AMD EPYC Processor Characterization for VDI on Cisco C245M8 and X215M8 with Omnissa Horizon White Paper
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid-cloud strategies, with Cisco® architecture, particularly the Cisco Unified Computing System™ (Cisco UCS®), at the core of on-premises infrastructure. The addition of the Cisco UCS X-Series, a modular, cloud-managed system, to the Cisco UCS portfolio has helped meet the needs of modern applications and enhance operational efficiency, agility, and scalability through a design that is both adaptable and future-ready. It combines the functionalities of both blade and rack servers, offering compute density, storage capacity, and expandability in a single system. The latest introduction of M8 servers, developed in collaboration with AMD, has achieved top performance results across several key categories, leading to faster application response times, improved user experiences, and the capability to handle the most demanding workloads for our customers.
This white paper provides data for the characterization of virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) workloads, including graphics-accelerated VDI solutions, on Cisco UCS M8 servers.
Key features of the Cisco UCS C245 M8 Rack Server:
● Processors: supports up to two 4th Gen or two 5th Gen AMD EPYC processors, providing high performance and flexibility for various workloads
● Memory: enhances performance for data-intensive applications with up to 6 TB of main memory with 24x 256 GB DDR5 6000 MT/s or DDR5 4800 MT/s DIMMs, depending on the CPU installed
● Storage: supports a versatile range of storage options, including hot-swappable small-form-factor (SFF) SAS/SATA and NVMe drives
● Management: is managed through Cisco Intersight®, including cloud-based lifecycle management
Key features of the Cisco UCS X215C M8 Compute Node:
● Processors: supports up to two 4th or 5th Gen AMD EPYC processors with up to 160 cores per processor, and up to 384 MB of Level 3 cache per CPU
● Memory: enhances performance for data-intensive applications with up to 6 TB of main memory, with 24x 256 GB DDR5 6000 MT/s or DDR5 4800 MT/s DIMMs, depending on the CPU installed
● Storage: supports a versatile range of storage options, including SSD/SATA and NVMe drives
● Management: is managed through Cisco Intersight, including cloud-based lifecycle management
VMware vSphere is a virtualization platform for holistically managing large collections of infrastructure (resources including CPUs, storage, and networking) as a seamless, versatile, and dynamic operating environment. Unlike traditional operating systems that manage individual machines, VMware vSphere aggregates the infrastructure of an entire data center to create a single powerhouse with resources that can be allocated quickly and dynamically to any application in need.
VMware vSphere 8.0 Update 2 has several new features and enhancements aimed at improving performance, compatibility, and security. Some of the updates are:
● vSphere Distributed Services Engine: now supports NVIDIA BlueField-2 DPUs for server designs from Fujitsu (Intel® Sapphire Rapids)
● vSphere Quick Boot: adds support for multiple servers, including models from Dell, Fujitsu, and Lenovo
● In-Band Error-Correcting Code (IB ECC) support: allows data-integrity checks on hardware platforms without ECC-type DDR memory
● Graphics and AI/ML workloads: provides enhanced support for Intel ATS-M
● Enhanced ESXi CPU scheduler: provides performance improvements for systems with high core count CPUs, such as Intel Sapphire Rapids
● Driver updates: includes updates for Broadcom, Mellanox, Marvell, and other drivers to enhance performance and support new hardware
● Virtual Hardware Version 21: supports up to 16 vGPU devices per VM and 256 vNVMe disks per VM
● Hot-Extend Shared vSphere Virtual Volumes disk: allows increasing disk size without downtime; this is beneficial for VM clustering solutions.
● USB 3.2 support: the virtual xHCI controller is now 20 Gbps–compatible.
● Read-only mode for virtual disks: improves performance by avoiding temporary redo logs
For more detailed information, you can refer to the VMware vSphere 8.0 Update 2 release notes.
The VMware vCenter Server provides unified management of all hosts and virtual machines from a single console and aggregates performance monitoring of clusters, hosts, and virtual machines. vCenter Server gives administrators deep insight into the status and configuration of computing clusters, hosts, virtual machines, storage, the guest OS, and other critical components of a virtual infrastructure. VMware vCenter manages the robust set of features available in a VMware vSphere environment.
The Omnissa Horizon 8 Version 2412 (Horizon 8 2412) includes significant updates to reflect the new Omnissa brand.
Here is a summary of the new features and enhancements in Omnissa Horizon 8 Version 2412:
● License activation: introduces a new licensing module following Omnissa’s divestiture from Broadcom. Users need to activate Horizon 8 with a new Omnissa license within 60 days to avoid restricted mode. The 15-day grace period for subscription licenses has been removed, requiring reactivation every 90 days unless you are using Omnissa Horizon Edge.
● Horizon Connection Server: enhancements include the capability to monitor schema master availability, improved NVIDIA Frame Rate Limiter settings, and support for dual IDP metadata files to ensure seamless authentication. Pool-management performance is improved, reducing task failures and outages.
● Horizon Console: administrators can now customize the admin console port and configure smart card authentication. Additional features include SAML authenticator encryption options and improved visibility of monitor settings in Horizon Blast sessions.
● Virtual desktops and applications: new features allow configuration of reconnection behavior for published applications and the capability to move applications between farms without recreating them. Administrators can terminate active sessions during VM restarts.
● Horizon Agent for Windows: support for Windows 11 2024 update and new metrics for Horizon Blast protocol are available. User-domain information is also collected for integration with Horizon Cloud Service next-gen.
● Horizon Agent for Linux: adds support for SUSE 15 SP6 and updates Debian support. Startup performance for Linux desktops is improved.
● Remote desktop features: screen sharing is now supported on Windows clients using Chrome and Edge C. Browser content redirection is possible from Linux desktops, and individual application sharing is enabled on Linux endpoints.
● Horizon 8 and Amazon WorkSpaces Core: supports FIPS 140-2-compliant algorithms and new features for manual farms and multi-session hosts with Windows Server 2019 and 2022. Administrators can manage power-optimized pools and update pool bundles.
● Omnissa Workspace ONE Experience Management: the Horizon Agent for Windows now sends client-side data from disconnected sessions to Experience Management for Horizon.
● Cloud-monitoring service users: users are advised to remain on the current version of Horizon Agent to retain telemetry in dashboards until migrating to Horizon Cloud Service next-gen.
Note: The Horizon 8 Version 2412 is NOT an ESB release.
For additional details, refer to the Omnissa documentation here.
Omnissa Horizon 8 test platform for AMD EPYC processors
This section provides an overview of the infrastructure setup for VDI deployment using Cisco UCS C245 M8 Rack Servers and Cisco UCS X215 M8 Compute Nodes with 4th Gen AMD EPYC CPUs for enterprise end-users with VMware vSphere 8.0 Update 2 and Omnissa Horizon 8 2412. This section does not cover the design details or configuration of components such as Cisco Nexus® and Cisco MDS switches and storage array systems because their designs and configurations conform to various Cisco Validated Designs for converged infrastructure and are covered widely elsewhere. This document focuses on the design elements and performance of the AMD platform for virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) deployments.
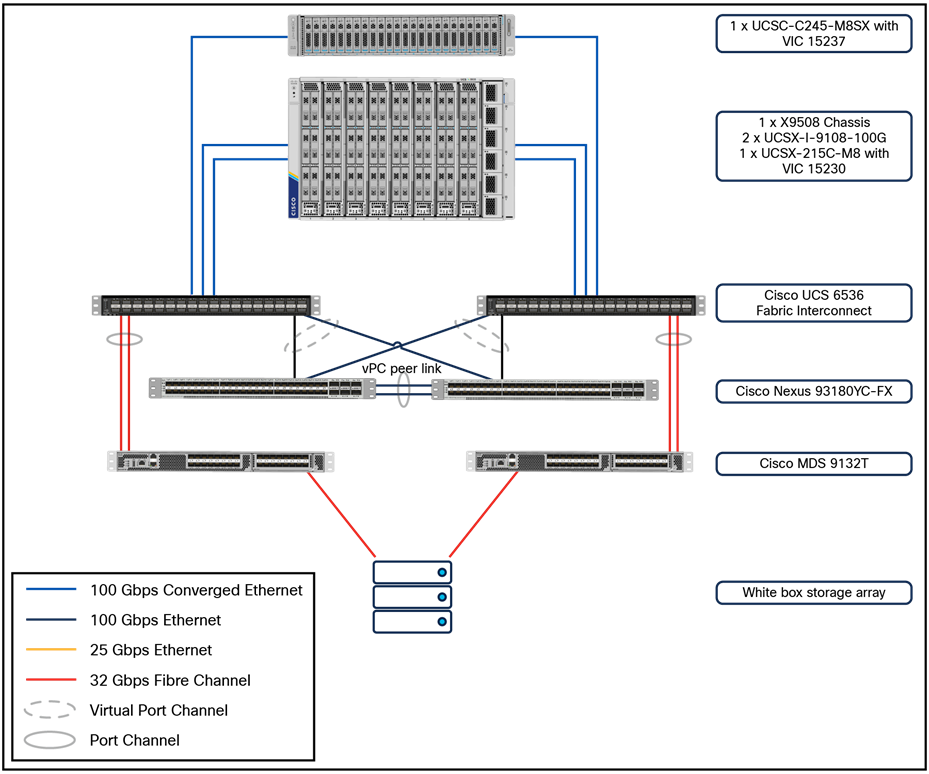
Physical architecture
Table 1 lists the software and hardware versions used in the solution described in this document.
Table 1. Software and firmware versions
| Component |
Version |
| Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect firmware |
4.3(5.240032) |
| Cisco UCS C245-M8SX server |
4.3(5.250001) |
| Cisco UCS VIC 15237 |
5.3(4.84) |
| Cisco UCS X215C-M8 blade |
5.3(0.250021) |
| Cisco UCS VIC 15230 |
5.3(4.86) |
| VMware vCenter Server Appliance |
8.0.2.00100 |
| VMware vSphere 8.0 U2 |
8.0.2, 22380479 |
Cisco UCS BIOS options for VDI workloads
A BIOS policy automates the configuration of BIOS settings on servers. Multiple BIOS policies that contain a specific grouping of BIOS settings, matching the needs of a server or servers, can be created.
Note: All BIOS tokens are not applicable to all servers. If unsupported tokens are pushed to a server, those tokens are ignored.
This section describes the options you should configure in the Cisco UCS M8 BIOS for VDI workloads.
Creating Cisco UCS BIOS policy
To create a server BIOS policy for VMware ESXi hosts, follow these steps:
1. Log in to Cisco Intersight with your Cisco ID and select admin role.
2. Choose Configure > Policies, and then click Create Policy.
3. Select BIOS, and then click Start.
4. On the General page, configure the following parameters:
◦ Select the Organization.
◦ Enter a name for your policy.
5. On the Policy Details page, configure the following BIOS policy options:
◦ Power and Performance -> CPPC: enabled
◦ Memory -> Numa Nodes per Socket: NPS4
6. Click Create.
Note: For more information, see Performance Tuning for Cisco UCS M8 Platforms with AMD EPYC 4th Gen and 5th Gen Processors.
Figure 2 shows the BIOS policy settings.
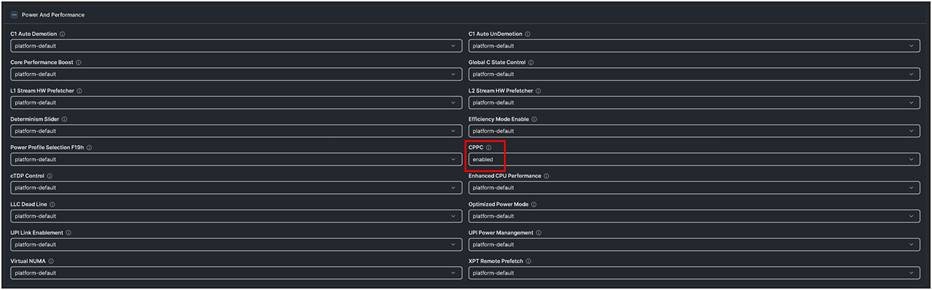
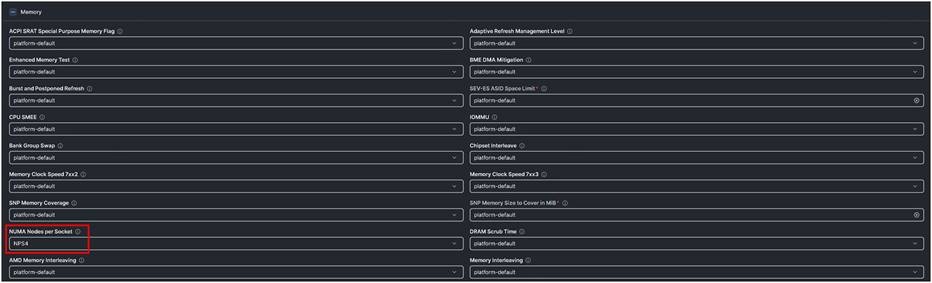
Cisco UCS M8 BIOS policy settings
The logical architecture used in the characterization of the Cisco UCS M8 servers is based on Cisco Validated Designs. This design is illustrated in Figure 3. For desktop virtualization, the deployment includes Omnissa Horizon 8 2412 running on VMware vSphere ESXi 8.0 U2.
This design is intended to provide a characterization for Omnissa Horizon 8 desktops on Cisco UCS M8 servers.
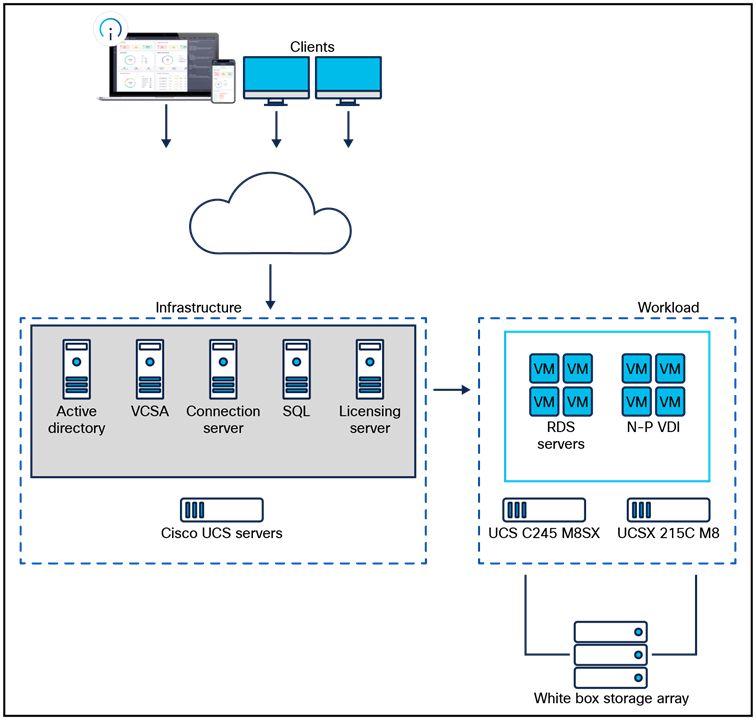
Logical architecture
Table 2. Software versions
| Component |
Version |
| Omnissa Horizon 8 2412 – Connection Server |
Release 8.14.0.13130026773 |
| Omnissa Horizon Agent 2412 |
Release 8.14.0.12994395200 |
| VMware Tools |
Release 12.3.0.22234872 |
Virtual machines must first be installed with the software components needed to build the golden images. Additionally, all available security patches for the Microsoft operating system and Microsoft Office should be installed.
The final step is the Omnissa Horizon Agent installation, then optimization with the Omnissa Horizon OS Optimization Tool (often referred to as OSOT).
Note: The images used contain the basic features needed to run the Login Enterprise workload.
The master target virtual machine was configured as outlined in Tables 3 and 4.
Table 3. Configuration of VDI virtual machines
| Configuration |
VDI virtual machines |
| Operating system |
Microsoft Windows 11 64-bit |
| Virtual CPU amount |
2 |
| Memory amount |
4-GB reserve for all guest memory |
| Network |
VMXNET3 |
| Virtual disk (vDisk) size |
96 GB |
| Additional software used for testing |
Microsoft Office LTSC Standard 2021 |
Table 4. Configuration of RDS virtual machines
| Configuration |
VDI virtual machines |
| Operating system |
Microsoft Windows Server 2022 64-bit |
| Virtual CPU amount |
4 |
| Memory amount |
24-GB reserve for all guest memory |
| Network |
VMXNET3 |
| Virtual disk (vDisk) size |
90 GB |
| Additional software used for testing |
Microsoft Office LTSC Standard 2021 |
It is essential to test the virtual desktops to ensure they fully meet the expected performance and accessibility standards.
One of the tools available for assessing virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) environments is Login Enterprise, developed by Login VSI. This industry-standard software simulates human-centric workloads to benchmark the capacity and performance of virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) solutions. Cisco Technical Marketing utilizes Login Enterprise to evaluate Cisco VDI architectures for Cisco Validated Designs (CVDs).
Login VSI helps organizations proactively manage the performance, cost, and capacity of their virtual desktops and applications wherever they reside – traditional, hybrid, or in the cloud. The Login Enterprise platform is 100 percent agentless and can be used in all major VDI and desktop-as-a-service (DaaS) environments, including Citrix, Omnissa (formerly the End-User Computing division of VMware), and Microsoft. With 360° proactive visibility, IT teams can plan and maintain successful digital workplaces with less cost, fewer disruptions, and lower risk. Founded in 2012, Login VSI is headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts, and Amsterdam, Netherlands. Visit www.loginvsi.com.
We used Login Enterprise to identify the maximum recommended workload for the AMD EPYC 4th Gen processors for VDI and RDSH knowledge workers (KWs):
● AMD EPYC 9554
VDI KW maximum recommended workload: 450 users
RDSH KW maximum recommended workload: 510 users
● AMD EPYC 9334
VDI KW maximum recommended workload: 230 users
RDSH KW maximum recommended workload: 256 users
The maximum recommended workload is used to plan for maintenance and failure scenarios.
Each customer’s environment and workloads are different. The density numbers shown here are starting points for your unique environment. They are not intended to be performance guarantees.
Below are the Login Enterprise Load Testing results for the VDI and RDSH maximum recommended workloads on specific Cisco servers.
Recommended workload of 450 VDI users on a Cisco UCS C245-M8SX server with a AMD EPYC 9554 64-Core Processor and 3 TB of DDR5 memory
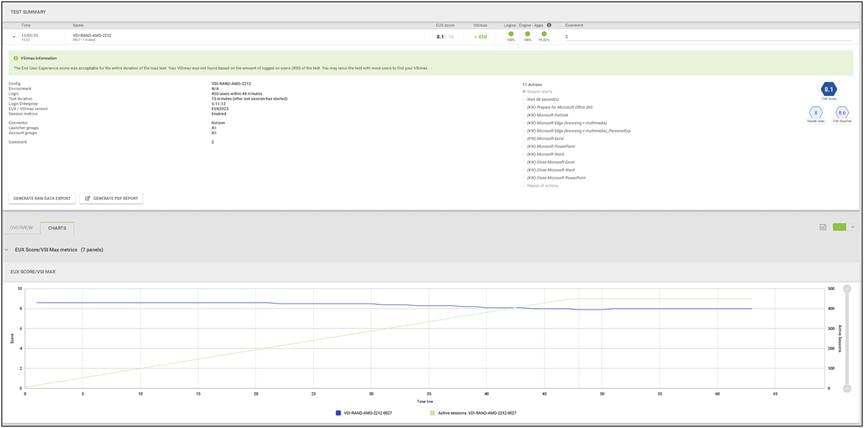
Load testing 450 VDI users with Login Enterprise - Test Summary
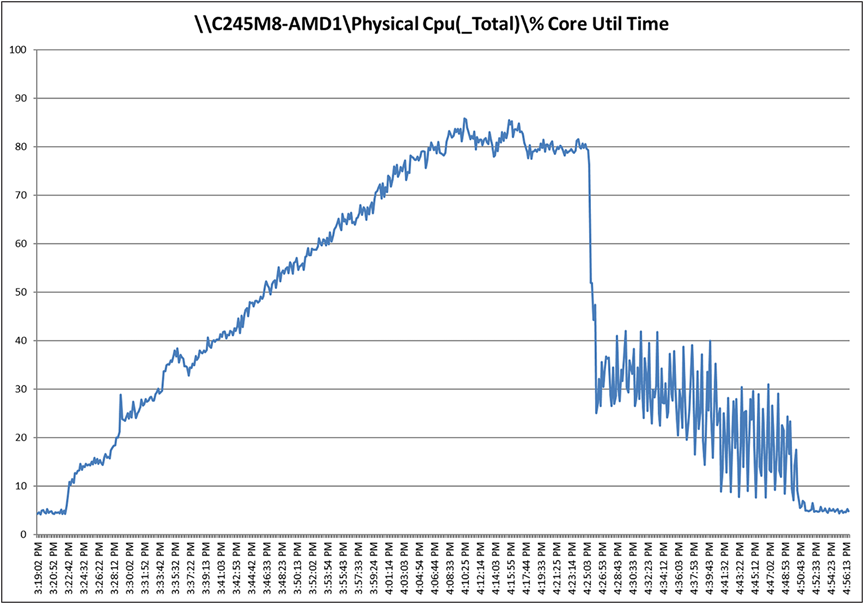
Cisco UCS C245 M8SX CPU utilization
Recommended workload of 510 RDS users on a Cisco UCS C245-M8SX server with a AMD EPYC 9554 64-Core Processor and 3 TB of DDR5 memory
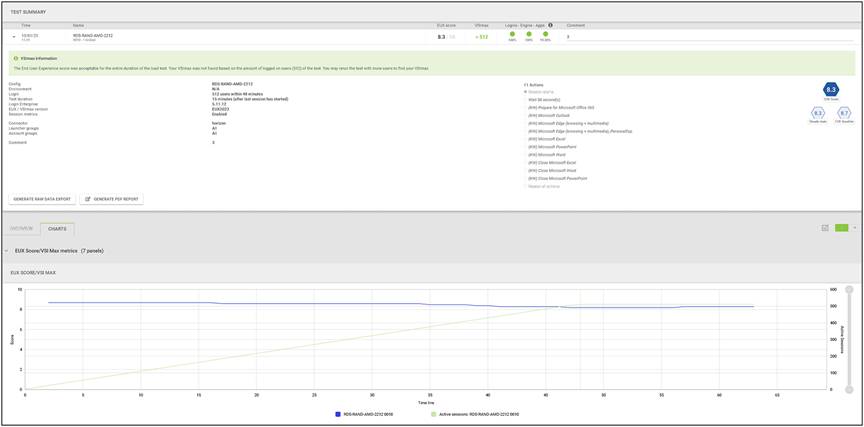
Load testing 510 RDS users with Login Enterprise - Test Summary
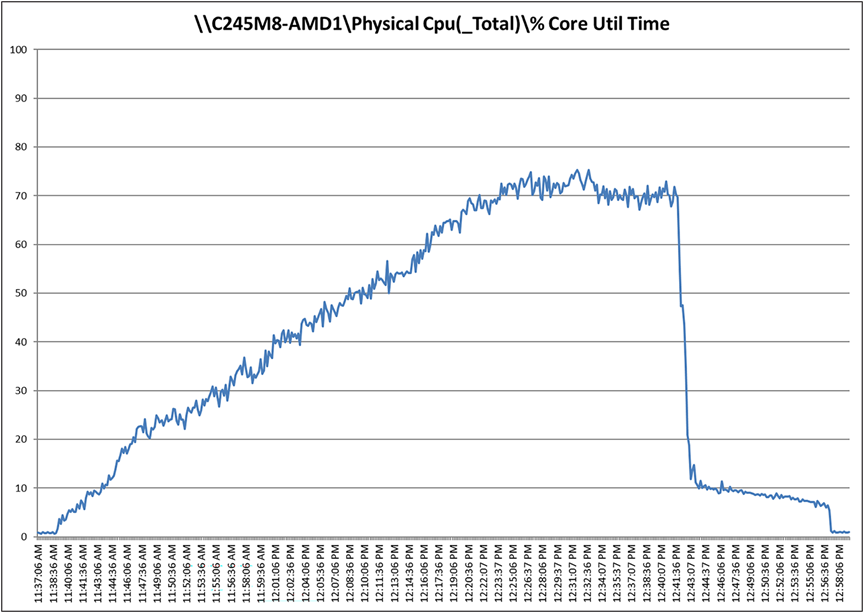
Cisco UCS C245 M8SX CPU utilization
Recommended workload of 230 VDI users on a Cisco UCSX 215C M8 server with a AMD EPYC 9334 32-Core Processor and 1.5 TB of DDR5 memory
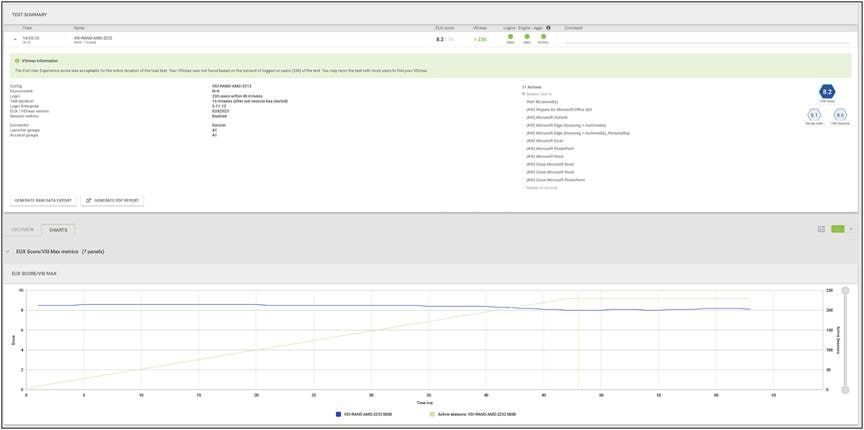
Load testing 230 VDI users with Login Enterprise - Test Summary
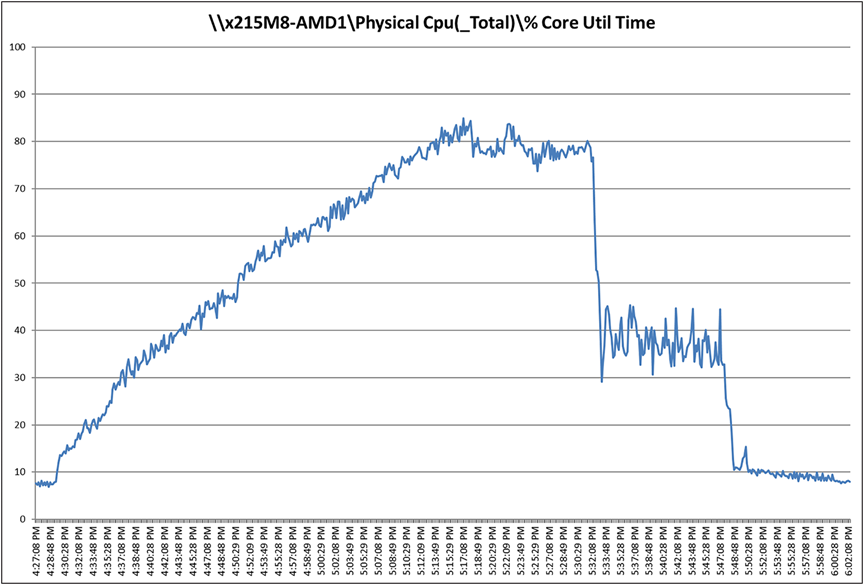
Cisco UCSX 215C M8 CPU utilization
Recommended workload of 256 RDS users on a Cisco UCSX 215C M8 server with a AMD EPYC 9334 32-Core Processor and 1.5 TB of DDR5 memory
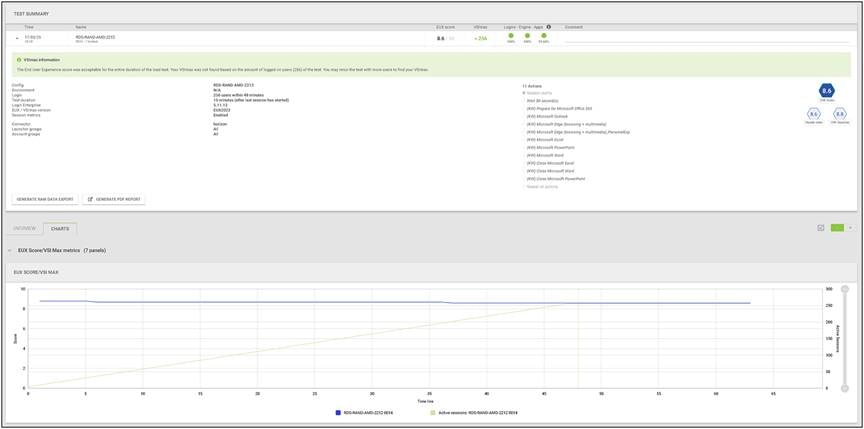
Load testing 256 RDS users with Login Enterprise - Test Summary
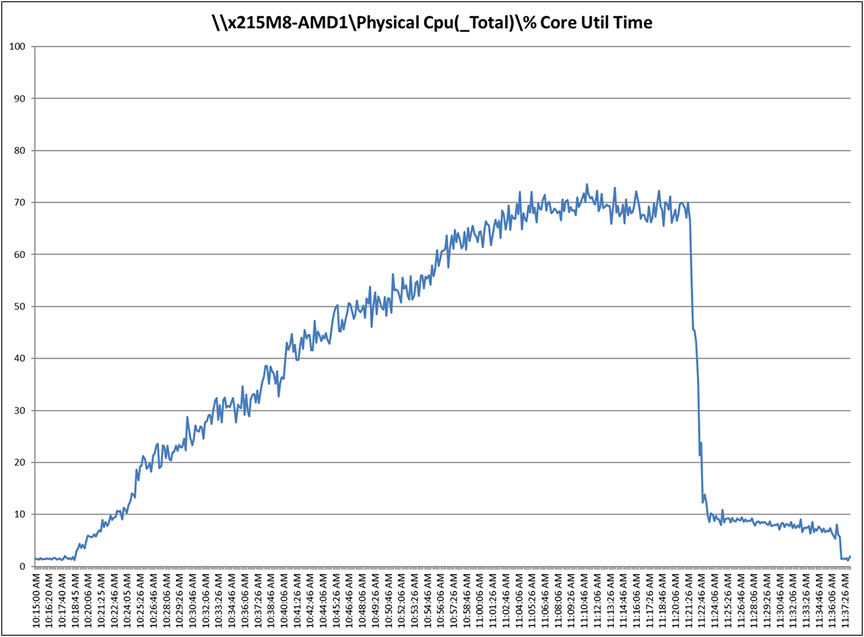
Cisco UCSX 215C M8 CPU utilization
For graphics-intensive workloads and enhanced-experience Windows 11 environments, you can utilize GPUs specifically designed for these purposes. Cisco UCS M8 servers support popular NVIDIA GPUs such as the NVIDIA A16, NVIDIA L40, and NVIDIA L4, which are commonly used in virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) setting.
Login Enterprise provides tools that enable you to gauge the performance of graphics-enhanced workloads effectively. The figures below show the results of a graphics-intensive knowledge worker workload using a 2Q vGPU profile on a single Cisco UCS C245 M8 Rack Server equipped with a single GPU.
NVIDIA L4 GPU test
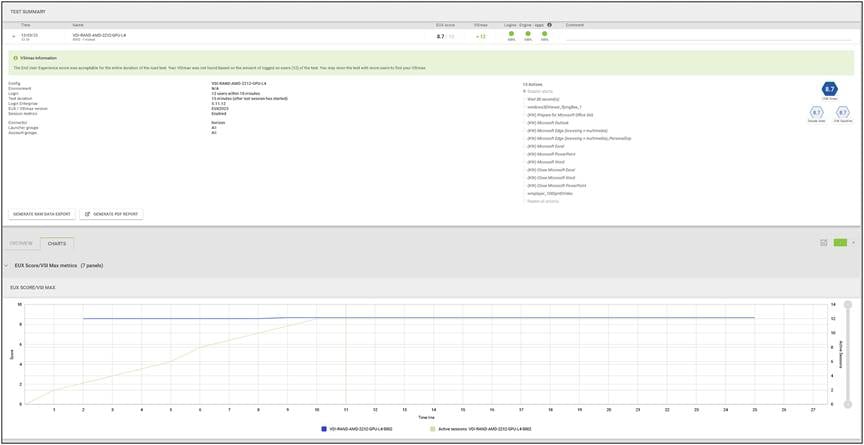
Load testing with Login Enterprise 12 users with NVIDIA L4-2Q vGPU profile - Test Summary
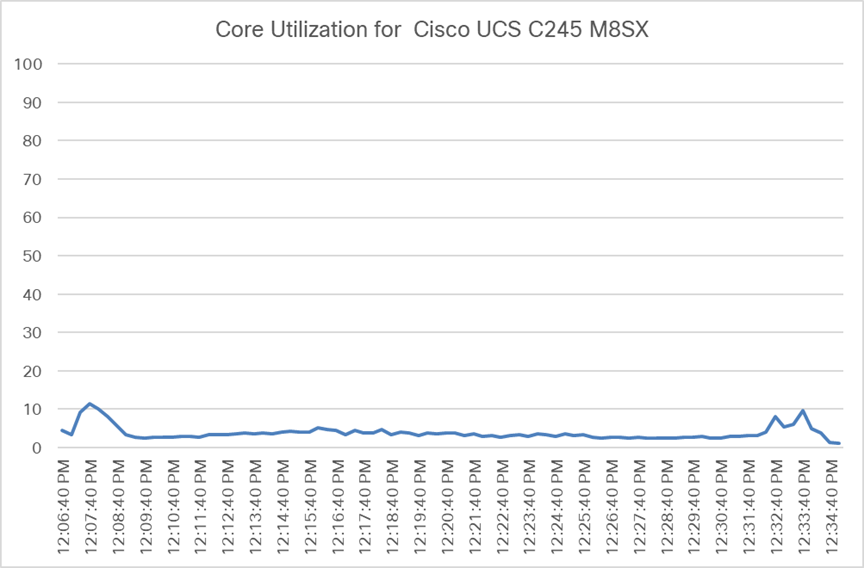
Load testing with Login Enterprise 12 users with NVIDIA L4-2Q vGPU profile - Cisco UCS C245 M8SX CPU core utilization
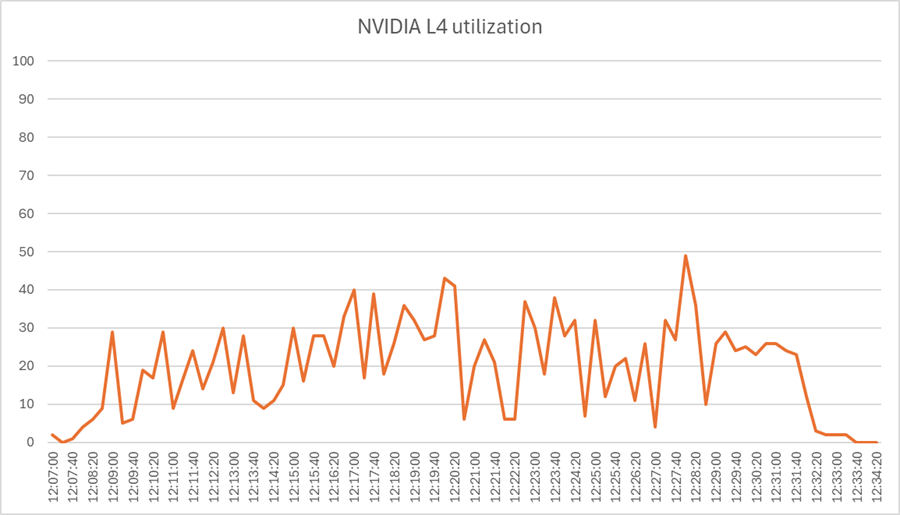
Load testing with Login Enterprise 12 users with NVIDIA L4-2Q vGPU profile - Cisco UCS C245 M8SX NVIDIA L4 utilization
NVIDA L40 GPU test
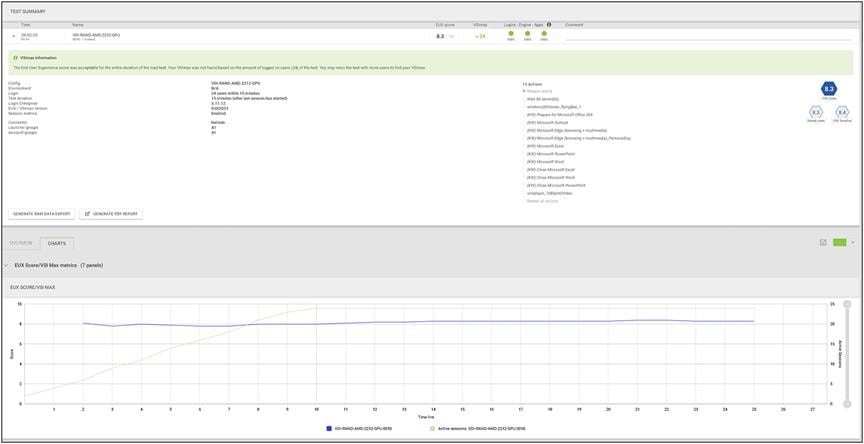
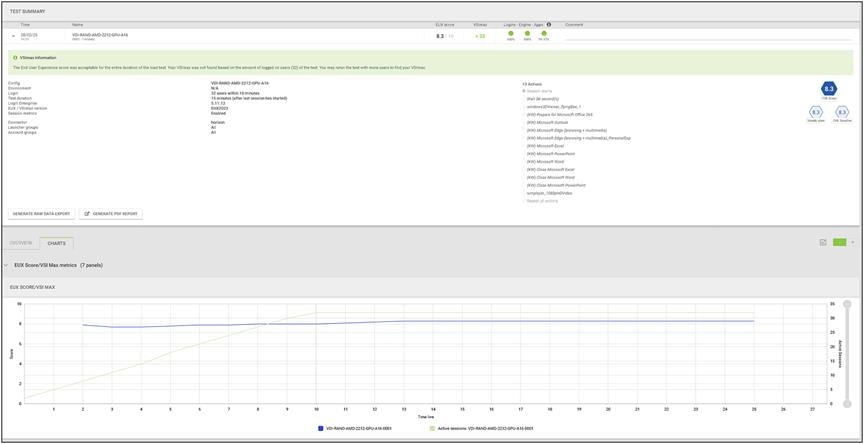
Load testing with Login Enterprise 24 users with NVIDIA L40-2Q vGPU profile - Test Summary
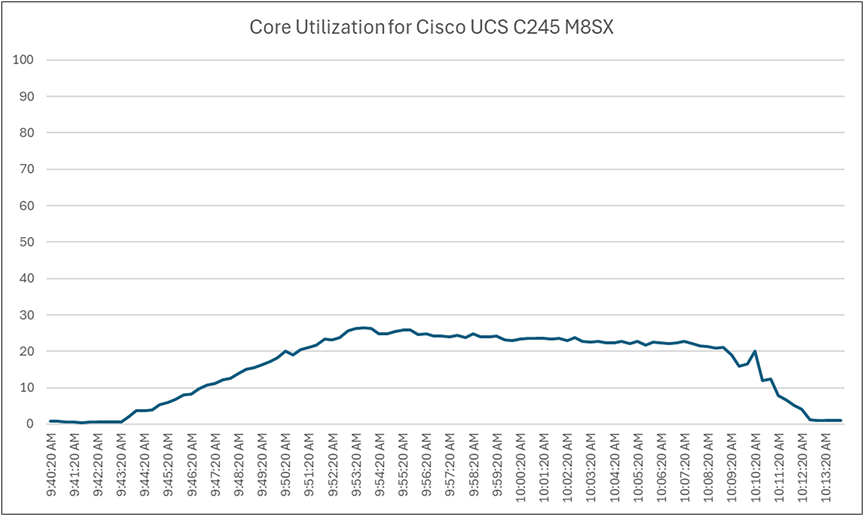
Load testing with Login Enterprise 24 users with NVIDIA L40-2Q vGPU profile - Cisco UCS C245 M8SX CPU core utilization
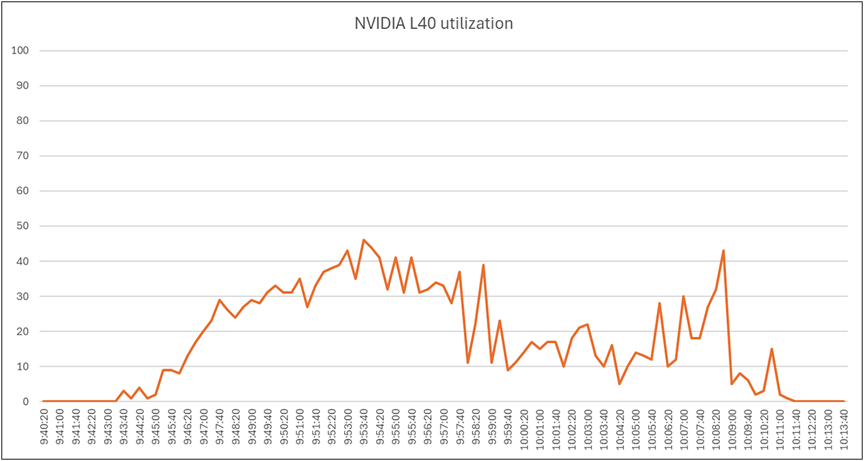
Load testing with Login Enterprise 24 users with NVIDIA L40-2Q vGPU profile - Cisco UCS C245 M8SX NVIDIA L40 utilization
NVIDIA A16 GPU test
Load testing with Login Enterprise 32 users with NVIDIA A16- Q2 vGPU profile - Test Summary
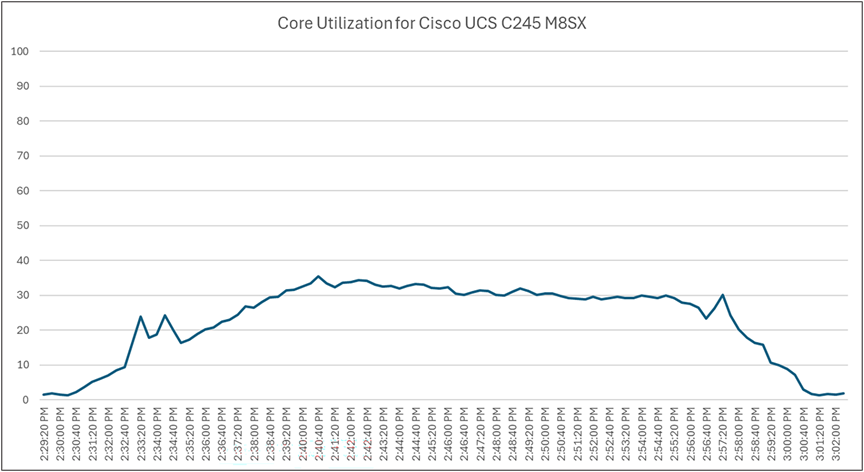
Load testing with Login Enterprise 32 users with NVIDIA A16-2Q vGPU profile - Cisco UCS C245 M8SX CPU core utilization
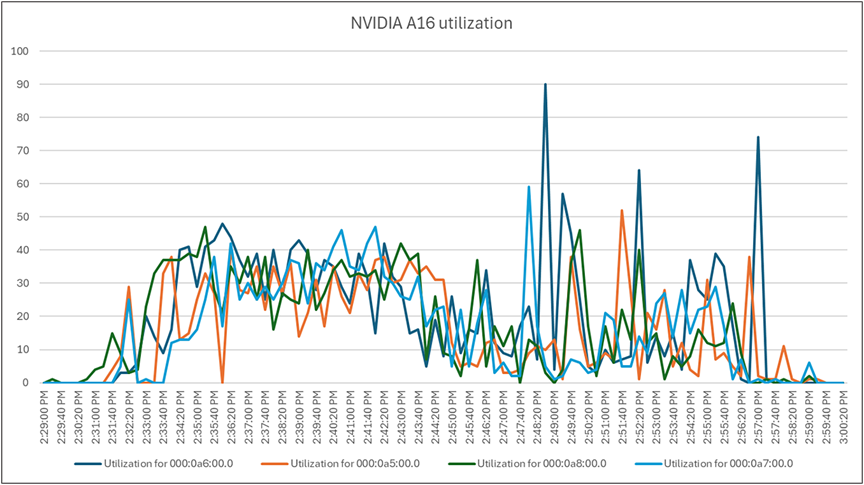
Load testing with Login Enterprise 32 users with NVIDIA A16-2Q vGPU profile - Cisco UCS C245 M8SX NVIDIA A16 utilization
Another tool widely used to evaluate the performance of workstations and graphics hardware by simulating real-world applications in areas such as digital content creation and visualization is SPECviewperf.
SPECviewperf is a benchmark that measures the 3D graphics performance of systems running under the OpenGL and DirectX APIs. It uses workloads, known as viewsets, which represent graphics content and behavior from actual applications. The benchmark includes viewsets for applications such as Autodesk 3ds Max, CATIA, Creo, Energy (based on rendering techniques used by the open-source OpendTect seismic visualization application), Autodesk Maya, Medical (demonstrating “slice rendering” and “rayscaling” using the Tuvok visualization library for rendering) , Siemens NX, and SolidWorks. Visit SPECviewperf benchmark.
The figures below show examples of the 3dsmax -07 viewset being run on virtual machines running Windows 11 with 4vCPUs and 16 GB of memory on supported graphic cards with a 4Q vGPU profile.
Note: No benchmark specific configurations were applied to virtual machines and/or hypervisor hosts.
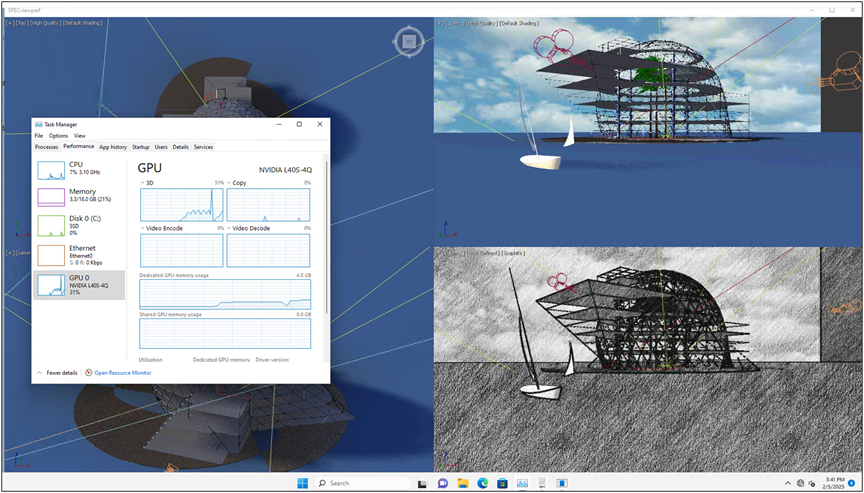
3dsmax viewset running on Windows 11virtual machine with 4vCPUs, 16 GB of memory and NVIDIA L40-4Q vGPU profile
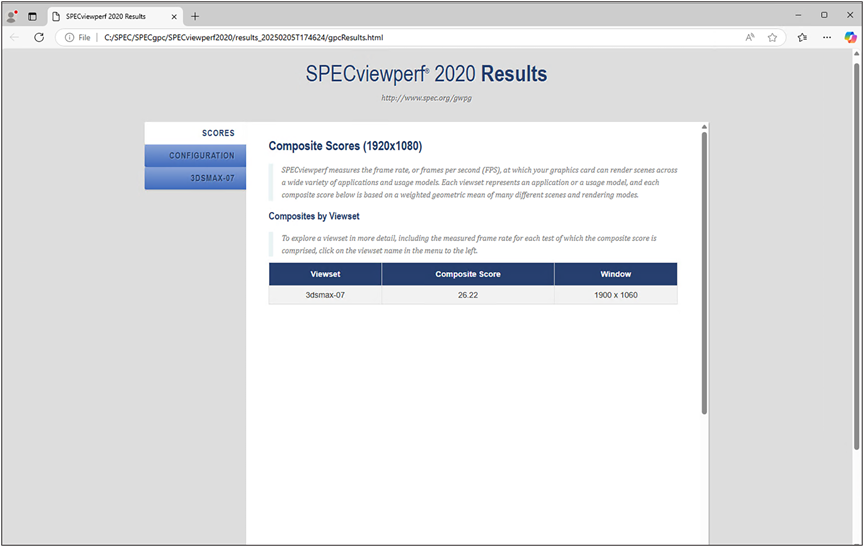
SPECviewperf 3dsmax result on Windows 11virtual machine with 4vCPUs, 16 GB of memory and NVIDIA L40-4Q vGPU profile
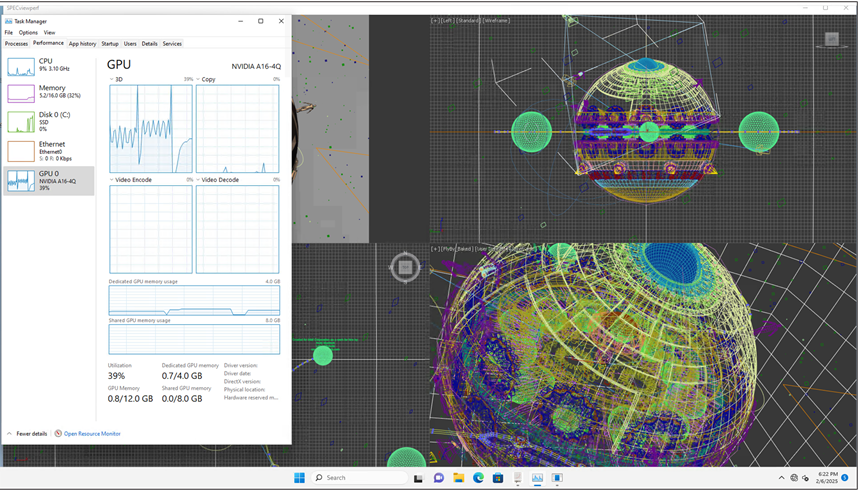
3dsmax viewset running on Windows 11virtual machine with 4vCPUs, 16 GB of memory and NVIDIA A16-4Q vGPU profile
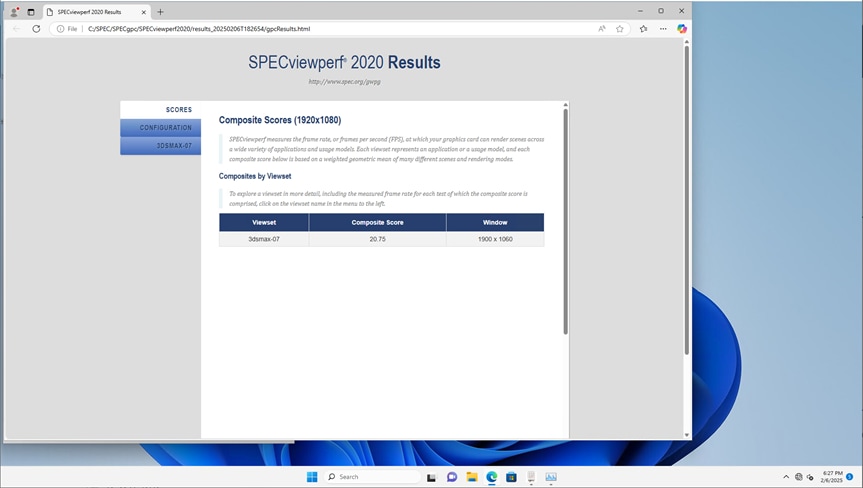
SPECviewperf 3dsmax result on Windows 11virtual machine with 4vCPUs, 16 GB of memory and NVIDIA A16-4Q vGPU profile
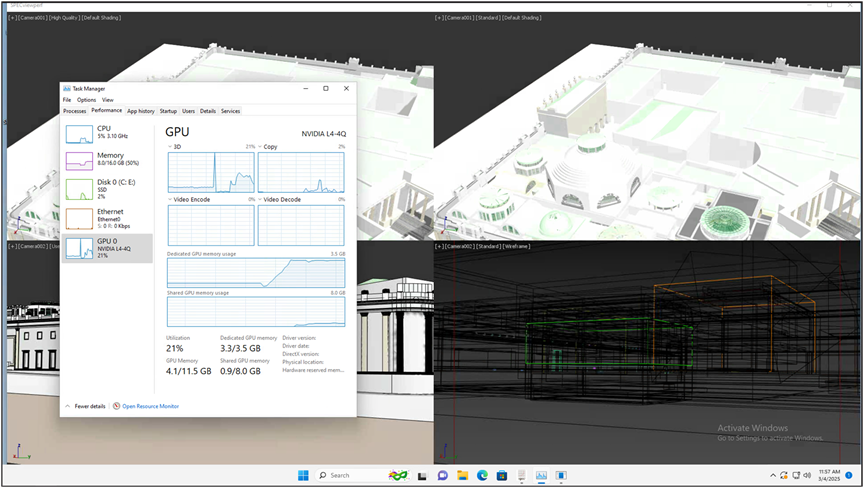
3dsmax viewset running on Windows 11virtual machine with 4vCPUs, 16 GB of memory and NVIDIA L4-4Q vGPU profile
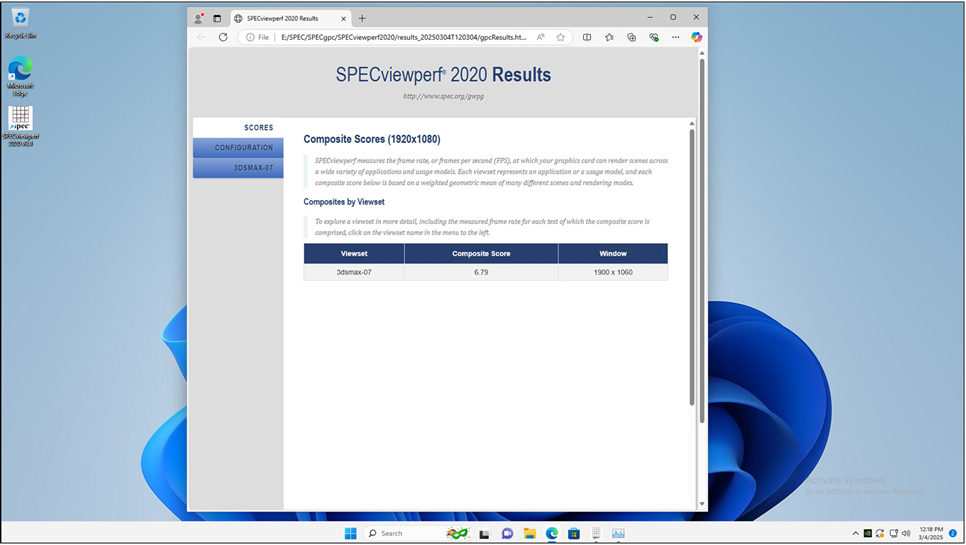
SPECviewperf 3dsmax result on Windows 11virtual machine with 4vCPUs, 16 GB of memory and NVIDIA L4-4Q vGPU profile
The Cisco UCS M8 compute platform is designed to excel at running virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) workloads. Its efficient architecture ensures that CPU performance isn't a limiting factor, while providing plenty of memory to support a large number of users. With support for powerful AMD EPYC Gen 4 and Gen 5 processors and the ability to integrate advanced GPUs, the M8 handles users running graphics-intensive tasks with ease. This combination of strong processing power and effective resource management makes the Cisco UCS M8 an excellent option for businesses seeking reliable and high-performance VDI solutions with Omnissa Horizon 8.
Vadim Lebedev, Technical Marketing Engineer, Cisco Systems, Inc.