- Index
- Preface
- Product Overview
-
- Configuring Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring VLANs
- Configuring Private VLANs
- Configuring Rapid PVST+
- Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree
- Configuring STP Extensions
- Configuring Port Channels
- Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces
- Configuring the MAC Address Table
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Configuring Traffic Storm Control
-
- Configuring Fibre Channel Interfaces
- Configuring Domain Parameters
- Configuring N-Port Virtualization
- Configuring VSAN Trunking
- Configuring SAN PortChannels
- Configuring and Managing VSANs
- Configuring and Managing Zones
- Distributing Device Alias Services
- Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
- Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
- Discovering SCSI Targets
- Advanced Features and Concepts
- Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Fabric Binding
- Configuring Fabric Configuration Servers
- Configuring Port Tracking
- Information About TACACS+
- Prerequisites for TACACS+
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Configuring TACACS+
- TACACS+ Server Configuration Process
- Enabling TACACS+
- Configuring TACACS+ Server Hosts
- Configuring Global Preshared Keys
- Configuring TACACS+ Server Preshared Keys
- Configuring TACACS+ Server Groups
- Specifying a TACACS+ Server at Login
- Configuring the Global TACACS+ Timeout Interval
- Configuring the Timeout Interval for a Server
- Configuring TCP Ports
- Configuring Periodic TACACS+ Server Monitoring
- Configuring the Dead-Time Interval
- Manually Monitoring TACACS+ Servers or Groups
- Disabling TACACS+
- Displaying TACACS+ Statistics
- Verifying TACACS+ Configuration
- Example TACACS+ Configuration
- Default Settings
Configuring TACACS+
This chapter describes how to configure the Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+) protocol on Nexus 5000 Series switches.
Information About TACACS+
The TACACS+ security protocol provides centralized validation of users attempting to gain access to a Nexus 5000 Series switch. TACACS+ services are maintained in a database on a TACACS+ daemon typically running on a UNIX or Windows NT workstation. You must have access to and must configure a TACACS+ server before the configured TACACS+ features on your Nexus 5000 Series switch are available.
TACACS+ provides for separate authentication, authorization, and accounting facilities. TACACS+ allows for a single access control server (the TACACS+ daemon) to provide each service (authentication, authorization, and accounting) independently. Each service is associated with its own database to take advantage of other services available on that server or on the network, depending on the capabilities of the daemon.
The TACACS+ client/server protocol uses TCP (TCP port 49) for transport requirements. Nexus 5000 Series switches provide centralized authentication using the TACACS+ protocol.
This section includes the following topics:
- TACACS+ Advantages
- User Login with TACACS+
- Default TACACS+ Server Encryption Type and Preshared Key
- TACACS+ Server Monitoring
TACACS+ Advantages
TACACS+ has the following advantages over RADIUS authentication:
- Provides independent AAA facilities. For example, the Nexus 5000 Series switch can authorize access without authenticating.
- Uses the TCP transport protocol to send data between the AAA client and server, making reliable transfers with a connection-oriented protocol.
- Encrypts the entire protocol payload between the switch and the AAA server to ensure higher data confidentiality. The RADIUS protocol only encrypts passwords.
User Login with TACACS+
When a user attempts a Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) login to a Nexus 5000 Series switch using TACACS+, the following actions occur:
1.![]() When the Nexus 5000 Series switch establishes a connection, it contacts the TACACS+ daemon to obtain the username and password.
When the Nexus 5000 Series switch establishes a connection, it contacts the TACACS+ daemon to obtain the username and password.

Note![]() TACACS+ allows an arbitrary conversation between the daemon and the user until the daemon receives enough information to authenticate the user. This action is usually done by prompting for a username and password combination, but may include prompts for other items, such as the user’s mother’s maiden name.
TACACS+ allows an arbitrary conversation between the daemon and the user until the daemon receives enough information to authenticate the user. This action is usually done by prompting for a username and password combination, but may include prompts for other items, such as the user’s mother’s maiden name.
2.![]() The Nexus 5000 Series switch will receive one of the following responses from the TACACS+ daemon:
The Nexus 5000 Series switch will receive one of the following responses from the TACACS+ daemon:
- ACCEPT—User authentication succeeds and service begins. If the Nexus 5000 Series switch requires user authorization, authorization begins.
- REJECT—User authentication failed. The TACACS+ daemon either denies further access to the user or prompts the user to retry the login sequence.
- ERROR—An error occurred at some time during authentication dither at the daemon or in the network connection between the daemon and the Nexus 5000 Series switch. If the Nexus 5000 Series switch receives an ERROR response, the Nexus 5000 Series switch tries to use an alternative method for authenticating the user.
The user also undergoes an additional authorization phase, if authorization has been enabled on the Nexus 5000 Series switch. Users must first successfully complete TACACS+ authentication before proceeding to TACACS+ authorization.
3.![]() If TACACS+ authorization is required, the Nexus 5000 Series switch again contacts the TACACS+ daemon and it returns an ACCEPT or REJECT authorization response. An ACCEPT response contains attributes that are used to direct the EXEC or NETWORK session for that user and determines the services that the user can access.
If TACACS+ authorization is required, the Nexus 5000 Series switch again contacts the TACACS+ daemon and it returns an ACCEPT or REJECT authorization response. An ACCEPT response contains attributes that are used to direct the EXEC or NETWORK session for that user and determines the services that the user can access.
Default TACACS+ Server Encryption Type and Preshared Key
You must configure the TACACS+ preshared key to authenticate the switch to the TACACS+ server. A preshared key is a secret text string shared between the Nexus 5000 Series switch and the TACACS+ server host. The length of the key is restricted to 63 characters and can include any printable ASCII characters (white spaces are not allowed). You can configure a global preshared secret key for all TACACS+ server configurations on the Nexus 5000 Series switch to use.
You can override the global preshared key assignment by explicitly using the key option when configuring an individual TACACS+ server.
TACACS+ Server Monitoring
An unresponsive TACACS+ server can delay the processing of AAA requests. A Nexus 5000 Series switch can periodically monitor an TACACS+ server to check whether it is responding (or alive) to save time in processing AAA requests. The Nexus 5000 Series switch marks unresponsive TACACS+ servers as dead and does not send AAA requests to any dead TACACS+ servers. A Nexus 5000 Series switch periodically monitors dead TACACS+ servers and brings them to the alive state once they are responding. This process verifies that a TACACS+ server is in a working state before real AAA requests are sent its way. Whenever an TACACS+ server changes to the dead or alive state, a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) trap is generated and the Nexus 5000 Series switch displays an error message that a failure is taking place before it can impact performance. See Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 TACACS+ Server States
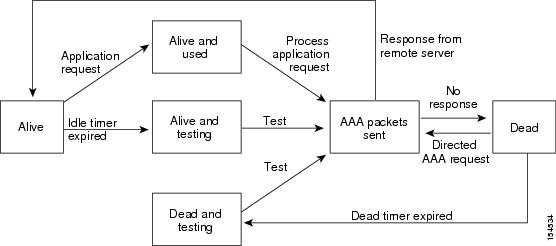

Note![]() The monitoring interval for alive servers and dead servers are different and can be configured by the user. The TACACS+ server monitoring is performed by sending a test authentication request to the TACACS+ server.
The monitoring interval for alive servers and dead servers are different and can be configured by the user. The TACACS+ server monitoring is performed by sending a test authentication request to the TACACS+ server.
Prerequisites for TACACS+
Guidelines and Limitations
Configuring TACACS+
This section includes the following topics:
- TACACS+ Server Configuration Process
- Enabling TACACS+
- Configuring TACACS+ Server Hosts
- Configuring Global Preshared Keys
- Configuring TACACS+ Server Preshared Keys
- Configuring TACACS+ Server Groups
- Specifying a TACACS+ Server at Login
- Configuring the Global TACACS+ Timeout Interval
- Configuring the Timeout Interval for a Server
- Configuring TCP Ports
- Configuring Periodic TACACS+ Server Monitoring
- Configuring the Dead-Time Interval
- Manually Monitoring TACACS+ Servers or Groups
- Disabling TACACS+

Note![]() If you are familiar with the Cisco IOS CLI, be aware that the Cisco NX-OS commands for this feature might differ from the Cisco IOS commands that you would use.
If you are familiar with the Cisco IOS CLI, be aware that the Cisco NX-OS commands for this feature might differ from the Cisco IOS commands that you would use.
TACACS+ Server Configuration Process
To configure TACACS+ servers, perform this task:
See the “Enabling TACACS+” section.
Step 2![]() Establish the TACACS+ server connections to the Nexus 5000 Series switch.
Establish the TACACS+ server connections to the Nexus 5000 Series switch.
See the “Configuring TACACS+ Server Hosts” section.
Step 3![]() Configure the preshared secret keys for the TACACS+ servers.
Configure the preshared secret keys for the TACACS+ servers.
See the “Configuring Global Preshared Keys” section and the “Configuring TACACS+ Server Preshared Keys” section.
Step 4![]() If needed, configure TACACS+ server groups with subsets of the TACACS+ servers for AAA authentication methods.
If needed, configure TACACS+ server groups with subsets of the TACACS+ servers for AAA authentication methods.
See the “Configuring TACACS+ Server Groups” section and the “Configuring AAA” section.
Step 5![]() If needed, configure any of the following optional parameters:
If needed, configure any of the following optional parameters:
See the “Configuring the Global TACACS+ Timeout Interval” section.
See the “Configuring TCP Ports” section.
Step 6![]() If needed, configure periodic TACACS+ server monitoring.
If needed, configure periodic TACACS+ server monitoring.
See the “Configuring Periodic TACACS+ Server Monitoring” section.
Enabling TACACS+
By default, the TACACS+ feature is disabled on the Nexus 5000 Series switch. To explicitly enable the TACACS+ feature to access the configuration and verification commands for authentication, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
(Optional) Copies the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
Configuring TACACS+ Server Hosts
To access a remote TACACS+ server, you must configure the IPv4 or IPv6 address or the hostname for the TACACS+ server on the Nexus 5000 Series switch. All TACACS+ server hosts are added to the default TACACS+ server group.You can configure up to 64 TACACS+ servers.
If a preshared key is not configured for a configured TACACS+ server, a warning message is issued if a global key is not configured. If a TACACS+ server key is not configured, the global key (if configured) is used for that server (see the “Configuring Global Preshared Keys” section and the “Configuring TACACS+ Server Preshared Keys” section).
Before you configure TACACS+ server hosts, you should do the following:
- Enable TACACS+ (see the “Enabling TACACS+” section).
- Obtain the IPv4 or IPv6addresses or the hostnames for the remote TACACS+ servers.
To configure TACACS+ server hosts, perform this task:
Configuring Global Preshared Keys
You can configure preshared keys at the global level for all servers used by the Nexus 5000 Series switch. A preshared key is a shared secret text string between the Nexus 5000 Series switch and the TACACS+ server hosts.
Before you configure preshared keys, you should do the following:
- Enable TACACS+ (see the “Enabling TACACS+” section).
- Obtain the preshared key values for the remote TACACS+ servers.
To configure global preshared keys, perform this task:
The following example shows how to configure global preshared keys:
Configuring TACACS+ Server Preshared Keys
You can configure preshared keys for a TACACS+ server. A preshared key is a shared secret text string between the Nexus 5000 Series switch and the TACACS+ server host.
To configure the TACACS+ preshared keys, perform this task:
The following example shows how to configure the TACACS+ preshared keys:
Configuring TACACS+ Server Groups
You can specify one or more remote AAA servers to authenticate users using server groups. All members of a group must belong to the TACACS+ protocol. The servers are tried in the same order in which you configure them.
You can configure these server groups at any time but they only take effect when you apply them to an AAA service. For information on AAA services, see the “Remote AAA Services” section.
To configure TACACS+ server groups, perform this task:
The following example shows how to configure a TACACS+ server group:
switch(config)# aaa group server tacacs+ TacServer
switch(config-tacacs+)# server 10.10.2.2
switch(config-tacacs+)# deadtime 30
Specifying a TACACS+ Server at Login
You can configure the switch to allow the user to specify which TACACS+ server to send the authenticate request by enabling the directed-request option. By default, a Nexus 5000 Series switch forwards an authentication request based on the default AAA authentication method. If you enable this option, the user can log in as username@hostname, where hostname is the name of a configured RADIUS server.

Note![]() User specified logins are only supported for Telnet sessions.
User specified logins are only supported for Telnet sessions.
To specify a TACACS+ server at login, perform this task:
Configuring the Global TACACS+ Timeout Interval
You can set a global timeout interval that the Nexus 5000 Series switch waits for responses from all TACACS+ servers before declaring a timeout failure. The timeout interval determines how long the Nexus 5000 Series switch waits for responses from TACACS+ servers before declaring a timeout failure.
Configuring the Timeout Interval for a Server
You can set a timeout interval that the Nexus 5000 Series switch waits for responses from a TACACS+ server before declaring a timeout failure. The timeout interval determines how long the Nexus 5000 Series switch waits for responses from a TACACS+ server before declaring a timeout failure.
To configure the timeout interval for a server, perform this task:
Configuring TCP Ports
You can configure another TCP port for the TACACS+ servers if there are conflicts with another application. By default, Nexus 5000 Series switches use port 49 for all TACACS+ requests.
To configure TCP ports, perform this task:
The following example shows how to configure TCP ports:
Configuring Periodic TACACS+ Server Monitoring
You can monitor the availability of TACACS+ servers. These parameters include the username and password to use for the server and an idle timer. The idle timer specifies the interval in which a TACACS+ server receives no requests before the Nexus 5000 Series switch sends out a test packet.You can configure this option to test servers periodically, or you can run a one-time only test.

Note![]() To protect network security, we recommend that you use a user name that is not the same as an existing username in the TACACS+ database.
To protect network security, we recommend that you use a user name that is not the same as an existing username in the TACACS+ database.
The test idle timer specifies the interval in which a TACACS+ server receives no requests before the Nexus 5000 Series switch sends out a test packet.

Note![]() The default idle timer value is 0 minutes. When the idle time interval is 0 minutes, periodic TACACS+ server monitoring is not performed.
The default idle timer value is 0 minutes. When the idle time interval is 0 minutes, periodic TACACS+ server monitoring is not performed.
To configure periodic TACACS+ server monitoring, perform this task:
The following example shows how to configure periodic TACACS+ server monitoring:
switch(config)# tacacs-server host 10.10.1.1 test username user1 password Ur2Gd2BH idle-time 3
Configuring the Dead-Time Interval
You can configure the dead-time interval for all TACACS+ servers. The dead-time interval specifies the time that the Nexus 5000 Series switch waits, after declaring a TACACS+ server is dead, before sending out a test packet to determine if the server is now alive.

Note![]() When the dead-timer interval is 0 minutes, TACACS+ servers are not marked as dead even if they are not responding. You can configure the dead-timer per group (see the “Configuring TACACS+ Server Groups” section).
When the dead-timer interval is 0 minutes, TACACS+ servers are not marked as dead even if they are not responding. You can configure the dead-timer per group (see the “Configuring TACACS+ Server Groups” section).
To configure the dead-time interval for all TACACS+ servers, perform this task:
Manually Monitoring TACACS+ Servers or Groups
To manually issue a test message to a TACACS+ server or to a server group, perform this task:
The following example shows how to manually issue a test message:
Disabling TACACS+

To disable TACACS+, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
(Optional) Copies the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
Displaying TACACS+ Statistics
To display the statistics the Nexus 5000 Series switch maintains for TACACS+ activity, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
switch# show tacacs-server statistics { hostname | ipv4-address | ipv6-address } |
For detailed information about the fields in the output from this command, see the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Command Reference.
Verifying TACACS+ Configuration
To display TACACS+ configuration information, perform one of the following tasks:
Example TACACS+ Configuration
The following example shows how to configure TACACS+:
Default Settings
Table 1-1 lists the default settings for TACACS+ parameters.
|
|
|
|---|---|
 Feedback
Feedback