Shaping on Dialer Interfaces
The Shaping on Dialer Interfaces feature provides support for Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) and Point-to-Point Protocol over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (PPPoA) configurations on dialer interfaces. The feature provides support for Modular QoS CLI (MQC)-based queuing and shaping that supports per-customer quality of service (QoS). Parent policies are attached to an Ethernet in the First Mile (EFM) interface, and child policies are attached to individual dialer interfaces. Class of service (CoS) values are set by applying a policy to the dialer interface. The feature also enables the collection of queuing statistics on the dialer interface and the polling of traffic counters for dialer interfaces.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for Shaping on Dialer Interfaces
-
The output queueing policy must have a parent class-default shaper, and any other queueing actions must be configured in a child policy.
Information About Shaping on Dialer Interfaces
QoS on PPP Session on Dialer Interfaces
The Shaping on Dialer Interfaces feature consolidates the output queueing and classification on the egress interface (where all the queueing features are run). The police and set features (such as CoS marking) also work in the output path.
MQC-based QoS queuing and shaping features can be used to attach flat class-default shaped policies to the EFM and attach HQoS parent-shaped policies to the dialer interface.
Policies are applied to the dialer interface using the service-policy command. In addition the related show and debug commands display policy and queueing statistics associated with the dialer target.
QoS Dialer Interface Topology
The following figure shows the supported topology for the Shaping on Dialer Interfaces feature:
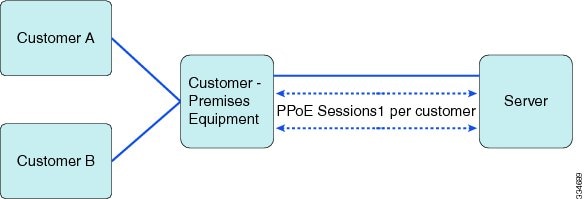
The Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) is shared between several customers. Each customer connects to the CPE through a VLAN on a Gigabit Ethernet port. The CPE connects to the service over a DSL using an EFM interface (this looks like an Ethernet connection but uses DSL) over which all the incoming VLANs will be forwarded. The traffic for each VLAN (customer) is transmitted in a separate PPP session. Each session is set up using a dialer interface.
How to Configure Shaping on Dialer Interfaces
Configuring an Output Queueing Policy for Dialer Interfaces
Before you begin
Because the dialer target is added to the dynamic target API, the output queueing policy must have a parent class-default shaper with any other queueing actions configured in a child policy.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- policy-map policy-map-name
- class class-name
- priority percent percentage
- exit
- class class-name
- bandwidth percent percentage
- exit
- class {class-name | class-default }
- fair-queue
- exit
- exit
- policy-map policy-map-name
- class class-default
- shape average target-bit-rate
- service-policy policy-map-name
- exit
- exit
- interface type number
- service-policy output policy-name
- exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
policy-map policy-map-name Example: |
Specifies the name of the policy map created earlier and enters policy-map configuration mode.
|
| Step 4 |
class class-name Example: |
Specifies the name of the class whose policy you want to create and enters policy-map class configuration mode. This class is associated with the class map created earlier.
|
| Step 5 |
priority percent percentage Example: |
Specifies that the amount of guaranteed bandwidth will be specified by the percent of available bandwidth. |
| Step 6 |
exit Example: |
Returns to policy-map configuration mode. |
| Step 7 |
class class-name Example: |
Specifies the name of the class whose policy you want to create and enters policy-map class configuration mode. This class is associated with the class map created earlier.
|
| Step 8 |
bandwidth percent percentage Example: |
Specifies that the amount of guaranteed bandwidth will be specified by the percent of total bandwidth. |
| Step 9 |
exit Example: |
Returns to policy-map configuration mode. |
| Step 10 |
class {class-name | class-default } Example: |
Specifies the name of the class whose policy you want to create and enters policy-map class configuration mode. This class is associated with the class map created earlier.
|
| Step 11 |
fair-queue Example: |
Enables flow-based fair queueing in this class. |
| Step 12 |
exit Example: |
Returns to policy-map configuration mode. |
| Step 13 |
exit Example: |
Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 14 |
policy-map policy-map-name Example: |
Specifies the name of a policy map and enters policy-map configuration mode.
|
| Step 15 |
class class-default Example: |
Creates the class-default class. |
| Step 16 |
shape average target-bit-rate Example: |
Specifies average rate traffic shaping as bits-per-second on an interface. |
| Step 17 |
service-policy policy-map-name Example: |
Configures a service policy policy map. |
| Step 18 |
exit Example: |
Returns to policy-map configuration mode. |
| Step 19 |
exit Example: |
Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 20 |
interface type number Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 21 |
service-policy output policy-name Example: |
Attaches a policy map to an output interface that will be used as the service policy for the interface. |
| Step 22 |
exit Example: |
Returns to global configuration mode. |
Configuring QoS for PPPoEoA for Dialer Interfaces
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- no ip address
- no atm ilmi-keepalive
- exit
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- pvc vpi/ vci
- vbr-nrt output-pcr output-scr
- pppoe-client dial-pool-number number
- exit
- exit
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- mtu ip-address
- ip address ip-address mask
- encapsulation encapsulation-type
- dialer pool number
- dialer-group number
- service-policy output name
- exit
- dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name permit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 4 |
no ip address Example: |
Disables IP processing on the interface. |
| Step 5 |
no atm ilmi-keepalive Example: |
Disables Interim Local Management Interface (ILMI) keepalives on the interface. |
| Step 6 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 7 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 8 |
pvc vpi/ vci Example: |
Creates an ATM permanent virtual circuit (PVC), and enters ATM virtual circuit configuration mode.
|
| Step 9 |
vbr-nrt output-pcr output-scr Example: |
Configures the variable bit rate-nonreal time (VBR-NRT) quality of service (QoS) and specifies the output peak cell rate (PCR), and output sustainable cell rate (SCR) for an ATM permanent virtual circuit (PVC). |
| Step 10 |
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number Example: |
Configures a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client and specifies the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) functionality. |
| Step 11 |
exit Example: |
Exits ATM virtual circuit configuration mode. |
| Step 12 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 13 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 14 |
mtu ip-address Example: |
Adjusts the maximum packet size or maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. |
| Step 15 |
ip address ip-address mask Example: |
Sets the primary IP address for the interface.
|
| Step 16 |
encapsulation encapsulation-type Example: |
Sets the encapsulation method used by the interface. |
| Step 17 |
dialer pool number Example: |
Specifies the dialing pool that the dialer interface uses to connect to a specific destination subnetwork. |
| Step 18 |
dialer-group number Example: |
Controls access by configuring the interface to belong to a specific dialing group. |
| Step 19 |
service-policy output name Example: |
Attaches a policy map to an output interface that will be used as the service policy for the interface. |
| Step 20 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 21 |
dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name permit Example: |
Defines a dial-on-demand routing (DDR) dialer list for dialing by protocol or by a combination of a protocol and a previously defined access list. |
Configuring QoS for PPPoE for Dialer Interfaces
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- ppp enable group group-name
- pppoe-client dial-pool-number number
- exit
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- mtu ip-address
- ip address ip-address mask
- encapsulation encapsulation-type
- dialer pool number
- dialer-group number
- service-policy output name
- exit
- dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name permit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 4 |
ppp enable group group-name Example: |
Enables PPPoE sessions on an Ethernet interface or subinterface. |
| Step 5 |
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number Example: |
Configures a PPPoE client and to specify the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) functionality. |
| Step 6 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 7 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 8 |
mtu ip-address Example: |
Adjusts the maximum packet size or maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. |
| Step 9 |
ip address ip-address mask Example: |
Sets the primary IP address for the interface.
|
| Step 10 |
encapsulation encapsulation-type Example: |
Sets the encapsulation method used by the interface. |
| Step 11 |
dialer pool number Example: |
Specifies the dialing pool that the dialer interface uses to connect to a specific destination subnetwork. |
| Step 12 |
dialer-group number Example: |
Controls access by configuring the interface to belong to a specific dialing group. |
| Step 13 |
service-policy output name Example: |
Attaches a policy map to an output interface that will be used as the service policy for the interface. |
| Step 14 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 15 |
dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name permit Example: |
Defines a dial-on-demand routing (DDR) dialer list for dialing by protocol or by a combination of a protocol and a previously defined access list. |
Configuring QoS for PPPoA for Dialer Interfaces
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- pvc vpi/ vci
- vbr-nrt output-pcr output-scr output-maxburstsize
- dialer pool-member number
- protocol protocol
- exit
- exit
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- mtu ip-address
- ip address ip-address mask
- encapsulation encapsulation-type
- dialer pool number
- dialer-group number
- service-policy output name
- exit
- dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name permit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 4 |
pvc vpi/ vci Example: |
Creates an ATM permanent virtual circuit (PVC), and enters ATM virtual circuit configuration mode.
|
| Step 5 |
vbr-nrt output-pcr output-scr output-maxburstsize Example: |
Configures the variable bit rate-nonreal time (VBR-NRT) quality of service (QoS) and specifies the output peak cell rate (PCR), output sustainable cell rate (SCR), and output maximum burst cell size for an ATM permanent virtual circuit (PVC). |
| Step 6 |
dialer pool-member number Example: |
Configures a physical interface to be a member of a dialer profiles dialing pool. |
| Step 7 |
protocol protocol Example: |
Configures a static map for an ATM permanent virtual circuit (PVC), switched virtual circuit (SVC), or virtual circuit (VC) class. |
| Step 8 |
exit Example: |
Exits ATM virtual circuit configuration mode. |
| Step 9 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 10 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 11 |
mtu ip-address Example: |
Adjusts the maximum packet size or maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. |
| Step 12 |
ip address ip-address mask Example: |
Sets the primary IP address for the interface.
|
| Step 13 |
encapsulation encapsulation-type Example: |
Sets the encapsulation method used by the interface. |
| Step 14 |
dialer pool number Example: |
Specifies the dialing pool that the dialer interface uses to connect to a specific destination subnetwork. |
| Step 15 |
dialer-group number Example: |
Controls access by configuring the interface to belong to a specific dialing group. |
| Step 16 |
service-policy output name Example: |
Attaches a policy map to an output interface that will be used as the service policy for the interface. |
| Step 17 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 18 |
dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name permit Example: |
Defines a dial-on-demand routing (DDR) dialer list for dialing by protocol or by a combination of a protocol and a previously defined access list, . |
Configuring QoS for Multiple Sessions on Dialer Interfaces
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- ppp enable group group-name
- pppoe-client dial-pool-number number
- pppoe-client dial-pool-number number
- pppoe-client dial-pool-number number
- exit
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- dialer pool number
- service-policy output name
- exit
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- dialer pool number
- service-policy output name
- exit
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- dialer pool number
- service-policy output name
- exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 4 |
ppp enable group group-name Example: |
Enables PPPoE sessions on an Ethernet interface or subinterface. |
| Step 5 |
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number Example: |
Configures a PPPoE client and to specify the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) functionality. |
| Step 6 |
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number Example: |
Configures a PPPoE client and to specify the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) functionality. |
| Step 7 |
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number Example: |
Configures a PPPoE client and to specify the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) functionality. |
| Step 8 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 9 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 10 |
dialer pool number Example: |
Specifies the dialing pool that the dialer interface uses to connect to a specific destination subnetwork. |
| Step 11 |
service-policy output name Example: |
Attaches a policy map to an output interface that will be used as the service policy for the interface. |
| Step 12 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 13 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 14 |
dialer pool number Example: |
Specifies the dialing pool that the dialer interface uses to connect to a specific destination subnetwork. |
| Step 15 |
service-policy output name Example: |
Attaches a policy map to an output interface that will be used as the service policy for the interface. |
| Step 16 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 17 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 18 |
dialer pool number Example: |
Specifies the dialing pool that the dialer interface uses to connect to a specific destination subnetwork. |
| Step 19 |
service-policy output name Example: |
Attaches a policy map to an output interface that will be used as the service policy for the interface. |
| Step 20 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
Applying CoS Values to a Dialer Interface
Class of Service (CoS) values are set by applying a policy to the dialer interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- policy-map policy-map-name
- class class-default
- set cos cos-value
- exit
- exit
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- service-policy output name
- exit
- interface type number [name-tag ]
- encapsulation encapsulation-type
- pppoe-client dial-pool-number number
- exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable Example: |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
policy-map policy-map-name Example: |
Specifies the name of the policy map created earlier and enters policy-map configuration mode.
|
| Step 4 |
class class-default Example: |
Creates the default class for traffic classification and enters policy-map class configuration mode. |
| Step 5 |
set cos cos-value Example: |
Specifies an IEEE 802.1Q CoS value from 0 to 7. |
| Step 6 |
exit Example: |
Returns to policy-map configuration mode. |
| Step 7 |
exit Example: |
Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 8 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 9 |
service-policy output name Example: |
Attaches a policy map to an output interface that will be used as the service policy for the interface. |
| Step 10 |
exit Example: |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
| Step 11 |
interface type number [name-tag ] Example: |
Configures an interface type and enters sub-interface configuration mode.
|
| Step 12 |
encapsulation encapsulation-type Example: |
Sets the encapsulation method used by the interface. |
| Step 13 |
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number Example: |
Configures a PPPoE client and to specify the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) functionality. |
| Step 14 |
exit Example: |
Returns to global configuration mode. |
Configuration Examples for Shaping on Dialer Interfaces
Example: Configuring Output Queuing Policy for a Dialer Interface
The following example shows how to configure parent and child policy maps and how to attach the parent map to the dialer interface:
Device(config)# policy-map childExample
Device(config-pmap)# class voice
Device(config-pmap-c)# priority percent 30
Device(config-pmap-c)# exit
Device(config-pmap)# class video
Device(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 50
Device(config-pmap-c)# exit
Device(config-pmap)# class class-default
Device(config-pmap-c)# fair-queue
Device(config-pmap-c)# exit
Device(config)# policy-map parent
Device(config-pmap)# class class-default
Device(config-pmap-c)# shape average 1000000
Device(config-pmap-c)# service-policy child
Device(config-pmap-c)# exit
Device(config)# interface dialer 0
Device(config-if)# service-policy output parent
Example: Configuring QoS for PPPoEoA for a Dialer Interface
Device(config)# interface ATM 0
Device(config-if)# no ip address
Device(config-if)# no atm ilmi-keepalive
Device(config-if)# exit
Device(config)# interface ATM 0.1 point-to-point
Device(config-if)# ip address 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.224
Device(config-if)# pvc 4/46
Device(config-if-atm-vc)# vbr-nrt 738 738
Device(config-if-atm-vc)# pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1
Device(config-if-atm-vc)# exit
Device(config-if)# exit
Device(config)# interface Dialer 0
Device(config-if)# mtu 1200
Device(config-if)# ip address 172.16.0.0 255.0.0.0
Device(config-if)# encapsulation ppp
Device(config-if)# dialer pool 1
Device(config-if)# dialer-group 1
Device(config-if)# service-policy output dialer-output-sp
!
Device(config)# dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
Example: Configuring QoS for a PPPoE on a Dialer Interface
Device(config)# interface ethernet 0/0
Device(config-if)# pppoe enable group global
Device(config-if)# pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1
Device(config-if)# exit
Device(config)# interface Dialer 0
Device(config-if)# mtu 1200
Device(config-if)# ip address 172.16.0.0 255.0.0.0
Device(config-if)# encapsulation ppp
Device(config-if)# dialer pool 1
Device(config-if)# dialer-group 1
Device(config-if)# service-policy output dialer-output-sp
Device(config-if)# exit
Device(config)# dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
Example: Configuring QoS for PPPoA on a Dialer Interface
Device(config)# interface ATM 0.1 point-to-point
Device(config-if)# ip address 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.224
Device(config-if)# pvc 4/46
Device(config-if-atm-vc)# vbr-nrt 738 738
Device(config-if-atm-vc)# dialer pool-member 1
Device(config-if-atm-vc)# protocol ppp dialer
Device(config-if-atm-vc)# exit
Device(config-if)# exit
Device(config)# interface Dialer 0
Device(config-if)# mtu 1200
Device(config-if)# ip address 172.16.0.0 255.0.0.0
Device(config-if)# encapsulation ppp
Device(config-if)# dialer pool 1
Device(config-if)# dialer-group 1
Device(config-if)# service-policy output dialer-output-sp
Device(config-if)# exit
Device(config)# dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
Example: Configuring QoS for Multiple Sessions on a Dialer Interface
Device(config)# interface ethernet 0/0
Device(config-if)# pppoe enable group global
Device(config-if)# pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1
Device(config-if)# pppoe-client dial-pool-number 2
Device(config-if)# pppoe-client dial-pool-number 3
Device(config-if)# exit
Device(config)# interface Dialer 0
Device(config-if)# dialer pool 1
Device(config-if)# service-policy output dialer-output-sp
Device(config-if)# exit
Device(config)# interface Dialer 1
Device(config-if)# dialer pool 2
Device(config-if)# service-policy output dialer-output-sp
Device(config-if)# exit
Device(config)# interface Dialer 2
Device(config-if)# dialer pool 3
Device(config-if)# service-policy output dialer-output-sp
Device(config-if)# exit
Example: Applying CoS Values to a Dialer Interface
Device> enable
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# policy-map output_cos
Device(config-pmap)# class class-default
Device(config-pmap-c)# set cos 1
Device(config-pmap-c)# exit
Device(config-pmap)# exit
Device(config)# interface Dialer 1
Device(config-if)# service-policy output output-cos
Device(config-if)# exit
Device(config)# interface Ethernet 0.10
Device(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 10
Device(config-subif)# pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1
Device(config-subif)# exit
Additional References for Shaping on Dialer Interfaces
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
QoS commands |
Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Command Reference |
|
MQC |
QoS: Modular QoS: Command-Line Interface Configuration Guide |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Shaping on Dialer Interfaces
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Shaping on Dialer Interfaces |
15.3(1)T Cisco IOS XE Release 3.13S |
The Shaping on Dialer Interfaces feature provides support for PPPoE/A configurations on dialer interfaces. |
 Feedback
Feedback