Introduction
This document describes common issues with URL filtering. The URL filtering feature on FireSIGHT Management Center categorizes traffic of monitored hosts and allows you to write a condition in an access control rule based on reputation.
URL Filtering Lookup Process
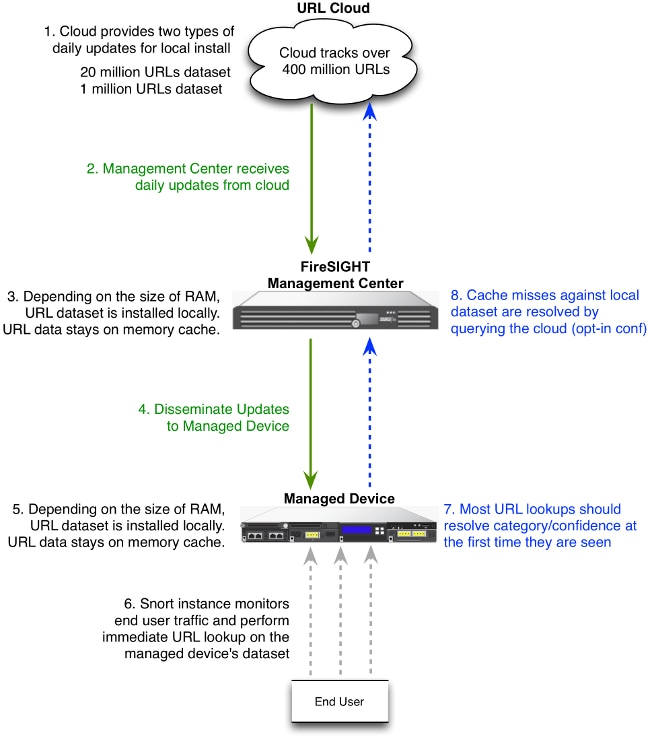
In order to accelerate the URL lookup process, the URL filtering provides a dataset that is installed on a Firepower System locally. Dependent upon the amount of memory (RAM) available on an appliance, there are two types of datasets:
| Type of Dataset |
Memory Requirement |
| On Version 5.3 |
On Version 5.4 or higher |
| 20 Million URL Dataset |
> 2GB |
> 3.4 GB |
| 1 Million URL Dataset |
<= 2GB |
<= 3.4 GB |
Cloud Connectivity Issues
Step 1: Check the Licenses
Is the License Installed?
You can add category and reputation-based URL conditions to access control rules without a URL Filtering license, however you cannot apply the access control policy until you first add a URL Filtering license to the FireSIGHT Management Center, then enable it on the devices targeted by the policy.
Is the License Expired?
If a URL Filtering license expires, access control rules with category and reputation-based URL conditions stop filtering URLs, and the FireSIGHT Management Center no longer contacts the cloud service.
Tip: Read URL Filtering on a FireSIGHT System Configuration Example in order to learn how to enable URL Filtering feature on a FireSIGHT System and apply URL Filtering license on a managed device.
Step 2: Check Health Alerts
The URL Filtering Monitor module tracks communications between the FireSIGHT Management Center and the Cisco cloud, where the system obtains its URL filtering (category and reputation) data for commonly visited URLs. The URL Filtering Monitor module also tracks communications between a FireSIGHT Management Center and any managed devices where you have enabled URL filtering.
In order to enable the URL Filtering Monitor module, go to the Health Policy Configuration page, choose URL Filtering Monitor. Click the On radio button for the Enabled option in order to enable use of the module for health status testing. You must apply the health policy to the FireSIGHT Management Center if you want your settings to take effect.
- Critical Alert: If the FireSIGHT Management Center fails to successfully communicate with or retrieve an update from the cloud, the status classification for that module changes to Critical.
- Warning Alert: If the FireSIGHT Management Center successfully communicates with the cloud, the module status changes to Warning if the Management Center cannot push new URL filtering data to its managed devices.
Step 3: Check DNS Settings
A FireSIGHT Management Center communicates with these servers during cloud lookup:
database.brightcloud.com
service.brightcloud.com
Once you make sure that both servers are allowed on the firewall, run these commands on the FireSIGHT Management Center and verify if the Management Center is able to resolve the names:
admin@FireSIGHT:~$ sudo nslookup database.brightcloud.com
admin@FireSIGHT:~$ sudo nslookup service.brightcloud.com
Step 4: Check Connectivity to the Required Ports
FireSIGHT Systems use ports 443/HTTPS and 80/HTTP in order to communicate with the cloud service.
Once you confirm that the Management Center is able to perform a successful nslookup, verify connectivity to port 80 and port 443 with telnet. The URL database is downloaded with database.brightcloud.com at port 443, while the unknown URL queries are done at service.brightcloud.com at port 80.
telnet database.brightcloud.com 443
telnet service.brightcloud.com 80
This output is an example of a successful telnet connection to database.brightcloud.com.
Connected to database.brightcloud.com.
Escape character is '^]'.
Access Control and Miscategorization Issues
Problem 1: URL with Unselected Reputation Level is Allowed / Blocked
If you notice a URL is allowed or blocked, but you did not select the reputation level of that URL in your Access Control Rule, read this section in order to understand how a URL filtering rule works.
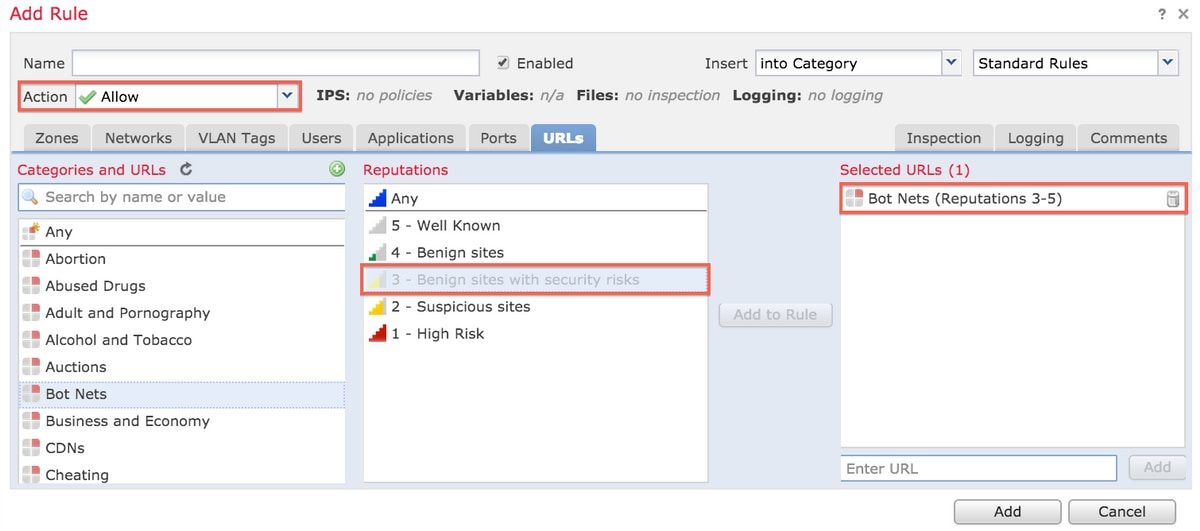
Rule Action is Allow
When you create a rule to Allow traffic based on a reputation level, selection of a reputation level also selects all of the reputation levels less secure than the level you originally selected. For example, if you configure a rule to allow Benign sites with security risks (level 3), it also automatically allows Benign sites (level 4) and Well known (level 5) sites.
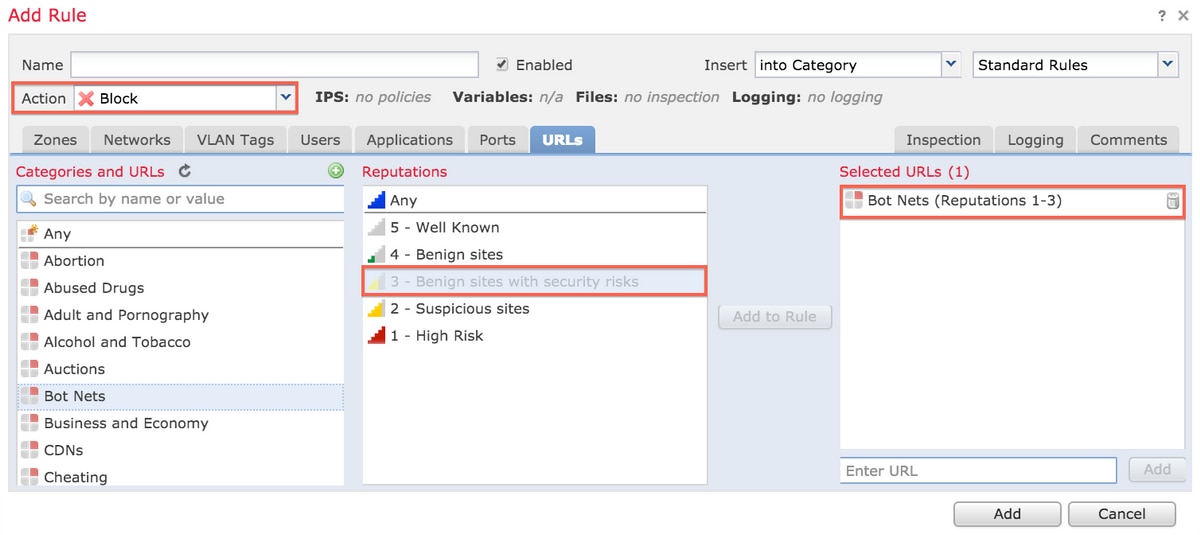
Rule Action is Block
When you create a rule to Block traffic based on a reputation level, selection of a reputation level also selects all of the reputation levels more severe than the level you originally selected. For example, if you configure a rule to block Benign Sites with security risks (level 3), it also automatically blocks Suspicious sites (level 2) and High risk (level 1) sites.
URL Selection Matrix
| Selected Reputation Level |
Selected Rule Action |
| High Risk |
Suspicious Site |
Benign Site with Security Risk |
Benign Site |
Well Known |
| 1 - High Risk |
Block, Allow |
Allow |
Allow |
Allow |
Allow |
| 2 - Suspicious Sites |
Block |
Block, Allow |
Allow |
Allow |
Allow |
| 3 - Benign Sites with Security Risk |
Block |
Block |
Block, Allow |
Allow |
Allow |
| 4 - Benign Sites |
Block |
Block |
Block |
Block, Allow |
Allow |
| 5 - Well Known |
Block |
Block |
Block |
Block |
Block, Allow |
Problem 2: Wildcard Does not Work in the Access Control Rule
FireSIGHT System does not support specification of a wildcard in a URL condition. This condition might fail to alert on cisco.com.
*cisco*.com
In addition, an incomplete URL might match against other traffic which causes an undesired result. When you specify individual URLs in URL conditions, you must carefully consider other traffic that might be affected. For example, consider a scenario where you want to explicitly block cisco.com. However, substring matching means that blocking cisco.com also blocks sanfrancisco.com, which might not be your intent.
When you enter a URL, enter the domain name and omit subdomain information. For example, type
cisco.com rather than
www.cisco.com. When you use
cisco.com in an
Allow rule, users could browse to any of these URLs:
http://cisco.com
http://cisco.com/newcisco
http://www.cisco.com
Problem 3: URL Category and Reputation are not Populated
If a URL is not in a local database and it is the first time that the URL is seen in traffic, a category or reputation might not be populated. This means that the first time an unknown URL is seen, it does not match the AC rule. Sometimes the URL lookups for commonly visited URLs might not resolve at the first time a URL is seen. This issue is fixed on Version 5.3.0.3, 5.3.1.2, and 5.4.0.2, 5.4.1.1.
Related Information




 Feedback
Feedback