Troubleshoot ACI OSPF Adjacencies
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes troubleshooting Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Adjacencies.
Topology
 Topology
TopologyOSPF Peering Configuration Requirements
OSPF is one of the protocols that you can enable between Cisco ACI and an external router. Cisco ACI supports all common options, such as OSPF area including backbone, various stub options, neighbor authentication, and other similar options.
An L3Out includes the routing protocol options, the switch-specific configuration (a node profile), and interface-specific settings (an interface profile). The OSPF-related parameters can be mainly configured in two places just like a normal router. The first one is Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF)-wide or Node-wide configuration such as area ID and area type that can be configured on the L3Out itself. The second one is interface level parameters such as OSPF hello interval or interface type (Broadcast, Point-to-Point(P2P)).
These are the requirements for OSPF adjacency to be established between the ACI border leaf and the external router:
- OSPF area ID and type must match
- OSPF Router ID must be unique
- The maximum transmission unit (MTU) must match (by default fabric sets it to 9000 and most Cisco IOS®/NXOS set it to 1500)
- OSPF Authentication Key and type must match (if used)
- OSPF Hello and Dead Intervals must match
- OSPF network type must match
The white paper provided a detailed explanation of the design concepts and options related to the ACI L3Out for the supporting routing protocols.
Reference the white paper if you are unfamiliar with the L3Out setup and other foundational requirements.
Troubleshooting OSPF Adjacency - General Checklist
Irrespective of whether the OSPF adjacency was up before or has never come up, it is best to validate the basic requirements first.
Step 1. Ping the remote end interface. This helps confirm if you have IP reachability to the far end which is a primary requirement for OSPF to come up.
iping -V <vrf> <remote_end_IP>
example:
BL-301# iping -V abc1:vrf-1 192.0.2.50
Step 2. Validate the basic configuration parameters:
- OSPF area ID and type must match
- OSPF Router ID must be unique
- MTU must match (by default fabric sets it to 9000 and most Cisco IOS/NXOS set it to 1500)
- OSPF Authentication Key and type must match (if used)
- OSPF Hello and Dead Intervals must match
- OSPF network type must match
The command outputs show the configuration attributes pushed to the leaf.
BL-301# show ip int bri vrf abc1:vrf-1 IP Interface Status for VRF "abc1:vrf-1"(137) Interface Address Interface Status vlan1 192.0.2.1/24 protocol-up/link-up/admin-up --> l3out SVI lo9 192.168.0.1/32 protocol-up/link-up/admin-up --> Router ID SVI
BL-301# show ip ospf interface vlan 1
Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up
IP address 192.0.2.1/24, Process ID default VRF abc1:vrf-1, area backbone
Enabled by interface configuration
State P2P, Network type P2P, cost 4
Index 84, Transmit delay 1 sec
1 Neighbors, flooding to 1, adjacent with 1
Timer intervals: Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Hello timer due in 00:00:03
No authentication
Number of opaque link LSAs: 0, checksum sum 0
BL-301# show int vlan 1 | egrep "MTU"
MTU 9000 bytes, BW 10000000 Kbit, DLY 1 usec
BL-301# show ip ospf vrf abc1:vrf-1 | grep Routing
Routing Process default with ID 192.168.0.1 VRF abc1:vrf-1 --> Router ID
Note down all the highlighted details and confirm the corresponding remote end parameters are in sync.
Troubleshooting OSPF Adjacency - Faults
[+]From the border Leaf we can identify the state of the neighbor state
BL-301# show ip ospf neighbors vrf abc1:vrf-1
<<EMPTY>>
[+] You can check the associated faults to the VRF.
BL-301# moquery -c faultInst -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(faultInst.dn,"abc1:vrf-1")' | egrep "code|rule|dn|descr|lastTransition"
<<EMPTY>>
There are some scenarios with no active faults in the environment but there can be one fault Record F1385 (protocol-ospf-adjacency-down) on the leaf that points us to the last time this neighborship was up or if never been in full state.
You can identify this with the moquery -c faultRecord -f 'fault.Inst.code=="F1385"' -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(faultRecord.dn,"abc1:vrf-1")' | grep dn command.
Check the number of fault records for any specific date with the moquery -c faultRecord -f 'fault.Inst.code=="F1385"' -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(faultRecord.dn,"abc1:vrf-1")' -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(faultRecord.created,"2024-01-01")' | egrep "dn" | wc -l command.
You must identify the OSPF interface and local and remote configured IPs.
[+] Identify the IP applied on the external device from the ARP associated to the interface
BL-301# moquery -c arpAdjEp -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(arpAdjEp.ifId,"vlan1")' | grep "ip "
ip : 192.0.2.50
Capturing Control Plane Traffic on Node
With the expected Source and Destination Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) from the border leaf, you can utilize the tcpdump utility to check.

Note: For this, the interface kpm_inb which allows you to see all CPU inband control plane network traffic is used.
[+] Capture a single OSPF hello packet using TCPDUMP coming for local BL OSPF IP 192.0.2.1
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.1 -vv -e -i kpm_inb
tcpdump: listening on kpm_inb, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
192.0.2.1 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 192.168.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
[+] Capture a single OSPF hello packet using TCPDUMP coming from external device OSPF IP 192.0.2.50
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.50 -vv -e -i kpm_inb
tcpdump: listening on kpm_inb, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
192.0.2.50 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 172.16.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
Wireshark Verification
You can capture OSPF and HOST-specific traffic in order to analyze it on Wireshark.
BL-301# tcpdump -i kpm_inb proto ospf -vv -e -w - | tee /data/techsupport/Node-XXX_OSPF.pcap | tcpdump -r - host any
BL-301# tcpdump -xxxvi kpm_inb 'proto ospf and (host <<X.X.X.X>> or host <<Y.Y.Y.Y>>)' -w /data/techsupport/Node-XXX_OSPF_HOST.pcap
BL-301# tcpdump -i kpm_inb proto ospf -vv -e -w - | tee /data/techsupport/Node-XXX_OSPF_HOST.pcap | tcpdump -r - host X.X.X.X
For pcap captures, you can use Wireshark filters by searching and using Analyze > Apply as a Column.
ospf.area_id = in order to identify AreaID
ospf.auth.type = in order to check the configured Auth Type to match
ospf.hello.hello_interval = in order to check for different MTUs
ospf.hello.router_dead_interval = in order to check for different dead interval configuration
ospf.srcrouter = RouterID
Troubleshooting Scenarios
Troubleshooting OSPF Adjacency: Area ID Mismatch
From APIC configuration with Area ID 0.0.0.42, navigate to Fabric > Tenants > Networking > L3Outs > <<L3outName>> > Policy > Main.
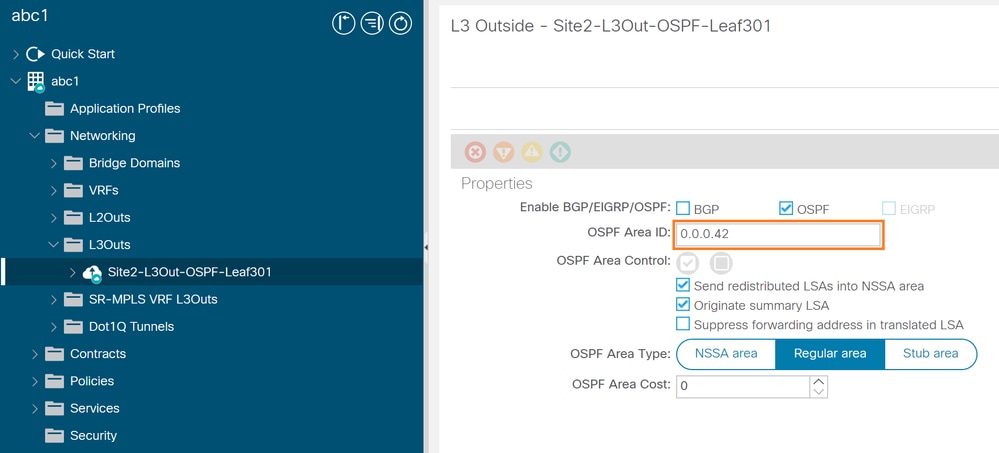 Wrong OSPF Area ID configured 0.0.0.42
Wrong OSPF Area ID configured 0.0.0.42
From the border leaf:
[+] Check OSPF interface details to confirm current area
BL-301# show ip ospf interface vlan 1 | grep area
IP address 192.0.2.1/24, Process ID default VRF abc1:vrf-1, area 0.0.0.42
Or
BL-301# moquery -c ospfIf -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIf.id,"vlan1")' | grep area
area : 0.0.0.42
[+] Capture a single packet TCPDUMP for local BL OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.1 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.1 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 192.168.0.1, Area 0.0.0.42, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
[+] Capture a single OSPF hello packet using TCPDUMP coming from external device OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.50 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.50 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 172.16.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
From External device:
NX-OS# show logging log | tail -n 100 | grep ospf-bootcamp
2023 Dec 28 15:17:09 NX-OS %OSPF-4-AREA_ERR: ospf-bootcamp [22263] (301-l3-abc1) Packet from 192.0.2.1 on Ethernet1/2 received for wrong area 0.0.0.42
NX-OS# show ip ospf interface Ethernet1/2 | grep area
Process ID bootcamp VRF 301-l3-abc1, area 0.0.0.0
Solution: Match OSPF Area to 0.0.0.0 or backbone on BL or 0.0.0.42 on the external device.
Troubleshooting OSPF Adjacency: Area Type Mismatch
From ACI GUI, configuration with Area type either NSSA or Stub, navigate to Fabric > Tenants > Networking > L3Outs > "L3outName" > Policy > Main.
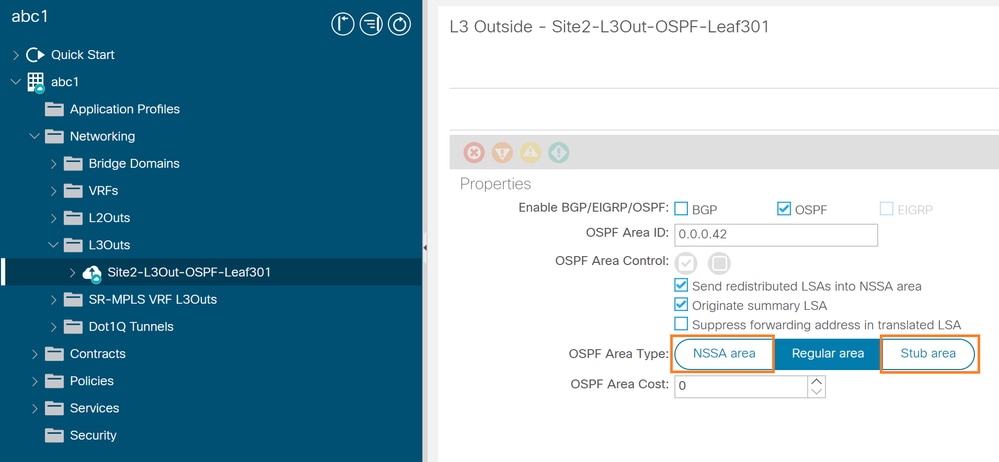 NSSA or Stub Area configuration.
NSSA or Stub Area configuration.
From the border leaf:
[+] Capture a single packet TCPDUMP for local BL OSPF IP
BL-301# moquery -c ospfArea -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfArea.dn,"abc1:vrf-1")' | egrep "type"
type : nssa
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.1 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.1 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 192.168.0.1, Area 0.0.0.42, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [NSSA]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
or
BL-301# moquery -c ospfArea -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfArea.dn,"abc1:vrf-1")' | egrep "type"
type : stub
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.1 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.1 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 192.168.0.1, Area 0.0.0.42, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [none]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
[+] Capture a single OSPF hello packet using TCPDUMP coming from external device OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.50 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.50 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 172.16.0.1, Area 0.0.0.42, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
From External device:
[+] Check OSPF interfaces con vrf
NX-OS# show ip int bri vrf 301-l3-abc1
IP Interface Status for VRF "301-l3-abc1"(21)
Interface IP Address Interface Status
Lo1001 110.1.0.1 protocol-up/link-up/admin-up
Eth1/2.1120 192.0.2.50 protocol-up/link-up/admin-up
NX-OS# show ip ospf interface Ethernet1/2 | grep area
Process ID bootcamp VRF 301-l3-abc1, area 0.0.0.0
Solution: Match OSPF Area type regularly on L3Out or match on from the external device.
Troubleshooting OSPF Adjacency: Duplicate Router ID
A duplicated router ID prevents the OSPF adjacency from forming. In ACI fabric, after configuring the OSPF router ID, the leaf creates a loopback with the router ID IP address. Because this address is used for loopback, you can not have it overlap with the interface IP used as it fails.
In this example, you can confirm it was misconfigured with the Router ID from the neighbor device.
From ACI GUI, navigate to Fabric > Tenants > Networking > L3Outs > "L3outName" > "Node-X" > Configured Nodes > topology/pod-Y/node-X.
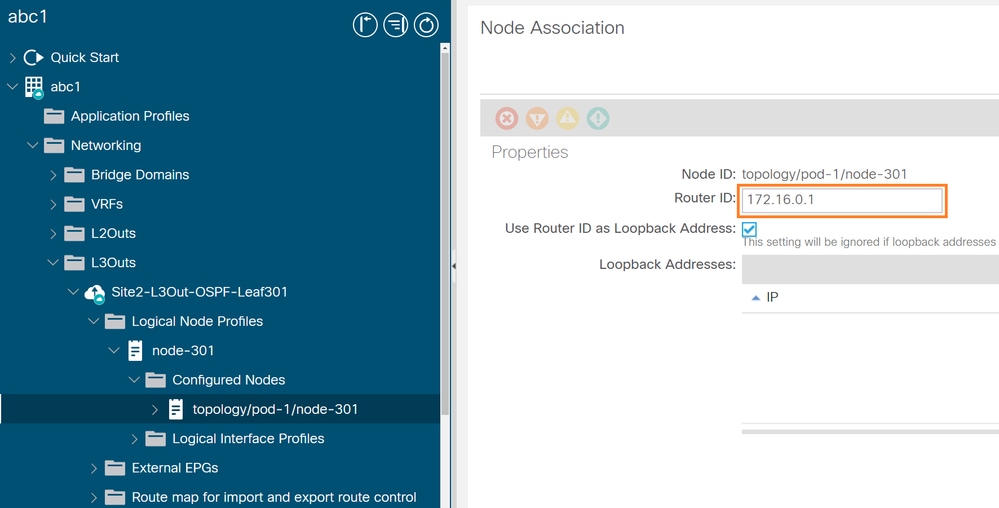 misconfigured with the Router ID from the neighbor device.
misconfigured with the Router ID from the neighbor device.
From the border leaf:
[+] Check OSPF interfaces associated with the VRF
BL-301# show ip int bri vrf abc1:vrf-1
IP Interface Status for VRF "abc1:vrf-1"(137)
Interface Address Interface Status
vlan1 192.0.2.1/24 protocol-up/link-up/admin-up
lo9 172.16.0.1/32 protocol-up/link-up/admin-up
[+] Capture a single packet TCPDUMP for local BL OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.1 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.1 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 172.16.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
[+] Capture a single OSPF hello packet using TCPDUMP coming from external device OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.50 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.50 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 48
Router-ID 172.16.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
From External device
NX-OS# show logging log | tail -n 100 | grep ospf-bootcamp
2024 Jan 4 13:55:36 NX-OS %OSPF-4-DUPRID: ospf-bootcamp [22263] (301-l3-abc1) Router 192.0.2.1 on interface Ethernet1/2.1120 is using our routerid, packet dropped
Solution: Use different router IDs on both devices.
 use different router ID's on both devices
use different router ID's on both devices
Troubleshooting OSPF Adjacency: MTU Mismatch
After two OSPF neighboring routers establish bi-directional communication and complete Designated Router (DR)/BDR election (on broadcast networks), the routers transition to the Exstart state. In this state, the neighboring routers establish an active/standby relationship and determine the initial database descriptor (DBD) sequence number to use while exchanging DBD packets.
Once the active/standby relationship has been negotiated (the router with the highest router ID becomes the active), the neighboring routers transition into the exchange state. In this state, the routers exchange DBD packets, which describe their entire link-state database. The routers also send link-state request packets, which request more recent link-state advertisements (LSA) from neighbors.
If the MTU settings for neighboring router interfaces do not match, the routers are stuck in in Exstart/Exchange State. This is because the router with the higher MTU sends a packet larger than the MTU set on the neighboring router, so the neighboring router ignores the packet.
From APIC GUI configuration with default inherit configuration, navigate to Fabric > Tenants > Networking > L3Outs > "L3outName" > "Node-X" > Logical Interface Profiles > OSPF Interface Profile.
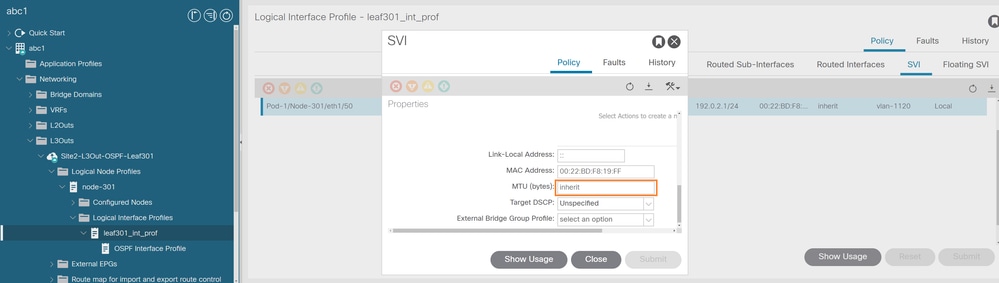 By default, ACI fabric sets the layer 3 interface MTU to 9000 instead of 1500
By default, ACI fabric sets the layer 3 interface MTU to 9000 instead of 1500
By default, ACI fabric sets the Layer 3 interface MTU to 9000 instead of 1500. Since the ACI has a higher MTU, it continues to accept the DBD packets from the external router and attempts to acknowledge them.
If the external router has a lower or higher MTU, it ignores the DBD packets along with ACK from ACI, continues to retransmit the initial DBD packet, and remains in the Exstart/Exchange state.
From the border leaf:
[+]From the border Leaf we can identify the state of the neighborship relation
BL-301# show ip ospf neighbors vrf abc1:vrf-1
OSPF Process ID default VRF abc1:vrf-1
Total number of neighbors: 1
Neighbor ID Pri State Up Time Address Interface
172.16.0.1 1 EXCHANGE/ - 01:10:05 192.0.2.50 Vlan1
[+] You can check the associated faults to the Tenant:VRF / OSPF interface
BL-301# moquery -c faultInst -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(faultInst.dn,"abc1:vrf-1\/if-\[vlan1\]")' | egrep "code|rule|dn|descr|lastTransition"
code : F1385
descr : OSPF adjacency is not full, current state Exchange
dn : topology/pod-1/node-301/sys/ospf/inst-default/dom-abc1:vrf-1/if-[vlan1]/adj-172.16.0.1/fault-F1385
lastTransition : 2023-12-28T12:26:23.369-05:00
rule : ospf-adj-ep-failed
title : OSPF Adjacency Down
code : F3592
descr : OSPF interface vlan1 mtu is different than neighbor mtu
dn : topology/pod-1/node-301/sys/ospf/inst-default/dom-abc1:vrf-1/if-[vlan1]/fault-F3592
lastTransition : 2023-12-28T12:26:23.369-05:00
rule : ospf-if-mtu-config-mismatch-err
[+] Identify the MTU applied on the OSPF interface
BL-301# show int vlan 1 | egrep "MTU"
MTU 9000 bytes, BW 10000000 Kbit, DLY 1 usec
[+] If the default configuration is on place there will be a missmatch with the 1500 default
BL-301# show ip ospf event-history adjacency | grep "neighbor mtu"
2023-12-28T12:24:31.986149000-05:00 ospf default [20751]: TID 21885:ospfv2_check_ddesc_for_nbr_state:492:(abc1:vrf-1-base) DBD from 192.0.2.50,neighbor mtu [1500] is smaller than if mtu 9000
[+] Or if the locally configured MTU is lower tham external router
[2023-12-28T14:05:48.495659000-05:00:T:ospfv2_check_ddesc_for_nbr_state:478] abc1:vrf-1DBD from 192.0.2.50,neighbor mtu [1500] is large than if mtu 1200
Possible solutions:
- Match the MTU on both devices
When an MTU is changed on either side, since the membership is already established it remains that way until the next negotiation and can be triggered for multiple reasons. For example, down physical interface, policy redeployment, leaf reload, upgrade, and so on.
Navigate to Fabric > Tenants > Networking > L3Outs > "L3outName" > "Node-X" > Logical Interface Profiles > OSPF Interface Profile as shown in the image.
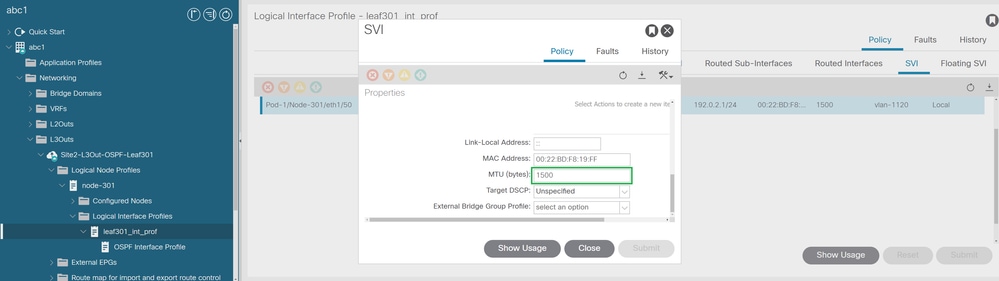 MTU configured to 1500
MTU configured to 1500
- MTU ignore in the Associated OSPF Interface Policy reestablishes the connectivity.
The issue with MTU ignore can appear when the OSPF database grows. When the MTUs differ by only a few bytes, the setup can work for a long time until you happen to stumble across the correct combination of LSAs that generate the DBD or update packet of just the right size.
Tests in a small lab work fine, but the production network can encounter unexpected behaviors.
Navigate to Fabric > Tenants > Networking > L3Outs > "L3outName" > "Node-X" > Logical Interface Profiles > OSPF Interface Profile > Associated OSPF Interface Policy as shown in the image.
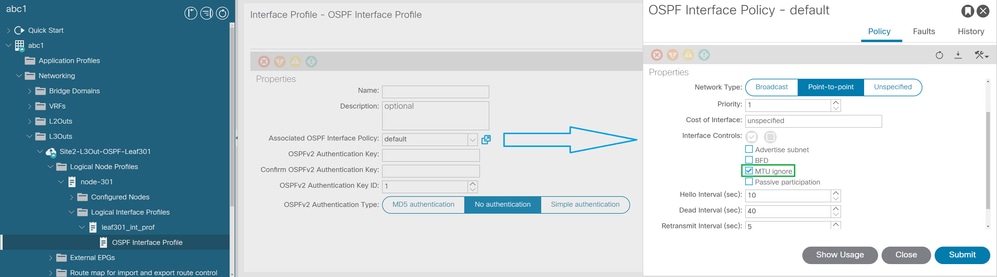 MTU ignore configuration
MTU ignore configuration
Troubleshooting OSPF Adjacency: Authentication Mismatch
You can enable authentication in OSPF in order to exchange routing update information securely. OSPF authentication can either be none (or null), simple, or MD5. The authentication method 'none' means that no authentication is used for OSPF and it is the default method. With simple authentication, the password goes in clear text over the network. With MD5 authentication, the password does not pass over the network.
These are the three different types of authentication supported by OSPF.
Null Authentication — This is also called Type 0 and it means no authentication information is included in the packet header. It is the default.
Simple Authentication — This is also called Type 1 and it uses simple clear-text passwords.
MD5 Authentication — This is also called Type 2 and it uses MD5 cryptographic passwords.
Authentication does not need to be set. However, if it is set, all peer routers on the same segment must have the same password and authentication method.
From ACI GUI, navigate to Fabric > Tenants > Networking > L3Outs > "L3outName" > "Node-X" > Logical Interface Profiles > OSPF Interface Profile as shown in the image.
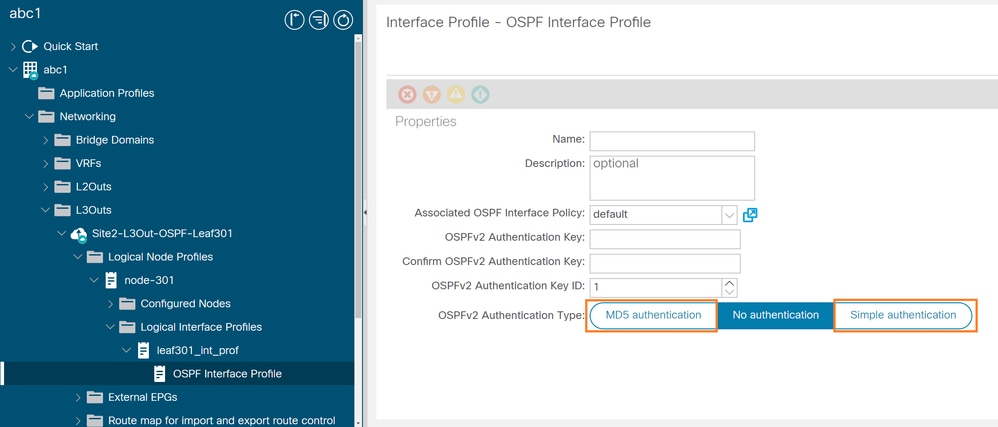 MD5 or Simple Authentications configured
MD5 or Simple Authentications configured
From CLI:
[+] Check Authentication type configured
APIC# moquery -c ospfIfP -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIfP.dn,"tn-abc1\/out-Site2-L3Out-OSPF-BL-301")' | grep authType
authType : simple
[+] Capture a single packet TCPDUMP for local BL OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.1 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.1 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 192.168.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: simple (1)
Simple text password: cisco
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
or
[+] Check Authentication type configured
APIC# moquery -c ospfIfP -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIfP.dn,"tn-abc1\/out-Site2-L3Out-OSPF-BL-301")' | grep authType
authType : md5
[+] Capture a single packet TCPDUMP for local BL OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.1 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.1 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 192.168.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: MD5 (2)
Key-ID: 1, Auth-Length: 16, Crypto Sequence Number: 0x026c0a34
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
[+] Capture a single OSPF hello packet using TCPDUMP coming from external device OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.50 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.50 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 48
Router-ID 172.16.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
[+] Live OSPF trace Decode for VRF
BL-301# log_trace_bl_print_tool /var/sysmgr/tmp_logs/ospfv2_1_trace.bl | tail -n 250 | grep abc1:vrf-1 | grep key
[2024-01-04T16:23:29.650806000-05:00:T:ospfv2_set_authentication:70] abc1:vrf-1out pkt on Vlan1: auth simple text: key cisco
or
[2024-01-04T16:24:22.794682000-05:00:T:ospfv2_set_authentication:96] abc1:vrf-1out pkt on Vlan1: auth md5: key cisco, key id 1 Seq 40635829 (time 1704403462)
From External device:
NX-OS# show logging log | tail -n 100 | grep ospf-bootcamp
2024 Jan 4 16:55:01 NX-OS %OSPF-4-AUTH_ERR: ospf-bootcamp [22263] (301-l3-abc1) Received packet from 192.0.2.1 on Ethernet1/2.1120 with bad authentication 1
or
2024 Jan 4 16:55:20 NX-OS %OSPF-4-AUTH_ERR: ospf-bootcamp [22263] (301-l3-abc1) Received packet from 192.0.2.1 on Ethernet1/2.1120 with bad authentication 2
Solution: Match authentications.
Troubleshooting OSPF Adjacency: Hello/Dead Timers Mismatch
OSPF hello packets are packets that an OSPF process sends to its OSPF neighbors in order to maintain connectivity with those neighbors. The hello packets are sent at a configurable interval (in seconds). The defaults are 10 seconds for an Ethernet link (for P2P and Broadcast Network Type). Hello packets include a list of all neighbors for which a hello packet has been received within the dead interval. The dead interval is also configurable (in seconds), and defaults to four times the value of the hello interval. The value of all hello intervals must be the same within a network. Likewise, the value of all dead intervals must be the same within a network.
These two intervals work together in order to maintain connectivity by indicating that the link is operational. If a router does not receive a hello packet from a neighbor within the dead interval, it declares that neighbor to be down.
If the default OSPF hello and dead timers are modified on ACI fabric, they must match the external router.
From ACI GUI, navigate to Fabric > Tenants > Networking > L3Outs > "L3outName" > "Node-X" > Logical Interface Profiles > OSPF Interface Profile > Associated OSPF Interface Policy as shown in the image.
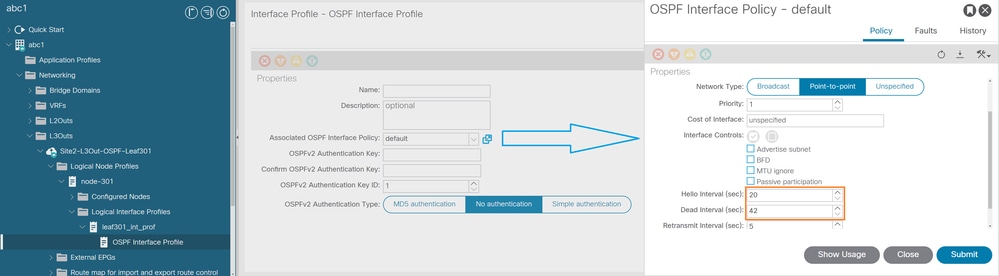 Custom Hello/Dead Timers
Custom Hello/Dead Timers
From the border leaf:
[+] Check OSPF interface configuration
BL-301# show ip ospf interface vlan 1 | egrep "Timer|Network"
State P2P, Network type P2P, cost 4
Timer intervals: Hello 20, Dead 42, Wait 42, Retransmit 5
Or
BL-301# moquery -c ospfIf -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIf.id,"vlan1")' | egrep "deadIntvl|helloIntvl|nwT"
deadIntvl : 42
helloIntvl : 20
nwT : p2p
Or
APIC# moquery -c ospfRsIfPol -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIfP.dn,"abc1\/out-Site2-L3Out-OSPF-BL-301")' | grep tnOspfIfPolName
tnOspfIfPolName : Custom_OSPF_Interface_Policy
APIC# moquery -c ospfIfPol -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIfPol.name,"Custom_OSPF_Interface_Policy")' | egrep "deadIntvl|helloIntvl|nwT"
deadIntvl : 42
helloIntvl : 20
nwT : p2p
[+] Capture a single packet TCPDUMP for local BL OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.1 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.1 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 192.168.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 20s, Dead Timer 42s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
[+] Capture a single OSPF hello packet using TCPDUMP coming from external device OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.50 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.50 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 172.16.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
From External device:
[+] Check OSPF interfaces con vrf
NX-OS# show ip int bri vrf 301-l3-abc1
IP Interface Status for VRF "301-l3-abc1"(21)
Interface IP Address Interface Status
Lo1001 110.1.0.1 protocol-up/link-up/admin-up
Eth1/2.1120 192.0.2.50 protocol-up/link-up/admin-up
[+] Check OSPF configuration by default Dead timer on NX-OS devices is 4 times hello interval
NX-OS# show run ospf all | section Ethernet1/2.1120 | grep hello
ip ospf hello-interval 10
[+] Check OSPF interface advertized parameters
NX-OS# show ip ospf interface Ethernet1/2.1120 | grep Timer
Timer intervals: Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Solution: Match OSPF Timers.
Troubleshooting OSPF Adjacency: Interface Type Mismatch
This section describes the troubleshooting when Broadcast or unspecified is configured on ACI and the External device is P2P.
Broadcast
- The Broadcast network type is the default for an OSPF-enabled ethernet interface
- The Broadcast network type requires that a link support Layer 2 Broadcast capabilities
- The Broadcast network type has a 10-second hello and 40-second dead timer (same as P2P)
- An OSPF Broadcast network type requires the use of a DR/BDR
Point-to-Point
- A P2P OSPF network type does not maintain a DR/BDR relationship
- The P2P network type has a 10-second hello and 40-second dead timer
- P2P network types are intended to be used between two directly connected routers
From ACI GUI, navigate to Fabric > Tenants > Networking > L3Outs > "L3outName" > "Node-X" > Logical Interface Profiles > OSPF Interface Profile > Associated OSPF Interface Policy as shown in the image.
 Broadcast or Unspecified Network type configured
Broadcast or Unspecified Network type configured
From the border leaf:
[+] Check OSPF neighborship relation
BL-301# show ip ospf neighbors vrf abc1:vrf-1
OSPF Process ID default VRF abc1:vrf-1
Total number of neighbors: 1
Neighbor ID Pri State Up Time Address Interface
172.16.0.1 1 INITIALIZING/DROTHER 00:06:42 192.0.2.50 Vlan1
[+] Check OSPF interface configuration
BL-301# moquery -c ospfIf -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIf.id,"vlan1")' | egrep "deadIntvl|helloIntvl|nwT"
deadIntvl : 40
helloIntvl : 10
nwT : bcast
or
BL-301# moquery -c ospfIf -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIf.id,"vlan1")' | egrep "deadIntvl|helloIntvl|nwT"
deadIntvl : 40
helloIntvl : 10
nwT : unspecified
Or
APIC# moquery -c ospfRsIfPol -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIfP.dn,"abc1\/out-Site2-L3Out-OSPF-BL-301")' | grep tnOspfIfPolName
tnOspfIfPolName : Custom_OSPF_Interface_Policy
APIC# moquery -c ospfIfPol -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIfPol.name,"Custom_OSPF_Interface_Policy")' | egrep "deadIntvl|helloIntvl|nwT"
deadIntvl : 40
helloIntvl : 10
nwT : bcast
APIC# moquery -c ospfIfPol -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(ospfIfPol.name,"Custom_OSPF_Interface_Policy")' | egrep "deadIntvl|helloIntvl|nwT"
deadIntvl : 40
helloIntvl : 10
nwT : unspecified
[+] Whether it is bcast or unspecified the interface will show as Broadcast
BL-301# show ip ospf interface vlan 1 | egrep "Timer|Network"
State DR, Network type BROADCAST, cost 4
Timer intervals: Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
[+] Capture a single packet TCPDUMP for local BL OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.1 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.1 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 48
Router-ID 192.168.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
Designated Router 192.0.2.1
Neighbor List:
172.16.0.1
[+] Capture a single OSPF hello packet using TCPDUMP coming from external device OSPF IP
BL-301# tcpdump src host 192.0.2.50 -vv -e -i kpm_inb -c 1
192.0.2.50 > ospf-all.mcast.net: OSPFv2, Hello, length 44
Router-ID 172.16.0.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External]
Hello Timer 10s, Dead Timer 40s, Mask 255.255.255.0, Priority 1
From External device:
[+] Check OSPF interfaces con vrf
NX-OS# show ip int bri vrf 301-l3-abc1
IP Interface Status for VRF "301-l3-abc1"(21)
Interface IP Address Interface Status
Lo1001 110.1.0.1 protocol-up/link-up/admin-up
Eth1/2.1120 192.0.2.50 protocol-up/link-up/admin-up
[+] Check OSPF configuration by default Dead timer on NX-OS devices is 4 times hello interval
NX-OS# show run ospf all | section Ethernet1/2 | grep network
ip ospf network point-to-point
[+] Check OSPF interface advertized parameters
NX-OS# show ip ospf interface Ethernet1/2 | grep type
State P2P, Network type P2P, cost 1
Verification Command Cheatsheet
These commands were referenced throughout this document in order to troubleshoot the different scenarios.
|
Node |
Commands |
Purpose |
|
ACI Switch |
|
Check the neighborship relation on VRF |
|
|
Check OSPF interfaces associated with the VRF |
|
|
|
You can check the associated faults to the VRF |
|
|
|
Check all OSPF interface details associated with the VRF |
|
|
|
Check the OSPF interface configuration |
|
|
|
Check the IP applied on the external device from the ARP associated to the interface |
|
|
|
Live OSPF trace Decode for VRF |
|
|
|
Capture OSPF traffic to analyze on Wireshark |
|
|
|
Capture specific traffic of HOST in order to analyze on Wireshark |
|
|
|
Capture SRC and DST-specific traffic of HOST in order to analyze on Wireshark |
|
|
|
Capture a single inband control plane for and specific host |
|
|
ACI APIC |
|
Check the Authentication type configured |
|
|
Check L3out Path configuration |
|
|
|
Check Fault historical records for fault F1385 protocol-ospf-adjacency-down |
|
|
|
Check L3out for custom Associated OSPF Interface Policy |
|
|
|
Check for custom Associated OSPF Interface Policy details |
|
|
NXOS Switch |
|
Check OSPF interfaces con vrf |
|
|
Check OSPF configuration |
|
|
|
Check the OSPF interface advertised parameters |
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
15-May-2024
|
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Luis ContrerasTechnical Consulting Engineer
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback