-
Cisco Unity Failover Configuration and Administration Guide, Release 3.1
-
Index
-
Preface
-
Configuring Cisco Unity Failover
-
Maintaining Cisco Unity Failover
-
About Cisco Unity Failover
-
Behavior of Cisco Unity Failover During Outages of Networked Components
-
Exiting and Starting the Cisco Unity Software and Server
-
Actions of the Configure Cisco Unity Failover Wizard
-
Uninstalling Failover on a Cisco Unity System
-
Line Connections Between the Phone System and the Cisco Unity Servers
-
Table Of Contents
Line Connections Between the Phone System and the Cisco Unity Servers
Analog Voice Line Connections for Failover
Connections with D/41EPCI Voice Cards
Connections with D/120JCT-LS or D/120JCT-Euro Voice Cards
Serial Data Cable Connections for Failover
Connections for the Serial Data Cables
Line Connections Between the Phone System and the Cisco Unity Servers
This appendix describes the line connections between a traditional circuit-switched phone system and the Cisco Unity servers for failover.
This appendix contains the following sections:
•
Analog Voice Line Connections for Failover
•
Serial Data Cable Connections for Failover
Analog Voice Line Connections for Failover
Traditional, circuit-switched phone systems typically have 25-pair or 32-pair cables to provide analog voice connections. It is common that the cable is broken into individual lines that may attach to a punchdown cross-connect block (for example, 66-Type), or it may terminate with RJ-11 or RJ-14 connectors to accept analog voice lines.
A punchdown cross-connect block or line splitters may be used to split the analog lines. It is possible to use these devices in combination to manage and split the lines.
Note
No devices other than those described in this appendix should be connected to the analog voice lines for any voice messaging port. Otherwise, the ring equivalency number (REN) may be exceeded and the Cisco Unity servers may not receive sufficient ring current to answer calls.
Requirements
The following components are required for common configurations:
•
Two or three analog voice patch cables for each port on the phone system.
•
The appropriate device to split the analog lines:
–
One or more punchdown cross-connect blocks (for example, 66-Type), installed and ready to accept lines.
–
One line splitter for every one or two ports on the phone system. The line splitter accepts both RJ-11 and RJ-14 connectors.
•
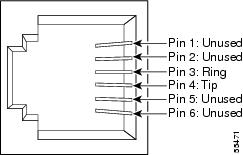
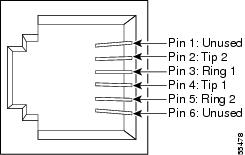
The appropriate connectors (RJ-11 and/or RJ-14) for the analog voice lines. Figure D-1 shows the pinout for the RJ-11 connector, and Figure D-2 shows the pinout for the RJ-14 connector.
Figure D-1 RJ-11 Connector Pinout
Figure D-2 RJ-14 Connector Pinout
Connections with D/41EPCI Voice Cards
The following figures illustrate common configurations:
•
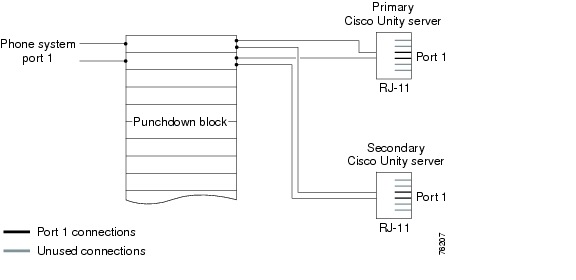
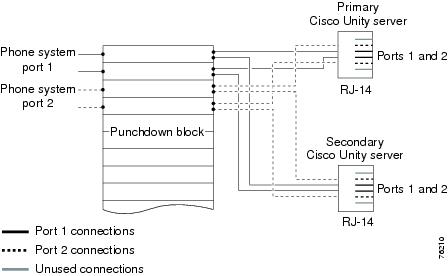
Figure D-3 shows the connections between a phone system, through a punchdown cross-connect block, and to the voice cards on the primary and secondary servers.
•
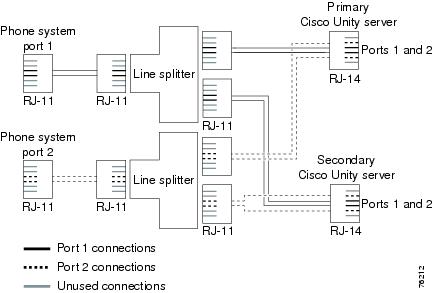
Figure D-4 shows the connections between a phone system with an RJ-11 connector and the D/41EPCI voice cards on the primary and secondary servers.
•
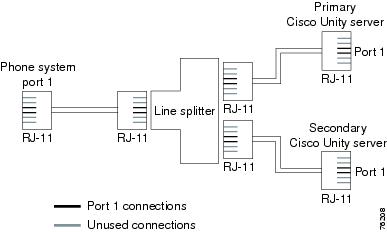
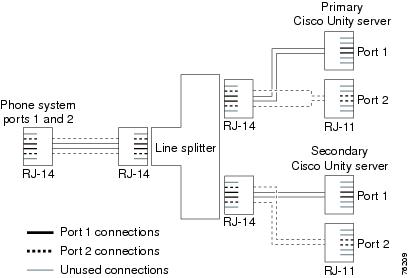
Figure D-5 shows the connections between a phone system with an RJ-14 connector and the D/41EPCI voice cards on the primary and secondary servers.
Figure D-3 Connections from the Phone System Through a Punchdown Block to D/41EPCI Voice Cards
Figure D-4 Connections for an RJ-11 Connector from the Phone System to D/41EPCI Voice Cards
Figure D-5 Connections from an RJ-14 Connector on the Phone System to D/41EPCI Voice Cards
Connections with D/120JCT-LS or D/120JCT-Euro Voice Cards
The following figures illustrate common configurations:
•
Figure D-6 shows the connections between a phone system, through a punchdown cross-connect block, and to the voice cards on the primary and secondary servers.
•
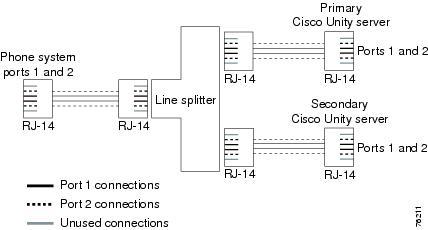
Figure D-7 shows the connections between a phone system with an RJ-14 connector and the D/120JCT-LS or D/120JCT-Euro voice cards on the primary and secondary servers.
•
Figure D-8 shows the connections between a phone system with an RJ-11 connector and the D/120JCT-LS or D/120JCT-Euro voice cards on the primary and secondary servers.
Figure D-6 Connections from the Phone System Through a Punchdown Block to D/120JCT-LS or D/120JCT-Euro Voice Cards
Figure D-7 Connections for an RJ-14 Connector from the Phone System to D/120JCT-LS or D/120JCT-Euro Voice Cards
Figure D-8 Connections for an RJ-11 Connector from the Phone System to D/120JCT-LS or D/120JCT-Euro Voice Cards
Serial Data Cable Connections for Failover
Only serial integrations (for example, SMDI, MCI, or PBXLink) use RS-232 serial data cables.
Connecting RS-232 serial cables between a circuit-switched phone system and the Cisco Unity primary and secondary servers varies depending on the number of serial ports the phone system has.
Requirements
The following components are required for phone systems with only one serial port:
•
Three RS-232 serial cables
•
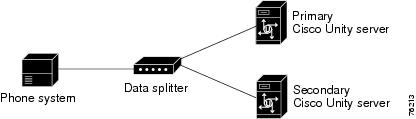
Data splitter unit (B&B Electronics 9-pin modem data splitter, model 9PMDS)
The following components are required for phone systems with multiple serial port:
•
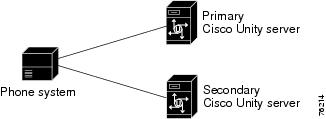
Two RS-232 serial cables
Connections for the Serial Data Cables
Figure D-9 shows the connections between the serial port on a phone system that has only one serial port to the serial ports on the Cisco Unity servers. Figure D-10 shows the connections between the serial ports on a phone system that has two serial ports to the serial ports on the Cisco Unity servers. The following figures do not show the analog voice lines, which are described in the "Analog Voice Line Connections for Failover" section.
Figure D-9 Serial Cable Connections from a Single Serial Port on the Phone System to the Serial Ports on the Cisco Unity Servers
Figure D-10 Serial Cable Connections from Multiple Serial Ports on the Phone System to the Serial Ports on the Cisco Unity Servers

 Feedback
Feedback