Introduction
This document describes how to configure the Cisco ASA firewall to capture the desired packets with the ASDM or the CLI.
Prerequisites
Requirements
This procedure assumes that the ASA is fully operational and is configured in order to allow the Cisco ASDM or the CLI to make configuration changes.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific hardware or software versions.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Related Products
This configuration is also used with these Cisco products:
- Cisco ASA Versions 9.1(5) and later
- Cisco ASDM Version 7.2.1
Background Information
This document describes how to configure the Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) Next-Generation Firewall in order to capture the desired packets with either the Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) or the Command Line Interface (CLI) (ASDM).
The packet capture process is useful to troubleshoot connectivity problems or monitor suspicious activity. In addition, it is possible to create multiple captures in order to analyze different types of traffic on multiple interfaces.
Configure
This section provides information used to configure the packet capture features that are described in this document.
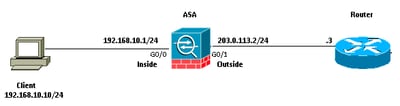
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Configurations
The IP address schemes used in this configuration are not legally routable on the Internet. They are RFC 1918 addresses that are used in a lab environment.
Configure Packet Capture with the ASDM
This example configuration is used in to capture the packets that are transmitted during a ping from User1 (inside network) to Router1 (outside network).
Complete these steps in order to configure the packet capture feature on the ASA with the ASDM:
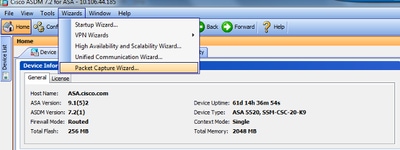
1. Navigate to Wizards > Packet Capture Wizard to start the packet capture configuration, as shown:
2. The Capture Wizard opens. Click Next.
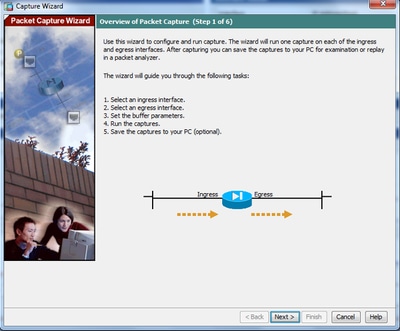
3.0 In the new window, provide the parameters that are used in to capture the ingress traffic.
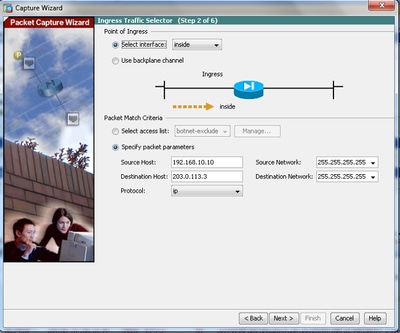
3.1 Select inside for the Ingress Interface and provide the source and the destination IP addresses of the packets to be captured, along with their subnet mask, in the respective space provided.
3.2 Choose the packet type to be captured by the ASA (IP is the packet type chosen here), as shown:
3.3 Click Next.
4.1 Select outside for the Egress Interface and provide the source and the destination IP addresses, along with their subnet mask, in the respective spaces provided.
If Network Address Translation (NAT) is performed on the Firewall, take this into consideration as well.
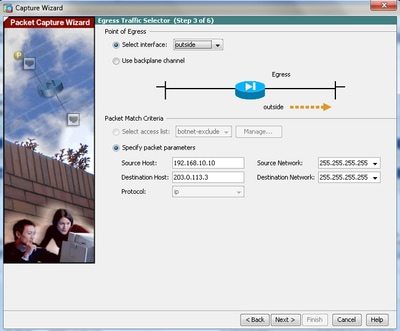
4.2 Click Next.
5.1 Enter the appropriate Packet Size and the Buffer Size in the respective space provided. This data is required for the capture to take place.
5.2 Check the Use circular buffer box to use the circular buffer option. Circular buffers never fill up.
As the buffer reaches its maximum size, older data is discarded and the capture continues.
In this example, circular buffer is not used, so the check box is not checked.
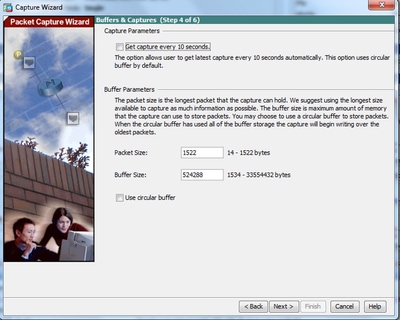
5.3 Click Next.
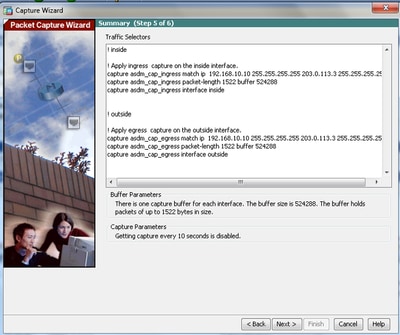
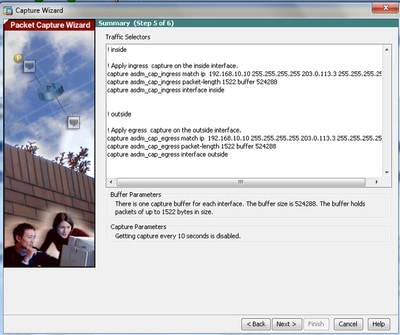
6.0 This window shows the Access-lists that must be configured on the ASA (so that the desired packets are captured) and the type of packets to be captured (IP packets are captured in this example).
6.1 Click Next.
7. Click Start in order to start the packet capture, as shown:
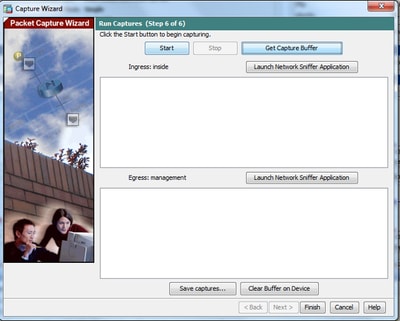
After the packet capture starts, attempt to ping the outside network from the inside network so that the packets that flow between the source and the destination IP addresses are captured by the ASA capture buffer.
8. Click Get Capture Buffer in order to view the packets that are captured by the ASA capture buffer.
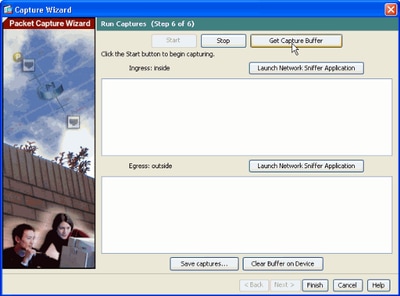
The captured packets are shown in this window for both the ingress and egress traffic.
9. Click Save captures to save the capture information.
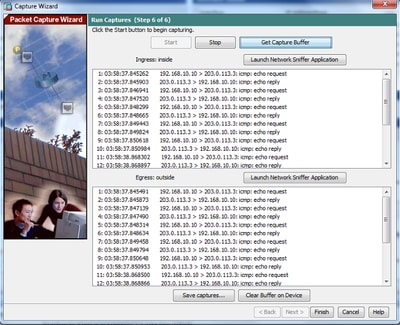
10.1 From the Save captures window, choose the required format in which the capture buffer is to be saved. This is either ASCII or PCAP.
10.2 Click the radio button next to the format names.
10.3 Click Save ingress capture or Save egress capture as required. The PCAP files can then be opened with capture analyzers, such as Wireshark, and it is the preferred method.
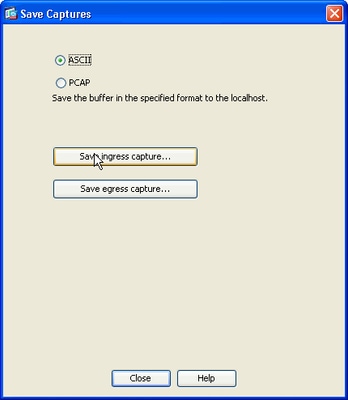
11.1 From the Save capture file window, provide the file name and the location where the capture file is to be saved.
11.2 Click Save.
12. Click Finish.
This completes the GUI packet capture procedure.
Configure Packet Capture with the CLI
Complete these steps in order to configure the packet capture feature on the ASA with the CLI:
- Configure the inside and outside interfaces as illustrated in the network diagram with the correct IP address and security levels.
- Start the packet capture process with the capture command in privileged EXEC mode. In this configuration example, the capture named capin is defined. Bind it to the inside interface, and specify with the match keyword that only the packets that match the traffic of interest are captured:
ASA# capture capin interface inside match ip 192.168.10.10 255.255.255.255
203.0.113.3 255.255.255.255
- Similarly, the capture named capout is defined. Bind it to the outside interface, and specify with the match keyword that only the packets that match the traffic of interest are captured:
ASA# capture capout interface outside match ip 192.168.10.10 255.255.255.255
203.0.113.3 255.255.255.255
The ASA now begins to capture the traffic flow between the interfaces. In order to stop the capture at anytime, enter the no capture command followed by the capture name.
Here is an example:
no capture capin interface inside
no capture capout interface outside
Available Capture Types on the ASA
This section describes the different types of captures that are available on the ASA.
- asa_dataplane - Captures packets on the ASA backplane that pass between the ASA and a module that uses the backplane, such as the ASA CX or IPS module.
ASA# cap asa_dataplace interface asa_dataplane
ASA# show capture
capture asa_dataplace type raw-data interface asa_dataplane [Capturing - 0 bytes]
- asp-drop drop-code - Captures packets that are dropped by the accelerated security path. The drop-code specifies the type of traffic that is dropped by the accelerated security path.
ASA# capture asp-drop type asp-drop acl-drop
ASA# show cap
ASA# show capture asp-drop
2 packets captured
1: 04:12:10.428093 192.168.10.10.34327 > 10.94.0.51.15868: S
2669456341:2669456341(0) win 4128 <mss 536> Drop-reason: (acl-drop)
Flow is denied by configured rule
2: 04:12:12.427330 192.168.10.10.34327 > 10.94.0.51.15868: S
2669456341:2669456341(0) win 4128 <mss 536> Drop-reason: (acl-drop)
Flow is denied by configured rule
2 packets shown
ASA# show capture asp-drop
2 packets captured
1: 04:12:10.428093 192.168.10.10.34327 > 10.94.0.51.15868: S
2669456341:2669456341(0) win 4128 <mss 536> Drop-reason: (acl-drop)
Flow is denied by configured rule
2: 04:12:12.427330 192.168.10.10.34327 > 10.94.0.51.15868: S
2669456341:2669456341(0) win 4128 <mss 536> Drop-reason: (acl-drop)
Flow is denied by configured rule
2 packets shown
- ethernet-type type - Selects an Ethernet type to capture. Supported Ethernet types include 8021Q, ARP, IP, IP6, LACP, PPPOED, PPPOES, RARP, and VLAN.
This example show how to capture ARP traffic:
ASA# cap arp ethernet-type ?
exec mode commands/options:
802.1Q
<0-65535> Ethernet type
arp
ip
ip6
pppoed
pppoes
rarp
vlan
cap arp ethernet-type arp interface inside
ASA# show cap arp
22 packets captured
1: 05:32:52.119485 arp who-has 10.10.3.13 tell 10.10.3.12
2: 05:32:52.481862 arp who-has 192.168.10.123 tell 192.168.100.100
3: 05:32:52.481878 arp who-has 192.168.10.50 tell 192.168.100.10
4: 05:32:53.409723 arp who-has 10.106.44.135 tell 10.106.44.244
5: 05:32:53.772085 arp who-has 10.106.44.108 tell 10.106.44.248
6: 05:32:54.782429 arp who-has 10.106.44.135 tell 10.106.44.244
7: 05:32:54.784695 arp who-has 10.106.44.1 tell xx.xx.xx.xxx:
- real-time - Displays the captured packets continuously in real-time. In order to terminate a real-time packet capture, press Ctrl-C. In order to permanently remove the capture, use the no form of this command.
- This option is not supported when you use the cluster exec capture command.
ASA# cap capin interface inside real-time
Warning: using this option with a slow console connection may
result in an excessive amount of non-displayed packets
due to performance limitations.
Use ctrl-c to terminate real-time capture
- Trace - Traces the captured packets in a manner similar to the ASA packet tracer feature.
ASA#cap in interface Webserver trace match tcp any any eq 80
// Initiate Traffic
1: 07:11:54.670299 192.168.10.10.49498 > 198.51.100.88.80: S
2322784363:2322784363(0) win 8192
<mss 1460,nop,wscale 2,nop,nop,sackOK>
Phase: 1
Type: CAPTURE
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
MAC Access list
Phase: 2
Type: ACCESS-LIST
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Implicit Rule
Additional Information:
MAC Access list
Phase: 3
Type: ROUTE-LOOKUP
Subtype: input
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
in 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 outside
Phase: 4
Type: ACCESS-LIST
Subtype: log
Result: ALLOW
Config:
access-group any in interface inside
access-list any extended permit ip any4 any4 log
Additional Information:
Phase: 5
Type: NAT
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
object network obj-10.0.0.0
nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface
Additional Information:
Dynamic translate 192.168.10.10/49498 to 203.0.113.2/49498
Phase: 6
Type: NAT
Subtype: per-session
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Phase: 7
Type: IP-OPTIONS
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Phase: 8
Type:
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Phase: 9
Type: ESTABLISHED
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Phase: 10
Type:
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Phase: 11
Type: NAT
Subtype: per-session
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Phase: 12
Type: IP-OPTIONS
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
Phase: 13
Type: FLOW-CREATION
Subtype:
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
New flow created with id 41134, packet dispatched to next module
Phase: 14
Type: ROUTE-LOOKUP
Subtype: output and adjacency
Result: ALLOW
Config:
Additional Information:
found next-hop 203.0.113.1 using egress ifc outside
adjacency Active
next-hop mac address 0007.7d54.1300 hits 3170
Result:
output-interface: outside
output-status: up
output-line-status: up
Action: allow
Note: On ASA 9.10+, the any keyword only captures packets with ipv4 addresses. The any6 keyword captures all ipv6 addressed traffic.
These are advanced settings that can be configured with Packet Captures.
Please review the command reference guide on how to set them.
- ikev1/ikev2 - Captures only Internet Key Exchange Version 1 (IKEv1) or IKEv2 protocol information.
- isakmp - Captures Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) traffic for VPN connections. The ISAKMP subsystem does not have access to the upper-layer protocols. The capture is a pseudo capture, with the physical, IP, and UDP layers combined together in order to satisfy a PCAP parser. The peer addresses are obtained from the SA exchange and are stored in the IP layer.
- lacp - Captures Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) traffic. If configured, the interface name is the physical interface name. This is useful when you work with Etherchannels in order to identify the present behavior of LACP.
- tls-proxy - Captures decrypted inbound and outbound data from the Transport Layer Security (TLS) proxy on one or more interfaces.
- webvpn - Captures WebVPN data for a specific WebVPN connection.
Caution: When you enable WebVPN capture, it affects the performance of the security appliance. Ensure that you disable the capture after you generate the capture files that are needed in order to troubleshoot.
Defaults
These are the ASA system default values:
- The default type is raw-data.
- The default buffer size is 512 KB.
- The default Ethernet type is IP packets.
- The default packet-length is 1,518 bytes.
View the Captured Packets
On the ASA
In order to view the captured packets, enter the show capture command followed by the capture name. This section provides the show command outputs of the capture buffer contents. The show capture capin command shows the contents of the capture buffer named capin:
ASA# show cap capin
8 packets captured
1: 03:24:35.526812 192.168.10.10 > 203.0.113.3: icmp: echo request
2: 03:24:35.527224 203.0.113.3 > 192.168.10.10: icmp: echo reply
3: 03:24:35.528247 192.168.10.10 > 203.0.113.3: icmp: echo request
4: 03:24:35.528582 203.0.113.3 > 192.168.10.10: icmp: echo reply
5: 03:24:35.529345 192.168.10.10 > 203.0.113.3: icmp: echo request
6: 03:24:35.529681 203.0.113.3 > 192.168.10.10: icmp: echo reply
7: 03:24:57.440162 192.168.10.10 > 203.0.113.3: icmp: echo request
8: 03:24:57.440757 203.0.113.3 > 192.168.10.10: icmp: echo reply
The show capture capout command shows the contents of the capture buffer named capout:
ASA# show cap capout
8 packets captured
1: 03:24:35.526843 192.168.10.10 > 203.0.113.3: icmp: echo request
2: 03:24:35.527179 203.0.113.3 > 192.168.10.10: icmp: echo reply
3: 03:24:35.528262 192.168.10.10 > 203.0.113.3: icmp: echo request
4: 03:24:35.528567 203.0.113.3 > 192.168.10.10: icmp: echo reply
5: 03:24:35.529361 192.168.10.10 > 203.0.113.3: icmp: echo request
6: 03:24:35.529666 203.0.113.3 > 192.168.10.10: icmp: echo reply
7: 03:24:47.014098 203.0.113.3 > 203.0.113.2: icmp: echo request
8: 03:24:47.014510 203.0.113.2 > 203.0.113.3: icmp: echo reply
Download from the ASA for Offline Analysis
There are a couple of ways to download the packet captures for analysis offline:
- Navigate to
https://<ip_of_asa>/admin/capture/<capture_name>/pcap
on any browser.
Tip: If you leave out the pcap keyword, then only the equivalent of the show capture <cap_name> command output is provided.
- Enter the copy capture command and your preferred file transfer protocol in order to download the capture:
copy /pcap capture:<capture-name> tftp://<server-ip-address>
Tip: When you troubleshoot an issue with the use of packet captures, Cisco recommends that you download the captures for offline analysis.
Clear a Capture
In order to clear the capture buffer, enter the clear capture <capture-name> command:
ASA# show capture
capture capin type raw-data interface inside [Capturing - 8190 bytes]
match icmp any any
capture capout type raw-data interface outside [Capturing - 11440 bytes]
match icmp any any
ASA# clear cap capin
ASA# clear cap capout
ASA# show capture
capture capin type raw-data interface inside [Capturing - 0 bytes]
match icmp any any
capture capout type raw-data interface outside [Capturing - 0 bytes]
match icmp any any
Enter the clear capture /all command in order to clear the buffer for all captures:
ASA# clear capture /all
Stop a Capture
The only way to stop a capture on the ASA is to disable it completely with this command:
no capture <capture-name>
Verify
There is currently no verification procedure available for this configuration.
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshoot information available for this configuration.














 Feedback
Feedback