Table Of Contents
Cisco AS5800 Voice-over-IP Card
Cisco AS5800 Voice-over-IP Card
The Cisco AS5800 Voice-over-IP (VoIP) card is a multi-DSP (digital signal processor) coprocessing board and software package that adds VoIP capabilities to the Cisco AS5800 platform. The Cisco AS5800 Voice-over-IP (VoIP) card is available in a fully-populated or half-populated hardware version, and in software versions that are referred to as high-complexity and medium complexity. The Cisco AS5800 CT1/CE1 trunk card resides in the dial shelf of the Cisco AS5800 platform. The onboard DSPs provide the signal processing functionality to convert voice/fax information into IP packets. The DSPs are mounted on 8 or 16 daughter cards or Digital Signal Processing Modules (DSPMs). The fully-populated version has 96 DSPs, and the half-populated version has 48 DSPs. Each DSP can handle as many as two high-complexity and up to four medium-complexity sessions. The Cisco AS5800 CT1/CE1 trunk cards support multiple voice codecs, fax relay, and H.323 signaling.
The fully-populated, high complexity version Cisco AS5800 CT1/CE1 trunk card supports up to 192 packetized voice/fax calls and a wide range of codecs including G.711, G.729, G.729a, G.726, G.728, and G.723.1. The fully-populated, medium complexity version supports as many as 336 voice connections and the G.711, G.729a, and G.726 codecs. The half-populated, high complexity version Cisco AS5800 CT1/CE1 trunk card supports up to 96 packetized voice/fax calls and a wide range of codecs including G.711, G.729, G.729a, G.726, G.728, and G.723.1. The half-populated, medium complexity version supports as many as 192 voice connections and the G.711, G.729a, and G.726 codecs. A Cisco AS5800 configured as a voice gateway can support as many as 1,344 voice calls (requires four fully-populated, medium complexity cards).
Note
For maximum port capacity, the Cisco AS5800 configured as a voice gateway must be running in split dial shelf configuration with two 7206VXR router shelves. Refer to the Cisco AS5800 Universal Access Server Operation, Administration, Maintenance, and Provisioning Guide for split dial shelf configuration information.
For detailed software configuration information, refer to Voice over IP for the Cisco AS5800, an online document available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/nubuvoip/voip5800/index.htm.
You can use the Cisco AS5800 CT1/CE1 trunk card in the following applications:
•
Toll bypass/Tandem
•
Geographically dispersed networking over WANs
•
Mixed voice/data services including wholesale voice and data
•
PC-to-phone gateway
•
Debit/calling card applications
•
Post paid applications
•
PSTN voice traffic offload to packet networks
•
Clearing house and open settlement protocol (OSP) applications
CautionIn certain countries, use of these products or provision of voice telephony over the Internet may be prohibited or subject to laws, regulations, or licenses, including requirements applicable to the use of the products under telecommunications and other laws and regulations; the customer must comply with all such applicable laws in the country or countries where the customer intends to use the product.
Hardware Features
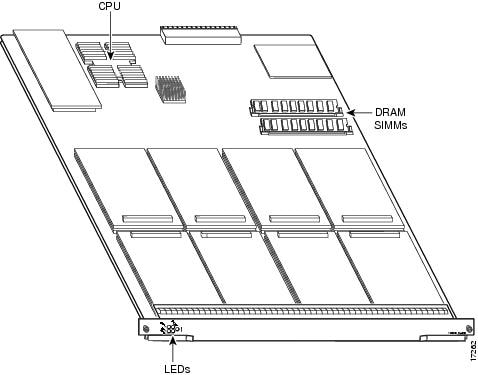
The Cisco AS5800 CT1/CE1 trunk card contains 8 (half-populated) or 16 (fully-populated) DSPMs and a 250-MHz CPU. The DSPMs are contained on 8 or 16 double-stacked daughtercards on the VoIP card.
The Cisco AS5800 VoIP card occupies a single slot in the Cisco 5814 dial shelf and connects to the LAN/WAN interface cards through the TDM backplane bus.
Figure 5-1 shows a side view of the Cisco AS5800 CT1/CE1 trunk card.
Figure 5-1 CT1/CE1 Trunk Card (Fully Populated Card Shown)
Software Features
High-complexity VoIP cards can handle two VoIP sessions per DSP. A Cisco AS5800 configured as a voice gateway and equipped with high-complexity CT1/CE1 trunk cards supports the following software features, codecs, and protocols:
•
H.323 call signaling (versions 1, 2, and 3)
•
H.323 gatekeeper support
•
The following codecs:
–
g711alaw G.711 A-Law 64,000 bps
–
g711ulaw G.711 u-Law 64,000 bps
–
g723r53 G.723.1 5,300 bps
–
g723r63 G.723.1 6,300 bps
–
g726r16 G.726 16,000 bps
–
g726r24 G.726 24,000 bps
–
g726r32 G.726 32,000 bps
–
g728 G.728 16,000 bps
–
g729abr8 G.729 ANNEX-A and B 8,000 bps
–
g729ar8 G.729 ANNEX-A 8,000 bps
–
g729r8 G.729 8,000 bps
•
Voice activity detection (VAD)
•
Echo cancellation (128 ms)
•
Interactive voice response (IVR) and authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) for two-stage dialing
•
T1/E1 PRI signaling and T1 CAS signaling
Medium-complexity VoIP cards can handle four VoIP sessions per DSP, but support fewer codecs. The medium-complexity CT1/CE1 trunk card supports the following software features, codecs, and protocols:
•
H.323 call signaling
•
H.323 gatekeeper support
•
The following codecs:
–
g711alaw G.711 A Law 64,000 bps
–
g711ulaw G.711 u Law 64,000 bps
–
g726r16 G.726 16,000 bps
–
g726r24 G.726 24,000 bps
–
g726r32 G.726 32,000 bps
–
g729abr8 G.729 ANNEX-A and B 8,000 bps
–
g729ar8 G.729 ANNEX-A 8,000 bps
–
g729r8 G.729 8,000 bps
•
Voice activity detection (VAD)
•
Echo cancellation (128 ms)
•
Interactive voice response (IVR) and authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) for two-stage dialing
•
T1/E1 PRI signaling and T1 CAS signaling
•
E1 R2 CAS signaling
•
NFAS
•
FG-B FG-D
Port densities that are supported on the VoIP card are listed in Table 5-1.
Table 5-1 Supported Port Densities
High
G.711, G.729, G.729a, G.726, G.728, G.723.1
full
192
half
96
Medium
G.711, G.729a, G.726
full
3361
half
192
1 Only 20 msec or higher packetization supported, VAD required.
For detailed software configuration information refer to Voice over IP for the Cisco AS5800, available at:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/nubuvoip/voip5800/index.htm.
Additional information relating to medium-complexity or half-populated VoIP cards for the Cisco AS5800 is at:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/acs_serv/as5800/12_2t/index.htm.
The show dial-shelf command does not indicate whether a VoIP card is fully-populated or half-populated, but it will indicate high-complexity (HC) or medium-complexity (MC). To find out how many DSPs are present on a VoIP card, use the show vrm vdevice summary command.
Note
Mixing high-complexity and medium-complexity VoIP cards in the Cisco AS5800 is only supported if all VoIP cards in one split of the shelf are of the same complexity. VoIP cards in the other split of the same Cisco 5814 dial shelf may be of the other type, but all VoIP cards in a split must be of the same type.
Indicators
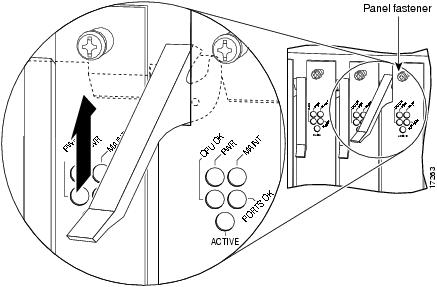
The Cisco AS5800 CT1/CE1 trunk card contains five front-panel status LEDs (see Table 5-2). Figure 5-2 shows the location of the status LEDs.
Figure 5-2 Front Panel LEDs
Software Requirements
The CT1/CE1 trunk card and the DSP modules require Cisco IOS Release 12.0(4) XL or higher on the Cisco AS5800.
For detailed software configuration information for high-complexity VoIP cards, refer to Voice over IP for the Cisco AS5800, available at:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/nubuvoip/voip5800/index.htm.
Additional information relating to medium-complexity or half-populated VoIP cards for the Cisco AS5800 is at:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/acs_serv/as5800/12_2t/index.htm.

 Feedback
Feedback