-
- Downstream Interface Configuration
- Upstream Interface Configuration
- DOCSIS Interface and Fiber Node Configuration
- DOCSIS Load Balancing Groups
- DOCSIS Load Balancing Movements
- DOCSIS 3.0 Downstream Bonding
- DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA Modulation Profiles
- Downstream Resiliency Bonding Group
- Downstream Channel ID Assignment
- Upstream Channel Bonding
- Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management
- Upstream Scheduler Mode
- Generic Routing Encapsulation
- Transparent LAN Service over Cable
- Downgrading Channel Bonding in Battery Backup Mode
- Energy Management Mode
-
- IP Access Control Lists
- Creating an IP Access List and Applying It to an Interface
- Creating an IP Access List to Filter IP Options, TCP Flags, Noncontiguous Ports
- Refining an IP Access List
- IP Named Access Control Lists
- IPv4 ACL Chaining Support
- IPv6 ACL Chaining with a Common ACL
- Commented IP Access List Entries
- Standard IP Access List Logging
- IP Access List Entry Sequence Numbering
- ACL IP Options Selective Drop
- ACL Syslog Correlation
- IPv6 Access Control Lists
- IPv6 Template ACL
- IPv6 ACL Extensions for Hop by Hop Filtering
-
- Call Home
- SNMP Support over VPNs—Context-Based Access Control
- SNMP Cache Engine Enhancement
- Onboard Failure Logging
- Control Point Discovery
- IPDR Streaming Protocol
- Usage-Based Billing (SAMIS)
- Frequency Allocation Information for the Cisco CMTS Routers
- Flap List Troubleshooting
- Maximum CPE and Host Parameters
- SNMP Background Synchronization
- Online Offline Diagnostics
- Index
Cisco Converged Broadband Routers Software Configuration Guide for DOCSIS 3.0
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- April 12, 2015
Chapter: Energy Management Mode
- Information About Energy Management Mode
- Prerequisites for Energy Management Mode
- Restrictions for the Energy Management Mode
- How to Configure the Energy Management Mode
- Verifying the Energy Management Mode
- Feature Information for Energy Management Mode
Energy Management Mode
Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) cable modems (CM) and CMTS support a low power energy mode referred to as the Energy Management 1x1 (EM) mode. During idle times, when the data rate demand of a user is met by the available capacity on a single upstream and downstream channel pair to which it is assigned, the CM switches to the Energy Management 1x1 mode. When the CM requires a higher data rate than that can be reliably provided on the single channel pair, the CMTS instructs the CM to return to the larger transmit and receive channel set.
Contents
- Information About Energy Management Mode
- Prerequisites for Energy Management Mode
- Restrictions for the Energy Management Mode
- How to Configure the Energy Management Mode
- Verifying the Energy Management Mode
- Feature Information for Energy Management Mode
Information About Energy Management Mode
The following sections provide more information about the Energy Management mode.
- Dynamic Downstream Bonding Group
- Flow Chart of the CM Power State
- Interaction with the Battery Mode
- Handling Energy Management Request Load
- Supervisor High Availability and Line Card Switchover
Dynamic Downstream Bonding Group
To support the Energy Management 1x1 (EM) mode feature, CMTS selects an upstream and a downstream channel pair for CM. The downstream and upstream channel assigned to the CMs should be available. If CMTS selects a channel that is not available, the downstream bonding channel might fail.
-
For upstream, it chooses the highest actual amiable bandwidth channel from the upstream channels currently used by the CM.
-
For downstream, CMTS chooses the current primary downstream channel used by the CM.
-
If the CM is online with channel bonding 1xN or Nx1, and requests to enter into the EM mode, CMTS does not change the upstream and the downstream channel if the original channel bonding is 1 and the Quality of Service (QoS) parameter is not updated.
-
CMTS checks the existing dynamic bonding groups (DBG), for an exact match in the target channel. -
If found, CMTS uses this bonding group to instruct the CM to enter into EM mode.
-
If there is no available DBG and there is an unused DBG, CMTS adds the primary channel into the unused DBG and instructs the CM to enter the EM mode.
-
If there is no available DBG and no unused DBG, CMTS logs a warning to notify you that a new DGB should be configured.
-
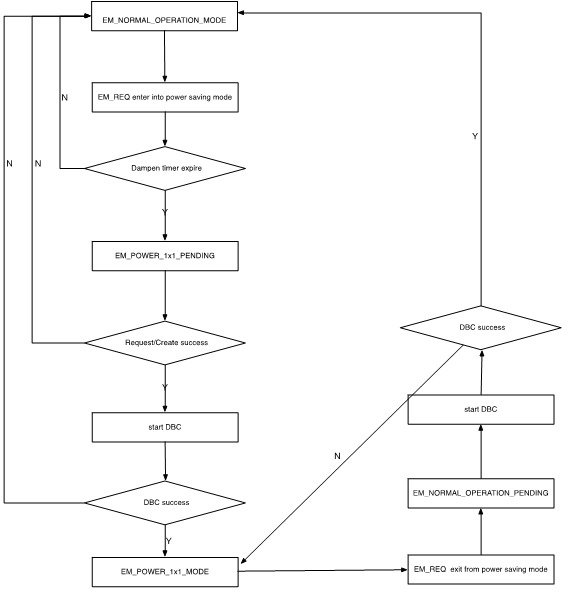
Flow Chart of the CM Power State
The following figure shows the flow chart of the CM power state:
Interaction with the Battery Mode
Energy management mode is similar to battery mode as they both enter the 1x1 mode to save power. But, both have a different purpose to enter the 1x1 mode, so there are some differences in their behavior. The purpose of EM mode is to save power when the traffic is low, and it has minimum impact on the normal service. The purpose of the battery mode is try to guarantee the voice service, especially the 911 call service, for which it may drop other services, if necessary.
The table below describes the behavior difference between energy management mode and battery mode.
|
|
Energy Management (EM) Mode |
Battery Mode (BM) |
|---|---|---|
|
QoS |
Minimum reserved rate service up to 200k. |
No minimum reserved rate. |
|
Multicast |
|
|
BM has higher priority than the EM mode. If a CM is already in EM mode and a power off occurs, CM enters into the BM. After the power is restored, the CM returns to the normal mode, and if the traffic is lower than the threshold, it re-enters the EM mode. The CM does not directly transfer from the BM to the EM mode.
The interaction between the battery mode and the energy management mode is illustrated in the figure below:
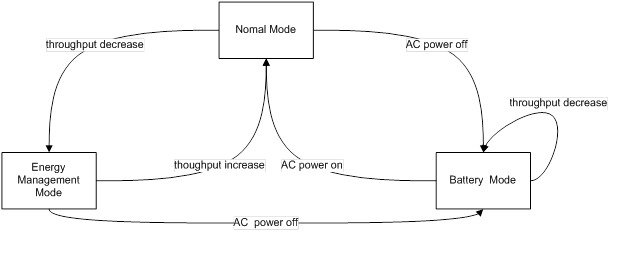
- When the CM is in normal mode and CMTS receives a request to enter the EM mode, CMTS instructs the CM to enter the EM mode with downstream bonding channel (DBC).
- When the CM is in EM mode and CMTS receives a request to leave the EM mode, CMTS instructs the CM to leave the EM mode to normal mode with DBC.
- When the CM is in normal mode and CMTS receives a message: CM operating on battery backup, CMTS instructs the CM to enter the BM mode with DBC.
- When the CM is in BM mode and CMTS receives a message: CM operating on AC power, CMTS instructs the CM to leave the BM mode to normal mode with DBC.
- When the CM is in EM mode and CMTS receives a message: CM operating on battery backup, CMTS instructs the CM to enter the BM mode with service flow re-admin.
- When the CM is in BM mode and CMTS receives a request to enter EM mode, CMTS waits until it receives the message: CM operating on AC power. It then instructs the CM to return to normal mode.
Handling Energy Management Request Load
When many CMs send EM requests at the same time, such as at the beginning or end of work hours, the traffic soars or slumps in a very short period and causes heavy load for CMTS. A throttle mechanism is adopted to avoid such load surge for CMTS.
The line card EM process defines a variable that indicates the current transactions handled by the process. When an energy management request is received and the maximum number of transactions is not met, CMTS handles this request and updates the counter of current transactions. When the maximum number of transactions is met, CMTS sends a temporary reject response. After a transaction is over or a CM goes offline, the counter of current transactions is updated.
Supervisor High Availability and Line Card Switchover
Energy Management feature supports supervisor high availability and line card switchover with limitations.
The active supervisor or line card syncs the EM mode data of a CM to the standby SUP or protected line card when the CM enters a stable EM status. When a CM enters or leaves the EM mode with an ongoing DBC process, the supervisor high availability or line card switchover causes the CM to enter into an offline or online status.
Prerequisites for Energy Management Mode
To enable the energy management mode, you must configure resiliency bonding group (RBG) and dynamic bonding group.
Restrictions for the Energy Management Mode
- Restrictions for CMTS High Availability
- Restrictions for Dynamic Bonding Group
- Restrictions for Interaction of CMTS with Other Features
- Restrictions for Configuration Change and Interface Shutdown
- Restrictions for In Service Software Upgrade
Restrictions for CMTS High Availability
-
If there is no DBG available, CMTS cannot create a new DBG on the protected line card and CMs cannot enter the EM mode.
-
Line card switchover is not supported when the CM enters the EM mode from the normal mode or exits the EM mode to the normal mode.
-
To reduce the operation of the EM mode, the information about the EM status is not synced with the protected line card. Hence, the EM status is cleared after the line card high availability.
Restrictions for Dynamic Bonding Group
To support the EM feature, CMTS configures separate DBG for each primary channel in each MAC domain. For example, if a MAC domain has eight primary channels, it will create eight DBGs for the MAC domain. This ensures that the EM does not fail due to lack of DBGs.
Restrictions for Interaction of CMTS with Other Features
- Voice
- Dynamic Bonding Change and Dynamic Channel Change and Related Applications
- Multicast
- Committed Information Rate
- Admission Control
- Battery Mode
- Attribute Mask
- Dynamic Service Addition
Voice
If a voice call is in progress, CMTS does not instruct the CM to enter into the EM mode.
When the CM is in the EM mode, and it receives a voice call, it adds a dynamic Unsolicited Grant Service (UGS) or Unsolicited Grant Service with activity detection (UGS-AD) service flow. During the voice call, the CM does not exit from the EM mode irrespective of the flow of traffic. Voice service is given the highest priority
Dynamic Bonding Change and Dynamic Channel Change and Related Applications
In D2.0 and D3.0 load-balance (static and dynamic), CM is not moved by load-balance when it is in EM mode.
For RF-adapt, CM is not relocated to an alternate logical channel by the RF-adapt when it is in EM mode.
Multicast
-
When the CM is in a multicast group, CMTS would reject the EM request for both bonded and non bonded multicast cases.
-
When the CM is in EM state and a multicast join request is received, CMTS discards this join request and forces the CM to exit the EM mode.
-
When the CM is in EM state and a voice call is in progress, and a new multicast join request is received, CMTS discards this join request and does not force the CM to exit the EM mode since the voice call is in progress.
-
There is a threshold for currently handled transactions. When there is multicast join request and the maximum transaction threshold has been reached, CMTS cannot instruct the CM to exit the EM mode. The multicast join is also be denied until the CM can exit the EM mode.
-
When the CM is in EM mode and needs to join PacketCable Multimedia (PCMM) multicast, you should send a GateSet request twice, so that the gate can be setup successfully. The first GateSet request only forces the modem to exit the EM mode, but does not set up the gate
Committed Information Rate
If the QoS is defined by the Minimum Reserved Rate service flow QoS parameter in excess of 200 kbps, when the CM enters into the EM mode, CMTS only provides 200 kbps as the minimum reserved rate. If the minimum reserved rates is less than 200 kbps, CMTS schedules the minimum reserved rate according to the service flow configuration when the CM enters into the EM mode.
CMTS records the Minimum Reserved Rate service flow QoS parameter when the CM enters into the EM mode. When the CM exits the EM mode, CMTS uses the original parameter.
When the CM enters the EM mode, it selects one of the CM upstream channels. If the service flow is completely on that upstream channel, the service flow parameter is not changed. This behavior is because the service flow is not moved into the DBC operation, and the change of the service flow parameter has no benefit
Admission Control
When a request is received to exit the EM mode and recovery to the original wideband interface is restricted due to an admission control failure, CMTS forces the CM to go offline and re-register to prevent it from getting stuck in the EM mode. In such a case, CMTS logs a warning message.
Battery Mode
When CMTS receives the status of the CM as operating on battery power, CMTS instructs the CM to enter into the BM. If the CM rejects the instruction received, CMTS keeps the modem in normal status.
When the CM is in BM and CMTS receives the status of the CM as operating on A/C power, CMTS instructs the CM to exit the BM. If the CM rejects the instruction received, CMTS forces the CM to go offline to prevent it from getting stuck in the battery mode. In such a case, CMTS logs a warning message.
Attribute Mask
When selecting an upstream or a downstream channel pair for energy management mode, CMTS selects channels that meet the requirements of the attribute masks for the existing service flows for the corresponding CM.
-
CMTS may require strict adherence to the required and forbidden attribute masks and thus deny entry into the EM mode if these masks cannot be met by the available individual channels in the MD-CM-SG.
-
CMTS may allow the CM to enter the EM mode while not meeting all the criteria for the attribute masks. In this case, CMTS logs a warning event notifying that the attribute masks are not maintained.
For the following case, CMTS supports approach two:
When the CM is instructed to enter into the EM mode and the selected target upstream and downstream channels do not adhere to the service flow attribute mask. For this conflict CMTS instructs the modem to enter into the EM mode. CMTS also logs a warning message to notify this conflict.
Dynamic Service Addition
When the CM is in EM mode, DSA request can still be set up even if the requested attributes can not be met with a single channel. In order to not effect voice services, the CM is not forced to exit the EM mode.
Restrictions for Configuration Change and Interface Shutdown
-
Shutdown of the upstream channel—Shutdown of the upstream channel recalculates the MD-US-SG-ID and assigns a new MD-US-SG-ID. In this case, the CM is not offline and internal data structure of the CM instance is not updated. DBC operation checks the MD-US-SG-ID, so when the CM enters into the EM mode there is a mismatch between the MD-US-SD-ID on the CM and the new MD-US-SG-ID. Hence, DBC fails and the CM cannot get into the EM mode.
-
Change in Upstream Service Group makes the CM in EM mode go offline—The US-SG configuration change blocks the DBC behavior and the CM gets stuck in the EM mode. To avoid this scenario, when there is a change in the Upstream Service Group (US-SG), such as shutdown or no shutdown of the upstream channels, CMTS makes the CM go offline. The CM should re-register as a normal CM with the wideband channel bonding including multiple channels.
-
Modify the original wideband interface—When the CM is in EM mode, change in the original wideband interface channels on the CM makes the CM go offline and re-register as a normal CM.
-
Disable or enable feature— When you disable this feature, CMTS does not force CMs to exit from the EM mode unless CMs sends a request. CMTS does not accept EM requests after the EM feature is disabled from the CLI.
Restrictions for In Service Software Upgrade
Currently, CMTS only supports In Service Software Upgrade (ISSU) between Cisco IOS-XE 3.18. ISSU between Cisco IOS-XE 3.17 and Cisco IOS-XE 3.18 is not supported. Hence, there is no limitation for ISSU upgrade and downgrade.
How to Configure the Energy Management Mode
This section describes how to configure the energy management feature on the Cisco cBR-8.
Contents
- Enabling Energy Management Mode
- Enabling Energy Management Mode per MAC Domain
- Configuring Initialization Ranging Technique in Dynamic Bonding Channel
- Configuring the Percentage for the Dynamic Channel Bandwidth
- Configuring the Queue Size for Energy Management
Enabling Energy Management Mode
To enable the energy management mode, complete the following procedure:
configure terminal cable reduction-mode energy-management enable
Verifying the Energy Management Mode
-
To verify if the CM is in EM mode, use the show cable modem command. If the cable modem is working in energy management mode, the MAC state is displayed with an "em" flag.
show cable modem D MAC Address IP Address I/F MAC Prim RxPwr Timing Num I State Sid (dBmv) Offset CPE P 7cb2.1b0f.ea72 40.4.58.4 C7/0/0/UB w-online(em) 2 0.00 1231 1 Y 54d4.6ffb.2f6b 40.4.58.24 C7/0/0/UB w-online 3 -0.50 1241 0 Y 0025.2ed9.9a22 40.4.58.3 C7/0/0/UB w-online 4 0.50 1240 0 Y -
To verify which CM is in EM mode and to get the original wideband and upstream channel information, use the show cable modem reduction-mode energy-management-mode command.
show cable modem reduction-mode energy-management-mode Orig BG Orig US Curr BG I/F MAC Address ID I/F bitmap RFs ID I/F Upstream ------- -------------- ---------------- -------- ----------------------------------------- C7/0/0 0025.2eaf.843e 897 Wi7/0/0:0 0x3B 4 252 Wi7/0/0:1 US0 C7/0/0 0025.2eaf.8356 897 Wi7/0/0:0 0x3B 4 252 Wi7/0/0:1 US0 C7/0/0 0015.d176.5199 897 Wi7/0/0:0 0x3B 4 252 Wi7/0/0:1 US0
Enabling Energy Management Mode per MAC Domain
CMTS supports the EM feature when enabled both globally and per MAC domain. Use the following procedure to enable energy management feature per MAC domain.
To enable the EM mode per MAC domain, complete the following procedure:
configure terminal interface cable slot/subslot/cable-interface-index cable reduction-mode energy-management enable
Configuring Initialization Ranging Technique in Dynamic Bonding Channel
The default value for the technique in init-ranging is set to 1 and the valid range is 1-4.
To configure the technique in init-ranging, complete the following procedure:
configure terminal cable reduction-mode energy-management ranging-init-techniquevalue
Configuring the Percentage for the Dynamic Channel Bandwidth
Make sure that you leave enough bandwith for the primary channel so that it can allocate dynamic channel bandwidth when it joins to a newly created DBG. The default percentage value is set to 5 and the valid range is 1-96.
To configure the percentage of dynamic channel bandwidth, complete the following procedure:
configure terminal cable reduction-mode energy-management dynamic-channel-percent value
Configuring the Queue Size for Energy Management
The default value for the queue size is set to 150 and the valid range is 50-10000.
To set the queue size of the energy management requests, complete the following procedure:
configure terminal cable reduction-mode energy-management process-queue-size value
-
Verifying the Energy Management Mode
This section describes how to verify the EM mode.
Contents
- Viewing the Basic Statistics for Energy Management Receive Request
- Verifying the Configuration Parameters
- Viewing Information Regarding a Cable Modem
Viewing the Basic Statistics for Energy Management Receive Request
To view the basic statistics for all energy management receive request events for a specific CM, use the show cable modem <cable if | mac_addr | ip_addr> reduction-mode energy-management-status command.
show cable modem c8/0/0 reduction-mode energy-management-status
I/F MAC Address Event TID Count Error Dups Time
C8/0/0 54d4.6ffb.2e21 Enter EM mode 1 1 0 1 Jul 16 21:38:18
Exit EM mode 1 1 0 0 Jul 16 21:38:39
C8/0/0 602a.d07c.4ec6 Enter EM mode 1 1 0 0 Jul 16 21:40:57
Exit EM mode 1 1 0 0 Jul 16 21:41:17
To clear the basic receive statistics for all EM_REQ events for a specified CM, use the clear cable modem <cable if | mac_addr | ip_addr> em-status command.
Verifying the Configuration Parameters
To verify the configuration parameters used in the CM configuration file, use the show cable modem <mac address> reduction-mode energy-management-param command.
show cable modem 54d4.6ffb.2e21 reduction-mode energy-management-param
Energy Management feature enable : Y
DS entry bitrate threshold(bps) : 100000
DS entry time threshold(s) : 120
DS exit bitrate threshold(bps) : 200000
DS exit time threshold(s) : 2
US entry bitrate threshold(bps) : 100000
US entry time threshold(s) : 120
US exit bitrate threshold(bps) : 200000
US exit time threshold(s) : 2
cycle period(s) : 300
Viewing Information Regarding a Cable Modem
To view all the information regarding a CM, use the show cable modem mac address verbose command.
show cable modem 54d4.6ffb.30fd verbose
MAC Address : 54d4.6ffb.30fd
IP Address : 40.4.58.14
IPv6 Address : 2001:40:4:58:741A:408D:7E4B:D7C8
Dual IP : Y
Prim Sid : 9
Host Interface : C7/0/0/UB
MD-DS-SG / MD-US-SG : 1 / 1
MD-CM-SG : 0x3C0101
Primary Wideband Channel ID : 897 (Wi7/0/0:0)
Primary Downstream : In7/0/0:2 (RfId : 722)
Wideband Capable : Y
RCP Index : 3
RCP ID : 00 10 00 00 08
Downstream Channel DCID RF Channel : 99 7/0/0:2
Downstream Channel DCID RF Channel : 97 7/0/0:0
Downstream Channel DCID RF Channel : 98 7/0/0:1
Downstream Channel DCID RF Channel : 100 7/0/0:3
Multi-Transmit Channel Mode : Y
Extended Upstream Transmit Power : 0dB
Upstream Channel : US0 US1
Ranging Status : sta sta
Upstream SNR (dB) : 36.12 32.55
Upstream Data SNR (dB) : -- --
Received Power (dBmV) : 0.00 0.00
Reported Transmit Power (dBmV) : 25.25 26.00
Peak Transmit Power (dBmV) : 54.00 54.00
Phy Max Power (dBmV) : 54.00 54.00
Minimum Transmit Power (dBmV) : 24.00 24.00
Timing Offset (97.6 ns): 1226 1226
Initial Timing Offset : 1229 973
Rng Timing Adj Moving Avg(0.381 ns): -1 0
Rng Timing Adj Lt Moving Avg : -7 0
Rng Timing Adj Minimum : -768 0
Rng Timing Adj Maximum : 0 64768
Pre-EQ Good : 0 0
Pre-EQ Scaled : 0 0
Pre-EQ Impulse : 0 0
Pre-EQ Direct Loads : 0 0
Good Codewords rx : 515 472
Corrected Codewords rx : 0 0
Uncorrectable Codewords rx : 0 0
Phy Operating Mode : atdma* atdma*
sysDescr :
Downstream Power : 0.00 dBmV (SNR = ----- dB)
MAC Version : DOC3.0
QoS Provisioned Mode : DOC1.1
Enable DOCSIS2.0 Mode : Y
Modem Status : {Modem= w-online(em), Security=disabled}
Capabilities : {Frag=N, Concat=N, PHS=Y}
Security Capabilities : {Priv=, EAE=Y, Key_len=}
L2VPN Capabilities : {L2VPN=N, eSAFE=N}
Sid/Said Limit : {Max US Sids=16, Max DS Saids=15}
Optional Filtering Support : {802.1P=N, 802.1Q=N, DUT=N}
Transmit Equalizer Support : {Taps/Symbol= 1, Num of Taps= 24}
Number of CPE IPs : 0(Max CPE IPs = 16)
CFG Max-CPE : 200
Flaps : 0()
Errors : 0 CRCs, 0 HCSes
Stn Mtn Failures : 0 aborts, 0 exhausted
Total US Flows : 1(1 active)
Total DS Flows : 1(1 active)
Total US Data : 7 packets, 2006 bytes
Total US Throughput : 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Total DS Data : 5 packets, 1202 bytes
Total DS Throughput : 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
LB group ID assigned (index) : 2151416065 (48131)
LB group ID in config file (index) : N/A (N/A)
LB policy ID : 0
LB policy ID in config file : 0
LB priority : 0
Tag :
Required DS Attribute Mask : 0x0
Forbidden DS Attribute Mask : 0x0
Required US Attribute Mask : 0x0
Forbidden US Attribute Mask : 0x0
Service Type ID :
Service Type ID in config file :
Active Classifiers : 2 (Max = NO LIMIT)
CM Upstream Filter Group : 0
CM Downstream Filter Group : 0
CPE Upstream Filter Group : 0
CPE Downstream Filter Group : 0
DSA/DSX messages : permit all
Voice Enabled : NO
DS Change Times : 0
Boolean Services : 2
CM Energy Management Capable : Y
CM Enable Energy Management : Y
CM Enter Energy Management : YES
Number of Multicast DSIDs Support : 16
MDF Capability Mode : 2
IGMP/MLD Version : MLDv2
FCType10 Forwarding Support : Y
Features Bitmask : 0x0
Total Time Online : 2h12m (2h12m since last counter reset)
CM Initialization Reason : NO_PRIM_SF_USCHAN
CFG Max IPv6 CPE Prefix : 16 (-1 used)
Feature Information for Energy Management Mode
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Energy Management Mode |
Cisco IOS-XE Release 3.18.0S |
This feature was introduced on Cisco cBR Series Converged Broadband Routers. |
 Feedback
Feedback