager 8.6.
The following interface is
not
supported for the UCR 2008 SCIP, MoIP, FoIP functionality, provided by this feature:
-
H.323 ICT (not supported in MER—
only
for Cisco Legacy V.150.1).
Cisco V.150.1 MER Network Architecture
The two types of endpoints in the MER network are:
-
SCIP–EI Phone: IP connectivity resides in IP network.
-
Analog STE interface, residing in an IP or DSN network.
The Cisco V.150.1 MER network architecture (shown in Figure 2) supports the following:
-
Gateway-to-gateway functionality for PSTN-STE endpoints.
-
FNBDT traffic for the same topology as in the Secure Communication Between IP Secure Endpoint and Trunk-Side STE Endpoint feature.
-
V.150.1 FoIP functionality with MGCP endpoints.
-
Voice gateway connectivity between DSN and IP network, and transports encrypted voice and data media.
Figure 2 Cisco V.150.1 MER Network Architecture
Configuration Task Flow
Configure Line-side Functionality of Gateway
To configure the line-side gateway, perform the following tasks (in some of these tasks, the command syntax has been abbreviated for clarity):
Configuring SCCP on Cisco IOS Gateways
SCCP messaging enables Cisco Unified Communications Manager endpoint call control using the STCAPP. To configure SCCP on the Cisco IOS gateway, perform the tasks in this section.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
sccp local
interface-type interface-number
4.
sccp ccm
{
ip-address
|
dns
}
identifier
identifier-number
[
port
port-number
] [
version
version-number
]
5.
sccp
6.
sccp ccm group
group-number
7.
associate ccm
identifier-number
priority
priortiy-number
8.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
enable
Router> enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
-
Enter your password if prompted.
|
Step 2
|
configure
terminal
Router# configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode.
|
Step 3
|
sccp local
interface-type interface-number
Router(config)# sccp local fastethernet 0/0
|
Selects the local interface that the SCCP application uses to register with Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
-
This is the interface whose MAC address is specified for SCCP gateway registration using the Cisco Unified Communications Manager autoconfiguration. For more information,refer to
Configure V.150 with Cisco Unified Communications Manager
-
interface-type
—Specifies the interface type that the SCCP application uses to register with the Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
-
interface-number
—Specifies the interface number that the SCCP application uses to register with the Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
|
Step 4
|
sccp ccm
{
ip-address
|
dns
}
identifier
identifier-number
[
port
port-number
] [
version
version-number
]
Router(config)# sccp ccm 10.1.1.1 version 7.0+
|
Adds a Cisco Unified Communications Manager server to the list of available servers and sets various parameters.
-
ip-address—
Specifies the IP address of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server.
-
identifier-number
—Identifies the Cisco Unified Communications Manager associated with the
group-number
value configured in Step 6. Valid entries are from 1 to 65535. There is no default value.
-
version
—Identifies the version number of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
|
Step 5
|
sccp
Router(config)# sccp
|
Enables SCCP and its related applications.
|
Step 6
|
sccp ccm group
group-number
Router(config)# sccp ccm group 1
|
Creates a Cisco Unified Communications Manager group.
-
group-number
—Associates the Cisco Unified Communications Manager group with the Cisco Unified Communications Manager group
identifier-number
configured in Step 3. Range is 1 to 65535. There is no default value.
|
Step 7
|
associate ccm
identifier-number
priority
priority-number
Router(config)# associate ccm 1 priority 1
|
Associates a Cisco Unified Communications Manager with a Cisco Unified Communications Manager group.
-
identifier-number—
Identifies the Cisco Unified Communications Manager associated with the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
group-number
configured in Step 6. Valid entries are from 1 to 65535. There is no default value.
-
priority-number— Priority of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager within the Cisco Unified Communications Manager group. Range is 1 to 4. There is no default value. The highest priority is 1.
|
Step 8
|
exit
Router(config)# exit
|
Exits the current configuration mode.
|
Configuring Modem Transport Methods for STCAPP Devices
This task configures modem transport methods for STCAPP devices. Perform this task to specify modem transport capability.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
stcapp register capability
voice-port
{ modem-relay | modem-passthrough | both }
4.
stcapp ccm group
group-id
5. stcapp
6.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
enable
Router> enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
-
Enter your password if prompted.
|
Step 2
|
configure
terminal
Router# configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode.
|
Step 3
|
stcapp register capability
voice-port
{modem-relay | modem-passthrough | both}
Router(config)# stcapp register capability 1/1/0 modem-relay
Router(config)# stcapp register capability 1/1/1 modem-passthrough
Router(config)# stcapp register capability 1/1/2 both
|
Specifies device modem transport capability.
-
voice-port
—Specifies the voice interface slot number.
-
modem-relay
—Specifies that the device supports V.150.1 modem relay.
-
modem-passthrough
—Specifies the device supports modem pass-through (voice band data)
-
both
—Specifies the device supports both modem relay and modem pass-through.
Note Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 15.1(4)M, the modem-relay or both option enables both the V.150.1 MER latent caps and V.150.1 virtual codec caps to be reported to Cisco Unified Communications Manager via the StationCapabilitiesResMessage.
When both sides of the call support V.150.1 MER caps and V.150.1 virtual codec caps, the V.150.1 MER cap is chosen and sent to the SCCP gateway during the call setup via ORC/SMT. Otherwise, the V.150.1 virtual codec caps are used.
Note The stcapp register capability command has three options:
–
modem relay
–
modem-passthrough
, which limits codec capabilities when registering
–
both
|
Step 4
|
stcapp ccm-group
group-id
Router(config)# stcapp ccm-group 1
|
Configures the Cisco Unified Communications Manager group number for use by the STCAPP.
|
Step 5
|
stcapp
Router(config)# stcapp
|
Enables the STCAPP.
|
Step 6
|
exit
Router(config)# exit
|
Exits the current configuration mode.
|
Configuring Modem Pass-through Calls
This task configures modem pass-through calls on the gateway. Perform this task to enable interoperation with the SCCP gateway running versions of Cisco IOS software prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.4(4)T that are not V.150.1-capable.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
voice service voip
4.
modem passthrough nse [payload-type
number
] codec {g711ulaw | g711alaw} [redundancy [maximum-sessions
sessions
]]
5. exit
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
enable
Router> enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
-
Enter your password if prompted.
|
Step 2
|
configure
terminal
Router# configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode.
|
Step 3
|
voice service voip
Router(config)# voice service voip
|
Enters voice-service configuration mode and specifies VoIP encapsulation.
|
Step 4
|
modem passthrough nse [payload-type
number
] codec {g711ulaw | g711alaw} [redundancy [maximum-sessions
sessions
]]
Router(config-voi-serv)# modem passthrough nse codec g711ulaw
|
Configures modem pass-through over VoIP globally for all dial peers.
|
Step 5
|
exit
Router(config-voi-serv)# exit
|
Exits the current configuration mode.
|
Configuring V.150.1 Modem Relay Parameters
This task configures optional V.150.1 modem-relay parameters. Configure these parameters to address specific network conditions for latency, redundancy, and V.14 parameters.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
voice service voip
4.
modem relay latency
milliseconds
5.
modem relay
sse redundancy interval
milliseconds
6.
modem relay
sse redundancy packet
number
7.
modem relay
sse t1
milliseconds
8.
modem relay
sse retries
value
9.
modem relay
sprt retries
value
10.
modem relay sprt v14 receive playback hold-time
milliseconds
11.
modem relay sprt v14 transmit hold-time
milliseconds
12.
modem relay sprt v14 transmit maximum hold-count
characters
13.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
enable
Router> enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
-
Enter your password if prompted.
|
Step 2
|
configure
terminal
Router# configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode.
|
Step 3
|
voice service voip
Router(config)# voice service voip
|
Enters voice service configuration mode and specifies VoIP encapsulation.
|
Step 4
|
modem relay latency
milliseconds
Router(config-voi-serv)# modem relay latency 250
|
Specifies the estimated one-way delay across the IP network.
-
Range is 100 to 1000. Default is 200.
|
Step 5
|
modem relay
sse redundancy interval
milliseconds
Router(config-voi-serv)# modem relay sse redundancy interval 25
|
Specifies the timer value for redundant transmission of SSEs.
-
Range is 5 to 50 ms. Default is 20.
|
Step 6
|
modem relay
sse redundancy packet
number
Router(config-voi-serv)# modem relay sse redundancy packet 2
|
Specifies the SSE packet transmission count before disconnecting.
-
Range is 1 to 5 packets. Default is 3.
|
Step 7
|
modem relay
sse t1
milliseconds
Router(config-voi-serv)# modem relay sse t1 2100
|
Specifies the repeat interval, in milliseconds (ms), for initial audio SSEs used for resetting the SSE protocol state machine (clearing the call) following error recovery.
-
Range is 500 to 3000 ms. Default is 1000.
|
Step 8
|
modem relay
sse retries
value
Router(config-voi-serv)# modem relay sse retries 5
|
Specifies the number of SSE packet retries, repeated every t1 interval, before disconnecting.
-
Range is 0 to 5. Default is 5.
|
Step 9
|
modem relay
sprt retries
value
Router(config-voi-serv)# modem relay sprt retries 10
|
Specifies the number of SPRT packet retries, repeated every t1 interval, before disconnecting.
-
Range is 0 to 10. Default is 10.
|
Step 10
|
modem relay sprt v14 receive playback hold-time
milliseconds
Router(config-voi-serv)# modem relay sprt v14 receive playback hold-time 32
|
Configures the time, in ms, to hold incoming data in the V.14 receive queue.
-
Range is 20 to 250. Default is 50.
|
Step 11
|
modem relay sprt v14 transmit hold-time
milliseconds
Router(config-voi-serv)# modem relay sprt v14 transmit hold-time 12
|
Configures the time to wait, in ms, after the first character is ready before sending the SPRT packet.
-
Range is 10 to 30. Default is 20.
|
Step 12
|
modem relay sprt v14 transmit maximum hold-count
characters
Router(config-voi-serv)# modem relay sprt v14 transmit maximum hold-count 22
|
Configures the number of V.14 characters to be received on the ISDN PSTN interface that will trigger sending the SPRT packet.
-
Range is 8 to 128. Default is 16.
|
Step 13
|
exit
Router(config-voi-serv)# exit
|
Exits the current configuration mode.
|
Configure Trunk-side Functionality of the Gateway
To configure the trunk side of the gateway, perform the following tasks:
Configuring the T1 Controller and Operating Parameters
To configure the T1 controller and operating parameters, perform the tasks in this section.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
controller
{
t1
|
e1
}
slot
/
port
4.
framing
{
sf
|
esf
}
5.
clock source
{
line
{
primary
|
secondary
} |
internal
}
6.
linecode
{
ami
|
b8zs
}
7.
cablelength short
length
8.
pri-group timeslots
timeslot-range
service mgcp
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
enable
Router> enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
-
Enter your password if prompted.
|
Step 2
|
configure
terminal
Router# configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode.
|
Step 3
|
controller
{
t1
|
e1
}
slot
/
port
Router(config)# controller t1 1/0
|
Configures a T1 or E1 controller and enters controller configuration mode.
-
Specify
t1
for a T1 controller.
-
slot
/
port
—Backplane slot number and port number on the interface. See your hardware installation manual for the specific values and slot numbers.
|
Step 4
|
framing
{
sf
|
esf
}
Router(config-controller)# framing esf
|
Selects the frame type for the T1 data line.
-
sf
—Specifies super frame as the T1 frame type.
-
esf
—Specifies extended super frame as the T1 frame type.
|
Step 5
|
clock source
{
line
{
primary
|
secondary
} |
internal
}
Router(config-controller)# clock source internal
|
Sets the T1 line clock source.
-
line
—Specifies that the interface will clock its transmitted data from a clock recovered from the line’s receive data stream. This is the default.
-
primary
—Primary TDM clock source.
-
secondary
—Secondary TDM clock source.
-
internal
—Selects the free running clock (also known as the internal clock) as the clock source.
|
Step 6
|
linecode
{
ami
|
b8zs
}
Router(config-controller)# linecode b8zs
|
Selects the line code for the T1 line.
-
ami
—Specifies alternate mark inversion (AMI) as the line code.
-
b8zs
—Specifies binary 8-zero substitution (B8ZS) as the line code. This is the default.
|
Step 7
|
cablelength short
length
Router(config-controller)# cablelength short 133
|
Sets the cable length 655 feet or shorter for Cisco routers.
-
133
—Specifies a cable length from 0 to 133 feet.
|
Step 8
|
pri-group timeslots
timeslot-range
service mgcp
Router(config-controller)# pri-group timeslots 1-24 service mgcp
|
Specifies an ISDN PRI group on the channelized T1 controller, and configures service type
mgcp
for Media Gateway Control Protocol service.
|
Configuring MGCP for Compatibility with Cisco Unified Communications Manager
To ensure proper operation of the Cisco V.150.1 MER feature on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager, perform the MGCP CLI configuration steps in this section.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
mgcp
4.
mgcp call-agent
[
ipaddr
|
hostname
] [
port
]
service-type mgcp
{
version
version-number
]
5.
mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec
{
all
|
low-bit-rate
}
mode
{
cisco
|
nse
|
out-of-band
|
nte-gw
|
nte-ca
}
6.
mgcp rtp unreachable timeout
timeout-value
[
action notify
]
7.
mgcp modem passthrough
{
voip
|
voaal2
}
mode
{
cisco
|
nse
}
8.
mgcp package-capability rtp-package
9.
no mgcp package-capability res-package
10.
mgcp package-capability sst-package
11.
no mgcp package-capability
fxr-package
12.
mgcp package-capability pre-package
13.
mgcp package-capability mdste-package
14. mgcp package-capability fm-package
15.
no mgcp timer
{
receive-rtcp
|
net-cont-test
|
nse-response t38}
timer
16.
mgcp sdp simple
17.
mgcp rtp payload-type
g726r16
static
18.
mgcp rtp payload-type nte
number
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
enable
Router> enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
-
Enter your password if prompted.
|
Step 2
|
configure
terminal
Router# configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode.
|
Step 3
|
mgcp
Router(config)# mgcp
|
Initiates the MGCP application.
|
Step 4
|
mgcp call-agent
[
ipaddr
|
hostname
] [
port
]
service-type mgcp
{
version
version-number
]
Router(config)# mgcp call-agent cisco-cm1 2427 service-type mgcp version 0.1
|
Specifies the call agent’s IP address or domain name, the port, and gateway control service type.
|
Step 5
|
mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec
{
all
|
low-bit-rate
}
mode
{
cisco
|
nse
|
out-of-band
|
nte-gw
|
nte-ca
}
Router(config)# mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec all mode nte-gw
|
Ensures accurate forwarding of digits on compressed codecs.
-
all
—Configures dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) relay to be used with all voice codecs.
-
low-bit-rate
—Configures DTMF relay to be used with only low-bit-rate voice codecs, such as G.729.
-
cisco
—Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) digit events are encoded using a proprietary format similar to Frame Relay as described in the FRF.11 specification. The events are transmitted in the same RTP stream as nondigit voice samples, using payload type 121.
-
nse
—RTP digit events are encoded using the format specified in RFC 2833, Section 3.0, and are transmitted in the same RTP stream as nondigit voice samples, using the payload type that is configured using the
mgcp tse payload
command.
-
out-of-band
—MGCP-digit events are sent using NTFY messages to the call agent (CA), which plays them on the remote gateway using RQNT messages with S: (signal playout request).
-
nte-gw
—RTP digit events are encoded using the format specified in RFC 2833, Section 3.0, and are transmitted in the same RTP stream as nondigit voice samples. The payload type is negotiated by the gateways before use. The configured value for the payload type is presented as the preferred choice at the beginning of the negotiation.
-
nte-ca
—Identical to the
nte-gw
keyword behavior except that the CA’s local connection options a: line is used to enable or disable DTMF relay.
|
Step 6
|
mgcp rtp unreachable timeout
timeout-value
[
action notify
]
Router(config)# mgcp rtp unreachable timeout 1000 action notify
|
Enables detection of an unreachable remote VoIP endpoint.
-
timeout-value
—Time, in milliseconds, that the system waits for voice packets from the unreachable endpoint. Range is 500 to 10000.
-
action notify
—Sends a notification when the timeout value has been exceeded.
|
Step 7
|
mgcp modem passthrough
{
voip
|
voaal2
}
mode
{
cisco
|
nse
}
Router(config)# mgcp modem passthrough voip mode nse
|
Sets the method for changing speeds that enables the gateway to send and receive modem and fax data in VoIP and Voice over ATM (VoATM) adaptation layer 2 (VoAAL2) configurations.
-
voip
—VoIP.
-
voaal2
—Voice over AAL2 calls using Annex K type 3 packets.
-
cisco
—Cisco-proprietary method for changing modem speeds, based on the protocol.
-
nse
—NSE-based method for changing modem speeds. For VoAAL2 configurations, AAL2 Annex K (type 3) is used.
|
Step 8
|
mgcp package-capability rtp-package
Router(config)# mgcp package-capability rtp-package
|
Enables the MGCP package capability type for RTP packages on the gateway.
|
Step 9
|
no mgcp package-capability res-package
Router(config)# no mgcp package-capability res-package
|
Disables the MGCP package capability type for RSVP packages on the gateway.
|
Step 10
|
mgcp package-capability sst-package
Router(config)# mgcp package-capability sst-package
|
Enables the MGCP package capability type for SST packages on the gateway.
|
Step 11
|
no mgcp package-capability fxr-package
Router(config)# no mgcp package-capability fxr-package
|
Disables the MGCP package capability type for FXR packages for fax transmissions on the gateway.
|
Step 12
|
mgcp package-capability pre-package
Router(config)# mgcp package-capability pre-package
|
Enables the MGCP package capability type for PRE packages on the gateway.
|
Step 13
|
mgcp package-capability mdste-package
Router(config)# mgcp package-capability mdste-package
|
Enables the MGCP package capability type for modem relay STE packages on the gateway.
-
Enables events and signals for modem connections enabling a secure communication path between IP-STE and STE.
|
Step 14
|
mgcp package-capability fm-package
Router(config)# mgcp package-capability fm-package
|
Enables DTMF via RFC 2833.
|
Step 15
|
no mgcp timer
{
receive-rtcp
timer
|
net-cont-test
timer
|
nse-response t38
timer
}
Router(config)#no mgcp timer receive-rtcp
|
Configures how a gateway detects the RTP stream host.
-
The
no
form of this command resets the default values.
|
Step 16
|
mgcp sdp simple
Router(config)# mgcp sdp simple
|
Specifies use of a subset of the Session Description Protocol (SDP).
-
Some call agents require this subset to send data through the network.
|
Step 17
|
mgcp rtp payload-type
g726r16
static
Router(config)# mgcp rtp payload-type g726r16 static
|
Specifies use of the G.726r16 codec for the RTP payload type for backward compatibility in MGCP networks.
-
g726r16
—Payload type for the G.726 codec at 16K.
-
static
—Static payload type.
|
Step 18
|
mgcp rtp payload-type nte
number
Router(config)# mgcp rtp payload-type nte 101
|
Configures the dynamic RTP payload type for RFC 2833 named telephone event (rtp-nte) packets when doing DTMF interworking.
-
The payload type is used for both transmitting and receiving, therefore it must be the same value that is used on the peer.
-
The
number
argument must be in the range of 96 to 127.
|
Configuring MGCP Parameters for Modem Relay
To configure MGCP parameters for modem relay, perform the tasks in this section.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
mgcp modem relay voip mode sse [redundancy {interval
number
|
packet
number
}] [
retries
value
] [
t1
time
]
4. mgcp modem relay voip sprt v14 {
receive playback hold-time
milliseconds |
transmit hold-time
milliseconds |
transmit maximum hold-count
characters}
5.
modem package-capability mdste-package
6.
mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec all mode nte-gw
7.
mgcp rtp payload-type nte 101
8.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
enable
Router> enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
-
Enter your password if prompted.
|
Step 2
|
configure
terminal
Router# configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode.
|
Step 3
|
mgcp modem relay voip mode sse [redundancy
{
interval
number
|
packet
number
}][
retries
value
] [
t1
time
]
Router(config)# mgcp modem relay voip mode sse redundancy packet 5
|
Specifies SSE modem-relay parameters.
-
redundancy
—(Optional) Packet redundancy for modem traffic during modem pass-through. By default redundancy is disabled.
-
interval
milliseconds
—Specifies the timer in milliseconds (ms) for redundant transmission of SSEs. Range is 5 to 50 ms. Default is 20.
-
packet
number
—Specifies the SSE packet retransmission count before disconnecting. Range is 1 to 5. Default is 3.
-
retries
value
—(Optional) Specifies the number of SSE packet retries, repeated every t1 interval, before disconnecting. Range is 0 to 5. Default is 5.
-
t1
milliseconds
—Specifies the repeat interval, in ms, for initial audio SSEs used for resetting the SSE protocol state machine (clearing the call) following error recovery. Range is 500 to 3000. Default is 1000.
|
Step 4
|
mgcp modem relay voip sprt v14
{
receive playback hold-time
milliseconds
| transmit hold-time
milliseconds
| transmit maximum hold-count characters}
Router(config)# mgcp modem relay voip sprt v14 transmit hold-time 250
|
Specifies SPRT modem-relay parameters.
-
receive playback hold-time
milliseconds
—Configures the time in ms to hold incoming data in the V.14 receive queue. Range is 20 to 250. Default is 50.
-
transmit hold-time
milliseconds
—Configures the time to wait, in ms, after the first character is ready before sending the SPRT packet. Range is 10 to 30. Default is 20.
-
transmit maximum hold-count
characters
—Configures the number of V.14 characters to be received on the ISDN public switched telephone network (PSTN) interface that will trigger sending the SPRT packet. Range is 8 to 128. Default is 16.
|
Step 5
|
modem package-capability mdste-package
Router(config)# mgcp package-capability mdste-package
|
Specifies the MGCP package capability type for the media gateway.
-
When the package type is entered as
mdste-package
, NoAudio Codec support is implicitly enabled because NoAudio codec can be used only when V.150.1 MER modem relay is also used in the call. NoAudio codec is not supported when there is no support for MER modem relay from the remote end. SSE-based T.38 support is implicitly enabled.
Note If the mgcp package-capability mdste-package command is not entered, NoAudio support and SSE-based T.38 support are implicitly disabled.
-
To have the secure RTP session, you must enter the
package
argument as
srtp-package
.
|
Step 6
|
mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec all mode nte-gw
Router(config)# mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec all mode nte-gw
|
Specifies that RTP digit events are encoded using the named telephony event (NTE) format specified in RFC 2833, Section 3.0, and are transmitted in the same RTP stream as nondigit voice samples.
-
The payload type is negotiated by the gateways before use. The configured value for the payload type is presented as the preferred choice at the beginning of the negotiation.
|
Step 7
|
mgcp rtp payload-type nte 101
Router(config)# mgcp rtp payload-type nte 101
|
Specifies use of NTE as the payload type and 101 is the value for the NTE payload for backward compatibility in MGCP networks.
|
Step 8
|
exit
Router(config)# exit
|
Exits the current configuration mode.
|
Troubleshooting Tips
The following options are provided to fix interoperability issues that may arise due to some additions made to the SDP content to ensure backward compatibility with existing Cisco UCMs running Cisco Legacy V.150.1. Although according to the V.150.1 specification these additions should not impact SDP parsing, the fail-safe option to remove them is provided. These options can be configured on a per-trunk or per-cluster basis:
-
No Filtering (Default)—No filtering is performed on SIP SDP content. This is the default option.
-
Remove V.150.1 MER—The SIP trunk removes MER lines in outbound SDP offers. Use this value to reduce ambiguity when a trunk is connected to a pre-V.150.1 MER Cisco UCM. On the legacy Cisco UCM versions used by Cisco internally during development testing, backward compatibility with legacy V.150.1 functionality worked without this option. However, it may be needed on older Cisco UCM versions.
-
Remove Pre-MER V.150.1—The SIP trunk removes any lines in outbound SDP offers that are not MER-compliant. If the trunk is to a MER-compliant LSC that cannot process an offer with pre-MER lines, choose this value. This option should be selected only when a non-Cisco LSC is misinterpreting or failing to operate on either a legacy V.150.1 offer or a MER+Legacy V.150.1 offer. A MER+Legacy V.150.1 offer can be identified by the presence of an “a=vndpar 2 15 2 ##” line at the end of the SDP. If third parties have coded their parsers appropriately, this option should not need to be used; it is mentioned here as a precaution.
Table 4 Chart of Modem Transport Methods
|
|
Secure Terminal Unit (STU)
|
(Secure Communication between IP Secure Endpoint and Line-Side STE Endpoint Gateway)
|
|
|
|
|
voice band data
|
voice band data
|
voice band data
|
None
|
On-net Secure Terminal Equipment
(Secure Communication Between IP Secure Endpoint and Line-Side STE Endpoint Gateway)
|
voice band data
|
voice band data
or
V.150.1 modem relay
|
voice band data
or
V.150.1 Modem Relay
|
V.150.1 modem relay
|
Secure Terminal Equipment (STE)
|
voice band data
|
voice band data
|
voice band data
|
V.150.1 modem relay
|
|
|
None
|
V.150.1 modem relay
|
V.150.1 modem relay
|
IP
|
Verifying and Troubleshooting the Cisco V.150.1 MER Configuration
To verify and troubleshoot the configuration of the Cisco V.150.1 MER feature, perform the steps in this section. The
show
commands provide information about the configuration. The
debug
commands are useful when problems are apparent in the system. The information in Step 10 provides guidelines for ensuring a correct configuration.
Table 5
in Step 9 provides a list of symptoms that may occur and possible resolutions to those problems.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
show voice dsp active
2.
show call active voice
3.
show stcapp device voice-port 1/0/0
4.
debug voice application stcapp all (device registration)
5.
debug voice application stcapp all (line-side call setup)
6.
debug voip rtp session named
7.
debug mgcp packets (registration)
8. debug mgcp packets
9.
debug mgcp all (MGCP trunk)
10. Review the information for compliance of your configuration.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
show voice dsp active
Use the
show voice dsp active
command to display status information for all DSP voice channels:
Router# show voice dsp active ----------------------------FLEX VOICE CARD 1 ----------------------- *DSP ACTIVE VOICE CHANNELS* DSP DSPWARE VOX DSP SIG DSP PAK TX/RX TYPE VERSION CODEC NUM CH TS VOICEPORT SLT NUM CH TS RST AI ABRT PACK COUNT ====== ========== ======== === == == ========= === === == == === == ==== === C5510 28.0.136 modem-rel 001 01 05 1/0/0 001 001 04 06 0 0 0 2912/3533 C5510 28.0.136 modem-rel 001 02 23 1/0:23 001 002 11 23 0 0 0 3458/3021 ------------------------END OF FLEX VOICE CARD 1 --------------------
Step 2
show call active voice
Use the
show call active voice
command to display call information for voice calls in progress:
Router# show call active voice Modem Relay Mode = signaling-assisted Modem Relay Local Rx Speed=9600 bps Modem Relay Local Tx Speed=9600 bps Modem Relay Remote Rx Speed=19200 bps Modem Relay Remote Tx Speed=19200 bps Modem Relay Phy Layer Protocol=v32 Modem Relay Ec Layer Protocol=v14 SPRTTotalInfoBytesReceived=806778 SPRTTotalInfoBytesSent=806562
Step 3
show stcapp device voice-port 1/0/0
Use the
show stcapp device voice-port 1/0/0
command to display call information for voice calls on a specific port:
Router# show stcapp device voice-port 1/0/0 Device Name: AN1A6D001760200 Device Security Mode : None Dialtone after remote onhook feature: activated Busytone after remote onhook feature: not activated Last Event: STCAPP_CC_EV_CALL_FEATURE CWT Repetition Interval: 0 second(s) (no repetition) Call State for Connection 1 (ACTIVE): TsConnected Local IP Addr: 10.10.10.139 Remote IP Addr: 10.10.10.139 Capability and Version : 0x20110000 Modulation and RFC2833 : 0xF0000005 SPRT Max Payload Chan0 : 0 SPRT Max Payload Chan2 : 0 SPRT Max Payload Chan3 : 0 SPRT Max WinSize Chan2 : 0 SSE Standard Support : 0x5 RFC2833 Payload Value : 101 NoAudio Payload Value : 0
Step 4
debug voice application stcapp all (device registration)
Use the
debug voice application stcapp all
command to display debugging information for the components of the STCAPP:
Router# debug voice application stcapp all *Jan 4 20:45:50.877: 1/0/0: Registering device *Jan 4 20:45:50.877: 1/0/0: stcapp_register_device *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_parse_control_msg: glob_ccm->version 9 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: SCCP(AN43E17E8B90200)rcvd RegisterAckMessage *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_appl_service_stop_timer: Stop A69DA3C timer *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_parse_control_msg_v1: rcvd register ack, ka_interval 30, for prof_id 0, appl_type 4 negotiated sccp version 21 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: RegisterAck msg rcvd in hex - 81 0 0 0 1E 0 0 0 4D 2F 44 2F 59 0 0 0 3C 0 0 0 15 20 F1 FF Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_parse_control_msg: glob_ccm->version 9 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: SCCP(AN43E17E8B90200)rcvd CapabilitiesReqMessage *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_generate_msg: msg_id 16 msg_len 296 pak_size 304 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: Codec list with pkt_period (cnt 16) - *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 257 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 257257 30, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 112 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 112112 20, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 114 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 114114 220, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 299 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 299299 20, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 300 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 300 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: v150_mr.cap_n_ver: 0x1120 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: v150_mr.mod_n_2833: 0xFF0F00F0300 0, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 301 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 301 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: v150_sprt_payload.chan0_max_payload: 35840 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: v150_sprt_payload.chan2_max_payload: 33792 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: v150_sprt_payload.chan3_max_payload: 35840 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: v150_sprt_payload.chan2_max_windows: 2048301 0, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 302 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 302 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: v150_sse.standdard_field 0x5000000302 0, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 111 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 111111 20, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 113 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 113113 220, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 4 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 44 20, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 2 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 22 20, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 11 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 1111 220, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 12 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 1212 220, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 15 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 1515 220, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 11 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 1111 220, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_rec->codec = 86 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: msg_cap->payload_caps = 86 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: codec_params=0300000086 120, *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_send_capabilities_rsp_msg_v21: CapRes msg txed in hex(including header) - pak->datagramsize 304, actual_len 272 *Jan 4 20:45:51.881: sccp_print_hex_msg: Len:272 Hex: 28 01 00 00 15 00 00 00 10 00 00 00 10 00 00 00 01 01 00 00 1E 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 70 00 00 00 14 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 72 00 00 00 DC 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 2B 01 00 00 14 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 2C 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 11 20 FF 0F 00 F0 2D 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 8C 00 84 00 8C 00 08 00 2E 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 05 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 6F 00 00 00 14 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 71 00 00 00 DC 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 14 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 14 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0B 00 00 00 DC 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0C 00 00 00 DC 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0F 00 00 00 DC 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0B 00 00 00 DC 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 56 00 00 00 78 00 00 00 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Step 5
debug voice application stcapp all (line-side call setup)
The
debug voice application stcapp all
can also be used to display debug information for call setup on the line-side:
Router# debug voice application stcapp all *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: sccp_parse_control_msg: glob_ccm->version 9 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: SCCP(AN43E17E8B90200)rcvd OpenReceiveChannel *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: OpenReceviceChannel msg rcvd in hex - 5 1 0 0 32 19 AC 1 35 0 0 1 14 0 0 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 32 19 AC 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 65 0 0 0 A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 A A A 8B 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 A0 F 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 11 20 FF F 0 F0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 65 0 0 0 0 0 0 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: OpenReceiveChannelMsg Info: conference_id = 28055858, pass_through_party_id = 16777269 msec_pkt_size = 20, compression_type = 4 qualifier_in.ecvalue = 0, g723_bitrate = 0, call_ref = 28055858 stream_pass_through_id = 0, rfc2833_payload_type = 101 codec_dynamic_payload = 0, codec_mode = 0 Encryption Info :: algorithm_id 0, key_len 0, salt_len 0 requestedAddrType = 0, source_ip_addr.ipAddrType = 0, source_ip_addr = 10.10.10.139, source_port_number = 4000, audio_level_adjustment = 0 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: v150 latent caps active: modem relay cap and version: 0x20110000 modulation and rfc2833: 0xF0000FFF sprt max payload for chan0: 0 chan2: 0 chan3: 0, max window for chan2: 0 sse standard support filed: 0x5 vendor support filed: 0x0 payload nse 0 rfc2833 101 sse 0 v150_sprt 0 noaudio 0 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: sccp_dcapi_extract_and_validate_srtp_context *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: STCAPP:stcapp_get_dcb_and_lcb *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: stcapp_get_dcb_and_lcb *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: stcapp_screen_api_event *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: event:STCAPP_DC_EV_MEDIA_OPEN_RCV_CHNL received. *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: stcapp_screen_open_rcv_chnl *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: active_ccb=0x11544A0, media_state is NO_MEDIA *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: ==> Received event:STCAPP_DC_EV_MEDIA_OPEN_RCV_CHNL *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: Call State:PROCEEDING *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: stcapp_open_rcv_chnl_eh *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: call_ref=28055858 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: stcapp_get_ccb_ptr *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: received ORC: rcv payload=101 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: stcapp_set_up_voip_leg *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: stcapp_get_ccb_ptr *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: In stcapp_set_up_voip_leg, local port allocated 21240 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: stcapp_set_up_modem_parms *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: STCAPP:Codec: 5 ptime :20, codecbytes: 160 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: CCM directive -> enabling MER modem relay *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: MR parms: sprt_retries=12, sprt_latency=200, sprt_rx_v14_pb_hold_time=50, sprt_tx_v14_hold_time=20, sprt_tx_v14_hold_count=16, gw_xid=1, dictsize=1024, stringlen=32, compressdir=3, sse_red_interval=20, sse_red_pkt_count=3, sse_t1=1000, sse_retries=3, rfc2833_bitmap=0 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: Info provided to RTPSPI - sess_mode:2, desired_qos 0, codec 5, pkt_period 20, *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: rem_port 4000, lr_port 21240, dtmf_mode 400, rcv_nte 101 nte 0 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: Sending ccIFCallSetupRequest for voip leg *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: ccIFCallSetRequest returned voip call id:12 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: MER modem relay configuration passed down ? call id:12 MR proto = 4 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: STCAPP:stcapp_find_ccb_by_call_id:ERROR:Invalid Call ID *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: stcapp_conn_db_insert_ccb *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: ccb=0x11544A0 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: call ccCallConnect for voice call_id 11 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: Media state is set to RECV_ONLY *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: Sending dcDeviceOpenReceiveChannelAck *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: ORChnlAck Info: codec:5, loc_ipaddr: 10.10.10.143, loc_port:21240, chnl_id:16777269 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: sccp_spi_orc_ack: enqueue spi evt SCCP_SPI_MEDIA_ORC_ACK, reg_name=AN43E17E8B90200 *Jan 4 20:56:33.266: 1/0/0: New State = CONNECTING *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: STCAPP:Receive CC event:: call_id=12, ccb=0x11544A0 *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: 1/0/0: ==> Received event:STCAPP_CC_EV_CALL_CONNECTED for CallId: 12 *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: 1/0/0: Call State:CONNECTING *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: 1/0/0: stcapp_call_connected_eh *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: 1/0/0: stcapp_create_conference *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: 1/0/0: Sending ccConferenceCreate to Symphony *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: 1/0/0: Conference created. voice call id:11, voip call id:12 *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: 1/0/0: No state change *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: sym_xapp_process_ccapi_events: minor is ZERO - should be non-zero for CCAPI event *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: sccp_generate_msg: msg_id 34 msg_len 40 pak_size 48 *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: sccp_open_receive_channel_ack_v14: going to send ack to CCM - status 0, ipaddr 10.10.10.143, port 21240, conn_id 16777269, prof_id 0 *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: sccp_open_receive_channel_ack_v14: OpenRecvChnlAck msg txed in hex(including header) - len 48 *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: sccp_print_hex_msg: Len:48 Hex: 28 00 00 00 15 00 00 00 22 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0A 0A 0A 8F F1 1D CE 99 F2 7F E0 98 50 10 0A F4 F8 52 00 00 35 00 00 01 32 19 AC 01 *Jan 4 20:56:33.270: sccp_transmit_msg: sending on socket 5 *Jan 4 20:56:33.274: sccp_parse_control_msg: msg_ptr 16127364, msg_len 172, msg_id 138 *Jan 4 20:56:33.274: sccp_parse_control_msg: glob_ccm->version 9 *Jan 4 20:56:33.274: SCCP(AN43E17E8B90200)rcvd StartMediaTransmission *Jan 4 20:56:33.274: StartMediaTrans msg rcvd in hex - 8A 0 0 0 32 19 AC 1 35 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 A A A 8B 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 A6 41 0 0 14 0 0 0 4 0 0 0 B8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 32 19 AC 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 65 0 0 0 A 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 11 20 FF F 0 F0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 65 0 0 0 0 0 0 *Jan 4 20:56:33.274: StartMediaTransmissionMsg Info: conference_id = 28055858, pass_through_party_id = 16777269 msec_pkt_size = 20, compression_type = 4 remote_ip_addr = 10.10.10.139, remote_port = 16806 qualifier_out.precedence_value = 184, qualifier_out.ssvalue = 0 qualifier_out.max_frames_per_pkt = 0, g723_bitrate = 0, call_ref = 28055858, stream_pass_through_id = 0 rfc2833_payload_type = 101 codec_dynamic_payload = 0, codec_mode = 0 Encryption Info :: algorithm_id 0, key_len 0salt_len 0 *Jan 4 20:56:33.274: v150 latent caps active: modem relay cap and version: 0x20110000 modulation and rfc2833: 0xF0000FFF sprt max payload for chan0: 0 chan2: 0 chan3: 0, max window for chan2: 0 sse standard support filed: 0x5 vendor support filed: 0x0 payload nse 0 rfc2833 101 sse 0 v150_sprt 0 noaudio 0
Step 6 debug sccp messages (line-side device registration)
?? Need output ??
Step 7
debug voip rtp session named
Use the
debug voip rtp session named
command to display debug information for session establishment:
Router# debug voip rtp session named *Jan 4 21:04:25.675: s=DSP d=VoIP payload 0x65 ssrc 0x1F2A sequence 0x811B timestamp 0x21C875DF *Jan 4 21:04:25.675: Pt:101 Evt:34 Pkt:0B 00 00 <Snd>>> *Jan 4 21:04:25.923: Pt:101 Evt:35 Pkt:0B 07 D0 <Snd>>> *Jan 4 21:04:29.283: <<<Rcv> Pt:118 Evt:12 Pkt:01 D8 2C
Step 8
debug mgcp packets (registration)
Use the
debug mgcp packets
command to display debug registration information for MGCP trunks:
Router# debug mgcp packets *Jan 4 17:50:50.547 EDT: MGCP Packet received from 10.10.10.132:2427---> AUEP 1581 S1/DS1-0/5@MER-CCM2GW8.cisco.com MGCP 0.1 *Jan 4 17:50:50.547 EDT: MGCP Packet sent to 10.10.10.132:2427---> L: p:10-20, a:PCMU;PCMA;G.nX64;NoAudio;telephone-event, fmtp:"telephone-event 0-15", b:64, e:on, gc:1, s:on, t:10, r:g, nt:IN;ATM;LOCAL, X+mdste/md:V150;V150merrelay, v:T;G;D;L;H;R;ATM;SST;FXR;PRE;X+mdste;FM L: p:10-220, a:G.729;G.729a;G.729b;telephone-event, fmtp:"telephone-event 0-15", b:8, e:on, gc:1, s:on, t:10, r:g, nt:IN;ATM;LOCAL, X+mdste/md:V150;V150merrelay, v:T;G;D;L;H;R;ATM;SST;FXR;PRE;X+mdste;FM L: p:10-110, a:G.726-16;G.728;telephone-event, fmtp:"telephone-event 0-15", b:16, e:on, gc:1, s:on, t:10, r:g, nt:IN;ATM;LOCAL, X+mdste/md:V150;V150merrelay, v:T;G;D;L;H;R;ATM;SST;FXR;PRE;X+mdste;FM L: p:10-70, a:G.726-24;telephone-event, fmtp:"telephone-event 0-15", b:24, e:on, gc:1, s:on, t:10, r:g, nt:IN;ATM;LOCAL, X+mdste/md:V150;V150merrelay, v:T;G;D;L;H;R;ATM;SST;FXR;PRE;X+mdste;FM L: p:10-50, a:G.726-32;telephone-event, fmtp:"telephone-event 0-15", b:32, e:on, gc:1, s:on, t:10, r:g, nt:IN;ATM;LOCAL, X+mdste/md:V150;V150merrelay, v:T;G;D;L;H;R;ATM;SST;FXR;PRE;X+mdste;FM L: p:30-270, a:G.723.1-H;G.723;G.723.1a-H;telephone-event, fmtp:"telephone-event 0-15", b:6, e:on, gc:1, s:on, t:10, r:g, nt:IN;ATM;LOCAL, X+mdste/md:V150;V150merrelay, v:T;G;D;L;H;R;ATM;SST;FXR;PRE;X+mdste;FM L: p:30-330, a:G.723.1-L;G.723.1a-L;telephone-event, fmtp:"telephone-event 0-15", b:5, e:on, gc:1, s:on, t:10, r:g, nt:IN;ATM;LOCAL, X+mdste/md:V150;V150merrelay, v:T;G;D;L;H;R;ATM;SST;FXR;PRE;X+mdste;FM M: sendonly, recvonly, sendrecv, inactive, loopback, conttest, data, netwloop, netwtest
Step 9
debug mgcp packets
Use the
debug mgcp packets
command to display debugging information about call setup on the MGCP trunk:
Router# debug mgcp packets a=cpar: a=T38FaxMaxDatagram:320 a=cpar: a=T38FaxUdpEC:t38UDPRedundancy *Jan 4 17:43:32.611 EDT: MGCP Packet received from 10.10.10.132:2427---> CRCX 1573 S1/DS1-0/23@MER-CCM2GW8.cisco.com MGCP 0.1 C: D000000001ac193b000000F500000003 L: p:20, a:PCMU;telephone-event, fmtp:"telephone-event 0-15,32-35", s:off, t:b8, X+mdste/md:v150merrelay *Jan 4 17:43:32.619 EDT: MGCP Packet sent to 10.10.10.132:2427---> m=audio 18938 RTP/AVP 0 101 100 118 a=rtpmap:101 telephone-event/8000 a=fmtp:100 192-194,200-202 a=X-cap: 1 audio RTP/AVP 100 a=X-cpar: a=rtpmap:100 X-NSE/8000 a=X-cpar: a=fmtp:100 192-194,200-202 a=X-cap: 2 image udptl t38 a=cdsc: 1 audio RTP/AVP 0 101 100 118 a=cdsc: 5 audio udpsprt 120 a=cpar: a=sprtmap:120 v150mr/8000 a=cpar: a=fmtp:120 mr=1;mg=0;CDSCselect=1;jmdelay=no;Versn=1.1;mrmods=1,3 a=cdsc: 6 image udptl t38 a=cpar: a=T38FaxVersion:3 a=cpar: a=T38MaxBitRate:33600 a=cpar: a=T38FaxRateManagement:transferredTCF a=cpar: a=T38FaxMaxBuffer:200 a=cpar: a=T38FaxMaxDatagram:320 a=cpar: a=T38FaxUdpEC:t38UDPRedundancy *Jan 4 17:43:32.659 EDT: MGCP Packet received from 10.10.10.132:2427---> MDCX 1574 S1/DS1-0/23@MER-CCM2GW8.cisco.com MGCP 0.1 C: D000000001ac193b000000F500000003 L: p:20, a:PCMU;telephone-event, fmtp:"telephone-event 32-35", s:off, t:b8, X+mdste/md:v150merrelay o=- 4 0 IN EPN S1/DS1-0/23@MER-CCM2GW8.cisco.com m=audio 17712 RTP/AVP 0 101 118 a=rtpmap:101 telephone-event a=cdsc: 1 audio RTP/AVP 0 101 118 a=cdsc: 4 audio udpsprt 120 a=cpar: a=sprtmap:120 v150mr/8000 a=cpar: a=fmtp:120 mr=1;mg=0;CDSCselect=1;jmdelay=no;Versn=1.1;mrmods=1,3 *Jan 4 17:43:32.663 EDT: MGCP Packet sent to 10.10.10.132:2427---> *Jan 4 17:43:38.579 EDT: MGCP Packet sent to 10.10.10.132:2427---> NTFY 714848268 *@MER-CCM2GW8.cisco.com MGCP 0.1 *Jan 4 17:43:38.579 EDT: MGCP Packet received from 10.10.10.132:2427--->
Step 10
debug mgcp all (MGCP trunk)
Use the
debug mgcp all
command to display session information for debugging the MGCP trunk:
*Jan 4 17:54:46.499 EDT: //53/0776534D8005/MGCP|S1/DS1-0/23|-1|-1/<VOICE>/mgcp_xlate_call_feature_type(1062):[lvl=2]mgcp_xlate_call_feature_type: feature 47 *Jan 4 17:54:46.499 EDT: //-1/xxxxxxxxxxxx/MGCP/mgcp_cr_and_init_evt_node(4596):[lvl=1]$$$ the node pointer 71E1B348 *Jan 4 17:54:46.499 EDT: //-1/xxxxxxxxxxxx/MGCP/mgcp_insert_node_to_preprocess_q(4518):[lvl=1]$$$enq to preprocess, qhead=71E1B348, qtail=71E1B348, count 1, evtptr=71E1B348 *Jan 4 17:54:46.499 EDT: //53/0776534D8005/MGCP|S1/DS1-0/23|-1|-1/<VOICE>/xlate_ccapi_ev(600):[lvl=1]MGCP APP gets CC_EV_CALL_FEATURE event: major code=EV_MEDIA_EVT, minor_code(d)=121, minor_code=v150merrelay, *pkg=67108864 *Jan 4 17:54:54.963 EDT: //53/0776534D8005/MGCP|S1/DS1-0/23|-1|-1/<VOICE>/mgcp_remove_old_ack(714):[lvl=1]Removing ack: (trans ID 1600) : 200 1600 OK m=audio 17748 RTP/AVP 0 101 100 118 a=rtpmap:101 telephone-event/8000 a=fmtp:100 192-194,200-202 a=X-cap: 1 audio RTP/AVP 100 a=X-cpar: a=rtpmap:100 X-NSE/8000 a=X-cpar: a=fmtp:100 192-194,200-202 a=X-cap: 2 image udptl t38 a=cdsc: 1 audio RTP/AVP 0 101 100 118 a=cdsc: 5 audio udpsprt 120 a=cpar: a=sprtmap:120 v150mr/8000 a=cpar: a=fmtp:120 mr=1;mg=**MSG 00002 TRUNCATED** **MSG 00002 CONTINUATION #01**0;CDSCselect=1;jmdelay=no;Versn=1.1;mrmods=1,3 a=cdsc: 6 image udptl t38 a=cpar: a=T38FaxVersion:3 a=cpar: a=T38MaxBitRate:33600 a=cpar: a=T38FaxRateM0anagement:transferredTCF a=cpar: a=T38FaxMaxBuffer:200 a=cpar: a=T38FaxMaxDatagram:320 a=cpar: a=T38FaxUdpEC:t38UDPRedundancy *Jan 4 17:54:55.047 EDT: //53/0776534D8005/MGCP|S1/DS1-0/23|-1|-1/<VOICE>/mgcp_remove_old_ack(714):[lvl=1]Removing ack: (trans ID 1601) : 200 1601 OK
Step 11 Review the following bullet items to verify compliance of your configuration:
-
STE devices operate over V.150.1 and VBD (FNBDT or STUIII).
-
IP Secure Endpoint devices operate only over V.150.1—there is no network-side DSP.
-
In Cisco Legacy V.150.1, if you configure an SCCP endpoint with the
both
keyword, that endpoint always uses modem pass-through when establishing connections to endpoints supporting both modem-passthrough and V.150.1 modem relay, such as other SCCP ports or MGCP-controlled PSTN trunks. If V.150.1 modem relay is desired, use the
modem relay
keyword when configuring STCAPP ports.
-
Use the
modem relay
keyword for STE devices to force V.150.1 when setting up STE-to-STE calls.
-
Make sure the global configuration
voice service voip modem passthrough
command is configured. This command provides fallback to VBD mode when your device is communicating with a legacy Cisco SCCP gateway or an STU on a gateway running the Secure Communication Between IP Secure Endpoint and Line-Side STE Endpoint feature.
-
Codec capabilities cannot be limited on an MGCP trunk. An MGCP trunk always registers with all supported codec capabilities.
Symptoms and Possible Solutions for Cisco V.150.1 MER
This section provides information about some possible problems or issues that may arise when you are configuring and operating the Cisco V.150.1 MER feature. Review the information in
Table 5
for symptoms and possible solutions to help ensure operability of the Cisco V.150.1 MER feature in your network.
Table 5 Common Issues and Possible Solutions
|
|
|
|
STE calls fail to secure
|
Wrong hardware such as gateway, VICs, or DSPs. Confirm that you have the correct configuration of DSPs (5510 family of DSPs—PVDMs included).
|
MGCP gateway is needed for trunks, and the SCCP gateway is needed for line-side devices. Both need to be configured on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager individually, but can run on same the physical gateway. The Cisco Unified Communications Manager supports MGCP version 0.1
|
Wrong Cisco IOS software image. Verify that the “adventerprisek9” image is used for trunks.
|
Legacy V.150.1 features are available only in Cisco IOS Release 12.4(4)T adventerprisek9 T-images and later releases. Cisco V.150.1 MER features are available beginning in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(4)M adventerprise9 image. Verify that the gateway is running a supported Cisco IOS image.
|
Cisco IOS STE/V.150.1 configuration commands are not present.
|
|
Trunk-side/off-net calls fail to secure
|
The MGCP
mgcp package-capability mdste-package
command is missing from the gateway configuration.
|
Verify that the MGCP trunk is configured correctly on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager. Verify that Enable V.150.1 subset is checked.
|
Delay, jitter, loss
|
Verify the network topology. Verify Quality of Service (QoS) settings. If using high-delay or error-prone links (for example, satellite connections), try configuring optional modem relay parameters such as SSE redundancy.
|
Dropped secure calls
|
T1 clocking errors can cause intermittent and dropped secure calls. Verify that the clocking on the T1 is accurate and correct.
|
|
On-net STE calls complete/secure, but off-net calls fail to secure
|
Unsupported PSTN gateway hardware or software.
|
Missing PSTN gateway in the MGCP Cisco IOS/Cisco Unified Communications Manager configuration.
|
PSTN gateway circuit errors (slips).
|
|
Started to configure trunk-side V.150.1, but all trunk-side calls fail
|
Mismatched MGCP PSTN gateway configuration.
|
Make sure the Enable V.150.1 subset checkbox is chosen in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager and the
package-capability mdste-package
command is configured for calls to proceed. If one piece is configured but the other is not, all calls across the MGCP-controlled trunk will fail, not just STE calls.
|
No audio after transitioning from secure to unsecure mode
|
MAC calls and busy trigger should be 1-to-1 on analog endpoints. (The symptom is caused whenyou are receiving a second call while in secure mode; you do not hear the call waiting tone.)
|
The V.150.1 (MER or Legacy) capabilities are lost over the SIP trunk
|
Ensure that appropriate V.150.1 SDP filtering options are set for the trunk. Filtering options are set via the trunks associated SIP Trunk Security Profile and the SIP V.150 Outbound Offer SDP filtering service parameter.
|

Note For problems with endpoints, such as phones, see the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL:
www.cisco.com/go/trademarks
. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2005, 2016 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.


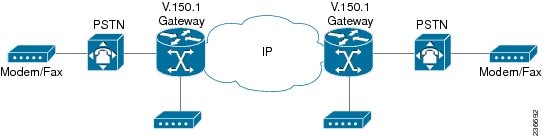

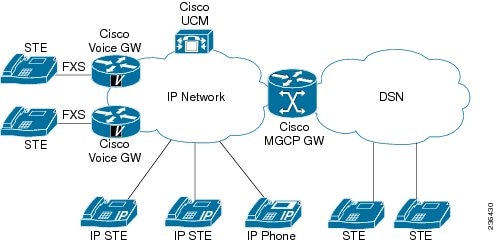


 Feedback
Feedback