Managing Tagged and Untagged VLAN IDs on the WAP371
Available Languages
Objective
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a group of end stations that are logically segmented by function, area, or application, without regard to the physical locations of the users. VLANs have the same attributes as physical LANs, but you can group end stations even if they are not physically located on the same LAN segment.
The management VLAN communicates with the main switch interface and has a default VLAN ID of 1. Additional VLANs can be created and configured on your network to separate traffic as desired. Each port on a device can be configured either as a trunk port or an access port.
A trunk port is capable of handling multiple VLANs, while the access port is capable of handling only one. The trunk port uses a tagging method in the form of a header to properly deliver the correct data to the appropriate VLAN. In comparison, an access port will handle all traffic as untagged information.
An attack on the management VLAN can compromise network security, so changing the management VLAN to a VLAN ID other than the default is recommended. Both the management and untagged VLAN IDs on the WAP371 access point are configured to VLAN 1 by default.
The objective of this article is to configure the management, tagged and untagged VLAN IDs on the WAP371 access point.
Applicable Devices
• WAP371
Software Version
• 1.1.2.3
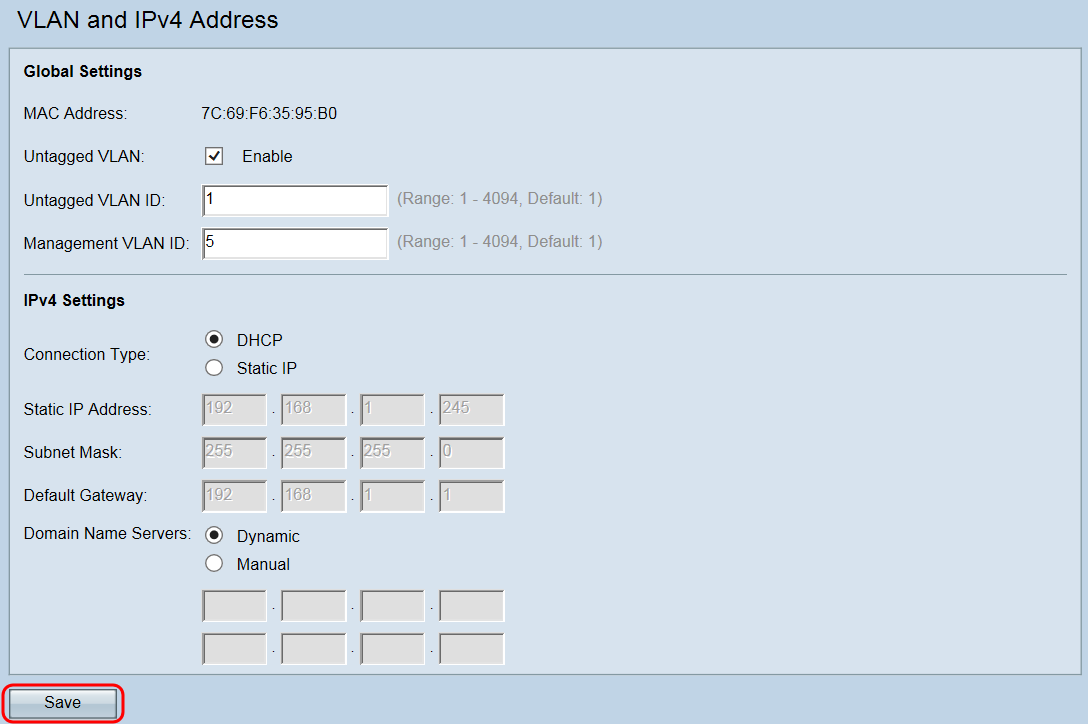
Global Settings
Step 1. Log in to the Access Point Configuration Utility and choose LAN > VLAN and IPv4 Address. The VLAN and IPv4 Address page opens:
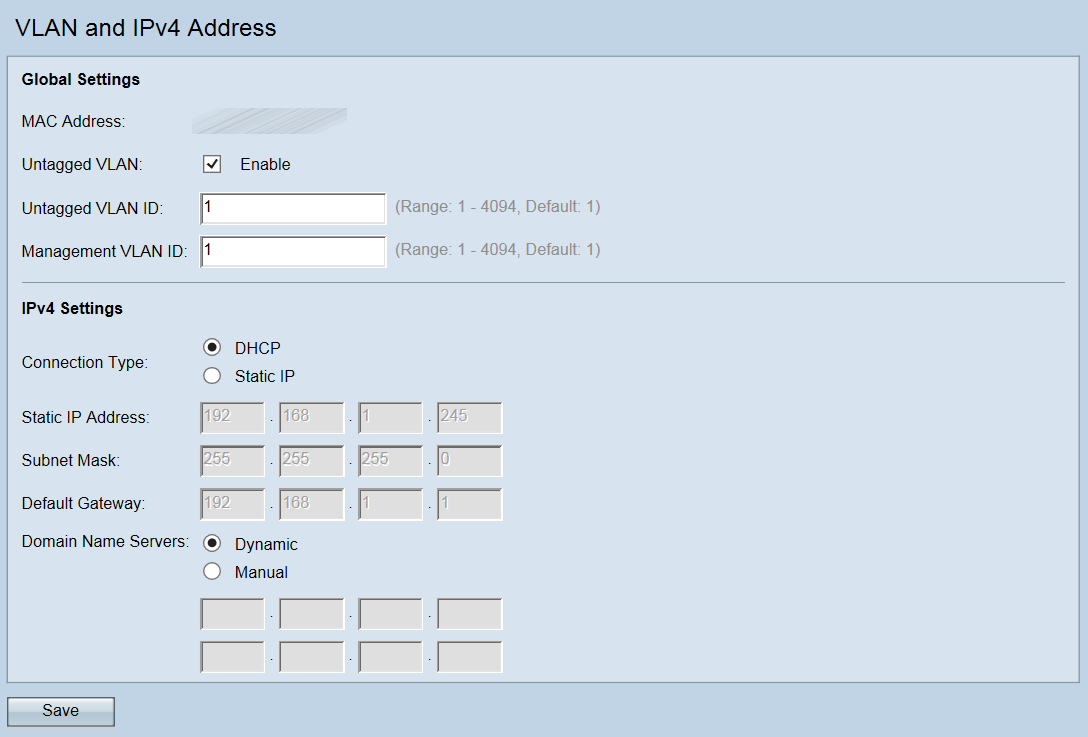
Note: The MAC Address field displays the MAC address of the Ethernet port on the WAP371. The WAP371 has only one Ethernet port.
Step 2. (Optional) To allow the device to receive traffic that is not tagged for a VLAN, check the Enable check box in the Untagged VLAN field. This function is used when the WAP’s LAN port is connected to an access port on another device that has a VLAN marked as untagged.
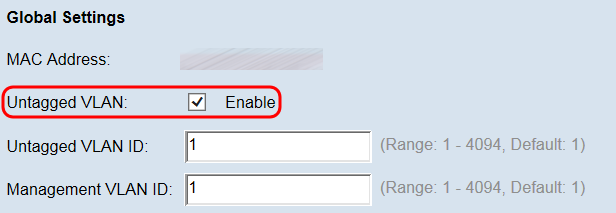
Note: If you did not enable an untagged VLAN, skip to Step 4.
Step 3. Enter the VLAN ID (between 1 and 4094) for the untagged VLAN in the Untagged VLAN ID field. The default ID is 1. Traffic that goes through this VLAN will not be tagged with a VLAN ID. This should be the same VLAN that is marked as untagged on the access port.
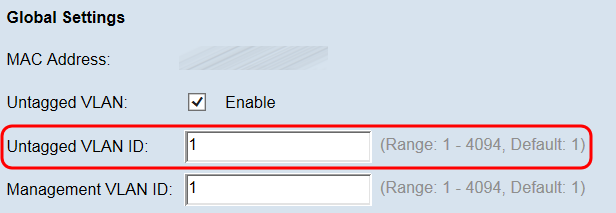
Note: VLAN 1 is the both default untagged VLAN and the default management VLAN. If you want to segregate management traffic from the untagged VLAN traffic, configure the new VLAN ID on your router, and then use this new VLAN ID on your WAP device.
Step 4. Enter the VLAN ID (between 1 and 4094) for the management VLAN in the Management VLAN ID field. The Management VLAN needs to be the same as the one on the switch or router to which the WAP is connected. For security purposes, the management VLAN ID should be changed from the default of 1.
Note: For the purpose of this tutorial we used a preconfigured router with VLAN ID 5 as the management VLAN, though any VLAN ID may be chosen. The router is connected to the WAP via Ethernet and has Inter-VLAN Routing enabled.
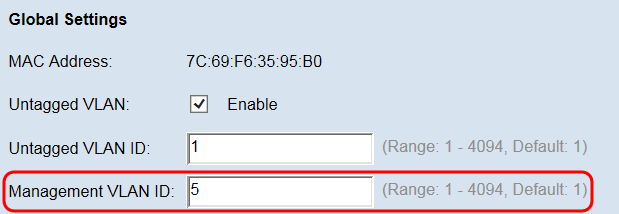
Step 5. Click Save to save the settings.
Note: After new settings are saved, the corresponding processes may be stopped and restarted. When this happens, the WAP device may lose connectivity. We recommend that you change WAP device settings when a loss of connectivity will least affect your wireless clients.
Note: To learn more about configuring IPv4 Settings, refer to the article Configure IPv4 and IPv6 Settings on the WAP371.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
11-Dec-2018
|
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback