Cisco IOS Telephony Services Version 2.01
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Cisco IOS Telephony Service Version 2.01
Phone Configuration Using a GUI
Remote Control of Cisco IP Phone with Basic TAPI-Capable PC Application
Voice Mail Message Waiting Indication
Cisco IOS Telephony Service Network Scenarios
Features Introduced in Version 1.0
Features Introduced in Version 2.0
Features Introduced in Version 2.01
Restrictions of Cisco IOS Telephony Service
Related Features and Documents
Supported Platforms and Devices
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Downloading Required System Files
Configuring DHCP for the Cisco IP Phone
Configuring Cisco IOS Telephony Service Mode
Obtaining the IP Address of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
Enabling Files on the TFTP Server
Associating Cisco IP Phones with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
Creating Directory Numbers for Cisco IP Phones (required)
Configuring Each Cisco IP Phone
Configuring Global Reset on Cisco IP Phones (optional)
Configuring Reset for Specific Cisco IP Phones (optional)
Verification and Troubleshooting
Verifying Cisco IOS Telephony Service Configuration
Troubleshooting the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
Additional Configuration Tasks
Configuring Date and Time (optional)
Configuring Dial-Plan Pattern (optional)
Configuring Local Directory (optional)
Configuring Keepalive (optional)
Configuring Interdigit Timeout (optional)
Configuring Three-Party G.711 Conference Calls (optional)
Configuring Music on Hold (optional)
Enabling Transfer of Calls (optional)
Configuring URL Provisioning (optional)
Configuring Speed-Dial (optional)
Configuring On-Hold Call Notification (optional)
Configuring Preference (optional)
Configuring Class of Restriction (optional)
Configuring Call Forward (optional)
Configuring Caller-ID Blocking (optional)
Applying Translation Rule (optional)
Disabling and Reenabling Huntstop (optional)
Enabling a Top-Line Description
Configuring Intercom (optional)
Configuring Paging for a Single Group
Configuring Paging for Multiple Groups
Configuring IVR Auto-Attendant (optional)
Configuring a Graphical User Interface
Configuring a GUI on the Router (required)
Getting Started with the GUI (required)
Configuring an Access Number for Voice Mail (required)
Configuring the Router for Cisco Unity Voice Mail (required)
Associating a Voice Mail Device (required)
Configuring Message Waiting Indication (optional)
Configuring Cisco Unity TSP (required)
Configuring Cisco Unity Ports (required)
Verifying Cisco Unity Configuration
DTMF Integration with Legacy Voice-Mail Devices (optional)
Configuring DTMF Patterns on the Router (required)
Configuring Integration Files on Legacy Voice-Mail Systems (required)
Integrating Cisco IOS Telephony Service with Applications
CiscoIOSTSP Download and Setup
Verifying Basic TAPI Operation
Monitoring and Maintaining Cisco IOS Telephony Service
admin-password (telephony-service)
admin-username (telephony-service)
date-format (telephony-service)
dialplan-pattern (telephony-service)
dn-webedit (telephony-service)
ip source-address (telephony-service)
max-conferences (telephony-service)
max-ephones (telephony-service)
mwi expires (telephony-service)
mwi sip-server (telephony-service)
pattern direct (vm-integration)
pattern ext-to-ext busy (vm-integration)
pattern ext-to-ext no-answer (vm-integration)
pattern trunk-to-ext busy (vm-integration)
pattern trunk-to-ext no-answer (vm-integration)
show telephony-service dial-peer
show telephony-service ephone-dn
show telephony-service voice-port
time-format (telephony-service)
timeouts interdigit (telephony-service)
time-webedit (telephony-service)
transfer-pattern (telephony-service)
Cisco IOS Telephony Service Version 2.01
August, 2002
Feature History
This document describes Cisco IOS Telephony Service, based on Cisco IOS software, on the Cisco 1751, Cisco 1760, Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 2600-XM series, Cisco 3600 series, Cisco IAD2420 series IADs, Cisco 3725, and Cisco 3745 routers. The Cisco IOS Telephony Service provides a telephony system perfect for a small office with a small number of extensions.

Note
You must purchase a feature license to turn this new feature on. You also need an account on Cisco.com to access the Cisco IP phone firmware versions.
This document includes the following sections:
•
Restrictions of Cisco IOS Telephony Service
•
Supported Platforms and Devices
•
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
•
Verification and Troubleshooting
•
Additional Configuration Tasks
•
Monitoring and Maintaining Cisco IOS Telephony Service
Feature Overview
Cisco IOS Telephony Service provides basic Cisco IP phone call-handling capabilities in a LAN environment on the Cisco routers. This service enables the Cisco multiservice routers to act as the Cisco IOS Telephony Service for the Cisco IP Phone 7960, Cisco IP Phone 7940, Cisco IP Phone 7910, and Cisco IP Conference Station 7935. This service also helps download phone software images and configures and manages the Cisco IP phones in your LAN. Cisco IOS Telephony Service provides a telephony system perfect for a small office with a small number of extensions.
Cisco IP Phones
Cisco IOS Telephony Service supports the Cisco IP Phone 7960, Cisco IP Phone 7940, Cisco IP Phone 7910, and Cisco IP Conference Station 7935.
Phone Firmware
The Cisco multiservice routers provide support for updating and storing of Cisco IP phone firmware. The Cisco IOS Telephony Service router also provides TFTP support for downloading the phone firmware files to the phone.

Note
When installing new Cisco IP phones to an ITS ATA device configuration, remove the tftp-server flash:XMLDefault.cnf.xml command temporarily until the new phones are installed properly. After the phones are installed and working correctly, restore the tftp-server flash:XMLDefault.cnf.xml command.
A way to verify correct phone load installation is to set registration debugging with the debug ephone register command, reset the phones, and look at the StationAlarmMessage displayed during phone re-registration. The "Load=" parameter should appear in the display, followed by an abbreviated version name corresponding to the phone load file
Phone Configuration
When Cisco IOS Telephony Service is configured, the Cisco IP phones receive initial configuration information and phone firmware from the TFTP server. In most cases, the Cisco IP phones obtain the IP address of their TFTP server with the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) option 150 command. For Cisco IOS Telephony Service operation, the TFTP server address obtained by the Cisco IP phones should point at the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router IP address. The Cisco IP phones attempt to transfer a configuration file called SEPDEFAULT.cnf. This file is automatically generated by the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router through the ip source-address command and placed in the router's Flash memory. The SEPDEFAULT.cnf file contains the IP address that the phones use to register for service, using the Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP). This IP address should correspond to a valid Cisco IOS Telephony Service router IP address (and may be the same as the router TFTP server address). Access to the SEPDEFAULT.cnf file must be granted through the tftp-server command on the router. For configuration information, see the "Required Configuration" section.
Phone Devices
Similarly, when an analog telephone adapter (ATA), such as ATA-186 is attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, the ATA receives very basic configuration information and firmware from the TFTP server XMLDefault.cnf.xml file. Access to the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file must be granted by using the tftp-server command on the router. The XMLDefault.cnf.xml file is automatically generated by the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router with the ip source-address command and is placed in the router's Flash memory. For configuration information, see the "Required Configuration" section.
Provisioning
The router provides a mechanism to provision Cisco IOS Telephony Service. This provisioning interface allows you to perform the following functions:
•
Assign directory numbers to the line appearances on each Cisco IP phone.
•
Assign numbers to the speed-dial buttons on each Cisco IP phone.
•
Assign caller identification information to each directory number.
•
Assign directory numbers to phones other than Cisco IP phones attached to the system by using the standard voice-port and dial-peer configuration CLI.
•
Provide dial-plan information to route calls either to public switched telephone network (PSTN) lines or voice network connections.
Hot-Plug Cisco IP Phones
The Cisco IP phones can be hot-plugged and unplugged to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router without requiring a router reboot or manual status reset.
Music on Hold
The Music on Hold (MOH) feature supports .au and .wav format files. Music on Hold works only for G.711 on-net VoIP calls and PSTN calls. For all other calls, Tone on Hold works where the user hears a periodic beep. The internal calls between Cisco IP phones do not get Music on Hold, instead they get Tone on Hold. For configuration information, see the "Configuring Music on Hold (optional)" section.
On-Hold Timeout Alert
This service adds an audible alert option as a reminder to the IP phone user that a call is waiting on-hold. For configuration information, see the "Configuring On-Hold Call Notification (optional)" section.
Three-Party G.711 Conference
Cisco IOS Telephony Service supports three-party conference for local and on-net calls. To participate in the conference, all conference participants must use G.711. This service also supports conversion between G.711 u-law and a-law. The maximum number of simultaneous conferences is platform-specific. For configuration information, see the "Configuring Three-Party G.711 Conference Calls (optional)" section.
Phone Configuration Using a GUI
The GUI interface is intended for two classes of users: the local administrators for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router and the end users of the Cisco IP phone. For each class of users, passwords can be set to prevent unauthorized personnel from accessing or changing Cisco IOS Telephony Service router configuration and Cisco IP phone configuration. Username and password are configured through the Cisco IOS CLI or through the GUI interface. For CLI configuration for the web access, see the "Configuring a GUI on the Router (required)" section.
Remote Control of Cisco IP Phone with Basic TAPI-Capable PC Application
Cisco IOS Telephony Service provides an interface that enables simple one-to-one remote control of a Cisco IP phone by an associated PC running CiscoIOSTSP, a Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) that supports placing outbound calls from an application address and phone address book. This interface is intended to support only basic TAPI services to enable caller-ID-based screen pops for incoming calls and to support simple outgoing call placement using one-click address-book style speed-dialing from the PC application. For an introduction to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service TSP interface, see the "Integrating Cisco IOS Telephony Service with Applications" section.

Note
This service does not add full TAPI support for multiple users or the multiple call handling required to implement complex features like automatic call distributor (ACD) or IP contact center (IPCC).
IVR Auto-Attendant
The IVR and Auto-Attendant mechanism can support the handling of inbound calls on FXO ports and outbound calls on FXS ports including analog phones configured through the plain old telephone system (POTS) and Cisco IP phones configured through the Cisco IP phone directory numbers (ephone-dn)—virtual FXS ports. The TCL scripts play prompts (welcome, phone number, store hours, and store locations), collect digits, and place calls. The IVR prompts must be downloaded on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router's Flash memory. The IVR prompts require an audio file (.au) format of 8-bit, u-law, and 8-KHz encoding. For configuration information, see the "Configuring IVR Auto-Attendant (optional)" section.
Customized Script
If you want Cisco to develop customized application scripts for you, contact the Developer Support group at developer-support@cisco.com. This is a fee based service.
In addition, if you are interested in developing TCL scripts, you can join the Cisco Developer Support Program. This program provides you with a consistent level of support. It also provides an easy process to open, update, and track issues using the Online Case tracking tool available at Cisco.com. This is also a fee based service.

Note
To participate in the Cisco Developer Support Program, you must have a signed Developer Support Agreement. For more details and for access to this agreement, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/570/index.html, or contact developer-support@cisco.com.
Voice Mail Message Waiting Indication
The message waiting indication (MWI) feature turns on the light indicator on the Cisco IP phone to inform you that you have a voice-mail message. For configuration information, see the "Configuring Message Waiting Indication (optional)" section.
Intercom
The Cisco IOS Telephony Service supports intercom functionality for one-way and press-to-answer voice connections. This is implemented using specially configured (from CLI or web only) speed-dial buttons that allow a call to be placed to the selected directory number (DN) and to make the called DN automatically answer the call in speakerphone mode, with mute activated. An alerting beep is played to the recipient as soon as the call is auto-answered. This provides a one-way voice path from the initiator to the recipient. To respond to the intercom call and open two-way voice, the recipient presses the Mute button to deactivate the mute (or in the case of a Cisco IP Phone 7910, lifts the handset). For configuration information, see the "Configuring Intercom (optional)" section.
Paging
The audio paging feature operates in a way similar to the intercom, but provides only one-way voice, with no press-to-answer option. A dummy DN that associates any number of local IP phones is created. The paging extension number is configured using the existing ephone-dn "number" parameter. Multiple paging DNs are supported per system. The paging number may be dialed from anywhere, including on-net calls. The paging audio stream is heard on all selected IP phones that are in the idle state, using speakerphone mode. The IP phone display shows the "name" information associated with the paging DN used to activate the page. The paging mechanism supports audio distribution using IP multicast, replicated unicast, and a mixture of both (so that multicast is used where possible, and unicast is used for specific phones that cannot be reached using multicast). For configuration information, see the "Configuring Paging (optional)" section.
URL Provisioning
The Cisco IP Phone 7960 and the Cisco IP Phone 7940 have customized function buttons that show the phone call status and activities on the display panels. These customized function buttons also invoke programmable non-call-related services. The four buttons—services, directories, messages, and information (the i button)—are linked to appropriate feature operations through programmable URLs. For configuration information, see the "Configuring URL Provisioning (optional)" section.

Note
You cannot customize the Settings button.
Specific URLs are provisioned on the Cisco IP phone; these URLs point to XML-based web pages formatted with XML tags that the Cisco IP phone understands and uses. When you press a function button, the Cisco IP phone uses the configured URL to access the appropriate XML web page for instructions. The web page sends instructions to the Cisco IP phone to display information on the screen for you to navigate. You can select options and enter information by using the softkeys and the scroll button.
Cisco IOS Telephony Service Network Scenarios
Figure 1 shows a typical deployment of a Cisco IOS Telephony Service router with several Cisco IP phones connected to it. The Cisco IOS Telephony Service router is connected to the PSTN. The router can also connect to a gatekeeper and a RADIUS billing server in the same network.
Figure 1 Cisco IOS Telephony Service for the Small and Medium Office
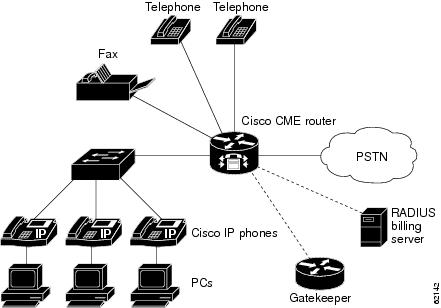
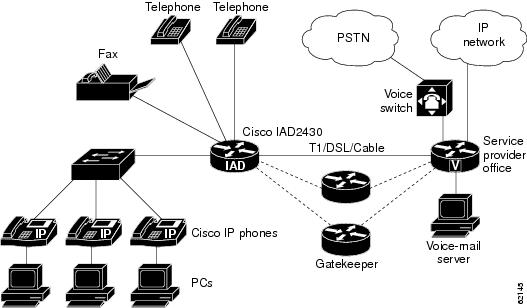
Figure 2 shows a branch office with several Cisco IP phones connected to a Cisco IAD2420 series IAD with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service. The Cisco IAD2420 series IAD is connected to a multiservice router at a service provider office. The multiservice router at the service provider office provides connection to the WAN and PSTN.
Figure 2 Cisco IOS Telephony Service for the Service Providers
Specifications
Cisco IOS Telephony Service supports 1 to 48 telephones, depending on the Cisco platforms. The following tables list the Cisco platforms, maximum number of Cisco IP phones, maximum number of directory numbers (DNs) or virtual voice ports, memory requirements for corresponding Cisco IOS releases:
•
Table 1—12.2(2)XT
•
Table 2—12.2(8)T
•
Table 3—12.2(11)T

Note
Although Cisco IOS can provide higher number of DNs for some of these platforms, the higher limitation may not apply in reality to your platform due to memory restrictions. We recommend that you follow the guidelines in the Specifications tables to configure your network.
Features Introduced in Version 1.0
Cisco IOS Telephony Service Version 1.0 introduced the following features supported on the Cisco IP phones:
•
Function keys
•
Dial-plan class of restriction (COR)
•
Call hold and retrieve
•
Call pickup of on-hold calls
•
Multiple lines per Cisco IP phone
•
Multiple line appearance across telephones
•
Call-forwarding functions: all, busy, and no answer
•
Call transferring
•
Speed dialing
•
Cisco IP phones derive the date and time from the router through Network Time Protocol (NTP)
•
Interworking with Cisco gatekeeper
•
Distinctive ringing: for external versus internal calls
•
Caller identification display and blocking
•
Analog Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) and Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) ports
•
On-net calls using Voice over IP (VoIP) H.323, Voice over Frame Relay (VoFR), and Voice over ATM (VoATM)
Features Introduced in Version 2.0
Cisco IOS Telephony Service Version 2.0 improves system manageability by providing a graphical user interface (GUI) using a standard web browser. Administrators who are not familiar with Cisco IOS command-line-interface (CLI) commands can now perform simple Cisco IP phone configuration changes using the GUI; for example, telephone number changes because of employee addition or turnover. This version also adds the following additional phone and basic voice-mail integration features:
•
Web browser phone administration interface
•
Web browser recent call history and activity display
•
Huntstop support
•
Translation rule support
•
Two-line support for Cisco IP Phone 7910
•
Cisco IP Conference Station 7935 support
•
Music on Hold (MOH)
•
Three-party G.711 conference calls
•
Distinctive ringing
•
Voice-mail integration with Active Voice using Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP), including message waiting indication
•
Cisco IP phone-to-phone intercom
•
Cisco IP phone audio paging system
•
On-hold call timeout alert
•
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) unsolicited message waiting notification support
•
Local phone directory display and search on Cisco IP phone
•
Cisco IP phone URL provisioning CLI
•
Basic Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) aware PC application support for incoming call caller-ID and outgoing call address-book dialing
•
Interactive voice response (IVR) and Auto-Attendant support per Cisco IP phone directory number using Toolkit Command Language (TCL)
•
Third-party H.323 call transfers
Features Introduced in Version 2.01
•
Support for a greater number of connected Cisco IP phones
•
Support for an increased number of directory numbers or virtual voice ports on Cisco IP phones
•
ATA-186
•
Top-line description for the Cisco IP Phone 7960 and Cisco IP Phone 7940
Restrictions of Cisco IOS Telephony Service
•
Cisco 1750 and Cisco 1751 do not support Quality of Service (QoS) features on the asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) link, Cisco Hoot and Holler over IP applications, and G.SHDSL WAN card supported in the current Cisco 1700 image sets.
•
Due to memory limitations, does not support Cisco 1750 in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)T.
•
Does not support Session initiation protocol (SIP) and Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) on-net calls.
•
Does not support first generation Cisco IP phones, such as Cisco IP Phone 30 VIP and Cisco IP Phone 12 SP+ are not supported.
•
Does not support any more Cisco IP phones than the maximum specified number in the "Specifications" section.
•
Does not support any more directory numbers than the maximum specified number in the "Specifications" section.
•
Does not support Element Management System (EMS) integration.
•
Does not support Cisco Voice Manager (CVM) support of IP phone configuration.
•
Does not support H.450 integration for MWI and on-net call transfers.
•
Does not support analog telephone call-transfer.
•
Does not support transfer with consult (with H.450 call transfer support).

Note
Standards-based H.323 call transfer for interworking with third-party H.323 endpoints is not supported because of lack of H.450 support.
•
Call transfer is supported only on the following:
–
VoFR, VoATM, and H.323 for Cisco gateway to Cisco gateway using H.323 nonstandard information element (both gateways running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)T)
–
FXO and FXS loopstart (analog)
–
FXO and FXS groundstart (analog)
–
E&M (analog) and DID (analog)
–
T1 channel associated signaling (CAS) with FXO and FXS groundstart signaling
–
T1 CAS with E&M signalling
–
All PRI and BRI switch types

Note
T1 CAS and PRI are not supported on the Cisco 1750 or Cisco 1751 routers.
•
Does not support MGCP fallback.
•
Does not support TAPI Version 2.1.

Note
Cisco IOS Telephony Service Version 2.0 implements only a small subset of TAPI functionality. It does support operation of multiple independent clients (for example, one client per phone line). The TSP support does not have full TAPI support for multiple user or multiple call handling, which is required for complex features such as automatic call distribution (ACD) and IP contact center (IPCC). Also, this TAPI version does not have direct media and voice-handling capabilities.
Related Features and Documents
•
Cisco IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Configuration Guide, Release 12.2
•
Cisco IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Command Reference, Release 12.2
•
Cisco IOS Debug Command Reference
•
Getting Started with the Cisco IP Phone 7910
•
Cisco IP Phone 7960 and 7940 Series At a Glance
•
Quick Reference Cisco IP Phone 7910 for IOS Telephony Service Version 2.0
•
Quick Reference Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940 for IOS Telephony Service Version 2.0
•
TCL IVR API Version 2.0 Programmer's Guide
•
Cisco 1750 Series Router Hardware Installation Guide
•
Cisco 1750 Voice-over-IP Software Configuration Guide
•
Cisco 1751 Router Hardware Installation Guide
•
Cisco 1751 Router Software Configuration Guide
•
Cisco IAD2420 Series Hardware Installation Guide
•
Cisco IAD2420 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
•
Cisco 2600 Series Hardware Installation Guide
•
Cisco 3600 Series Hardware Installation Guide
•
Cisco 3700 Series Hardware Installation Guide
Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 series routers
Supported Platforms and Devices
•
Cisco 1750 routers

Note
Due to memory limitations, Cisco 1750 is not supported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)T.
•
Cisco 1751 routers

Note
The Cisco 1750 and Cisco 1751 platforms do not support Quality of Service (QoS) features on the asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) link, Cisco Hoot and Holler over IP applications, and G.SHDSL WAN card supported in the current Cisco 1700 image sets.
•
Cisco 2600 series
•
Cisco 2600XM series
•
Cisco 2691 router
•
Cisco 3600 series
•
Cisco IAD2420 series
•
Cisco 3725 routers
•
Cisco 3745 routers
Cisco IP Phones
•
Cisco IP Phone 7910
•
Cisco IP Phone 7940
•
Cisco IP Phone 7960
•
Cisco IP Conference Station 7935
•
ATA-186
Determining Platform Support Through Cisco Feature Navigator
Cisco IOS software is packaged in feature sets that support specific platforms. To get updated information regarding platform support for this service, access Cisco Feature Navigator. Cisco Feature Navigator dynamically updates the list of supported platforms as new platform support is added for the feature.
Cisco Feature Navigator is a web-based tool that enables you to quickly determine which Cisco IOS software images support a specific set of features and which features are supported in a specific Cisco IOS image. You can search by feature or release. Under the release section, you can compare releases side by side to display both the features unique to each software release and the features in common.
Cisco Feature Navigator is updated regularly when major Cisco IOS software releases and technology releases occur. For the most current information, go to the Cisco Feature Navigator home page at the following URL:
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Standards
No new or modified standards are supported by this service.
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this service.
To obtain lists of supported MIBs by platform and Cisco IOS release, and to download MIB modules, go to the Cisco MIB web site on Cisco.com at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml
RFCs
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this service.
Prerequisites
•
IP routing must be enabled.
•
Network must be configured with DHCP.
•
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)T or later release is required.
•
Appropriate Cisco IP phone firmware versions that support the Cisco IP Phone 7960, Cisco IP Phone 7940, and Cisco IP Phone 7910 models, and Cisco IP Conference Station 7935 are required. To get the appropriate Cisco IP phone firmware versions, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/ip-key

Note
You must purchase a feature license to turn this new feature on. You also need an account on Cisco.com to access the Cisco IP phone firmware versions.
•
Memory requirements are dependent on the platform and the number of supported Cisco IP phones. See "Specifications" section for details.
Configuration Tasks
Perform the following configuration tasks on your router. Each task in the list is required.
Configuration Prerequisites
Before you start the basic configuration of Cisco IOS Telephony Service on your router, perform the following tasks. Each task in the list is required.
•
Downloading Required System Files
•
Configuring DHCP for the Cisco IP Phone
Downloading Required System Files
To download required image from the Software Center and to download other required system files, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/ip-key and perform the following tasks.

Note
If you need to replace individual files, go to the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/ip-iostsp
Step 1
Download the desired Cisco IOS software image from Software Center to the routers's Flash memory. Software Center button is located on the left panel.
Step 2
Get the appropriate Cisco IP phone firmware and download the firmware file to the router's Flash memory.
Step 3
Get the following GUI files and uncompress the two files:
•
GUI_Files.tar for UNIX
•
GUI_Files.zip for Windows
When you uncompress the two GUI files, you get the following files:
•
admin_user.html
•
telephony_service.html
•
normal_user.html
•
ephone_admin.html
•
logohome.gif
Download the files to the router's Flash memory.
Step 4
Get the music-on-hold files and download the files to the router's Flash memory.
Step 5
Get the TCL IVR script and download the files to the router's Flash memory.
Step 6
Download the CiscoIOSTSP.zip file to a convenient location on your PC. You need the TSP files to setup individual PCs for the Cisco IP phone user. For further details, see "CiscoIOSTSP Download and Setup" section.
Configuring DHCP for the Cisco IP Phone
When the Cisco IP phone is turned on, it automatically queries for a DHCP server. Then the DHCP server responds by assigning an IP address to the Cisco IP phone. The IP address of the TFTP server is also provided through DHCP option 150. The Cisco IP phone then attempts to get the configuration file SEPDEFAULT.cnf and phone firmware from the TFTP server.

Note
The SEPDEFAULT.cnf file is autogenerated in the router's Flash memory when Cisco IOS Telephony Service is configured.
You can configure DHCP for the Cisco IP phones by performing any of the following tasks:
•
Configuring the DHCP IP Address Pool
•
Configuring the DHCP IP Address for Each Cisco IP Phone
Configuring the DHCP IP Address Pool

Note
This process creates a large shared pool of IP addresses, where all DHCP clients receive the same information, including the option 150 TFTP server IP address. This can be a problem if some (non-IP phone) clients need to use a different TFTP server address.
To globally configure DHCP for all Cisco IP phones and other devices attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring the DHCP IP Address for Each Cisco IP Phone
To configure DHCP for each Cisco IP phone connected to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring DHCP Relay

Note
By default, the Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature is enabled on your router. If the feature is disabled, enable the Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature on your router.
To configure DHCP Relay on the LAN interface where the Cisco IP phones are connected and enable the Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
:
For further details about DHCP configuration, refer to the Cisco IOS DHCP Server document.
Required Configuration
See the following sections for configuration tasks for Cisco IOS Telephony Service. Each task in the list is required except the tasks that are marked as optional.
•
Configuring Cisco IOS Telephony Service Mode
•
Obtaining the IP Address of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
•
Enabling Files on the TFTP Server
•
Associating Cisco IP Phones with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
•
Creating Directory Numbers for Cisco IP Phones (required)
•
Configuring Each Cisco IP Phone
•
Configuring Global Reset on Cisco IP Phones (optional)
•
Configuring Reset for Specific Cisco IP Phones (optional)
Configuring Cisco IOS Telephony Service Mode
To enable Cisco IOS Telephony Service, enter the following command beginning in global configuration mode to enter the telephony-service configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)# telephony-service
Enters telephony-service configuration mode.
Obtaining the IP Address of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
To obtain the IP address of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, enter the following command in telephony-service configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config-telephony-service)# ip source-address ip-address [port port] [any-match | strict-match]
Identifies the IP address and port number the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router uses for the IP phone service. The default port is 2000.
The ip source-address command helps the router to autogenerate the SEPDEFAULT.cnf file and the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file, which are stored in the router's Flash memory. The SEPDEFAULT.cnf file contains the IP address of one of the Ethernet ports of the router to which the phone should register; the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file contains the IP address of one of the Ethernet ports of the router to which the ATA adapter should register. These files are specific to the router and cannot be shared by multiple routers.
Use the any-match keyword to instruct the router to permit Cisco IP phone registration, and use the strict-match keyword to instruct the router to reject Cisco IP phone registration attempts if the IP server address used by the phone does not exactly match the source-address.
TipMake sure that the SEPDEFAULT.cnf file and the XMLDefault.cnf.xml files are registered to the TFTP server. See "Enabling Files on the TFTP Server" section.
Enabling Files on the TFTP Server
When the Cisco IP phone contacts the TFTP server, it requests a configuration (SEPDEFAULT.cnf) file. The SEPDEFAULT.cnf file contains the IP address of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.

Tip
Make sure that the router's Flash memory contains the SEPDEFAULT.cnf file, the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file, and the appropriate phone firmware before enabling access to the phone firmware.
To enable access to the configuration file and phone firmware files on the TFTP server, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Associating Cisco IP Phones with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
Before associating the Cisco IP phones, see "Specifications" section to find out the maximum number of Cisco IP phones you can have on your Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
To associate Cisco IP phones with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, enter the following commands in telephony-service configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config-telephony-service)#
max-ephones max phonesConfigures the maximum number of Cisco IP phones supported by the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. The default is 0. The maximum number of IP phones is platform dependent. See "Specifications" section for details.
Note
You can increase the number of phones; but after the maximum allowable number is configured, you cannot reduce the maximum number without rebooting the router.
Step 2
Router(config-telephony-service)#
max-dn max directory numberConfigures maximum number of directory numbers supported by the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. The default is 0. The maximum directory number is platform dependent. See "Specifications" section for details.
Note
You can increase the directory numbers; but after the maximum allowable number is configured, you cannot reduce the maximum number without rebooting the router.
Step 3
Router(config-telephony-service)#
load {7960-7940 | 7910 | 7935} firmwareIdentifies the Cisco IP phone firmware used by the Cisco IP phone type. You must enter this command for each type of phone.
Note
The Cisco IP Phone 7960 and Cisco IP Phone 7940 have the same phone firmware.
Note
When you enter the load command, you do not use the extension of the file; for example, .bin.
TimesaverATA does not use the load command. For details see "Enabling Files on the TFTP Server" section.
Creating Directory Numbers for Cisco IP Phones (required)
To create directory numbers for Cisco IP phones, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone-dn dn-tagEnters ephone-dn configuration mode and configure the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines. The maximum directory number is platform dependent. See the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone-dn)# number number [secondary number] [no-reg [both | primary]]
Configures a valid number for the Cisco IP phone. The secondary keyword allows you to associate a second telephone number with an ephone-dn so that the IP phone line can be called by dialing either the main or the secondary phone number.
Unless you specify one of the option keywords (both or primary) after the no-reg keyword, the secondary number is not registered.
Step 3
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
name nameConfigures a username associated with a directory number.
You must follow the pattern specified in the directory command in telephony-service configuration mode to associate the usernames for the directory. The pattern for the usernames for the directory is set either with first-name-first or last-name-first.
Configuring Each Cisco IP Phone

Note
Each Cisco IP phone must be configured individually on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to receive support in the LAN environment. You must assign a number to the phone lines by entering the ephone-dn command and then you configure each physical Cisco IP phone by entering the ephone command.
To register each Cisco IP phone on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone tagEnters ephone (Ethernet phone) configuration mode to register Cisco IP phones. The maximum Cisco IP phone limit is platform dependent. See the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone)# mac-address mac-address
Specifies the MAC address of the registering phone.
Step 3
Router(config-ephone)#
button button-number:dn-tag button-number:dn-tagAssigns a button number to the Cisco IP phone directory number. The argument button-number:dn-tag, for example, can use the values 1:1, 2:4, or 3:14. In this example, button 1 corresponds to directory number 1 (ephone-dn 1), button 2 corresponds to directory number 4, and button 3 corresponds to directory number 14. The buttons correspond to the phone lines on the Cisco IP phone.
Configuring Global Reset on Cisco IP Phones (optional)
To globally reset the Cisco IP phones associated with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router after the required configuration is complete, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring Reset for Specific Cisco IP Phones (optional)
To reset a specific Cisco IP phone after the required configuration is complete, enter the following commands in global configuration mode:
Verification and Troubleshooting
•
Verifying Cisco IOS Telephony Service Configuration
•
Troubleshooting the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
Verifying Cisco IOS Telephony Service Configuration
To verify that the Cisco IOS Telephony Service is enabled, follow these steps:
Step 1
Enter the show run command to verify the configuration.
Step 2
Enter the show telephony-service all command to verify that Cisco IOS Telephony Service router is enabled.
Step 3
Verify that DHCP is configured.
Step 4
Verify that TFTP is configured.
Step 5
Enter the dir command to verify that the SEPDEFAULT.cnf file, XMLDefault.cnf.xml file, and the phone firmware files are stored in the router's Flash memory.
Step 6
Enter the show ephone [mac-address] command to verify all Cisco IP phones in the network.
Troubleshooting the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
To troubleshoot the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Enter the show ephone command to display all registered phones. If no phones are registered, then perform the following tasks:
a.
Configure the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
b.
Check DHCP configuration, including the default router and the TFTP server address (option 150).
c.
Use the dir command to check that the required files are in the router's Flash memory.
d.
Check that the tftp-server command is set for the required files.
e.
Use the debug ephone register mac-address command to display Cisco IP phone registration activity.
f.
Use the debug ip dhcp command to confirm DHCP operation.
Step 2
Enter the show ephone command to display all registered phones. If phones are registered and are displayed, then perform the following:
a.
Check that the phone button binding to the directory number is correct.
b.
Check that the Cisco IP phones show as registered.
c.
Verify the IP parameter settings on the Cisco IP phone, using the Settings display on the phone.
d.
Check that the keepalive count is being updated when you enter the show ephone command.
e.
Reset the phone and observe the re-registration by entering the debug ephone register mac-address command to display the Cisco IP phones.
f.
Enter the show ephone-dn summary command to check the state of the Cisco IP phone lines.
g.
Check the IP address of the phone and attempt to ping the address.
Step 3
Use the debug ephone keepalive command to set keepalive debugging for the Cisco IP phones.
Step 4
Use the debug ephone state command to set state debugging for the Cisco IP phones.
To troubleshoot other areas of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the following commands:
•
To set detail debugging for a Cisco IP phone, use the debug ephone detail command.
•
To set error debugging for a Cisco IP phone, use the debug ephone error command.
•
To set message waiting indication (MWI) debugging for a Cisco IP phone, use the debug ephone mwi command.
•
To set call statistics debugging for a Cisco IP phone use the debug ephone statistics command
•
To provide voice-packet-level debugging and print the contents of one voice packet in every 1024 voice packets, use the debug ephone pak command.
•
To provide raw low-level protocol debugging display for all SCCP messages, use the
debug ephone raw command.•
To provide debugging for local directory search, use the debug ip http token command
•
To troubleshoot HTTP authentication problems, use the debug ip http authentication command
•
To show the URLs accessed from the router, use the debug ip http url command.
•
To display HTTP server transaction processing, use the debug ip http transaction
For further debugging, you can use the debug commands in the Cisco IOS Debug Command Reference,
Cisco IOS Release 12.2.Additional Configuration Tasks
See the following sections for additional configuration tasks for Cisco IOS Telephony Service. Each task in the list is optional.
•
Configuring Date and Time (optional)
•
Configuring Dial-Plan Pattern (optional)
•
Configuring Local Directory (optional)
•
Configuring Keepalive (optional)
•
Configuring Interdigit Timeout (optional)
•
Configuring Three-Party G.711 Conference Calls (optional)
•
Configuring Music on Hold (optional)
•
Enabling Transfer of Calls (optional)
•
Configuring URL Provisioning (optional)
•
Configuring Speed-Dial (optional)
•
Configuring On-Hold Call Notification (optional)
•
Configuring Preference (optional)
•
Configuring Class of Restriction (optional)
•
Configuring Call Forward (optional)
•
Configuring Caller-ID Blocking (optional)
•
Applying Translation Rule (optional)
•
Disabling and Reenabling Huntstop (optional)
•
Enabling a Top-Line Description
•
Configuring Intercom (optional)
•
Configuring Paging (optional)
•
Configuring IVR Auto-Attendant (optional)
Configuring Date and Time (optional)
To configure date and time format, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring Dial-Plan Pattern (optional)
To configure a dial-plan pattern, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring Local Directory (optional)
To configure the local directory, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring Keepalive (optional)
To configure sending keepalive messages, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring Interdigit Timeout (optional)
To configure interdigit timeout value for all Cisco IP phones, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)# telephony-service
Enters telephony-service configuration mode.
Step 2
Router(config-telephony-service)# timeouts interdigit seconds
Configures the interdigit timeout value for all Cisco IP phones attached to the router.
The interdigit timeout specifies the number of seconds that the system waits after the caller has entered the initial digit or a subsequent digit of the dialed string. If the timeout ends before the destination is identified, a tone sounds and the call ends. This value is important when using variable-length dial peer destination patterns (dial plans). For more information on setting dial plans, see the "Configuration Dial Plans, Dial Peers, and Digit Manipulation" chapter of the Cisco IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Configuration Guide, Release 12.2.
The seconds argument is the interdigit timeout wait time in seconds. A valid entry is an integer from 2 to 120 seconds. The default is 10 seconds.
Configuring Three-Party G.711 Conference Calls (optional)
To configure three-party G.711 conference calls for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring Music on Hold (optional)
The Music on Hold (MOH) feature supports .au and .wav format files. Music on Hold works only for G.711 on-net VoIP calls and PSTN calls. For all other calls, Tone on Hold works where the user hears a periodic beep. The internal calls between Cisco IP phones do not get Music on Hold, instead they get Tone on Hold.
To configure Music on Hold), enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Enabling Transfer of Calls (optional)
To enable call transfer between Cisco IP phones and non-IP phones, enter the following commands beginning in telephony-service configuration mode:
Configuring URL Provisioning (optional)
The Cisco IP Phone 7960 and Cisco IP Phone 7940 can support four URLs in association with the four programmable feature keys on the IP phones. The four feature keys on the IP phone: directories, information, messages, and services are configured using the keywords. The fifth key—settings—is managed entirely by the phone. Operation of these services is determined by the IP phone capabilities and the content of the referenced URL.
To configure URL provisioning, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring Speed-Dial (optional)
To configure speed-dial for numbers that are used frequently, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone tagEnters ephone configuration mode to register Cisco IP phones. The maximum number of Cisco IP phones is platform dependent. For details, see the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone)#
speed-dial button-number directory-numberSets speed-dial buttons on a Cisco IP phone.
Note
Although 20 speed dials can be configured on the Cisco IP phone, ATA phones support only 9 speed-dials with Cisco IOS Telephony Service: *1, *2, *3,*4,*5,*6,*7,*8, and *9.
Configuring On-Hold Call Notification (optional)
To configure on-hold audible notification on the Cisco IP phone to alert the user about on-hold calls, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone-dn dn-tagEnters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines. The maximum directory number is platform dependent. For details, see the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone-dn)# number number
Configures a valid directory number for the Cisco IP phone that receives on-hold call notification.
Step 3
Router(config-ephone-dn)# name name
Assigns the IP phone number a name for display.
Step 4
Router(config-ephone-dn)# hold-alert timeout {idle | originator | shared}
Sets audible alert notification on the Cisco IP phone for alerting the user about on-hold calls. The timeout parameter specifies the time interval in seconds from the time the call is placed on hold to the time the on-hold audible alert is generated. The alert is repeated at the end of the set timeout.
When the idle keyword is enabled, a one-second burst of ringing on the phone is generated on the IP phone that placed the call into the hold state, only if the phone is in the idle state. If the phone is in active use, no on-hold alert is generated.
When the originator keyword is enabled, a one-second burst of ringing is generated on the phone that placed the call into the hold state if the phone is in the idle state. If the phone is in use on another call, an audible beep is generated (call-waiting tone).
Note
From the perspective of the originator of the call on-hold, the shared and the originator keywords provide the same functionality.
When the shared keyword is enabled, a one second ring burst is generated for all the idle phones which share the same line appearance. If the phones are in use, they do not get an audio beep alert. Only the phone that initiated the call, if busy, hears a call-waiting beep.
Configuring Preference (optional)
To configure preference, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone-dn dn-tagEnters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines. The maximum directory number is platform dependent. For details, see the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
preference preference-orderSets preference for the attached dial peer for a directory number. The range is from 0 to 10. The default is 0.
Configuring Class of Restriction (optional)
Class of restriction (COR) is used to specify which incoming dial peer can use which outgoing dial peer to make a call. Each dial peer can be provisioned with an incoming and an outgoing COR list.
To configure COR on the dial peers associated with a directory number, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone-dn dn-tagEnters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines. The maximum directory number is platform dependent. For details, see the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
cor {incoming | outgoing} cor-list-nameConfigures a class of restriction (COR) on the dial peers associated with a directory number. For more information on setting COR, see the "Configuring Dial Peer Matching Features" section in the "Configuration Dial Plans, Dial Peers, and Digit Manipulation" chapter of the Cisco IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Configuration Guide, Release 12.2.
Configuring Call Forward (optional)
To configure forwarding calls to other Cisco IP phones, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone-dn dn-tagEnters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines. The maximum directory number is platform dependent. For details, see the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone-dn)# number number
Configures a valid directory number for the Cisco IP phone that receives on-hold call notification.
Step 3
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
call-forward all directory-numberConfigures call-forwarding for all incoming calls on one of the lines of a Cisco IP phone to another telephone.
Step 4
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
call-forward busy directory-numberConfigures call-forwarding to another number when the Cisco IP phone is busy.
Step 5
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
call-forward noan directory-number timeout secondsConfigures call-forwarding to another number when no answer is received from the Cisco IP phone.
The timeout keyword sets the waiting time before the call is forwarded to another phone. The time is set in seconds. The range is 3 to 60,000.
Note
It is mandatory to specify and enter a timeout number in seconds, otherwise an error message "incomplete command" will appear on the console.
Configuring Caller-ID Blocking (optional)
To configure caller-ID blocking for outbound calls from a Cisco IP phone, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone-dn dn-tagEnters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines. The maximum directory number is platform dependent. For details, see the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
caller-id blockConfigures caller-ID blocking for outbound calls originated from the ephone-dn. This commands requests that the far-end gateway device blocks display of the calling party information, for calls received by the far-end gateway from the ephone-dn. This configuration does not affect the ephone-dn calling party information display for inbound calls received by the ephone-dn.
By default, caller ID is not blocked on calls originating from the Cisco IP phone.
Applying Translation Rule (optional)
Translation rules are a powerful general purpose number manipulation mechanism supported by Cisco IOS software that can be used to perform operations such as automatically adding telephone area and prefix codes to dialed numbers. The translation rules are applied to the voice ports created by the ephone-dn.
To apply a translation rule to numbers dialed by Cisco IP phone users, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone-dn dn-tagEnters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines. The maximum directory number is platform dependent. For details, see the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
translate {called | calling} translation-rule-tagSelects a translation rule to numbers dialed by Cisco IP phone users. The called keyword translates the called number, and the calling keyword translates the calling number.
Note
Appropriate translation rules should be created on the VoIP configuration level, for the translate command to take effect.
The translation-rule-tag argument is the reference number of the translation rule. Valid entries are 1 to 2,147,483,647. For further details, see the "Configuration Dial Plans, Dial Peers, and Digit Manipulation" chapter of the Cisco IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Configuration Guide, Release 12.2.
Disabling and Reenabling Huntstop (optional)

Note
In ephone-dn configuration mode, huntstop is set by default.
To disable or to reenable huntstop, enter the following commands in ephone-dn configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone-dn dn-tagEnters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines. The maximum directory number is platform dependent. For details, see the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
no huntstopDisables huntstop.
Step 3
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
huntstopEnables huntstop.
Enabling a Top-Line Description
To enable a alphanumeric description label in the top black bar on the display screen for a Cisco IP Phone 7960 and Cisco IP Phone 7940 connected to a Cisco IOS Telephony router, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode.
The following example shows the configuration for a top black bar description for ephone-dn 5 which is associated with extension number 8001:
ephone-dn 5number 8001description 408 555 1212Configuring Intercom (optional)
The intercom configuration dedicates a pair of ephone-DNs for use as a "press to talk" two-way intercom between two IP phones. Intercom lines cannot be used in shared-line configurations. If an ephone-dn is configured for intercom operation, it must be associated to one IP phone only. The intercom attribute causes an IP phone line (ephone-dn) to operate as auto-dial for outbound calls and auto-answer-with-mute for inbound calls.
To configure intercom, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)#
ephone-dn dn-tagEnters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines. The maximum directory number is platform dependent. For details, see the "Specifications" section.
Step 2
Router(config-ephone-dn)# number number
Configures a valid intercom number for the Cisco IP phone that receives the intercom.
Step 3
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
name nameConfigures a username associated with a directory number to receive the intercom.
"Intercom" is used in place of the name argument.
Step 4
Router(config-ephone-dn)# intercom directory number [barge-in | no-auto-answer] [label label]
Defines the directory number for the Cisco IP phone that connects with another IP phone for the intercom feature. The intercom command dedicates a pair of ephone-DNs for use as a "press to talk" two-way intercom between two IP phones. The barge-in keyword allows inbound intercom calls to force an existing call into the call-hold state and allows the intercom call to be immediately answered. The no-auto-answer keyword creates a connection for the IP phone line resembling private line automatic ringdown (PLAR). The label keyword defines a text label for the intercom.
Step 5
Router(config-ephone-dn)#
Repeat Steps 1 to Step 4 for the second Cisco IP phone that requires the intercom feature.
Note
For the intercom feature to work, you must configure both Cisco IP phones.
Step 6
Router(config-ephone-dn)# exit
Exits ephone-dn configuration mode.
Step 7
Router(config)#
ephone tag(Optional) Enters ephone configuration mode to register Cisco IP phones.
Step 8
Router(config-ephone)#
button button-number:dn-tag button-number:dn-tag button-number:dn-tag(Optional) Assigns a button number to the Cisco IP phone directory number. The argument button-number:dn-tag, for example, can use the values 1:1, 2:4, and 3:14. The third set ephone tag 3 is set to the intercom directory number 14, so that the third button (directory number) is set to receive the intercom.
The following example shows intercom configuration between two Cisco IP phones:
ephone-dn 18number A5001name "intercom"intercom A5002 barge-inephone-dn 19name "intercom"number A5002intercom A5001 barge-inephone 4button 1:2 2:4 3:18ephone 5button 1:3 2:6 3:19In this example, directory number (ephone-dn) 18 and directory number (ephone-dn) 19 are set as an intercom pair. Directory number (DN) 18 is associated with button 3 of Cisco IP phone (ephone) 4 and directory number (DN) 19 is associated with button number 3 of Cisco IP phone (ephone) 5. Button 3 on both Cisco IP phone 4 and Cisco IP phone 5 are set as a pair to provide intercom service to each other.
Configuring Paging (optional)
To configure paging, complete the following tasks:
•
Configuring Paging for a Single Group
•
Configuring Paging for Multiple Groups
Configuring Paging for a Single Group
The paging feature configures the ephone-dn number to act as an extension number to broadcast unicast audio paging to idle Cisco IP phones. Cisco IP phones must be associated with the ephone-dn tag number of the paging ephone-dn, or need to be included indirectly through a paging group from another paging ephone-dn. The audio paging feature operates in a similar fashion to intercom, but provides only one-way voice, with no press-to-answer option. A directory number (DN) is created, which associates the IP phone as part of a paging group.
To configure paging for a single group of phones in your network—for example,
for one department—enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
The configuration example follows:
ephone-dn 20number 2000paging ip 224.0.1.20 port 2000ephone-dn 21number 2001paging ip 224.0.1.21 port 2000ephone 1button 1:1paging-dn 20ephone 2button 1:2paging-dn 20ephone 3button 1:3paging-dn 21ephone 4button 1:4paging-dn 21In this example paging calls to 2000 are multicast to Cisco IP phones 1 and 2, and paging calls to 2001 go to Cisco IP phones 3 and 4.
Configuring Paging for Multiple Groups
To configure paging for multiple groups of phones in your network—for example—for combining several departments like Marketing, Engineering, or Finance, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
The following example shows how to set paging groups:
ephone-dn 20number 2000paging ip 224.0.1.20 port 2000ephone-dn 21number 2001paging ip 224.0.1.21 port 2000ephone-dn 22number 2002paging ip 224.0.2.22 port 2000paging group 20,21ephone 1button 1:1paging-dn 20ephone 2button 1:2paging-dn 20ephone 3button 1:3paging-dn 21ephone 4button 1:4paging-dn 21ephone 5button 1:5paging-dn 22In this example, paging calls to 2000 go to ephones 1 and 2, and paging calls to 2001 go to ephones 3 and 4. Calls to 2002 go to ephones 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. Ephones 1 and 2 are included into paging ephone-dn 22 through membership of ephone-dn 20 in the paging group. Ephones 3 and 4 are included into paging ephone-22 through membership of ephone-dn 21 in the paging group. Ephone 5 is directly included as using paging-dn 22.
Configuring IVR Auto-Attendant (optional)
To configure IVR for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, see the "Configuring TCL IVR Applications" chapter of the Cisco IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Configuration Guide, Release 12.2.
The following example shows how to configure IVR for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router:
call application voice auto_att_flash flash://vespa_aa_ipks_2.4.tclcall application voice auto_att_flash aa-pilot 6000call application voice auto_att_flash operator 21111call application voice auto_att_flash language 1 encall application voice auto_att_flash set-location en 0 flash://To configure an application for the Cisco IP phone directory number, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration command:
The following example shows how to configure an application for a particular Cisco IP phone directory number:
ephone-dn 1application <application name> = auto_att_flashThe following example shows how to configure an application for a POTS dial peer:
dial-peer voice 100 potsapplication <application name> = auto_att_flashThe following example shows how to configure an application for a voice dial peer:
dial-peer voice 100 voipapplication <application name> = auto_att_flashAdvanced Configuration Tasks
•
Configuring a Graphical User Interface
•
DTMF Integration with Legacy Voice-Mail Devices (optional)
•
Integrating Cisco IOS Telephony Service with Applications
Configuring a Graphical User Interface
The Cisco IOS Telephony Service graphical user interface (GUI) provides you with comprehensive management features to help configure and maintain the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. It also provides limited features for end users of the Cisco IP phones. As the administrator, you must set up a username and password for yourself to allow administrator-level login to the GUI and you must set up the username and password for the Cisco IP phone end user to allow end-user level login to the GUI.
See the following sections for configuration tasks for the GUI. Each task in the list is identified as either required or optional.
•
Configuring a GUI on the Router (required)
•
Getting Started with the GUI (required)
Configuring a GUI on the Router (required)
To configure the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router for GUI, perform the following tasks:
•
Enabling an HTTP Server on Cisco IOS Software
Enabling an HTTP Server on Cisco IOS Software
The HTTP server in Cisco IOS is disabled; so to use GUI, you must enable the HTTP server. To access the GUI through the web browser, perform the following tasks in global configuration mode:
Setting Up GUI
To set up a username and password for yourself to allow administrator-level login to the GUI and to set up the username and password for the Cisco IP phone end users, enter the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:

Note
After completing the GUI configuration, access the GUI for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service through the web browser.
Getting Started with the GUI (required)
To access the Cisco IP phones through the GUI interface on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router complete the following tasks:
•
Logging In as the Administrator
•
Setting Up for the Cisco IP Phone End User
Logging In as the Administrator

Note
Make sure that the GUI configuration is completed on the router side.
You can assign, modify, or delete usernames and passwords through the GUI interface. You can also assign and modify Cisco IP phones and directory numbers for an end user.
To access the GUI, complete the following steps:
Step 1
Access the GUI for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service by going to the following URL:
http://ip_address/telephony_service.html
where ip_address is the router IP address of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.Step 2
When you go to the telephony_service.html page, you see the window shown in Figure 3. Enter your username and password, and click Submit.

Note
The window shown in Figure 3 is the common login page for you and the Cisco IP phone end user.
Figure 3 Cisco IOS Telephony Service GUI Login Page

After you identify yourself as the administrator and enter the correct username and password, you see the window shown in Figure 4. This is the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Home Page for the administrator. You can use all the options from the Main Menu.

Tip
For information on a specific page, click Help Information. The links work only in the Microsoft Internet Explorer browser, version 5.5 and later versions.
Figure 4 Cisco IOS Telephony Service Home Page for the Administrator

Setting Up for the Cisco IP Phone End User
As the administrator, you also must set a username and password for each Cisco IP phone end user. After you have assigned a username and password for the end user, the user can log in to the GUI to change the password, search local telephone numbers, and change speed-dial settings for the user's IP phone.
To provide GUI access to the Cisco IP phone end user, complete the following steps:
Step 1
Access the GUI interface for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service by going to the following URL:
http://ip_address/telephony_service.html
where ip_address is the router IP address of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.Step 2
When you go to the telephony_service.html page, you see the window shown in Figure 5. To provide the Cisco IP phone user personal login and initial password, enter the username and initial password of the end user and click Submit to log in as the end user.

Note
The window shown in Figure 5 is the common login window for you and the Cisco IP phone end user.
Figure 5 Cisco IOS Telephony Service GUI Login Window

When the Cisco IP phone users log in to the GUI, they see the window as shown in Figure 6. This page allows the Cisco IP phone users to change the password, search local telephone numbers, and change speed-dial settings for their individual IP phone.
Figure 6 Cisco IOS Telephony Service GUI User Main Window

Verifying GUI Configuration

Note
The configuration changes made on the GUI automatically reset and change the settings on the Cisco IP phone.
Check the Cisco IP phone display screen to verify each configuration change made on the GUI interface.
Integrating Voice Mail
The Cisco Unity Voice Mail system supports voice-mail integration with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service. If you want voice-mail integration, you must configure the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router for voice mail and then configure the Cisco Unity software on the PC to get voice-mail service.
See the following sections for configuration tasks for integrating voice mail. Each task in the list is identified as either required or optional.
•
Configuring an Access Number for Voice Mail (required)
•
Configuring the Router for Cisco Unity Voice Mail (required)
•
Associating a Voice Mail Device (required)
•
Configuring Message Waiting Indication (optional)
•
Configuring Cisco Unity TSP (required)
•
Configuring Cisco Unity Ports (required)
Configuring an Access Number for Voice Mail (required)
You must configure an access number to connect to the voice-mail system. This number is required for any kind of voice-mail integration.

Note
The same number is configured on all the Cisco IP phone directory number to connect to voice mail. For more information, see "Configuring the Router for Cisco Unity Voice Mail (required)" section.
To configure the telephone number that is speed-dialed when the message button on a Cisco IP phone is pressed, enter the following commands beginning in telephony-service configuration mode:
Following is an example of the configuration:
telephony-servicevoicemail 4001
Configuring the Router for Cisco Unity Voice Mail (required)
To configure a voice-mail system on a Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, you allocate and configure one or more Cisco IP phone directory numbers (DN) to link your Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to your voice-mail system. Use a Cisco IP phone DN and configure it with the same access number for the voice-mail (configured in telephony-service configuration mode), for example 4001. This configuration is required for all voice-mail system integration, including Cisco Unity Voice Mail.
To create virtual voice-mail ports, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
The following is a typical configuration example:
ephone-dn 32number 4001name "VOICEMAIL1"no huntstoppreference 0!ephone-dn 33number 4001name "VOICEMAIL2"no huntstoppreference 1!ephone-dn 34number 4001name "VOICEMAIL3"no huntstoppreference 2!ephone-dn 35number 4002name "MWI ONLY"
In the example above, there are four ephone-dns configured to provide four voice-mail access ports. Three of the ephone-dns are configured with the same extension number to provide ports dedicated for leaving and retrieving voice messages. The fourth ephone-dn is provided for use as a MWI access port. The first three ephone-dns are configured with the same extension number (4001), using preferences
0, 1, and 2; so if the first port is busy, the call goes to the second port, and so on. Port 4 is configured with the extension number 4002 and is used for MWI dial-out notification by the Cisco Unity Voice Mail system. Separate access ports are required for voice access and MWI access to prevent problems with call collision between voice calls placed by the Cisco IOS Telephony Service to the Cisco Unity Voice Mail system, and MWI calls placed in the opposite direction.Associating a Voice Mail Device (required)
To associate the actual voice-mail device (vm-device-id) to the phone number, associate the Cisco IP phone with the voice-mail device.

Note
The default vm-device-id name is CiscoUM-VI and it should match the Device name prefix configuration on the Cisco Unity Telephony Service Provider (TSP) side. You also must complete the configuration on the TSP side.
To associate a voice-mail device to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, enter the following tasks beginning in ephone configuration mode:
Following is an example of the configuration. In this example, the vm-device-id is used within the ephone configuration in place of the mac-address parameter that is used for configuring a regular Cisco IP phone:
ephone 5vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI1button 1:32!ephone 6vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI2button 1:33!ephone 7vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI3button 1:34!ephone 8vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI4button 1:35
Configuring Message Waiting Indication (optional)
The message waiting indication (MWI) mechanism turns on the light indicator on Cisco IP phones to inform you that you have a voice-mail message. Figure 7 shows a network with a Cisco IP phone and a Cisco IOS Telephony Service router connected to a Cisco Unity Voice Mail system.
Figure 7 Basic MWI Network

To configure the MWI mechanism, perform the following tasks:
•
Configuring the SIP-Based MWI Server
•
Configuring MWI for Each Directory Number
•
Configuring a Directory Number for MWI Notification
Configuring the SIP-Based MWI Server
To configure the IP address and port for the SIP-based message waiting indication (MWI) server, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring MWI for Each Directory Number
To configure message waiting indication (MWI) notification for each directory number (DN), use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring a Directory Number for MWI Notification
MWI integration on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router is performed by dedicating Cisco IP phone directory numbers (ephone-DNs) to process MWI status notification calls originating from the
Cisco Unity Voice Mail system. You must allocate a minimum of one MWI processing ephone-dn for each MWI ephone-dn access port. The MWI processing ephone-dn extension numbers are configured to match the MWI dial-out notification numbers configured on the Cisco Unity Voice Mail system.To configure MWI notification for an individual DN attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Following is a configuration example:
ephone-dn 32number 8000 secondary 8001mwi on-off
In the example above, the Cisco Unity Voice Mail system places MWI notification calls to the extension numbers 8000 and 8001 to activate and de-activate message waiting lights. The DN responds to calls placed to extension numbers 8000 and 8001, and trigger a MWI ON event when 8000 is called, and a MWI OFF event when 8001 is called.
MWI Mechanism
The MWI mechanism is initiated after someone leaves a voice-mail message. The internal MWI mechanism of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router is explained in Figure 8.
Figure 8 MWI Mechanism

In the network topology in Figure 8, the following takes place:
1.
The Cisco IP phone with the extension 2001 receives a call and the call is not answered.
2.
The Cisco IP phone with the extension 2001 forwards the call to the voice-mail access port 4001.
3.
The Cisco Unity Voice Mail system (extension 4001) stores the new message for extension 2001.
4.
The Cisco Unity Voice Mail then places an MWI notification call to the MWI processing ephone-dn 8000 (through the MWI access port 4002) with the calling party ID for the notification call set to 2001.
5.
The Cisco IOS Telephony Service directory number (DN) 8000 accepts the MWI notification call and switches on the message waiting light for extension 2001.
The Cisco IOS Telephony Service router can convey MWI information to the Cisco IP phone DNs if the Cisco IP phones are associated with the router.
If the Cisco IP phones are not associated with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router connected to the Cisco Unity Voice Mail system, the MWI information is conveyed by using the MWI relay feature. For further details, see the "Configuring MWI Relay" section.
Configuring MWI Relay
MWI relay is required when one Cisco Unity Voice Mail system is shared by multiple Cisco IOS Telephony Service routers. All Cisco IOS Telephony Service routers can to do MWI relay using the SIP subscriber and notifier mechanism. Figure 9 shows a network topology with MWI relay mechanism. The Cisco IOS Telephony Service router attached to the Cisco Unity Voice Mail system, running the SIP MWI relay server, is the SIP notifier and the other remote Cisco IOS Telephony Service routers are the SIP subscribers.
To configure MWI relay notification to individual IP phones attached to remote Cisco IOS Telephony Service routers, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
The following example shows the MWI configuration for the central site Router 1, the MWI notifier:
telephony-servicemwi relaymwi expires 8600The MWI SIP configuration should be added for each directory number (DN) on the remote router that requires MWI service. For more information, see the "Configuring the SIP-Based MWI Server" section. The following is a configuration example for a remote Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, Router 2, the MWI subscriber:
telephony-servicemwi sip-server 1.10.12.1!ephone-dn 1number 6001mwi sip!When a voice-mail system has MWI information for any extension local or remote, it dials the central site Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. When the central site receives the MWI information, it attempts to find out whether the extension is local to the central site. If it cannot find the extension, it passes the MWI information to its notifier interface of SIP MWI. If the notifier interface on central site has the extension as a subscriber, it relays the MWI information to the remote Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
In Figure 9, Router 1 is the central site Cisco IOS Telephony Service router—the MWI notifier—and uses the MWI integration mechanism described earlier to interface with the Cisco Unity Voice Mail system. The Cisco IP phone directory numbers on Router 2 and Router 3 register with Router 1 by using the SIP subscriber mechanism. Router 1 as the SIP notifier recognizes the Cisco IP phone directory numbers associated with Router 2 and Router 3 to relay MWI.
Figure 9 Network with MWI Relay

MWI Relay Mechanism
The MWI relay mechanism is initiated after someone leaves a voice-mail message on the remote voice-mail message system. In the network topology in Figure 9, the following takes place:
1.
The Cisco IP phone with the extension 5001 receives a call and the call is not answered.
2.
The Cisco IP phone with the extension 5001 forwards the call to the voice-mail access port 4001.
3.
The Cisco Unity Voice Mail system (extension 4001) stores the new message for extension 5001.
4.
Cisco Unity Voice Mail then places a MWI notification call to the MWI processing ephone-dn 8000 (through the MWI access port 4002) to the central Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, Router 1, with the calling party ID for the notification as extension 5001.
5.
Router 1, acting as the SIP notifier, relays MWI notification to Router 3, one of the SIP subscribers.
6.
Router 3, the local Cisco IOS Telephony Service router for extension 5001, turns the MWI light to ON on the Cisco IP phone 5001.
Configuring Cisco Unity TSP (required)
To configure Cisco Unity Voice Mail software, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Go to the Start>Settings>Control Panel>Phone and Modem Options and the Phone and Modem Options window appears. Click on the Advanced tab and select Av-Cisco Service Provider and click Configure, shown in Figure 10 and the Av-Cisco Service Provider window appears, shown in Figure 11.
Figure 10 Phone and Modem Options Window

Step 2
Add the IP address of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router in the Av-Cisco Service Provider dialog box, shown in Figure 11. Click OK.
Figure 11 Av-Cisco Service Provider Dialog Box

Step 3
In the Av-Cisco Service Provider Settings dialog box, shown in Figure 12, perform the following steps.
Figure 12 Av-Cisco Service Provider Settings Dialog Box

a.
Confirm the IP address of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
b.
Confirm the number of Cisco Unity ports.
c.
Confirm the Device name prefix. The default name is CiscoUM-VI. The voice-mail device name must match the device name configured on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
d.
Enter the directory numbers next to MessageWaitingOnDN and MessageWaitingOffDN.

Note
These directory numbers must match the extension numbers configured on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
e.
Confirm that the CallManager Device List displays the correct number of Cisco Unity Ports.
f.
Click OK.
Step 4
The Av-Cisco Service Provider dialog box, shown in Figure 11 reappears. Click Test.
If you do not receive an error message, click OK.Step 5
Restart Cisco Unity.
Step 6
To modify any configuration, repeat Step 1 through Step 4.
Configuring Cisco Unity Ports (required)

Note
After Cisco Unity software is installed on the PC, you see two icons on the desktop: System Administration and Status Monitor.
The port configuration on the Cisco Unity software must match the port configuration on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. To configure the Cisco Unity ports, you must perform the following steps:
Step 1
Click the System Administration icon on the desktop. The screen shown in Figure 13 appears.
Figure 13 System Administration Window

Step 2
In the System menu, click Ports. The Port Configuration dialog box, shown in Figure 14, appears.
Step 3
To match the settings from Cisco Unity, click on port number 1 and select Answer Calls. Make sure that Dial Out MWI is not selected, as shown in Figure 14.
Step 4
Click on port number 2 and repeat Step 3.
Step 5
Click on port number 3 and repeat Step 3.
Step 6
Click on port 4. Make sure that the Answer Calls option is not selected and that the Dial Out MWI option is selected, as shown in Figure 14.
Figure 14 Port Configuration Window

Verifying Cisco Unity Configuration
To verify Cisco Unity configuration, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Go to Start>Settings>Control Panel>Telephony>Telephony Drivers>Unity Service Provider for CallManager. Select Configure. The Av-Cisco Service Provider window appears, as shown in Figure 15.
Step 2
Click Test in the Av-Cisco Service Provider window, shown in Figure 15, and complete the subsequent steps as needed.
Figure 15 Av-Cisco Service Provider Window

Troubleshooting Tips
On the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
If you are having problems with calls not getting forwarded to the Cisco Unity Voice Mail or problems with the MWI light not turning on or off, use the debug commands for debugging the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to verify that the appropriate calls are set up between
Cisco Unity and the router.On the Cisco Unity TSP
For specific problems on the Cisco Unity side, refer to the Cisco Unity documentation. Go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/unity24/tsg/tsg246.pdf
DTMF Integration with Legacy Voice-Mail Devices (optional)
For dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) integrations, information on how to route incoming or forwarded calls is sent by the telephone system in the form of DTMF digits. The DTMF digits are in the form of a pattern and depend on the voice-mail system connected to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. These patterns are required for the DTMF integration with most voice-mail systems. The DTMF integration configuration on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router works with any analog voice-mail system. Voice-mail systems are designed to respond to DTMF after the system has answered the incoming calls. The following tasks are required.
•
Configuring DTMF Patterns on the Router (required)
•
Configuring Integration Files on Legacy Voice-Mail Systems (required)
Configuring DTMF Patterns on the Router (required)
The Cisco IOS Telephony Service router provides flexibility for the integration with any legacy voice-mail system. You can configure multiple tags and tokens for each pattern, depending on the voice-mail system and type of access. The tag in the configuration pattern must match the number defined in the voice-mail system's integration file to identify the type of call. The keywords—CGN, CDN, and FDN—define the type of call information sent to the voice-mail system.
To configure DTMF pattern on the router for voice-mail integration, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:

Note
Although it is unlikely that you will use multiple instances of the CGN, CDN, or FDN keyword in a single command line, it is permissible to do so.
Configuring Integration Files on Legacy Voice-Mail Systems (required)
To configure the integration files on the third-party legacy voice-mail system, follow the instructions in the accompanying voice-mail system documents. You must design the DTMF integration patterns appropriately, so that the voice-mail system and the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router work with each other.
Integrating Cisco IOS Telephony Service with Applications
The PC applications software for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service—CiscoIOSTSP, a Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) service provider software package—works as an interface between the TAPI running on Microsoft Windows and the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. This software:
•
Communicates with the TAPI using the Telephony Service Provider Interface (TSPI).
•
Implements a required set of application programming interfaces (APIs) and works with TAPI.
•
Enables other TAPI-based applications to provide call control to the Cisco IP phones connected to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.

Note
The Cisco IOS Telephony Service Version 2.01 implements only a small subset of TAPI functionality. It supports only TAPI clients that operate on one phone line at a time. The CiscoIOSTSP support does not have full TAPI support for multiple users or for complex features. Also, this TAPI version does not have direct media and voice handling capabilities.
The CiscoIOSTSP software increases your personal productivity, because you can handle phone call management from your PC without picking up the handset or dialing the numbers on the dial pad. The following features are available:
•
Answering incoming calls
•
Forwarding incoming calls to voice mail
•
Address book dialing (placing outbound calls from an application address and phone and address book)
•
Screen pop-ups with caller-ID (caller-ID-based screen pop-ups for incoming calls; simple outgoing call placement using one-click address-book style speed-dialing from the PC application)
•
Placing calls on hold

Note
CiscoIOSTSP software does not support media or voice. Media or voice is sent to the phone.
CiscoIOSTSP Download and Setup
On the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
Step 1
On the router collect the following information for TSP configuration:
•
Identify the Cisco IP phone that needs to be associated and controlled by a TAPI client.
•
Get the username and password for the Cisco IP phone by entering the show ephone command.
•
Get the IP address or name of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router (if DNS is enabled) and the port number by entering the show telephony-service command.
On the PC

Note
Download the CiscoIOSTSP.zip file from http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/ip-iostsp to your PC. Uncompress the Zip file and run the Setup program on the PC where you want to install the TSP, and that is running Windows 2000.
Step 1
Make sure that there is network connectivity between your PC and the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. To verify the network connectivity, enter the ping ip address command on your PC, specifying the IP address of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
Step 2
Install CiscoIOSTSP.zip by running the Setup program that was downloaded. This program installs the following DLL files in the system directory of the PC.
•
CiscoIOSTSP.tsp
•
CiscoIOSTUISP.dll
•
LogTrace.dll

Note
After the DLL files are installed, a configuration dialog window, Cisco IOS Telephony Service Provider, appears before the installation is complete (shown in Figure 16).
Step 3
Enter the information in the required fields in the dialog box, as shown in Figure 16.
a.
Enter the username and password that will be used by the Cisco IP phone user.
b.
Enter the IP address and port number of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
c.
Set the Synchronous Timeout response from the Cisco IOS Telephony Service to the desired value in seconds. (The default is 3 seconds.)
d.
If you are using the headset, check the Using HeadSet box.
Figure 16 Cisco IOS Telephony Service Provider Configuration Dialog Box


Note
When the Trace box is checked, the trace function slows down the TAPI application. Use the trace feature for troubleshooting. For further information, see the "Troubleshooting TSP" section.
Step 4
Restart the PC, following the prompt.

Note
After the PC restarts, you have the option to launch third-party applications, such as ACT! or Phone Dialer software. For further information on third-party applications, see the documents provided by those vendors.
Modifying TSP Configuration
On the PC
Step 1
To change the initial TSP configuration, select the Phone and Modem option in the control panel. The name of the option may vary, depending on the operating system.
Step 2
Select the Advanced tab in the Phone and Modem Options dialog box, displaying Cisco IOS Telephony Service Provider in the Providers list (shown in Figure 17).
Figure 17 Phone and Modem Options Dialog Box
Step 3
Select Cisco IOS Telephony Service Provider and click Configure, shown in Figure 17.

Note
The configuration dialog box, shown in Figure 16, appears.
Step 4
Enter the information in the required fields in the dialog box, shown in Figure 16.
Step 5
After changing username, password and IP address or port of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Provider, close all the TAPI applications for the changes to take effect. If any services, such as Remote Access ConnectionManager, that depend on the Telephony service are running, restart the system for the changes to take effect. You might get a prompt to reboot your system.
Removing TSP
Step 1
Select Cisco IOS Telephony Service Provider under the Control Panel and click on the Change/Remove button to remove the TSP software.
Step 2
Go to the Add Remove Programs option under the Control Panel and remove the TSP files from your PC.
Verifying Basic TAPI Operation
To verify basic TAPI operations, perform the following:
Step 1
Place an incoming call from another Cisco IP phone to the phone you are verifying.
Step 2
Place an outgoing call from the Cisco IP phone you are verifying.
Troubleshooting TSP
On the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Router
•
Verify the IP address and the port number for the router and make sure that they match those on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
•
Verify connectivity between the phone and the router.
•
If the TSP fails to connect to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, a message box with title "Cisco IOS Telephony Service TSP status" displays the cause for failure.
•
If the Line or Address are not listed in the Preferences>Dialer dialog box:
–
Verify that the user name and password have been configured correctly (case sensitive) and that Synchronous timeout is configured to a reasonable value (3 seconds).
–
Verify that the IP address and the port number for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router match those on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
–
Verify connectivity between the Cisco IP phone and the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
•
Check the Trace box as shown in Figure 18. The trace feature runs the trace utility logs and saves the files in a specified trace file.

Note
To save the trace utility logs, name a file that you can recognize to save the trace utility logs. Each time you run the trace log, a new trace file is created. So you may need to regularly clean up the old trace files that are not required.
Figure 18 Using Trace in Cisco IOS Telephony Service Provider Configuration Dialog Box

On the PC
If the Cisco IOS Telephony Service Provider is not listed as one of the available providers in the Control Panel>Phone and Modem Options>Add dialog box, verify whether all the DLL files have been installed in the PCs system directory.
Monitoring and Maintaining Cisco IOS Telephony Service
To monitor and maintain the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, enter the following commands:
Configuration Examples
This section provides the following configuration example for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service:
!version 12.2no parser cacheno service single-slot-reload-enableservice timestamps debug uptimeservice timestamps log uptimeno service password-encryption!hostname 3620!logging rate-limit console 10 except errors!!ip dhcp pool mypoolnetwork 30.0.0.0 255.255.0.0option 150 ip 30.0.0.1default-router 30.0.0.1!ip subnet-zero!!no ip domain-lookup!no ip dhcp-client network-discoverylcp max-session-starts 0!!!translation-rule 1Rule 0 85... 919785!!!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 30.0.0.1 255.255.0.0duplex autospeed auto!interface Serial0/0no ip addressshutdownno fair-queueclockrate 2000000!interface Serial0/1no ip addressshutdownclockrate 2000000!ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 30.0.0.10ip http server!!!tftp-server flash:SEPDEFAULT.cnftftp-server flash:XMLDefault.cnf.xmltftp-server flash:P004E302.bintftp-server flash:P003E302.binsnmp-server packetsize 4096snmp-server managercall rsvp-sync!voice-port 1/0/0!voice-port 1/0/1!!mgcp profile default!dial-peer cor customname call911name call1800name call1900!!dial-peer cor list allowallmember call911member call1800member call1900!dial-peer cor list allow1800member call1800!dial-peer cor list alloww1800and1900member call1800member call1900!!!telephony-serviceload 7910 P004E320load 7960-7940 P003E320url information http://30.0.0.51/GetTelecasterHelpText.ASPurl directories http://30.0.0.4/localdirectoryurl services http://30.0.0.51/12345/i_want_url/how_long_is_this_url/test.htmlip source-address 30.0.0.1 port 2000max-ephones 24max-dn 48max-conferences 4keepalive 30dialplan-pattern 1 408735.... extension-length 4 no-regdialplan-pattern 2 919785.... extension-length 4 no-regvoicemail 4001admin-username Adminadmin-password testdn-webedittime-webeditmwi sip-server 1.2.172.5mwi expires 99999moh minuet.autime-format 12date-format mm-dd-yytransfer-pattern 1...transfer-pattern 2...transfer-pattern 7...transfer-pattern 3...interdigit timeout 5!!ephone-dn 1number 1111name John E. Doecall-forward busy 4001call-forward noan 4001 timeout 10cor incoming allowalltranslate called 1hold-alert 15 idle!!ephone-dn 2number 2222name John A. Doecall-forward busy 4001call-forward noan 4001 timeout 10cor incoming allow1800cor incoming alloww1800and1900cor incoming allowall 2 4000 - 4999cor incoming allowall 2 4000 - 5000hold-alert 30 originator!!ephone-dn 3number 3333name john A. doecall-forward busy 4001call-forward noan 4001 timeout 10cor outgoing alloww1800and1900!!ephone-dn 4number 1222name Joe Mathewhold-alert 45 shared!!ephone-dn 5number 2111name Raj Haridas!!ephone-dn 6number 3111name Hari Haran!!ephone-dn 7number 4111name Mike Adler!!ephone-dn 8number 7111name Mike Adlerintercom A2222 barge-in!!ephone-dn 9number 4444name "test test"!!ephone-dn 10number ABCD1111intercom ABCD2222!!ephone-dn 11number ABCD2222intercom ABCD1111!!ephone-dn 12number A5004intercom A5003!!ephone-dn 13number A5003intercom A5004!!ephone-dn 14number 1333!!ephone-dn 15number ABCD3333intercom ABCD4444!!ephone-dn 16number ABCD4444intercom ABCD3333!!ephone-dn 18number ABCD1133intercom ABCD3311 barge-in!!ephone-dn 19number ABCD3311intercom ABCD1133 barge-in!!ephone-dn 21number 1010name "paging"paging!!ephone-dn 22number A5333intercom A5444!!ephone-dn 23number A5444intercom A5333!!ephone-dn 30number 8000mwi on!!ephone-dn 31number 8001mwi off!!ephone-dn 32number 4001name "VOICEMAIL1"no huntstoppreference 0!!ephone-dn 33number 4001name "VOICEMAIL2"no huntstoppreference 1!!ephone-dn 40number 2333!!ephone-dn 41number 1222!!ephone-dn 48number 3030name "sharma anil"paging ip 224.1.1.112 port 2001!!ephone 1mac-address 0003.6B54.BB15button 1:1 2:4 3:14 4:10 6:18paging-dn 21!!!ephone 2mac-address 0003.6B09.63CFbutton 1:2 2:5 3:40 4:11 5:12paging-dn 21!!!ephone 3mac-address 0003.6B54.C20Fbutton 1:3 2:6 3:22 4:13 5:15 6:19paging-dn 21!!!ephone 4mac-address 0003.6B40.892Abutton 1:9 3:7 5:16paging-dn 21!!!ephone 6vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI1button 1:32!!!ephone 7vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI2button 1:33!!!line con 0line aux 0line vty 0 4login!!endCommand Reference
This section documents new commands. All other commands used with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2 command reference publications.
•
admin-password (telephony-service)
•
admin-username (telephony-service)
•
call-forward busy (ephone-dn)
•
call-forward noan (ephone-dn)
•
date-format (telephony-service)
•
dialplan-pattern (telephony-service)
•
directory (telephony-service)
•
dn-webedit (telephony-service)
•
ip source-address (telephony-service)
•
keepalive (telephony-service)
•
max-conferences (telephony-service)
•
max-ephones (telephony-service)
•
mwi relay (telephony-service)
•
mwi expires (telephony-service)
•
mwi sip-server (telephony-service)
•
pattern direct (vm-integration)
•
pattern ext-to-ext busy (vm-integration)
•
pattern ext-to-ext no-answer (vm-integration)
•
pattern trunk-to-ext busy (vm-integration)
•
pattern trunk-to-ext no-answer (vm-integration)
•
show telephony-service dial-peer
•
show telephony-service ephone
•
show telephony-service ephone-dn
•
show telephony-service voice-port
•
time-format (telephony-service)
•
timeouts interdigit (telephony-service)
•
time-webedit (telephony-service)
•
transfer-pattern (telephony-service)
•
voicemail (telephony-service)
admin-password (telephony-service)
To set a password for the local system administrator of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the admin-password command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable the password for the local system administrator, use the no form of this command.
admin-password password
no admin-password password
Syntax Description
password
Password used by the administrator to prevent unauthorized access to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router or Cisco IP phone configuration.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The admin-password command sets a password for the local system administrator to prevent unauthorized access to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router or Cisco IP phone configuration. The specific password for the local system administrator is associated with the username set with the admin-username command. The password and the username for the local system administrator, as a pair, are associated with a specific Cisco IP phone.

Note
The password and username are used from the graphical user interface (GUI) interface for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service administration.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the password U2021 for an administrator:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# admin-password U2021Related Commands
admin-username (telephony-service)
To set the username for the local system administrator of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the admin-username command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable the username, use the no form of this command.
admin-username username
no admin-username username
Syntax Description
username
Assigned username for the administrator; designed to prevent unauthorized access to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router or Cisco IP phone configuration.
Defaults
The default username is Admin.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The admin-username command sets the username for the local system administrator of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to prevent unauthorized access to the router or Cisco IP phone configuration. The specific username of the local administrator is associated with the password set with the admin-password command. The username and password for the local system administrator, as a pair, are associated with a specific Cisco IP phone.

Note
The username and password are used from the graphical user interface (GUI) interface for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service administration.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the username for a local administrator:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# admin-username sganeshRelated Commands
application (ephone-dn)
To select the session-level application for each Cisco IP phone directory number, use the application command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
application application-name
no application application-name
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The application command selects the session-level application for each Cisco IP phone directory number. Use this command to assign a tool command language (TCL) interactive voice response (IVR) application to the Cisco IP phone directory number (ephone-dn).
Examples
The following example shows how to set the IVR application for directory number 1:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn) application TCLIVRRelated Commands
ephone-dn
Enters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines.
button (ephone)
To associate directory numbers (ephone-dn) with individual buttons on a Cisco IP phone, use the button command in ephone configuration mode. To delete directory numbers from the buttons on a Cisco IP phone, use the no form of this command.
button button-number:dn-tag button-number:dn-tag
no button button-number:dn-tag button-number:dn-tag
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The button command assigns telephone lines to the Cisco IP phones by assigning a button number to the Cisco IP phone directory number.
Telephone services such as call waiting and three-party conferences require a minimum of two phone lines (ephone-dn) to be available and configured on the Cisco IP phone. The Cisco IP Phone 7910 has only one physical line button. To support call waiting and three-party conferences on a Cisco IP Phone 7910, a second (hidden) line is required. This line can not be selected directly using a line button. You can access the second line when you press the conference button.
Examples
The following example shows how to assign a button number on the phone to directory number tags:
Router(config)# ephone 1Router(config-ephone)# button 1:1 2:4 3:16 4:19Related Commands
call-forward all (ephone-dn)
To configure call-forwarding for all the incoming calls on one of the lines of a Cisco IP phone to another telephone, use the call-forward all command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable call-forwarding, use the no form of this command.
call-forward all directory-number
no call-forward all [directory-number]
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The call-forwarding feature is applied to the individual telephone line associated with a directory number and cannot be configured for all the directory numbers of a Cisco IP phone. The call-forward all command enables call forwarding for all the incoming calls on one of the lines of a Cisco IP phone to another telephone. Using the directory number attribute is optional, when using the no form of this command.

Note
The call-forward all command takes precedence over the call-forward busy and call-forward noan commands.
Examples
The following example shows how to set call-forwarding of all calls on line 1, directory number 5001, to directory number 5005. All incoming calls destined for extension 5001 are forwarded to another Cisco IP phone with the extension number 5005:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn)# number 5001Router(config-ephone-dn)# call-forward all 5005Related Commands
call-forward busy (ephone-dn)
To configure call-forwarding to another number when the Cisco IP phone is busy, use the call-forward busy command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable call-forwarding during busy, use the no form of this command.
call-forward busy directory-number
no call-forward busy [directory-number]
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The call-forwarding feature is applied to the individual telephone line associated with a directory number and cannot be configured on all directory numbers of the Cisco IP phone. The call-forward busy command enables call-forwarding to another number when the Cisco IP phone is busy. Using the directory number attribute is optional, when using the no form of this command.
Examples
The following example shows how to set call-forwarding of incoming calls to another Cisco IP phone with the directory number 5005 when line 1, directory number 5001, is busy:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn)# number 5001Router(config-ephone-dn)# call-forward busy 5005Related Commands
call-forward noan (ephone-dn)
To configure call-forwarding to another number when no answer is received from a Cisco IP phone, use the call-forward noan command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable call-forwarding, use the no form of this command.
call-forward noan directory-number timeout seconds
no call-forward noan [directory-number]
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The call-forwarding feature is applied to the individual telephone line associated with a directory number and cannot be configured for all the directory numbers of the Cisco IP phone. The call-forward noan command enables call-forwarding to another number when no answer is received from a Cisco IP phone. The timeout keyword sets the waiting time before the call is forwarded to another phone. The time is set in seconds. The range is 3 to 60,000 seconds. Using the directory number attribute is optional, when using the no form of this command.
Examples
The following example shows how to set call-forwarding of incoming calls to directory number 5005 when line 1, directory number 5001, does not answer. The timeout before the call is forwarded to the directory number 5005 is set for 10 seconds.
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn)# number 5001Router(config-ephone-dn)# call-forward noan 5005 timeout 10Related Commands
caller-id block (ephone-dn)
To enable caller-ID blocking for outbound calls, use the caller-id block command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable caller ID, use the no form of this command.
caller-id block
no caller-id block
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
Caller ID is not blocked on calls originating from a Cisco IP phone.
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The caller-id block command sets caller-ID blocking for outbound calls originated from the ephone-dn. This commands requests that the far-end gateway device block display of the calling party information, for calls received by the far-end gateway from the ephone-dn. This command does not effect the ephone-dn calling party information display for inbound calls received by the ephone-dn.
Examples
The following example shows how to set caller ID blocking for the directory number 5001:
Router(config) ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn)# number 5001Router(config-ephone-dn)# caller-id blockRelated Commands
cor (ephone-dn)
To configure a class of restriction (COR) on the dial peers associated with a directory number, use the cor command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable COR associated with a directory number, use the no form of this command.
cor {incoming | outgoing} cor-list-name
no cor cor-list-name
Syntax Description
incoming
COR list to be used by incoming dial peers.
outgoing
COR list to be used by outgoing dial peers.
cor-list-name
COR list name.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The cor command sets the dial-peer class of restriction (COR) parameter for dial peers and the directory numbers created for the Cisco IP phones associated with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. The COR functionality provides the ability to deny certain call attempts based on the incoming and outgoing class of restrictions provisioned on the dial peers. This functionality provides flexibility in network design, allows users to block calls (for example, to 900 numbers), and applies different restrictions to call attempts from different originators.
COR is used to specify which incoming dial peer can use which outgoing dial peer to make a call. Each dial peer can be provisioned with an incoming and an outgoing COR list.
Examples
The following example shows how to set dial-peer COR parameter for incoming calls to dial-peer 1:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn)# cor incoming corlist1Related Commands
date-format (telephony-service)
To set the date display format on all the Cisco IP phones attached to the router, use the date-format command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable the date display format, use the no form of this command.
date-format {mm-dd-yy | dd-mm-yy}
no date-format {mm-dd-yy | dd-mm-yy}
Syntax Description
mm-dd-yy
Set to month, day, and year. Each slot needs a two-digit number. This format is the default setting.
dd-mm-yy
Set to day, month, and year. Each slot needs a two-digit number.
Defaults
The default is set to mm-dd-yy.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The date-format command sets the date display format on all Cisco IP phones attached to the router.
Examples
The following example sets the date format on the Cisco IP phones to date, month, and year:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# date-format dd-mm-yyRelated Commands
telephony-service
Enables Cisco IOS Telephony Service and enters telephony-service configuration mode.
debug ephone alarm
To set SkinnyStation alarm messages debugging for the Cisco IP phone, use the debug ephone alarm command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ephone alarm [mac-address mac-address]
no debug ephone alarm [mac-address mac-address]
Syntax Description
mac-address
(Optional) Defines the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
mac-address
(Optional) Specifies the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug ephone alarm command shows all the SkinnyStation alarm messages sent by the Cisco IP phone. Under normal circumstances, this message is sent by the Cisco IP phone just before it registers, and the message has the severity level for the alarm set to "Informational" and contains the reason for the phone reboot or re-register. This type of message is entirely benign and does not indicate an error condition.
If the mac-address keyword is not used, the debug ephone alarm command debugs all Cisco IP phones that are registered to the router. You can remove debugging for the Cisco IP phones that you do not want to debug by using the mac-address keyword with the no form of this command.
You can enable or disable debugging on any number of Cisco IP phones. To see the Cisco IP phones that have debugging enabled, enter the show ephone command and look at the debug field in the output. When debugging is enabled for a Cisco IP phone, the debug output is displayed for the directory numbers associated with the Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows a SkinnyStation alarm message that is sent before the Cisco IP phone registers:
Router# debug ephone alarmphone keypad resetCM-closed-TCPCM-bad-stateRelated Commands
debug ephone detail
To set detail debugging for the Cisco IP phone, use the debug ephone detail command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ephone detail [mac-address mac-address]
no debug ephone detail [mac-address mac-address]
Syntax Description
mac-address
(Optional) Defines the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
mac-address
(Optional) Specifies the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug ephone detail command includes the error and state levels.
If the mac-address keyword is not used, the debug ephone detail debug command debugs all Cisco IP phones that are registered to the router. You can remove debugging for the Cisco IP phones that you do not want to debug by using the mac-address keyword with the no form of this command.
You can enable or disable debugging on any number of Cisco IP phones. To see the Cisco IP phones that have debugging enabled, enter the show ephone command and look at the debug field in the output. When debugging is enabled for a Cisco IP phone, the debug output is displayed for the directory numbers associated with the Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows a sample output of detail debugging of the Cisco IP phone with MAC address 0030.94c3.8724. The sample is an excerpt of some of the activities that takes place during call setup, connected state, active call, and the call being disconnected:
Router# debug ephone detail mac-address 0030.94c3.8724Ephone detail debugging is enabled1d04h: ephone-1[1]:OFFHOOK..1d04h: Skinny Call State change for DN 1 SIEZE..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 1 DN 1 TsOffHook..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:SetLineLamp 1 to ON..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:KeypadButtonMessage 5..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:KeypadButtonMessage 0..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:KeypadButtonMessage 0..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:KeypadButtonMessage 2..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:Store ReDial digit: 5002.SkinnyTryCall to 5002 instance 1..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:Store ReDial digit: 50021d04h: ephone-1[1]:SkinnyTryCall to 5002 instance 1..1d04h: Skinny Call State change for DN 1 ALERTING..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 1 DN 1 TsRingOut..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:SetLineLamp 1 to ON1d04h: SetCallInfo calling dn 1 dn 1calling [5001] called [5002]..1d04h: ephone-1[1]: Jane calling1d04h: ephone-1[1]: Jill..1d04h: SkinnyUpdateDnState by EFXS_RING_GENERATEfor DN 2 to state RINGING..1d04h: SkinnyGetCallState for DN 2 CONNECTED..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:SetLineLamp 3 to ON1d04h: ephone-1[1]:UpdateCallState DN 1 state 4 calleddn 2..1d04h: Skinny Call State change for DN 1 CONNECTED..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:OpenReceive DN 1 codec 4:G711Ulaw64k duration 10 ms bytes 80..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:OpenReceiveChannelAck 1.2.172.21 port=201801d04h: ephone-1[1]:Outgoing calling DN 1 Far-ephone-2 called DN 21d04h: SkinnyGetCallState for DN 1 CONNECTED..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 3 DN 2 TsOnHook..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:SetLineLamp 3 to OFF..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 1 DN 1 TsOnHook..1d04h: ephone-1[1]:Clean Up Speakerphone state1d04h: ephone-1[1]:SpeakerPhoneOnHook1d04h: ephone-1[1]:Clean up activeline 11d04h: ephone-1[1]:StopTone sent to ephone1d04h: ephone-1[1]:Clean Up phone offhook state1d04h: SkinnyGetCallState for DN 1 IDLE1d04h: called DN -1, calling DN -1 phone -11d04h: ephone-1[1]:SetLineLamp 1 to OFF1d04h: UnBinding ephone-1 from DN 11d04h: UnBinding called DN 2 from DN 11d04h: ephone-1[1]:ONHOOK1d04h: ephone-1[1]:SpeakerPhoneOnHook1d04h: ephone-1[1]:ONHOOK NO activeline...Related Commands
debug ephone error
To set error debugging for the Cisco IP phone, use the debug ephone error command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ephone error [mac-address mac-address]
no debug ephone error [mac-address mac-address]
Syntax Description
mac-address
(Optional) Defines the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
mac-address
(Optional) Specifies the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug phone error command cancels debugging at the detail and state level.
If the mac-address keyword is not used, the debug ephone error debug command debugs all Cisco IP phones that are registered to the router. You can remove debugging for the Cisco IP phones that you do not want to debug by using the mac-address keyword with the no form of this command.
You can enable or disable debugging on any number of Cisco IP phones. To see the Cisco IP phones that have debugging enabled, enter the show ephone command and look at the debug field in the output. When debugging is enabled for a Cisco IP phone, the debug output is displayed for the directory numbers associated with the Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows a sample output of error debugging for the Cisco IP phone with MAC address 0030.94c3.8724:
Router# debug ephone error mac-address 0030.94c3.8724EPHONE error debugging is enabledsocket [2] send ERROR 11Skinny Socket [2] retry failureRelated Commands
debug ephone keepalive
To set keepalive debugging for the Cisco IP phone, use the debug ephone keepalive command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ephone keepalive [mac-address mac-address]
no debug ephone keepalive [mac-address mac-address]
Syntax Description
mac-address
(Optional) Defines the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
mac-address
(Optional) Specifies the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug ephone keepalive command sets keepalive debugging.
If the mac-address keyword is not used, the debug ephone keepalive debug command debugs all Cisco IP phones that are registered to the router. You can remove debugging for the Cisco IP phones that you do not want to debug by using the mac-address keyword with the no form of this command.
You can enable or disable debugging on any number of Cisco IP phones. To see the Cisco IP phones that have debugging enabled, enter the show ephone command and look at the debug field in the output. When debugging is enabled for a Cisco IP phone, the debug output is displayed for the directory numbers associated with the Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows a sample output of the keepalive status for the Cisco IP phone with MAC address 0030.94C3.E1A8:
Router# debug ephone keepalive mac-address 0030.94c3.E1A8EPHONE keepalive debugging is enabled for phone 0030.94C3.E1A81d05h: ephone-1 Set interface FastEthernet0/0 ETHERNET1d05h: ephone-1[1]:Keepalive socket[1] SEP003094C3E1A81d05h: ephone-1 Set interface FastEthernet0/0 ETHERNET1d05h: ephone-1[1]:Keepalive socket[1] SEP003094C3E1A81d05h: Skinny Checking for stale sockets1d05h: ephone-1 Set interface FastEthernet0/0 ETHERNET1d05h: ephone-1[1]:Keepalive socket[1] SEP003094C3E1A81d05h: ephone-1 Set interface FastEthernet0/0 ETHERNET1d05h: ephone-1[1]:Keepalive socket[1] SEP003094C3E1A81d05h: Skinny active socket list (3/96): 1 2 4Related Commands
debug ephone mwi
To set message waiting indication (MWI) debugging for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the debug ephone mwi command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ephone mwi
no debug ephone mwi
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug ephone mwi command sets message waiting indication debugging for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. Since the MWI protocol activity is not specific to any individual Cisco IP phone, setting the MAC address keyword qualifier for this command is not useful.

Note
Unlike the other related debug ephone commands, the mac-address keyword does not help debug a particular Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows a sample output of the message waiting indication status for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router:
Router# debug ephone mwiRelated Commands
debug ephone pak
To provide voice packet level debugging and to print the contents of one voice packet in every 1024 voice packets, use the debug ephone pak command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ephone pak [mac-address mac-address]
no debug ephone pak [mac-address mac-address]
Syntax Description
mac-address
(Optional) Defines the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
mac-address
(Optional) Specifies the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug ephone pak command provides voice packet level debugging and prints the contents of one voice packet in every 1024 voice packets.
If the mac-address keyword is not used, the debug ephone pak debug command debugs all Cisco IP phones that are registered to the router. You can remove debugging for the Cisco IP phones that you do not want to debug by using the mac-address keyword with the no form of this command.
You can enable or disable debugging on any number of Cisco IP phones. To see the Cisco IP phones that have debugging enabled, enter the show ephone command and look at the debug field in the output. When debugging is enabled for a Cisco IP phone, the debug output is displayed for the directory numbers associated with the Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows a sample output of packet debugging for the Cisco IP phone with MAC address 0030.94c3.8724:
Router# debug ephone pak mac-address 0030.94c3.8724EPHONE packet debugging is enabled for phone 0030.94c3.872401:29:14: ***ph_xmit_ephone DN 3 tx_pkts 5770 dest=10.2.1.1 orig len=32pakcopy=0 discards 27 ip_enctype 0 0 last discard: unsupported payload type01:29:14: to_skinny_duration 130210 offset -30 last -40 seq 0 adj 001:29:14: IP: 45B8 003C 0866 0000 3F11 3F90 2800 0001 0A02 010101:29:14: TTL 63 TOS B8 prec 501:29:14: UDP: 07D0 6266 0028 000001:29:14: sport 2000 dport 25190 length 40 checksum 001:29:14: RTP: 8012 16AF 9170 6409 0E9F 000101:29:14: is_rtp:1 is_frf11:0 vlen:0 delta_t:160 vofr1:0 vofr2:0scodec:11 rtp_bits:8012 rtp_codec:18 last_bad_payload 1901:29:14: vencap FAILED01:29:14: PROCESS SWITCH01:29:15: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console01:29:34: ***SkinnyPktIp DN 3 10.2.1.1 to 40.0.0.1 pkts 4880 FAST sw01:29:34: from_skinny_duration 15091001:29:34: nw 3BBC2A8 addr 3BBC2A4 mac 3BBC2A4 dg 3BBC2C4 dgs 2A01:29:34: MAC: 1841 080001:29:34: IP: 45B8 0046 682E 0000 3E11 E0BD 0A02 0101 2800 000101:29:34: TTL 62 TOS B8 prec 501:29:34: UDP: 6266 07D0 0032 000001:29:34: sport 25190 dport 2000 length 50 checksum 001:29:34: RTP: 8012 55FF 0057 8870 3AF4 C39401:29:34: RTP: rtp_bits 8012 seq 55FF ts 578870 ssrc 3AF4C39401:29:34: PAYLOAD:01:29:34: 1409 37C9 54DE 449C 3B42 0446 3AAB 182E01:29:34: 56BC 5184 58E5 56D3 13BE 44A7 B8C401:29:34:01:29:37: ***ph_xmit_ephone DN 3 tx_pkts 6790 dest=10.2.1.1 orig len=32pakcopy=0 discards 31 ip_enctype 0 0 last discard: unsupported payload type01:29:37: to_skinny_duration 153870 offset -150 last -40 seq 0 adj 001:29:37: IP: 45B8 003C 0875 0000 3F11 3F81 2800 0001 0A02 010101:29:37: TTL 63 TOS B8 prec 501:29:37: UDP: 07D0 6266 0028 000001:29:37: sport 2000 dport 25190 length 40 checksum 001:29:37: RTP: 8012 1AAF 9173 4769 0E9F 000101:29:37: is_rtp:1 is_frf11:0 vlen:0 delta_t:160 vofr1:0 vofr2:0Related Commands
debug ephone raw
To provide raw low-level protocol debugging display for all Skinny Client Control Protocol messages, use the debug ephone raw command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ephone raw [mac-address mac-address]
no debug ephone raw [mac-address mac-address]
Syntax Description
mac-address
(Optional) Defines the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
mac-address
(Optional) Specifies the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug ephone raw command provides raw low-level protocol debug display for all Skinny Client Control Protocol messages. The debug display provides byte level display of Skinny TCP socket messages.
If the mac-address keyword is not used, the debug ephone raw debug command debugs all Cisco IP phones that are registered to the router. You can remove debugging for the Cisco IP phones that you do not want to debug by using the mac-address keyword with the no form of this command.
You can enable or disable debugging on any number of Cisco IP phones. To see the Cisco IP phones that have debugging enabled, enter the show ephone command and look at the debug field in the output. When debugging is enabled for a Cisco IP phone, the debug output is displayed for the directory numbers associated with the Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows a sample output of raw protocol debugging for the Cisco IP phone with MAC address 0030.94C3.E1A8:
Router# debug ephone raw mac-address 0030.94c3.E1A8EPHONE raw protocol debugging is enabled for phone 0030.94C3.E1A81d05h: skinny socket received 4 bytes on socket [1]0 0 0 01d05h:1d05h: SkinnyMessageID = 01d05h: skinny send 4 bytes4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 01d05h: socket [1] sent 12 bytes OK (incl hdr) for ephone-(1)1d06h: skinny socket received 4 bytes on socket [1]0 0 0 01d06h:1d06h: SkinnyMessageID = 01d06h: skinny send 4 bytes4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 01d06h: socket [1] sent 12 bytes OK (incl hdr) for ephone-(1)Related Commands
debug ephone register
To set registration debugging for the Cisco IP phone, use the debug ephone register command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ephone register [mac-address mac-address]
no debug ephone register [mac-address mac-address]
Syntax Description
mac-address
(Optional) Defines the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
mac-address
(Optional) Specifies the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug ephone register command sets registration debugging for the Cisco IP phones.
If the mac-address keyword is not used, the debug ephone register debug command debugs all Cisco IP phones that are registered to the router. You can remove debugging for the Cisco IP phones that you do not want to debug by using the mac-address keyword with the no form of this command.
You can enable or disable debugging on any number of Cisco IP phones. To see the Cisco IP phones that have debugging enabled, enter the show ephone command and look at the debug field in the output. When debugging is enabled for a Cisco IP phone, the debug output is displayed for the directory numbers associated with the Cisco IP phone.
Syntax Description
The following example shows a sample output of registration debugging for the Cisco IP phone with MAC address 0030.94c3.8724:
Router# debug ephone register mac-address 0030.94c3.8724Ephone registration debugging is enabled1d06h: New Skinny socket accepted [1] (2 active)1d06h: sin_family 2, sin_port 50778, in_addr 10.1.0.211d06h: skinny_add_socket 1 10.1.0.21 507781d06h: ephone-(1)[1] StationRegisterMessage (2/3/12) from 10.1.0.211d06h: ephone-(1)[1] Register StationIdentifier DeviceName SEP003094C3E1A81d06h: ephone-(1)[1] StationIdentifier Instance 1 deviceType 71d06h: ephone-1[-1]:stationIpAddr 10.1.0.211d06h: ephone-1[-1]:maxStreams 01d06h: ephone-(1) Allow any Skinny Server IP address 10.1.0.6...1d06h: ephone-1[1]:RegisterAck sent to ephone 1: keepalive period 30.Related Commands
debug ephone state
To set state debugging for the Cisco IP phone, use the debug ephone state command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ephone state [mac-address mac-address]
no debug ephone state [mac-address mac-address]
Syntax Description
mac-address
(Optional) Defines the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
mac-address
(Optional) Specifies the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug ephone state command sets state debugging for the Cisco IP phones.
If the mac-address keyword is not used, the debug ephone state debug command debugs all Cisco IP phones that are registered to the router. You can remove debugging for the Cisco IP phones that you do not want to debug by using the mac-address keyword with the no form of this command.
You can enable or disable debugging on any number of Cisco IP phones. To see the Cisco IP phones that have debugging enabled, enter the show ephone command and look at the debug field in the output. When debugging is enabled for a Cisco IP phone, the debug output is displayed for the directory numbers associated with the Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows a sample output of state debugging for the Cisco IP phone with MAC address 0030.94c3.E1A8:
Router# debug ephone state mac-address 0030.94c3.E1A8EPHONE state debugging is enabled for phone 0030.94C3.E1A81d06h: ephone-1[1]:OFFHOOK1d06h: ephone-1[1]:SIEZE on activeline 01d06h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 1 DN 1 TsOffHook1d06h: ephone-1[1]:Skinny-to-Skinny call DN 1 to DN 2 instance 11d06h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 1 DN 1 TsRingOut1d06h: ephone-1[1]:Call Info DN 1 line 1 ref 158 called 5002 calling 50011d06h: ephone-1[1]: Jane calling1d06h: ephone-1[1]: Jill1d06h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 3 DN 2 TsRingIn1d06h: ephone-1[1]:Call Info DN 2 line 3 ref 159 called 5002 calling 50011d06h: ephone-1[1]: Jane calling1d06h: ephone-1[1]: Jill1d06h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 3 DN 2 TsCallRemoteMultiline1d06h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 1 DN 1 TsConnected1d06h: ephone-1[1]:OpenReceive DN 1 codec 4:G711Ulaw64k duration 10 ms bytes 801d06h: ephone-1[1]:OpenReceiveChannelAck 1.2.172.21 port=240101d06h: ephone-1[1]:StartMedia 1.2.172.22 port=246121d06h: DN 1 codec 4:G711Ulaw64k duration 10 ms bytes 801d06h: ephone-1[1]:CloseReceive1d06h: ephone-1[1]:StopMedia1d06h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 3 DN 2 TsOnHook1d06h: ephone-1[1]:SetCallState line 1 DN 1 TsOnHook1d06h: ephone-1[1]:SpeakerPhoneOnHook1d06h: ephone-1[1]:ONHOOK1d06h: ephone-1[1]:SpeakerPhoneOnHook1d06h: SkinnyReportDnState DN 1 ONHOOKRelated Commands
debug ephone statistics
To set call statistics debugging for the Cisco IP phone, use the debug ephone statistics command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ephone statistics [mac-address mac-address]
no debug ephone statistics [mac-address mac-address]
Syntax Description
mac-address
(Optional) Defines the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
mac-address
(Optional) Specifies the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug ephone statistics command provides a debug monitor display of the periodic messages from the Cisco IP phone to the router. These include transmit-and-receive packet counts and an estimate of drop packets. The call statistics can also be displayed for live calls using the show ephone command.
If the mac-address keyword is not used, the debug ephone statistics debug command debugs all Cisco IP phones that are registered to the router. You can remove debugging for the Cisco IP phones that you do not want to debug by using the mac-address keyword with the no form of this command.
You can enable or disable debugging on any number of Cisco IP phones. To see the Cisco IP phones that have debugging enabled, enter the show ephone command and look at the debug field in the output. When debugging is enabled for a Cisco IP phone, the debug output is displayed for the directory numbers associated with the Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows a sample output of statistics debugging for the Cisco IP phone with MAC address 0030.94C3.E1A8:
Router# debug ephone statistics mac-address 0030.94C3.E1A8EPHONE statistics debugging is enabled for phone 0030.94C3.E1A81d06h: Clear Call Stats for DN 1 call ref 1621d06h: Clear Call Stats for DN 1 call ref 1621d06h: Clear Call Stats for DN 1 call ref 1621d06h: Clear Call Stats for DN 2 call ref 1631d06h: ephone-1[1]:GetCallStats line 1 ref 162 DN 1: 50011d06h: ephone-1[1]:Call Stats for line 1 DN 1 5001 ref 1621d06h: ephone-1[1]:TX Pkts 0 bytes 0 RX Pkts 0 bytes 01d06h: ephone-1[1]:Pkts lost 4504384 jitter 0 latency 01d06h: ephone-1[1]:Src 0.0.0.0 0 Dst 0.0.0.0 0 bytes 80 vad 0 G711Ulaw64k1d06h: ephone-1[1]:GetCallStats line 1 ref 162 DN 1: 50011d06h: STATS: DN 1 Packets Sent 01d06h: STATS: DN 2 Packets Sent 01d06h: ephone-1[1]:Call Stats found DN -1 from Call Ref 1621d06h: ephone-1[1]:Call Stats for line 0 DN -1 5001 ref 1621d06h: ephone-1[1]:TX Pkts 275 bytes 25300 RX Pkts 275 bytes 253001d06h: ephone-1[1]:Pkts lost 0 jitter 0 latency 0Related Commands
debug mwi relay errors
To debug message waiting indication (MWI) relay errors, use the debug mwi relay errors command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug mwi relay errors
no debug mwi relay errors
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug mwi relay errors command provides a debug monitor display of any error messages, when MWI Relay Server (Cisco IOS Telephony Server) is trying to do MWI Relay to extensions on remote ITS.
Examples
The following examples show errors when MWI Relay Server tries to do a MWI Relay to extension 7004, but location of 7004 is not known to the MWI Relay Server.
Router# debug mwi relay errors mwi-relay error info debugging is onRouter#01:46:48: MWI-APP: mwi_notify_status: No ClientID (7004) registeredRelated Commands
debug mwi relay events
To set MWI relay events debugging, use the debug mwi relay events command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug mwi relay events
no debug mwi relay events
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The debug mwi relay events command provides a debug monitor display of events, when MWI Relay Server (IOS Telephony Server) is trying to do MWI Relay to extensions on remote ITS.
Examples
The following debug messages are shown when MWI Relay server tries to send MWI Information to remote client 7001 and the location of 7001 is known by the MWI Relay Server
Router# debug mwi relay eventsmwi-relay events info debugging is on01:45:34: mwi_notify_status: Queued event for mwi_app_queue01:45:34: MWI-APP: mwi_app_process_event:01:45:34: MWI-APP: mwi_app_process_event: MWI Event for ClientID(7001)@(1.8.17.22)Related Commands
description (ephone-dn)
To enable a alphanumeric description label in the top black bar on the display screen for a Cisco IP Phone 7960 and Cisco IP Phone 7940, use the description command in ephone configuration mode. To remove the alphanumeric description label, use the no form of this command.
description text-string-with-spaces
no description text-string-with-spaces
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The description command enables a meaningful alphanumeric description label in the top black bar on the display screen for a Cisco IP Phone 7960 and Cisco IP Phone 7940 connected to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. The description consists of a text string up to 16 characters in length, including spaces, and is associated with the first (top) button of the Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example sets DN 5 (extension number 8001) with the description 408 555 1212 for the top line display:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 5Router(config-ephone-dn)# number 8001Router(config-ephone-dn)# description 408 555 1212Related Commands
ephone-dn
Enters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines.
number
Configures a valid number for the Cisco IP phone.
dialplan-pattern (telephony-service)
To create a global prefix that can be used to expand the abbreviated extension numbers into fully qualified E.164 numbers, use the dialplan-pattern command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable, use the no form of this command.
dialplan-pattern tag pattern extension-length length [no-reg]
no dialplan-pattern tag [pattern extension-length length]
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Directory numbers for the Cisco IP phones are expected to be entered in extension number format. The extension number should be greater or equal to the extension length. Otherwise, the extension number cannot be converted to a qualified E.164 number. The dialplan-pattern command creates a global prefix that can be used to expand the abbreviated extension numbers to fully qualified E.164 numbers. The dialplan-pattern is also required to register the Cisco IP phone lines with a gatekeeper. The dialplan-pattern command can resolve an incoming call with a full E.164 number to a Cisco IP phone extension number.
The extension-length keyword enables the system to convert a full E.164 telephone number back to an extension number for the purposes of caller-ID display, received, and missed call lists. For example, a company uses extension number range 5000-5099 across several sites, with only the extensions 5000-5009 present on the local router. An incoming call from 5044 arrives from the company's internal VoIP H.323 network and this call includes the calling number as 4083335044 in its full E.164 format.
The no-reg keyword provides dialing flexibility. You have the option not to register some specific numbers to the gatekeeper so that those numbers can be used for other telephony services.
When the called number matches the dial-plan pattern, the call is considered a local call and has a distinctive ringing identifying the call as internal. Any call that does not match the dial-plan pattern, is considered an external call and has a distinctive ringing different from the internal ringing. The valid dial-plan pattern with the lowest tag is used as a prefix to all local Cisco IP phones.
Examples
The following example shows how to create dialplan-pattern 1 for extension numbers 5001 to 5099 with the telephone prefix starting with 408333. If the following example is set, the routers sees that the 4083335044 matches dialplan-pattern 1, and uses the extension-length keyword to extract the last four digits of the number 5044 and present this as the caller ID for the incoming call.
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# dialplan-pattern 1 40833350.. extension-length 4 no-regRelated Commands
directory (telephony-service)
To define Cisco IP phone local directory naming order, use the directory command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable the directory URL, use the no form of this command.
directory {first-name-first | last-name-first}
no directory {first-name-first | last-name-first}
Syntax Description
first-name-first
First name is entered first in the Cisco IP phone directory name field.
last-name-first
Last name is entered first in the Cisco IP phone directory name field.
Defaults
The local directory support is enabled by default.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The directory command defines the local directory naming order and points to the directory access to any HTTP location. The actual directory of names and phone numbers is built using the name command and the number command under ephone-dn configuration mode.
When the command is set to first-name-first keyword, you see the directory information displayed on the phone, for example, Jane E. Smith; and when the command is set with the last-name-first keyword, you see the directory information displayed on the phone, for example, Smith, Jane E.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure the local directory with the first name first:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# directory first-name-firstThe following example shows how to configure the local directory with the last name first:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# directory last-name-firstRelated Commands
dn-webedit (telephony-service)
To enable adding of directory numbers through a web interface, use the dn-webedit command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
dn-webedit
no dn-edit
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
Disabled
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The dn-webedit command enables adding of the directory through the Cisco IOS Telephony Service web-based graphical user interface (GUI). If dn-webedit command is enabled, the GUI administrator can modify and assign the phone numbers associated with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. This may not be desirable in cases where the set of numbers used by the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router are part of a larger telephone network. Disabling dn-webedit prevents the administrator from allocating phone numbers and also prevents assignment of numbers that may already be used elsewhere in the network.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable editing of directory numbers through the web-based GUI interface:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# dn-webeditRelated Commands
ephone
To enter the Ethernet phone (ephone) configuration mode, use the ephone command in global configuration mode. To disable the ephone configuration mode, use the no form of this command.
ephone tag
no ephone tag
Syntax Description
Defaults
No Cisco IP phone is configured.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This is a top-level command used to configure Cisco IP phones on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. By default, no Cisco IP phone is configured. Therefore, you must manually enter the number of Cisco IP phones you need to configure in your network by entering the max-ephones and max-dn commands.
Examples
The following example shows how to enter ephone configuration mode for phone 4:
Router(config)# ephone 4Router(config-ephone)#Related Commands
ephone-dn
To configure the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines, voice-mail ports, message waiting indication (MWI) code, and to enter ephone-dn configuration mode, use the ephone-dn command in global configuration mode. To disable the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines, use the no form of this command.
ephone-dn dn-tag
no ephone-dn dn-tag
Syntax Description
Defaults
No directory number is configured.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This is a top-level command used to configure Cisco IP phones on the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. By default, no directory number is configured. Therefore, you must manually enter the number of Cisco IP phones you need to configure in your network by entering the max-ephones and max-dn commands.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines and enters ephone-dn configuration mode:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn)#Related Commands
hold-alert (ephone-dn)
To set audible alert notification on the Cisco IP phone for alerting the user about on-hold calls, use the hold-alert command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
hold-alert timeout {idle | originator | shared}
no hold-alert timeout {idle | originator | shared}
Syntax Description
Defaults
Audible alert for on-hold calls is disabled by default. Only a visual indication is provided.
Command Modes
Ephone-dn
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The hold-alert command sets audible alert notification on the Cisco IP phone for alerting the user about on-hold calls. The timeout parameter specifies the time interval in seconds from the time the call is placed on hold to the time the on-hold audible alert is generated. The alert is repeated every timeout seconds.
When the idle keyword is enabled, a one-second burst of ringing on the phone is generated on the IP phone that placed the call into the hold state, only if the phone is in the idle state. If the phone is in active use, no on-hold alert is generated.
When the originator keyword is enabled, a one-second burst of ringing is generated on the phone that placed the call into the hold state if the phone is in the idle state. If the phone is in use on another call, an audible beep is generated (call-waiting beep).

Note
From the perspective of the originator of the call-on-hold, the shared and the originator keywords provide the same functionality.
When the shared keyword is enabled, a one second ring burst is generated for all the idle phones which share the same line appearance. If the phones are in use, they do not get an audio beep alert. Only the phone that initiated the call, if busy, hears a call-waiting beep.
Examples
The following example shows how to set call set audible alert notification to idle on the Cisco IP phone for alerting the user about on-hold calls:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn)# number 1111Router(config-ephone-dn)# name phone1Router(config-ephone-dn)# hold alert 10 idleRelated Commands
ephone-dn
Enters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines.
huntstop (ephone-dn)
To set the huntstop attribute for the dial peers associated with the Cisco IP phone lines, use the huntstop command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable huntstop, use the no form of this command.
huntstop
no huntstop
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
Huntstop is set by default.
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
In the ephone-dn configuration mode, the huntstop attribute is set by default for the dial peers associated with the Cisco IP phone lines on a line-by-line basis. This allows you to prevent hunt-on-busy from redirecting a call to a busy phone into a dial-peer setup with a catch-all default destination.

Note
Use the no huntstop command only if you want to disable huntstop.
Examples
The following example shows how to disable huntstop for the destination dial peer with the extension 5001. The huntstop for the dial-peer is set to OFF and prevents calls to extension 5001 from being re-routed to the on-net H.323 dial-peer for 5... (The three decimal points are used as wildcards.) destination when 5001 is busy.
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn)# number 5001Router(config-ephone-dn)# no huntstopThe following example shows a typical configuration where ephone-dn huntstop (default) is required:
ephone-dn 1number 5001ephone 4button 1:1mac-address 0030.94c3.8724dial-peer voice 5000 voipdestination-pattern 5...session target ipv4:223.223.223.223In the previous example, the huntstop attribute is set to ON by default and prevents calls to extension 5001 from being re-routed to the on-net H.323 dial-peer for 5... when the 5001 extension is busy.
The following example shows another instance in which huntstop is not desired and is explicitly disabled:
ephone-dn 1number 5001no huntstoppreference 1call-forward noan 6000ephone-dn 2number 5001preference 2call-forward busy 6000call-forward noan 6000ephone 4button 1:1 2:2mac-address 0030.94c3.8724dial-peer voice 6000 potsdestination-pattern 6000huntstopport 1/0/0description answering-machineIn this example, ephone 4 is configured with two lines, each with the same extension number 5001. This is done in order to allow the second line to provide call waiting notification for extension number 5001 when the first line is in use. Setting no huntstop on the first line (ephone-dn 1) allows incoming calls to hunt to the second line (ephone-dn 2) on ephone 4 when the ephone-dn 1 line is busy.
The ephone-dn 2 has call-forwarding set to extension 6000, which corresponds to a locally attached answering machine connected to a Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) voice-port. In this example, the plain old telephone service (POTS) dial-peer for extension 6000 also has the dial-peer huntstop attribute explicitly set to prevent further hunting.
Related Commands
intercom (ephone-dn)
To define the directory number for the Cisco IP phone that connects with another Cisco IP phone for the intercom feature, use the intercom command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
intercom directory number [barge-in | no-auto-answer] [label label]
no intercom directory number
Syntax Description
Defaults
By default, intercom functionality is disabled for the ephone-dn.
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The intercom command dedicates a pair of ephone-dns for use as a "press to talk" two-way intercom between two IP phones. Intercom lines cannot be used in shared line configurations. If an ephone-dn is configured for intercom operation, it must be associated to one Cisco IP phone only. The intercom attribute causes an IP phone line (ephone-dn) to operate as auto-dial for outbound calls and auto-answer-with-mute for inbound calls.
The barge-in keyword allows inbound intercom calls to force an existing call into the call-hold state and allows the intercom call to be immediately answered. The label keyword defines a text label for the intercom. The no-auto-answer keyword creates a connection for the IP phone line resembling a private line, automatic ringdown (PLAR).
Examples
The following example shows how to set the intercom on Cisco IP phone directory number 1:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn) number A5001Router(config-ephone-dn) name "intercom"Router(config-ephone-dn) intercom A5002 barge-inThe following example shows intercom configuration between two Cisco IP phones:
ephone-dn 18number A5001name "intercom"intercom A5002 [barge-in]ephone-dn 19number A5002name "intercom"intercom A5001 [barge-in]ephone 4button 1:2 2:4 3:18ephone 5button 1:3 2:6 3:19In this example, directory number (ephone-dn) 18 and directory number (ephone-dn) 19 are set as an intercom pair. Directory number (DN) 18 is associated with button 3 of Cisco IP phone (ephone) 4 and directory number (DN) 19 is associated with button number 3 of Cisco IP phone (ephone) 5. Button 3 on both Cisco IP phone 4 and Cisco IP phone 5 are set as a pair to provide intercom service to each other.
The intercom feature acts as a combination speed-dial PLAR and auto-answer with mute. If the barge-in attribute is set on the DN receiving the intercom call, the existing call is forced into the hold state, and the intercom call is accepted. If the phone user has the handset off hook (that is, not in speakerphone mode), the user hears a warning beep, and the intercom call is immediately connected with two-way audio. If the phone user is using speakerphone mode, the intercom connects with the microphone mute activated.

Note
Dialing in to an intercom by any caller and auto-dial to a nonintercom destination are not prohibited. Calls to an intercom dn originated by a nonintercom caller triggers auto-answer. To prevent nonintercom originators from manually dialing to an intercom destination, use of the special A, B, C, or D dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) digits in the intercom phone numbers is recommended because these digits cannot be dialed from a normal phone.
Related Commands
ephone-dn
Enters ephone-dn configuration mode and configures the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines.
ip source-address (telephony-service)
To enable the router to receive messages from the Cisco IP phones through the specified IP addresses and ports, use the ip source-address command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable the router from receiving messages from Cisco IP phones, use the no form of this command.
ip source-address ip-address [port port] [any-match | strict-match]
no ip source-address ip-address [port port] [any-match | strict-match]
Syntax Description
Defaults
The default port is 2000.
The default for the server address match is any-match.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The ip source-address command is a mandatory command. The Cisco IOS Telephony Service router does not start if the IP address and the port information are not provided. If the port number is not provided, then the default is port 2000. The IP address is usually the IP address of the Ethernet port to which the phones are connected.
Use the any-match keyword to instruct the router to permit Cisco IP phone registration, and use the strict-match keyword to instruct the router to reject IP phone registration attempts if the IP server address used by the phone does not exactly match the source-address.
The ip source-address command enables the router to receive messages from the Cisco IP phones through the specified IP address and port.
The ip source-address command helps the router to autogenerate the SEPDEFAULT.cnf file and the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file, which are stored in the router's Flash memory. The SEPDEFAULT.cnf file contains the IP address of one of the Ethernet ports of the router to which the phone should register; the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file contains the IP address of one of the Ethernet ports of the router to which the ATA adapter should register.

Note
The SEPDEFAULT.cnf file and the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file are specific to the router and cannot be shared by multiple routers.
At some point, you must use the following commands to enable access to the SEPDEFAULT.cnf file and XMLDefault.cnf.xml file:
Router# tftp-server flash:SEPDEFAULT.cnfRouter# tftp-server flash:XMLDefault.cnf.xmlThe Flash file system on some routers limits the number of times the Flash file can be written to or modified. After this limit is exceeded, the Flash memory must be manually erased and the files contained in the Flash file must be reloaded.
The ip source-address command can write or modify the SEPDEFAULT.cnf file or the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file only when parameters are actually changed. The file is not deleted by executing the no ip source-address command. However, the SEPDEFAULT.cnf file or the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file can be manually removed using the delete command.
If the ip source-address command is executed with changed parameters after the Flash file write limit is exceeded, the command fails. To see the detailed operation of the ip source-address command, turn on the debug ephone detail command.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the IP source address and port:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# ip source-address 1.6.21.4 port 2000 strict-matchRelated Commands
keepalive (telephony-service)
To configure the time interval between sending keepalive messages to the router used by the Cisco IP phones, use the keepalive command in telephony-service configuration mode. To return to the default, use the no form of this command.
keepalive seconds
no keepalive seconds
Syntax Description
seconds
The interval time in seconds. The range is 10 to 65,535 seconds. The default timeout is set at 30 seconds.
Defaults
The default is 30 seconds.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The keepalive command configures the time interval between sending keepalive messages to the router used by the Cisco IP phone. The default is 30 seconds. If the router fails to receive three successive keepalive messages, it considers the phone to be out of service until the phone re-registers.
Examples
The following example shows how to set keepalive timeout at 40 seconds:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# keepalive 40Related Commands
load (telephony-service)
To download a new phone firmware on the Cisco IP phones, use the load command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable a new phone firmware on the Cisco IP phones, use the no form of this command.
load {7960-7940 | 7910 | 7935} phone-load
no load {7960-7940 | 7910 | 7935} phone-load
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use the load command to download a new phone firmware on the Cisco IP phones. You must enter this command for each type of phone. The Cisco IP Phone 7960 and Cisco IP Phone 7940 have the same phone firmware. The phone firmware should be downloaded on the HTTP server of the router.

Note
When you enter the load command, you do not use the extension of the file, for example, .bin.
Examples
The following example shows how to download the correct phone firmware for the specific Cisco IP phones:

Note
The file names are case-sensitive.
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# load 7960-7940 P003E302Router(config-telephony-service)# load 7910 P004E302Router(config)# tftp-server flash:P003E302.binRouter(config)# tftp-server flash:P004E302.bin
Note
The .bin suffix is not required by the load command; however, the .bin suffix is required by the tftp-server command.
The Cisco IP phone is updated with a different phone firmware only when the Cisco IP phone reboots.
Related Commands
loopback-dn (ephone-dn)
To create a virtual loopback voice port (loopback-dn) to establish a demarcation point for VoIP calls and supplementary services, use the loopback-dn command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To delete a loopback-dn configuration, use the no form of this command.
loopback-dn dn-tag [forward number-of-digits] [prefix prefix-digit-string] [suffix suffix-digit-string] [retry seconds] [auto-con]
no loopback-dn
Syntax Description
Defaults
All calls are set to forward all digits and not to strip any digits.
Prefix is not defined.
Suffix is not defined.
Retry is disabled.
Automatic connection is disabled.Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The loopback-dn command is used to configure two ephone-dn virtual voice ports as back-to-back-connected voice-port pairs. A call presented on one side of the loopback-dn pair is reoriginated as a new call on the opposite side of the loopback-dn pair. The forward, prefix, and suffix keywords can be used to manipulate the original called number that is presented to the incoming side of the loopback-dn pair to generate a modified called number to use when reoriginating the call at the opposite side of the loopback-dn pair. For loopback-dn configurations, you must always configure ephone-dn virtual voice ports as cross-coupled pairs.

Note
Use of loopback-dn configurations within a VoIP network should be restricted to resolving critical network interoperability service problems that cannot otherwise be solved. Loopback-dn configurations are intended to be used in VoIP network interworking situations in which the only other alternative would be to make use of back-to-back-connected physical voice ports. Loopback-dn configurations emulate the effect of a back-to-back physical voice-port arrangement without the expense of the physical voice-port hardware. A disadvantage of loopback-dn configurations is that, because digital signal processors (DSPs) are not involved in a loopback-dn arrangement, the configuration does not support interworking or transcoding between calls that use different voice codecs. In many cases, the use of back-to-back physical voice ports that do use DSPs to resolve VoIP network interworking issues is preferred, because it introduces fewer restrictions in terms of supported codecs and call flows. Also, loopback-dns do not support T.38 fax relay.

Note
Cisco recommends that you create the basic ephone-dn configuration for both ephone-dn entries before configuring the loopback-dn option under each ephone-dn. The loopback-dn mechanism should be used only in situations where the voice call parameters for the calls on either side of the loopback-dn use compatible configurations; for example, compatible voice codec and DTMF relay parameters. Loopback-dn configurations should only be used for G.711 voice calls.
The loopback-dn arrangement allows an incoming telephone call to be terminated on one side of the loopback-dn port pair and a new pass-through outgoing call to be originated on the other side of the loopback-dn port pair. The loopback-dn port pair normally works with direct cross-coupling of their call states; the alerting call state on the outbound call segment is associated with the ringing state on the inbound call segment.
The loopback-dn mechanism allows for call operations (such as call transfer and call forward) that are invoked for the call segment on one side of the loopback-dn port pair to be isolated from the call segment that is present on the opposite side of the loopback-dn port pair. This approach is useful when the endpoint devices associated with the two different sides have mismatched call transfer and call forwarding capabilities. The loopback-dn arrangement allows for call transfer and call forward requests to be serviced on one side of the loopback-dn port pair by creating hairpin-routed calls when necessary. The loopback-dn arrangement avoids the propagation of call transfer and call forward requests to endpoint devices that do not support these functions.
The loopback-dn command provides options for controlling the called-number digits that are passed through from the incoming side to the outgoing side. The available digits can be manipulated with the forward, prefix, and suffix keywords.
The forward keyword defines the number of digits in the original called number to forward to the other ephone-dn in the loopback-dn pair. The default is set to forward all digits. The forward keyword can be used with any combination of the prefix and suffix keywords.
The prefix keyword defines a string of digits to add in front of the forwarded number.
The suffix keyword is most commonly used to add a terminating "#" (pound-sign) character to the end of the forwarded number to indicate that no more digits should be expected. The pound-sign character indicates to the call-routing mechanism that is processing the forwarded number that the forwarded number is complete. Providing an explicit end-of-number character also avoids a situation in which the call-processing mechanism waits for the interdigit timeout period to expire before routing the call onward using the forwarded number.

Note
The Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) requires that arguments with character strings that start with the pound-sign (#) character be enclosed within quotation marks; for example, "#".
The retry keyword is used to suppress a far-end busy indication on the outbound call segment. Instead of returning a busy signal to the call originator (on the incoming call segment), a loopback-dn presents alerting or ringing tone to the caller and then periodically retries the call to the final far-end destination (on the outgoing call segment). This is not bidirectional. To prevent calls from being routed into the idle outgoing side of the loopback-dn port pair during the idle interval that occurs between successive outgoing call attempts, configure the outgoing side of the loopback-dn without a number so that there is no number to match for the inbound call.
The auto-con keyword is used to configure a premature trigger for a connected state for an incoming call segment while the outgoing call segment is still in the alerting state. This setup forces the voice path to open for the incoming call segment and support the generation of in-band call progress tones for busy, alerting, or ringback. The disadvantage of the auto-con keyword is premature opening of the voice path during the alerting stage and also triggering of the beginning of billing for the call before the call has been answered by the far end. These disadvantages should be considered carefully before you use the auto-con keyword.
Examples
The following example creates a loopback-dn configured with the forward and prefix keywords:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 7Router(config-ephone-dn)# loopback-dn 15 forward 5 prefix 41The following example creates a loopback-dn that appends the pound-sign (#) character to forwarded numbers to indicate the end of the numbers:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 7Router(config-ephone-dn)# loopback-dn 16 suffix "#"The following example shows a loopback-dn configuration that pairs ephone-dns 15 and 16.An incoming call (for example, from VoIP) to 4085550101 matches ephone-dn 16. The call is then reoriginated from ephone-dn 15 and sent to extension 50101. Another incoming call (for example, from a local IP phone) to extension 50151 matches ephone-dn 15. It is reoriginated from ephone-dn 16 and sent to 4085550151.
ephone-dn 15number 5015.loopback-dn 16 forward 5 prefix 40855caller-id blockno huntstop!!ephone-dn 16number 408555010.loopback-dn 15 forward 5caller-id blockno huntstop!Related Commands
mac-address (ephone)
To configure the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone, use the mac-address command in ephone configuration mode. To disable the MAC address of the Cisco IP phone, use the no form of this command.
mac-address mac-address
no mac-address mac-address
Syntax Description
mac-address
Identifies a specific Cisco IP phone. The MAC address is typically found on a sticker located on the bottom of the Cisco IP phone.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The mac-address command configures the MAC address of a specific Cisco IP phone to uniquely identify the Cisco IP phone. The MAC address is printed on a sticker and placed under each Cisco IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure the actual MAC address CCFBA.321B.96FA for a Cisco IP phone:
Router(config-ephone)# mac-address CFBA.321B.96FARelated Commands
max-conferences (telephony-service)
To set the maximum number of simultaneous three-party conferences supported by the router, use the max-conferences command in telephony-service configuration mode. To return to the default conferencing numbers, use the no form of this command.
max-conferences max-conference numbers
no max-conferences max-conference numbers
Syntax Description
Defaults
The default is half of the maximum simultaneous three-party conferences numbers per platform.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The max-conferences command supports three-party conferences for local and on-net calls only when all conference participants are using G.711. Conversion between G.711 u-law and a-law is supported. Mixing of the media streams is supported by the Cisco IOS processor. The maximum number of simultaneous conferences is limited to the platform-specific maximum.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the maximum number of conferences for a Cisco IP phone to 4:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# max-conferences 4Related Commands
telephony-service
Enables Cisco IOS Telephony Service and enters telephony-service configuration mode.
max-dn (telephony-service)
To set the maximum number of directory numbers that can be supported by the router, use the max-dn command in telephony-service configuration mode. To return to the default directory numbers, use the no form of this command.
max-dn max directory numbers
no max-dn
Syntax Description
Defaults
The default is 0.
Syntax Description
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The max-dn command limits the number of extensions (ephone-dns) available in a Cisco CME system. The maximum number of extensions is platform- and version-dependent. Use CLI help to determine the maximum number of extensions you can set, as shown in this example:
Router(config-telephony-service)# max-dn ?<1-192> Maximum directory numbers supported
Note
You can increase the directory numbers; but after the maximum allowable number is configured, you cannot reduce the limit of the directory numbers without rebooting the router.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the maximum number of directory numbers to 12:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# max-dn 12Related Commands
max-ephones (telephony-service)
To configure the maximum number of Cisco IP phones that can be supported by the router, use the max-ephones command in telephony-service configuration mode. To return to the default number of Cisco IP phones, use the no form of this command.
max-ephones max phones
no max-ephones
Syntax Description
Defaults
The default is 0.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The max-ephones command limits the number of Cisco IP phones supported on the router. The maximum number you can set is platform- and version-dependent. Use CLI help to determine the maximum number of ephones you can set, as shown in this example:
Router(config-telephony-service)# max-ephones ?<1-48> Maximum phones to support
Note
You can increase the number of phones; but after the maximum allowable number is configured, you cannot reduce the limit of the Cisco IP phones without rebooting the router.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the maximum number of Cisco IP phones to 24 for a Cisco router:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# max-ephones 24Related Commands
moh (telephony-service)
To configure Music On Hold (MOH), use the moh command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable music on hold, use the no form of this command.
moh filename
no moh filename
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The moh command configures .au and .wav format music files. Music on hold only works for G.711 calls and on-net VoIP and PSTN calls. For all other calls, tone on hold works where the user hears a periodic beep. The internal calls between Cisco IP phones do not get music on hold, instead the IP phones get tone on hold. The MOH files are downloaded to the router's Flash memory.

Note
The music on hold file can be in .wav or.au file format; however, the file format must contain 8-bit 8KHz data, for example, CCITT a-law or u-law data format.
Examples
The following example sets the music on hold with the music files:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# moh minuet.wavRouter(config-telephony-service)# moh minuet.auRelated Commands
telephony-service
Enables Cisco IOS Telephony Service and enters telephony-service configuration mode.
mwi (ephone-dn)
To configure specific Cisco IP phone directory numbers to receive message waiting indication (MWI) notification from an external voice-mail system, use the mwi command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
mwi {off | on | on-off}
no mwi {off | on | on-off}
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The mwi command configures specific Cisco IP phone directory numbers to receive message waiting indication (MWI) notification from an external voice-mail system. The notification is set for all the Cisco IP phones connected to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. The external voice-mail systems are often able to communicate MWI status by making telephone calls to dummy extension numbers, where the MWI information is embedded in either the called or calling party IP phone number. This command cannot be configured unless the number command is configured under ephone-dn configuration mode.
Examples
The following example shows how to set message waiting indication to ON:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn) number 8000Router(config-ephone-dn) mwi onThe following example shows how to set message waiting indication to OFF.Router(config)# ephone-dn 2Router(config-ephone-dn) number 8001Router(config-ephone-dn) mwi offThe following example shows how to set message waiting indication to ON-OFF for the primary and secondary number, where the MWI information is embedded in the calling party number:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 3Router(config-ephone-dn) number 8002 secondary 8003Router(config-ephone-dn) mwi on-offIn the example above, a call placed by the voice-mail system to 8002 turns on the MWI light for the extension number indicated by the calling party number for the MWI call. A call placed to 8003 turns the MWI light off.
The following example shows how to set message waiting indication to ON-OFF for the primary and secondary number, where the MWI information is embedded in the called party number:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 20Router(config-ephone-dn) number 8000*....*1 secondary 8000*....*2Router(config-ephone-dn) mwi on-offIn the example above, a call placed by the voice-mail system to 8000*5001*1 turns the MWI light for extension 5001 on. A call to 8000*5001*2 turns the MWI light off.
Related Commands
mwi relay (telephony-service)
To enable the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to relay message waiting indication (MWI) information to remote Cisco IP phones, use the mwi relay command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable MWI relay, use the no form of this command.
mwi relay
no mwi relay
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The mwi relay command enables the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to relay MWI information to remote Cisco IP phones. The Cisco IOS Telephony Service router at the central site acts as a notifier after the mwi relay command is configured.
Examples
The following example shows how to set MWI relay:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# mwi relayRelated Commands
mwi expires (telephony-service)
To set the expire timer for registration for either the client or server, use the mwi expires command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable the expire timer for a subscription, use the no form of this command.
mwi expires seconds
no mwi expires seconds
Syntax Description
Defaults
Default is set to 86,400 seconds (24 hours).
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The mwi expires command sets the expire timer for registration for either the client or server.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the MWI expires time to 10 seconds:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# mwi expires 10Related Commands
mwi sip (ephone-dn)
To subscribe an extension in a Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to receive message waiting indication (MWI) notification from a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) protocol-based MWI server, use the mwi sip command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To delete the configuration, use the no form of this command.
mwi sip
no mwi sip
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The mwi sip command subscribes an extension in a Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to receive message waiting indication (MWI) notification from a SIP MWI server. This integrates a Cisco IOS Telephony Service router with a SIP-protocol-based MWI service.
Examples
The following example shows how to subscribe MWI notification from an external SIP MWI server requests the SIP MWI server to send MWI notification messages to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router for the extension number:
Router(config) ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn) number 5001Router(config-ephone-dn) name John SmithRouter(config-ephone-dn) mwi sipRouter(config) telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service) mwi sip-server 223.223.0.5This command requests that the SIP server configured for the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router send MWI notification messages through the SIP protocol for extension 5001.
Related Commands
mwi sip-server (telephony-service)
To configure IP address and port for the external Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)-based message waiting indication (MWI) server, use the mwi sip-server command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable the MWI server, use the no form of this command.
mwi sip-server ip-address [[transport tcp | transport udp] | [port port number] | [reg-e164]]
no mwi sip-server ip-address
Syntax Description
Defaults
Default transport layer protocol is TCP.
Default port number is 5060 (SIP standard port).
Default registration is with an extension number.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The mwi sip-server command configures the IP address of an external SIP MWI server. This IP address is used in conjunction with the mwi sip (ephone-dn) command to subscribe individual ephone-dn extension numbers to the MWI SIP server's notification list. SIP MWI client runs TCP as default.
The transport tcp keyword is the default setting. The transport udp keyword allows you to integrate with SIP MWI client. The optional port keyword is used to specify a port number. The default SIP port number is 5060. The default registration is with an extension number, so the reg-e164 keyword allows you to register with an E.164 ten digit number.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the MWI for the SIP server and set the individual ephone-dn extension numbers to the MWI SIP server's notification list:
Router(config) ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn) number 5001Router(config-ephone-dn) name John SmithRouter(config-ephone-dn) mwi sipRouter(config) telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service) mwi sip-server 223.223.0.5 transport udpRelated Commands
name (ephone-dn)
To configure a username associated with a directory number, use the name command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable a username associated with a directory number, use the no form of this command.
name name
no name name
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The name command configures a username associated with a directory number. The name variable information is used to provide caller ID for calls originated on the Cisco IP phone directory number. The name command is also used to generate directory information for XML directory accessible from a Cisco IP phone directories button.

Note
You must follow the pattern specified in the directory command under the telephony-service configuration mode to associate the username for the directory. The pattern for the surnames for the directory is set either with first-name-first or last-name-first.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure the username John Smith with the pattern first-name-first:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn) name John SmithThe following example shows how to configure the username Jane Smith with the pattern last-name-first:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn) name Smith, JaneRelated Commands
number (ephone-dn)
To configure a valid number for the Cisco IP phone, use the number command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable a number for the Cisco IP phone, use the no form of this command.
number number [secondary number] [no-reg [both | primary]]
no number number [secondary number] [no-reg [both | primary]]
Syntax Description
Defaults
No secondary phone number is associated with the ephone-dn.
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The number command configures a valid number for the Cisco IP phone. The secondary keyword allows you to associate a second telephone number with an ephone-dn so that the Cisco IP phone line can be called by dialing either the main or secondary phone number. The secondary number may contain wildcards; for example, 50.. (number 50 followed by wildcards). The no-reg keyword specifies an E.164 number in the dial-peer to not register to the gatekeeper. If you do not specify either both or primary after the no-reg keyword, then only the secondary number is not registered.
Examples
The following example shows that 5001 is set as the primary extension number for a Cisco IP phone and 0 as the secondary number. This allows the telephone number 5001 to act as a regular extension number and also to act as the operator line such that callers who dial 0 are routed to the phone line with extension number 5001.
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn)# number 5001 secondary 0In the following example, 5001 is set as the primary extension number for a Cisco IP phone and "500." (the number 500 followed by a decimal point) is set as the secondary number. This allows any calls to extension numbers in the range 5000-5009 to be routed to extension 5001 in the event that the actual extension number dialed cannot be found. For example, IP phones may be active in the system with lines that correspond to 5001, 5002, 5004, 5005, and 5009. A call to 5003 or 5006-5009 would be unable to locate a phone with the 5003 or 5006-5008 extensions, so the call would be routed to extension 5001.
Router(config-ephone-dn)# number 5001 secondary 500.
Related Commands
paging (ephone-dn)
To set paging numbers that can be called to broadcast an audio page to a group of Cisco IP phones, use the paging command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
paging [ip multicast-address port udp-port-number]
no paging [ip multicast-address port udp-port-number]
Syntax Description
Defaults
A Cisco IP phone directory number is not configured as a paging number
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The paging command configures the ephone-dn number to act as an extension number to use to broadcast audio paging to idle Cisco IP phones. Cisco IP phones must be associated with the paging directory number (ephone-dn) using the ephone-dn tag number of the paging ephone-dn or are included indirectly through a paging group from another paging ephone-dn.
When the optional ip keyword followed by the multicast-address argument is used, the paging is set for multicast paging. If an IP multicast address is not configured, IP phones are paged individually using IP unicast transmission (to a maximum of ten IP phones). The recommended operation is with an IP multicast address. When multiple paging extensions are configured, each extension should use a unique IP multicast address.
Examples
The following example configures IP multicast paging:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 20Router(config-ephone-dn) number 2000Router(config-ephone-dn) paging ip 224.0.1.1 port 2000The configuration is as follows:
ephone-dn 20number 2000paging ip 224.0.1.20 port 2000ephone-dn 21number 2001paging ip 224.0.1.21 port 2000ephone 1button 1:1paging-dn 20ephone 2button 1:2paging-dn 20ephone 3button 1:3paging-dn 21ephone 4button 1:4paging-dn 21In this example paging calls to 2000 are multicast to Cisco IP phones (ephones) 1 and 2; paging calls to 2001 go to ephones 3 and 4.

Note
The maximum number of unique IP address and router physical interfaces (or subinterfaces) combinations supported for output of audio paging voice packets is ten. Paging using a single IP multicast address that requires output on three different Ethernet interfaces represents use of three counts out of the maximum ten. The limit of ten is likely to be exceeded only if unicast addressing is used for the paging ephone-dn or if individual IP phones are configured for unicast paging support only.
Related Commands
paging group (ephone-dn)
To set the audio paging directory number for a large combined group, use the paging group command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To remove a paging group, use the no form of this command.
paging group paging-ephone-dn-tag-list, paging-ephone-dn-tag-list
no paging group paging-ephone-dn-tag-list, paging-ephone-dn-tag-list
Syntax Description
Defaults
By default, paging is disabled on all Cisco IP phones
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The paging group command is used to combine small sets of phones associated with individual paging directory numbers (ephone-dns) into a large combined group so that a page can be sent to large numbers of phones at once. To remove a paging group, use the no form of the command. All ephone-dn tags included in the list must have the paging command set.
The use of paging groups allows phones to participate in a small local paging set (for example, paging to four phones in a company's shipping and receiving department) but also supports company-wide paging when needed (for example by combining the paging sets for shipping and receiving, with paging sets for accounting, customer support, and sales into a paging group).
Examples
The following example shows how to set paging groups:
ephone-dn 20number 2000paging ip 224.0.1.20 port 2000ephone-dn 21number 2001paging ip 224.0.1.21 port 2000ephone-dn 22number 2002paging ip 224.0.2.22 port 2000paging group 20,21ephone 1button 1:1paging-dn 20ephone 2button 1:2paging-dn 20ephone 3button 1:3paging-dn 21ephone 4button 1:4paging-dn 21ephone 5button 1:5paging-dn 22In this example, paging calls to 2000 go to Cisco IP phones (ephones) 1 and 2, and paging calls to 2001 go to ephones 3 and 4. Calls to 2002 go to ephones 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. Ephones 1 and 2 are included in paging directory number (ephone-dn) 22 through membership of ephone-dn 20 in the paging group. Ephones 3 and 4 are included in paging ephone-dn 22 through membership of ephone-dn 21 in the paging group. Ephone 5 is directly subscribed to paging-dn 22. Note that multicast addresses always take the form of 224.x.x.x.
Related Commands
paging-dn (ephone)
To set an audio paging directory number for each Cisco IP phone, use the paging-dn command in ephone configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
paging-dn paging-dn-number-tag {multicast | unicast}
no paging-dn paging-dn-number-tag {multicast | unicast}
Syntax Description
Defaults
By default, paging is disabled on all Cisco IP phones
Command Modes
Ephone configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The paging-dn command sets an audio paging directory number (DN) for each Cisco IP phone. The audio paging feature operates in a fashion similar to intercom, but provides only one-way voice, with no press-to-answer option. A DN is created, which is associated with a certain number of local IP phones. The paging extension number is configured using the existing number command under ephone-dn configuration mode. Multiple paging DNs can be supported for each system. The paging number can be dialed from anywhere, including on-net calls. The paging audio stream is heard on all selected Cisco IP phones that are in the idle state through the speakerphone mode. The IP phone display shows the "name" information associated with the paging DN used to activate the page. During an active paging, incoming or outgoing call for an answered or initiated call, disconnects the IP phone from the paging output.
The paging mechanism supports audio distribution using IP multicast, replicated unicast, and a mixture of both (so that multicast is used where possible, and unicast is used with specific phones that cannot be reached through multicast).
Each Cisco IP phone can be associated with only one paging directory number (paging-dn); however, paging-dns may be grouped in order to join groups of IP phones together. Only single-level grouping is supported (no support for groups of groups). This allows for paging to IP phones for individual departments (for example, sales, support, shipping, and accounting) and then allows these sets to be combined into a group for "all employees" or "everyone in building 2". Any number of phones may be added into the same paging set using multicast. A Cisco IP phone (ephone) may directly belong to only a single paging set. A paging set consists of all phones configured with the same paging-dn. Each paging set uses a DN.
Examples
The following example shows how to set up an ephone-dn for multicast paging:
ephone-dn 22name Paging Shippingnumber 5001paging ip 224.1.1.10 port 2000ephone 4mac 0030.94c3.8724button 1:1 2:2paging-dn 22 multicastThis example creates a paging number for 5001 on ephone-dn 22 and adds ephone 4 as a member of the paging set. Multicast is set for the paging-dn. Note that multicast addresses always take the form of 224.x.x.x.

Note
For unicast paging to all phones, omit the IP multicast address in the ephone-dn configuration. For unicast paging to a specific phone using an ephone-dn configured for multicast, add the unicast keyword after the paging-dn command in ephone configuration mode.
Each ephone-dn used for paging can support a maximum of ten distinct targets (IP addresses and interfaces). A multicast address counts as a single target for each physical interface in use (regardless of the number of phones connected via the interface). Each unicast target counts as a single target, such that paging that does not use multicast at all is limited to paging ten phones. For example, ten IP phones paged through multicast on Fast Ethernet interface 0/1.1 plus five IP phones paged through multicast on FastEthernet interface 0/1.2, is counted as two targets.
For simultaneous paging to more than one paging ephone-dn, Cisco recommends that you use different IP multicast addresses (not just different port numbers) for paging configuration. Note that multicast addresses always take the form of 224.x.x.x.
Related Commands
pattern direct (vm-integration)
To configure the dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) digit pattern forwarding necessary to activate the voice-mail system when the user presses the messages button on the phone, use the pattern direct command in voicemail integration configuration mode. To disable DTMF digit pattern forwarding when the user presses the messages button on the phone, use the no form of this command.
pattern direct tag1 {CGN | CDN | FDN} [tag2 {CGN | CDN | FDN}]
[tag3 {CGN | CDN | FDN}] [tag4]no pattern direct tag1 {CGN | CDN | FDN} [tag2 {CGN | CDN | FDN}]
[tag3 {CGN | CDN | FDN}] [tag4]Syntax Description

Note
Although it is unlikely that you will use multiple instances of the CGN, CDN, or FDN keyword in a single command line, it is permissible to do so.
Defaults
This feature is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Voice-mail integration configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The pattern direct command is used to configure the sequence of DTMF digits passed to a voice-mail system attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router through one or more voice ports. When a call is placed directly from a Cisco IP phone attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, the voice-mail system expects to receive a sequence of DTMF digits at the beginning of the call that identify the mailbox of the user calling the voice-mail system accompanied by a string of digits indicating that the caller is attempting to access the designated mailbox in order to retrieve messages.
Examples
The following example sets the DTMF pattern for a calling number ($CGN) for a direct call to the voice-mail system:
Router(config) vm-integrationRouter(config-vm-integration) pattern direct 2 CGNRelated Commands
pattern ext-to-ext busy (vm-integration)
To configure the dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) digit pattern forwarding necessary to activate the voice-mail system once an internal extension attempts to connect to a busy extension and the call is forwarded to voicemail, use the pattern ext-to-ext busy command in voicemail integration configuration mode. To disable DTMF digit pattern forwarding when an internal extension calls a busy extension and the call is forwarded to a voice-mail system, use the no form of this command.
pattern ext-to-ext busy tag1 {CGN | CDN | FDN} [tag2 {CGN | CDN | FDN}]
[tag3 {CGN | CDN | FDN}] [tag4]no pattern ext-to-ext busy tag1 {CGN | CDN | FDN} [tag2 {CGN | CDN | FDN}]
[tag3 {CGN | CDN | FDN}] [tag4]Syntax Description

Note
Although it is unlikely that you will use multiple instances of the CGN, CDN, or FDN keyword in a single command line, it is permissible to do so.
Defaults
This feature is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Voice-mail integration configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The pattern ext-to-ext busy command is used to configure the sequence of DTMF digits passed to a voice-mail system attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router through one or more voice ports. When a call is routed to the voice-mail system by call forward on busy from a Cisco IP phone attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, the voice-mail system expects to receive a sequence of digits identifying the mailbox associated with the forwarding phone together with digits that identify the extension number of the calling IP phone.
Examples
The following example sets the DTMF pattern for a local call forwarded on busy to the voice-mail system:
Router(config) vm-integrationRouter(config-vm-integration) pattern ext-to-ext busy 7 FDN * CGN *Related Commands
pattern ext-to-ext no-answer (vm-integration)
To configure the dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) digit pattern forwarding necessary to activate the voice-mail system once an internal extension fails to connect to an extension and the call is forwarded to voicemail, use the pattern ext-to-ext no-answer command in voicemail integration configuration mode. To disable DTMF digit pattern forwarding, use the no form of this command.
pattern ext-to-ext no-answer tag1 {CGN | CDN | FDN} [tag2 {CGN | CDN | FDN}]
[tag3 {CGN | CDN | FDN}] [tag4]no pattern ext-to-ext no-answer tag1 {CGN | CDN | FDN} [tag2 {CGN | CDN | FDN}]
[tag3 {CGN | CDN | FDN}] [tag4]Syntax Description

Note
Although it is unlikely that you will use multiple instances of the CGN, CDN, or FDN keyword in a single command line, it is permissible to do so.
Defaults
This feature is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Voice-mail integration configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The pattern ext-to-ext no-answer command is used to configure the sequence of DTMF digits passed to a voice-mail system attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router through one or more voice ports. When a call is routed to the voice-mail system by call forward on no-answer from an IP phone attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, the voice-mail system expects to receive a sequence of digits identifying the mailbox associated with the forwarding phone together with digits that identify the extension number of the calling IP phone.
Examples
The following example sets the DTMF pattern for a local call forwarded on no-answer to the voice-mail system:
Router(config) vm-integrationRouter(config-vm-integration) pattern ext-to-ext no-answer 5 FDN * CGN *Related Commands
pattern trunk-to-ext busy (vm-integration)
To configure the dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) digit pattern forwarding necessary to activate the voice-mail system once an external trunk call reaches a busy extension and the call is forwarded to voicemail, use the pattern trunk-to-ext busy command in voicemail integration configuration mode. To disable DTMF digit pattern forwarding when an external trunk call reaches a busy extension and the call is forwarded to a voice-mail system, use the no form of this command.
pattern trunk-to-ext busy tag1 {CGN | CDN | FDN} [tag2 {CGN | CDN | FDN}]
[tag3 {CGN | CDN | FDN}] [tag4]no pattern trunk-to-ext busy tag1 {CGN | CDN | FDN} [tag2 {CGN | CDN | FDN}]
[tag3 {CGN | CDN | FDN}] [tag4]Syntax Description

Note
Although it is unlikely that you will use multiple instances of the CGN, CDN, or FDN keyword in a single command line, it is permissible to do so.
Defaults
This feature is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Voice-mail integration configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The pattern trunk-to-ext busy command is used to configure the sequence of DTMF digits passed to a voice-mail system attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router through one or more voice ports. When a call is routed to the voice-mail system by call forward on busy from an IP phone attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, the voice-mail system expects to receive a sequence of digits identifying the mailbox associated with the forwarding phone together with digits indicating that the call originated from a PSTN or VoIP caller.
Examples
The following example sets the DTMF pattern for call forwarding when an external trunk call reaches a busy extension and the call is forwarded to the voice-mail system:
Router(config) vm-integrationRouter(config-vm-integration) pattern trunk-to-ext busy 6 FDN * CGN *Related Commands
pattern trunk-to-ext no-answer (vm-integration)
To configure the dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) digit pattern forwarding necessary to activate the voice-mail system when an external trunk call reaches an unanswered extension and the call is forwarded to voicemail, use the pattern trunk-to-ext no-answer command in voicemail integration configuration mode. To disable DTMF digit pattern forwarding when an external trunk call reaches another extension where the called party does not answer and the call is forwarded to a voice-mail system, use the no form of this command.
pattern trunk-to-ext no-answer tag1 {CGN | CDN | FDN} [tag2 {CGN | CDN | FDN}]
[tag3 {CGN | CDN | FDN}] [tag4]no pattern trunk-to-ext no-answer tag1 {CGN | CDN | FDN} [tag2 {CGN | CDN | FDN}]
[tag3 {CGN | CDN | FDN}] [tag4]Syntax Description

Note
Although it is unlikely that you will use multiple instances of the CGN, CDN, or FDN keyword in a single command line, it is permissible to do so.
Defaults
This feature is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Voice-mail integration configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The pattern trunk-to-ext no-answer command is used to configure the sequence of DTMF digits passed to a voice-mail system attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router through one or more voice ports. When a call is routed to the voice-mail system by call forward on no-answer from an IP phone attached to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, the voice-mail system expects to receive a sequence of digits identifying the mailbox associated with the forwarding phone together with digits indicating that the call originated from a PSTN or VoIP caller.
Examples
The following example sets the DTMF pattern for call forwarding when an external trunk call reaches an unanswered extension and the call is forwarded (FDN) to a voice-mail system:
Router(config) vm-integrationRouter(config-vm-integration) pattern trunk-to-ext no-answer 4 FDN * CGN *Related Commands
preference (ephone-dn)
To set preference order for the directory number associated with a Cisco IP phone, use the preference command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To put the directory number in default preference order, use the no form of this command.
preference preference-order
no preference preference-order
Syntax Description
preference-order
The preference order is 0 to 10. 0 is the highest preference and 10 is the lowest preference.
Defaults
The default is 0 (the highest preference)
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The preference command sets preference order for the directory number (ephone-dn) associated with a Cisco IP phone. Use the preference command to indicate the preference order for matching dial peers in Cisco IP phone virtual dial-peer group. Setting the preference enables the desired dial peer to be selected when multiple dial peers within a hunt group are matched for a dial string.
Examples
The following example sets a preference of 2 for the directory number 3000:
Router(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn)# number 3000Router(config-ephone-dn)# preference 2The configuration is as follows:
ephone-dn 4number 1222preference 0!!ephone-dn 5number 1222preference 1In this example, number 1222 under directory number (ephone-dn) 4 has a higher preference than the number 1222 under ephone-dn 5.
Related Commands
reset (ephone)
To reset the Cisco IP phones in ephone configuration mode, use the reset command in ephone configuration mode.
reset

Note
The reset command does not have a no form.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The reset command resets the Cisco IP phone in ephone configuration mode.
The reset command does not have a no form.
Examples
The following example shows how to reset the Cisco IP phones:
Router(config)# ephone 1Router(config-ephone)# resetRelated Commands
reset (telephony-service)
To reset the Cisco IP phones associated with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the reset command in telephony-service configuration mode.
reset {all seconds | mac-address mac-address}

Note
The reset command does not have a no form.
Syntax Description
all
All Cisco IP phones.
seconds
Time interval, in seconds, between each phone reset. The range is from 0 to 15 seconds.
mac-address mac-address
MAC address of a particular Cisco IP phone.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The reset command resets the Cisco IP phones attached to the router. You can use the all keyword to reset all Cisco IP phones attached to the router or to reset a specific Cisco IP phone by entering the mac-address keyword and the MAC address of that specific Cisco IP phone.
The reset command does not have a no form.
Examples
The following example shows how to reset all Cisco IP phones:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# reset allThe following example shows how to configure the Cisco IP phone with the MAC address CFBA.321B.96FA:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# reset mac-address CFBA.321B.96FARelated Commands
show ephone
To display Cisco IP phone output, use the show ephone EXEC command.
show ephone [mac-address | summary | registered | unregistered | 7910 | 7940 | 7960 | ringing | offhook | dn dn-tag | remote | telephone-number phone-number]
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The show ephone command displays statistical information for registered and unregistered Cisco IP phones. If a MAC address is not specified, all phones that can be identified by the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router are displayed. This command includes several keywords to enable you to get different types of output specific to your needs.
Examples
The following is a sample output from the show ephone command:
Router# show ephoneephone-1 Mac:0003.E3E7.F627 TCP socket:[1] activeLine:1 REGISTEREDmediaActive:1 offhook:1 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0IP:10.0.0.51 50570 Telecaster 7940 keepalive 49button 1: dn 1 number 3001 CONNECTEDActive Call on DN 1:3001 10.0.0.51 31808 to 1.2.159.100 22708Tx Pkts 452 bytes 41584 Rx Pkts 452 bytes 41584 Lost 0Jitter 0 Latency 0ephone-2 Mac:0030.94C3.E1A8 TCP socket:[2] activeLine:1 REGISTEREDmediaActive:1 offhook:1 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0IP:1.2.159.100 50942 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 78button 1: dn 2 number 3002 CONNECTEDActive Call on DN 2:3002 1.2.159.100 22708 to 10.0.0.51 31808Tx Pkts 452 bytes 41584 Rx Pkts 452 bytes 41584 Lost 0Jitter 0 Latency 0ephone-3 Mac:0030.94C3.F946 TCP socket:[-1] activeLine:0 UNREGISTEREDmediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0IP:10.2.1.2 52163 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 59ephone-4 Mac:0030.94C3.F43A TCP socket:[-1] activeLine:0 UNREGISTEREDmediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0IP:10.2.1.1 51768 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 59The following is a sample output from the show ephone mac-address command for the Cisco IP phone with the MAC address 0030.94C3.F43A:
Router# show ephone 0030.94c3.f43aephone-3 Mac:0030.94C3.F43A TCP socket:[3] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDmediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0IP:1.5.81.13 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 28button 1: dn 3 number 5003 IDLEbutton 2: dn 5 number 5005 IDLEbutton 3: dn 6 number 5006 IDLEspeed dial 1:3005speed dial 2:3006The following is a sample output from the show ephone dn dn-tag command:
Router# show ephone dn 5Tag 5, Normal or Intercom dnephone 1, mac-address 0030.94C3.CAA2, line 2ephone 2, mac-address 0030.94c2.9919, line 3The following is a sample output from the show ephone 7910 command:
Router# show ephone 7910ephone-5 Mac:0004.DD1E.56ED TCP socket:[1] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDmediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:0IP:10.30.0.83 52234 Telecaster 7910 keepalive 270 max_line 2 dual-linebutton 1: dn 15 number 5000 IDLEbutton 2: dn 16 number 5500 IDLEThe following is a sample output from the show ephone 7960 command:
Router# show ephone 7960ephone-11 Mac:0007.0EA6.2AA9 TCP socket:[13] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDmediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:0IP:10.30.0.53 52548 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 272 max_line 6button 1: dn 16 number 9001 IDLEbutton 2: dn 17 number 9002 IDLEbutton 3: dn 18 number 9003 IDLEbutton 4: dn 26 number A5001 auto dial A5002 IDLEbutton 5: dn 31 number 1111 IDLEspeed dial 1:8001ephone-12 Mac:0002.B9EB.0CB1 TCP socket:[14] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDmediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 paging 0 debug:0IP:10.30.0.54 50387 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 272 max_line 6button 1: dn 20 number 9005 IDLEbutton 2: dn 21 number 9006 IDLEbutton 3: dn 22 number 9007 IDLEbutton 4: dn 23 number 9008 IDLEbutton 5: dn 30 number 1110 IDLEThe following is a sample output from the show ephone registered command:
Router# show ephone registeredephone-1 Mac:0653.D6B4.C601 TCP socket:[4] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-2 Mac:0653.D6B4.C602 TCP socket:[6] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-3 Mac:0653.D6B4.C603 TCP socket:[2] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-4 Mac:0653.D6B4.C604 TCP socket:[7] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-5 Mac:0653.D6B4.C605 TCP socket:[9] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-6 Mac:0653.D6B4.C608 TCP socket:[1] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-7 Mac:0653.D6B4.C609 TCP socket:[8] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-8 Mac:0653.D6B4.C614 TCP socket:[5] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-9 Mac:0653.D6B4.C622 TCP socket:[11] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-10 Mac:0653.D6B4.C623 TCP socket:[3] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-11 Mac:0007.0EA6.2AA9 TCP socket:[13] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-12 Mac:0002.B9EB.0CB1 TCP socket:[14] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-13 Mac:0653.D6B4.C625 TCP socket:[10] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDephone-14 Mac:0653.D6B4.C624 TCP socket:[12] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDThe following is a sample output from the show ephone telephone-number phone-number command:
Router# show ephone telephone-number 4085998001DP tag: 1, primaryTag 1, Normal or Intercom dnephone 1, mac-address 0030.94c3.CAA2, line 1Table 4 provides an alphabetic listing of the command fields in the sample output.
The following is a sample output from the show ephone summary command:
Router# show ephone summaryephone-1 Mac:0030.94C3.37CB TCP socket:[-1] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDmediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0IP:10.1.1.1 Telecaster 7910 keepalive 45 1:1sp1:5002 sp2:5003ephone-2 Mac:0030.94C3.F96A TCP socket:[-1] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDmediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0IP:10.1.1.2 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 45 1:2 2:3 3:4sp1:5004 sp2:5001ephone-3 Mac:0030.94C3.F946 TCP socket:[-1] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDmediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0IP:10.2.1.2 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 59ephone-4 Mac:0030.94C3.F43A TCP socket:[-1] activeLine:0 REGISTEREDmediaActive:0 offhook:0 ringing:0 reset:0 reset_sent:0 debug:0IP:10.2.1.1 Telecaster 7960 keepalive 59Table 5 provides an alphabetic listing of the command fields in the sample output.
Related Commands
show ephone-dn
To display a Cisco IP phone destination number of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the show ephone-dn EXEC command.
show ephone-dn [tag | summary]
Syntax Description
tag
(Optional) Destination number tag. The destination number can be from 1 to 24.
summary
(Optional) Summary of all Cisco IP phone destination numbers.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following is sample output from the show ephone-dn command:
Router# show ephone-dn 1EFXS 50/0/1 Slot is 50, Sub-unit is 0, Port is 1Type of VoicePort is EFXSOperation State is UPAdministrative State is UPNo Interface Down FailureDescription is not setNoise Regeneration is enabledNon Linear Processing is enabledMusic On Hold Threshold is Set to -38 dBmIn Gain is Set to 0 dBOut Attenuation is Set to 0 dBEcho Cancellation is enabledEcho Cancel Coverage is set to 8 msPlayout-delay Mode is set to defaultPlayout-delay Nominal is set to 60 msPlayout-delay Maximum is set to 200 msConnection Mode is normalConnection Number is not setInitial Time Out is set to 10 sInterdigit Time Out is set to 10 sRinging Time Out is set to 180 sCompanding Type is u-lawRegion Tone is set for USWait Release Time Out is 30 sStation name None, Station number 5001Caller ID Info Follows:Standard BELLCOREVoice card specific Info Follows:Digit Duration Timing is set to 100 msThe following is sample output from the show ephone-dn summary command:Router# show ephone-dn summaryPORT DN STATE MWI_STATE CODEC VAD VTSP STATE VPM STATE======== ========== ============ ======== === ================= ============50/0/1 DOWN NONE - - - EFXS_ONHOOK50/0/2 DOWN SUBSCRIBED - - - EFXS_ONHOOK50/0/3 DOWN NONE - - - EFXS_ONHOOK50/0/4 DOWN CONNECTING - - - EFXS_ONHOOKTable 6 provides an alphabetic listing of the command fields in the sample output.
Related Commands
show ephone-dn loopback
To display information about loopback ephone-dns that have been created in a Cisco CallManager Express (Cisco CME) system, use the show ephone-dn loopback command in privileged EXEC mode.
show ephone-dn loopback
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following example displays information for a loopback using ephone-dn 21 and ephone-dn 22:
Router# show ephone-dn loopbackLOOPBACK DN status (min 21, max 22):DN 21 51... Loopback to DN 22 CH1 IDLECallingDn -1 CalledDn -1 Called Calling G711Ulaw64kStrip NONE, Forward 2, prefix 10 retry 10 Media 0.0.0.0 0callID 0 srcCallID 0 ssrc 0 vector 0DN 22 11... Loopback to DN 21 CH1 IDLECallingDn -1 CalledDn -1 Called Calling G711Ulaw64kStrip NONE, Forward 2, prefix 50 retry 10 Media 0.0.0.0 0callID 0 srcCallID 0 ssrc 0 vector 0Significant fields in the output from this command are described in Table 1, in alphabetical order.
Related Commands
show mwi relay clients
To display registration information for the list of message waiting indication (MWI) relay clients, use the show mwi relay EXEC command.
show mwi relay clients
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The show mwi relay command displays registration information for the list of message waiting indication (MWI) relay clients.
Examples
The following is sample output from the show mwi relay clients command:
Router# show mwi relay clientsClient IPADDR EXPIRES(sec) MWI============ =============== ============ ====4089028653 1.8.17.25 89077 ON6508876543 1.8.17.34 87654 OFFRelated Commands
mwi relay
Enables the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to relay message waiting indication (MWI) information to remote Cisco IP phones.
show telephony-service admin
To display the username and password association of the local administrator of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the show telephony-service admin EXEC command.
show telephony-service admin
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following is sample output from the show telephony-service admin command:
Router# show telephony-service admin
admin_username Adminadmin_password wordedit DN through Web: enabled.edit TIME through web: enabled.assign IP Address through Web: disabled.Related Commands
show telephony-service all
To display the detailed configuration of all Cisco IP phones, voice ports, and dial peers of the
Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the show telephony-service all EXEC command.show telephony-service all
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following is sample output from the show telephony-service all command:
Router# show telephony-service allCONFIG======ip source-address 10.0.0.1 port 2000max-ephones 24max-dn 24dialplan-pattern 1 408734....voicemail 11111transfer-pattern 510734....keepalive 30ephone-dn 1number 5001huntstopephone-dn 2number 5002huntstopcall-forward noan 5001 timeout 8ephone-dn 3number 5003huntstopephone 1mac-address 0030.94C3.37CBtype 0button 1:1speed-dial 1 5002speed-dial 2 5003cos 0!ephone 2mac-address 0030.94C3.F96Atype 0button 1:2 2:3 3:4speed-dial 1 5004speed-dial 2 5001cos 0!voice-port 50/0/1station-id number 5001!voice-port 50/0/2station-id number 5002timeout ringing 8!dial-peer voice 20025 potsdestination-pattern 5001huntstopport 50/0/1dial-peer voice 20026 potsdestination-pattern 5002huntstopcall-forward noan 5001port 50/0/2dial-peer voice 20027 potsdestination-pattern 5003huntstopport 50/0/3Table 7 provides an alphabetic listing of the command fields in the sample output.
Related Commands
show telephony-service dial-peer
To display the Cisco IP phone dial peers of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the show telephony-service dial-peer EXEC command.
show telephony-service dial-peer
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The dial peers cannot be edited manually. You can change the dial peers by entering the ephone-dn command.
Examples
The following is sample output from the show telephony-service dial-peer command:
Router# show telephony-service dial-peerdial-peer voice 20025 potsdestination-pattern 5001huntstopport 50/0/1dial-peer voice 20026 potsdestination-pattern 5002huntstopcall-forward noan 5001port 50/0/2dial-peer voice 20027 potsdestination-pattern 5003huntstopport 50/0/3dial-peer voice 20028 potsdestination-pattern 5004huntstopport 50/0/4Table 8 provides an alphabetic listing of the command fields in the sample output.
Related Commands
show telephony-service ephone
To display configuration for the Cisco IP phones, use the show telephony-service ephone EXEC command.
show telephony-service ephone
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following is sample output from the show telephony-service ephone command:
Router# show telephony-service ephoneephone 1mac-address 0030.94C3.37CBtype 0button 1:1speed-dial 1 5002speed-dial 2 5003cos 0!ephone 2mac-address 0030.94C3.F96Atype 0button 1:2 2:3 3:4speed-dial 1 5004speed-dial 2 5001cos 0!Table 9 provides an alphabetic listing of the command fields in the sample output.
Related Commands
show telephony-service ephone-dn
To display the Cisco IP phone destination number output of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the show telephony-service ephone-dn EXEC command.
show telephony-service ephone-dn
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following is sample output from the show telephony-service ephone-dn command:
Router# show telephony-service ephone-dnephone-dn 1number 5001huntstopephone-dn 2number 5002huntstopcall-forward noan 5001 timeout 8ephone-dn 3number 5003huntstopephone-dn 4number 5004huntstopTable 10 provides an alphabetic listing of the command fields in the sample output.
Related Commands
show telephony-service voice-port
To display virtual voice-port configuration of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the show telephony-service voice-port EXEC command.
show telephony-service voice-port
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Displays virtual voice port configuration of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router. Each Cisco IP phone corresponds to a virtual voice port. For example, Cisco IP phone directory number 7 corresponds to virtual voice port 50/0/7. The virtual voice-port provides the telephone line associated with the Cisco IP phone directory number (ephone-dn).
Examples
The following is sample output from the show telephony-service voice-port command:
Router# show telephony-service voice-portvoice-port 50/0/1station-id number 5001!voice-port 50/0/2station-id number 5002timeout ringing 8!voice-port 50/0/3station-id number 5003!voice-port 50/0/4station-id number 5004!Table 11 provides an alphabetic listing of the command fields in the sample output.
Related Commands
speed-dial (ephone)
To set speed-dial buttons on a Cisco IP phone, use the speed-dial command in ephone configuration mode. To disable speed-dial buttons on a Cisco IP phone, use the no form of this command.
speed-dial button-number directory-number
no speed-dial button-number directory-number
Syntax Description
button-number
Speed-dial string tag for the Cisco IP phone speed-dial button number. The button number ranges from 1 to 4.
directory-number
Directory number on a phone.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The speed-dial command sets speed-dial buttons on a Cisco IP phone.

Note
If more speed-dial buttons are defined than are actually supported by the physical phone, then the extra speed-dial configurations are ignored.

Note
Although 20 speed dials can be configured on the Cisco IP phone, ATA phones support only 9 speed-dials with Cisco IOS Telephony Service: *1, *2, *3,*4,*5,*6,*7,*8, and *9.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the speed-dial button 1 for the directory number 5001:
Router(config)# ephone 1Router(config-ephone)# speed-dial 1 5001Related Commands
telephony-service
To enable Cisco IOS Telephony Service and enter telephony-service configuration mode, use the telephony-service command in global configuration mode. To disable Cisco IOS Telephony Service, use the no form of this command.
telephony-service
no telephony-service
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The telephony-service command is the top-level command for all other commands related to Cisco IOS Telephony Service configuration.
Examples
The following example shows how to enter the telephony-service configuration mode:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)#Related Commands
time-format (telephony-service)
To set the time display format on all the Cisco IP phones attached to the router, use the time-format command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable the time display format, use the no form of this command.
time-format {12 | 24}
no time-format {12 | 24}
Syntax Description
Defaults
The default is set to 12 hours.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The time-format command sets the time display format on all the Cisco IP phones attached to the router.
Examples
The following example sets the time format on the Cisco IP phones to the 24-hour setting:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# time-format 24Related Commands
telephony-service
Enables Cisco IOS Telephony Service and enters telephony-service configuration mode.
timeouts interdigit (telephony-service)
To configure the interdigit timeout value for all Cisco IP phones attached to the router, use the timeouts interdigit command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable the interdigit timeout value, use the no form of this command.
timeouts interdigit seconds
no timeouts interdigit seconds
Syntax Description
seconds
Interdigit timeout duration, in seconds, set on the timer for all the Cisco IP phones. Valid entries are from 2 to 120 seconds.
Defaults
The default is 10 seconds.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The timeouts interdigit command specifies the number of seconds the system waits after a caller enters the initial digit or a subsequent digit of the dialed string. The timeouts interdigit timer is activated when the caller enters a digit and is restarted each time the caller enters subsequent digits until the destination address is identified. If the configured timeout value is exceeded before the destination address is identified, a tone sounds and the call is terminated. The default is 10 seconds.
To disable the timeouts interdigit timer, set the seconds value to zero.
Examples
The following example shows the interdigit timeout value set to 5 seconds for all Cisco IP phones:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# timeouts interdigit 5In this example, the 5 seconds refers to the time in seconds after which an incompletely dialed number will timeout. For example, if you dial nine digits (408739898) instead of the required 10 digits (4087398984) you hear a busy tone after 5 "timeout" seconds.Related Commands
time-webedit (telephony-service)
To enable setting time through the web interface, use the time-webedit command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
time-webedit
no time-webedit
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The time-webedit command allows a local administrator of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to change and set time through the graphical user interface (GUI).
Examples
The following example shows how to enable web editing of time:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# time-webeditRelated Commands
dn-webedit
Enables adding of directory numbers through a web interface.
telephony-service
Enables Cisco IOS Telephony Service and enters telephony-service configuration mode.
transfer-pattern (telephony-service)
To allow transfer of telephone calls by Cisco IP phones to other phone numbers, use the transfer-pattern command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable transfer of calls to other numbers, use the no form of this command.
transfer-pattern transfer-pattern
no transfer-pattern
Syntax Description
Defaults
Cisco IP phone to Cisco IP phone transfer only.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The transfer-pattern command allows you to transfer a call to non-IP phone numbers. The call is established between the other calling party and the new recipient. By default, all Cisco IP phone directory numbers are allowed as transfer targets.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the transfer pattern:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# transfer-pattern 52540..A maximum of 32 transfer patterns can be entered. In the previous example, 52540.. (the two decimal points are used here as wild cards) permits transfers to any numbers in the range 525-4000 to 525-4099.Related Commands
translate (ephone-dn)
To select a translation rule to numbers dialed by the Cisco IP phone users, use the translate command in ephone-dn configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
translate {called | calling} translation rule tag
no translate {called | calling} translation rule tag
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone-dn configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The translate command allows you to select a preconfigured number translation rule to modify the number dialed by a specific extension (ephone-dn). The called keyword translates the called number, and the calling keyword translates the calling number.

Note
For the translate command to take effect, appropriate translation rules should be created on the VoIP configuration level.
Translation rules are a powerful general purpose number manipulation mechanism supported by Cisco IOS that can be used to perform operations such as automatically adding telephone area and prefix codes to dialed numbers. The translation rules are applied to the voice ports created by the ephone-dn.
Examples
The following example shows how to set translation rule 20 to the number called by the Cisco IP phone:
Router(config)# translation-rule 20Router(config-translate)# rule 0 1234 2345 abbreviatedRouter(config)# ephone-dn 1Router(config-ephone-dn) translate called 20Related Commands
url (telephony-service)
To provision URLS for the Cisco IP phones connected to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router, use the url command in telephony-service configuration mode. To remove URLs, use the no form of this command.
url {directory | information | messages | services} url
no url {directory | information | messages | services} url
Syntax Description
directory
The directory URL.
information
The information URL
messages
The messages URL.
services
The services URL.
url
An URL string.
Defaults
By default, the router automatically uses the local directory service.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The url command provisions URLS for use by the connected Cisco IP phones. The Cisco IP Phone 7960 and Cisco IP Phone 7940 can support four URLs in association with the four programmable feature keys on the IP phones. The four feature keys are directories, information, messages, and services. (The fifth key—settings—is managed entirely by the phone.) Operation of these services is determined by the Cisco IP phone capabilities and the content of the referenced URL. The purpose of the url command is simply to provision the URLs through the SEPDEFAULT.cnf configuration file supplied by the
Cisco IOS Telephony Service router to the Cisco IP phones during phone registration. You can disable local directory by entering url directories none. You must reset the Cisco IP phones before the url command can take effect.
Note
Provisioning of the directory URL to select an external directory resource disables the Cisco IOS Telephony Service local directory service.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure the url command to provision the information, directories, and services keys:
Router(config) telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service) url information http://1.4.212.4/CCMUser/GetTelecasterHelpText.aspRouter(config-telephony-service) url directories http://1.4.212.11/localdirectoryRouter(config-telephony-service) url services http://1.4.212.4/CCMUser/123456/urltest.htmlThe messages key is configured by the voicemail command. This key acts like a redial key to retrieve messages from a specified telephone number.
Related Commands
telephony-service
Enables Cisco IOS Telephony Service and enters telephony-service configuration mode.
username (ephone)
To assign a phone user a login account username and password to permit user login to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router through a web browser, use the username command in ephone configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
username username password password
no username username password password
Syntax Description
username
The username of the local Cisco IP phone user.
password
Enables password for the Cisco IP phone user.
password
Password string.
Defaults
The default username for the administrator is Admin.
Command Modes
Ephone configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The username command assigns a login account username and password for a phone user and establishes a login account associated with each Cisco IP phone (ephone).
A login account must also be created to allow Telephone Application Programming Interface (TAPI)-aware PC applications to register with the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router and exercise remote control operation of a Cisco IP phone.

Note
This configuration can be completed only by you, the local system administrator of the Cisco IOS Telephony Service router.
This configuration permits the phone user to log in to the Cisco IOS Telephony Service to view and change attributes associated only with the user's IP phone.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the username and password:
Router(config)# ephone 1Router(config-ephone)# username sganesh password 9golfRelated Commands
vm-device-id (ephone)
To define the voice-mail ID string, use the vm-device-id command in ephone configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
vm-device-id id-string
no command id-string
Syntax Description
id-string
Voice-mail device port identification (ID) string. For example, CiscoUM-VI1 for the first port and CiscoUM-VI2 for the second port.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Ephone configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The vm-device-id command defines the voice-mail device ID string. The voice-mail port registers with a device-ID instead of a MAC address. To distinguish among different voice-mail ports, voice-mail device ID is used. The voice-mail device ID is configured to a Cisco IP phone port which maps to a corresponding voice-mail port.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the voice-mail device ID to CiscoUM-V11:
Router(config) ephone 1Router(config-ephone) vm-device ID CiscoUM-VI1Related Commands
voicemail (telephony-service)
Configures the telephone number that is speed-dialed when the message button on a Cisco IP phone is pressed.
vm-integration
To enter voice-mail integration configuration mode and enable voice-mail integration with dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) and analog voice-mail systems, use the vm-integration command in global configuration mode. To disable voice-mail integration, use the no form of this command.
vm-integration
no vm-integration
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The vm-integration command allows you to enter the voice-mail integration configuration mode and allows integration with DTMF and analog voice-mail systems.
Examples
The following example shows how to enter the voice-mail integration configuration mode:
Router(config) vm-integrationRouter(config-vm-integration)Related Commands
voicemail (telephony-service)
To configure the telephone number that is speed-dialed when the message button on a Cisco IP phone is pressed, use the voicemail command in telephony-service configuration mode. To disable the messages button, use the no form of this command.
voicemail phone-number
no voicemail
Syntax Description
Defaults
No phone number is configured and the messages button is ineffective.
Command Modes
Telephony-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The voicemail command configures the telephone number that is speed-dialed when the message button on a Cisco IP phone is pressed. The same telephone number is configured for voice mail for all Cisco IP phones connected to the router.
The default behavior is that no phone number is configured and the messages button is ineffective.
Examples
The following example shows that the phone number 914085551000 is set as the speed-dial number that is dialed to retrieve messages when the messages button is pressed:
Router(config)# telephony-serviceRouter(config-telephony-service)# voicemail 914085551000The number 914085551000 is called when the Cisco IP phone messages button is pressed to retrieve messages.
Related Commands
telephony-service
Enables Cisco IOS Telephony Service and enters telephony-service configuration mode.
vm-device-id (ephone)
Defines the voice-mail ID string.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback