Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Optical Services Module Installation and Verification Note
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Fiber Interface Specifications
Installing a GBIC with a Handle
Installing a GBIC with Plastic Clips
Removing a GBIC with Plastic Clips
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Cisco Product Security Overview
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco Technical Support Website
Definitions of Service Request Severity
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Optical Services Module Installation and Verification Note
Product Numbers:
This publication provides procedures for installing and connecting Optical Services Modules (OSMs) in Cisco 7600 series routers and Catalyst 6500 series switches.
The OSMs are supported in the Cisco 7600 series routers and Catalyst 6500 series switches. The OSMs are supported with the following system configurations:
•
Supervisor Engine 2, Policy Feature Card 2 (PFC2), and Multilayer Switch Feature Card 2 (MSFC2)
•
Supervisor Engine 2, PFC2, MSFC2, and Switch Fabric Module (SFM) or SFM2
•
Supervisor Engine 720, PFC3A, and MSFC3
•
Supervisor Engine 720 with PFC3B, and MSFC3
•
Supervisor Engine 720 with PFC3BXL, and MSFC3
Refer to the Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 12.1 E on the Catalyst 6500 and Cisco 7600 MSFC, the Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 12.1 E on the Catalyst 6000 and Cisco 7600 Supervisor Engine and MSFC, and the Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 12.2 SX on the Catalyst 6500 and Cisco 7600 Supervisor Engine 720 publications for complete information about the chassis, modules, software features, protocols, and MIBs supported by the OSMs.
Note
You can access release notes at the World Wide Web locations listed in the "Obtaining Documentation" section.
Contents
This publication contains these sections:
•
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
•
Preparing to Install the OSMs
•
Documentation Feedback, page 34
•
Cisco Product Security Overview
•
Obtaining Technical Assistance
•
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Document Revision History
OL-5075-8
April, 2005
•
Added Cisco 7604 router and Catalyst 6504 switch.
•
Added Document Revision History table.
Overview
Table 1 describes the Cisco 7600 series router and Catalyst 6500 series chassis.
The OSMs are installed as follows:
•
In the horizontal slots of the Cisco 7603, 7604, 7606, and 7613 routers
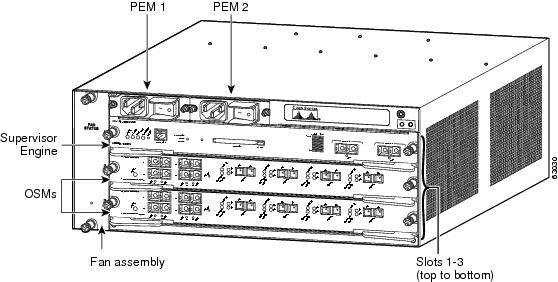
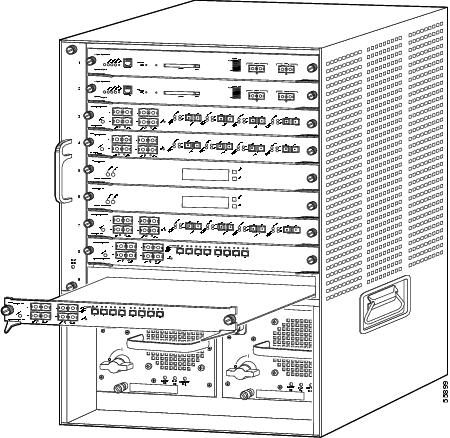
The slot numbering is the same in the 3-slot, 4-slot, 6-slot, and 13-slot chassis (see Figure 1).
•
In the horizontal slots of the Catalyst 6503, 6504, 6506, 6509, and 6513 switches
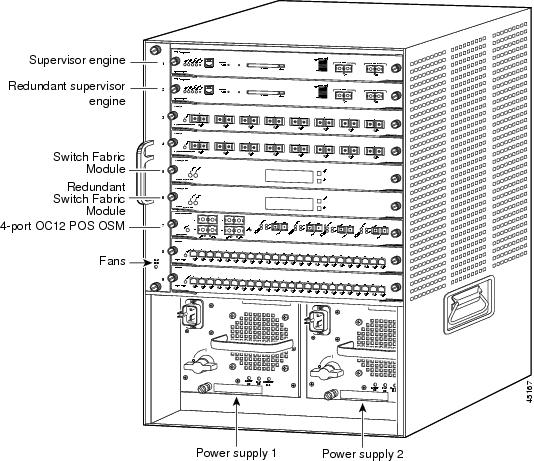
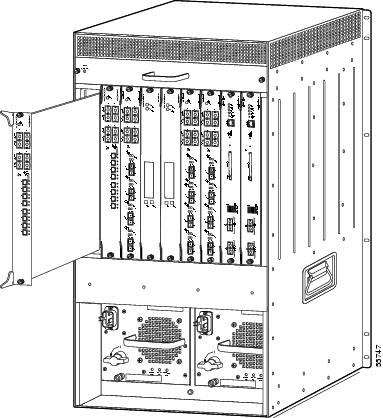
The slot numbering is the same in the 3-slot, 4-slot, 6-slot, 9-slot, and 13-slot chassis (see Figure 2).
•
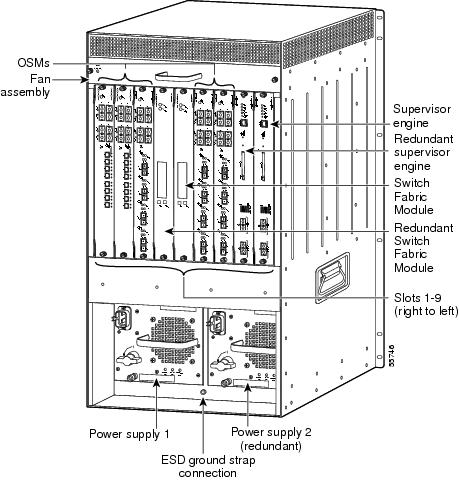
In the vertical slots of the Cisco 7609 router and Catalyst 6509-NEB switch (see Figure 3)
The horizontal slots are numbered from top to bottom; the vertical slots are numbered from right to left.
Figure 1 Slots on the Cisco 7603 Router
Figure 2 Slots on the Catalyst 6509 Switch
Note
Slot numbers are on left side of assembly.
Figure 3 Slots on the Cisco 7609 Router and Catalyst 6509-NEBS-A Switch
In all chassis, slot 1 is reserved for the supervisor engine. Slot 2 can contain an additional redundant supervisor engine in case the supervisor engine in slot 1 fails. If a redundant supervisor engine is not required, slot 2 is available for a module. Module filler plates, which are blank module carriers, are installed in empty slots to maintain consistent airflow through the chassis.
Optical Services Modules
Table 2 lists the OSMs that are described in this publication.
Table 2 Optical Services Modules
OSM-2OC12-POS-MM, -SI, -SL
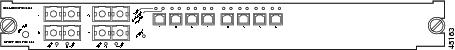
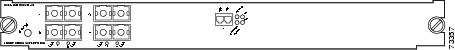
OSM-2OC12-POS-MM+, -SI+2-port OC-12 POS1 , plus 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports (requires GBICs2 ). The module has SC fiber connectors for use with MMF3 and SMF4 . See Figure 4.
OSM-4OC12-POS-MM, -SI, -SL
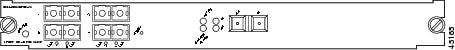
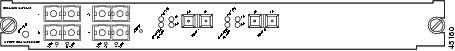
OSM-4OC12-POS-SI+4-port OC-12 POS, plus 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports (requires GBICs). The module has SC fiber connectors for use with MMF and SMF. See Figure 5.
OSM-4OC3-POS-SI
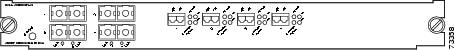
OSM-4OC3-POS-SI+4-port OC-3 POS, plus 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports (requires GBICs). The module has MT-RJ connectors for use with MMF and SMF. See Figure 6.
OSM-8OC3-POS-SI, -SL
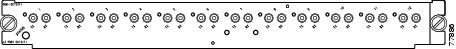
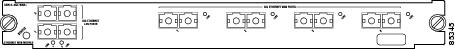
OSM-8OC3-POS-SI+, -SL+8-port OC-3 POS, plus 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports (requires GBICs). The module has MT-RJ connectors for use with MMF and SMF. See Figure 7.
OSM-1OC48-POS-SS, -SI, -SL
OSM-1OC48-POS-SS+, -SI+, -SL+1-port OC-48 POS, plus 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports (requires GBICs). The module has SC fiber connectors for use with SMF. See Figure 8.
OSM-2OC48/1DPT-SS, -SI, -SL
2-port OC-48 DPT5 /POS, plus 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports (requires GBICs). The module has LC fiber connectors for use with SMF. See Figure 9.
OSM-1CHOC12/T3-SI
1-port channelized OC-12 T3, plus 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports (requires GBICs). The module has LC fiber connectors for use with SMF. See Figure 10.
OSM-4CHOC3/T1-SI6
4-port channelized OC-3, plus 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports (requires GBICs). The module has LC fiber connectors for use with SMF.See Figure 11
OSM-12CT3/DS0
12-port channelized T3. The module has mini-SMB connectors for use with 75-ohm copper coaxial cable. See Figure 12.
OSM-1CHOC12/T1-SI
1-port channelized OC-12 T1, plus 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports (requires GBICs). The module has LC fiber connectors for use with SMF. See Figure 13.
OSM-2OC12-ATM-MM, SI
OSM-2OC12-ATM-MM+, SI+2-port OC-12 ATM6 , plus 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports (requires GBICs). The module has SC fiber connectors for use with MMF and SMF. See Figure 14.
OSM-2+4GE-WAN+
2-port Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet LAN and 4-port Layer 3 Gigabit Ethernet WAN (all ports require GBICs). See Figure 15
1 POS = Packet over SONET.
2 GBICs = Gigabit Interface Converters; GBICs are available in three styles (SX, LX/LH, and ZX) and have an SC connector for use with either MMF or SMF.
3 MMF = multimode fiber.
4 SMF = single-mode fiber.
5 DPT = Dynamic Packet Transport.
6 ATM = Asynchronous Transfer Mode.
Figure 4 2-Port OC-12c POS OSM
Figure 5 4-Port OC-12c POS OSM
Figure 6 4-Port OC-3 POS OSM
Figure 7 8-Port OC-3 POS OSM
Figure 8 1-Port OC-48 POS OSM
Figure 9 2-Port OC-48 DPT/POS OSM
Figure 10 1-Port Channelized OC-12 T3 OSM
Figure 11 4-Port Channelized OC-3 OSM
Figure 12 12-Port Channelized T3 OSM
Figure 13 1-Port Channelized OC-12 T1 OSM
Figure 14 2-Port OC-12c ATM OSM
Figure 15 2-Port Gigabit Ethernet LAN and 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet WAN Services Module
Features
Note
You can locate software features in the Optical Services Modules Software Configuration Note at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/core/cis7600/cfgnotes/osm_inst/index.htmThe OSM hardware features include:
•
Default memory configuration of 64 MB with Error Checking and Correction (ECC) (single-bit error detection and correction; 2-bit error detection); upgradable to 128 MB, 256 MB, or 512 MB.
•
Four Gigabit Ethernet Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) ports that provide basic Layer 2 configurations.
Note
The four Gigabit Ethernet ports on the OSM-4GE-WAN-GBIC WAN Services Module support forwarding of distributed IP services as well as Ethernet over Multiprotocol Label Switching (EoMPLS), Destination Sensitive Services (DSS), and Versatile Traffic Management and Shaping (VTMS).
Note
The four Gigabit Ethernet ports are not available on the OSM-12CT3/DS0.
•
System status and port status LEDs. For information on the LEDs, refer to the Cisco 7600 Series Internet Router Module Installation Guide.
The following connectors and transceivers are used by the OSMs:
•
The OC-48 POS OSM uses an SC connector and has the following transceiver options:
–
Single-mode short-reach (SS) optical interface
–
Single-mode intermediate-reach (SI) optical interface
–
Single-mode long-reach (SL) optical interface
•
The OC-12 POS OSM uses SC connectors and has the following transceiver options:
–
Multimode short-reach (MM) optical interface
–
Single-mode intermediate-reach (SI) optical interface
–
Single-mode long-reach (SL) optical interface
•
The OC-3 POS OSM uses MT-RJ connectors and has the following transceiver options:
–
Multimode short-reach (MM) optical interface
–
Single-mode intermediate-reach (SI) optical interface
–
Single-mode long-reach (SL) optical interface
•
The OC-48 DPT/POS OSM uses LC connectors and has the following transceiver options:
–
Single-mode short-reach (SS) optical interface
–
Single-mode intermediate-reach (SI) optical interface
–
Single-mode long-reach (SL) optical interface
•
The channelized OC-3 and OC-12 OSM uses a single-mode intermediate-reach (SI) optical interface with an LC connector.
•
The OC-48 OSM uses a single-mode short-reach (SS) optical interface with an LC connector.
•
The OC-12 ATM OSM uses SC connectors and has the following transceiver options:
–
Multimode short-reach (MM) optical interface
–
Single-mode intermediate-reach (SI) optical interface
•
The channelized DS3 OSM uses mini-SMB connectors for use with RG-179 75-ohm copper coaxial cable. The following cable options are available:
–
2-MINISMB/BNC-M—Two 10-foot (3-meter) cables with mini-SMB to male BNC connectors
–
2-MINISMB/BNC-F—Two 10-foot (3-meter) cables with mini-SMB to female BNC connectors
–
2-MINISMB-OPEN—Two 82-foot (25-meter) cables with mini-SMB connectors, open-ended
Safety Overview
Safety warnings appear throughout this publication in procedures that, if performed incorrectly, may harm you. A warning symbol precedes each warning statement.
Warning
Before you install, operate, or service the system, read the Site Preparation and Safety Guide. This guide contains important safety information you should know before working with the system. Statement 200
Warning
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 148
Warning
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool, or you could shock yourself. Statement 94
Warning
Blank faceplates and cover panels serve three important functions: they prevent exposure to hazardous voltages and currents inside the chassis; they contain electromagnetic interference (EMI) that might disrupt other equipment; and they direct the flow of cooling air through the chassis. Do not operate the system unless all cards, faceplates, front covers, and rear covers are in place. Statement 142
Warning
Because invisible radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
Warning
Do not stare into the beam or view it directly with optical instruments. Statement 29
Warning
Avoid eye or skin exposure to direct or scattered radiation. Statement 31
Required Tools
These tools are required to install an OSM in the Cisco 7600 series router or Catalyst 6500 series switch:
•
Number 1 Phillips screwdriver
•
Wrist strap or other grounding device
•
Antistatic mat or antistatic foam
Whenever you handle an OSM, always use a wrist strap or other grounding device to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD). For information on preventing ESD, see the "Preventing ESD" section of the Site Preparation and Safety Guide.
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a transfer of electrostatic charge between bodies of different electrostatic potentials, such as an operator and a piece of electrical equipment. It occurs when electronic components are improperly handled, and it can damage equipment and impair electrical circuitry. Electrostatic discharge is more likely to occur with the combination of synthetic fibers and dry atmosphere.
Step 1
Always follow these steps to prevent ESD when you remove and replace components:
Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap that you provide, ensuring that it makes good skin contact.
CautionTo properly guard against ESD damage and shocks, the wrist strap and cord must operate effectively.
Step 2
Do not touch any exposed contact pins or connector shells of interface ports that do not have a cable attached.
If cables are connected at one end only, do not touch the exposed pins at the unconnected end of the cable.
Note
This device is intended for use in residential and commercial environments only.
CautionPeriodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap, which should be between 1 and 10 megohms (Mohms).
Preparing to Install the OSMs
Warning
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 148
Before installing OSMs, you must install the Cisco 7600 series router or Catalyst 6500 series switch chassis and at least one supervisor engine.
For information on installing the chassis, refer to the Cisco 7603 and 7606 Router Installation Guide, the Cisco 7609 Router Installation Guide, or the Catalyst 6500 Series Installation Guide.
The OSMs are Class 1 laser products.
Warning
Because invisible radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
Installing the OSMs
This section describes how to install the OSMs in the Cisco 7600 series router and Catalyst 6500 series switches. Make sure that you have an open slot available for the new module.
CautionTo prevent ESD damage, handle modules by the carrier edges only.
Warning
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool, or you could shock yourself. Statement 94
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
Warning
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 148
To install an OSM in the Cisco 7600 series router or Catalyst 6500 series switch, perform these steps:
Step 1
Choose a slot for the OSM. Check that there is enough clearance to accommodate any interface equipment that you will connect directly to the module ports. If possible, place modules between empty slots that contain only module filler plates.
Step 2
Fully open both ejector levers on the OSM.
Step 3
Depending on the orientation of the slots in the chassis (horizontal or vertical), continue to either of these procedures:
Horizontal slots
a.
Position the OSM in the slot. (See Figure 16.)
b.
Carefully slide the OSM into the slot until the EMI gasket on the top edge of the module contacts the module in the slot above and both ejector levers have started to close.
Figure 16 Chassis with Horizontal Slots
c.
Using the thumb and forefinger of each hand, simultaneously push in the left and right levers to fully seat the module in the backplane connector.
Note
Always use the ejector levers when installing or removing modules. A module that is partially seated in the backplane will cause the system to halt and subsequently crash.
Vertical slots
a.
Position the OSM in the slot. (See Figure 17.)
b.
Carefully slide the OSM into the slot until the EMI gasket on the right edge of the module contacts the module in the slot to the right and both ejector levers have started to close.
Figure 17 Chassis with Vertical Slots
c.
Using the thumb and forefinger of each hand, simultaneously push in the top and bottom levers to fully seat the OSM in the backplane connector.
Note
Always use the ejector levers when installing or removing the modules. A module that is partially seated in the backplane will cause the system to halt and subsequently crash.
Step 4
Use a screwdriver to tighten the captive installation screws on the OSM.
Attaching Cables to the OSM
This section describes the following topics:
•
Fiber Interface Specifications
Warning
If the symbol of suitability with an overlaid cross appears above a port, you must not connect the port to a public network that follows the European Union standards. Connecting the port to this type of public network can cause severe injury or damage your router. Statement 162
Connector Types
This section describes the types of connectors associated with the OSMs.
SC-Type Connector
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
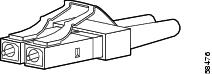
The SC-type connector (see Figure 18) is used to connect the OSMs to optical networks using both multimode fiber (MMF) and single-mode fiber (SMF).
Figure 18 SC-Type Fiber-Optic Connector
LC-Type Connector
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
The LC-type connector (see Figure 19) is used to connect the OC-48 DPT/POS, channelized OC-12, and OC-48 OSMs to optical networks using both MMF and SMF.
Figure 19 LC-Type Fiber-Optic Connector
MT-RJ Connector
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
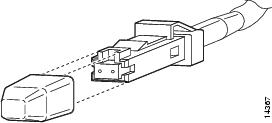
MT-RJ connectors provide a high-density optical connection between the OSM and the network. (See Figure 20.) When you are connecting MT-RJ cables to a module, make sure you firmly press the connector plug into the socket. The upper edge of the plug must snap into the upper front edge of the socket. You may hear an audible click. Gently pull on the plug to confirm whether or not the plug is locked into the socket.
Figure 20 MT-RJ Interface Cable Connector
Always make sure that you insert the connector completely into the socket. This step is especially important when you are making a connection between a module and a long distance (2 km) or a suspected highly attenuated network. If the link LED does not light, remove the network cable plug and reinsert it firmly into the module socket. Dirt or skin oils might have accumulated on the plug faceplate (around the optical-fiber openings) to generate significant attenuation, which reduces the optical power levels below threshold levels so that a link cannot be made.
CautionWhen you disconnect the fiber-optic cable from the module, grip the body of the connector. Do not grip the connector jacket sleeve. Gripping the sleeve can, over time, degrade the fiber-optic cable termination in the MT-RJ connector.
To disconnect the plug from the socket, press down on the raised portion on top of the plug (releasing the latch). You should hear an audible click indicating the latch has released. Carefully pull the plug out of the socket.
To clean the MT-RJ plug faceplate:
Step 1
Use a lint-free tissue soaked in 99 percent pure isopropyl alcohol to gently wipe the faceplate.
Step 2
Carefully wipe the faceplate with a dry lint-free tissue.
Step 3
Remove any residual dust from the faceplate with compressed air before installing the cable.
Note
Make sure that dust caps are installed on all unused module connectors and unused network fiber-optic cable connectors.
Mini-SMB Connector
The mini-SMB connector (see Figure 21) is used to connect the channelized DS3 OSMs to optical networks using RG-179 75-ohm copper coaxial cable.
Figure 21 Mini-SMB Cable Connector
The following cable options are available:
•
2-MINISMB/BNC-M—Two 10-foot (3-meter) cables with mini-SMB to male BNC connectors
•
2-MINISMB/BNC-F—Two 10-foot (3-meter) cables with mini-SMB to female BNC connectors
•
2-MINISMB-OPEN—Two 82-foot (25-meter) cables with mini-SMB connectors, open-ended
Fiber Interface Specifications
This section describes these topics:
OC-3, OC-12, and OC-48 POS
The specification for optical fiber transmission defines two types of fiber: single mode and multimode. Within the single-mode category, three transmission types are defined: short reach, intermediate reach, and long reach. Within the multimode category, only short reach is available.
Table 3 lists the specifications for OC-3, Table 4 lists the specifications for OC-12 OSM interfaces, and Table 5 lists the specifications for OC-48 OSM interfaces.
Gigabit Ethernet
Table 6 provides cabling specifications for the 1000BASE-X interfaces, including the Gigabit Ethernet GBIC interfaces. The minimum cable distance for all GBICs listed (MMF and SMF) is 6.5 feet (2 meters).
Table 6 Gigabit Ethernet Maximum Transmission Distances
SX2
850
MMF
62
62
50
50160
200
400
500722 ft (220 m)
902 ft (275 m)
1640 ft (500 m)
1804 ft (550 m)LX/LH
1300
MMF3
62
50
50500
400
5001804 ft (550 m)
1804 ft (550 m)
1804 ft (550 m)SMF (LX/LH)
9/104
-
6.2 mi (10 km)
ZX5
1550
SMF6
9/10
8-
-43.5 mi (70 km)7
62.1 mi (100 km)
1 Number listed is core size. The cladding size is usually 125 microns.
2 MMF only.
3 Patch cord required. (See the "Patch Cord" section for details.)
4 ANSI/TIA/EIA-568-A specifies that the nominal "mode field diameter" shall be 8.7 to 10.0 microns with a tolerance of +/- 0.5 microns at 1310 nm.
5 You can have a maximum of 24 1000BASE-ZX GBICs per system to comply with FCC Class A.
6 Dispersion-shifted single-mode fiber-optic cable.
7 The minimum link distance for ZX GBICs is 6.2 miles (10 km) with an 8-dB attenuator installed at each end of the link. Without attenuators, the minimum link distance is 24.9 miles (40 km).
Patch Cord
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
The mode-conditioning patch cord (Cisco product number CAB-GELX-625 or equivalent) prevents overdriving the receiver for short lengths of MMF and reduces differential mode delay for long lengths of MMF.
Note
The patch cord is required to comply with IEEE standards. IEEE found that link distances could not be met with certain types of fiber-optic cable due to a problem in the center of some fiber-optic cable cores. The solution is to launch light from the laser at a precise offset from the center by using the patch cord. At the output of the patch cord, the LX/LH GBIC complies with the IEEE 802.3z standard for 1000BASE-LX. For more information, see the "Differential Mode Delay" section.
Note
Cisco Gigabit Ethernet products have been tested and evaluated to comply with the standards listed. Equivalent cables should also meet these standards.
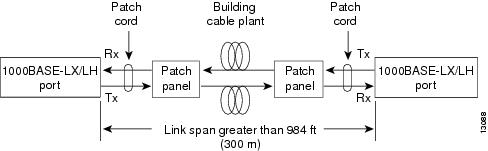
Figure 22 shows a typical configuration using the patch cord.
Figure 22 Patch Cord Configuration
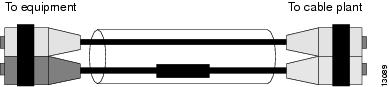
Patch Cord Installation
Plug the end of the patch cord labeled "To equipment" into the GBIC. (See Figure 23.) Plug the end labeled "To cable plant" into the patch panel. The patch cord is 9.84 feet (3 meters) long and has duplex SC-type male connectors at each end.
Figure 23 Patch Cord Installation
Differential Mode Delay
When an unconditioned laser source designed for operation on an SMF cable is directly coupled to an MMF cable, differential mode delay (DMD) might occur. DMD can degrade the modal bandwidth of the fiber-optic cable. This degradation causes a decrease in the link span (the distance between the transmitter and the receiver) that can be reliably supported.
The Gigabit Ethernet specification (IEEE 802.3z) outlines parameters for Ethernet communications at a gigabit-per-second rate. The specification offers a higher-speed version of Ethernet for backbone and server connectivity using existing deployed MMF cable by defining the use of laser-based optical components to propagate data over MMF cable.
Lasers function at the baud rates and longer distances required for Gigabit Ethernet. The 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet Task Force has identified the DMD condition that occurs with particular combinations of lasers and MMF cable. The results create an additional element of jitter that can limit the reach of Gigabit Ethernet over MMF cable.
With DMD, a single laser light pulse excites a few modes equally within an MMF cable. These modes, or light pathways, then follow two or more different paths. These paths might have different lengths and transmission delays as the light travels through the cable.
With DMD, a distinct pulse propagating down the cable no longer remains a distinct pulse or, in extreme cases, might become two independent pulses. Strings of pulses can interfere with each other making it difficult to recover data.
DMD does not occur in all deployed fibers; it occurs with certain combinations of worst-case fibers and worst-case transceivers. Gigabit Ethernet experiences this problem because of its very high baud rate and its long MMF cable lengths. SMF cable and copper cable are not affected by DMD.
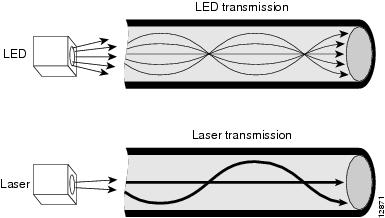
MMF cable has been tested for use only with LED sources. LEDs can create an overfilled launch condition within the fiber-optic cable. The overfilled launch condition describes the way LED transmitters couple light into the fiber-optic cable in a broad spread of modes. The generated light that shines in multiple directions can overfill the existing cable space and excite a large number of modes, similar to a light bulb radiating light into a dark room. (See Figure 24.)
Figure 24 LED Transmission Compared to Laser Transmission
Lasers launch light in a more concentrated fashion. A laser transmitter couples light into only a fraction of the existing modes or optical pathways present in the fiber-optic cable. (See Figure 24.)
The solution is to condition the laser light launched from the source (transmitter) so it spreads the light evenly across the diameter of the fiber-optic cable making the launch look more like an LED source to the cable. The objective is to scramble the modes of light to distribute the power more equally in all modes and prevent the light from being concentrated in just a few modes.
An unconditioned launch, in the worst case, might concentrate all of its light in the center of the fiber-optic cable, exciting only two or more modes equally.
A significant variation in the amount of DMD is produced from one MMF cable to the next. No reasonable test can be performed to survey an installed cable plant to assess the effect of DMD.
GBIC Installation
The GBIC is a hot-swappable input/output device that plugs into a Gigabit Ethernet port, linking the module port with the fiber-optic network.
GBIC Models
GBICs are available in the three optical models listed in Table 7. The three optical models differ in the distance that light can be sent through a fiber-optic network. These GBICs are available in the two physical models shown in Figure 25.
Table 7 GBIC Optical Models
Short wavelength (1000BASE-SX)
WS-G5484
Long wavelength/long haul (1000BASE-LX/LH)
WS-G5486
Extended distance (1000BASE-ZX)
WS-G5487
Figure 25 GBIC Physical Models
A copper GBIC, the WS-G5483, is available. The WS-G5483 provides 1000BASE-T full-duplex connectivity between the GBIC-compatible modules, supervisor engines, and the network up to a distance of 328 feet (100 m). See Figure 26.
Figure 26 Copper GBIC (WS-G5483)
Additionally, there are 32 fixed-wavelength GBICs that support the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) 100 GHz wavelength grid.The dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) GBICs are shown in Figure 27 and listed in Table 8.
Figure 27 DWDM and CWDM GBICs
Finally, there are eight coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) GBICs A set of eight CWDM GBICs are available for use with the CWDM Passive Optical System. The CWDM GBICs are shown in Figure 27 and listed in Table 9.
Note
For information on the CWDM Passive Optical System, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/interfaces_modules/transceiver_modules/installation/note/78_16565.html.
When installing GBICs, do the following:
Warning
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool, or you could shock yourself. Statement 94
•
Insert a 10-dB inline optical attenuator between the fiber-optic network and the receiving port on the 1000BASE-ZX GBIC at each end of the link if the link length is less than 15.5 miles (25 km).
•
Insert a 5-dB inline optical attenuator between the fiber-optic network and the receiving port on the 1000BASE-ZX GBIC at each end of the link if the link is greater than 15.5 miles (25 km), but less than 31 miles (50 km).
•
When using the 1000BASE-LX/LH GBIC with 62.5-micron diameter MMF, you must install a mode-conditioning patch cord (Cisco product number CAB-GELX-625 or equivalent) between the GBIC and the MMF cable on both the transmit and receive ends of the link. The mode-conditioning patch cord is required for link distances less than 328 feet (100 m) or greater than 984 feet (300 m).
You can have a maximum of 24 1000BASE-ZX GBICs per system to comply with FCC Class A.
This section provides procedures for installing and removing a GBIC. For additional information on GBICs, refer to the Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) Module and Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) GBIC Module Installation Information and Specifications.
Note
Refer to the "Working with Lasers" section in the Site Preparation and Safety Guide before proceeding.
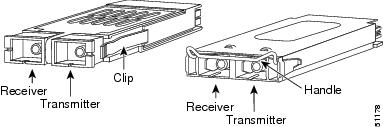
There are three locking mechanisms available to secure the GBIC in the module:
•
A locking handle
•
Two clips (one on each side of the GBIC)
•
Plastic clips
There are three methods of installation and removal; the one you use depends on your GBIC model.
•
Installing a GBIC with a Handle
•
Installing a GBIC with Plastic Clips
•
Removing a GBIC with a Handle
•
Removing a GBIC with Plastic Clips
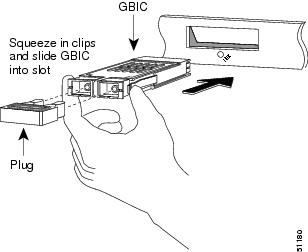
Installing a GBIC with Clips
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
To install a GBIC that has clips, perform these steps:
Step 1
Remove the GBIC from its protective packaging.
Step 2
Check the label on the GBIC to verify that the GBIC is the correct model (SX, LX/LH, or ZX) for your network.
Step 3
Grip the sides of the GBIC with your thumb and forefinger and insert the GBIC into the module socket (see Figure 28).
Note
GBICs are keyed to prevent incorrect insertion.
Figure 28 Installing a GBIC with Clips
Step 4
Slide the GBIC through the flap covering the socket opening until you hear a click indicating the GBIC is locked into the slot.
Step 5
When you are ready to attach the network interface fiber-optic cable, remove the plug from the GBIC optical bore and save the plug for future use.
Installing a GBIC with a Handle
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
To install a GBIC that has a handle, perform these steps:
Step 1
Remove the GBIC from its protective packaging.
Step 2
Check the label on the GBIC to verify that the GBIC is the correct model (SX, LX/LH, or ZX) for your network.
Step 3
Remove the plug from the optical bore.
Step 4
Slide the GBIC into the module socket. (See Figure 29.) You can install the GBIC with the handle either up or down.
a.
If the handle is up during insertion, you must lower the handle after insertion to lock the GBIC in place.
b.
If the handle is down during insertion, you will hear a click that indicates that the GBIC is locked in place.
Step 5
Verify that the GBIC handle is in the down position.
Figure 29 Installing a GBIC with a Handle
Installing a GBIC with Plastic Clips
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
CautionInstalling this product in or connecting this product to an unauthorized device might damage the device. Refer to the online 1000BASE-T GBIC Switch Compatibility Matrix posted with the GBIC documentation on Cisco.com for the list of products that support the GBIC.
To install a GBIC with plastic clips, follow these steps:
Step 1
Remove the GBIC from the protective packaging.
Step 2
Check the label on the GBIC to verify that the GBIC is the correct model (SX, LX/LH, or ZX) for your network.
Step 3
Grip the two plastic clips with your thumb and forefinger.
Step 4
Insert the GBIC into the module slot until you hear a click. The click means the GBIC is locked in the slot.
Removing a GBIC with Clips
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
If you are removing a GBIC that has clips, perform these steps:
Step 1
Disconnect the network fiber cable from the GBIC SC-type connector.
Step 2
Release the GBIC from the slot by simultaneously squeezing the two plastic tabs (one on each side of the GBIC).
Step 3
Slide the GBIC out of the module slot.
A flap drops down to protect the Gigabit Ethernet module connector.
Step 4
Place the GBIC in an antistatic bag.
Removing a GBIC with a Handle
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
If you are removing a GBIC with a handle, perform these steps:
Step 1
Disconnect the network fiber-optic cable from the GBIC SC-type connector.
Step 2
Rotate the handle up to release the GBIC from the slot.
Step 3
Grip the handle or the sides of the GBIC and slide the GBIC out of the slot.
A flap drops down to protect the slot.
Step 4
Place the GBIC in an antistatic bag.
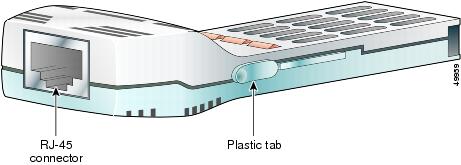
Removing a GBIC with Plastic Clips
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125
If you are removing a GBIC with plastic clips, perform these steps:
Step 1
Disconnect the network fiber-optic cable from the RJ-45 connector.
Step 2
Release the GBIC from the slot by simultaneously squeezing the two plastic tabs to release the GBIC from the slot.
Step 3
Slide the GBIC out of the slot.
Step 4
Place the GBIC in an antistatic bag.
Warning
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. Statement 1040
Verifying the Installation
Enter the show module command to verify that the system acknowledges the new modules and has brought them online.
This example shows the output of the show module command:
Router# show moduleMod Ports Card Type Model Serial No.--- ----- -------------------------------- ------------------ -----------1 2 Catalyst 6000 supervisor 2 (Active) WS-X6K-SUP2-2GE SAD04460M9T4 4 8-port CHOC-12/DS3 SI OSM-8CHOC12/T3-SI SAD0513000F5 0 Switching Fabric Module-128 (Active) WS-C6500-SFM SAD0445044Y6 0 Switching Fabric Module-128 (Standby) WS-C6500-SFM SAD044904RN7 4 2-port CHOC-48/DS3 SS OSM-2CHOC48/T3-SS SAD051409DW8 16 SFM-capable 16 port 1000mb GBIC WS-X6516-GBIC SAD04470AUK9 16 SFM-capable 16 port 1000mb GBIC WS-X6516-GBIC SAD044908JGMod MAC addresses Hw Fw Sw Status--- -------------------------------- ------ ------ ----- -------1 00d0.c0d4.0454 to 00d0.c0d4.0455 1.1 6.1(3) 6.2(0.116) Ok4 00d0.9738.a7e5 to 00d0.9738.a824 0.303 12.1(2001061 12.1(2001061 Ok5 0001.0002.0003 to 0001.0002.0003 1.0 6.1(3) 6.2(0.116) Ok6 0001.0002.0003 to 0001.0002.0003 1.0 6.1(3) 6.2(0.116) Ok7 00d0.9738.aa25 to 00d0.9738.aa64 0.202 12.1(2001061 12.1(2001061 Ok8 0001.c9d9.aa98 to 0001.c9d9.aaa7 2.0 6.1(3) 6.2(0.116) Ok9 00d0.c0d4.0e5c to 00d0.c0d4.0e6b 2.0 6.1(3) 6.2(0.116) OkMod Sub-Module Model Serial Hw Status--- ----------------------- --------------- ---------- ------- -------1 Policy Feature Card 2 WS-F6K-PFC2 SAD0443026F 1.0 Ok1 Cat6k MSFC 2 daughterboard WS-F6K-MSFC2 SAD04380K8K 1.1 OkRouter#Related Documentation
The following related publications are available:
•
Cisco 7600 Series Router Installation Guide
•
Cisco 7600 Series Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide, 12.1E
•
Cisco 7600 Series Router Cisco IOS Command Reference, 12.1E
•
Cisco 7600 Series Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide, 12.2SX
•
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco 7600 Series Routers
•
Catalyst 6500 Series Switches Installation Guide
•
Catalyst 6500 Series Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide, 12.1E
•
Catalyst 6500 Series Cisco IOS Command Reference, 12.1E
•
Catalyst 6500 Series Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide, 12.2SX
•
Catalyst 6500 Series Cisco IOS Command Reference, 12.2SX
•
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Catalyst 6500 Series Switches
For information about MIBs, refer to this url: http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on Cisco.com. Cisco also provides several ways to obtain technical assistance and other technical resources. These sections explain how to obtain technical information from Cisco Systems.
Cisco.com
You can access the most current Cisco documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/psa/default.html
You can access the Cisco website at this URL:
You can access international Cisco websites at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/web/siteassets/locator/index.html
Documentation DVD
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a Documentation DVD package, which may have shipped with your product. The Documentation DVD is updated regularly and may be more current than printed documentation. The Documentation DVD package is available as a single unit.
Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order a Cisco Documentation DVD (product number DOC-DOCDVD=) from the Ordering tool or Cisco Marketplace.
Cisco Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/
Cisco Marketplace:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Ordering Documentation
You can find instructions for ordering documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/Illus_process/PDI/pdi.htm
You can order Cisco documentation in these ways:
•
Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order Cisco product documentation from the Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/
•
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by calling Cisco Systems Corporate Headquarters (California, USA) at 408 526-7208 or, elsewhere in North America, by calling 1 800 553-NETS (6387).
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service and Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
Cisco Product Security Overview
Cisco provides a free online Security Vulnerability Policy portal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.html
From this site, you can perform these tasks:
•
Report security vulnerabilities in Cisco products.
•
Obtain assistance with security incidents that involve Cisco products.
•
Register to receive security information from Cisco.
A current list of security advisories and notices for Cisco products is available at this URL:
If you prefer to see advisories and notices as they are updated in real time, you can access a Product Security Incident Response Team Really Simple Syndication (PSIRT RSS) feed from this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_psirt_rss_feed.html
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products
Cisco is committed to delivering secure products. We test our products internally before we release them, and we strive to correct all vulnerabilities quickly. If you think that you might have identified a vulnerability in a Cisco product, contact PSIRT:
•
Emergencies — security-alert@cisco.com
•
Nonemergencies — psirt@cisco.com
Tip
We encourage you to use Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) or a compatible product to encrypt any sensitive information that you send to Cisco. PSIRT can work from encrypted information that is compatible with PGP versions 2.x through 8.x.
Never use a revoked or an expired encryption key. The correct public key to use in your correspondence with PSIRT is the one that has the most recent creation date in this public key server list:
http://pgp.mit.edu:11371/pks/lookup?search=psirt%40cisco.com&op=index&exact=on
In an emergency, you can also reach PSIRT by telephone:
•
1 877 228-7302
•
1 408 525-6532
Obtaining Technical Assistance
For all customers, partners, resellers, and distributors who hold valid Cisco service contracts, Cisco Technical Support provides 24-hour-a-day, award-winning technical assistance. The Cisco Technical Support Website on Cisco.com features extensive online support resources. In addition, Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) engineers provide telephone support. If you do not hold a valid Cisco service contract, contact your reseller.
Cisco Technical Support Website
The Cisco Technical Support Website provides online documents and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. The website is available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Access to all tools on the Cisco Technical Support Website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can register at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Note
Use the Cisco Product Identification (CPI) tool to locate your product serial number before submitting a web or phone request for service. You can access the CPI tool from the Cisco Technical Support Website by clicking the Tools & Resources link under Documentation & Tools. Choose Cisco Product Identification Tool from the Alphabetical Index drop-down list, or click the Cisco Product Identification Tool link under Alerts & RMAs. The CPI tool offers three search options: by product ID or model name; by tree view; or for certain products, by copying and pasting show command output. Search results show an illustration of your product with the serial number label location highlighted. Locate the serial number label on your product and record the information before placing a service call.
Submitting a Service Request
Using the online TAC Service Request Tool is the fastest way to open S3 and S4 service requests. (S3 and S4 service requests are those in which your network is minimally impaired or for which you require product information.) After you describe your situation, the TAC Service Request Tool provides recommended solutions. If your issue is not resolved using the recommended resources, your service request is assigned to a Cisco TAC engineer. The TAC Service Request Tool is located at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/servicerequest
For S1 or S2 service requests or if you do not have Internet access, contact the Cisco TAC by telephone. (S1 or S2 service requests are those in which your production network is down or severely degraded.) Cisco TAC engineers are assigned immediately to S1 and S2 service requests to help keep your business operations running smoothly.
To open a service request by telephone, use one of the following numbers:
Asia-Pacific: +61 2 8446 7411 (Australia: 1 800 805 227)
EMEA: +32 2 704 55 55
USA: 1 800 553-2447For a complete list of Cisco TAC contacts, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/support/tsd_contact_technical_support.html
Definitions of Service Request Severity
To ensure that all service requests are reported in a standard format, Cisco has established severity definitions.
Severity 1 (S1)—Your network is "down," or there is a critical impact to your business operations. You and Cisco will commit all necessary resources around the clock to resolve the situation.
Severity 2 (S2)—Operation of an existing network is severely degraded, or significant aspects of your business operation are negatively affected by inadequate performance of Cisco products. You and Cisco will commit full-time resources during normal business hours to resolve the situation.
Severity 3 (S3)—Operational performance of your network is impaired, but most business operations remain functional. You and Cisco will commit resources during normal business hours to restore service to satisfactory levels.
Severity 4 (S4)—You require information or assistance with Cisco product capabilities, installation, or configuration. There is little or no effect on your business operations.
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Information about Cisco products, technologies, and network solutions is available from various online and printed sources.
•
Cisco Marketplace provides a variety of Cisco books, reference guides, and logo merchandise. Visit Cisco Marketplace, the company store, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
•
Cisco Press publishes a wide range of general networking, training and certification titles. Both new and experienced users will benefit from these publications. For current Cisco Press titles and other information, go to Cisco Press at this URL:
•
Packet magazine is the Cisco Systems technical user magazine for maximizing Internet and networking investments. Each quarter, Packet delivers coverage of the latest industry trends, technology breakthroughs, and Cisco products and solutions, as well as network deployment and troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, customer case studies, certification and training information, and links to scores of in-depth online resources. You can access Packet magazine at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac123/ac114/about_cisco_packet_magazine.html
•
Internet Protocol Journal is a quarterly journal published by Cisco Systems for engineering professionals involved in designing, developing, and operating public and private internets and intranets. You can access the Internet Protocol Journal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac123/ac147/about_cisco_the_internet_protocol_journal.html
•
World-class networking training is available from Cisco. You can view current offerings at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/web/learning/index.html
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the "Related Documentation" section.
CCSP, the Cisco Square Bridge logo, Follow Me Browsing, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Access Registrar, Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Empowering the Internet Generation, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, FormShare, GigaDrive, GigaStack, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, Linksys, MeetingPlace, MGX, the Networkers logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Packet, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, ProConnect, RateMUX, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, StrataView Plus, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, and VCO are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0501R)
)