
Table Of Contents
Basic Troubleshooting RPR-IEEE for the Uplink Card
Using the show controller rpr-ieee Command
Using the show controllers rpr-ieee 1/1 transceiver Command
Using the show rpr-ieee topology Command
Using the show rpr-ieee protection Command
Basic Troubleshooting SRP for the Uplink Card
Using the show controller srp Command
Using the show srp topology Command
Using the show srp ips Command
Basic Troubleshooting Ethernet for the Access Card
Verifying Interface Configuration
FastEthernet/GigabitEthernet Is up
Cleaning the Fiber-Optic Connections
Troubleshooting
This section contains basic troubleshooting guidance for the Cisco 10720 Internet Router and components.
•
Basic Troubleshooting RPR-IEEE for the Uplink Card
•
Basic Troubleshooting SRP for the Uplink Card
•
Basic Troubleshooting Ethernet for the Access Card
Basic Troubleshooting RPR-IEEE for the Uplink Card
This section provides basic troubleshooting guidelines for RPR-IEEE on the RPR/SRP uplink card. For additional information about RPR-IEEE configurations, refer to the Cisco IOS Software Configuration for the Cisco 10720 Internet Router publication. For additional Cisco IEEE 802.17 related documentation, see the "Related Documentation" section on page xix.
The following sections present information on show commands, verification steps, and alarm messages:
•
Using the show controller rpr-ieee Command
•
Using the show rpr-ieee topology Command
•
Using the show rpr-ieee protection Command
Using the show controller rpr-ieee Command
Verify the following using the show controller rpr-ieee command:
•
RX optics readout values are within specifications. For example: RX readout values: -11 dBm - Within specifications, RX readout values: -15 dBm - Within specifications
•
Error counters are not incrementing.
•
There are no active defects or alarms. For example, Active Alarms: None
•
Proper clocking configuration for each span (East and West). For example,
Clock source: Internal•
Proper hosts are on the proper side. For example, Remote span id: East, Remote span id: West
The following example shows sample output from this command:
Router# show controllers rpr-ieee 1/1Interface RPR-IEEE1/1Hardware is OC48 RPR-IEEERPR-IEEE1/1 - West Span (Ringlet0 RX, Ringlet1 TX)SFP Module West is VALIDOPTICSTX power -4 (+/- 3) dBmRX power -5 (+/- 3) dBmNo Active AlarmsNo Active WarningsSECTIONLOF = 0 LOS = 0 BIP(B1) = 0LINEAIS = 0 RDI = 0 FEBE = 0 BIP(B2) = 0PATHAIS = 0 RDI = 0 FEBE = 0 BIP(B3) = 0LOP = 0 NEWPTR = 0 PSE = 0 NSE = 0Active Defects: NoneActive Alarms: NoneAlarm reporting enabled for: SLOS SLOF PLOPFraming : SONETRx SONET/SDH bytes: (K1/K2) = 0/0 S1S0 = 0 C2 = 0x16Tx SONET/SDH bytes: (K1/K2) = 0/0 S1S0 = 0 C2 = 0x16 J0 = 0x1Clock source : InternalFramer loopback : NonePath trace buffer : StableRemote hostname : EAST-DRemote interface: RPR-IEEE1/1Remote IP addr : 1.1.1.1Remote side id : EASTBER thresholds: SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6IPS BER thresholds(B3): SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6TCA thresholds: B1 = 10e-6 B2 = 10e-6 B3 = 10e-6biff (6:57:52 PM): RPR-IEEE1/1 - East Span (Ringlet1 RX, Ringlet0 TX)SFP Module East is VALIDOPTICSTX power -4 (+/- 3) dBmRX power -5 (+/- 3) dBmNo Active AlarmsNo Active WarningsSECTIONLOF = 0 LOS = 0 BIP(B1) = 0LINEAIS = 0 RDI = 0 FEBE = 0 BIP(B2) = 0PATHAIS = 0 RDI = 0 FEBE = 0 BIP(B3) = 0LOP = 0 NEWPTR = 0 PSE = 0 NSE = 0Active Defects: NoneActive Alarms: NoneAlarm reporting enabled for: SLOS SLOF PLOPFraming : SONETRx SONET/SDH bytes: (K1/K2) = 0/0 S1S0 = 0 C2 = 0x16Tx SONET/SDH bytes: (K1/K2) = 0/0 S1S0 = 0 C2 = 0x16 J0 = 0x1Clock source : InternalFramer loopback : NonePath trace buffer : StableRemote hostname : WEST-DRemote interface: RPR-IEEE1/1Remote IP addr : 1.1.1.3Remote side id : WESTBER thresholds: SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6IPS BER thresholds(B3): SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6TCA thresholds: B1 = 10e-6 B2 = 10e-6 B3 = 10e-6Using the show controllers rpr-ieee 1/1 transceiver Command
Use the transceiver keyword to display additional information about the status of the small form-factor pluggable (SFP) module used in an RPR port.
Router# show controllers rpr-ieee 1/1 transceiverShow Transceiver: West SpanStatic informationID: SFP transceiverExtended ID: 4Connector: LCSONET compliance: OC48SRGigabit Ethernet compliance: unspecifiedFibre Channel link length: unspecifiedFibre Channel transmitter technology: unspecifiedFibre Channel transmission media: unspecifiedFibre Channel speed: unspecifiedEncoding: reservedBit Rate: 2500 MbpsSingle mode fiber supported length: 2 kmUpper bit rate limit: unspecifiedLower bit rate limit: unspecifiedDate code (yyyy/mm/dd): 2004/04/21Vendor PN: SCP6828-C5-BNEVendor revision number: DVendor serial number: ECL0817001LTransceiver status informationDiagnostics calibration is externalTemperature 39 (+/-3 Celsius)Voltage in transceiver 3232600 uV (+/- 10 mV)TX bias 8940 uA (+/- 100uA)TX power 316000 nW / -5 dBm (+/- 3dBm)RX power 300200 nW / -5 dBm (+/- 3dBm)No Active AlarmsNo Active WarningsAlarm Thresholds:high lowTemperature 96 C -44 CVoltage 4000000 uV 0 uVTX bias 70000 uA 0 uATX power 1000000 nW / 0 dBm 50100 nW / -13 dBmRX power 1008300 nW / 0 dBm unspecifiedWarning Thresholds:high lowTemperature 91 C - 9 CVoltage 3600000 uV 3000000 uVTX bias 60000 uA 0 uATX power 630900 nW / -2 dBm 79400 nW / -11 dBmRX power 1008300 nW / 0 dBm unspecifiedShow Transceiver: East SpanStatic informationID: SFP transceiverExtended ID: 4Connector: LCSONET compliance: OC48SRGigabit Ethernet compliance: unspecifiedFibre Channel link length: unspecifiedFibre Channel transmitter technology: unspecifiedFibre Channel transmission media: unspecifiedFibre Channel speed: unspecifiedEncoding: reservedBit Rate: 2500 MbpsSingle mode fiber supported length: 2 kmUpper bit rate limit: unspecifiedLower bit rate limit: unspecifiedDate code (yyyy/mm/dd): 2004/04/21Vendor PN: SCP6828-C5-BNEVendor revision number: DVendor serial number: ECL0817001MTransceiver status informationDiagnostics calibration is externalTemperature 38 (+/-3 Celsius)Voltage in transceiver 3230800 uV (+/- 10 mV)TX bias 8724 uA (+/- 100uA)TX power 285600 nW / -5 dBm (+/- 3dBm)RX power 309900 nW / -5 dBm (+/- 3dBm)No Active AlarmsNo Active WarningsAlarm Thresholds:high lowTemperature 96 C -44 CVoltage 4000000 uV 0 uVTX bias 70000 uA 0 uATX power 1000000 nW / 0 dBm 50100 nW / -13 dBmRX power 1008300 nW / 0 dBm unspecifiedWarning Thresholds:high lowTemperature 91 C - 9 CVoltage 3600000 uV 3000000 uVTX bias 60000 uA 0 uATX power 630900 nW / -2 dBm 79400 nW / -11 dBmRX power 1008300 nW / 0 dBm unspecifiedUsing the show arp Command
Use the show arp command to verify that the correct Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table is loaded.
The following example shows sample output from this command:
Router# show arpProtocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Internet 1.1.1.1 154 0001.0001.0001 RPR-IEEE-W RPR-IEEE1/1 Internet 1.1.1.3 155 0003.0003.0003 RPR-IEEE-E RPR-IEEE1/1 Internet 1.1.1.2 - 0002.0002.0002 RPR-IEEE RPR-IEEE1/1 Internet 200.1.1.1 - 0001.64ff.0601 ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1 Router#Verifying Clocking
There are two modes of clocking for the rpr-ieee interface, LINE and INTERNAL. Clocking works over dark fiber.
•
INTERNAL means that the rpr-ieee interface uses its internal 20ppm or Stratum-3 clock. LINE means it takes timing from the other span of the line.
•
Having both spans with clocking set to INTERNAL is the default configuration and results in normal operation.
•
Having both spans with clocking set to LINE is not advised and will result in bit interleaved parity (BIP) errors over time.
•
Pairing opposite spans of a connection with one spans INTERNAL and one span LINE is acceptable, but not necessary.
Ideal clocking is achieved when all interfaces have the clocking set to INTERNAL. The following example shows this configuration:
router(config)# interface rpr-ieee 1/1router(config-if)# rpr-ieee clock-source internal Eastrouter(config-if)# rpr-ieee clock-source internal WestPASS-THRU Mode
The rpr-ieee line card acts as an optical regenerator when it is operating in PASS-THRU mode. PASS-THRU mode isolates the node. This mode is activated when the interface is placed in shutdown mode, or the node is not receiving layer 2 keepalives on span East or span West.
Use the shutdown interface configuration command to place the router rpr-ieee interface in PASS-THRU mode.
PASS-THRU mode is a useful troubleshooting tool for isolating which node on the ring is faulty.
The following example shows sample output from this command:
Router# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.Router(config)#interface RPR-IEEE 1/1Router(config-if)#shutdownRouter(config-if)#endRouter#3d06h: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by tty13d06h: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface RPR-IEEE1/1, changed state to administratively down3d06h: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface RPR-IEEE1/1, changed state to downVerifying the PASS-THRU Mode
Use the show rpr-ieee ips EXEC command to verify that the rpr-ieee node is in PASS-THRU mode, which occurs when the interface is administratively down.
The following example shows sample output from this command:
Router# show rpr-ieee protectionRPR-IEEE1/1 is administratively downRouter#Using the show rpr-ieee topology Command
Use the show rpr-ieee topology EXEC command to verify that topology is valid.
The following example shows sample output from this command:Router# show rpr-ieee topologyRing Topology: CLOSED (STABLE)Configured protection mode: WRAPPINGJumbo preference: SET (ring supports JUMBOS)Number of nodes onringlet0: 3 ringlet1: 3Checksum: 0x001800D6Index (Ri 0) MAC IP Address Edge W/E Request W/E1 0001.0001.0001 1.1.1.1 NO/NO IDLE/IDLE2 0003.0003.0003 1.1.1.3 NO/NO IDLE/IDLE3 0002.0002.0002 1.1.1.2 NO/NO IDLE/IDLEIndex (Ri 1) MAC IP Address Edge W/E Request W/E1 0003.0003.0003 1.1.1.3 NO/NO IDLE/IDLE2 0001.0001.0001 1.1.1.1 NO/NO IDLE/IDLE3 0002.0002.0002 1.1.1.2 NO/NO IDLE/IDLEUsing the show rpr-ieee protection Command
The show rpr-ieee protection command displays the status of the 802.17 topology-protection. It contains information such as the neighbors found on each ringlet, the protection mode/status and the topology checksum values/status.
The following example shows sample output from this command:
Router# show rpr-ieee protectionProtection Information for Interface RPR-IEEE1/1MAC AddressesWest Span (Ringlet 0 RX) neighbor 0001.0001.0001East Span (Ringlet 1 RX) neighbor 0003.0003.0003Station MAC address 0002.0002.0002TP frame sending timers:fast timer: 10 msecslow timer: 1x100 msec (100 msec)Protection holdoff timers:L1 Holdoff Keepalive DetectionWest Span 0x10 msec ( 0 msec) West Span 3 msecEast Span 0x10 msec ( 0 msec) East Span 3 msecConfigured protection mode: WRAPPINGProtection StatusRing is IDLEProtection WTR period is 10 sec. (timer is inactive)Self Detected Requests Remote RequestsWest Span IDLE West Span IDLEEast Span IDLE East Span IDLEDistant RequestsEast Span IDLE West Span IDLEWest Span Failures: none East Span Failures: noneIf the ring reports an "OPEN" state in the topology, there is a link failure in the ring, the details in the ringlet indices will pinpoint the failure location by indicating the Edge location and the Request (reason) for the Edge.
Fiber Misconnection
Use the show rpr-ieee EXEC command to check for misconnected fiber cables, for example, span East to span East or TX to TX. The message, "Misconnection Alarm" shows at the top of the show rpr-ieee command output when there is a fiber misconnection.
•
One alarm—the problem is with another node on the ring. For example, span East connected to span East.
•
Two alarms—the problem is your node. For example, span East to span East and span West to span West.
Basic Troubleshooting SRP for the Uplink Card
This section provides basic troubleshooting guidelines for SRP on the DPT, POS/DPT, and RPR/SRP uplink cards. For additional information about SRP configurations, refer to the Cisco IOS Software Configuration for the Cisco 10720 Internet Router publication. For additional Cisco SRP-related documentation, see the "Related Documentation" section on page xix.
The following sections present information on show commands, verification steps, and alarm messages:
•
Using the show controller srp Command
•
Using the show srp topology Command
•
Using the show srp ips Command
Using the show controller srp Command
Verify the following using the show controller srp command:
•
RX optics readout values are within specifications. For example: RX readout values: -11 dBm - Within specifications, RX readout values: -15 dBm - Within specifications
•
Error counters are not incrementing.
•
There are no active defects or alarms. For example, Active Alarms: None
•
Proper clocking configuration for each side (A and B). For example,
Clock source : Internal•
Proper hosts are on the proper side. For example, Remote side id : A,
Remote side id : BRouter# show controllers srpInterface SRP1/1Hardware is OC48 SRPSRP1/1 - Side A (Outer RX, Inner TX)OPTICSRX readout values: -11 dBm - Within specifications
SECTIONLOF = 0 LOS = 0 BIP(B1) = 0LINEAIS = 0 RDI = 0 FEBE = 0 BIP(B2) = 0PATHAIS = 0 RDI = 0 FEBE = 0 BIP(B3) = 0LOP = 0 NEWPTR = 0 PSE = 0 NSE = 0Active Defects: NoneActive Alarms: None
Alarm reporting enabled for: SLOS SLOF PLOPFraming : SONETRx SONET/SDH bytes: (K1/K2) = 0/0 S1S0 = 0 C2 = 0x16Tx SONET/SDH bytes: (K1/K2) = 0/0 S1S0 = 0 C2 = 0x16 J0 = 0x1Clock source : Internal
Framer loopback : NonePath trace buffer : StableRemote hostname : M0415BRemote interface: SRP2/0Remote IP addr : 48.1.1.2Remote side id : B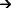 BER thresholds: SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6IPS BER thresholds(B3): SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6TCA thresholds: B1 = 10e-6 B2 = 10e-6 B3 = 10e-6SRP1/1 - Side B (Inner RX, Outer TX)OPTICS
BER thresholds: SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6IPS BER thresholds(B3): SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6TCA thresholds: B1 = 10e-6 B2 = 10e-6 B3 = 10e-6SRP1/1 - Side B (Inner RX, Outer TX)OPTICSRX readout values: -15 dBm - Within specifications
SECTIONLOF = 0 LOS = 0 BIP(B1) = 0LINEAIS = 0 RDI = 0 FEBE = 0 BIP(B2) = 0PATHAIS = 0 RDI = 0 FEBE = 0 BIP(B3) = 0LOP = 0 NEWPTR = 0 PSE = 0 NSE = 0Active Defects: None
Active Alarms: None
Alarm reporting enabled for: SLOS SLOF PLOPFraming : SONETRx SONET/SDH bytes: (K1/K2) = 0/0 S1S0 = 0 C2 = 0x16Tx SONET/SDH bytes: (K1/K2) = 0/0 S1S0 = 0 C2 = 0x16 J0 = 0x1Clock source : Internal
Framer loopback : NonePath trace buffer : StableRemote hostname : M0415BRemote interface: SRP2/0Remote IP addr : 48.1.1.2Remote side id : A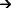 BER thresholds: SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6IPS BER thresholds(B3): SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6TCA thresholds: B1 = 10e-6 B2 = 10e-6 B3 = 10e-6Router#
BER thresholds: SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6IPS BER thresholds(B3): SF = 10e-3 SD = 10e-6TCA thresholds: B1 = 10e-6 B2 = 10e-6 B3 = 10e-6Router#Using the show arp Command
Use the show arp command to verify that the correct Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table is loaded.
Router# show arpProtocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type InterfaceInternet 48.1.1.2 181 0001.6340.9100 SRP-B SRP1/1Internet 48.1.1.10 - 0001.64ff.3100 SRP2 SRP1/1Internet 194.16.3.1 68 0001.64ff.3103 ARPA FastEthernet2/3Internet 194.16.2.1 123 0001.64ff.3102 ARPA FastEthernet2/2Internet 194.16.1.1 - 0001.64ff.3101 ARPA FastEthernet2/1repetitive output removedRouter#Verifying Clocking
There are two modes of clocking for the SRP interface, LINE and INTERNAL. Clocking works over dark fiber.
•
INTERNAL means that the SRP interface uses its internal 20ppm or Stratum-3 clock. LINE means it takes timing from the other side of the line.
•
Having both sides with clocking set to INTERNAL is the default configuration and results in normal operation.
•
Having both sides with clocking set to LINE is not advised and will result in bit interleaved parity (BIP) errors over time.
•
Pairing opposite sides of a connection with one side INTERNAL and one side LINE is acceptable, but not necessary.
Ideal clocking is achieved when all interfaces have the clocking set to INTERNAL. The following example shows this configuration:
router(config)# interface srp 1/1router(config-if)# srp clock-source internal Arouter(config-if)# srp clock-source internal BPASS-THRU Mode
The SRP line card acts as an optical regenerator when it is operating in PASS-THRU mode. PASS-THRU mode isolates the node. This mode is activated when the interface is placed in shutdown mode, or the node is not receiving layer 2 keepalives on side A or side B.
Use the shutdown interface configuration command to place the router SRP interface in PASS-THRU mode.
PASS-THRU mode is a useful troubleshooting tool for isolating which node on the ring is faulty.
Router# config terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.Router(config)# interface srp 1/1Router(config-if)# shutdownRouter(config-if)# endRouter#23:42:25: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console23:42:27: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface SRP1/1, changed state to administratively down23:42:28: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface SRP1/1, changed state to downVerify the PASS-THRU Mode
Use the show srp ips EXEC command to verify that the SRP node is in PASS-THRU mode, which occurs when the interface is administratively down.
Router# show srp ipsSRP1/1 is administratively downRouter#Using the show srp topology Command
Use the show srp topology EXEC command to verify that the topology packets are being sent and received.
router# show srp topologyTopology Map for Interface SRP1/1Topology pkt. sent every 5 sec. (next pkt. after 0 sec.)Last received topology pkt. 00:00:04Nodes on the ring: 3Hops (outer ring) MAC IP Address Wrapped Name0 0001.64ff.1580 48.1.1.3 No M0426C1 0001.6347.9700 48.1.1.2 No M0426B2 00b0.c280.cf00 48.1.1.1 No M0426ABy default, the maximum acceptable time for the last topology packet to be received is 5 seconds. If the last received packet value is higher than 5 seconds, topology packets are being lost on the ring.
Using the show srp ips Command
The show srp ips command displays the status of the IPS protocol. It contains information such as the direct neighbors' address, the wrap state, the failures state and the latest transmitted and received IPS packets of the SRP node. It also indicates that the interface is administratively up and not in PASS-THRU mode. (See the "PASS-THRU Mode" section.)
router# show srp ipsIPS Information for Interface SRP1/1MAC AddressesSide A (Outer ring RX) neighbor 00b0.c280.cf00Side B (Inner ring RX) neighbor 0001.6347.9700Node MAC address 0001.64ff.1580IPS StateSide A not wrapped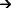 Side B not wrapped
Side B not wrapped Side A (Inner ring TX) IPS pkt. sent every 1 sec. (next pkt. after 1 sec.)Side B (Outer ring TX) IPS pkt. sent every 1 sec. (next pkt. after 1 sec.)inter card bus enabledIPS WTR period is 60 sec. (timer is inactive)Node IPS State: idleIPS Self Detected Requests IPS Remote RequestsSide A IDLE Side A IDLESide B IDLE Side B IDLEIPS messages received
Side A (Inner ring TX) IPS pkt. sent every 1 sec. (next pkt. after 1 sec.)Side B (Outer ring TX) IPS pkt. sent every 1 sec. (next pkt. after 1 sec.)inter card bus enabledIPS WTR period is 60 sec. (timer is inactive)Node IPS State: idleIPS Self Detected Requests IPS Remote RequestsSide A IDLE Side A IDLESide B IDLE Side B IDLEIPS messages receivedSide A (Outer ring RX) {00b0.c280.cf00,IDLE,SHORT}, TTL 128Side B (Inner ring RX) {0001.6347.9700,IDLE,SHORT}, TTL 128IPS messages transmittedSide A (Outer ring RX) {0001.64ff.1580,IDLE,SHORT}, TTL 128Side B (Inner ring RX) {0001.64ff.1580,IDLE,SHORT}, TTL 128Any status other than IDLE, SHORT indicates that errors are present.
If the value "none" is present in IPS packets received, there is a problem on the ring.
Fiber Misconnection
Use the show srp EXEC command to check for misconnected fiber cables, for example, side A to side A or TX to TX. The message, "Misconnection Alarm" shows at the top of the show srp command output when there is a fiber misconnection.
•
One alarm—the problem is with another ring on the node. For example, side A connected to side A.
•
Two alarms—the problem is your node. For example, side A to side A and side B to side B.
Alarm Messages
The following alarm messages display on the console. The suggested solutions cover the most commonly observed errors.
See the following tables for specific alarms and solutions.
Alarm Messages
The following alarm messages report to the console. See Table 4-1 through Table 4-8 for specific alarms and solutions.
The suggested solutions listed below are to the most commonly observed errors:
•
Keepalive Alarm Messages for All Uplink Cards, Table 4-1
•
IEEE 802.17 RPR Wrap Messages, Table 4-2
•
IEEE 802.17 RPR Unwap Messages, Table 4-3
•
Other IEEE 802.17 RPR Alarm Messages, Table 4-6
•
SRP Unwrap Message, Table 4-8
Table 4-3 IEEE 802.17 RPR Unwap Messages
RPR-IEEE1/1 unwrapped on span EAST (wrap cause cleared)
Wrap cleared; Wait to Restore timer expired.
None.
Table 4-5 IEEE 802.17 RPR Un-Steer Messages
RPR-IEEE1/1 unprotected on span EAST (protection cause cleared)
Protection cleared; Wait to Restore timer expired.
Table 4-8 SRP Unwrap Message
SRP1/1 unwrapped on side B (side A Wrap cause cleared)
Wrap cleared, Wait to Restore timer expired
None.
Note
The solutions provided do not cover all possible problems related to specific alarms.
Basic Troubleshooting Ethernet for the Access Card
This section provides some basic troubleshooting guidelines for Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces on the access card. For additional information about troubleshooting Ethernet configurations, refer to the Cisco IOS Software Configuration for the Cisco 10720 Internet Router publication. For additional Cisco Ethernet-related documentation, refer to "Related Documentation" section on page xix.
The following sections present basic troubleshooting tips for hardware and simple software tasks.
•
Verifying Interface Configuration
•
FastEthernet/GigabitEthernet Is up
Verifying Interface Configuration
Use the show interfaces FastEthernet slot/port command to verify the configuration of a Fast Ethernet interface.
Router# show interfaces FastEthernet 2/1FastEthernet2/1 is up, line protocol is upHardware is Fast Ethernet, address is 0001.64ff.3101 (bia0001.64ff.3101)Internet address is 194.16.1.1/24MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not setKeepalive set (10 sec)Auto-duplex, Auto Speed, 100BaseTX/FXARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00Last input never, output 00:00:04, output hang neverLast clearing of "show interface" counters 00:00:13Queueing strategy: PXF First-In-First-OutOutput queue 0/8192, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec0 packets input, 0 bytesReceived 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored0 watchdog, 0 multicast0 input packets with dribble condition detected1 packets output, 64 bytes, 0 underruns0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped outRouter#Use the show interfaces GigabitEthernet slot/port command to verify the configuration of a Gigabit Ethernet interface.
Router# show interfaces GigabitEthernet 2/1GigabitEthernet2/1 is up, line protocol is upInternet address is 195.16.1.1/16MTU 9100 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit, DLY 10 usec, rely 255/255, load 0/255Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not setKeepalive not setFull-duplex mode, link type is autonegotiation, media type is SXoutput flow-control is off, input flow-control is offARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00Last input 00:00:02, output 00:00:00, output hang neverLast clearing of "show interface" counters 03:41:33Queueing strategy: PXF First-In-First-OutOutput queue 0/8192, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops30 second input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec30 second output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no bufferReceived 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored0 watchdog, 0 multicast, 0 pause input1 packets output, 64 bytes, 0 underruns0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped outRouter#FastEthernet/GigabitEthernet Is up
If the interface is down, check the following conditions:
•
The cable is fully connected.
•
The cable is bent or damaged. If the cable is bent or damaged, the signal will be degraded.
•
A hardware failure has not occurred. Observe the LEDs or use the show commands to determine if a failure has occurred. If the hardware has failed, replace the card or cable.
•
If the interface is administratively down, use the no shutdown command to enable the interface.
See the "Verifying Interface Configuration" section for an example output that shows interface status.
Line Protocol Is up
Check to see if the status is line protocol is up, in the first line of the output; see the "Verifying Interface Configuration" section. The status of the interface follows the slot/port configuration:
•
The line protocol software processes determine that the line is unusable. Swap the cable.
•
Check local or remote interface for misconfiguration.
•
Swap interface module when there is a hardware failure.
Duplex Mode Setting
The local interface duplex mode configuration should match the remote interface configuration. See the "Verifying Interface Configuration" section for an example output that shows duplex settings. Confirm that duplex settings are the same on both ends of the connection.
Speed Mode
The local interface speed mode field should match the remote interface configuration. See the "Verifying Interface Configuration" section for an example output that shows speed settings. Speed setting display is shown in the following line:
10/100/autoOutput Hang
The output hang provides the number of hours, minutes, and seconds since the last reset caused by a lengthy transmission. For example, the output hang data is located on line 9 of the show interfaces GigabitEthernet 2/1 router output:
Last input never, output 00:00:04, output hang neverSee the "Verifying Interface Configuration" section for a complete example output that shows output hang data.
CRC Field Counters
Excessive noise will cause high CRC errors accompanied by a low number of collisions. Perform the following checks if you encounter high CRC errors:
•
Check the cables for damage.
•
Verify that the correct cables are being used for the appropriate access card. For cabling specifications, refer to the Cisco 10720 Internet Router Access Card Installation and Configuration publication.
Late Collision
The console will display the following message when late collisions are detected:
Port 2/X - Late collision detected. Possible duplex mismatch.Late collisions result from either of the following conditions:
•
Ethernet cables are too long.
•
Duplex mode does not match the remote interface.
For example, the late collisions data is located on line 22 of the show interfaces FastEthernet 2/1 router output:
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferredSee the "Verifying Interface Configuration" section for a complete example of the output that identifies late collisions.
Carrier Signal
The lost carrier, no carrier numbers track the number of lost carrier detect signals that have occurred.
•
If the transmit clock signal is not active, check the interface for malfunction.
•
Check for a cable problem.
•
Carrier signal resets can occur when an interface is in one of the following states:
–
Looped back.
–
Shut down.
Cleaning the Fiber-Optic Connections
For information about cleaning fiber-optic cable connectors and receptacles, see the Inspection and Cleaning Procedures for Fiber-Optic Connections document. It provides detailed illustrations and photos of procedures and equipment required to properly clean fiber-optic connections.

