-
- IP Access List Features Roadmap
- IP Access List Overview
- Creating an IP Access List and Applying It to an Interface
- Creating an IP Access List to Filter IP Options TCP Flags Noncontiguous Ports or TTL Values
- Refining an IP Access List
- Displaying and Clearing IP Access List Data Using ACL Manageability
- Controlling Access to a Virtual Terminal Line
- Access List-Based RBSCP
- ACL IP Options Selective Drop
- ACL Authentication of Incoming rsh and rcp Requests
- Configuring Lock-and-Key Security for Dynamic Access Lists
- Configuring IP Session Filtering of Reflexive Access Lists
- Configuring TCP Intercept and Preventing Denial-of-Service Attacks
-
- Configuring Context-based Access Control
- Application Firewall - Instant Message Traffic Enforcement
- Cisco IOS Firewall MIB
- Cisco IOS Firewall Performance Improvements
- Cisco IOS Firewall Stateful Failover
- Cisco IOS Firewall Support for TRP
- Email Inspection Engine
- ESMTP Support for Cisco IOS Firewall
- Firewall ACL Bypass
- Firewall N2H2 Support
- Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP
- Firewall Support for SIP
- Firewall Support of Skinny Client Control Protocol
- Firewall Websense URL Filtering
- Granular Protocol Inspection
- HTTP Inspection Engine
- Inspection of Router-Generated Traffic
- TCP Out-of-Order Packet Support for Cisco IOS Firewall and Cisco IOS IPS
- Transparent Cisco IOS Firewall
- Virtual Fragmentation Reassembly
- VRF Aware Cisco IOS Firewall
- Configuring Port to Application Mapping
- Configuring Cisco IOS Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
- Configuring IP Security Options
- Finding Feature Information
- Contents
- Prerequisites for Firewall Support for TRP
- Restrictions for Firewall Support for TRP
- Information About Firewall Support for TRP
- How to Configure a Firewall to Support TRP in Voice Networks
- Configuration Examples for Firewall and TRP in a Voice Network
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Firewall Support for TRP
Cisco IOS Firewall Support for TRP
To guarantee service and security, the deployment of voice services over IP networks requires special handling of secondary channels within the network. When Trust Relay Points (TRPs) are implemented in voice networks, the networks must account for the following caveats when handling the opening of secondary channels.
•![]() Networks do not always see the signaling messages. (The signaling messages are most likely encrypted.)
Networks do not always see the signaling messages. (The signaling messages are most likely encrypted.)
•![]() Networks that do see signaling messages cannot deep inspect the messages.
Networks that do see signaling messages cannot deep inspect the messages.
•![]() Networks use other means to learn about the media channels that are being negotiated and opened.
Networks use other means to learn about the media channels that are being negotiated and opened.
Consequently, transparent entities, such as the Cisco IOS Firewall, that are operating on the networks, must process media channels differently.
This feature enables Cisco IOS Firewall to process Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN). STUN messages open connections between ports for secondary channels, known as pinholes, which are necessary for implementation of TRPs in voice networks.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the "Feature Information for Firewall Support for TRP" section.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Contents
•![]() Prerequisites for Firewall Support for TRP
Prerequisites for Firewall Support for TRP
•![]() Restrictions for Firewall Support for TRP
Restrictions for Firewall Support for TRP
•![]() Information About Firewall Support for TRP
Information About Firewall Support for TRP
•![]() How to Configure a Firewall to Support TRP in Voice Networks
How to Configure a Firewall to Support TRP in Voice Networks
•![]() Configuration Examples for Firewall and TRP in a Voice Network
Configuration Examples for Firewall and TRP in a Voice Network
•![]() Feature Information for Firewall Support for TRP
Feature Information for Firewall Support for TRP
Prerequisites for Firewall Support for TRP
Before configuring STUN to open pinholes for data, ensure that the voice protocol control packets in your network are not blocked by the Cisco IOS Firewall.
Restrictions for Firewall Support for TRP
•![]() You must configure different agent IDs under a single parameter map. If different agent IDs are configured under two different parameter maps and then the STUN inspection of the two parameter maps are out in the same policy map (per the sample configuration below), the firewall will drop the packet. For example, if you are sending a packet with agent ID 21, the firewall will check the first class map called "stun-ice" and then drop the packet because it did not find a match in that class map.
You must configure different agent IDs under a single parameter map. If different agent IDs are configured under two different parameter maps and then the STUN inspection of the two parameter maps are out in the same policy map (per the sample configuration below), the firewall will drop the packet. For example, if you are sending a packet with agent ID 21, the firewall will check the first class map called "stun-ice" and then drop the packet because it did not find a match in that class map.
parameter-map type protocol-info stun-ice cfd1 authorization agent-id 20 shared-secret 12345flower12345 cat-window 15 authorization agent-id 22 shared-secret 12345cisco54321 cat-window 15 parameter-map type protocol-info stun-ice cfd2 authorization agent-id 21 shared-secret 12345flower54321 cat-window 15
!
class-map type inspect match-all stun-ice match protocol stun-ice cfd1 class-map type inspect match-any stun-ice1 match protocol stun-ice cfd2 !
policy-map type inspect policy_test class type inspect class_1 pass class type inspect sip_ctrl_channel inspect class type inspect stun-ice inspect class type inspect stun-ice1 inspect class class-default drop
Information About Firewall Support for TRP
•![]() How Cisco IOS Firewall Supports TRP in a Voice Network
How Cisco IOS Firewall Supports TRP in a Voice Network
•![]() How Cisco IOS Firewall Supports Partial SIP Inspection
How Cisco IOS Firewall Supports Partial SIP Inspection
Cisco IOS Firewall
The Cisco IOS Firewall extends the concept of static access control lists (ACLs) by introducing dynamic ACL entries that open on the basis of the necessary application ports on a specific application and close these ports at the end of the application session. The Cisco IOS Firewall achieves this functionality by inspecting the application data, checking for conformance of the application protocol, extracting the relevant port information to create the dynamic ACL entries, and closing these ports at the end of the session. The Cisco IOS Firewall is designed to easily allow a new application inspection whenever support is needed.
How Cisco IOS Firewall Supports TRP in a Voice Network
The following information describes the deployment scenarios supported by the Cisco IOS Firewall with TRP present in a voice network:
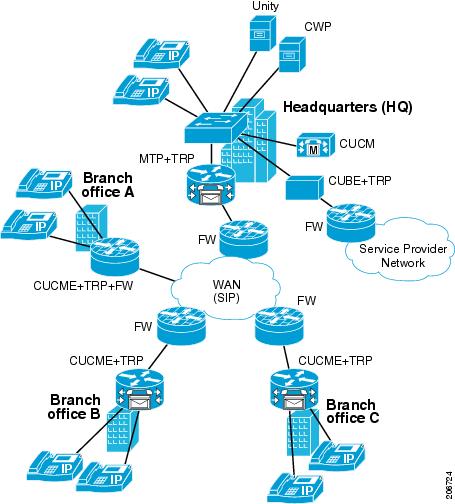
•![]() For the Cisco IOS Firewall that is running on a Cisco router without TRP, STUN packets are processed as regular passthrough packets. To open a pinhole for secondary channels, the firewall must be able to recognize the STUN packets.
For the Cisco IOS Firewall that is running on a Cisco router without TRP, STUN packets are processed as regular passthrough packets. To open a pinhole for secondary channels, the firewall must be able to recognize the STUN packets.
•![]() For the Cisco IOS Firewall that is running on a Cisco router with TRP (Branch Office A in Figure 1), the firewall will intercept and act on the STUN packets that are sent from the TRP on its WAN side. Cisco IOS firewall validates the Cisco Proprietary Cisco Flow-Data information on the STUN packet and opens the data-channel pinholes for voice traffic. The Cisco Flow-Data has information to authenticate that the message is from a valid TRP device.
For the Cisco IOS Firewall that is running on a Cisco router with TRP (Branch Office A in Figure 1), the firewall will intercept and act on the STUN packets that are sent from the TRP on its WAN side. Cisco IOS firewall validates the Cisco Proprietary Cisco Flow-Data information on the STUN packet and opens the data-channel pinholes for voice traffic. The Cisco Flow-Data has information to authenticate that the message is from a valid TRP device.
•![]() The phones do not yet support STUN. If the firewall has to open pinholes between phones, TRP should send one-sided STUN messages addressed to each phone so the firewall can see the messages and open the pinholes. Without the support of STUN messages from TRP, the firewall would not be able to open the necessary pinholes for the phones to communicate.
The phones do not yet support STUN. If the firewall has to open pinholes between phones, TRP should send one-sided STUN messages addressed to each phone so the firewall can see the messages and open the pinholes. Without the support of STUN messages from TRP, the firewall would not be able to open the necessary pinholes for the phones to communicate.
Figure 1 Architecture for Cisco IOS Firewall in a TRP Network Solution
How Cisco IOS Firewall Supports Partial SIP Inspection
Cisco IOS Firewall TRP support enables Cisco IOS Firewall to process UDP STUN messages that open pinholes for secondary channels, which are necessary for implementation of TRPs in voice networks.
Previous implementations of Cisco IOS Firewall, SIP clients could negotiate with the server to dynamically open control channels on a port, which could not be supported using the access-group class map. In addition, SIP traffic was sent through the firewall without any protocol conformance checks.
To overcome these issues, Cisco IOS Firewall supports partial SIP inspection. This allows the SIP Application-level Gateway (ALG) to parse the entire SIP message, including the Session Description Protocol (SDP) part to check for protocol conformance, but does not allows SIP ALG to open pinholes for media information found in the SDP message. The STUN ALG is allowed to open the pinholes in the firewall.
Because partial SIP inspection decouples the media channel from the SIP control channel, SIP ALG can no longer depend on media channel inactivity to timeout the control sessions. Therefore, the SIP ALG implementation in this environment depends on the UDP timeout configured on the router. Because the default setting is low (30 seconds), you must set the UDP timeout value to a value slightly longer than the SIP call duration, when configuring the system.

Note ![]() In Cisco IOS Release 12.4(22)T, if you need to allow SIP control traffic, you must configure the match access-group filter. This filter allows SIP traffic to pass through the firewall without the protocol conformance check (Deep Packet Inspection).
In Cisco IOS Release 12.4(22)T, if you need to allow SIP control traffic, you must configure the match access-group filter. This filter allows SIP traffic to pass through the firewall without the protocol conformance check (Deep Packet Inspection).
TRP Messages
TRP uses the following message types to control how the Cisco IOS Firewall manages sessions:
•![]() Keep-Alive messages
Keep-Alive messages
To keep the Cisco IOS Firewall media sessions active the TRP generates authenticated keep-alive messages which must be validated to keep the session open. The keep-alive messages are valid only for a configured length of time, which is configured on the call-control entity (CCE). The Cisco IOS Firewall must receive a new message within the configured time, otherwise it closes the pinhole. The keep-alive message has the Cryptographic Authentication Token (CAT) obtained from the CCE which must be validated by the Cisco IOS Firewall before the keep-alive message is accepted.
•![]() Periodic Open messages
Periodic Open messages
The CAT (obtained from the CCE) is valid only for the CAT-life seconds setting configured on the CCE. After that time TRP gets a new CAT and sends a new message with the new CAT. This periodic open message specifies the keys that the Cisco IOS Firewall uses to authenticate the keep-alive messages until the next new CAT is obtained. Therefore, if the Cisco IOS Firewall does not receive a new CAT with the time specified by the CAT-life seconds, the media session closes as it cannot authenticate any keep-alive messages.
•![]() Close pinhole message
Close pinhole message
If the Cisco IOS Firewall receives a STUN message from TRP that indicates that a session should be active for 0 seconds (Seconds-Active = 0), it first validates the packet, then generates a syslog message and then allows the message to pass through the Cisco IOS Firewall so that other firewalls on the path can also see the message and close their session, finally it closes the session.
•![]() STUN messages from a remote party
STUN messages from a remote party
When TRP is configured on both the caller and the called side, the Cisco IOS Firewall receives 2 STUN messages for the same session. The Cisco IOS Firewall does not validate STUN messages from the remote party, instead it drops the packets and generates a syslog message.
How to Configure a Firewall to Support TRP in Voice Networks
•![]() Configuring a Policy to Allow STUN Messages
Configuring a Policy to Allow STUN Messages
•![]() Configuring Maps to Allow Partial SIP Inspection
Configuring Maps to Allow Partial SIP Inspection
•![]() Configuring a Parameter Map for TRP Support
Configuring a Parameter Map for TRP Support
Configuring a Policy to Allow STUN Messages
Perform this task to configure a policy to allow STUN messages.
Prerequisites
If the firewall is configured on the same device as the TRP, the STUN policy needs to be applied on the zone-pair between self and out zones.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ![]() class-map type inspect [match any | match all] class-map-name
class-map type inspect [match any | match all] class-map-name
4. ![]() match protocol stun-ice stun-ice-parameter-map
match protocol stun-ice stun-ice-parameter-map
5. ![]() exit
exit
6. ![]() class-map type inspect [match any | match all] class-map-name
class-map type inspect [match any | match all] class-map-name
7. ![]() match access-group {access-group | name access-group-name}
match access-group {access-group | name access-group-name}
8. ![]() match protocol stun-ice stun-ice-parameter-map
match protocol stun-ice stun-ice-parameter-map
9. ![]() exit
exit
10. ![]() policy-map type inspect policy-map-name
policy-map type inspect policy-map-name
11. ![]() class type inspect class-name
class type inspect class-name
12. ![]() inspect
inspect
13. ![]() exit
exit
14. ![]() class type inspect class-name
class type inspect class-name
15. ![]() inspect
inspect
16. ![]() exit
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Maps to Allow Partial SIP Inspection
Perform this task to define a parameter map that does not create or open a media channel when the parameter map is attached to the SIP class map.
Prerequisites
Because partial SIP inspection decouples the media channel from the SIP control channel, SIP ALG can no longer depend on media channel inactivity to timeout the control sessions. Therefore, the SIP ALG implementation in this environment depends on the UDP timeout configured on the router. Because the default setting is low (30 seconds), you must set the UDP timeout value to a value slightly longer than the SIP call duration, when configuring the system.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ![]() parameter-map type protocol-info sip parameter-map-name
parameter-map type protocol-info sip parameter-map-name
4. ![]() disable open-media-channel
disable open-media-channel
5. ![]() exit
exit
6. ![]() class-map type inspect class-map-name
class-map type inspect class-map-name
7. ![]() match protocol sip parameter-map-name
match protocol sip parameter-map-name
8. ![]() exit
exit
Configuring a Parameter Map for TRP Support
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ![]() parameter-map type protocol-info stun-ice parameter-map-name
parameter-map type protocol-info stun-ice parameter-map-name
4. ![]() authorization agent-id shared-secret password cat-window number
authorization agent-id shared-secret password cat-window number
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Firewall and TRP in a Voice Network
•![]() Example: Cisco IOS Firewall Support of STUN Messages in Voice Network Configuration
Example: Cisco IOS Firewall Support of STUN Messages in Voice Network Configuration
Example: Cisco IOS Firewall Support of STUN Messages in Voice Network Configuration
The following example shows how to configure a Cisco IOS Firewall policy to support STUN messages:
parameter-map type protocol-info stun-ice abc1
authorization agent-id 10 password letmein CAT-window 3
class-map type inspect stun-traffic
match protocol stun-ice abc1
class-map type inspect voice-control-traffic
match access-group 101
match protocol udp
policy-map type inspect voice-traffic
class type inspect voice-control-traffic
inspect
class type inspect stun-traffic
inspect
access-list 101 permit ip 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
! Allow SIP control packets to ensure the Cisco IOS firewall does not open secondary ! channels for media.
!
access-list 101 permit tcp any any eq 5060 access-list 101 permit udp any any eq 5060
!
class-map type inspect voice-control-traffic
match access-group 101
!
policy-map type inspect policy_test
class type inspect voice-control-traffic inspect
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the Cisco IOS Firewall Support for TRP feature.
Related Documents
|
|
|
|---|---|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
Additional firewall commands |
|
Zone-based policy firewall |
Standards
|
|
|
|---|---|
None |
— |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
None |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
|
|
|
|---|---|
None |
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for Firewall Support for TRP
Table 1 lists the features in this module and provides links to specific configuration information.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.

Note ![]() Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
 Feedback
Feedback