Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine Release Notes
This document provides an overview of Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine and the known bugs and limitations for this release.
Overview of Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine
Network operators are facing challenges to support the exponential growth of network traffic while addressing the pressure to efficiently run network operations. Providing quick service and network resolutions is vital for the business to remain viable. Network operators need a toolset to help automate bandwidth optimization and efficiently steer traffic with little operator intervention. Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine fulfills this need by providing real-time network optimization capabilities that allow operators to effectively maximize network utility as well as increase service velocity.
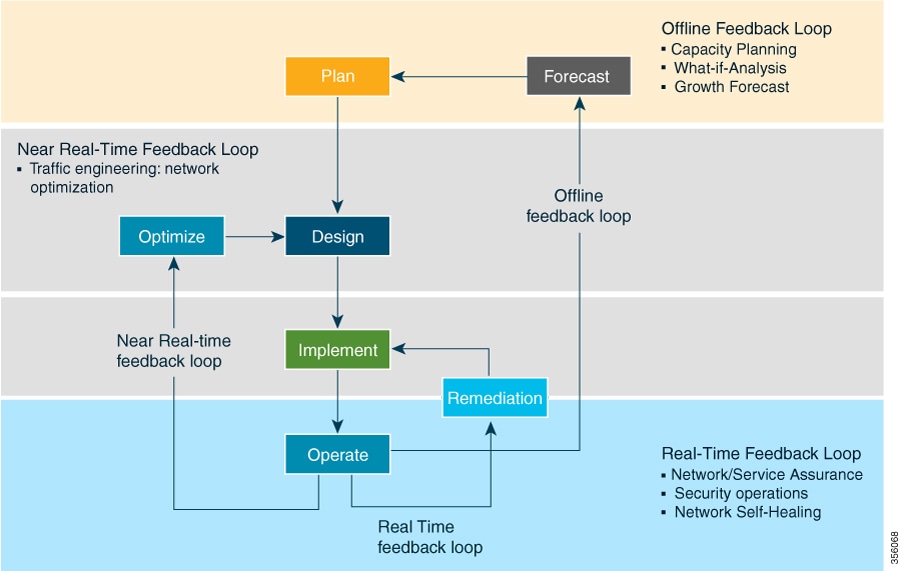
In a typical lifecycle, there is always a feedback loop that traditionally is done manually through human intervention. With network automation, the objective is to automate the feedback loop to enable quicker reaction to network events and faster determination on actions to perform on the network. Looking at the following figure, Crosswork Optimization Engine is built to fulfill the need for a closed-loop optimization loop as described under “Near Real-Time Feedback Loop”. Through Crosswork Optimization Engine, the operator would be able to define the optimization intent, implement the intent, and continuously monitor, track, and react to maintain the original intent.
Real-time Visibility
End-to-end visibility is important to any network operator to run their network effectively. Crosswork Optimization Engine not only provides this visibility, but also the ability to visualize the network across different layers (optical to IP) and the relationship between each layer. Crosswork Optimization Engine leverages IETF-standard BGP-LS protocol to discover IP network automatically, including the following features:
-
Real-time visibility: Provides the network operator with a true representation of the actual topology
-
Hierarchical topology view: Enables operators to define the different levels of granularity in the topology visualization
Simplified SR Policy Lifecycle Management
Crosswork Optimization Engine also provides an easy to use UI to manage the SR policy lifecycle. The UI enables the network operator to perform the following tasks:
-
Create, modify, and remove SR policies using an intuitive workflow
-
Continuously track SR policy dynamic path computations to maintain SLA objectives
-
Preview an SR policy before deploying it to the network
Extensibility through Function Packs
The Crosswork Optimization Engine framework enables function packs that can later be developed in the field to support additional use cases that are not available out of the box. Contact your Cisco service representative to discuss this option. In Crosswork Optimization Engine 1.0, there are two function packs available for purchase: Bandwidth on Demand (BWoD) and Bandwidth Optimization (BWopt). For information on these function packs and instructions on how to use and enable them, see the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine User Guide.
Documentation
Open Bugs
The following are descriptions of the open bugs in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 1.0:
|
Bug ID |
Description |
|---|---|
|
In an unlikely dual SR-PCE setup where all links (except the connection to Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine and sync link) to one of the SR-PCE fails, then topology will not be accurate. . When this happens, fix the connectivity issue, or delete both SR-PCEs from the Provider page and re-add the one that is reachable. |
|
|
In a dual SR-PCE setup, SR policies behave inappropriately (instead of being removed) after the delegated SR-PCE reloads. The workaround is to do the following after an SR-PCE reloads:
|
|
|
In some cases, when an SR policy that was created via the UI is automatically deleted (intentional and expected) from Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, a warning message does not appear. For example, if the source PCC is reloaded, the UI created SR policy disappears and the user is not informed. |
|
|
In a dual SR-PCE setup, when the delegated SR-PCE of an existing SR policy with disjoint group goes down, the following incorrect behavior occurs:
|
|
|
Two nodes incorrectly appear instead of one when the node hostname has a period (.) in its name. For example: A node with the name “calif.router1” will show one node as “calif” and the other node as “calif.router1”. |
|
|
When creating an SR policy that has a path along two devices that have multiple links, the path does not appear in the Preview window before deployment. |
|
|
Device collection stops when the Collection Infra application (cli-robo-collector service) has a Degraded status. The workaround is to navigate to . Click Restart on the Degraded cli-robot-collector service. |
|
|
Color cannot be numerically sorted. This problem is seen when you click on the Color column from the SR Policies window. |
Cisco Bug Search Tool
You can use the Cisco Bug Search Tool to search for a specific bug or to search for all bugs in a release.
-
Go to the Cisco Bug Search Tool.
-
Enter your registered Cisco.com username and password, and click Log In.
The Bug Search page opens.

Note -
Use any of these options to search for bugs, and then press Enter (Return) to initiate the search:
— To search for a specific bug, enter the bug ID in the Search For field.
— To search for bugs based on specific criteria, enter search criteria, such as a problem description, a feature, or a product name, in the Search For field.
— To search for bugs based on products, enter or choose the product from the Product list. For example, enter Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine.
— To search for bugs based on releases, in the Releases list choose whether to search for bugs affecting a specific release, bugs that were fixed in a specific release, or both. Then enter one or more release numbers in the Releases field.
-
When the search results are displayed, use the filter tools to narrow the results. You can filter the bugs by status, severity, and so on.
 Tip |
To export the results to a spreadsheet, click Export Results to Excel. |
Accessibility Features
For a list of accessibility features in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, visit https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/accessibility/voluntary-product-accessibility-templates.html (VPAT) website, or contact accessibility@cisco.com.
All product documents except for some images, graphics, and charts are accessible. If you would like to receive the product documentation in audio format, braille, or large print, contact accessibility@cisco.com.
 Feedback
Feedback